Kinetic Particle Theory
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
1
New cards
State the arrangement of particles in the SOLID state (Packed, Arrangement)
Particles are packed closely in an orderly arrangement
2
New cards
State the arrangement of particles in a LIQUID state (Packed, Arrangement)
Particles are packed fairly close in a disorderly arrangement
3
New cards
State the arrangement of particles in the GAS state
Particles are spaced very far apart and randomly arranged
4
New cards
State the movement of particles in SOLID state
Particles can only vibrate about their fixed positions as they are held in fixed positions by strong forces of attraction between them
5
New cards
State the movement of particles in LIQUID state
Particles are able to slide past each other throughout the liquid. Particles are still held by strong forces of attraction between them
6
New cards
State the movement of particles in GAS state
Particles can move randomly and freely in all directions at great speeds because the forces of attraction between the particles are weak.
7
New cards
Discuss the three properties of Gas (Shape and Volume, Density and Compression)
* Gas can be compressed easily due to the large empty space between particles
* Not dense
* No definite volume and shape
* Not dense
* No definite volume and shape
8
New cards
Discuss the three properties of Liquid (Shape and Volume, Density and Compression)
* Cannot be compressed
* No definite shape, has definite volume
* Dense but not hard
* No definite shape, has definite volume
* Dense but not hard
9
New cards
Discuss the three properties of SOLID (Shape and Volume, Density and Compression)
* Cannot be compressed
* Definite volume and shape
* Dense and hard
* Definite volume and shape
* Dense and hard
10
New cards
State the transfer of heat, arrangement of particles, forces of attraction and movement during melting/sublimation/evaporation/boiling
Heat is taken
particles become further apart
Forces of attraction become weaker
Movement is faster
particles become further apart
Forces of attraction become weaker
Movement is faster
11
New cards
State the transfer of heat, arrangement of particles, forces of attraction and movement during condensation and freezing
* Heat is given out
* Particles become closer together
* Forces of attraction become stronger
* Movement is slower
* Particles become closer together
* Forces of attraction become stronger
* Movement is slower
12
New cards
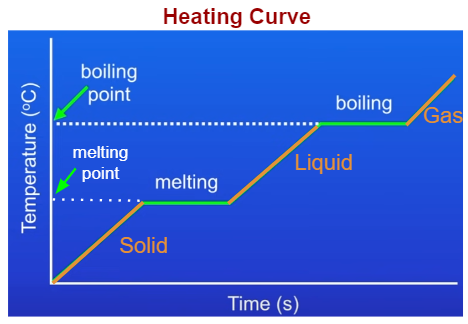
Draw a melting curve, and state the point at which the melting point is, and name the states of substance at each stage.
* Melting occurs at fixed temperature.
13
New cards
Draw a freezing curve, and state the point at which the freezing point is, and name the states of substance at each stage.
* Freezing occurs at a fixed temperature. Note that the freezing point is also the melting point of a substance.

14
New cards
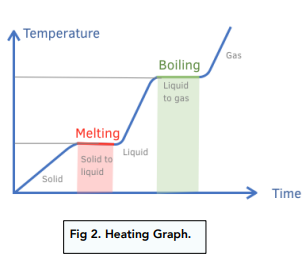
Draw a boiling curve, and state the point at which the boiling point is, and name the states of substance at each stage.
* Boiling occurs at a fixed temperature.
15
New cards
State the differences between boiling and evaporation
* Boiling occurs only at boiling point (fixed temperature), Evaporation occurs at any temperature between melting point and boiling point.
* Boiling takes place throughout liquid and evaporation takes place only at surface.
* Boiling is a rapid process. Evaporation is a slow process.
* Boiling takes place throughout liquid and evaporation takes place only at surface.
* Boiling is a rapid process. Evaporation is a slow process.
16
New cards
Name two evidences of diffusion
* Invert a jar of air over a jar of bromine vapour. Over time, both jars become reddish brown.
* Fill a jar with plain water and add a drop of potassium manganate (VII). Colour of potassium manganate (VII) will spread throughout water even without stirring
* Fill a jar with plain water and add a drop of potassium manganate (VII). Colour of potassium manganate (VII) will spread throughout water even without stirring
17
New cards
Define diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a higher concentration to a lower concentration due to the *random and constant movement of its particles*
18
New cards
State the factors affecting diffusion
* Temperature : The higher the temperature, the greater the kinetic energy particles have so they move faster (higher rate of diffsn)
* Relative molecular mass of particles : The larger the relative molecular mass, the slower the rate of diffusion
* Relative molecular mass of particles : The larger the relative molecular mass, the slower the rate of diffusion
19
New cards

Explain why the ring is formed nearer to HCl
* The Mr of HCl is 36.5. The Mr of NH3 is 17. The relative molecular mass of HCl is greater than that of NH3. As such, HCl molecules diffuse slower than NH3 molecules. HCl molecules travel a shorter distance than NH3 molecules and ammonium chloride is formed nearer to HCl
