NPTE Practice w/Explanations Pt. 2
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
195 Terms
A male patient complains of having significant weight gain in the abdomen and in the face. The labs show high levels of cortisol and elevated blood glucose and high levels of ACTH coming from the pituitary gland. The patient MOST LIKELY has this diagnosis:
A. Addison Disease
B. Hasimoto's Disease
C. Cushing's Disease
D. Parathyroidism
C. Cushing’s Disease - Cushing (everything bigger)
A. Addison Disease - related to cortisol (hypo/decreased cortisol), primary adrenal insufficiency
Addison's disease caused by an autoimmune response which attacks the outer cortex of the adrenal gland. Some signs and symptoms of Addison's disease include: abdominal pain, abnormal menstrual periods, dehydration, depression, diarrhea, dizziness, loss of appetite, hypoglycemia, hypotension, muscle weakness, nausea, patches of dark skin around scars/skin fold and joints, sensitivity to cold, unexplained weight loss, weight loss, worsening fatigue
B. Hashimoto’s Disease - caused by hypothyroid issues (low level of TSH)
C. Cushing’s Disease - high level of cortisol, elevated blood glucose, high ACTH
D. Parathyroidism - don't know whether it is hypo or hyperthyroidism
A 28-year-old professional mountain bike rider presents to cardiac rehabilitation after suffering a MI 6 months ago. Which exercise test would be MOST beneficial in order to assess aerobic capacity and create an aerobic conditioning program?
A. Bruce protocol
B. Lower extremity ergometry
C. Six-Minute Walk test
D. Step test
B. Lower extremity ergometry
It is related to pedaling which is most related to the biking
A. Bruce protocol - VO2 max (30 min)
C. Six-Minute Walk test - Good method for endurance
A young adult underwent right Achilles tendon repair 6 weeks
ago and is now able to fully weight bear. The PT is giving him
advice on proper shoe modification. Which of the following
would be BEST for the patient to utilize?
A. Normal shoes
B. Shoes with 1 1.5 cm heel lift
C. Shoes with lower than the regular heel
D. Shoes with 5 cm heel lift
Reference
B. Shoes with 1 1.5 cm heel lift
put in slight PF posture to protect the achilles tendon
type of fracture of the distal forearm in which the broken end of the radius in volar direction?
A. colles fracture
B. Smith fracture
B. Smith fracture
How many C/S, T/S, L/S exists?
A. 10
B. 15
C. 24
D. 30
C. 24
C/S: 7
T/S: 12
L/S: 5
morning at 7, lunch at 12, dinner at 5
Angles of the vertebrae on C/S?
A. 45
B. 60
C. 90
A. 45
Angles of the vertebrae on T/S?
A. 45
B. 60
C. 90
B. 60
Angles of the vertebrae on L/S?
A. 45
B. 60
C. 90
C. 90
How many percent of facet joints bear the compressive load of the spine?
A. 30%
B. 45%
C. 60%
A. 30%
When you put traction, how much percent of body weight that the C/S can afford?
A. 10%
B. 20%
C.30%
A. 10%
When you put traction, how much percent of body weight that the L/S can afford?
A. 30%
B. 40%
C. 50%
C. 50%
Degeneration of intervertebral disc?
A. Spondylosis
B. Spondylolysis
C. Spondylolisthesis
D. Retrolisthesis
A. Spondylosis
losis -degeneration
Defect in pars interarticularis or the arch of the
vertebra?
A. Spondylosis
B. Spondylolysis
C. Spondylolisthesis
D. Retrolisthesis
B. Spondylolysis
lysis - breaking, defect
Forward displacement of one vertebra over another?
A. Spondylosis
B. Spondylolysis
C. Spondylolisthesis
D. Retrolisthesis
C. Spondylolisthesis
lis - defect
thesis -slipping
Backward displacement of one vertebra on another?
A. Spondylosis
B. Spondylolysis
C. Spondylolisthesis
D. Retrolisthesis
D. Retrolisthesis
Retro - backward
what is the condition in which a child has too much curvature (kyphosis) in the middle of the back?
Scheunemann's disease
A PT examines a patient complaining of tingling into the 4th and 5th
digits with muscle wasting over the hypothenar eminence. The PT
suspects ulnar neuropathy and decides to examine the integrity of
the nerve. Which of the following testing procedure would be the
BEST?
A. Have the patient flex both wrists while holding them for one minute
B. Have the patient make a fist around the thumb and perform ulnar
deviation
C. Have the patient grasp a piece of paper between their first and second
fingers while the examiner pulls the paper and monitors for first finger
D. Have the patient perform extension of the 3rd digit of the hand
against examiner resistance
C. Have the patient grasp a piece of paper between their first and second fingers while the examiner pulls the paper and monitors for first finger (Froment Sign)
Adductor pollicis connected to ulnar N.
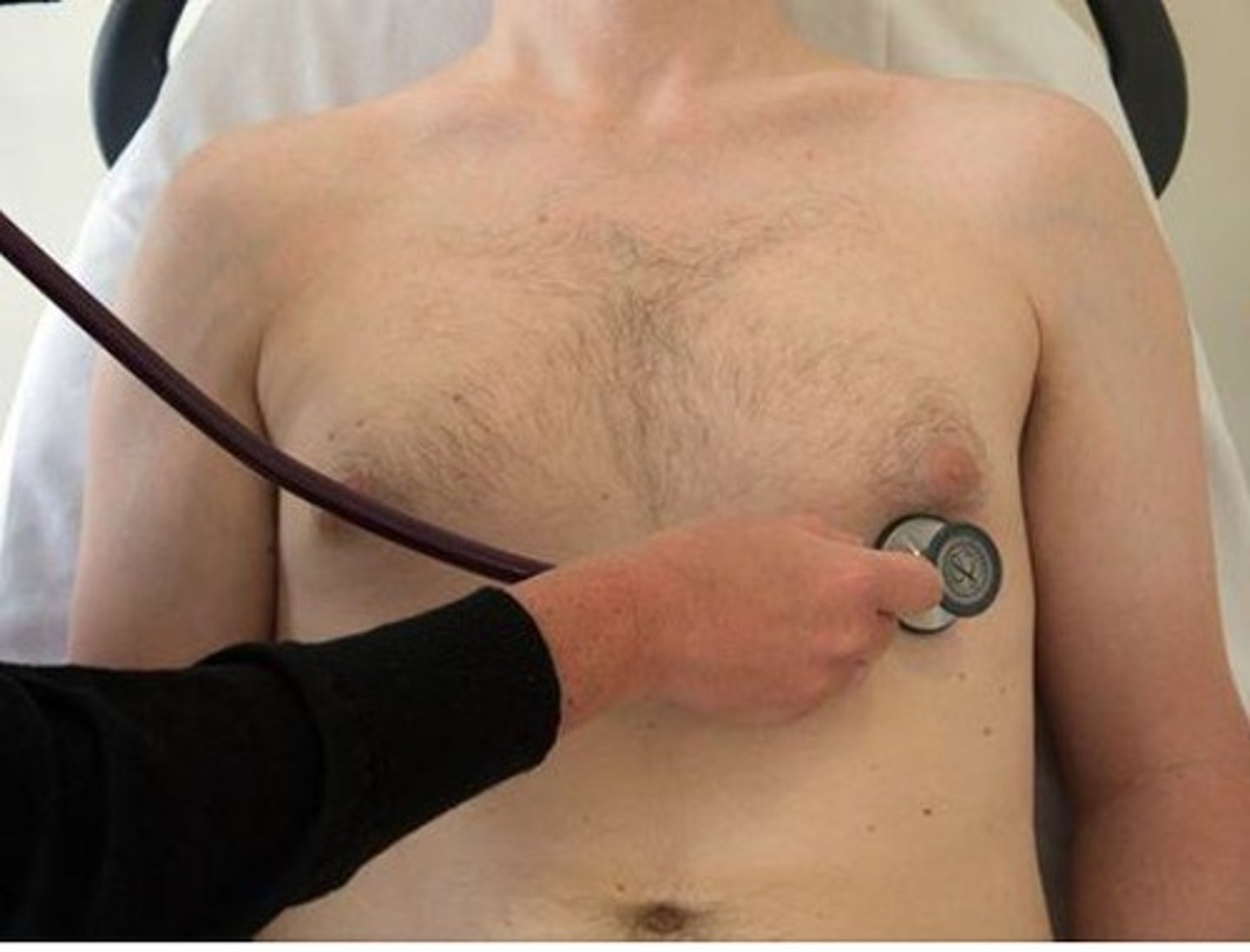
A 48
year old male patient reports of shortness of
breath and swelling in lower extremities. During the
baseline examination, the PT examines patient's
heart sounds before starting an exercise program.
Which valve is being auscultated in the picture?
A. Tricuspid valve
B. Pulmonary valve
C. Mitral Valve
D. Aortic Valve
C. Mitral Valve
A low back pain patient's Oswestry Disability Questionnaire score was 18 points. 4 weeks later, the score is 50 points. Which of the following is the BEST option for the physical therapist?
A. Continue physical therapy until the patient returns to a score
of 60
B. Discharge the patient as there is an improvement.
C. Document the improvement and start a home exercise program
D. Ask the patient to have a physician consult
D. Ask the patient to have a physician consult
disability increase - need to discuss with physician
A 60
year old patient sustained a fall on an outstretched arm and
hand (wrist in extension). He says that when he fell "the elbow was
straight and his hand was out away from his body". This resulted in
tendency for the forearm & hand to move into valgus. What
structures are vulnerable to injury?
Three weeks later, the fracture is well healed now and he is not
osteoporotic but presents with wrist stiffness. As his physical
therapist what would you like to do to improve wrist arthro
kinematics.
A 44 year old female patient arrived to a clinic after
sustaining a fall involving a hand/wrist injury. Upon
examination, the PT observed the radius dislocated in a
volar direction. Which of the following conditions would
MOST likely match this description?
A. Smith's Fracture
B. Colle's Fracture
C. Scaphoid Fracture
D. Dinner fork Deformity
A. Smith’s Fracture
Garden Spade Deformity is seen with Smith Fx
Dinner for deformity is seen with Colle's fx
A PT is evaluating a 34 year old female patient with a vague diagnosis of low back pain. The patient displays a positive Thomas test. Which sub-phase of the gait cycle will MOST likely show limitation in the hip ROM?
A. Loading response
B. Initial contact
C. Midstance
D. Terminal stance
D. Terminal stance
requires the most hip extension
Which of the following is NOT an expected sign seen
in a patient with facial nerve (CN VII) palsy.
A. Hyperacusis
B. Absence of sensation in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue
C. Absence of corneal reflex
D. Decreased lacrimation
B. Absence of sensation in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue
Spondylolisthesis vs Stenosis:
Spondylolisthesis
• Fracture Ant (Antero-listheis)/Retrolisthesis
• X-ray view (Lateral)
• B lateral fracture pars interarticularis
• Contraindication ex’s Extension (No extension)
Stenosis:
• Diagnostic Test MRI
• While you walk on the ramps, the pt with stenosis feels comfortable going UP the ramp (stay spine in a flexed position)
• Flexion Ex’s
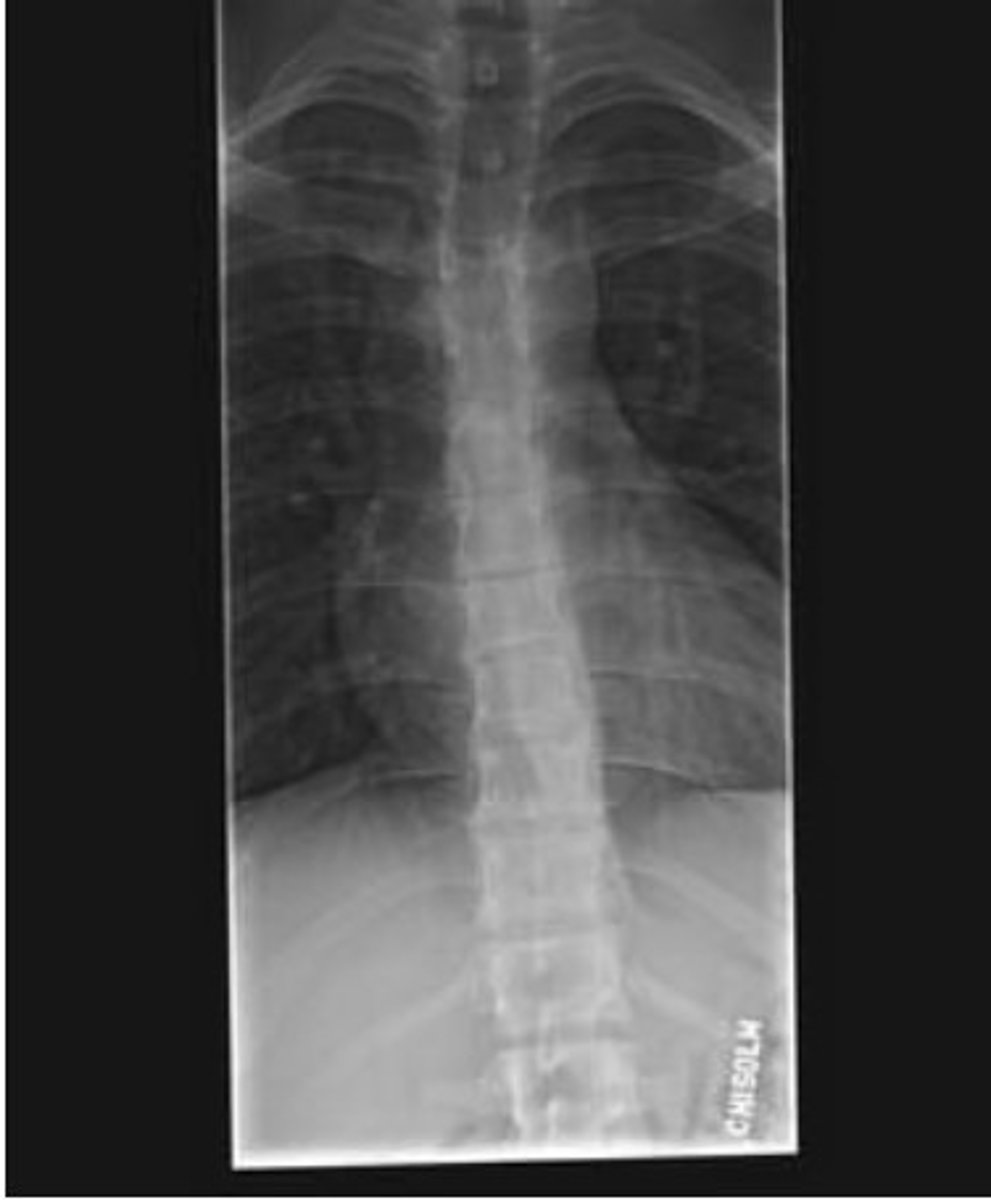
A PT is evaluating a 20-year-old male patient with a history of midback pain. Radiographic findings are shown in the picture. MRI reveals anterior wedging of the T7 9 vertebral bodies. What is the MOST appropriate diagnosis?
A. Ankylosing spondylitis
B. Osteogenesis imperfecta
C. Scheuermann's disease
D. Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
C. Scheunemann's disease
anterior wedging of T7 and T9 (kyphosis)
The T 1 to T8 seems very crowded
The patient age is 20 y/o - not the osteogenesis
with MRI - Schmorl Nodes
What is spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita?
inherited bone growth disorder that result in short stature (dwarfism), skeletal abnormalities, and problem with vision and hearing. This condition affects the bone of the spine (spondylo-) and ends (epiphyses) of the long bone in the etc...
JOINT MOTION ARTHROKINEMATICS
• Rolling
• Sliding
• Spinning
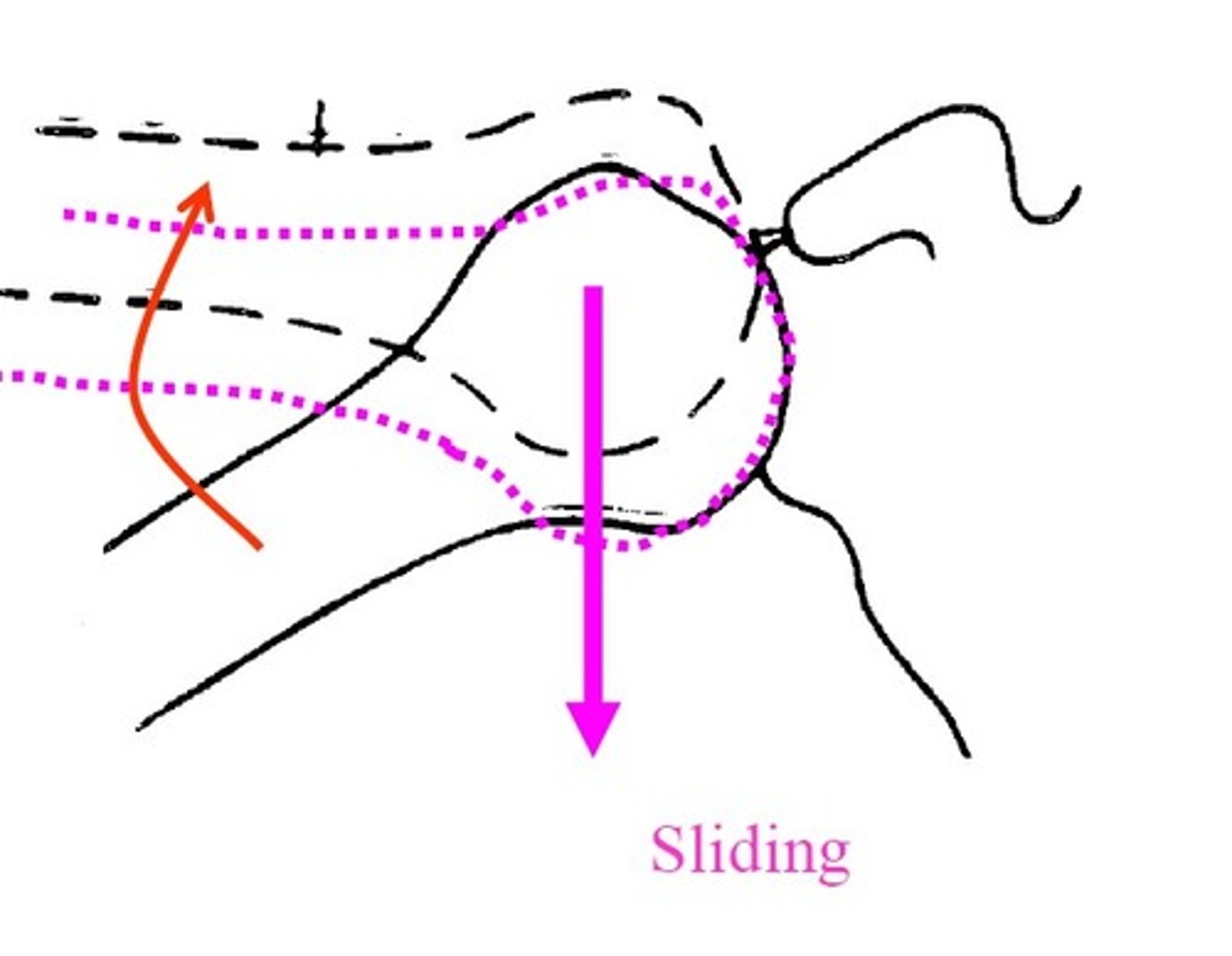
JOINT MOTION OSTEOKINEMATICS
• Movement of Segments Gross Movement
• Expressed in terms of ROM
• Hypermobility / Hypomobility
• Hypomobility at one joint can lead to Hypermobility
at another joint
• Examples Excessive plantarflexion
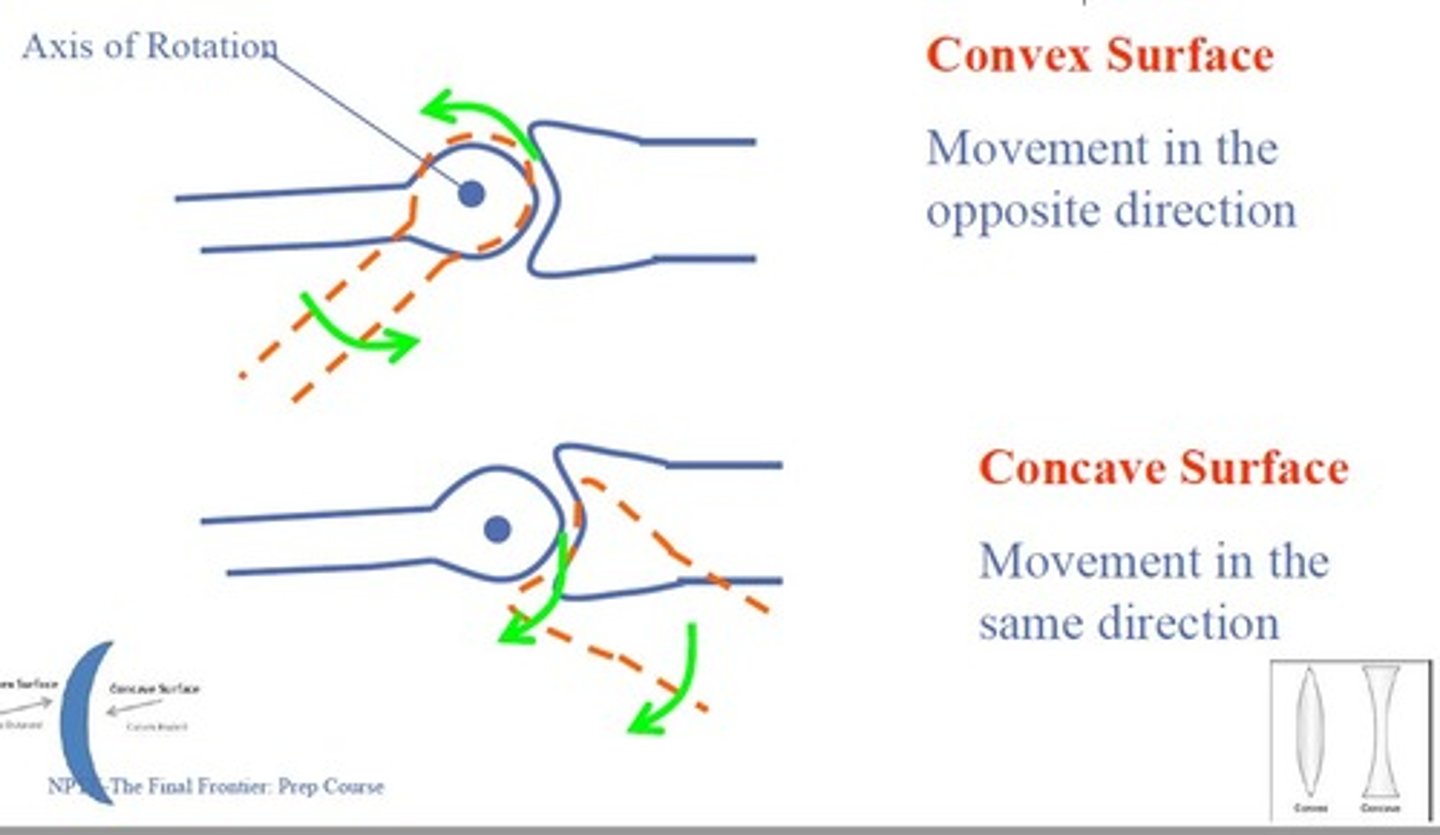
Concave / Convex rule
Describes movement of Articular Surface & Shaft
Convex Surface
Movement in the opposite direction
Concave Surface
Movement in the same direction
A PT is evaluating a 34 year old female patient with a vague diagnosis of low back pain. The patient displays a
positive Thomas test. Which sub phase of the gait cycle
will MOST likely show limitation in the hip ROM?
A PT is testing the active shoulder range of motion of a 45
year old female patient. The PT asks the patient to move the
shoulder to full medial/internal rotation. During medial
rotation at the shoulder joint (GH joint), the humerus will
slide:
A. Anteriorly
B. Superiorly
C. Inferiorly
D. Posteriorly
D. Posteriorly (based on JOSPT; the official MSK journal of APTA)
IR - posterior glide
ER - anterior glide
If the question include Adhesive Capsulitis, then the direction is posterior-inferior glide
A patient presents with throbbing of the shoulder. He
demonstrates limited active and passive motion of the
shoulder joint, and increased pain with both motions.
The best initial intervention is:
Notice above, the question highlights BOTH passive and active motion of the shoulder, as well as pain (TWICE). For this reason, an intervention focused on pain would be first priority.
A patient demonstrated painful ROM in horizontal abduction
movement during the range of motion examination of the shoulder.
Which of the following joint mobilization techniques is MOST
appropriate for the patient?
A. Large amplitude oscillations performed at the beginning of the
range of motion in an anterior-inferior direction
B. Small amplitude oscillations into tissue resistance up to the
limit of available motion in an posterior superior direction
C. Large amplitude oscillations within the available range of
motion in an anterior inferior direction
D. Small amplitude oscillations into tissue resistance at the limit
of available joint motion in a posteroinferior direction
A patient who is 3 months post right ankle fracture has an
active range of motion of 0 to 30 of dorsiflexion and 0 to
10 of plantar flexion. To restore motion required for normal
walking, which of the following joint mobilization techniques
the PT should perform?
A. Anterior glide of the talus
B. Lateral glide of the calcaneus
C. Medial glide of the calcaneus
D. Posterior glide of the talus
A. Anterior glide of the talus
Which segments have the largest motions in flexion/extension?
A. C/S
B. T/S
C. L/S
A. C/S (C5/C6)
Which C/S segments have the largest motions in flexion/extension?
First: C5/C6
Second: C4/C5
Which T/S segments have the largest motions in flexion/extension?
First: T12/L1
Second: T11/T12
Which L/S segments have the largest motions in flexion/extension?
First: L5/S1
Second: L4/L5
Which segments have the largest motions in axial rotation?
C1/C2
Which T/S segments have the largest motions in axial rotation?
T1/T2
Which L/S segments have the largest motions in axial rotation?
L2/L3
Which segments have the largest motions in lateral flexion?
C4/C5
A 36-year-old female is experiencing chronic pain and
tenderness in her cervical spine at the level of C5 C6
vertebrae. The physician diagnoses reduced space between the vertebrae. What will be the MOST appropriate PT intervention?
A. Provide an ice pack to relieve pain
B. Perform cervical mobilization by moving the C5 vertebrae anteriorly
C. Perform cervical mobilization by moving the C6 vertebrae anteriorly
D. Provide ultrasound therapy to relieve pain
B. Perform cervical mobilization by moving the C5 vertebrae anteriorly
increase the flexion of C5/C6; P/A direction of C5 - increase the gap
The manual therapy technique appropriate to correct a
bilateral closing restriction of T2 on T3 is:
A. Central PA glide on the spinous process of T3 while
stabilizing T2.
B. Central PA glide on the spinous process of T2 while
stabilizing T3.
C. Unilateral PA glide on the right transverse process of T3
while stabilizing T2.
D. Unilateral PA glide on the left transverse process of T3
while stabilizing T2.
A. Central PA glide on the spinous process of T3 while
stabilizing T2
increase the extension of T2/T3 - closing the gap
P/A glide of T3
The PT is trying to improve the closure of the right T4/5
facet joint. The mobilizing hand of the PT for P/A mobilization techniques should be placed at:
A. Transverse processes of right T5
B. Spinous processes of T5
C. Transverse processes of right T4
D. Transverse processes of left T5
A. Transverse processes of right T5
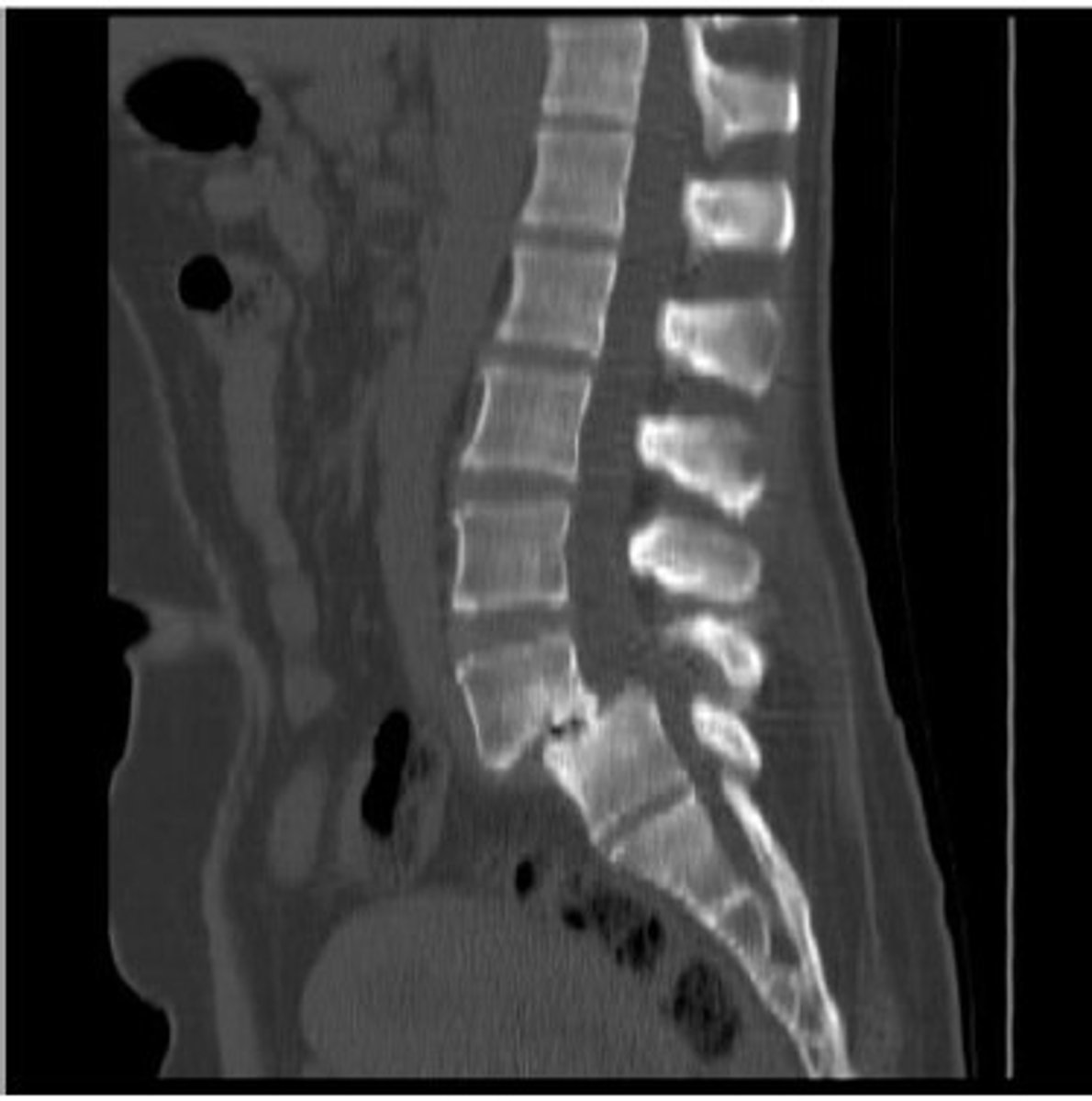
During the examination, the patient reports increased
pain while standing. Pain is alleviated with lumbar
flexion and sitting. Which special test will be positive to
confirm the diagnosis shown in the picture ?
A. Stork standing test
B. Gillet Test
C. Van Gelderen bicycle test
D. Quadrant Test
Spondylolisthesis
Answer: A. Stork standing test
B. Gillet test - SI clusters
C. Van Gelderen bicycle test - spinal stenosis
Which of the following motions will close the right
lumbar facet joints from a neutral position?
A. Lumbar extension, right side flexion, left rotation
B. Lumbar extension, left side flexion, right rotation
C. Lumbar flexion, right side flexion, left rotation
D. Lumbar flexion, left side flexion, right rotation
A. Lumbar extension, right side flexion, left rotation
A 36 year old patient experiences limitation with left side
bending and left rotation at the C5/6 junction. What is
the MOST appropriate intervention?
A. Apply P/A glide at left C5
B. Apply A/P glide at left C5
C. Apply P/A glide at right C5
D. Apply P/A glide at right C6
C. Apply P/A glide at right C5
On examining a patient with a decreased trunk side
bending to the left, the PT finds a left closing restriction
between L2 L3 vertebrae. What is the MOST
appropriate intervention to improve the restriction?
A. Apply PA glide on L2 transverse process on the right side
B. Apply PA glide on L4 transverse process on the right side
C. Apply PA glide on L4 transverse process on the left side
D. Apply PA glide on L3 transverse process on the left side
D. Apply PA glide on L3 transverse process on the left side
A 45 years old female patient with chronic low back pain is
visiting outpatient clinic for her first treatment visit. The PT
begins training the stability muscles. Which is the FIRST
exercise taught to the patient for stabilization training?
A. Begin training with awareness of safe spinal motions and the neutral spine position
B. Begin training aggressive pelvic tilt exercises
C. Begin training lumbar stabilization exercises sitting on exercise
ball with extremity motion and flexed spine position
D. Begin training supine single leg lifts training the core
A. Begin training with awareness of safe spinal motions and the neutral spine position
Two DPT students are reviewing the literature for the effects of Swiss ball exercises on LBP outcomes. According to levels of evidence, which studies provide the BEST evidence for support of the use of Swiss ball exercises?
A. Clinical case report
B. Multicenter randomized controlled trials
C. Clinical case series
D. Cross-Sectional studies
B. Multicenter randomized controlled trials
A cross-sectional study - is a type of observational study design. In a cross-sectional study, the investigator measures the outcome and the exposures in the study participants at the same time
Cohort study - compare the groups
Three DPT students are looking at the effects of drugs on
falls. The students are using data from previous patient
medical records to compare drug usage in fallers and
non-fallers. Which of the following will be the MOST
appropriate study design?
A. Clinical case report
B. Retrospective cohort
C. Randomized controlled trials
D. Prospective cohort
B. Retrospective cohort
Which of the following instruments is MOST appropriate for measuring patients' quality of life?
A. Dynamic Gait Index (DGI)
B. Oswestry low back pain disability index (ODI)
C. Timed up and go test (TUG)
D. Medical Outcomes Study 36 item short form (SF 36)
D. Medical Outcomes Study 36 item short form (SF 36)
explanation: B is too specific only for the back not for QOL
Medical Outcome Study (MOS): resulted in the development of 36 items short form for measuring patient's QOL. It is self report that covers eight domains of physical functioning, role limitation due to physical problems, role limitations due to emotional problems, fatigue, and general health perceptions
A researcher is collecting ROM data on volleyball players during shoulder abduction motion. The results of the tests are BEST categorized as which of the following types of data?
A. Interval data
B. Ordinal data
C. Nominal data
D. Ratio data
D. Ratio data (true 0 exist)
B. Ordinal (rank) - MMT or MLT
A. Interval (true 0 doesnt exist) - temperature, BMI
C. Nominal (groups) - men vs women
What is the Quality?
A. Nominal & Ordinal
B. Ratio & Interval
A. Nominal & Ordinal
What is the Quantity?
A. Nominal & Ordinal
B. Ratio & Interval
B. Ratio & Interval
The PT will measure the distance between the spinous process to the inferior angle at 0, 60, and 100 abductions at three different time points. One of the MOST important factors for the success of this study is:
A. Face validity
B. Intra-rater reliability
C. Inter-rater reliability
D. Content validity
B. Intra rater reliability
Two PTs perform a test on a patient using the Oswestry Disability Index. The patient visit is Monday (M) and Wednesday (W). One PT reports scores of 29 and 30 on M & W; other PT scored 36 and 37 (M&W). This is indicative of a problem in:
A. Concurrent validity
B. Intrarater reliability
C. Interrater reliability
D. Construct validity
C. Interrater reliability
What is your true personality color
(not asked on the NPTE)?
A. Blue
B. Gold
C. Orange
D. Green
A. Blue
A 65-year-old patient arrives comes to the PT clinic. The patient reports that since morning, he has felt pain down both arms, has had shortness of breath, and has continued to perspire. What is the MOST appropriate intervention?
A. Evaluate the cervical spine and provide pectoral stretches to decrease bilateral arm pain.
B. Evaluate the cervical spine and provide scapular strengthening exercises to decrease bilateral arm pain.
C. Treat the patient with TENS and recommend that the patient follow up with a physician within 3 days.
D. Immediately contact emergency medical services.
D. Immediately contact emergency medical services.
Focused on Safety
Severe symptoms: Perspire (sweat), SOB, pain down arms
A PT receives a referral for a patient who is one-week status post CVA. When observing the patient lying in bed, PT notes that the patient's calf and foot are edematous. The patient reports that the area is somewhat painful. The PT should:
A. Discontinue the examination and wait till the swelling on the patient's leg decreases
B. Order compression stockings for the patient to relieve the edema
C. Continue with the examination and have the patient perform ankle pump exercises
D. Inform the physician of the situation and discontinue the examination
D. Inform the physician of the situation and discontinue the examination
Edema on calf and foot -DVT
A researcher is collecting data on the effect of muscle stretching on passive hip range of motion in 20 patients. The researcher will provide stretching every day for a week and measure ROM every day. Which of the following experimental designs is the MOST appropriate for this type of study?
A. Divide the patients into 2 groups with 10 subjects in the experimental and 10 in the control group, measure ROM on day 7.
B. Divide the patients into 2 groups with 3 subjects in the experimental and 17 in the control group, measure ROM on days 1 and 7.
C. Divide the patients into 2 groups with 10 subjects in the experimental and 10 in the control group, measure ROM on days 1 and 7.
D. Divide the patients into 2 groups with 10 subjects in the experimental and 10 in the control group. For the experimental group, measure ROM every day. For the control group, measure ROM only on day 1.
C. Divide the patients into 2 groups with 10 subjects in the experimental and 10 in the control group, measure ROM on days 1 and 7.
Pretest-Posttest Design
A physical therapist is evaluating the specificity of the Phalen test in a group of computer programmers. Which of the following results indicates a true negative finding?
A. Patients with a history of wrist pain and carpal tunnel syndrome will test negatively.
B. Patients with a history of wrist pain and carpal tunnel syndrome
will test positively.
C. Patients with no history of wrist pain and carpal tunnel syndrome will test negatively.
D. Patients with no history of wrist pain and carpal tunnel syndrome
will test positively.
C. Patients with no history of wrist pain and carpal tunnel syndrome will test negatively.
Find whether it's true? and check whether they got negative or positive
Decide if it is a true or a false story, and then match the last word of the question with the last word of the answer choice
What is the Gold standard of validity?
A. Content validity
B. Construct validity
C. Concurrent validity
D. Face validity
C. Concurrent validity
Concurrent Validity is the Gold standard
A physical therapist is evaluating the sensitivity of a balance test in a group of older adults. Which of the following results indicates a true positive finding?
A. Patients with a history of falls test negatively.
B. Patients with a history of falls test positively.
C. Patients with no history of falls test negatively.
D. Patients with no history of falls test positively.
B. Patients with a history of falls test positively.
A physical therapist is examining a 25-year-old male who had a recent fall while fixing the roof. The patient seems distracted and the PT has difficulty maintaining the patient's attention. Which area of the brain is MOST likely injured?
A. Frontal lobe
B. Temporal lobe
C. Parietal lobe
D. Occipital lobe
A. Frontal lobe
Think Frontal Lobe as CEO - who mostly make decisions and maintaining the attention
A 65-year-old patient presents to the clinic post CVA. The PT reviews the angiogram and identifies a blockage of the upper division of the left MCA. Which of the following conditions is the PT MOST likely to note upon performing an evaluation?
A. Weakness in the left upper extremity
B. Presence of non-expressive aphasia
C. Left homonymous hemianopia
D. Presence of expressive aphasia
D. Presence of expressive aphasia (Brocka's)
upper-division - Brocka's (same side)
Expressive aphasia - Brocka's aphasia
Non-expressive aphasia - Wernicke's aphasia
A. right
C. right
B. not Wernicke's
A PT is examining a 45 old patient who presents with weakness and tingling in the lower extremities over the past 2 weeks. Which of the following examination findings would MOST likely confirm the diagnosis of Guillain Barré syndrome?
A. Hypertonicity in the affected muscles
B. Positive Babinski sign
C. Diminished tendon reflexes
D. Presence of clonus with rapid passive foot dorsiflexion
C. Diminished tendon reflexes
GBS: LMN disease that polyneuropathy and weakness and tingling that has distal to proximal progression
e.g., ALS: UMN and LMN disease (includes ALL symptoms)
e.g., CVA, Multiple Sclerosis- UMN symptoms
A, B, D - signs of UMN disease
C - LMN diseae
A PT is performing cranial nerve testing on a 58-year-old male patient. The patient has ptosis, lateral strabismus, and a dilated pupil in the right eye. Which of the following cranial nerve test results is MOST likely to be abnormal?
A. Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
B. Optic nerve (CN II)
C. Facial nerve (CN VII)
D. Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
A. Oculomotor nerve (CN III) - Motor
signs of oculomotor N
Lateral strabismus - lateral shift of eye - happening due to issues with medial rectus (motor) - oculomotor N
ptosis - dropping eye - levator palpebrae (motor) - oculomotor N
dilated pupil - (motor) oculomotor N
B. optic is sensory
LR 6 - lateral rectus - CN 6, abducens N
SO4 - superior oblique - CN 4, trochlear N - look down and in
O3 - other muscles (superior-inferior medial recti and inferior oblique) - CN 3, Oculomotor N - look up and in & out
What is ptosis?
drooping upper eyelid
What is strabismus?
misalignment of the eyes
When is the patient going down the stairs or reading newspapers, what CN is most likely important?
A. CN4
B. CN6
C. CN3
D. CN2
CN 4 - to look down and in
which other ones? CN 6
A PT is performing cranial nerve tests on a patient. Which of the following is LEAST appropriate to assess the integrity of the facial nerve?
A. Ask the patient to show their teeth
B. Ask the patient to puff out both cheeks
C. Apply sugar or saline solution to the anterior part of the
tongue and ask the patient to identify
D. Have patient clench teeth and hold against resistance
D. Have patient clench teeth and hold against resistance
C - sensory part of Facial N
D - do not allow to open up the mouth - motor - CN V (trigeminal N)
A patient complains of sudden onset of mild hearing loss on the left side. Weber's test findings show sound lateralized to the right ear. Rinne test was consistent with air conduction greater than bone conduction on both sides. Which of the following is the MOST likely?
A. Right side sensorineural hearing loss
B. Left side conduction hearing loss
C. Right side conduction hearing loss
D. Left side sensorineural hearing loss
D. Left side sensorineural hearing loss
Problem is left
Weber - Louder on R
Rinne - AC > BC
A PT administers a series of cranial nerve tests to a patient with a confirmed lower motor neuron disease. Assuming the patient has a lesion impacting the right hypoglossal nerve, which clinical presentation would be most likely?
A. right-sided tongue atrophy and deviation toward the left with tongue protrusion
B. right-sided tongue atrophy and deviation toward the right with tongue protrusion
C. left sided tongue atrophy and deviation toward the left with
tongue protrusion
D. left sided tongue atrophy and deviation toward the right with
tongue protrusion
B. right-sided tongue atrophy and deviation toward the right with tongue protrusion
Lick your Lesion
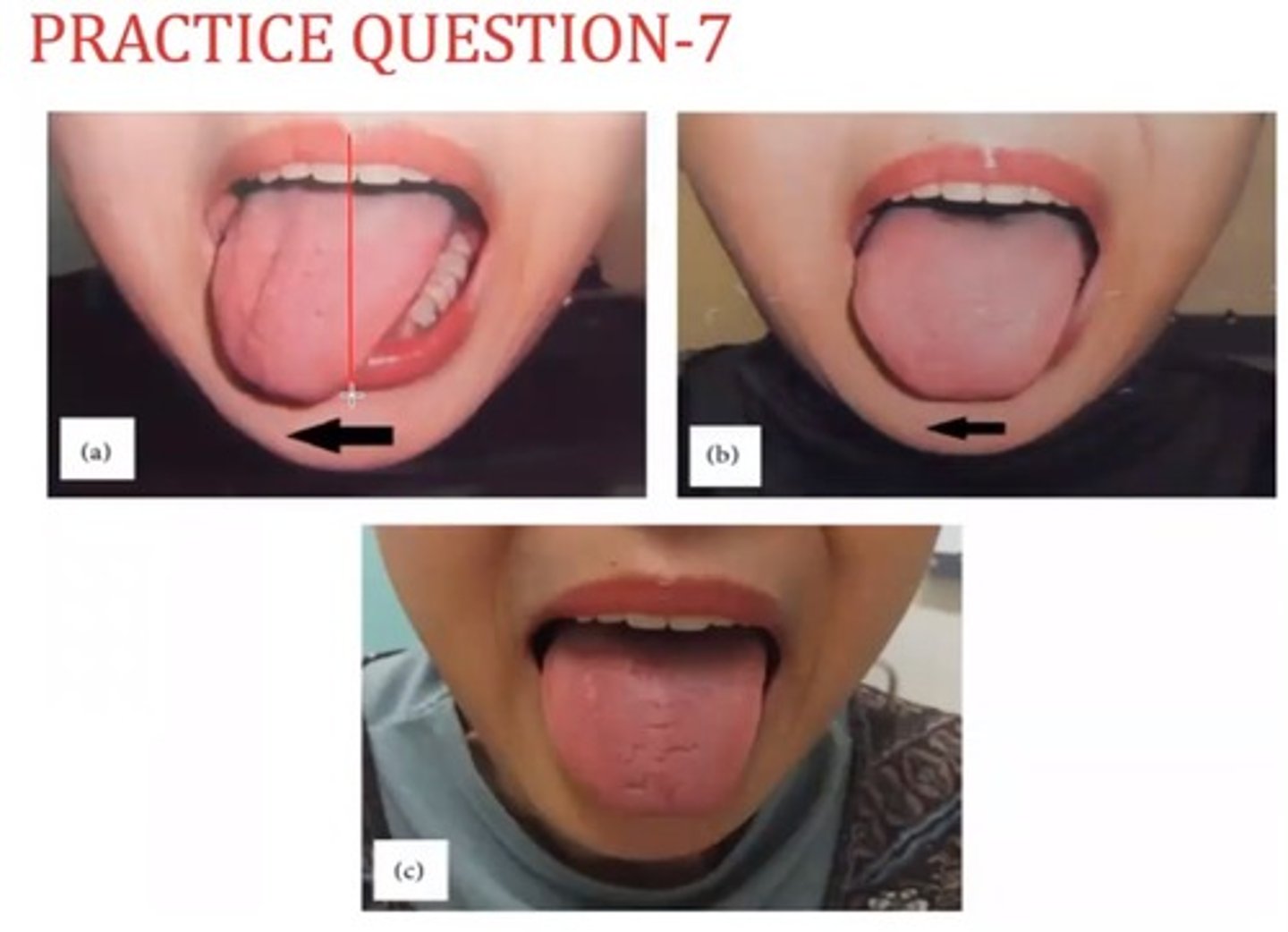
A
PT was testing gag reflex in a 45 old male complaining of sudden change of voice quality. When PT asks the patient to say " Ahh ", the PT finds the patient presentation picture below, Which cranial nerve is MOST likely affected? (Failure to rise, Deviated to Left)
A. Left vagus nerve
B. Right vagus nerve
C. Left glossopharyngeal nerve
D. Right glossopharyngeal nerve
B. Right vagus nerve
CN 9. Glossopharyngeal N - Sensory
CN 10. Vagus N - motor
gag reflex - sensory - glossopharyngeal N (CN 9)
"Ahhh" sound - motor component - Vagus N (CN 10)
failure to rise (activate) on R side - R side affected
A 45-year-old patient diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease is being assessed by the PT for the first time. When evaluating a patient with ALS, the PT should suspect which of the following cranial nerve LEAST likely to be involved?
A. Glossopharyngeal nerve ( CN IX)
B. Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
C. Vagus nerve (CN X)
D. Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
B. Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
Vestibulocochlear N - sensory
ALS - Lou Gehrig's disease - affecting motor and muscles - won't effect on hearing
Glossopharyngeal N, Vagus N, Hypoglossal N - includes motor
Which of the following is NOT an expected sign seen in a patient with facial nerve (CN VII) palsy.
A. Hyperacusis
B. Absence of sensation in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue
C. Absence of corneal reflex
D. Decreased lacrimation
https://prezi.com/view/TA4oyc2VwESP4O2bhBsu
B. Absence of sensation in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue
sensation and taste are different
Hyperacusis - CN 7 - related to palsy
absence of corneal reflex (각막반사) - eye lid movement
D - lacrimation - secretion of tear from eye
A PT is performing an exercise stress test on a 45-year-old male patient. The patient resting values are BP 130/90 mm Hg. HR 75 bpm and RR 24 breaths/min. Which of the following is an ABNORMAL response to vigorous aerobic exercise?
A. Diastolic blood decreases to 88 mm Hg
B. Diastolic blood pressure increases to 100 mm Hg
C. Respiratory rate increases to 34 breaths/minute
D. Systolic blood pressure decreases to 100 mm Hg
D. Systolic blood pressure decreases to 100 mm Hg
drop 20 mmHg
Systolic BP should not be falling down. The systolic BP should go up
The patient's medical history includes hypercholesterolemia, and type 2 diabetes. The patient's SBP is between 120 129 and DBP is less than 80. Which of the following categories MOST appropriately describes the type of hypertension?
A. Normal
B. Elevated
C. Pre-hypertension
D. Stage 1
B. Elevated
Normal - SBP should less than 120
prehypertension - no longer use anymore with new guideline
Stage I - should be higher
A 32-year-old healthy male is working out on a stationary bike in an outpatient physical therapy clinic. After the first 4 minutes of constant load, submaximal exercise, VO 2 reaches a steady state, indicating that:
A. Level of lactic acid in the blood has reached a steady state.
B. The ATP demand is being met aerobically.
C. The exercise can be continued for 4 hours without further increase in heart rate.
D. The respiratory rate is insufficient to meet the ATP demand.
B. The ATP demand is being met aerobically.
A - anaerobic
B - answer
C - four hours doesn't make sense
D - sufficient instead of insuficient
A 30 years old male client visits a town which is 9000 feet above sea level. What are the INITIAL cardiovascular responses during his first few days in town?
A. Increased BP, increased cardiac output with tachycardia, and no significant changes in SV.
B. Decreased BP, decreased cardiac output with bradycardia, and increased SV.
C. Increased BP, decreased cardiac output with bradycardia, and increased SV.
D. Decreased BP, increased cardiac output with tachycardia, and increased SV.
A. Increased BP, increased cardiac output with tachycardia, and no significant changes in SV.
HR goes up, CO goes up, BP goes up, SV stays
Tachy - 100, Brady - 60
raise up the altitude -> exciting first time seeing her - increase BP, increase CO, similar SV
CO - HR * SV (increase HR, BP, and CO)
A PT is working on rehabilitating a 29-year-old ACL repair patient using aquatic therapy. The patient is immersed to the level of the sternoclavicular notch. Which of the following is the MOST expected response during aquatic therapy?
A. Decreased cardiac output
B. Decreased systolic blood pressure
C. Increased heart rate
D. Increased V0 2 max
B. Decreased systolic blood pressure
relaxed in the water (less stress) - opposite of excitement
- HR decreases
- SBP decreases
- CO increases
- SV increases
- Vital Capacity - decreases due to hydrostatic pressure around the lung would not allow fully expand the lung
54-year-old male patient's chart states that they have been taking beta-blockers for the past 5 years. Prior to starting an exercise training program, the patient should receive an explanation of the:
A. Greater benefits from cardiovascular exercise to be achieved at lower SBP rather than at higher SBP levels.
B. Need to use measures other than heart rate to determine the intensity of exercise.
C. Greater benefits from cardiovascular exercise to be achieved at lower HR than at higher HR levels.
D. Need for longer warm-up periods and cool down periods during exercise sessions.
B. Need to use measures other than heart rate to determine the intensity of exercise.
Beta-blocker will lower the HR and you should use RPE, MET or etc to determine the intensity of exercise
A 45-year-old male with a BMI of 38 kg/m 2 is enrolled in a 6-week fitness training program. Which is the MOST appropriate measure to assess change in fitness from pre and post fitness training?
A. The time it takes for the heart rate to return to baseline
B. Resting respiration rate at pre-training
C. Rating on a Wong baker scale
D. Increase in blood pressure during exercise
A. The time it takes for the heart rate to return to baseline
A PT is treating a patient with complaints of chest pain. The PT attempts to assess heart sounds with a stethoscope. Which of the following is true about the first sound during auscultation of the heart?
A. The first sound is of the closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves
B. The first sound is of the closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves
C. The first sound is of the opening of the aortic and pulmonic valves
D. The first sound is of the opening of the mitral and tricuspid valves
B. The first sound is of the closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves
The increased metabolic demand placed on the heart
during exercise can be best estimated by examining the
A. Systolic blood pressure
B. Rate product pressure
C. Diastolic blood pressure
D. Heart rate
B. Rate product pressure
Myocardial O2 demand = Rate Product pressure: HR * BP = RPP
This is used to determine the myocardial O2 demand of a patient at the onset of chest pain symptoms
A PT examines the output from a single lead
electrocardiogram of a patient in an outpatient clinic.
The ECG strip is shown in the picture below. PT should
determine the heart rate of the patient as
A. 110 beats per minute
B. 70 beats per minute
C. 80 beats per minute
D. 50 beats per minute
C. 80 beats per minute
large box is 0.2 sec
large large box is 1 second
6 sec - 8 beats
60 sec - 80 beats
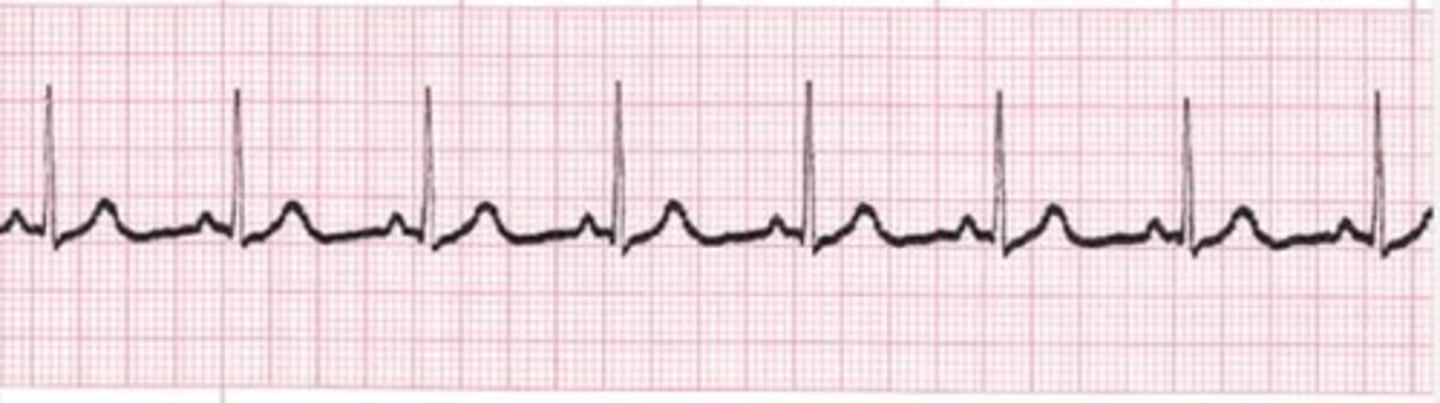
A 68-year-old patient is performing a Bruce protocol on an inclined treadmill. The PT is monitoring the patient using ECG leads. During the exercise, the PT sees the first-degree AV block ECG pattern shown. The PT's BEST response should be
A. Stop the treadmill session immediately and call the cardiologist
B. Continue without any modifications and monitor ECG
C. Reduce the treadmill speed and monitor ECG
D. Stop the treadmill, have the patient rest, and then resume at a lower intensity
B. Continue without any modifications and monitor ECG
1st degree AV block is not a severe issue and common symptoms show to athletes. and no treatment. However, monitor the ECG just in case
keep going with exercise bcz Bruce protocol is a test checking the maximal exercise test (VO2 max)
A 50-year-old male patient is diagnosed with a second-degree heart block type II. What would a physical
Does the therapist expect to find on the ECG strip?
A. An increase in PR interval lengths with no dropped beats
B. No relationship between P waves and QRS complexes
C. A gradual increase in PR interval length in all the beats
preceding a dropped beat
D. Normal PR intervals in all the beats preceding a dropped beat
D. Normal PR intervals in all the beats preceding a dropped beat
A- 1st degree
B - 3rd degree
C - predictable (gradual increase)
D - looks normal but suddenly drop (unpredictable)
A patient's electrocardiogram shows a new ST-segment elevation from baseline and a sinus rhythm of 68 beats per minute. What is the MOST likely diagnosis?
A. Bradycardia
B. Low blood pressure
C. Acute myocardial infarction
D. Congestive heart failure
C. Acute myocardial infarction
ST-segment elevation -Myocardial infarction
A Bradycardia - less than 60 bpm
A 58-year-old male is performing a Bruce protocol in your
clinic with ECG leads attached. During the protocol, the
PT sees the picture shown below. What are the MOST likely
diagnosis and interventions?
A. Myocardial ischemia that has an elevation of the ST segment greater than 1 mm and the PT should stop the protocol
B. Myocardial infarction that has an elevation of the ST segment less than 1 mm and the PT should stop the protocol and call 911
C. Myocardial ischemia that has an elevation of the ST segment less than 1 mm and the PT should stop the protocol
D. Myocardial infarction that has an elevation of the ST segment greater than 1 mm and the PT should stop the protocol and call 911
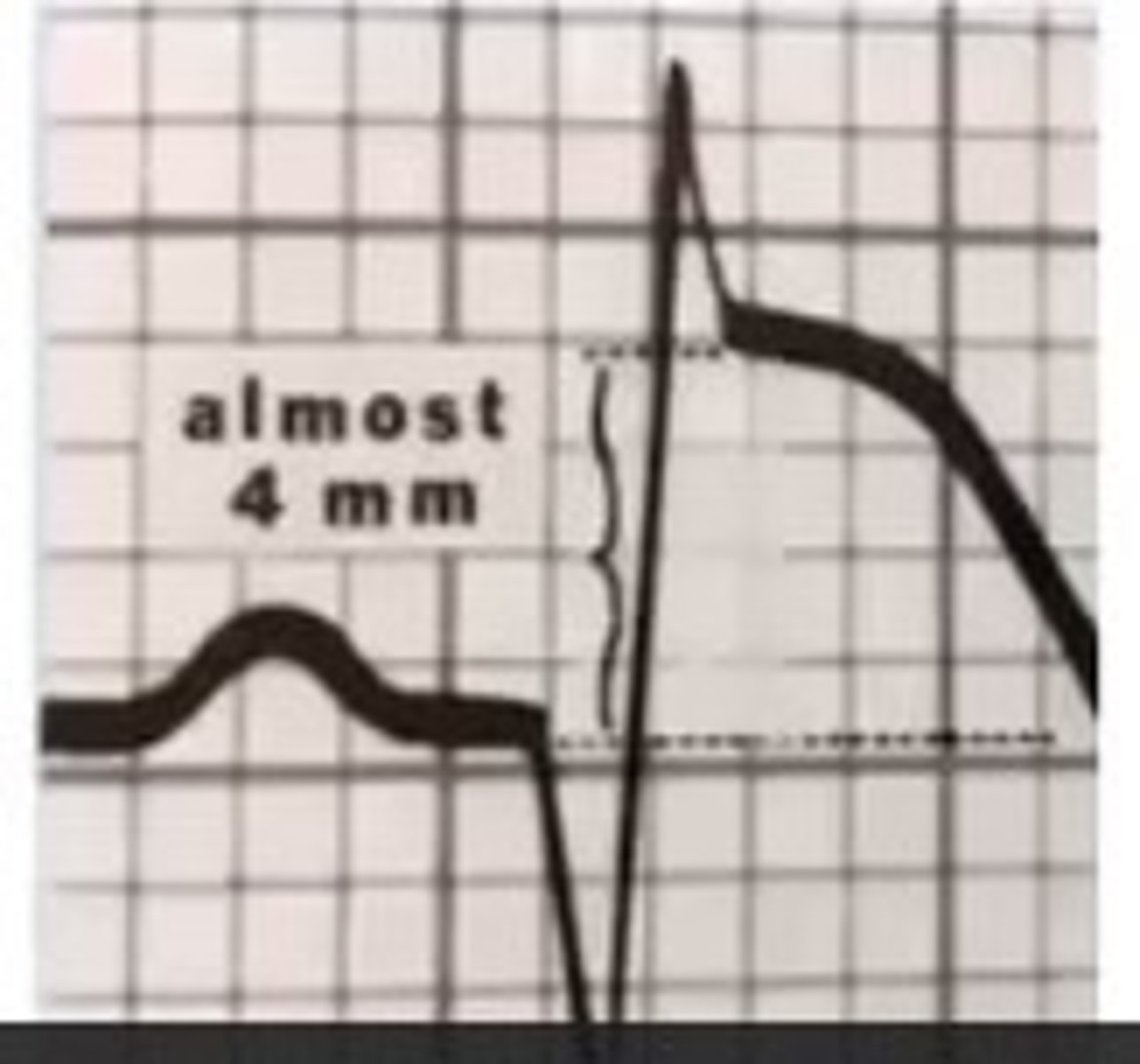
D. Myocardial infarction that has an elevation of the ST segment greater than 1 mm and the PT should stop the protocol and call 911
if the elevation of ST-segment with exercise is
less than 1mm is okay
more than 1 mm is dangerous and call 911
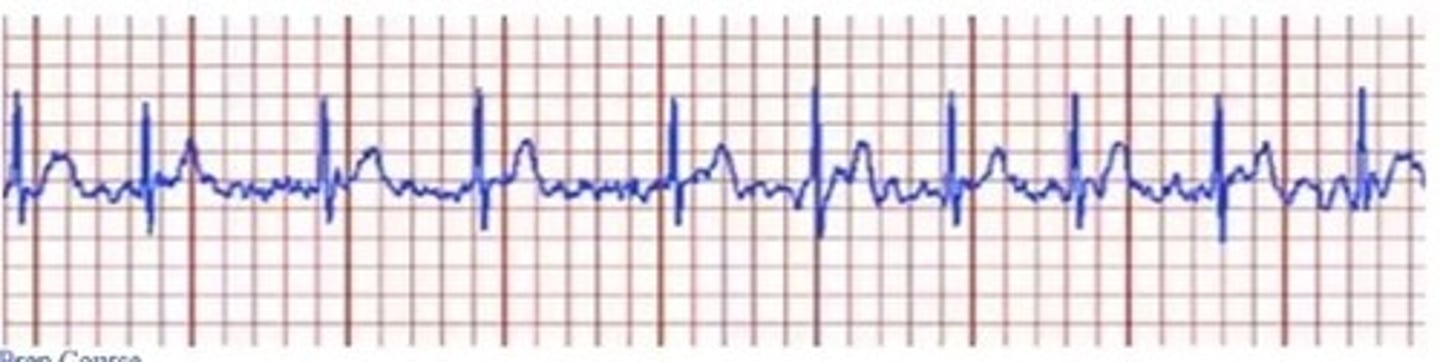
A PT is ambulating a 75-year-old male who is in recovering from a prostatectomy procedure. The patient complains of palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. What should be the interpretation and immediate action according to the ECG strip shown below?
A. Ventricular fibrillation; Call for a defibrillator
B. Premature ventricular contractions; Take him to his bed and monitor for changes in ECG.
C. Atrial Fibrillation; Stop exercise and report to the physician.
D. 3rd degree heart block; Activate emergency.
C. Atrial Fibrillation; Stop exercise and report to the physician
A. QRS looks normal
PVC - no P wave
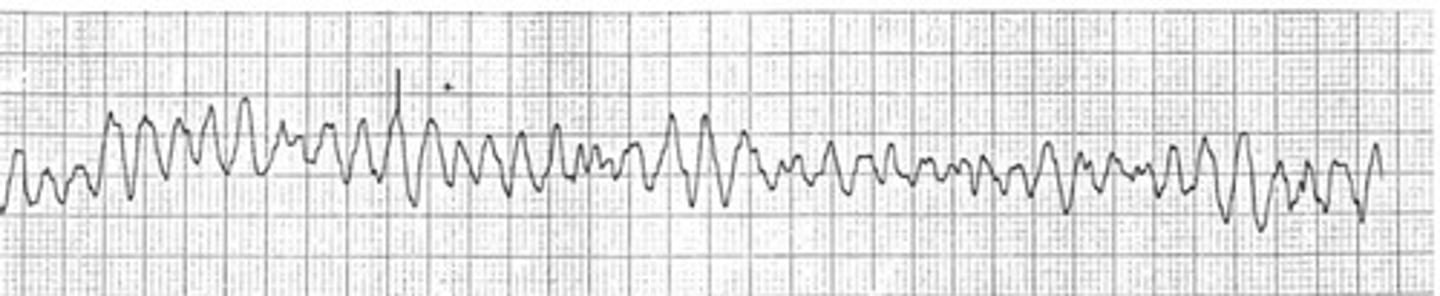
A physical therapist is performing joint mobilization on a
patient in the outpatient clinic. The PT notes the electrocardiogram in the photograph. The physical therapist's INITIAL response should be to:
A. Continue with joint mobilizations at the same intensity
B. Continue with joint mobilizations at a lower intensity
C. Stop the treatment and monitor ECG for 10 minutes.
D. Activate the emergency system or call 911
D. Activate the emergency system or call 911
V-fib - ER and call 911
A patient 1-month post-myocardial infarction is being seen
in a clinic. When increasing the patient to 5 MET's of workload, the therapist notes that the ECG reads 1 unifocal
PVC. The PT's IMMEDIATE action should be:
A. Continue to exercise and increase the intensity
B. Stop exercise because a patient is undergoing ischemia
C. Keep exercising at a lower intensity, consultation with a physician is not required here.
D. stop the exercise and consult with a physician before starting any exercise
C. Keep exercising at a lower intensity, consultation with a physician is not required here.
A PT is performing assessing the lung function of a
patient with a diagnosis of COPD. The PT would like to
assess the amount of air in the lungs after a NORMAL
exhalation. Which of the following parameters is the PT
referring to?
A. Functional residual capacity
B. Tidal volume
C. Expiratory reserve volume
D. Vital capacity
A. Functional residual capacity
RV + ERV
A 58 year old patient has chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. Which of these pulmonary test results will NOT
be increased when compared with those of a 58 year old
healthy individual?
A. Total lung capacity.
B. FEV1/FVC ratio.
C. Residual volume.
D. Functional residual capacity.
B. FEV1/FVC ratio.
expiratory decreases
A 78-year-old patient has an acute exacerbation of COPD. The patient has an FEV1 of 70% with FEV1/FVC<70% and has shortness of breathing during ambulation. According to the GOLD classification, the patient would MOST likely be classified as:
A. Very severe
B. Severe
C. Moderate
D. Mild
C. Moderate
1. Rule of Extremes - remove most severe cases
2. Acute - moderate...
A 58-year-old patient has the chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. During an examination, a PT finds that a patient
has a weak wet cough. Which of the following is MOST
appropriate to help this patient clear secretions?
A. Assisted coughing in the supine position
B. Postural drainage in side-lying position
C. Huffing
D. Manual or mechanical percussion
C. Huffing
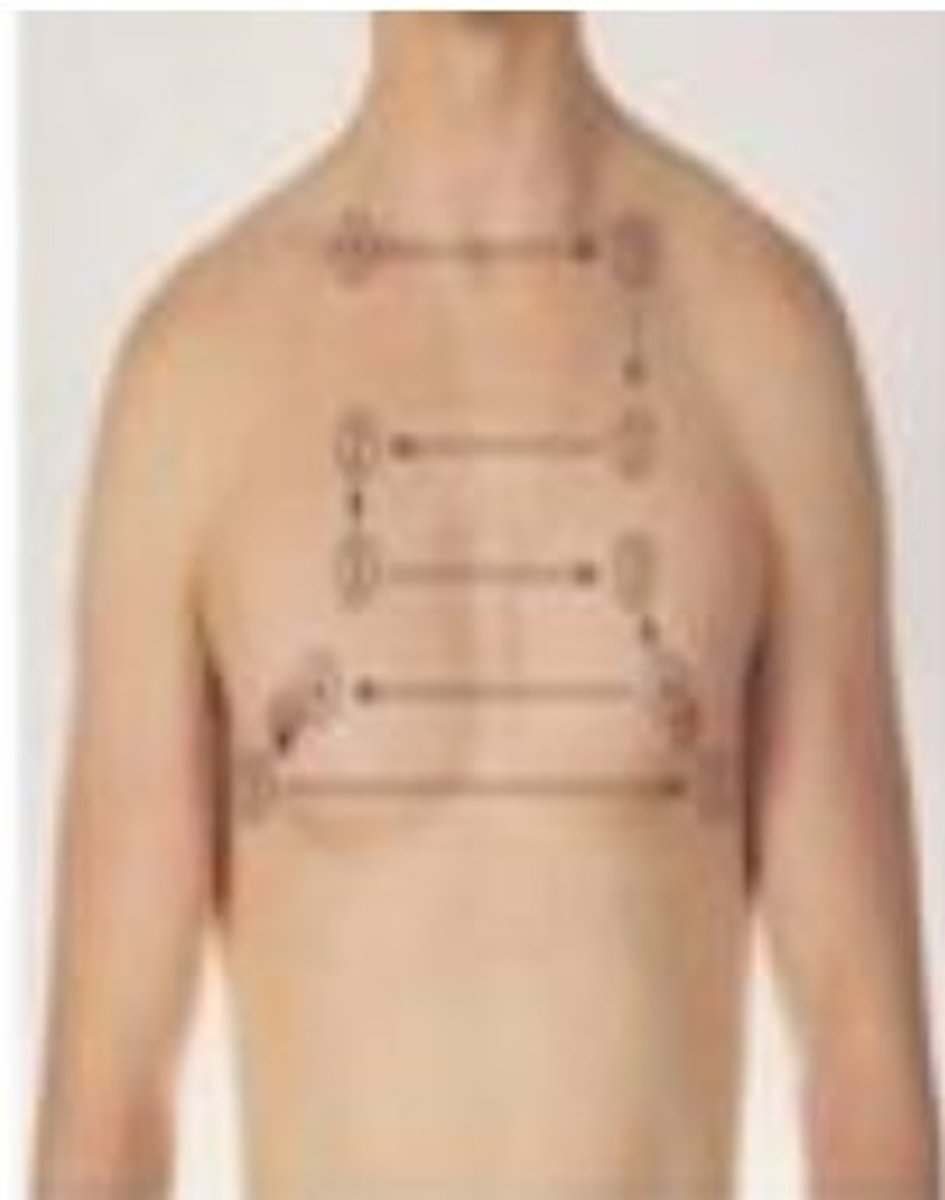
A physical therapist is examining a 41-year-old male patient in an outpatient clinic. Which of the following sound is PT auscultating?
A. Vesicular sounds
B. Mitral valve
C. Pulmonary valve
D. Tracheal sounds
A. Vesicular sounds
Tracheal: heard over trachea
Bronchial: heard in large airways in anterior chest near 2nd and 4rd intercostal space
Broncho-vesicular: posterior chest between scapula
Vesicular - most lung fields