Axial Skeleton Test
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Cranial bones
8 bones that enclose the cranial cavity (fluid filled chamber that cushions and supports brain)
Inner surface acts as attachment point for blood vessels, nerves and membrane’s stabilizing brain position
Outer surface acts as attatchment for for muscles that move eyes, jaws and head
Calvaria (skullcap) is the roof of the skull formed by occipital, parietal and frontal bones
Occipital bone (1)
External occipital crest: Attachment for ligament that helps stabilize neck vertebrae
Parietal bones (2)
Frontal bone (1)
Temporal bones (2)
Sphenoid bone (1)
Bat shaped
Ethmoid bone (1)
Facial bones
14 bones that protect digestive and respiratory tracts and provide attachment points for muscular control of facial expressions and assistance in manipulation of food
Maxillary bones (2)
Support upper teeth
Form inferior orbital rim, upper jaw, lateral margins of external nares and part of hard palate
Palatine bones (2)
Nasal bones (2)
Bridge of nose
Inferior nasal conchae (2)
Zygomatic bones (2)
Cheekbone
Lacrimal bones (2)
Medial wall of orbit
Tears
Vomer (1)
Inferior portion of nasal septum
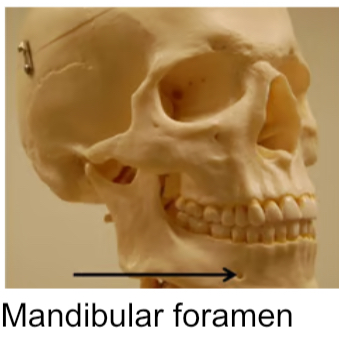
Mandible (1)
Lower jaw
Only movable bone
External auditory meatus
Tube like opening for ear canal
Begins on lateral surface of temporal bone and ends at tympanic membrane
Mastoid process
Rounded projection posterior to external acoustic meatus
Part of inferior temporal bone
Attachment for muscles that rotate/ extend head
Suture
Immovable joint between skull bones of adults
Dense fibrous connective tissue
Squamous suture
Attaches temporal to parietal bones
Coronal suture
Attaches frontal to parietal bones
Sagittal suture
Attaches parietal bones
Lambdoid suture
Attaches occipital to parietal bones
Sutural bones may be present along this
Palatine bone
Posterior portion of hard plate and contributes to floor of each orbit
Occipital condyle
Rounded processes on each side of foramen magnum
Articulates with atlas
Connects skull with vertebrae
Foramen magnum
Large medial opening connecting cranial cavity to vertebral canal
Surrounds connection b/w brain and spinal cord
In occipital bone
Zygomatic arch
Bony bridge on side of head created by zygomatic and temporal bones
Facial structure, connect facial bones to cranium and attach to chewing muscles
Nasal conchae bones
Scroll like projections on each lateral wall of nasal cavity
Superior and middle part of ethmoid, inferior own bone
Create turbulence in air entering nasal cavity
Increase epithelial surface to warm and humidify inhaled air
Ethmoid bone
Forms anteromedial floor of cranium, roof of nasal cavity, part of nasal septum and medial orbital wall
Cribeform plate: Form roof of nasal cavity and anteromedial cranial floor; nasal foramina permit passage of olfactory nerves
Crista gali; bony ridge projection for attachment of membranes covering brain; superior to cribriform plate; “cocks comb”
Perpendicular plate: Form upper part of nasal septum
Sella turcica
Part of sphenoid bone
Saddle shaped depression
Houses pituitary gland
Sinuses
Chamber within bone, normally filled with air
Lighten skull
Lined w/ mucous membrane → filter air before reach lungs and moisten
Nasal
Paranasal
Ethmoid
Sphenoid
Frontal
Maxillary
Hyoid bone
Associated bone; not attached to another bone
Supports larynx
Attachment site for larynx, pharynx and tongue
Functions of axial skeleton
Supports and protects the brain, spinal cord, and organs in the trunk's body cavities.
Provides attachment sites for muscles that:
Adjust position of head, neck, and trunk.
Vertebral column helps maintain upright position
Perform respiratory movements.
Stabilize the appendicular skeleton (supports limbs).
Vertebral column transfer body weight to lower limbs
Cervical vertebrae
7
Location: Neck
Small body, large foramen
Long, bifid spinous process
Has transverse foramina
Protects vertebral arteries/ veins serving brain
Include atlas and axis
Vertebra prominens (C7)
Long, prominent spinous process felt at base of neck making it good landmark
Function: Support skull, stabilize relative positions of brain and spinal cord and allow controlled head movement
Thoracic vertebrae
12
Location: Chest
Medium heart shaped body
Long, slender spinous process
Costal facets for rib articulation
Functions: Support head, neck, upper limbs and chest and articulates w/ ribs to allow change in volume of thoracic cage
Lumbar vertebrae
5
Location: Inferior back
Big oval body W/ small triangular foramen
Blunt, broad spinous process
Short transverse process
Support most weight
Sacrum
5, fuse after puberty (complete ~25-30) 2/ transverse lines marking former boundaries
Functions: Protect reproductive, digestive and urinary organs and attach axial skeleton to appendicular
Base: Broad, superior surface; ala/ wing extends from each base side; Sacral foramina: Intervertebral foramina of fused disc; Apex: narrow inferior portion; superior articular process w/ last lumbar vertebrae
Coccyx
3-5 fused vertebrae (begin at age 26)
Attachment for pelvic floor muscles
Tailbone
Atlas
C1
No spinous process or body
Large round formaen
Articulates w/ occipital condyles
Allows nodding yes
Axis
C2
Has dens/ odontoid process on superior surface to bind to atlas by transverse ligament
Allow shaking head no
Primary/kyphotic curves
Develop before birth; curve posteriorly
Thoracic: Accommodates thoracic organs
Sacral: Accommodates abdominopelvic organs
Secondary/lordotic curves
Develop after birth; curve anteriorly
Cervical curve: Develops as infant lifts head, balances head on neck.
Lumbar curve: Develops with ability to stand, balances trunk weight over lower limbs
Scoliosis
“S-shaped” curve
Structure of basic vertebrae
Vertebral Body: Transfers weight along column (gets bigger as go down).
Vertebral Arch: Forms posterior and lateral margins of vertebral foramen.
Laminae: Form roof of vertebral foramen.
Pedicles: Form sides of vertebral arch.
Spinous process: Projects posteriorly from laminae fusion (e.g., granny hunch).
Transverse processes: Project laterally from pedicles/laminae junction (muscle attachment, rib articulation).
Articular Processes: Extend superiorly/inferiorly to articulate with adjacent vertebrae.
Articular facet: Smooth surface for joints.
Superior articular processes: Articulate with inferior processes of superior vertebra.
Inferior articular processes: Articulate with superior processes of inferior vertebra.
Vertebral Foramen: Opening framed by body and arch.
Vertebral Canal: Formed by successive vertebral foramina, encloses spinal cord.
Intervertebral Discs: Fibrocartilage pads separating vertebral bodies providing shock absorption and support
Intervertebral Foramina: Spaces between successive pedicles, allow nerve/blood vessel passage.
Vertebrosternal ribs
“True” ribs
Connected to sternum w/ individual costal cartilage
Ribs 1-7
Vertebrochondral ribs
Connect to sternum by shared costal cartilage
Ribs 8-10
Part of “false” ribs
Vertebral ribs
No connection to sternum
Ribs 11-12
Floating ribs
Part of false ribs
Parts of sternum
Manubrium
Trapezoid shaped
Superior portion
Articulates w/ clavicles and 1st rib pair
Body
Inferior to manubrium
Articulates w/ rib pairs 2-7
Xiphoid process
Inferior to sternum body
How should CPR be administered to minimize injury
Do not press on the xiphoid process, as it could break, puncturing the lung
Use 2 finger rule: Place palm 2 fingers above xiphoid process tip (where lowest ribs meet at bottom of breastbone)\
Ribs like bucket handle: Push down → ribs move in; pull up → ribs move out: sternum moves accordigly
Affects width and depth of thoracic cage, increasing/ decreasing w/ volume
Structure of nasal septum
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone (superior)
Vomer (inferior)
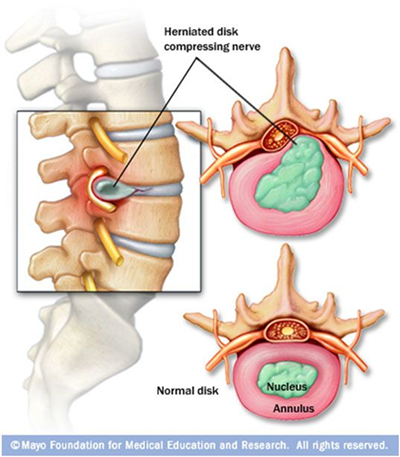
Herniated/ slipped disc
Occurs when fibrocartilage of intervertebral discs stressed or cracked
Inner, pulp like center protrudes out, causing pressure on spinal cord or nerve
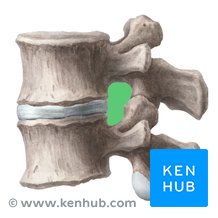
Intervertebral foramen
Spaces formed b/w successive pedicles
Allows nerve/ blood vessel passage
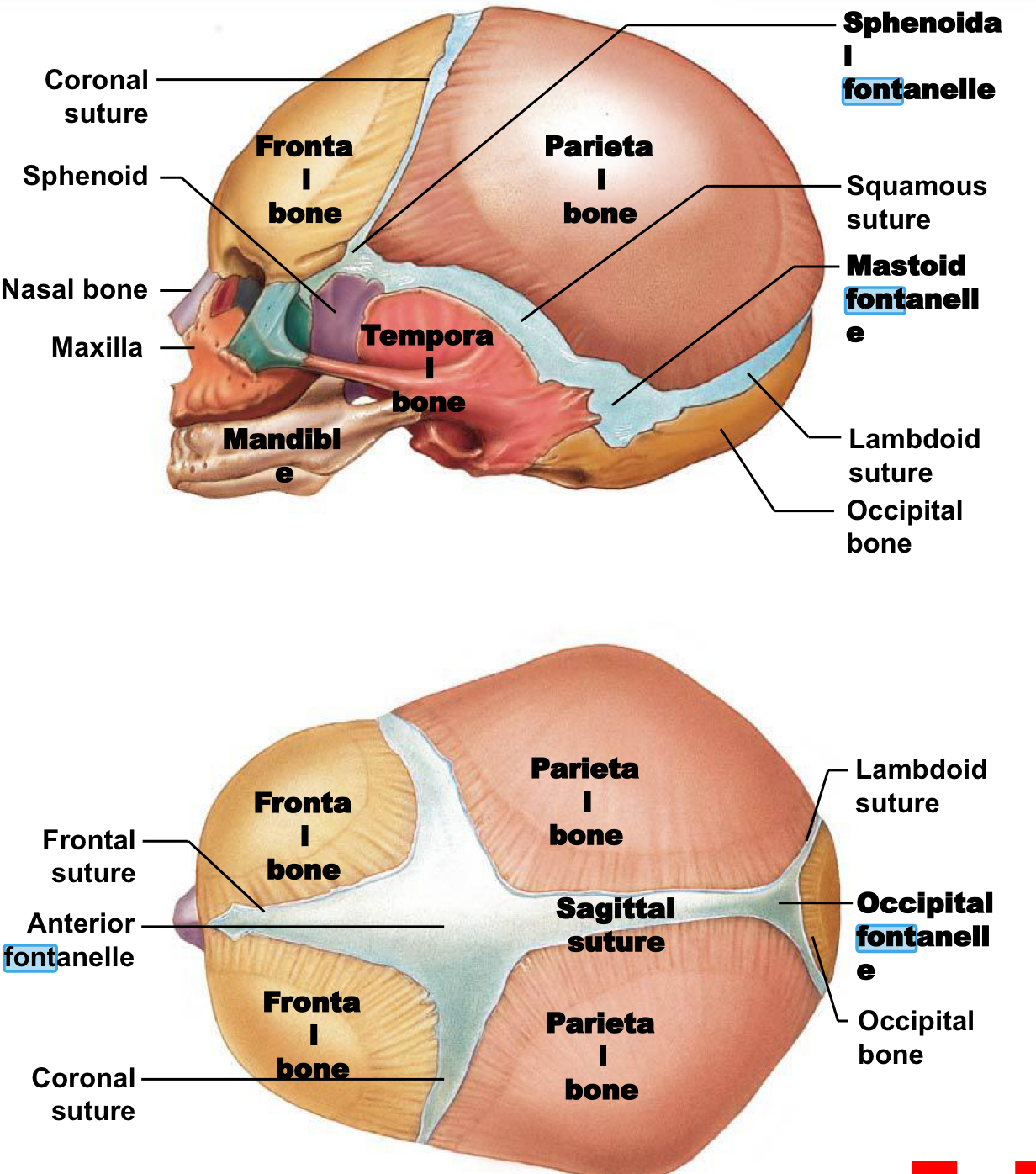
Fontanelles
Large fibrous areas between cranial bones.
Ease head passage through birth canal and allow cranial growth for brain development.
Replaced by sutures over time.
All replaced before age 5 (when brain growth slows).
Anterior Fontanelle ("soft spot"):
Large, diamond shape intersection of frontal, sagittal, and coronal sutures.
Largest, persists until ~age 2.
Shallow (dehydration), bulging (increased pressure), pulses with heartbeat (covers major blood vessel)
Posterior/occipital fontanelle small, triangular intersection where occipital and parietal bones meet
Close w/ 1st few months
Sphenoid and mastoid fontanelles (2 each)
Projection functions
Tendon and ligament attachment
At joints where adjacent bones articulate
Depression/ grooves/ tunnels functions
Sites for blood vessels or nerves to lie alongside or project into bone
Process
Any projection/ bumb
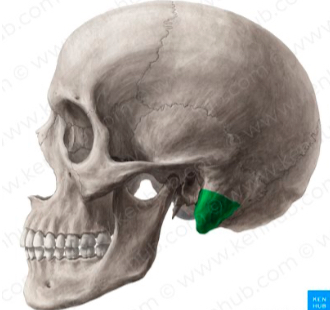
Tubercle
Small, rounded projection
Wannabe trochanter
For muscle attatchment
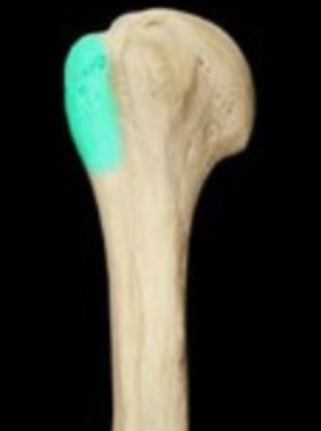
Tuberosity
Small, rough projection that takes up a broad area
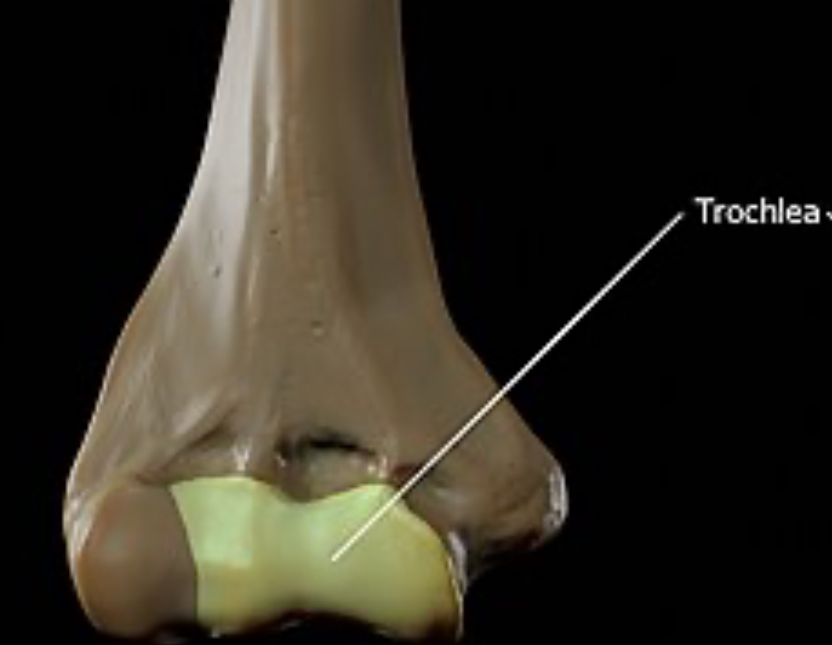
Trochlea
Smooth, grooved articular process shaped like a pulley
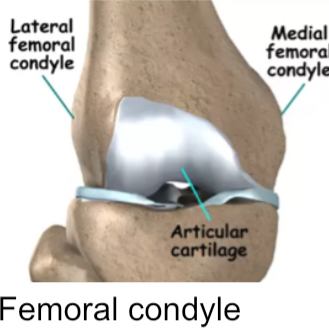
Condyle
Smooth, rounded articular process
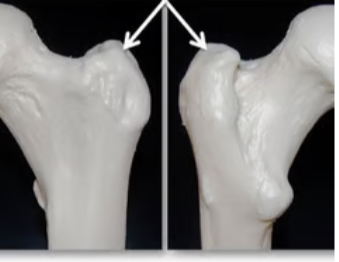
Trochanter
Large, rough projection
Proximal femur only
Muscle attatchment
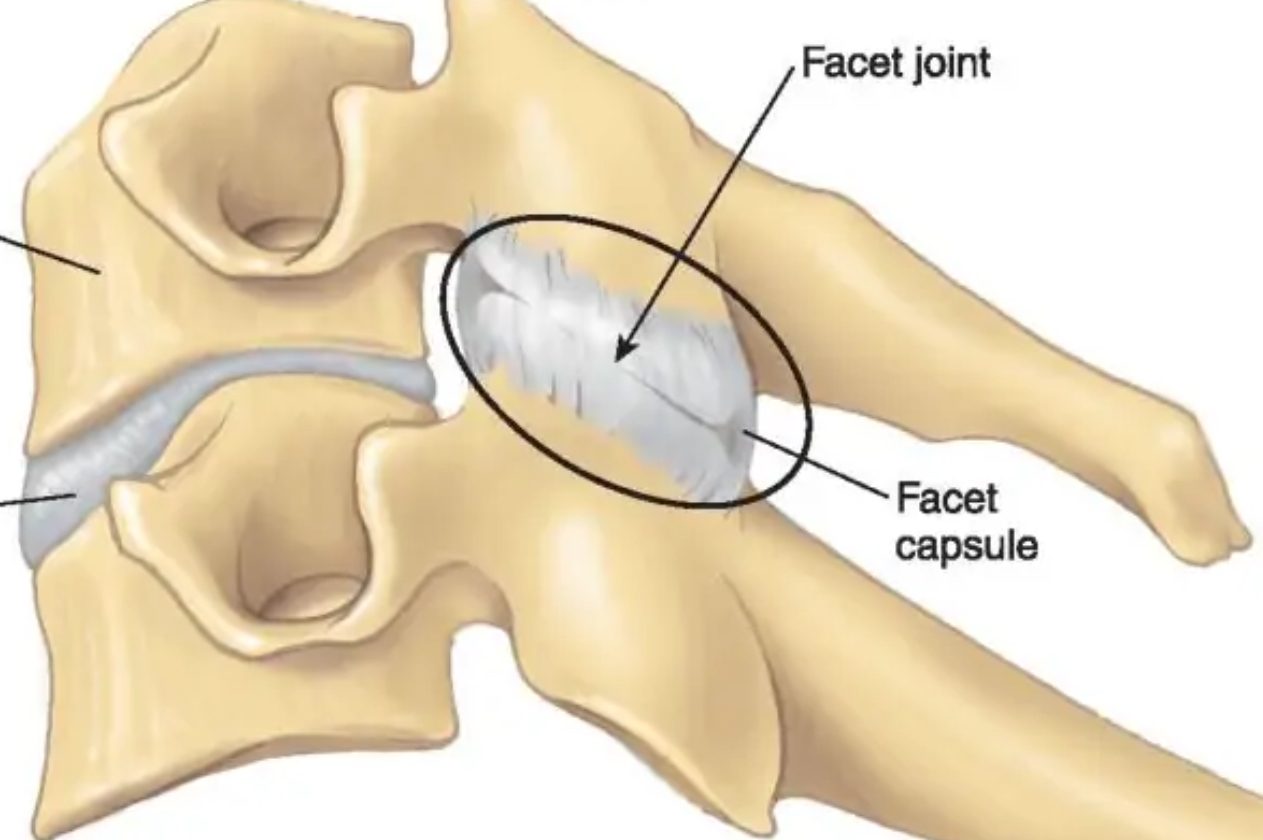
Facet
Small, flat articular surface
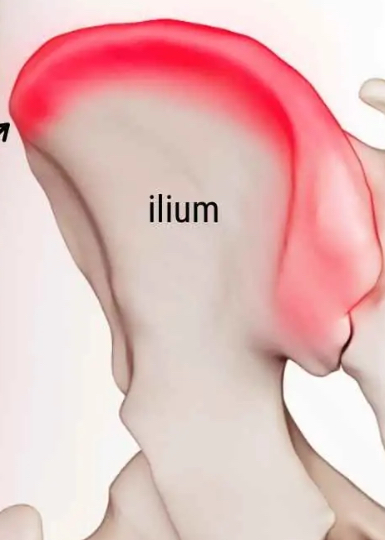
Crest
Prominent ridge
Line
Low ridge, more delicate than a crest
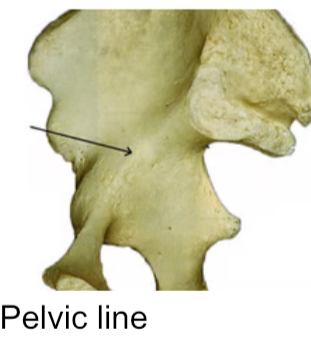
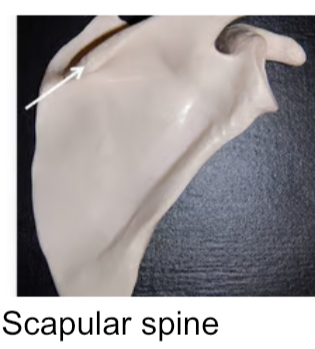
Spine
Pointed/ narrow process
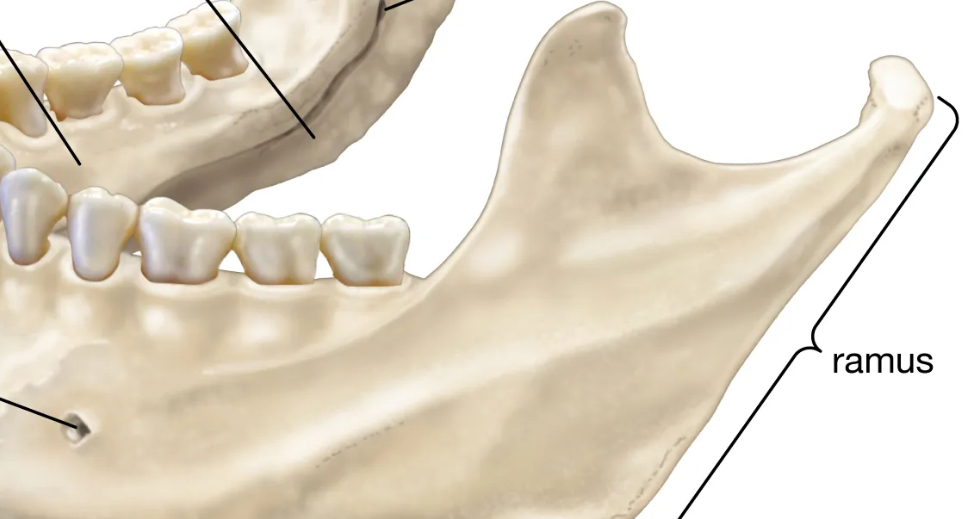
Ramus
extension of bone that makes angle with rest of structure
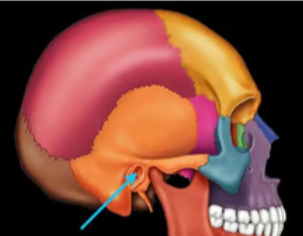
Canal/ meatus
Large passageway through bone
Foramen
Small, rounded passageway for blood vessels or nerves to pass through bone
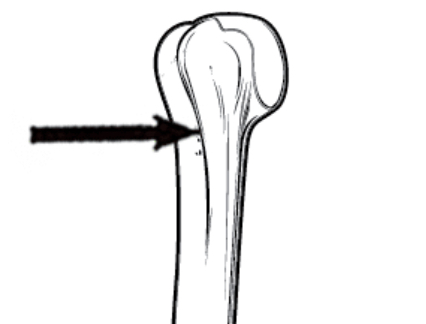
Fissure
Elongated cleft or gap

Sulcus
Deep, narrow groove
Fossa
Shallow depression/ recess in bone surface