Edexcel GCSE 9-1 Biology - SB1: Key Concepts in Biology
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SB1: Key Concepts in Biology Paper 1 + 2 Specification: https://qualifications.pearson.com/content/dam/pdf/GCSE/Science/2016/Specification/GCSE_Biology_Spec.pdf
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
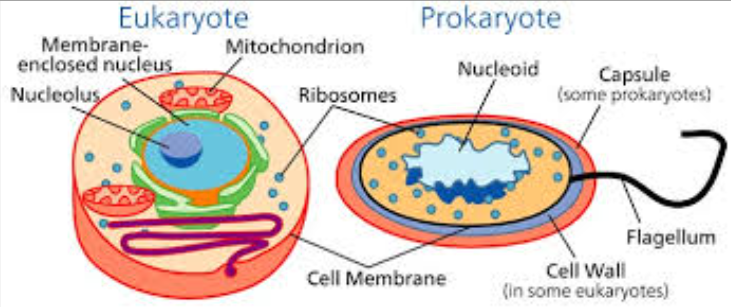
Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
prokaryotes:
contains NO membrane bound organelles
e.g. NO nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria
contains plasma membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, loop of chromosomal DNA
examples include: bacteria
eukaryotes:
contain membrane bound organelles
e.g. nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria etc.
examples include:
plant + animal cells, fungi
What is the function of a cell membrane?
separates cell from external environment; controls passage of organic molecules, ions, water, oxygen, and wastes into and out of the cell
found in prokaryotes, animal + plant cells
What is the function of a nucleus?
cell organelle that houses DNA and directs synthesis of ribosomes and proteins
found in animal and plant cells
What is the function of cytoplasm?
provides structure to cell; site of many chemical reactions; medium in which organelles are found
found in prokaryotes, animal + plant cells
What is the function of mitochondria?
site of aerobic respiration
found in animal + plant cells
What are the function of ribosomes?
protein synthesis (where proteins are made)
found in prokaryotes, animal + plant cells
What is the function of a cell wall?
protection and gives the cell structure
made from cellulose
found in plant cells
What is the function of a vacuole?
contains cell sap
keeps the cell turgid
found in plant cells
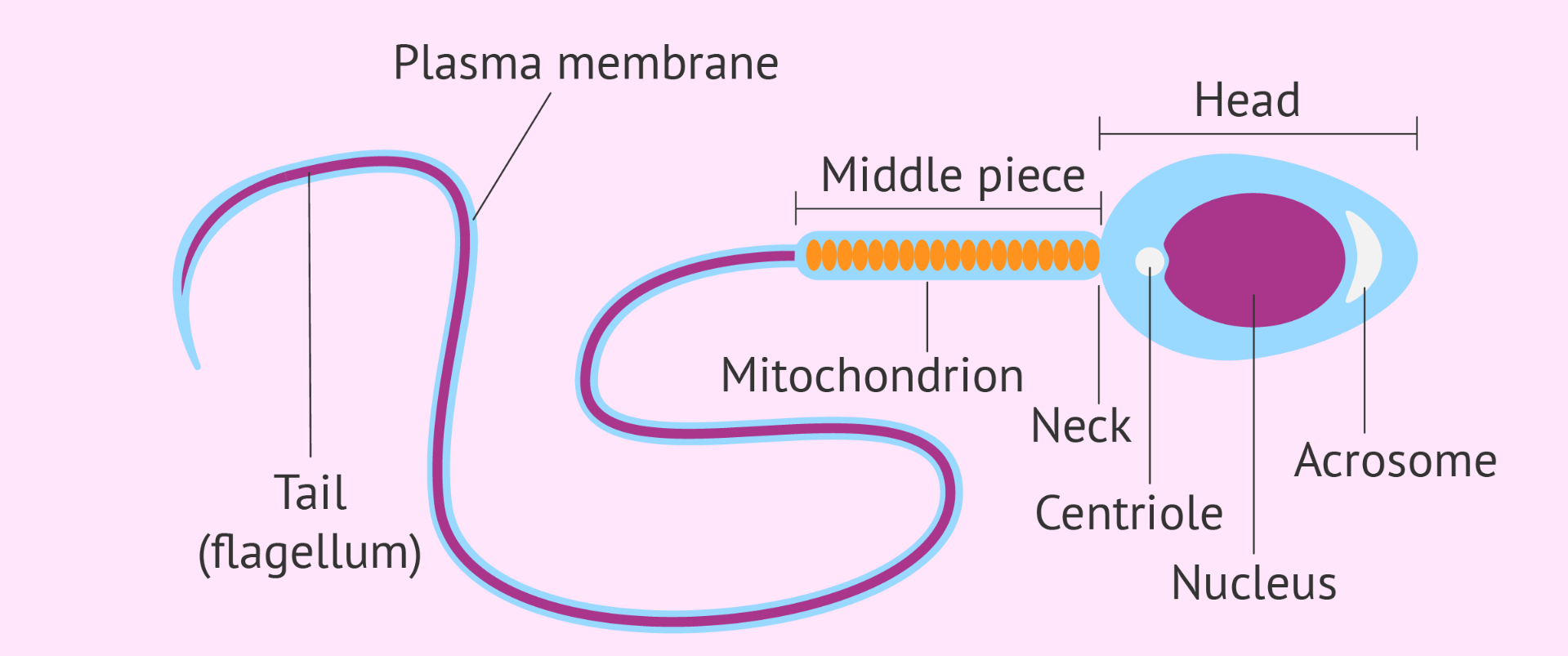
How are sperm cells adapted to their functions?
acrosome - essential for gamete fusion, particularly for binding to and penetration of the jelly coat of an egg cell
contains enzymes which prevents a second sperm fertilising the egg cell
haploid nucleus - contains one set of chromosomes as it’s a gamete
many mitochondria - release a lot of energy quickly for the movement of the cell
long tail (flagellum) - moves side to side so the cell can “swim” forward
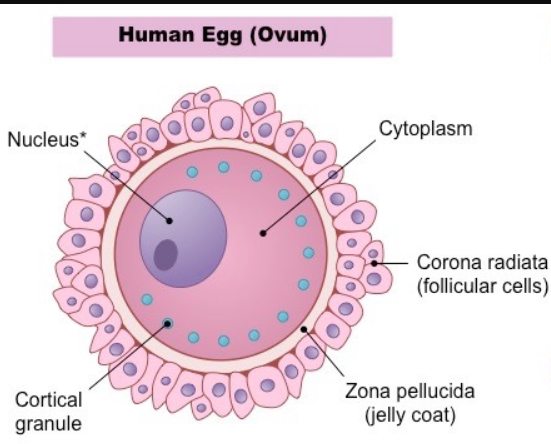
How are egg cells adapted to their functions?
cell membrane hardens after fertilisation - protects the egg as it moves through the oviduct
jelly layer hardens after the sperm cell nucleus and egg cell nuclei fuse - prevents a second sperm from fertilising the egg cell
haploid nucleus - contains one set of chromosomes as it’s a gamete
large store of nutrients in the cytoplasm - provide a source of energy for mitosis and growth after fertilisation
jelly layer surrounding the cell membrane - helps the cell burrow through the jelly like layer surrounding an egg cell
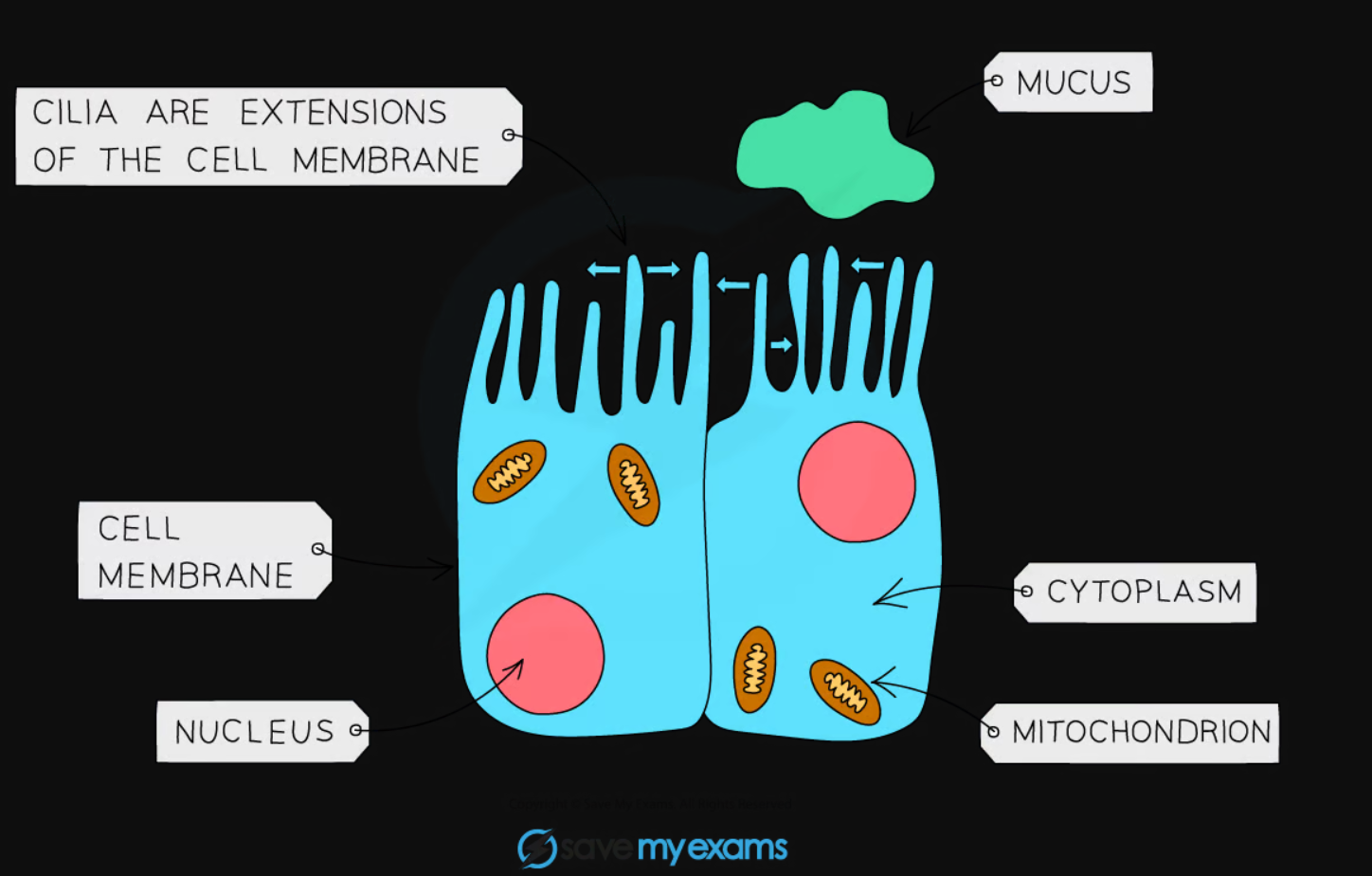
How are ciliated epithelial cells adapted to their functions?
diploid nucleus - contains two sets of chromosomes as it’s a body cell
fine hair like extensions to the cell membrane - sweeps from side to side to move things across the cell surface
lines oviducts - moves the egg cell from the ovary to the uterus
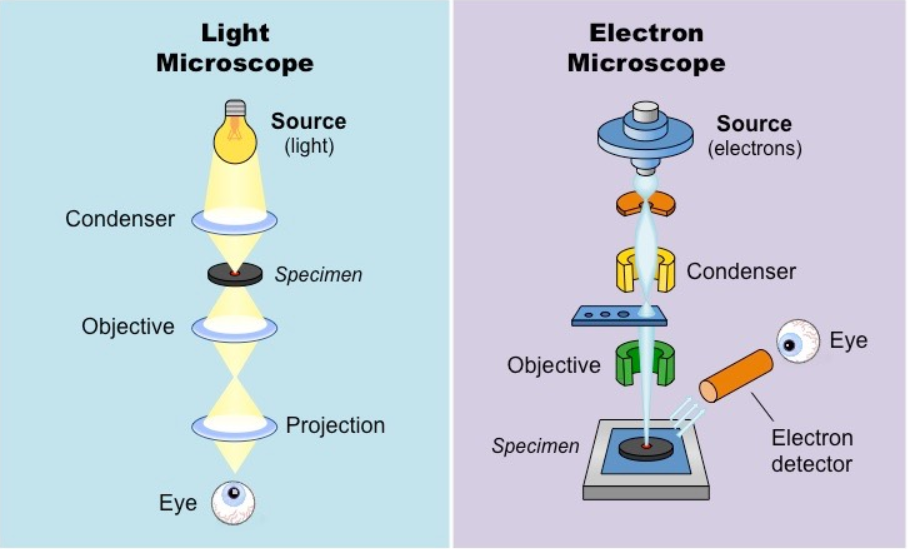
Explain how changes in microscope technology, including electron microscopy, have enabled us to see cell structures and organelles with more clarity and detail than in the past and increased our understanding of the role of sub-cellular structures
light microscopes use visible light to illuminate specimens, allowing us to visualise cells and their components
electron microscopes employ a beam of electrons instead of visible light
these microscopes have higher magnification and superior resolving power compared to light microscopes
have contributed to increased understanding of the role of sub-cellular structures as it allows us to find the intricacies of cells and organelles in greater depth and clarity
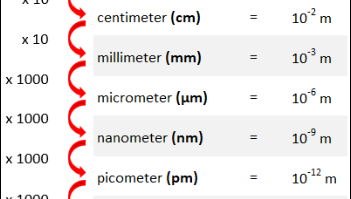
Convert between millimetres, micrometres, nanometres and picometres
x1000
Define an enzyme
enzyme - a biological catalyst which speeds up a reaction without being used up
enzymes are proton molecules, and so are made up of (100-1000) amino acids which are made in protein synthesis
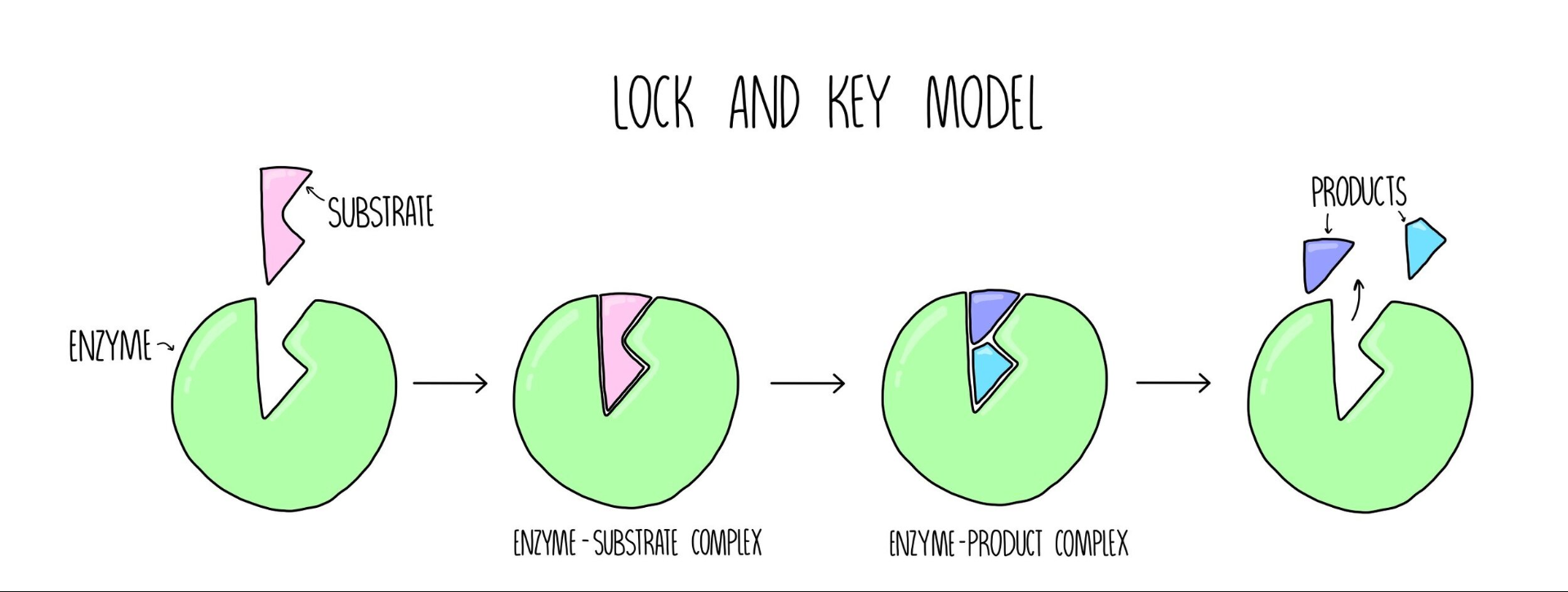
Explain the mechanism of enzyme action including the active site and enzyme specificity
lock and key model
substrates are specific and complementary to active sites
substrates => whatever is reacting with the enzyme

Describe how proteins turn into amino acids
proteins are made up of (a string of) many different amino acids
proteins are broken down into protease then into amino acids
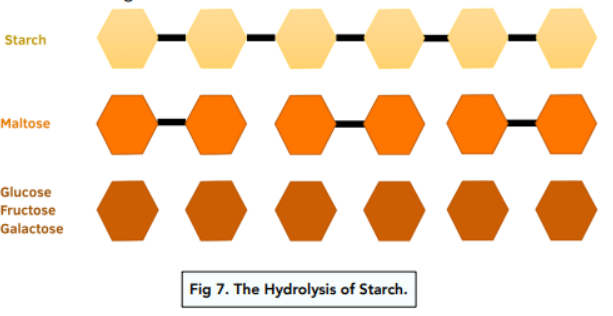
Describe how carbohydrates turn into glucose
carbs are made up of (a string of) glucose molecules
amylase breaks down carb molecules into glucose
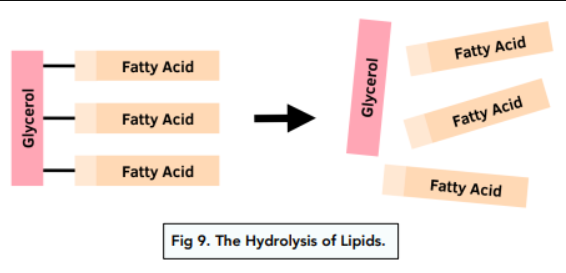
Describe how lipids turn into fatty acids and glycerol
lipids are made up of (a string of) fatty acids and glycerol molecules
lipase breaks down the fat molecules into fatty acids and glycerol
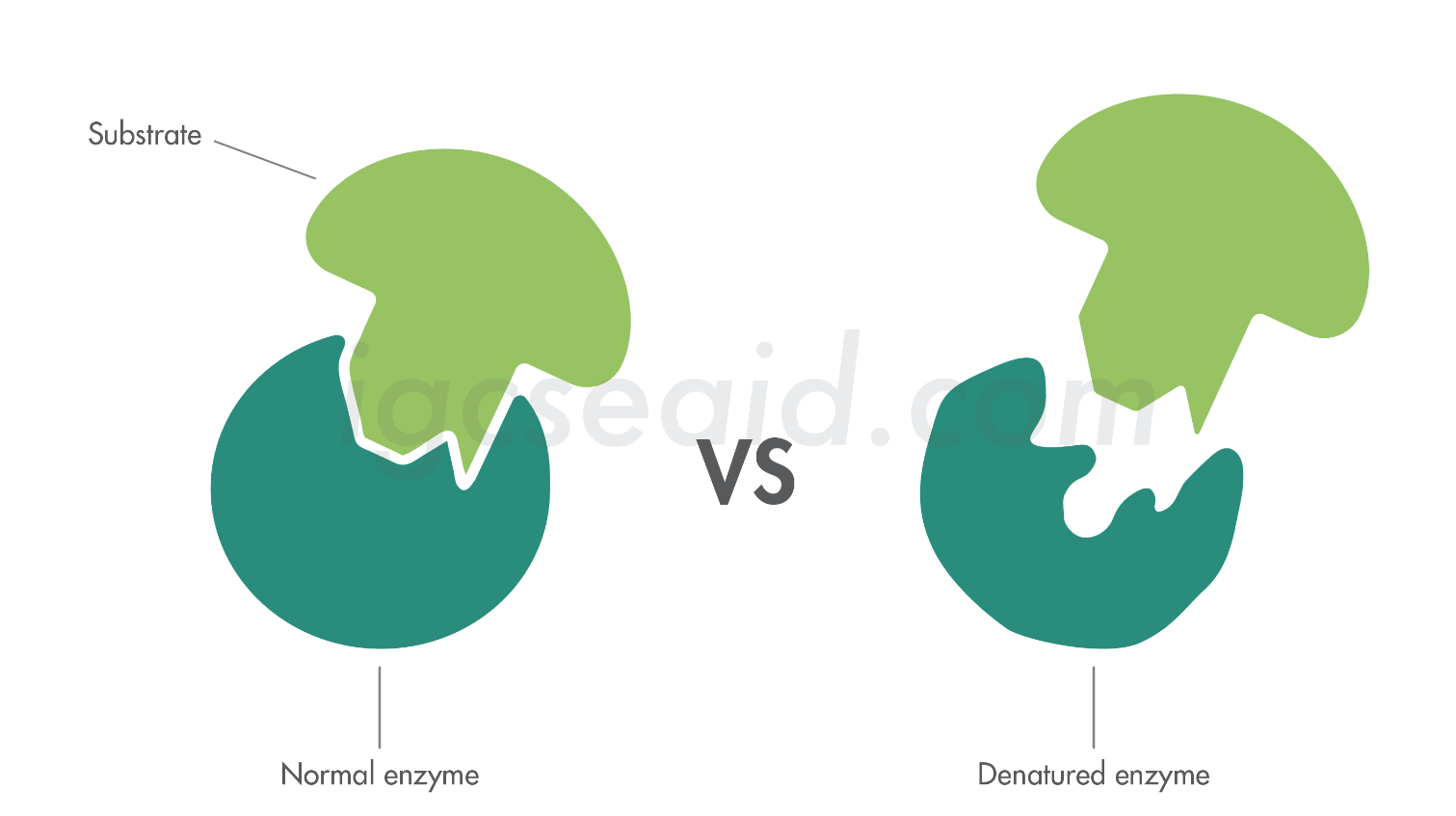
Explain how enzymes can be denatured due to changes in the shape of the active site
denaturation alters an enzyme’s active site shape so the enzyme is not complementary to the active site => affect its function
State the calculations for rate of reaction
Rate of reaction:
1/time
OR
(substrate used/product made)/time
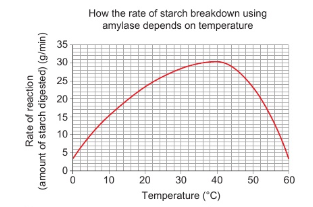
Explain the effects of temperature on enzyme activity
higher temperature generally increases the rate of reaction
more collisions occur along molecules, increasing the likelihood of substrate binding to the enzyme’s active site
beyond the enzyme’s optimum temp, enzymes denature due to excessive heat
denaturation disrupts the enzyme’s structure making it less effective
rate of chem reactions will initially rise with temp but declines as enzymes denature
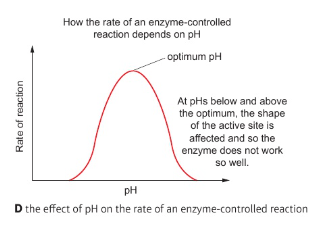
Explain the effects of pH on enzyme activity
each enzyme has an optimum pH at which it is the most effective
changes in pH alter the ionisation of amino acids
altered charges affect hydrogen bonding within the protein, leading to a change in shape
if the new shape is ineffective, enzyme activity decreases

Explain the effects of substrate concentration on enzyme activity
at lower substrate concentrations, active sites on most enzyme molecules remain unfilled
as substrate concentration increases, more collisions occur
enzymes are more likely to encounter reactant molecule
the maximum velocity of a reaction is reached when active sites are almost continuously filled
beyond this point, further substrate increase does not boost the rate
What is the rate calculation for enzyme activity?
rate = change/time

What is the test for identifying starch? How is it completed?
iodine test:
place a small amount (about one spatula or 1 cm³ if the sample is liquid) of the food sample on a dish
using a dropper, add a few drops of iodine solution onto the food sample
observe any change in the colour of the solution
if starch is present in the sample, the iodine solution will turn blue-black
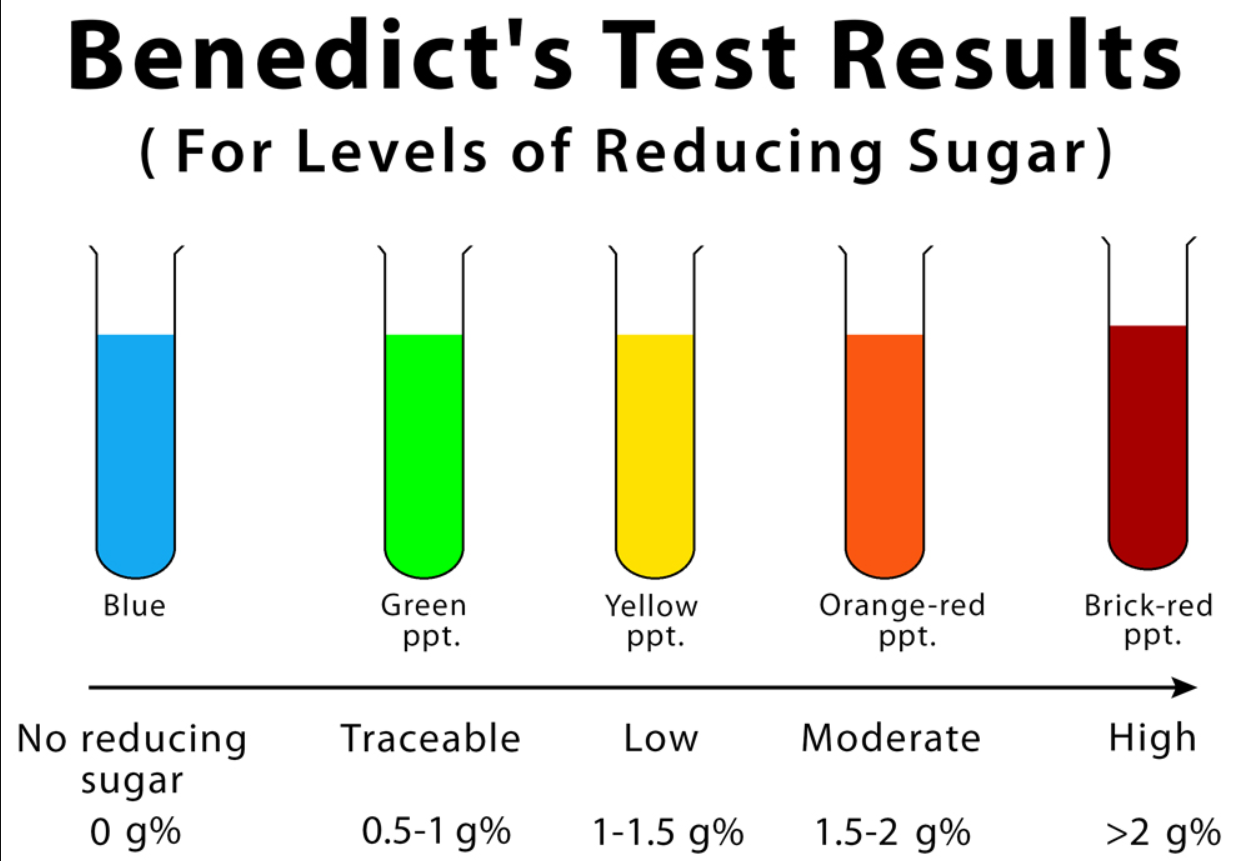
What is the test for identifying reducing sugars? How is it completed?
benedict’s test:
take 1 ml of the sample to be tested
add 2 ml of Benedict’s reagent to the sample
heat the mixture in a boiling water bath for 3 to 5 minutes
if reducing sugars are present, a brick-red precipitate of cuprous oxide (Cu2O) will form
glucose not present: remains blue
little bit of glucose present: clear blue => green
lots of glucose present: clear blue => brick red + precipitate
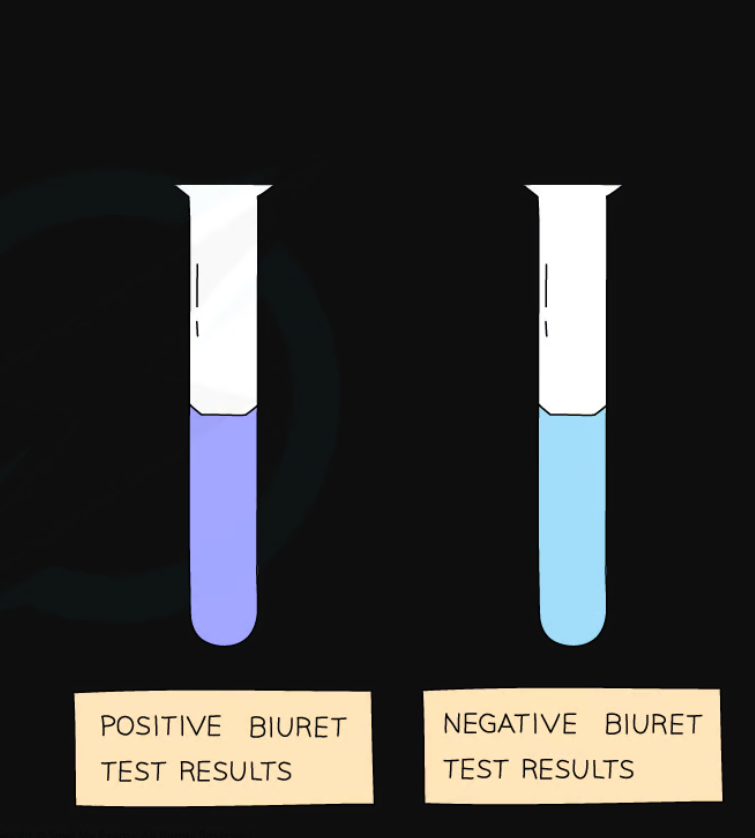
What is the test for identifying proteins? How is it completed?
biuret test:
take a liquid sample of the substance you want to test for proteins
add biuret solution A to the sample and mix it carefully
trickle a little biuret solution B down the side of the tube
observe the area where the two solutions meet
if proteins are present, a positive colour change will be from blue => purple
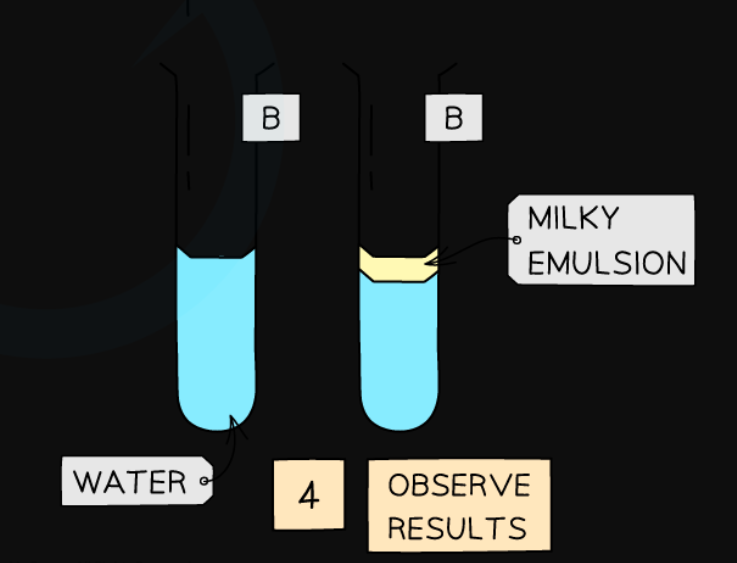
What is the test for identifying fats? How is it completed?
ethanol emulsion test:
take the sample to be tested
add ethanol to the sample and shake to mix
transfer the mixture to a test tube containing water
if lipids are present, a milky emulsion will form (the solution appears cloudy)
positive appearance change: clear => cloudy
more lipids present = more obvious milky solution
no lipids = solution remains clear
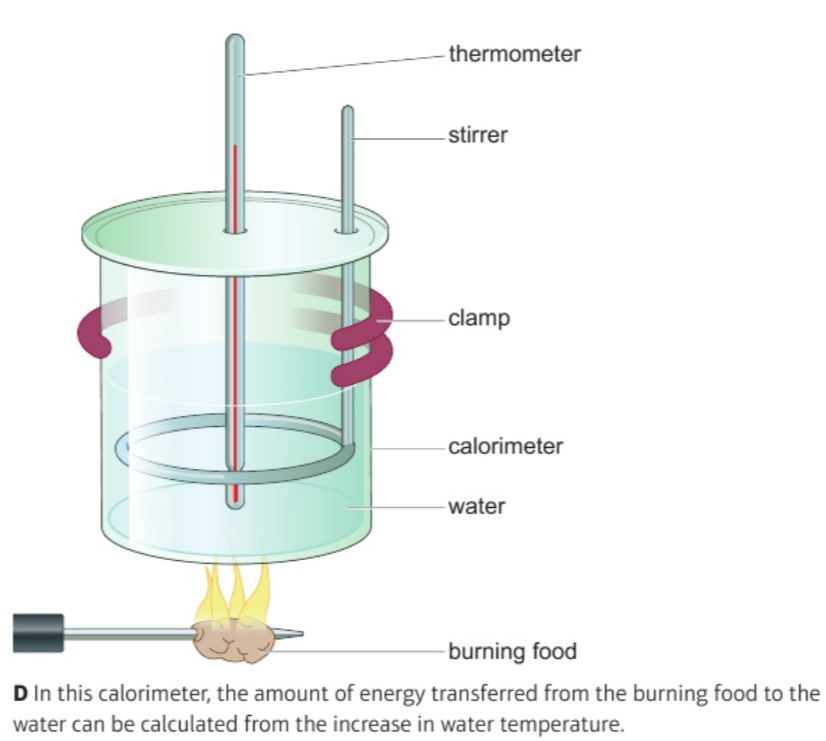
Explain how the energy contained in food can be measured using calorimetry
energy transferred (Joules) = (mass of water (g) × 4.2 J/g°C × temperature increase (°C)) ÷ mass of food (g)
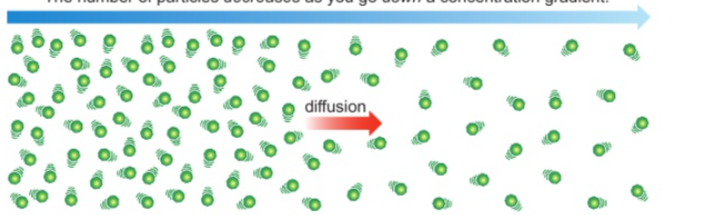
Explain how substances are transported into and out of cells by diffusion
a passive process in which particles move from an area of high concentration => low concentration
doesn’t require any energy
how oxygen leaves a leaf
involves transport of solutes
follows concentration gradient
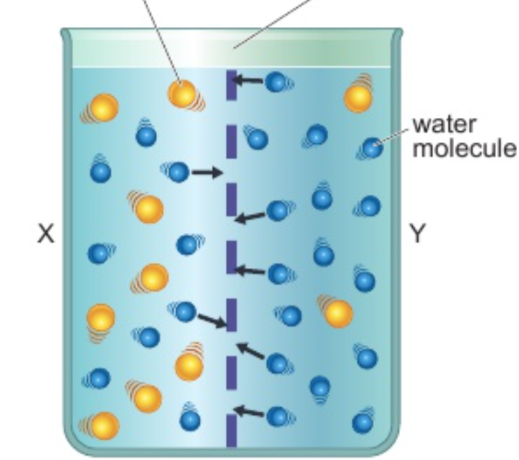
Explain how substances are transported into and out of cells by osmosis
the net movement of water molecules from a solution with high concentration to a solution with low concentration through a cell’s partially (semi) permeable membrane
how water keeps plant cells turgid
follows concentration gradient
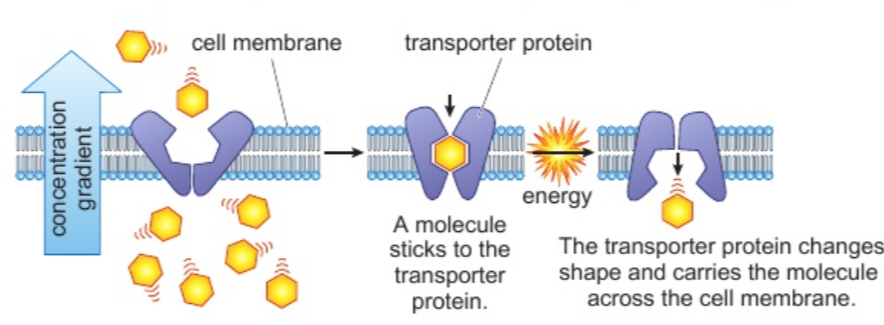
Explain how substances are transported into and out of cells by active transport
the process of molecules going from a low concentration => high concentration
requires a protein pump + energy
against a concentration gradient
how minerals get into a root hair cell
Calculate percentage gain and loss of mass in osmosis
percentage mass change:
(finish mass - start mass)/start mass * 100