Art History: Early Islamic Architecture and the Umayyad Dynasty, Carolingian Empire: another "New Rome", Romanesque Architecture, Medival Ethiopia, Gothic Architecture (copy)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
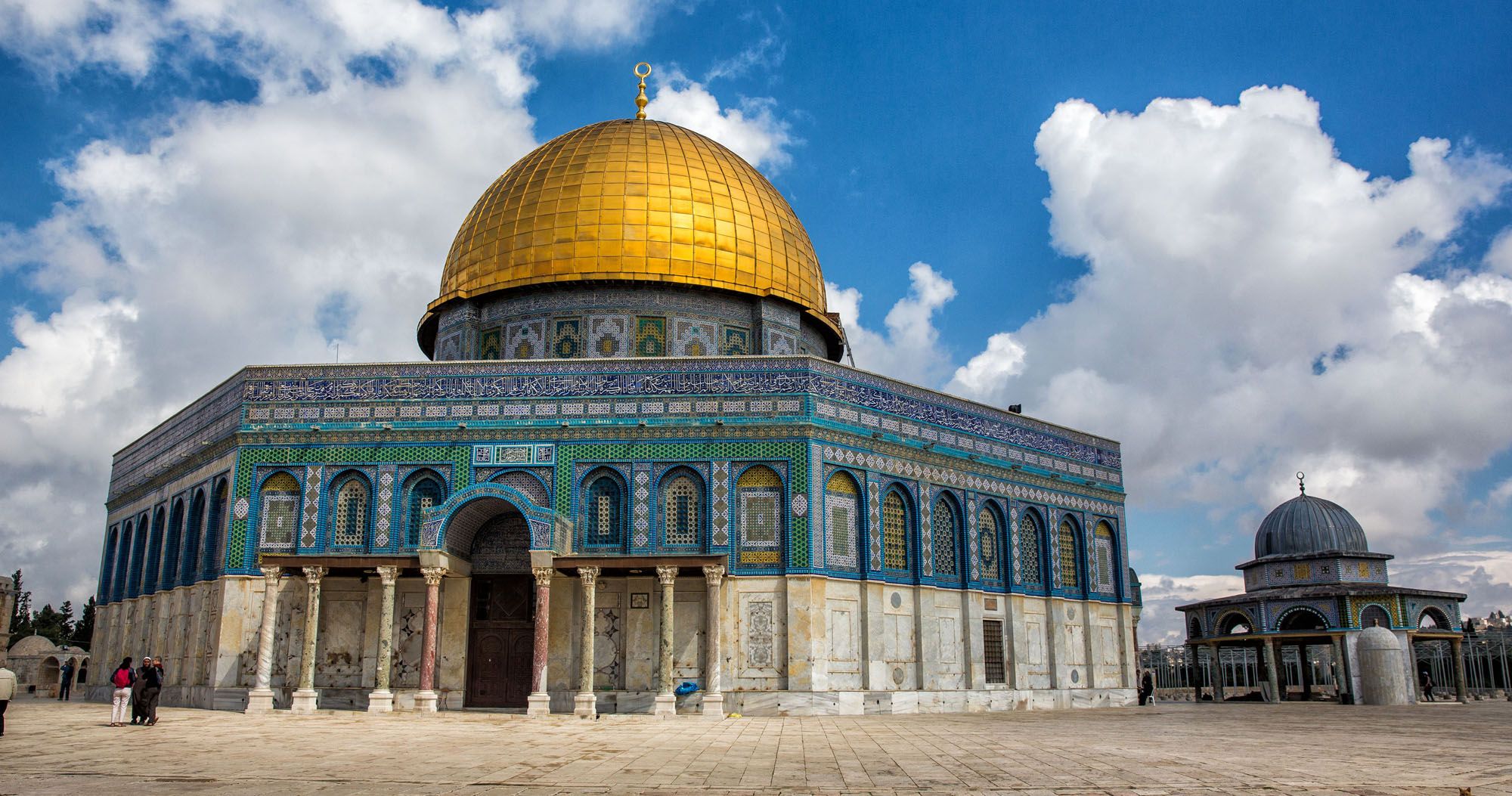

Dome of the Rock, c.690, Jerusalem, present-day Israel, interior decoration includes marble, mosaics gold
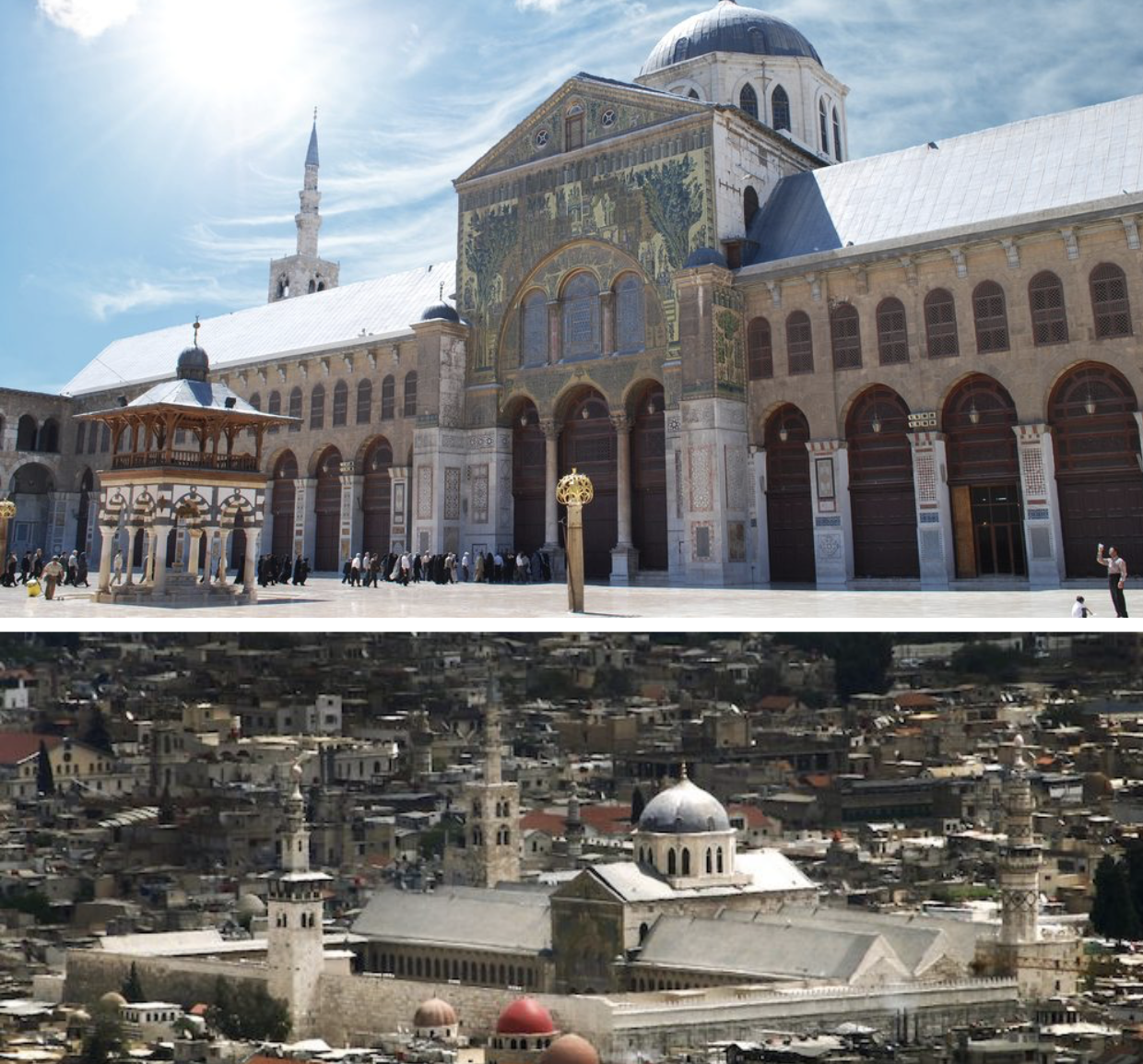

Great Mosque of Damascus, c.715, Damascus, present-day Syria, stoneconstruction decorated with marble revetment and mosaics, columns reused from the earlier Christian Church on the site
Caliph
political and religious leader, considered a successor to Muhammad
Corvée system
required artisans and other skilled laborers from many conqured areas to work on major state projects
Foundation Stone
The Foundation Stone or the Noble Rock is the rock at the center of the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem, a stone in the foundation of a building
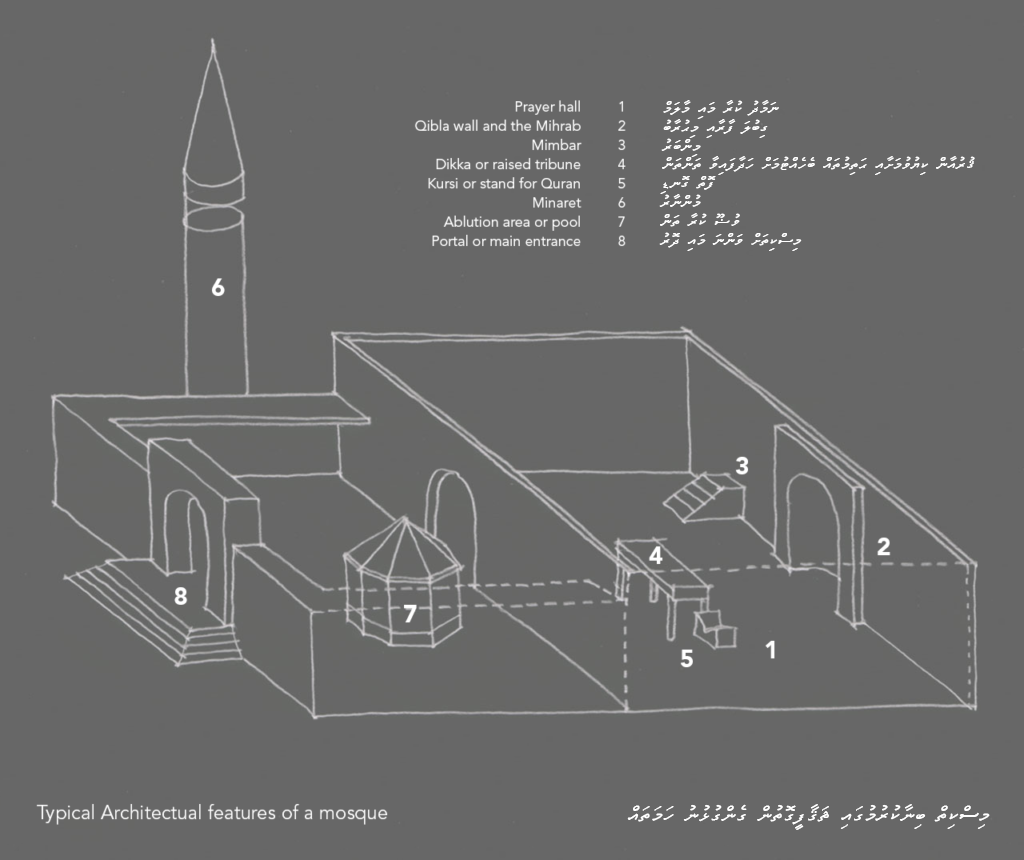
Mihrab
a niche in the wall of a mosque, at the point nearest to Mecca, toward which the congregation faces to pray.
Mosque
a Muslim place of worship.
Qibla wall
the wall in a mosque that faces Mecca. The mihrab is a niche in the qibla wall indicating the direction of Mecca; usually the most ornate part of a mosque, highly decorated and often embellished with inscriptions from the Qur'an
Umayyad Caliphate
capital at Damascus, overthrown by Abbasid Caliphate in 750 continues in Spain, coexisted with christians, Jews, and others in conquered areas required corvée system
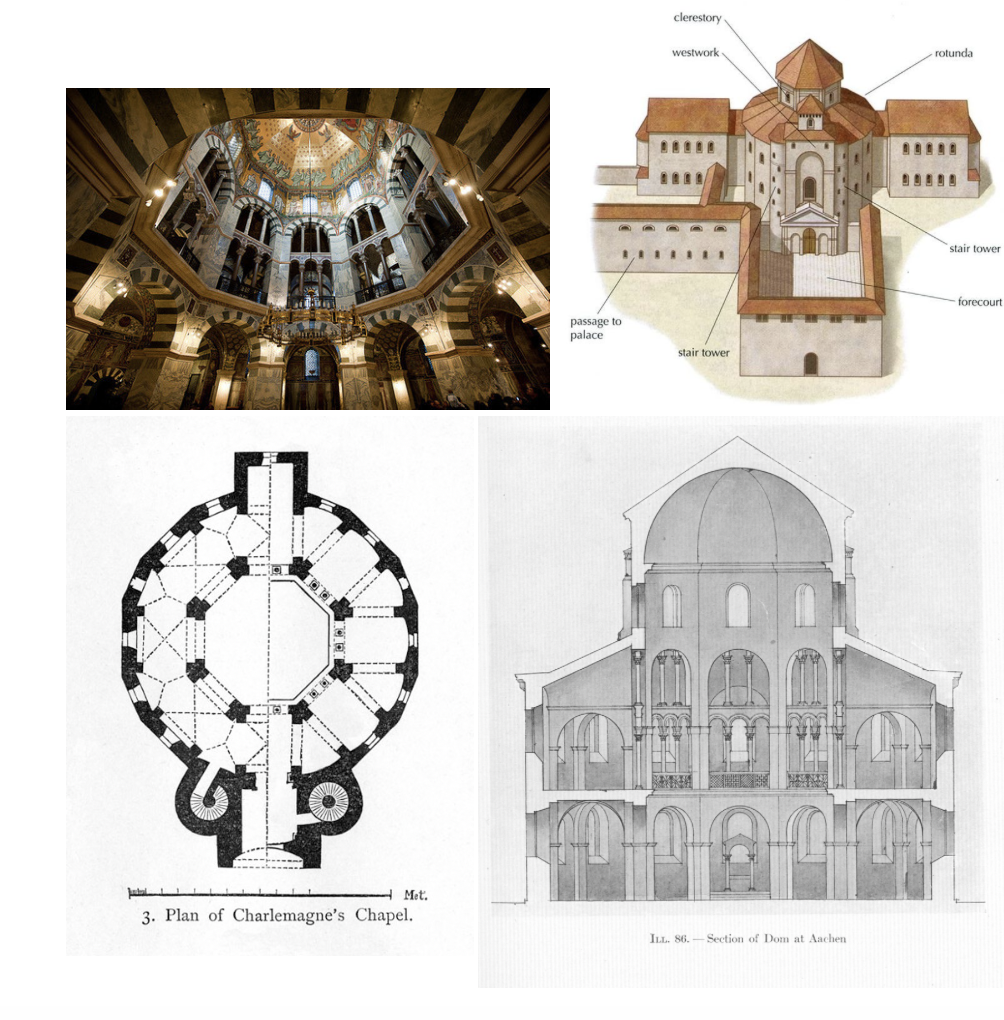
Charlemagne’s Palace Chapel, c. 800, Aachen present-day Germany, materials: marble, mosaic, brass
Charlemagne
r. 768-814, King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and Emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 800, Charlemagne succeeded in uniting the majority of Western Central Europe, and was the first recognized emperor to rule in the west
Odo of Metz
fl.(flourished-active in field) 790-810, an architect of Armenian origin who lived during Charlemagne's reign in the Carolingian Empire. He is the earliest known architect born north of the Alps
Renovatio Romani imperii
"renewal of the empire of the Romans") was a formula declaring an intention to restore or revive the Roman Empire.
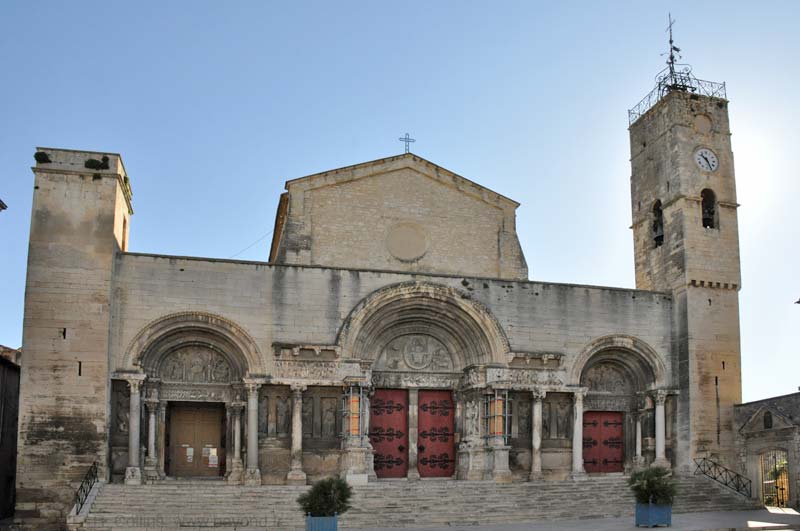

Abbey of St Gilles du Gard, west façade, c 1150, st-gilles, present-day france, limestone and white marble
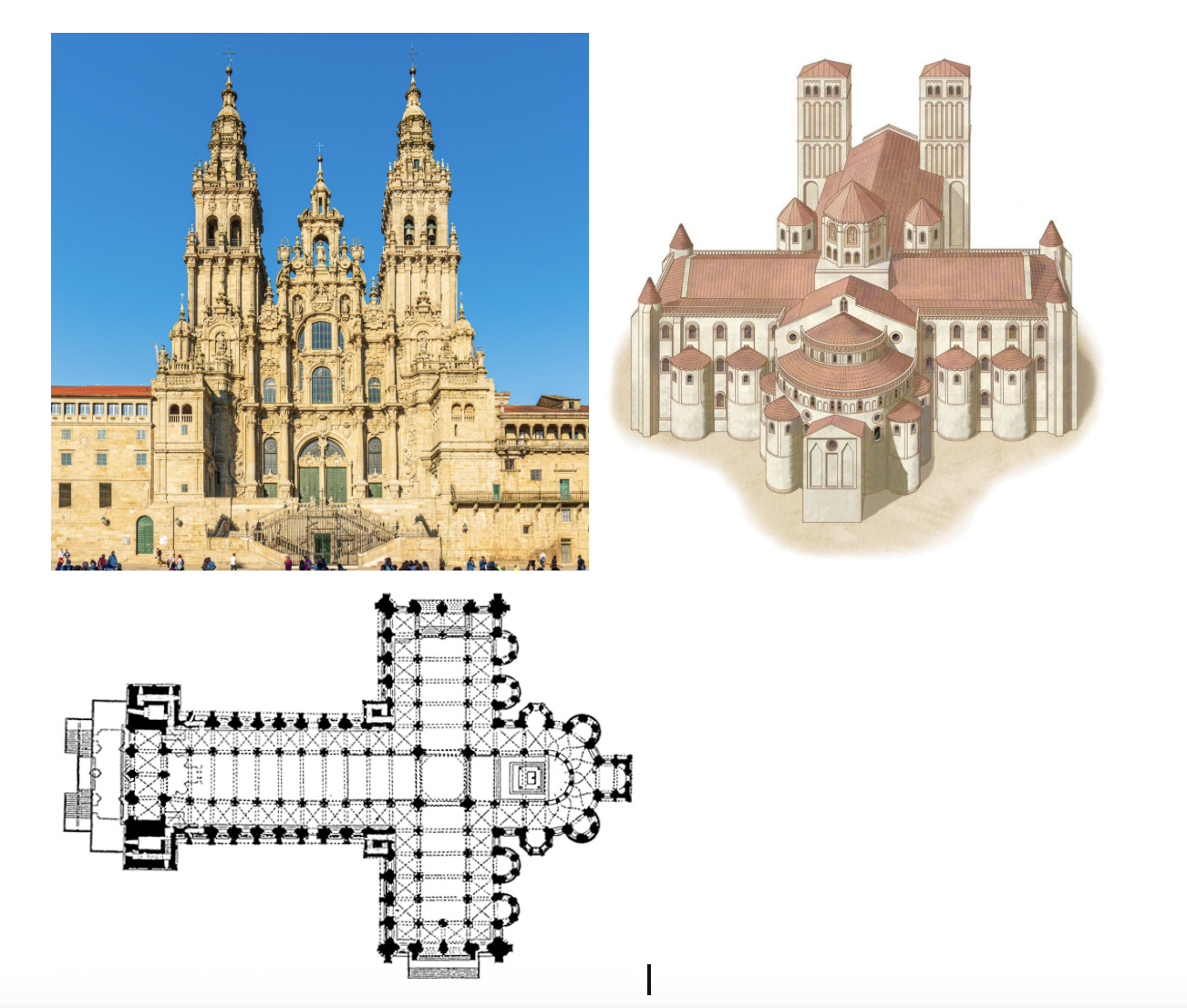
Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, 12th century (1078-1188), Compostela, present-day Spain, granite
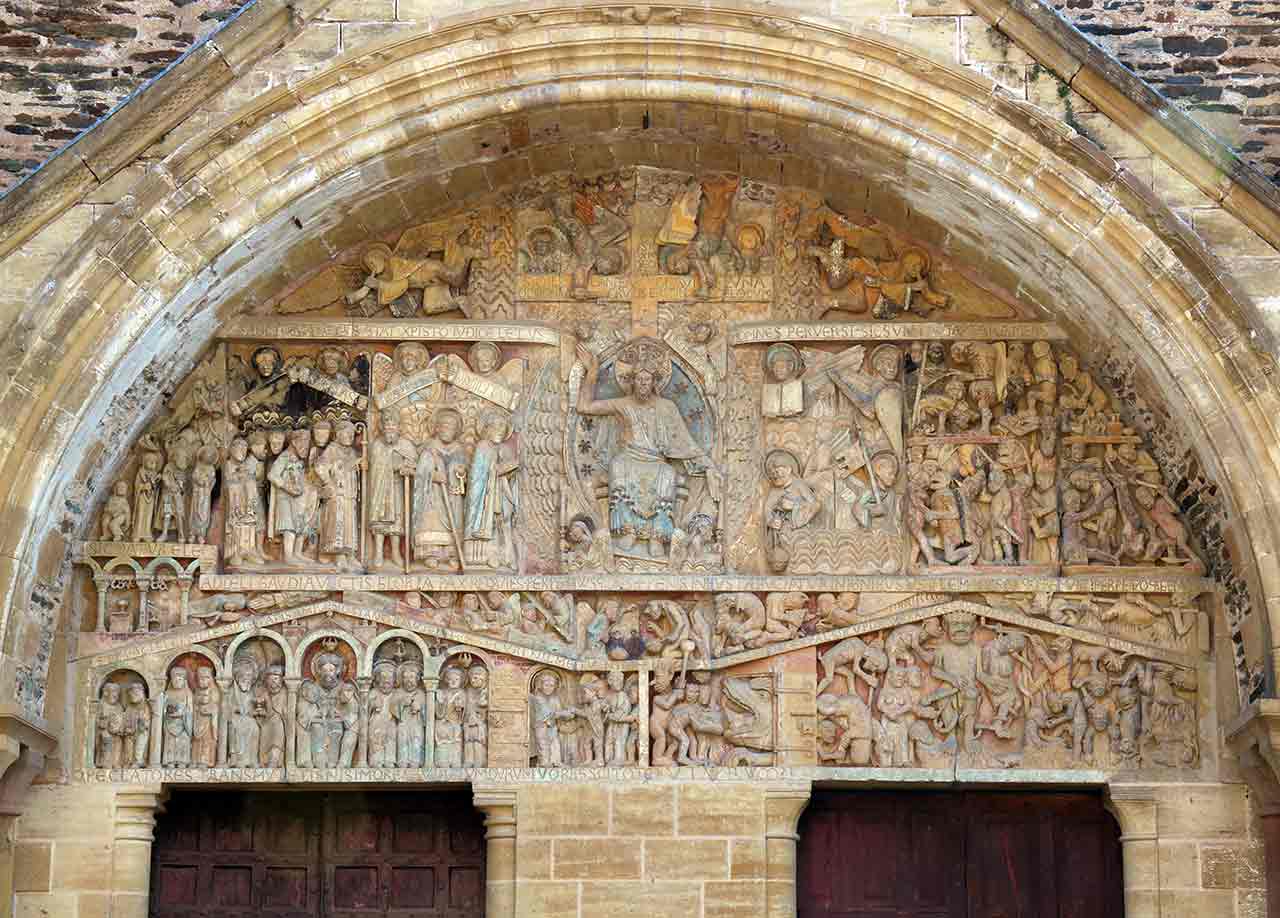
Tympanum at the Abbey of Ste Foy, c. 1100, Conques, present-day France, Limestone and traces of paint
arcade
a series of arches supported by columns (round vertical supports) or piers (squared vertical supports)
Ashlar masonry/dressed stone
a type of stone construction where all stones are dressed or cut to a uniform shape, size, and surface appearance
barrel vault
a vault forming a half cylinder, series of arches
bay
area between two piers, usually geometrically proportional to the crossing
classism
using forms of classical architecture as a starting point
compound pier
support structure with a central core surrounded by engaged elements
crossing
intersection of nave and transept (the junction of the four arms of a cruciform (cross-shaped) church)
cult of saints
Veneration of saints in Christian tradition, involving prayers, relics, and pilgrimages to their shrines for intercession and blessings.
gallery
any covered passage that is open at one side, such as a portico or a colonnade
groin vault
produced by the intersection at right angles of two barrel vault
lantern tower
a tall construction above the junction of the four arms of a cruciform (cross-shaped) church, with openings through which light from outside can shine down to the crossing
pilgrimage
A journey to visit the shrine of a saint or places associated with their earthly life
portal
A portal is an opening in a wall of a building, gate or fortification, especially a grand entrance to an important structure
radiating chapels
Small, semi-circular chapels arranged around the apse of large church
round arch
an arch formed in a continuous curve(more than half a circle), weight from stones goes to more down on piers instead of out
tranverse arch
Supporting arch which runs across the vault from side to side, dividing the bays. it usually projects down from the surface of the vault.
Tympanum
a vertical recessed triangular or semicircle space forming the center of a pediment, typically decorated.
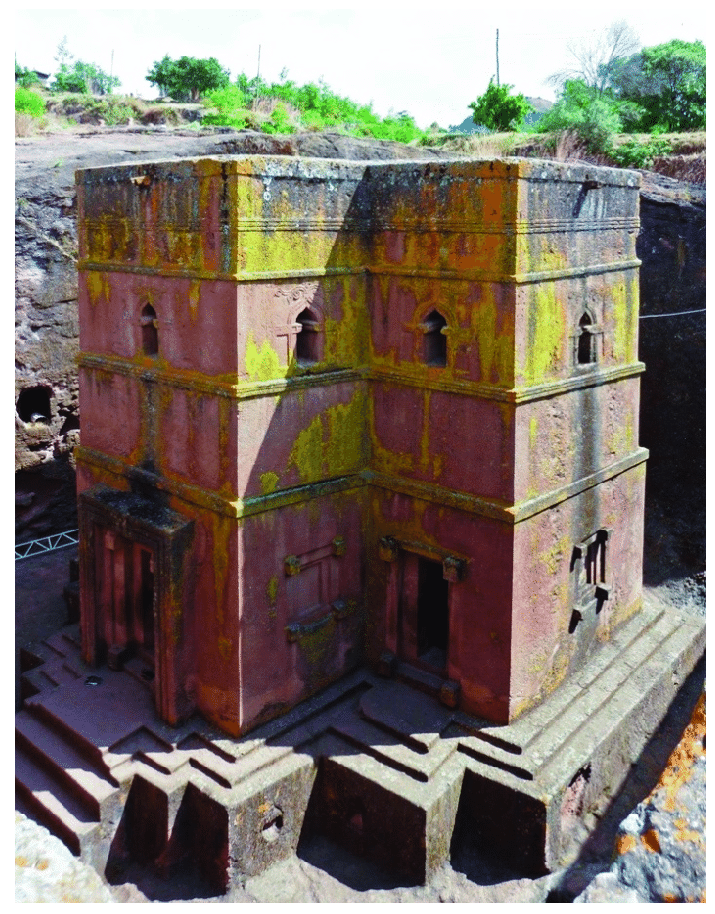

Bete Gyorgis (church of St George), 12th or 13th century, Lalibela, present-day Ethiopia, carved from the “living rock”
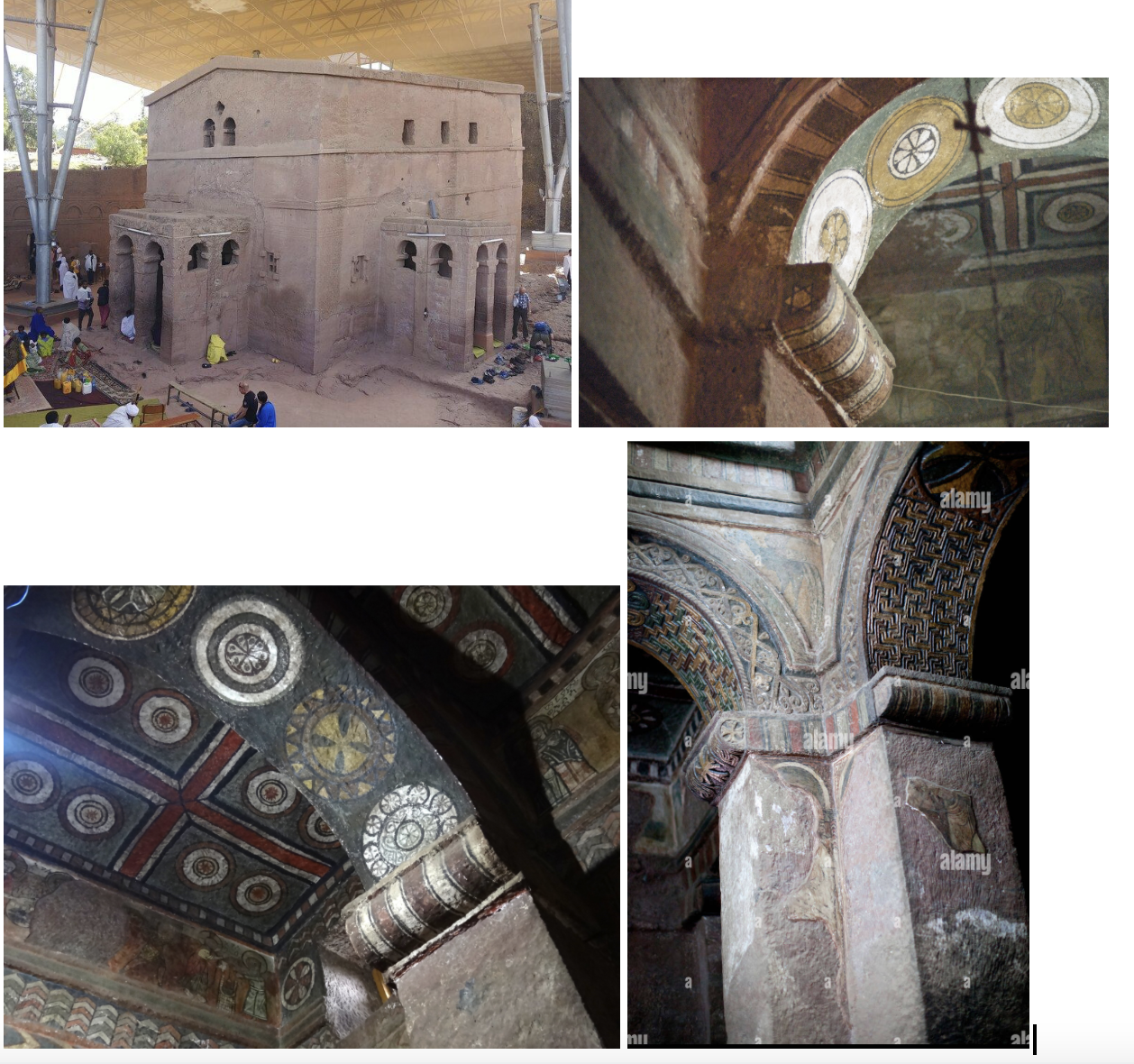

Bete Maryam (church of St Mary), 12th or 13th century, Lalibela, present-day Ethiopia, carved from the “living rock” and painted
Gebre Mesqel Lalibela
r. 1181-1221, a king of the Zagwe dynasty, developed city Lalibela, venerated as a saint by the Orthodox Tewwahedo Churches, credited with creation of rock-hewn chuches (supposedly modeled them after Jerusalem)
Rock-hewn church
carved from living rock
Zagwe Dynasty
c. 1140-1270, capital lalibela, developed and named for King Gerbre Mesqel Lalibela (venerated saint)
Minaret, Minbar, Mihrab, Qibla Wall, courtyard, prayer room
Minaret, Minbar, Mihrab, Qibla Wall, courtyard, prayer room
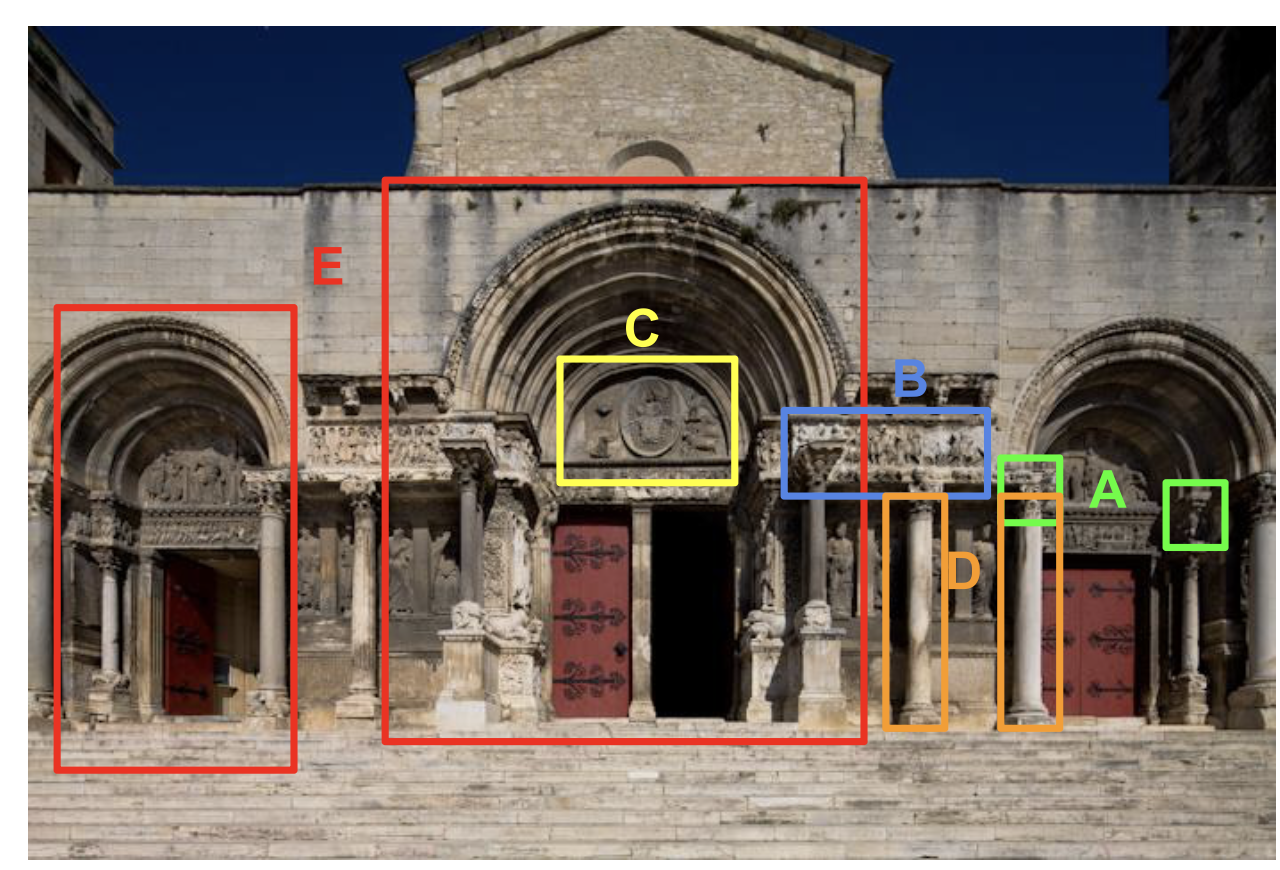
A=Capitals, B=Frieze, C=Tympanum, D=Columns, E=Portal
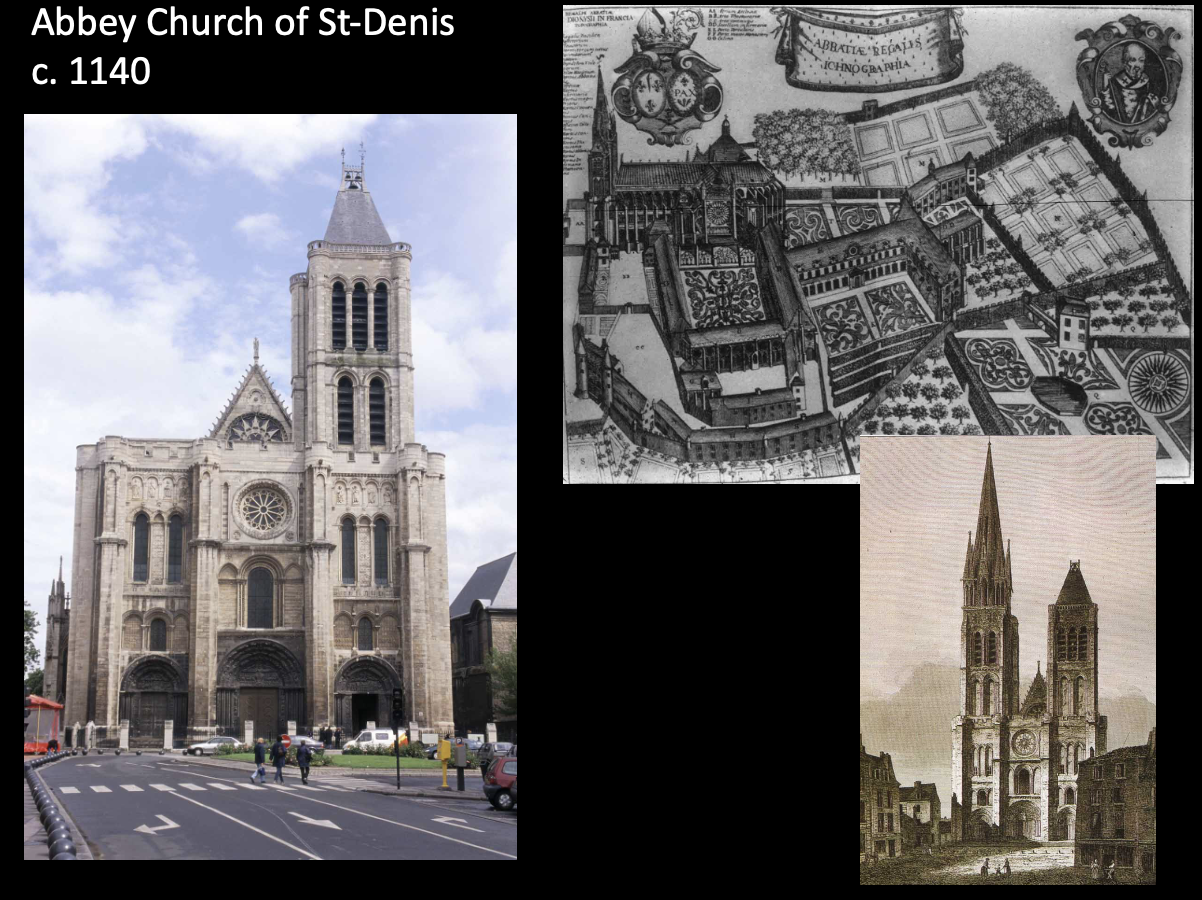

Abbey Church of St-Denis, choir, c.1140, Paris, present-day France, limestone, stained glass
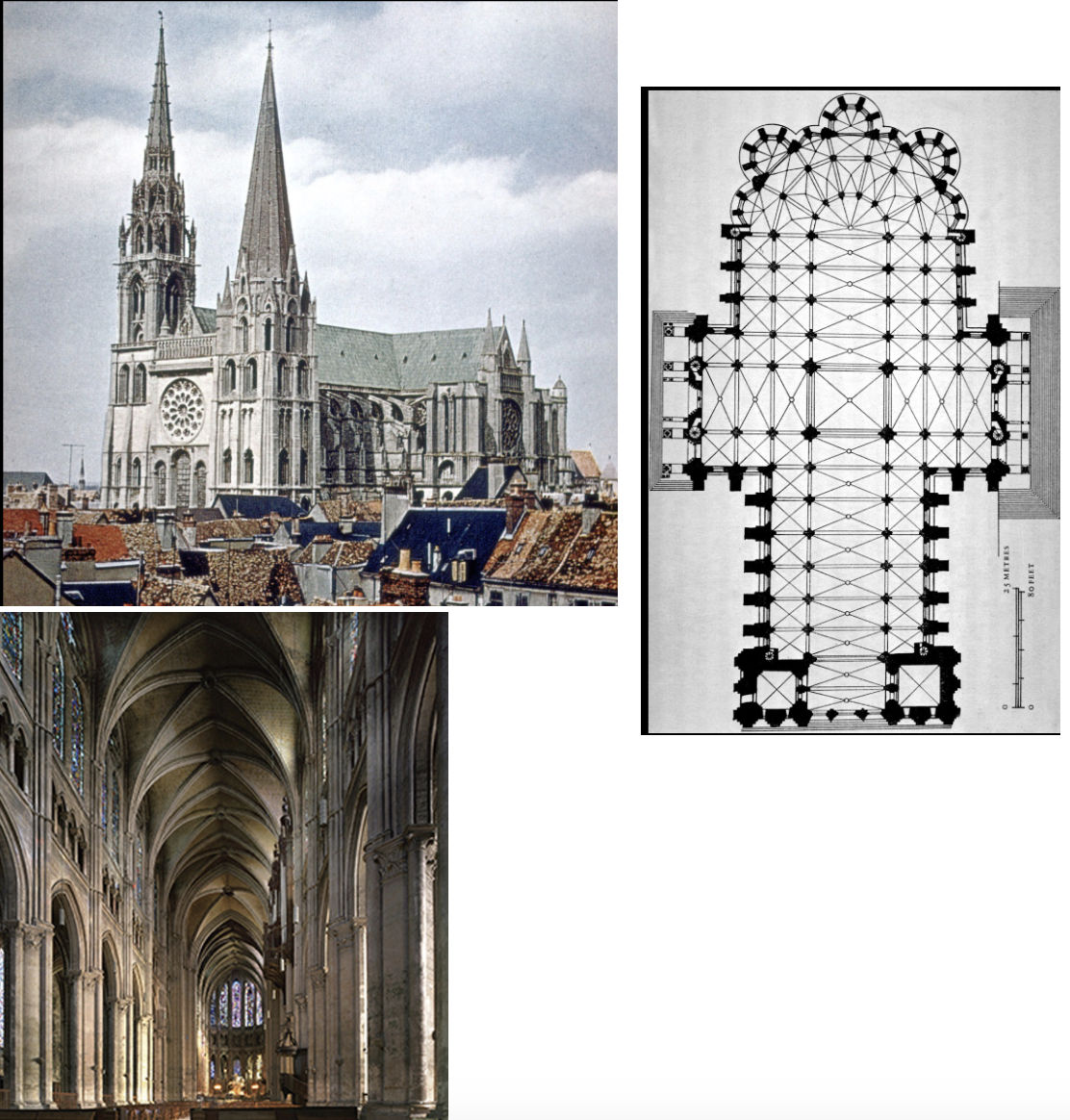
Cathedral of Notre-Dame at Chartres, c. 1200 and later, Chartres, present-day France, limestone, stained glass
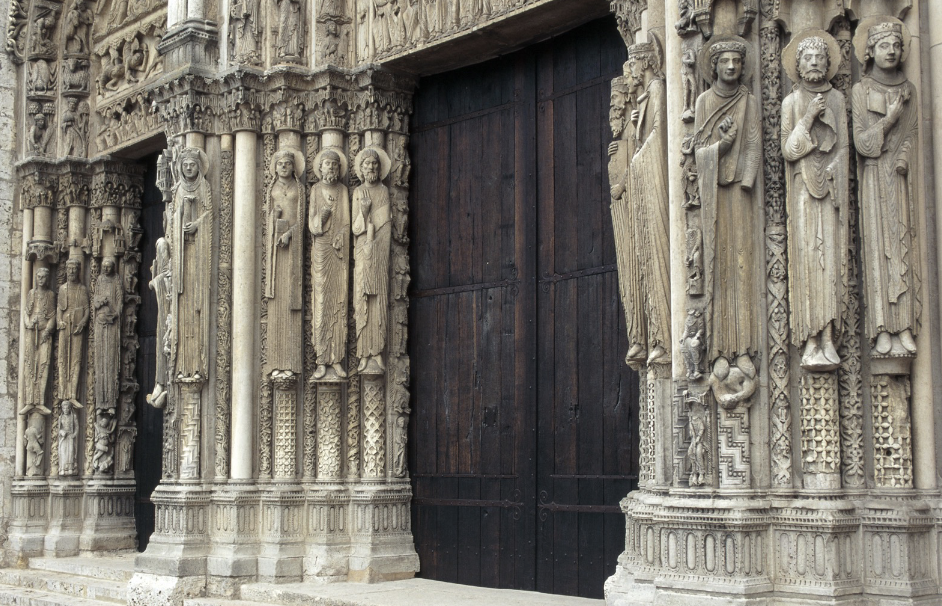

West Portal Jamb Figures at Chartres Cathedral, c. 1150, Chartres, present-day France, limestone

South Transept Portal Jamb Figures at Chartres Cathedral, c 1230, Chartres, present-day France limestone
Abbey church
Abbot Suger, d 1151
Capetian dynasty
Cathedral
Chevet
Choir
Collegiate Gothic
Contrapposto
Flying Buttress
Gargoyle
Ile de France
Jamb figure
Lancet window
Mullion
Pointed Arche
Ribbed groin vault
Rose window
stained glass
string course
tracery
webbing (in a vault)