The Periodic Table
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Imported from quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
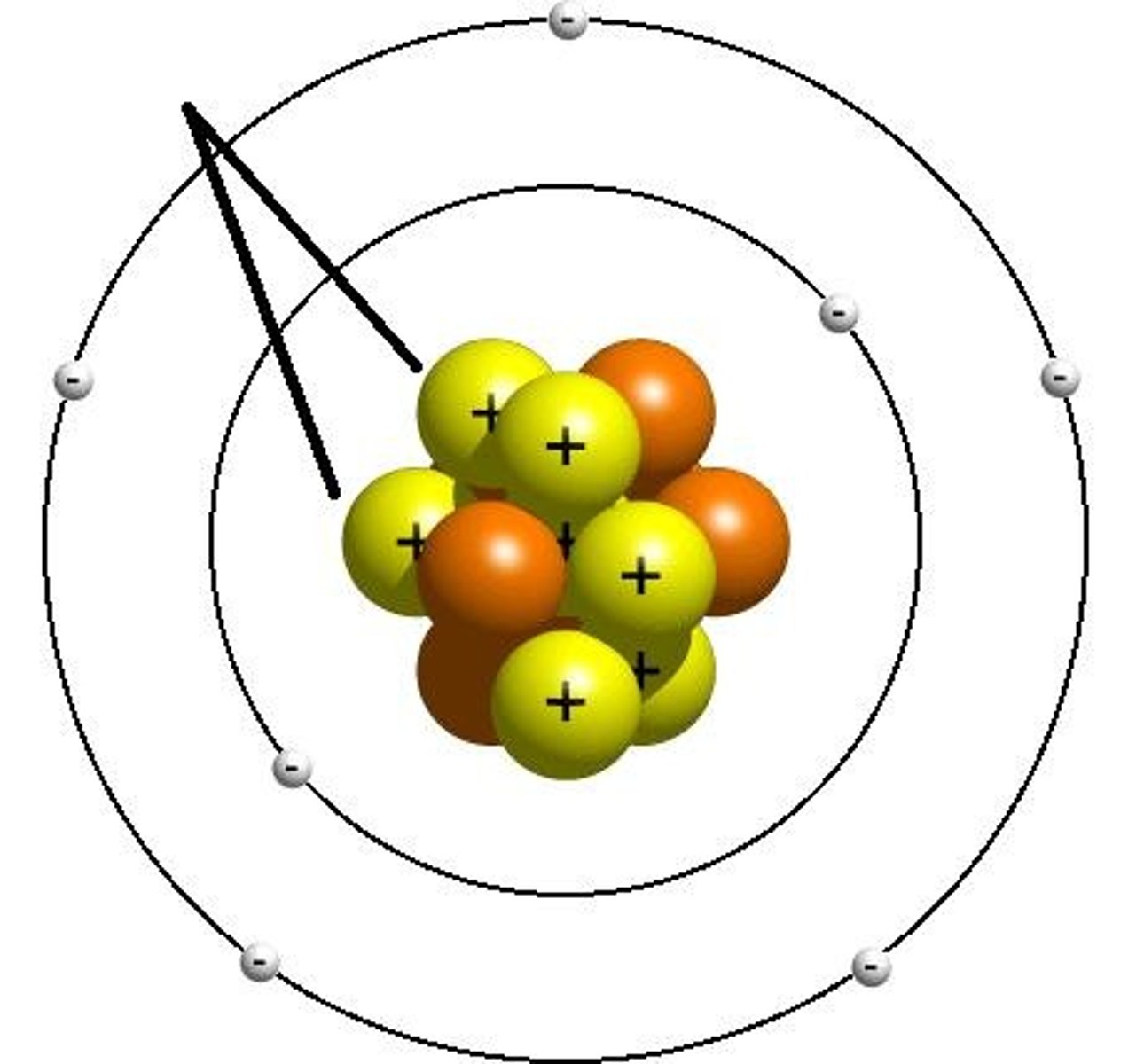
Atom
Smallest particle of an element
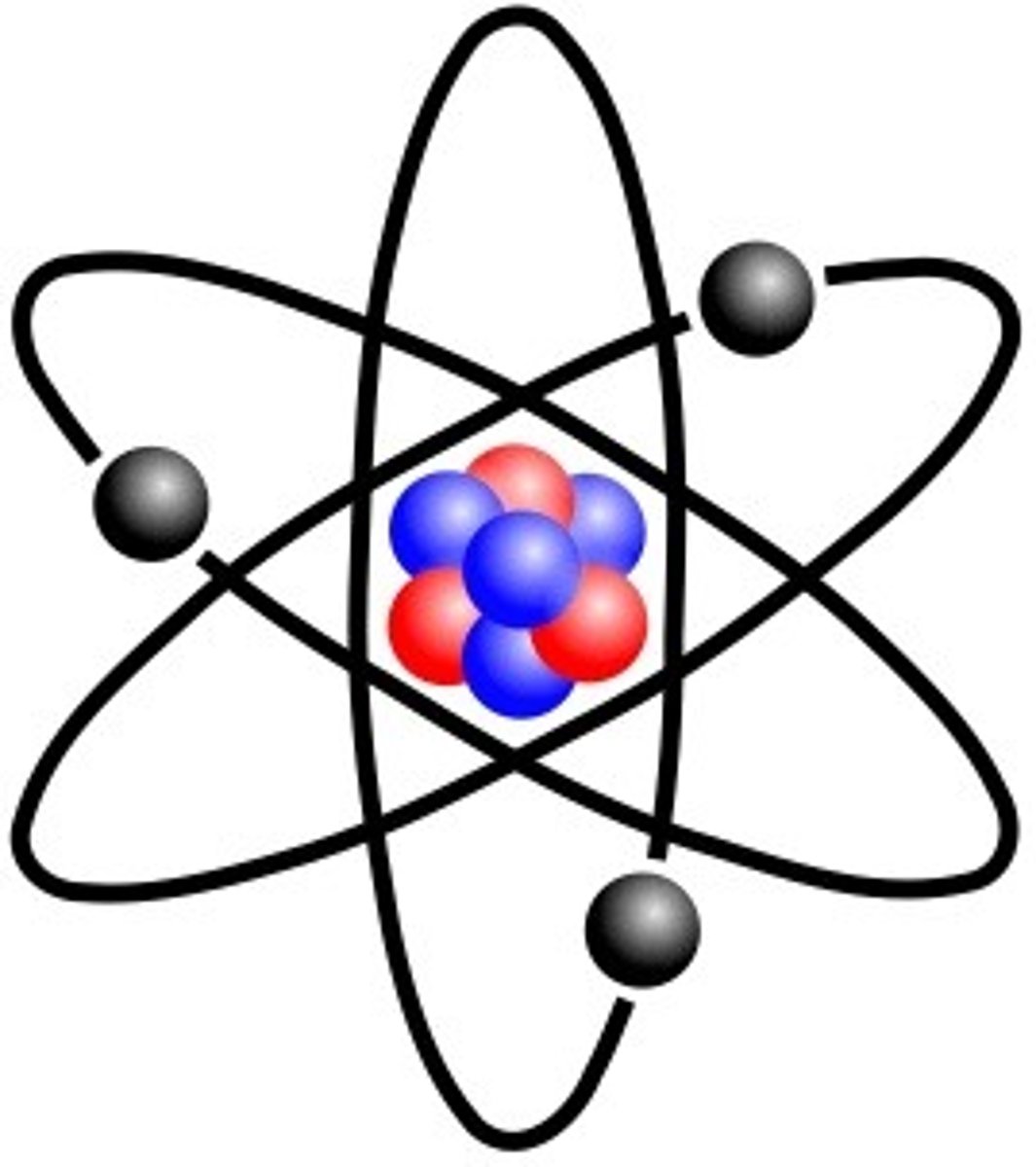
Proton
Positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom

Neutron
Particle with no charge found in the nucleus of an atom

Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom

Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
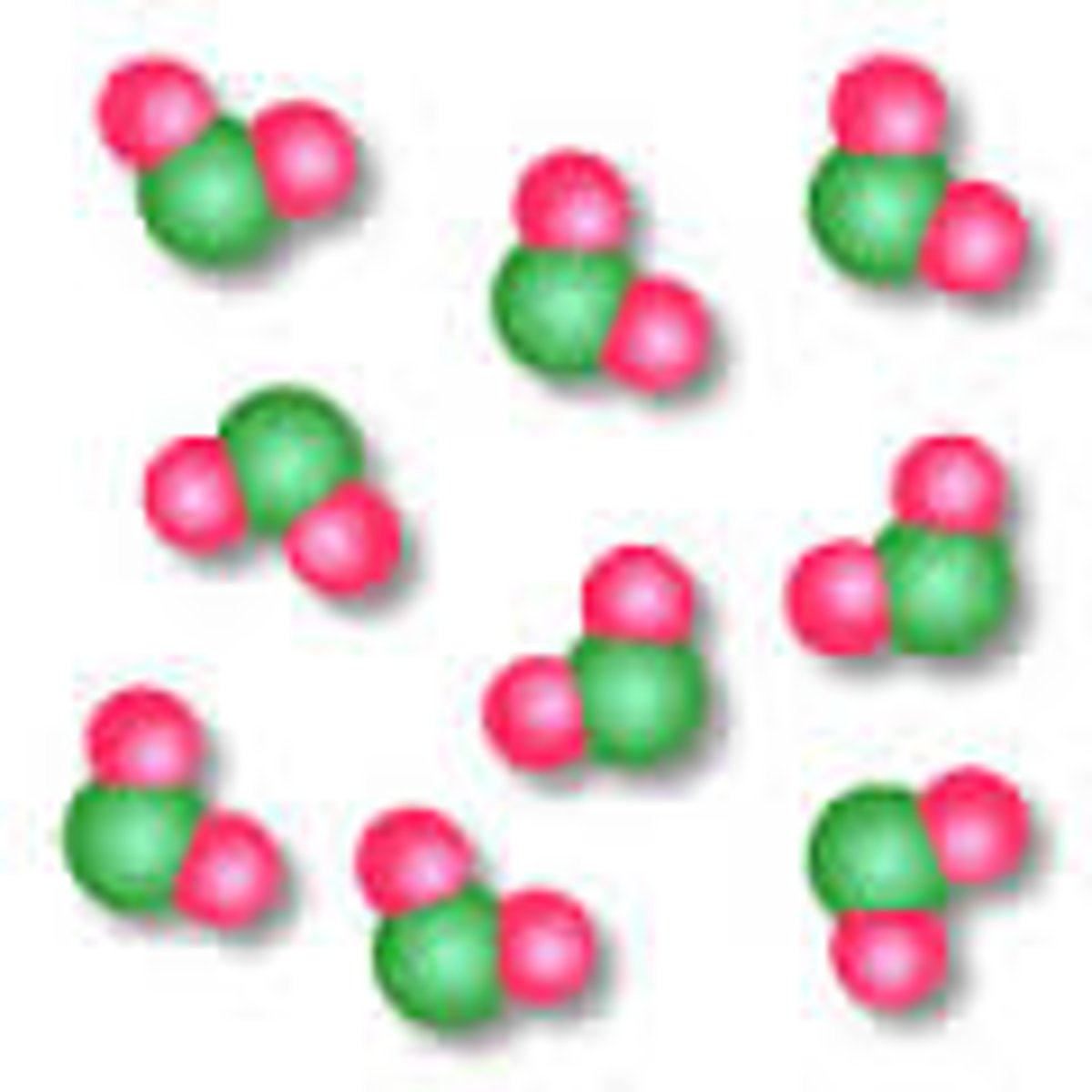

Molecule
Two or more atoms bonded together
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
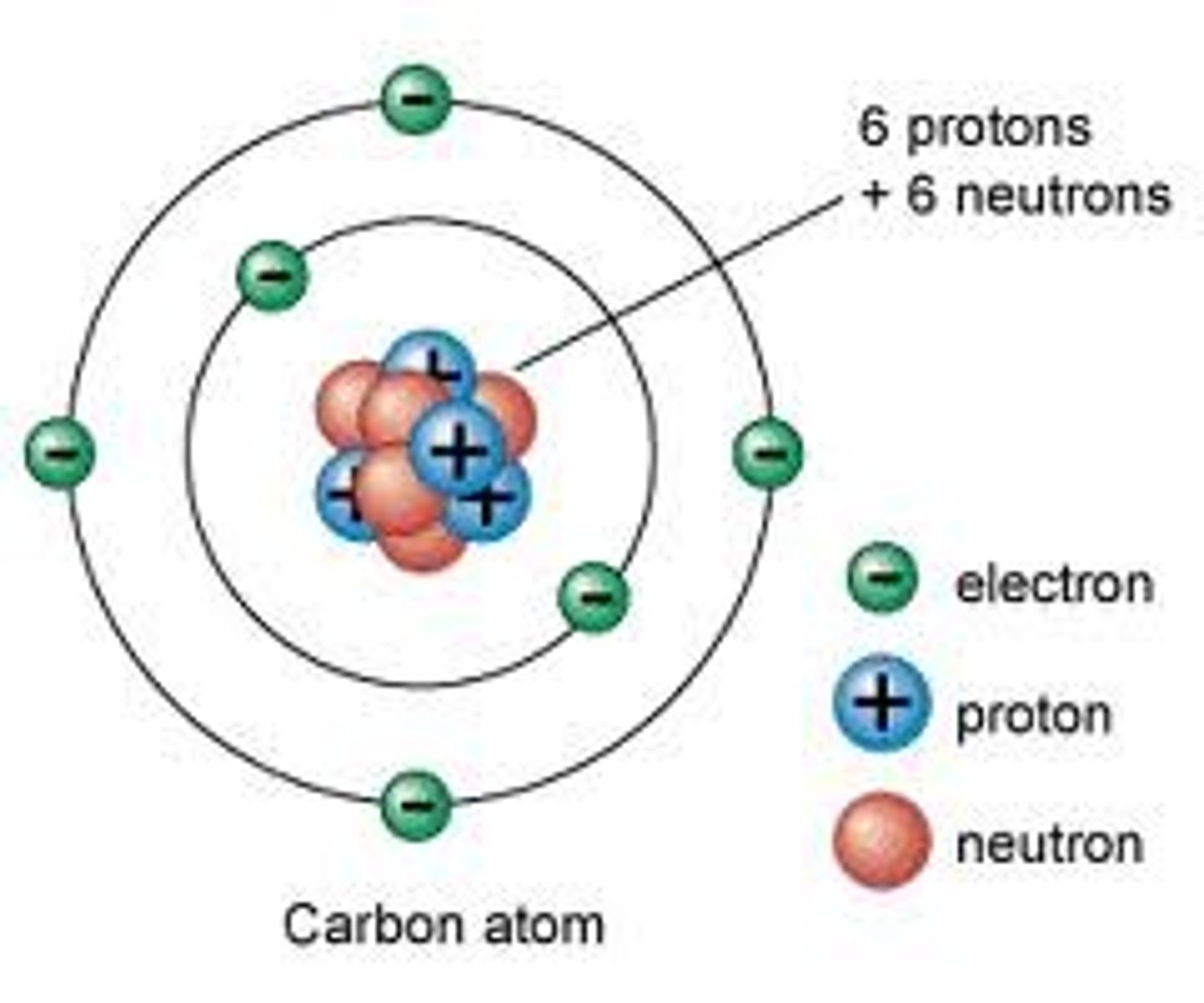
Mass Number
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
Nuclide Symbol
Symbol that indicates the atomic number, mass number, and identity of a nucleus
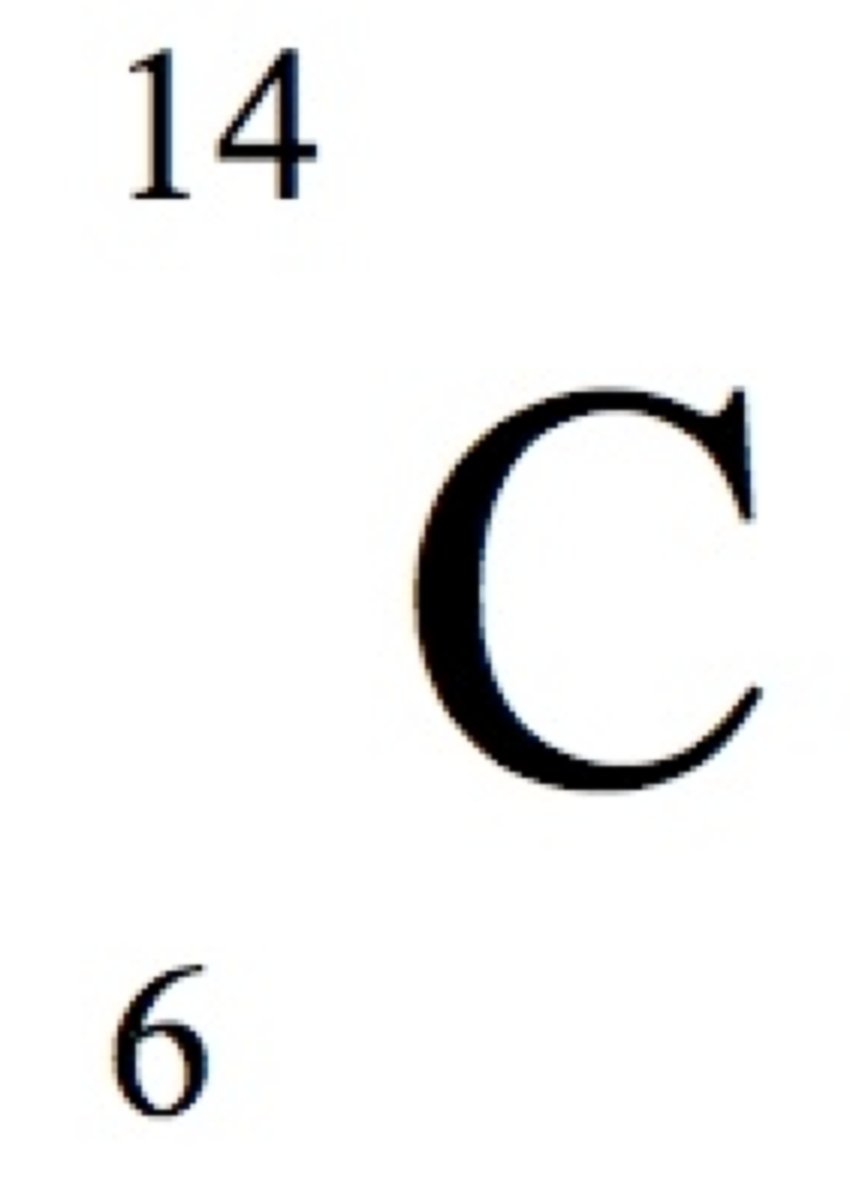
Electron Shell
A grouping of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom
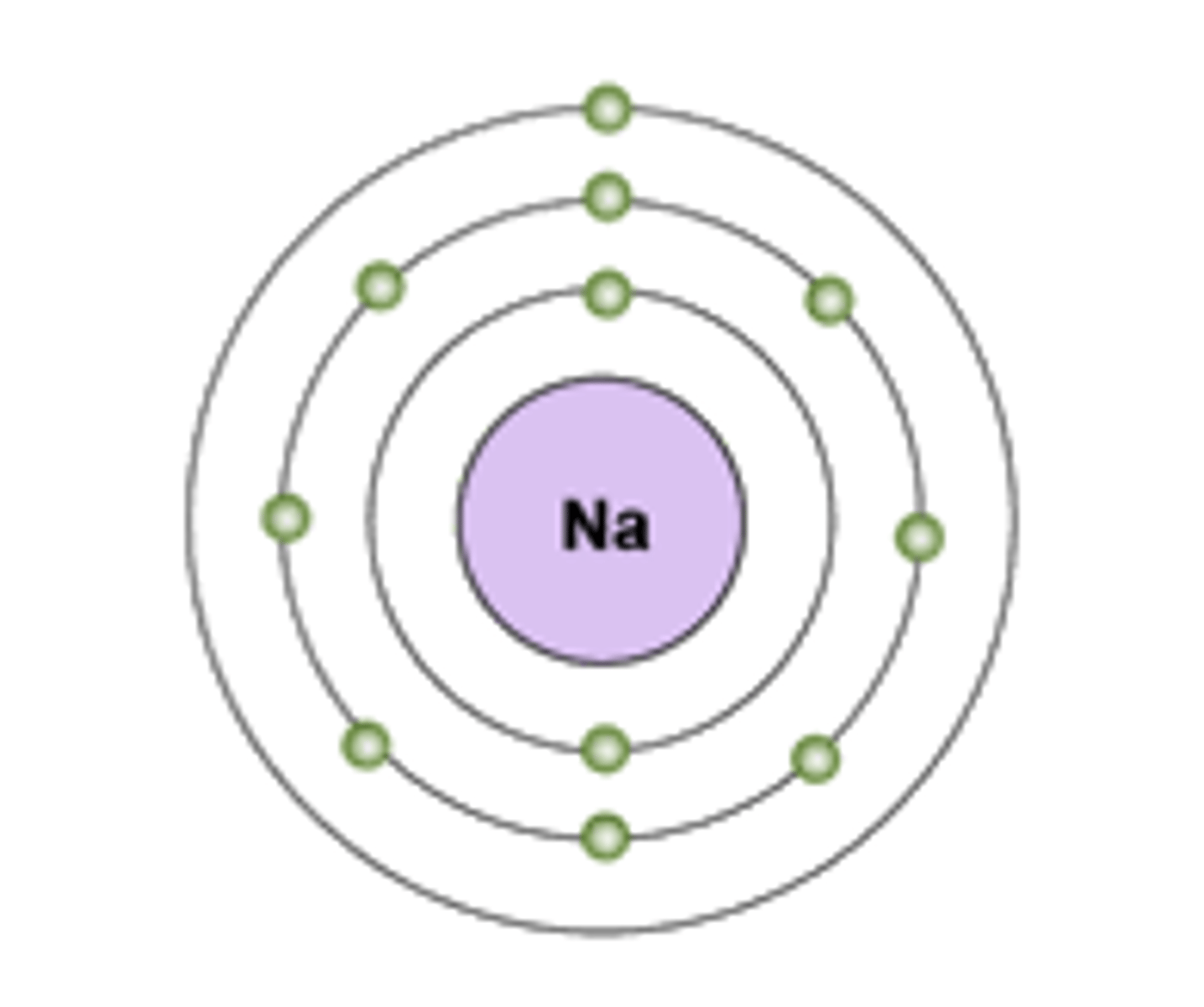
Subatomic Particle
Particles found within the atom, mainly protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Periodic Table
A table that shows the elements, their atomic number, symbol, and average atomic mass; elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together.
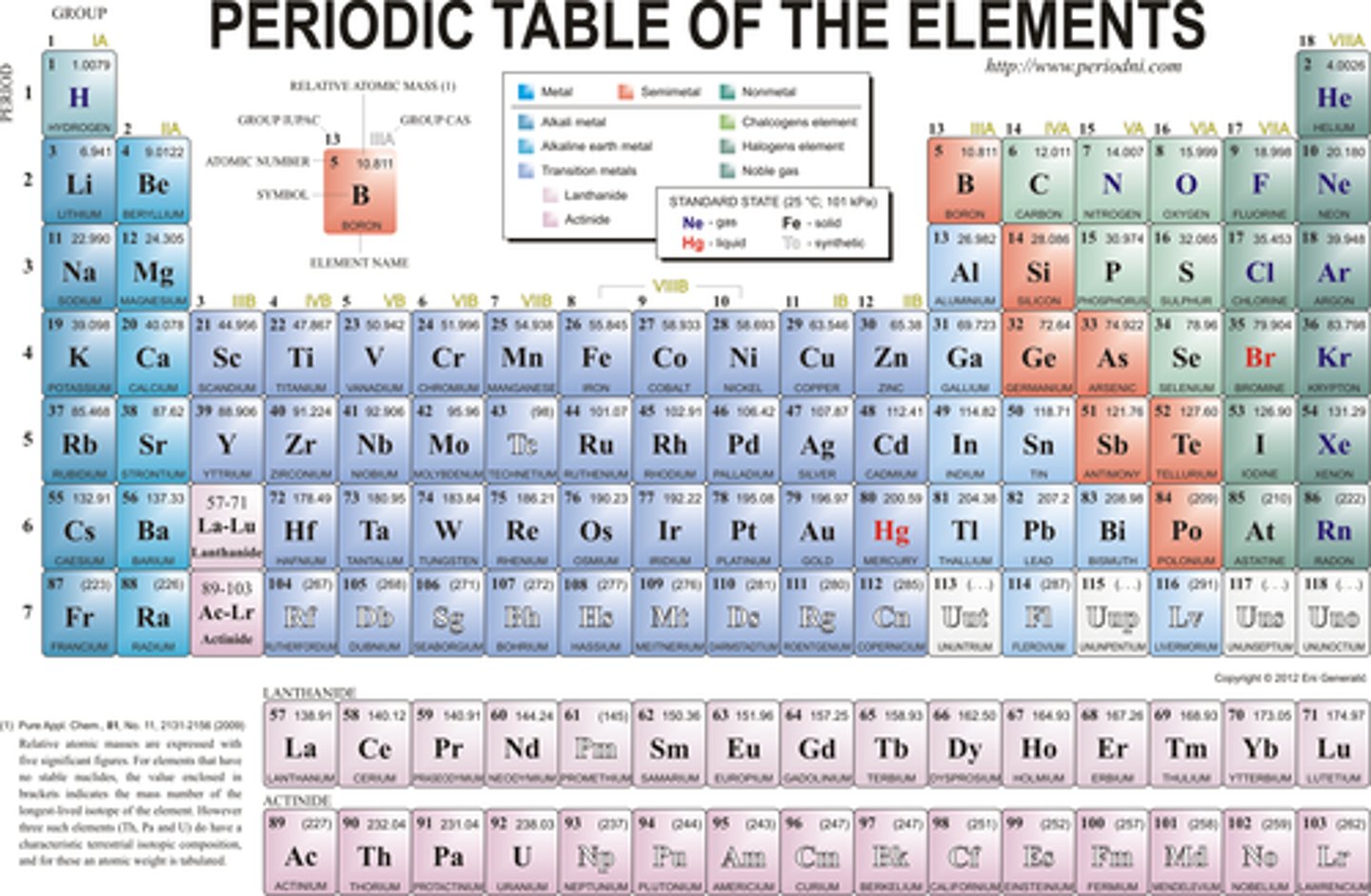
Group
Vertical column in the periodic table
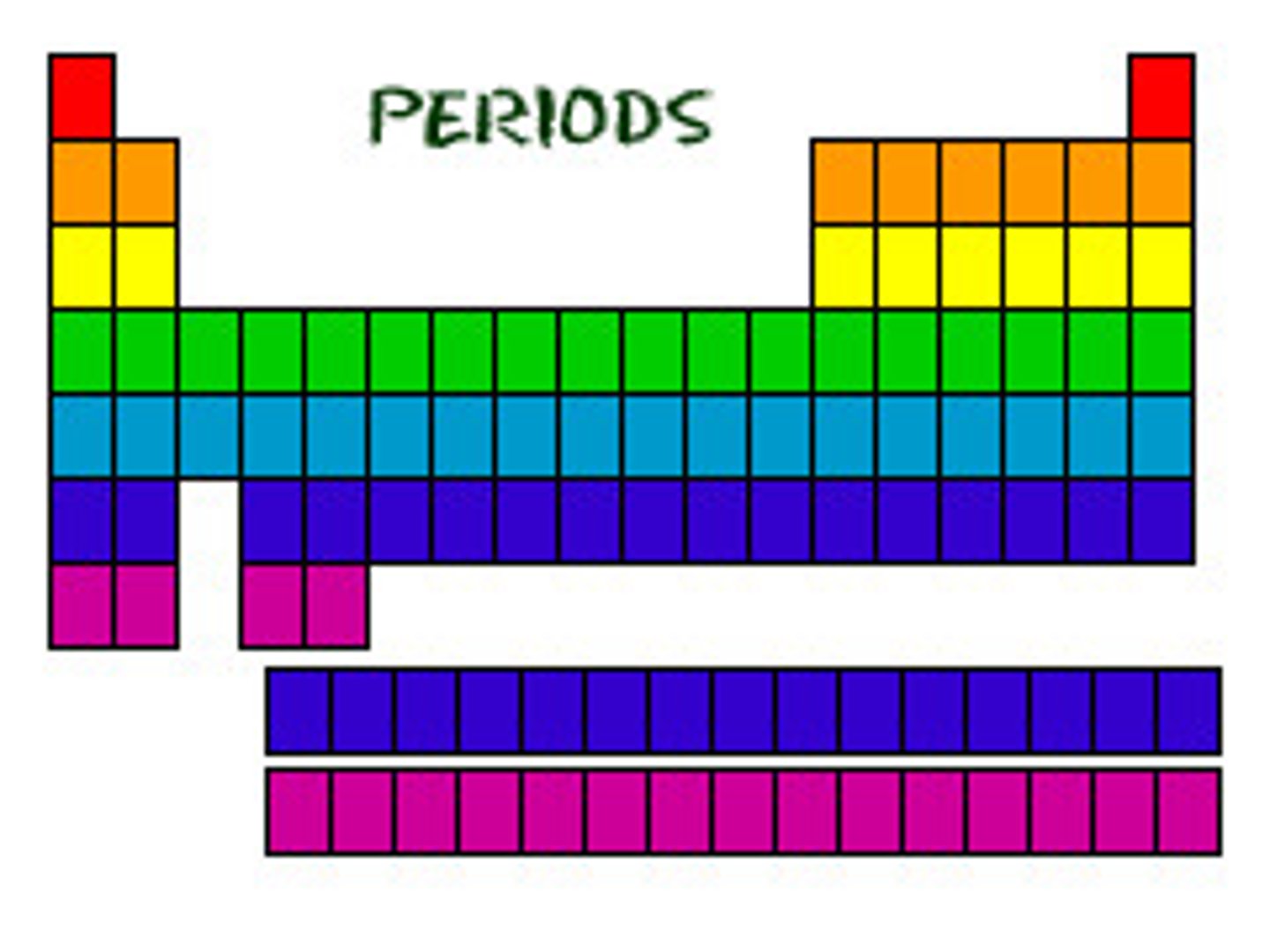
Period
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
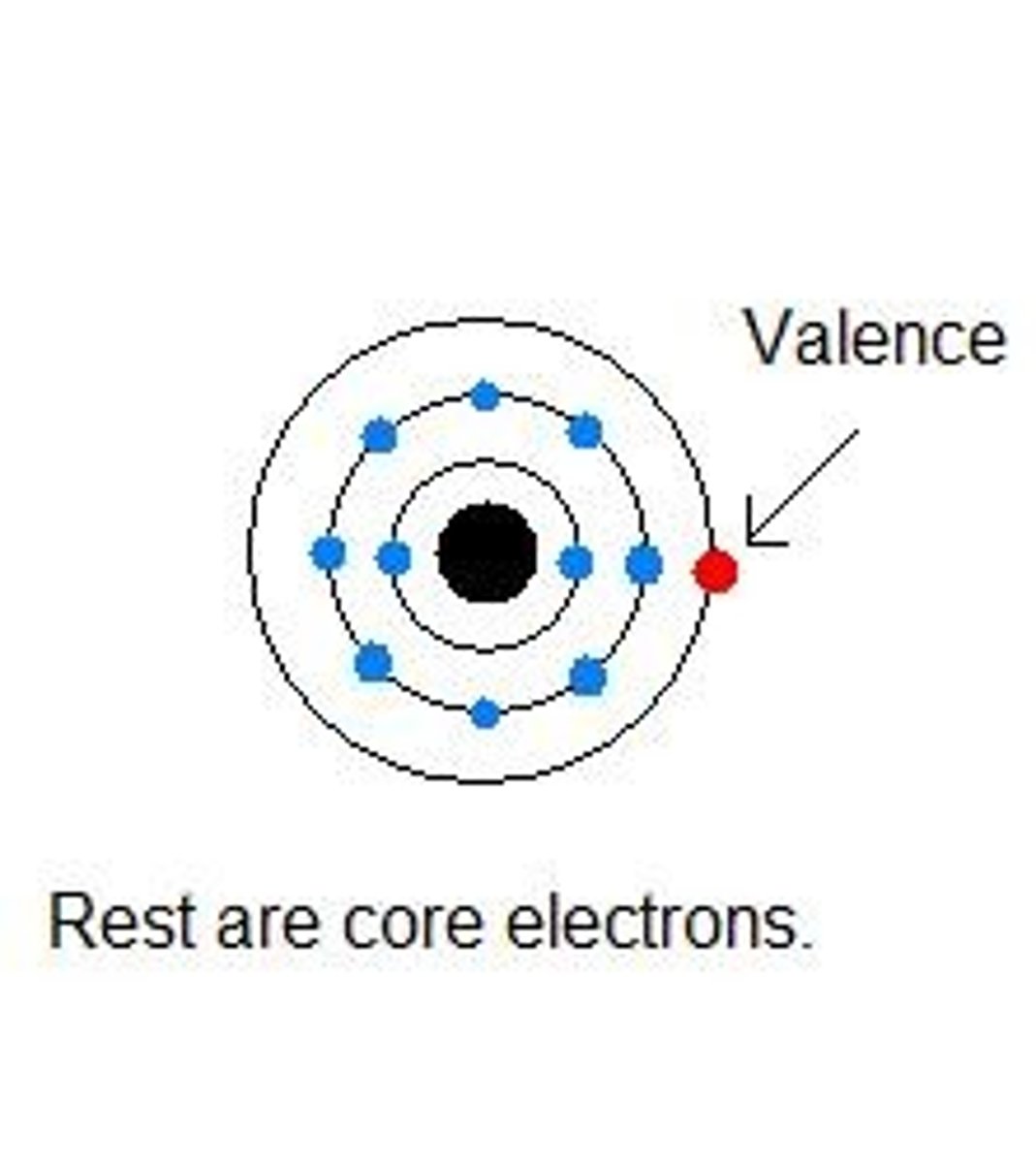
Metals
Elements that are good conductors of electric current and heat.
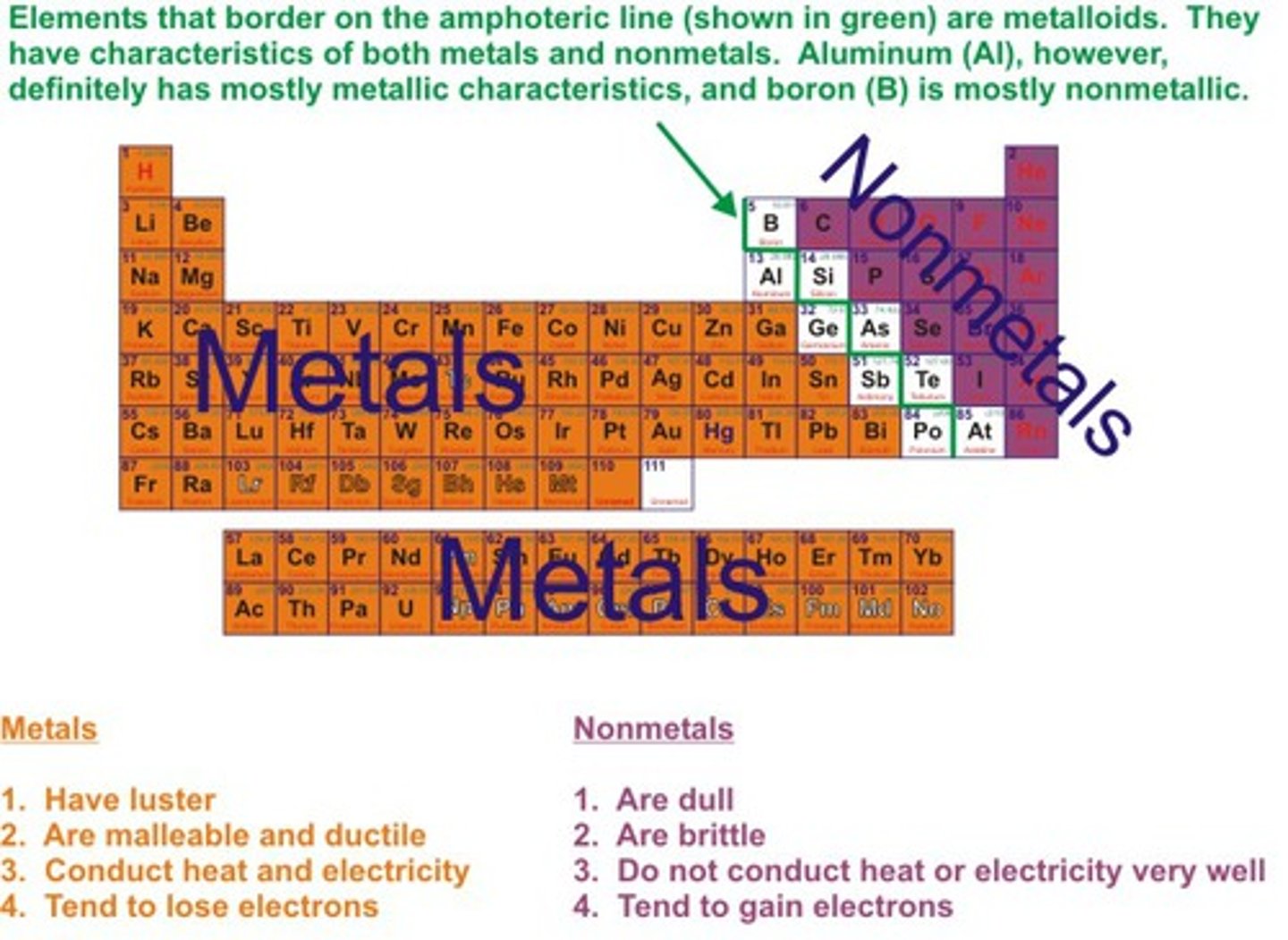
Non-metals
Elements that are usually dull in appearance, poor conductors of heat and electricity, usually gases at room temperature
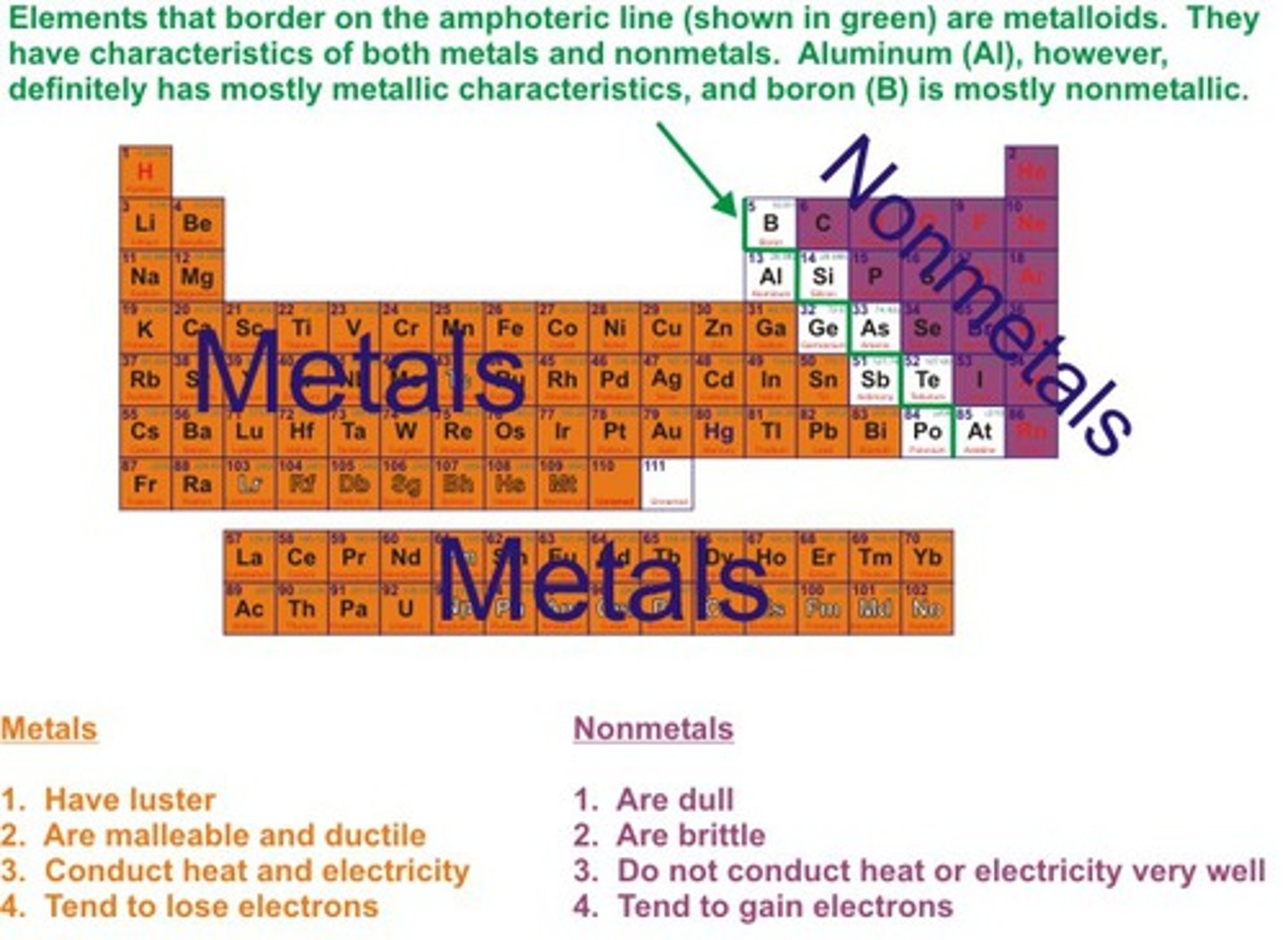
Metalloids
Elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals.
Alkali Metals
Elements found in group 1 of the Periodic Table
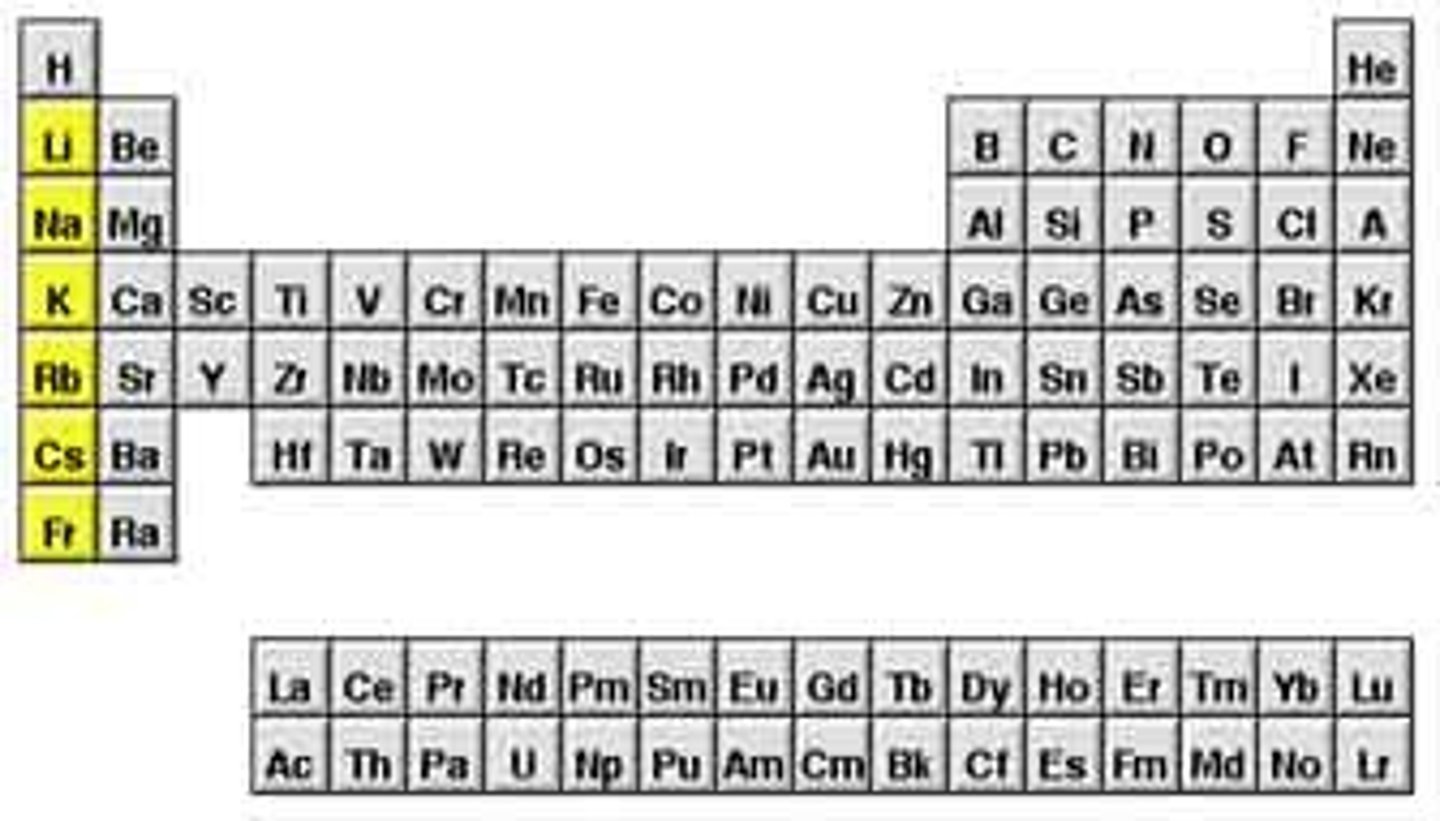
Alkaline Earth Metals
Elements found in group 2 of the Periodic Table
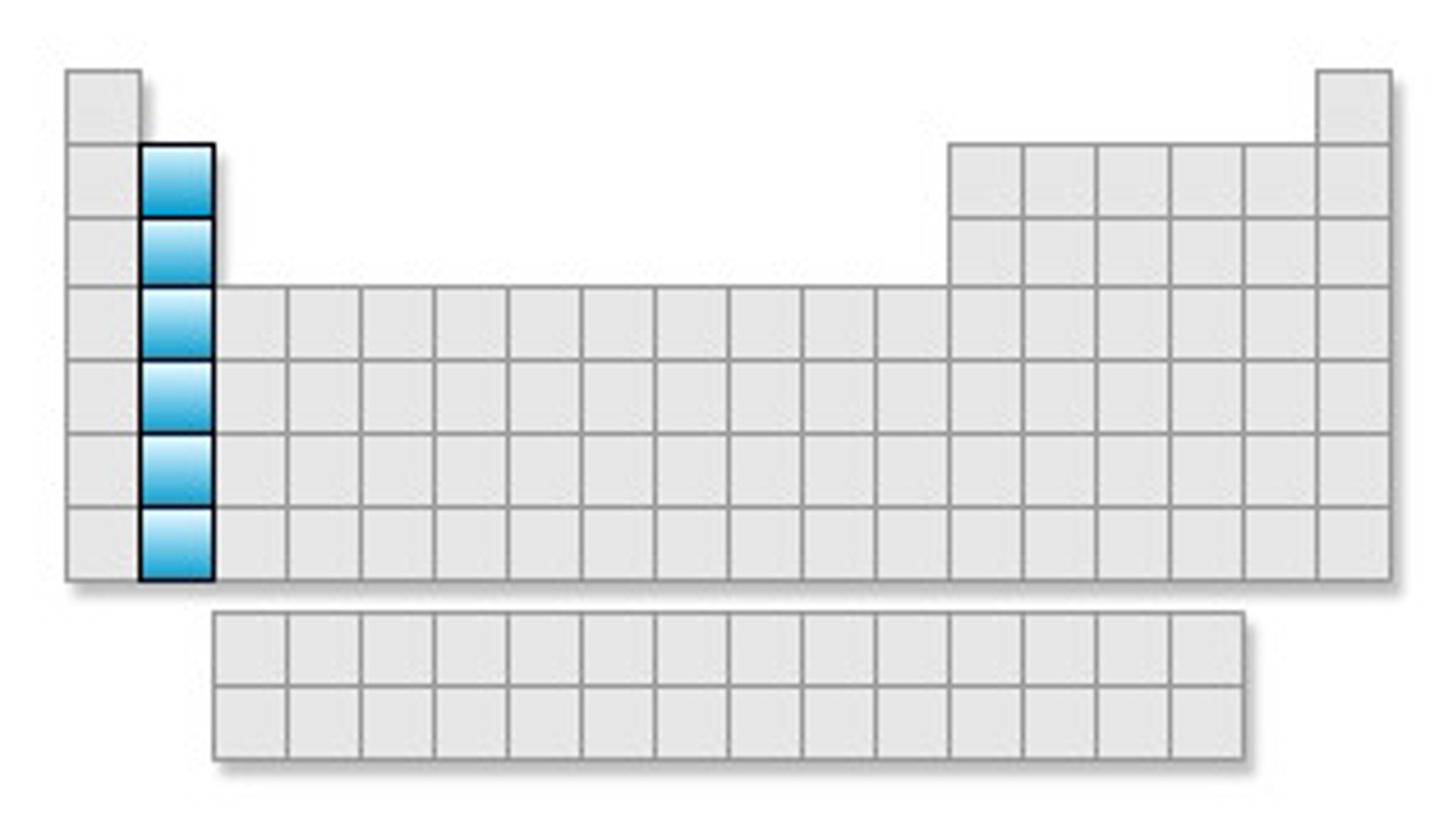
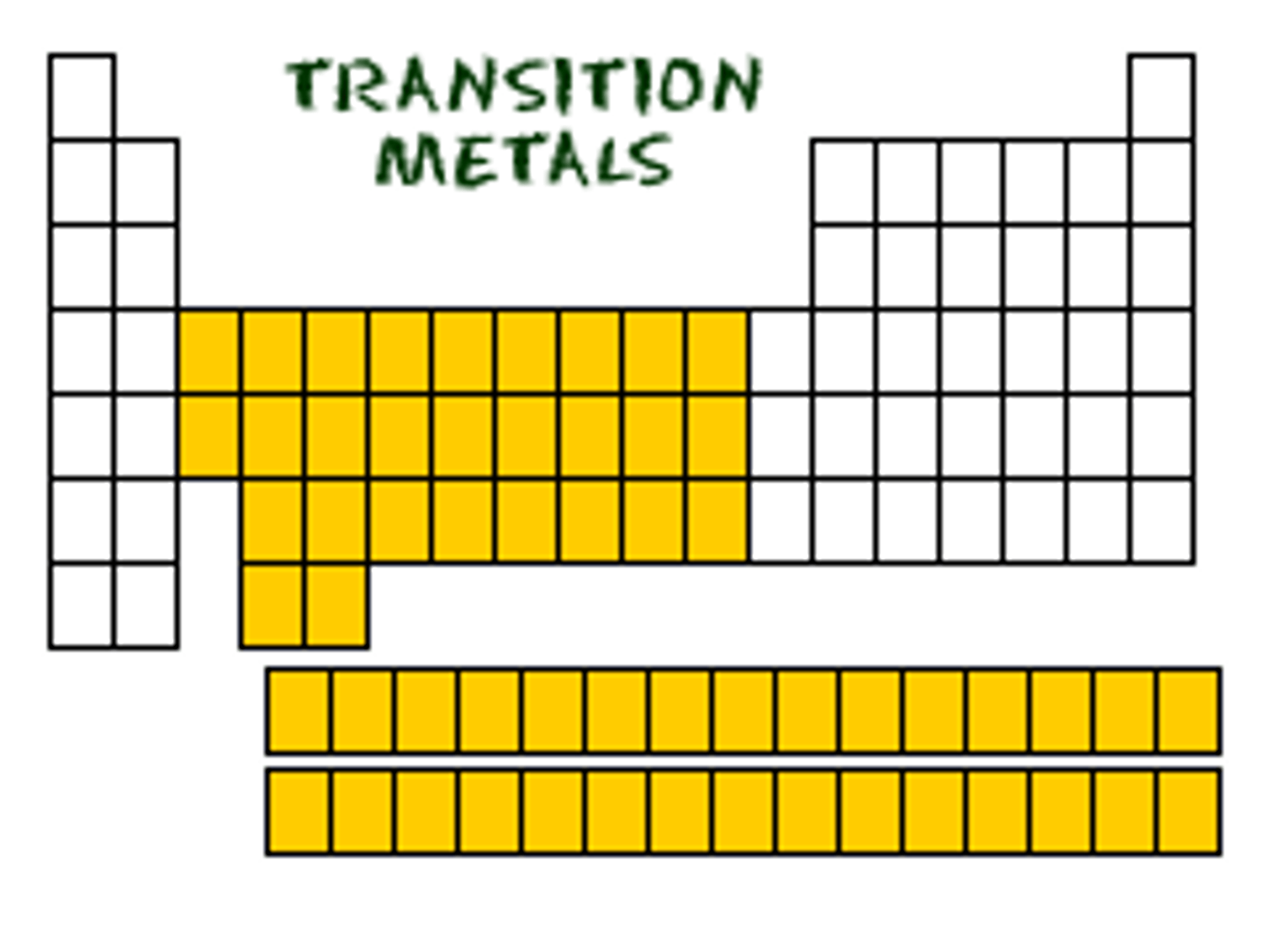
Transition Metals
Elements found in groups 3 - 12 of the Periodic Table
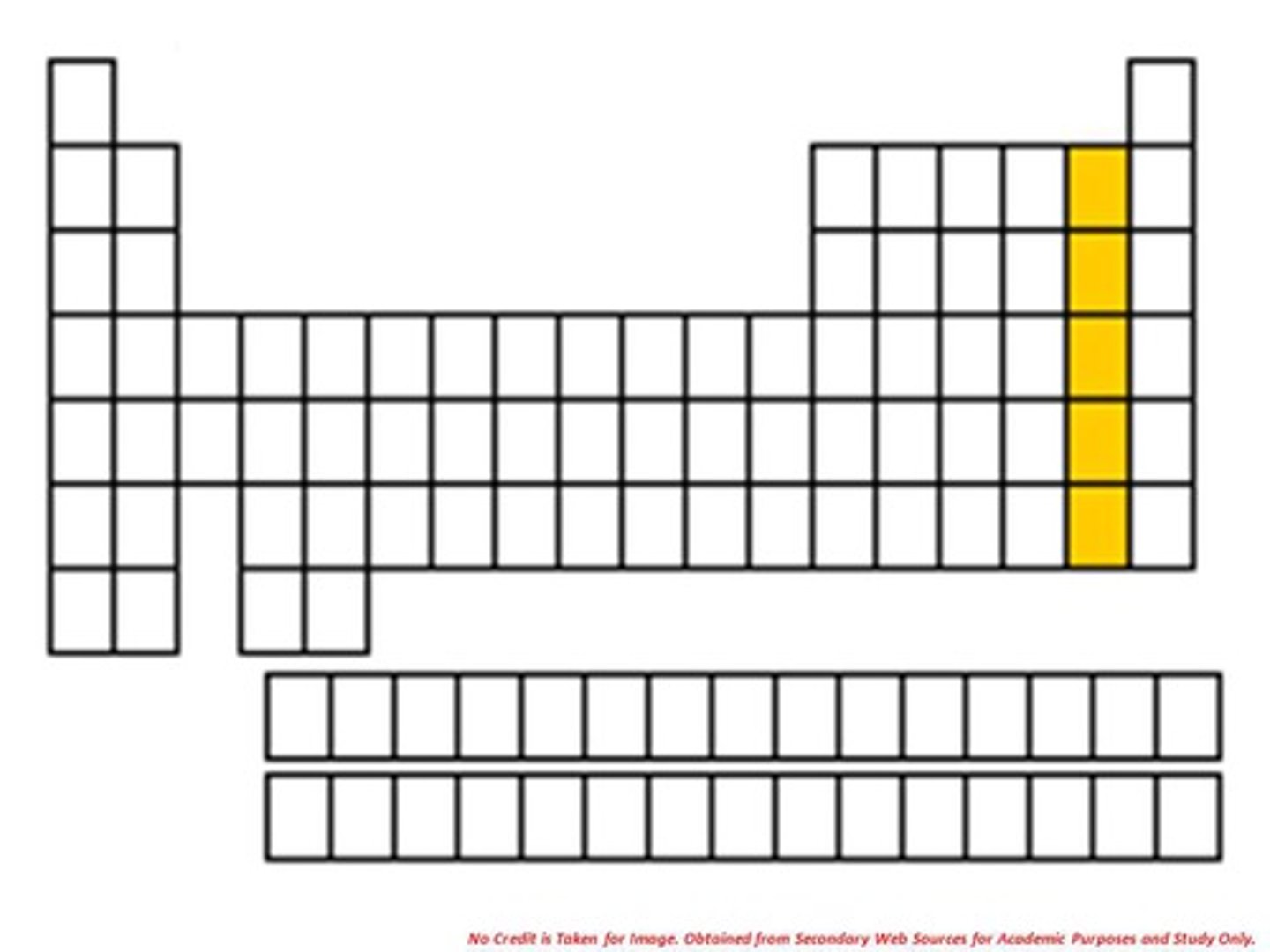
Halogens
Elements found in group 17 of the Periodic Table
Lanthanoids
the top period of the 2 below
Conductor
A material that allows heat and electricity to pass through it.

Ductile
A term used to describe a material that can be pulled out into a long wire.

Tensile Strength
A measure of how much stress from pulling, or tension, a material can withstand before breaking.
Density
Mass per unit volume of a substance.
Reactivity
The property that describes how readily a substance combines chemically with other substances
Stable
Not easily changed
Electron Configuration
the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals/shells of an atom
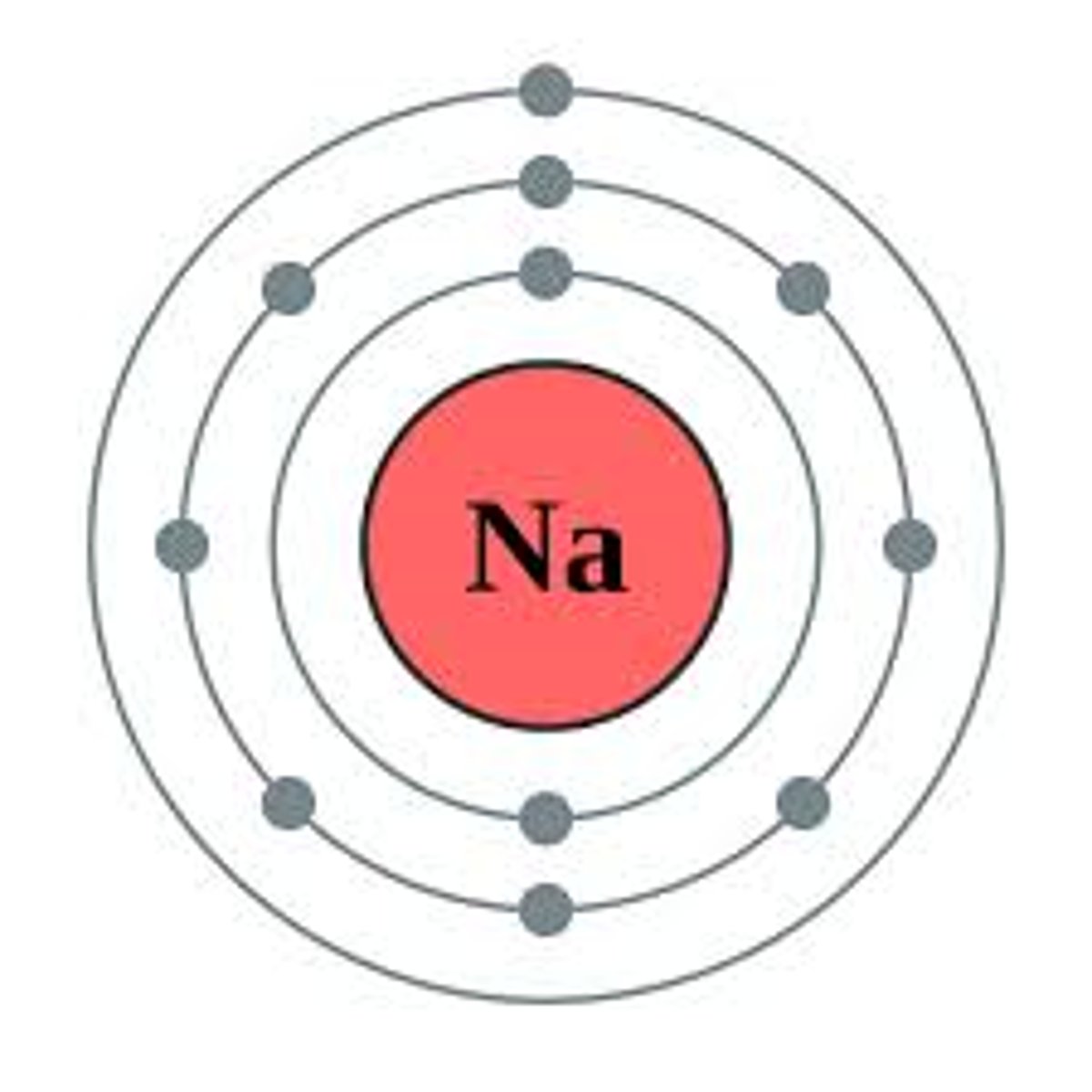
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
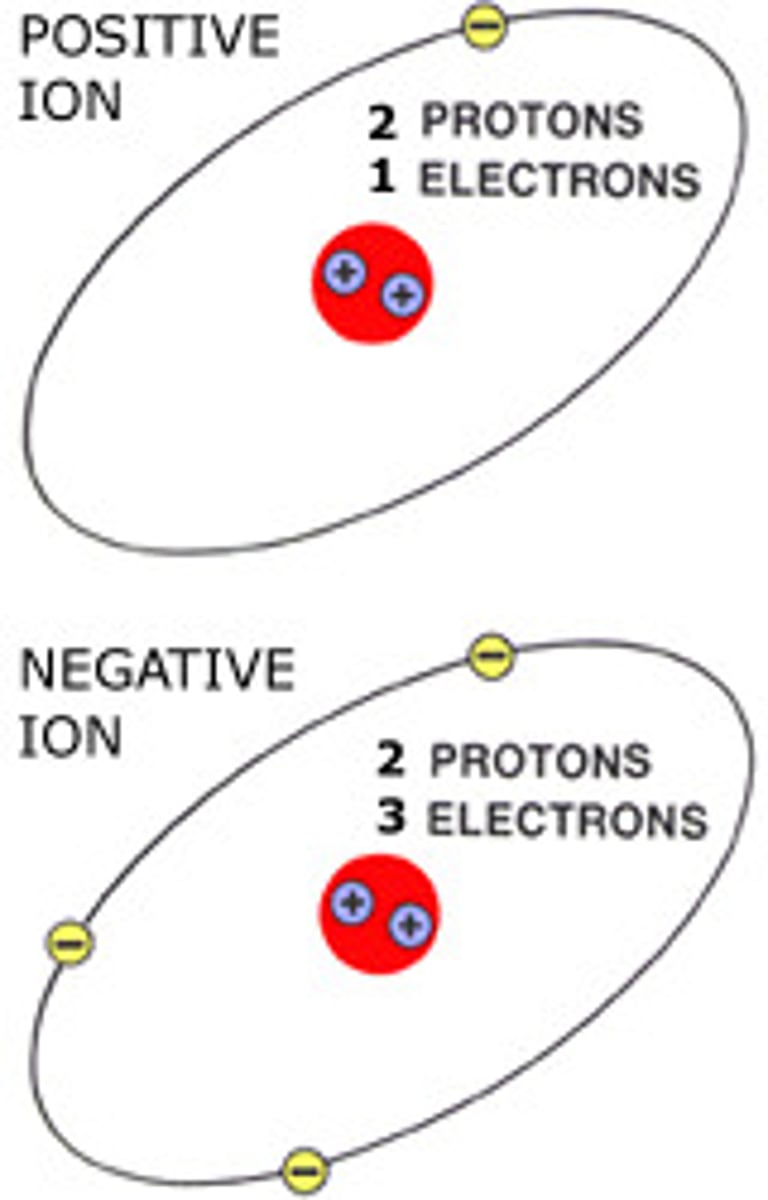
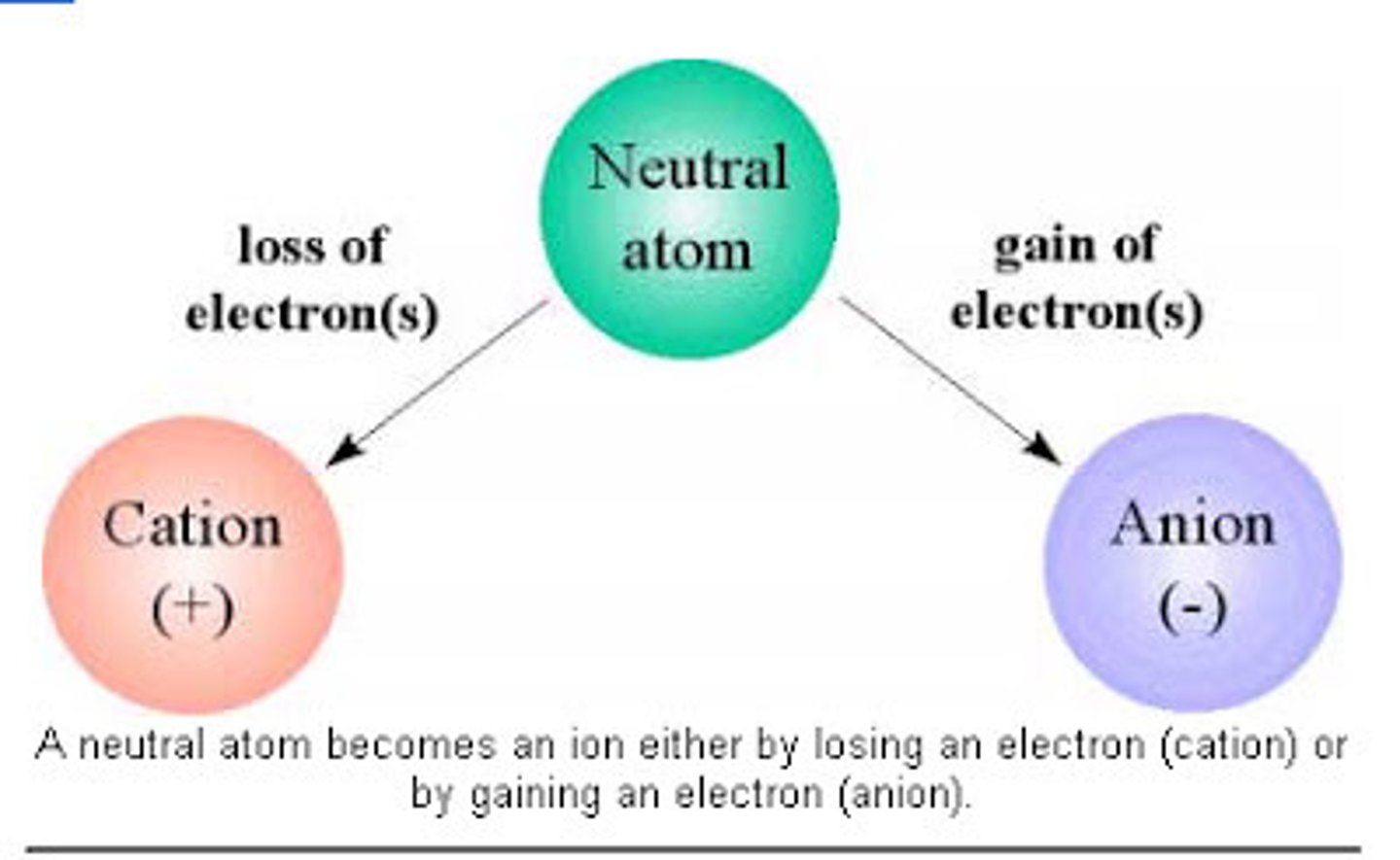
Cation
A positively charged ion (loses electrons)
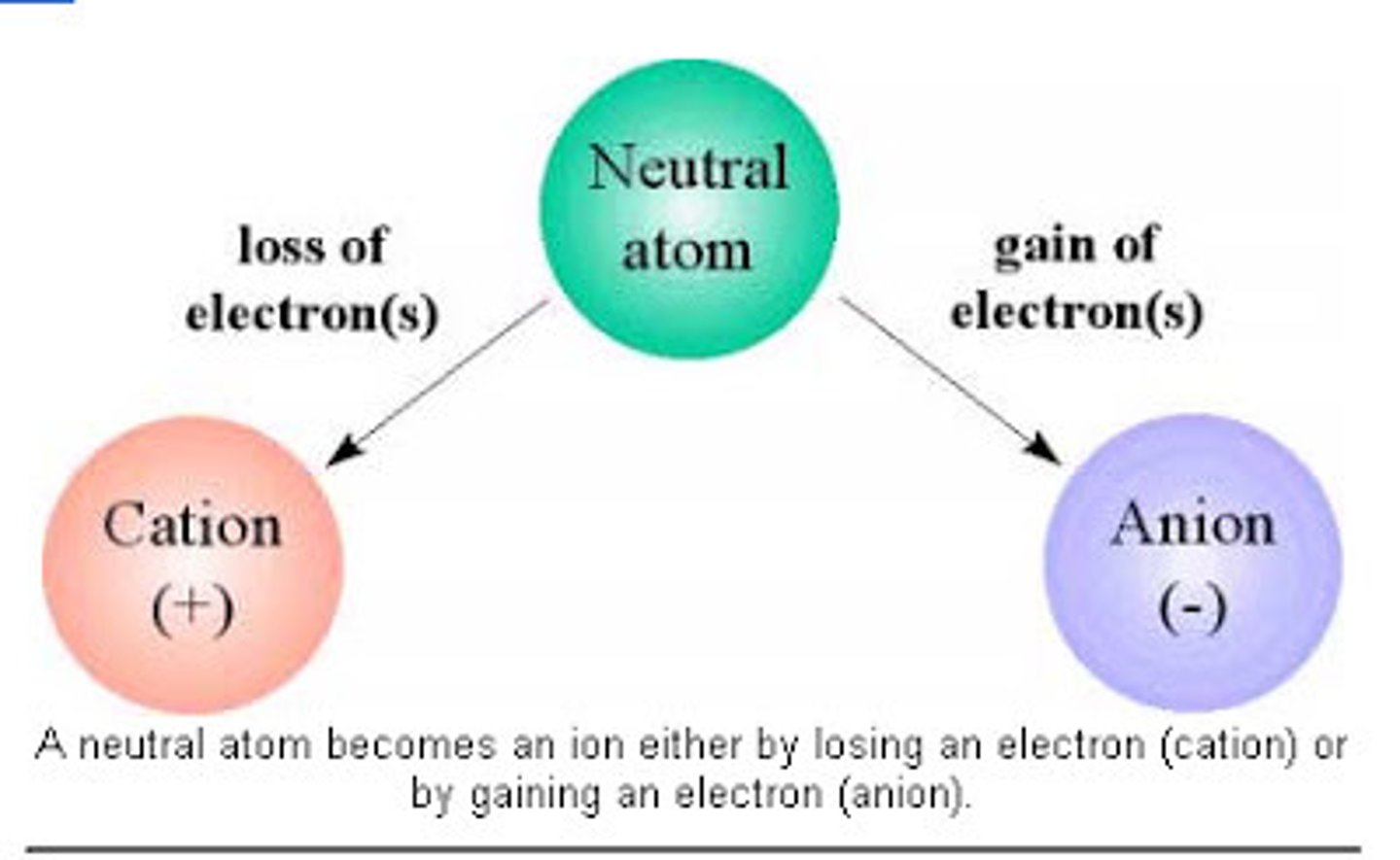
Anion
A negatively charged ion (gains electrons)
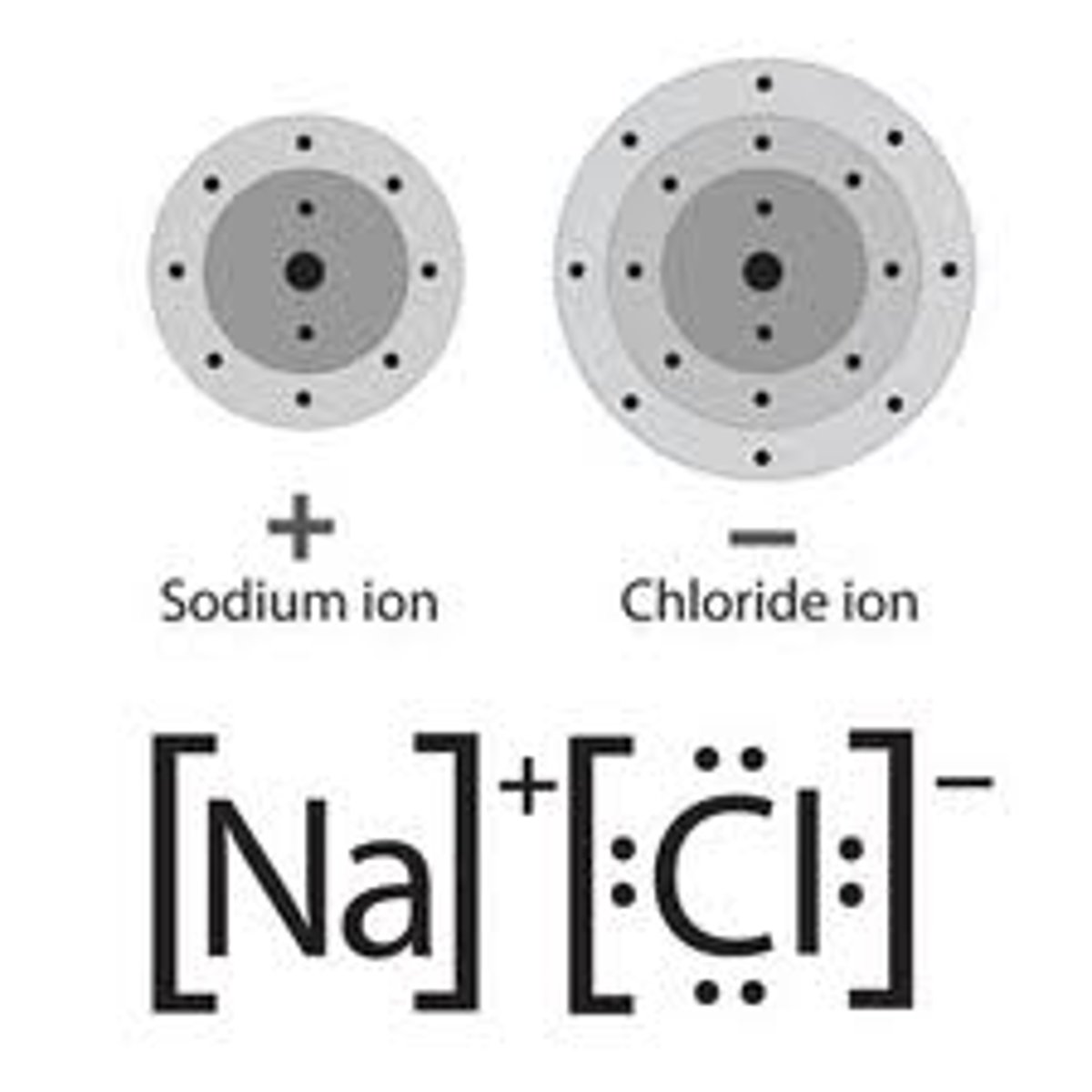
Ionic bonding
Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between cations and anions
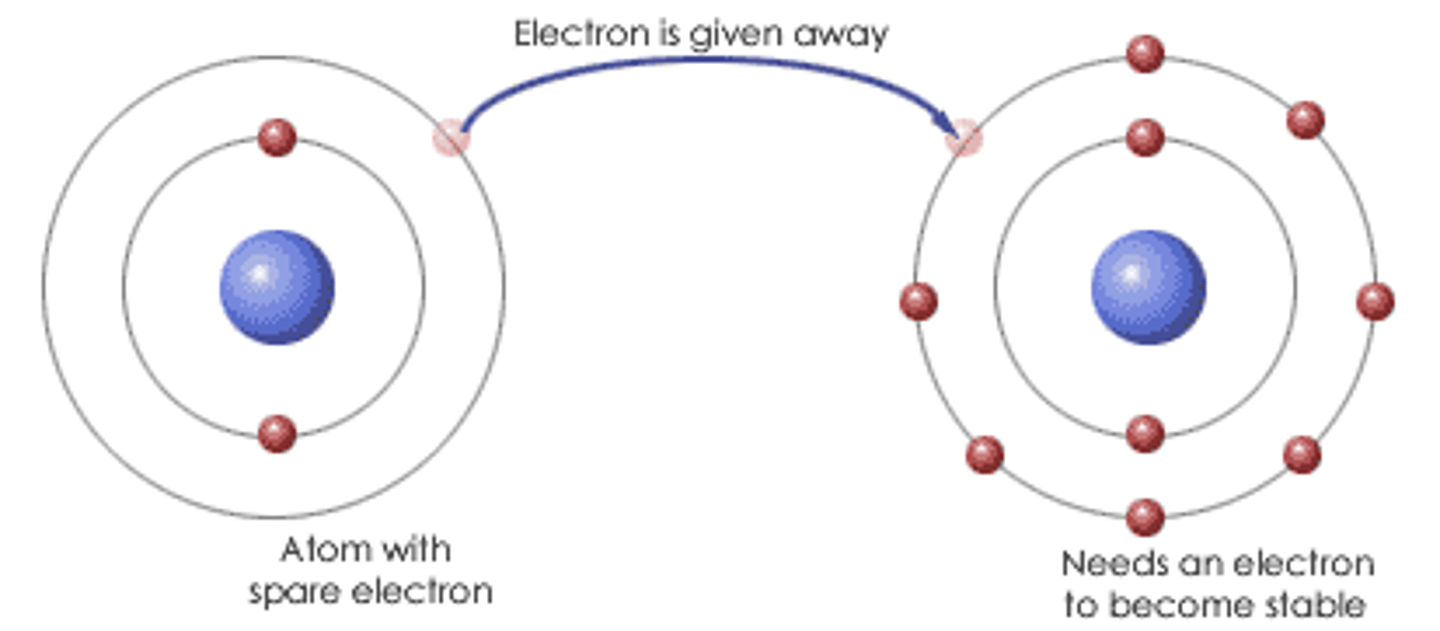
Ionic compound
composed of positive and negative ions that are combined so that the numbers of positive and negative charges are equal
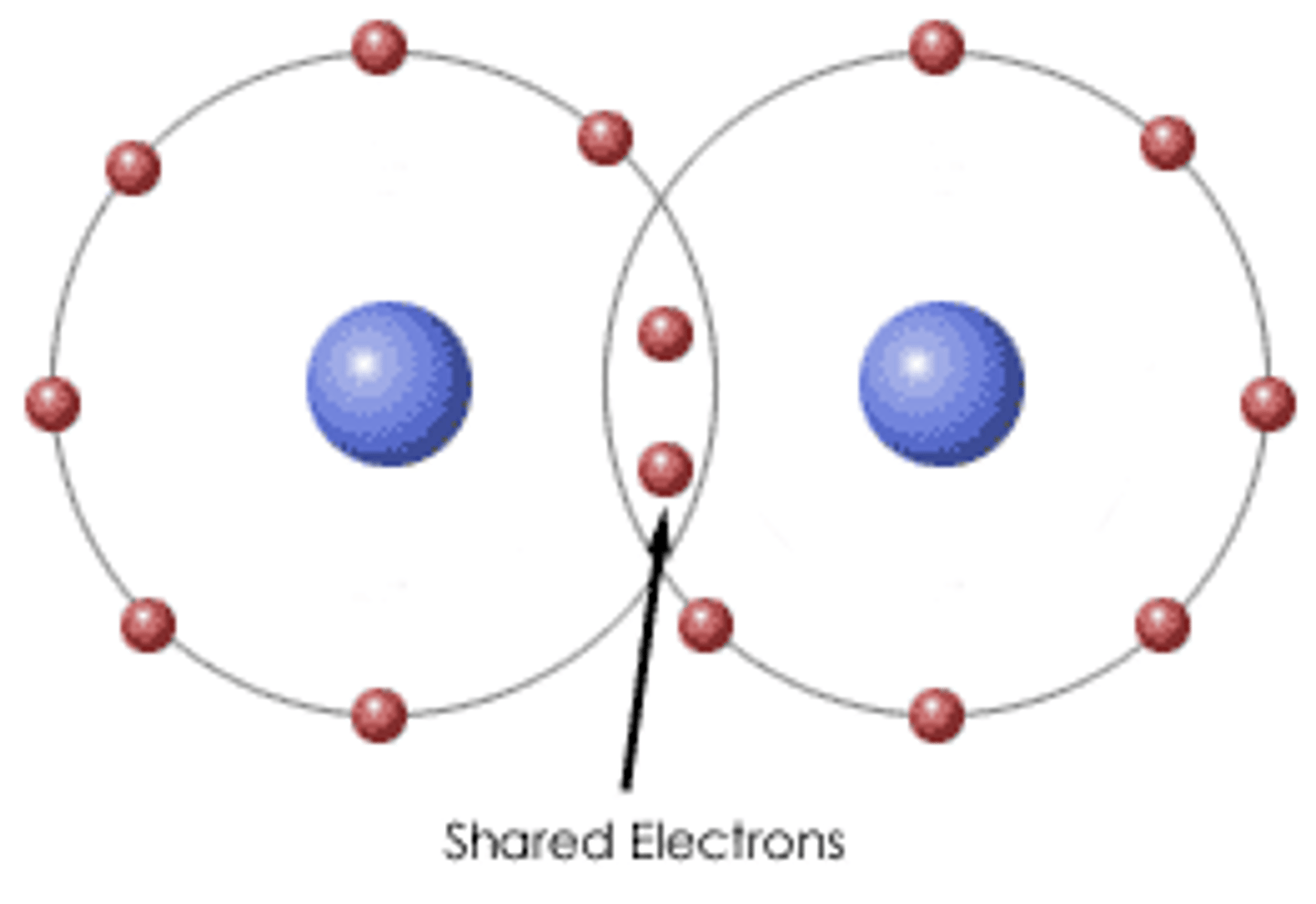
Covalent bonding
a bond formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
Reactivity
The ease and speed with which an element combines, or reacts, with other elements and compounds.
Alkali metals
group 1
Alkaline earth metals
group 2
transition metals
the short section in the middle, excluding the lanthanides and actinides
Post transition metals
Sn, Pb to A, and group 13, excluding B and Nh
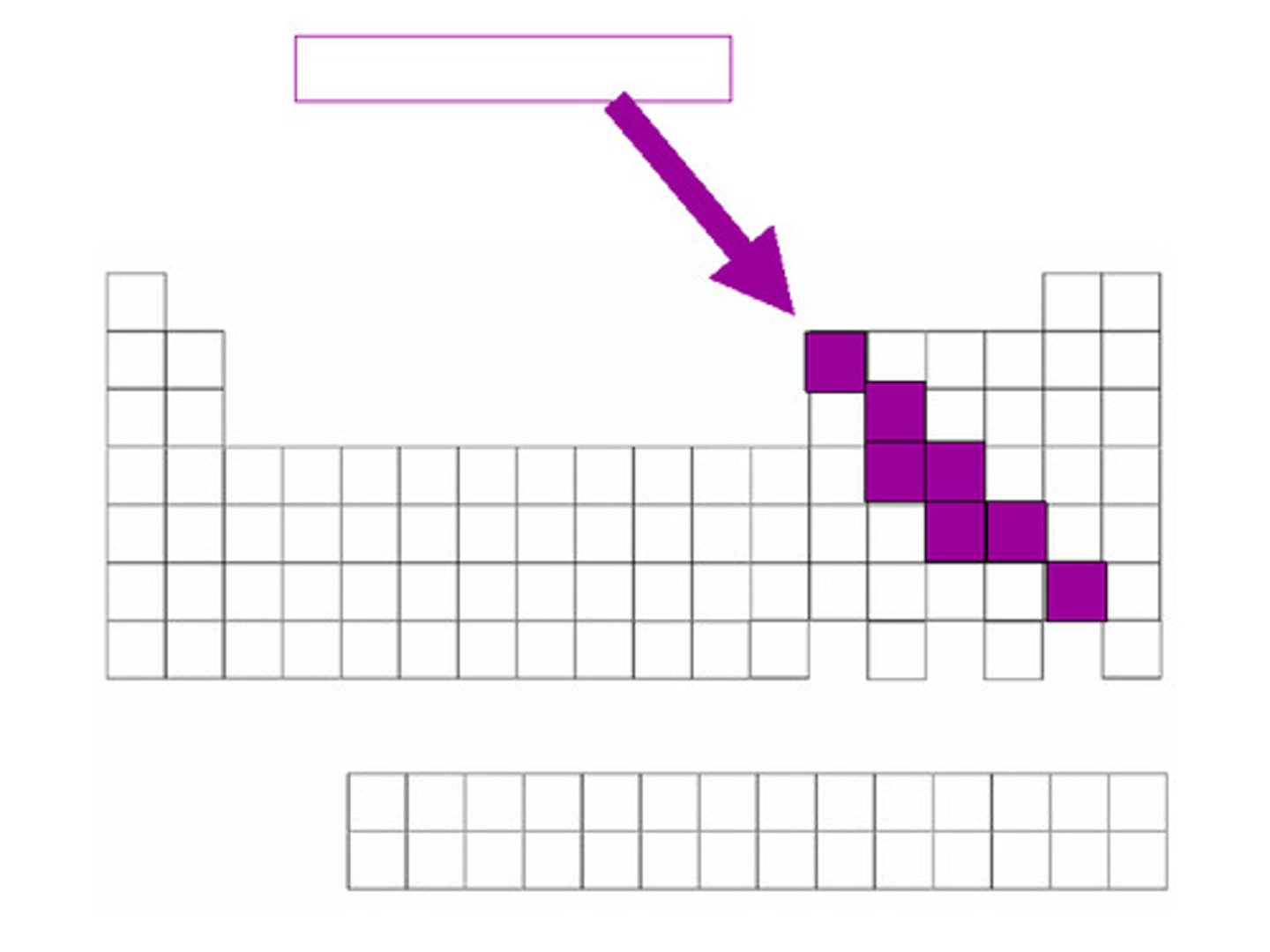
Metalloids
A set of stairs going from Te upwards to the left to B
Reactive non-metals
Above metalloids, in groups 14-16
Noble gases
Group 18 - Og
Actinides
the bottom most group
halogens
group 17