ch. 10 - photosynthesis
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Autotrophs
organisms that can create their own food from inorganic materials
Heterotrophs
organisms that cannot create their own food and must consume other organisms for energy
Outer membrane
membrane separating the chloroplast from the surrounding cytoplasm
Inner membrane
a second membrane just inside the outer membrane
Intermembrane space
the space between the inner and outer membranes
Thylakoid membrane
a system of membranes found inside the chloroplast used for the light reaction of photosynthesis
Granum
stacks of thylakoid discs
Stroma
the fluid outside of the thylakoid membranes but inside the inner membrane where the Calvin cycle takes place
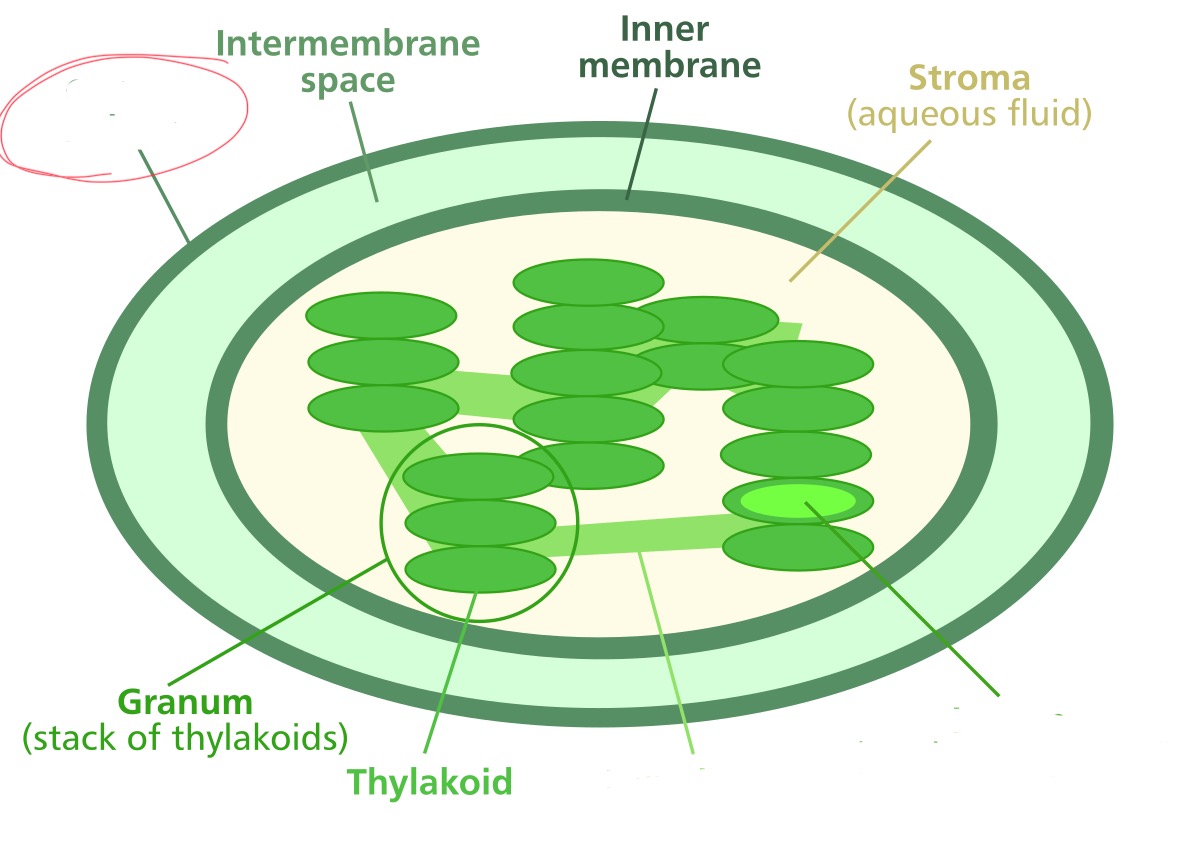
What structure is it pointing to?
outer membrane
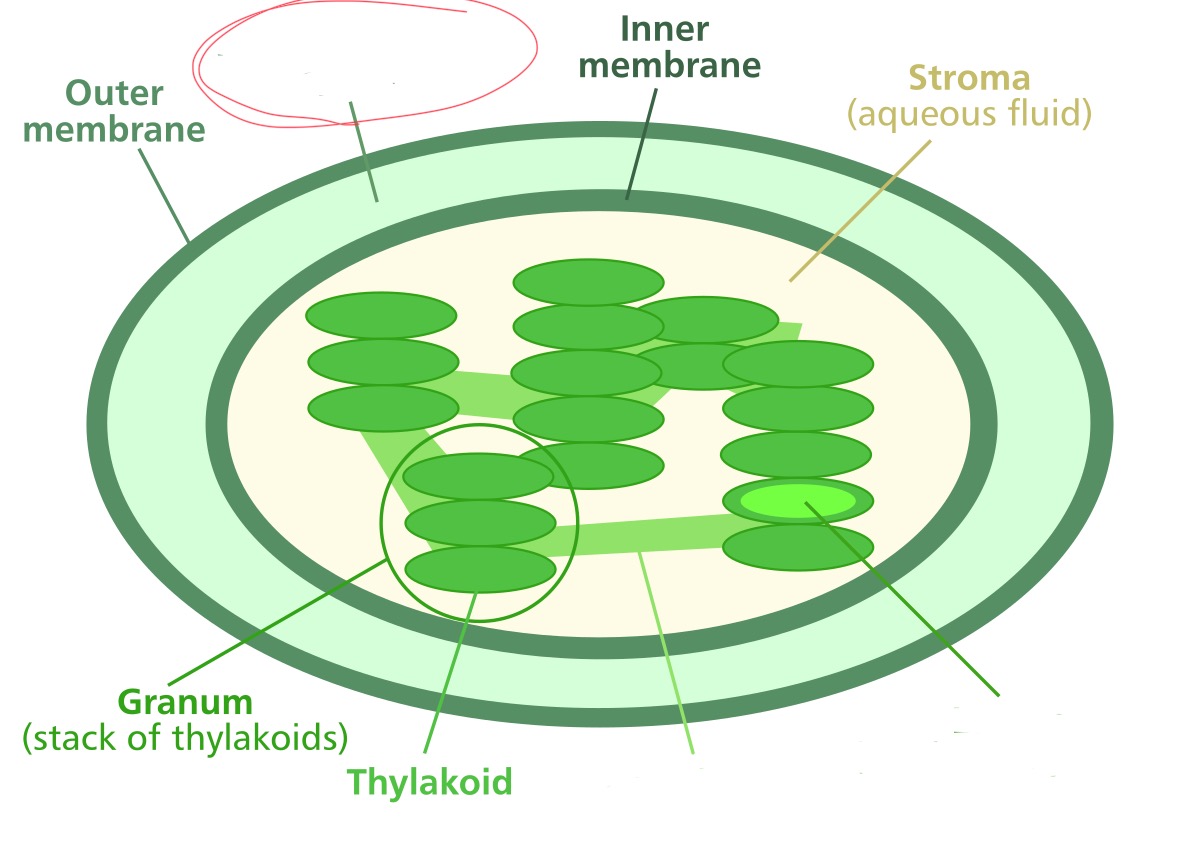
What structure is it pointing to?
intermembrane space
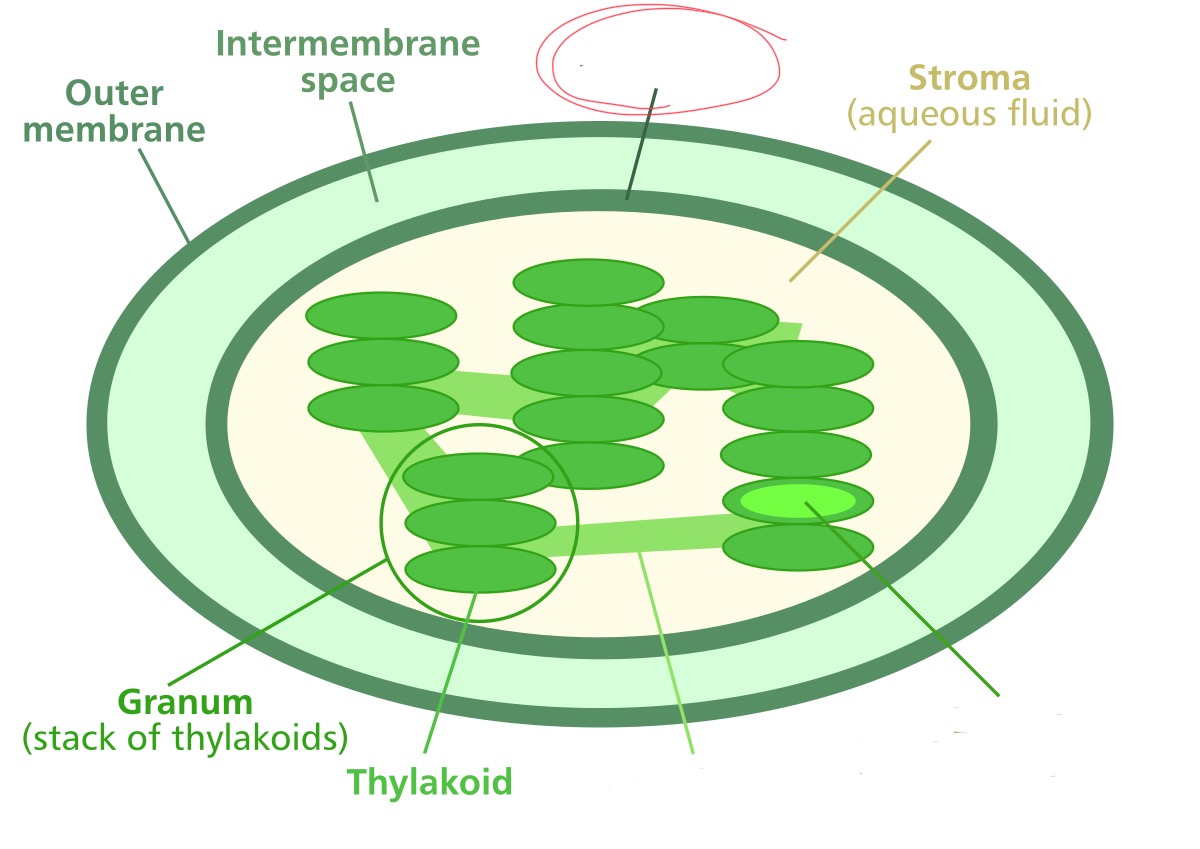
What structure is it pointing to?
inner membrane
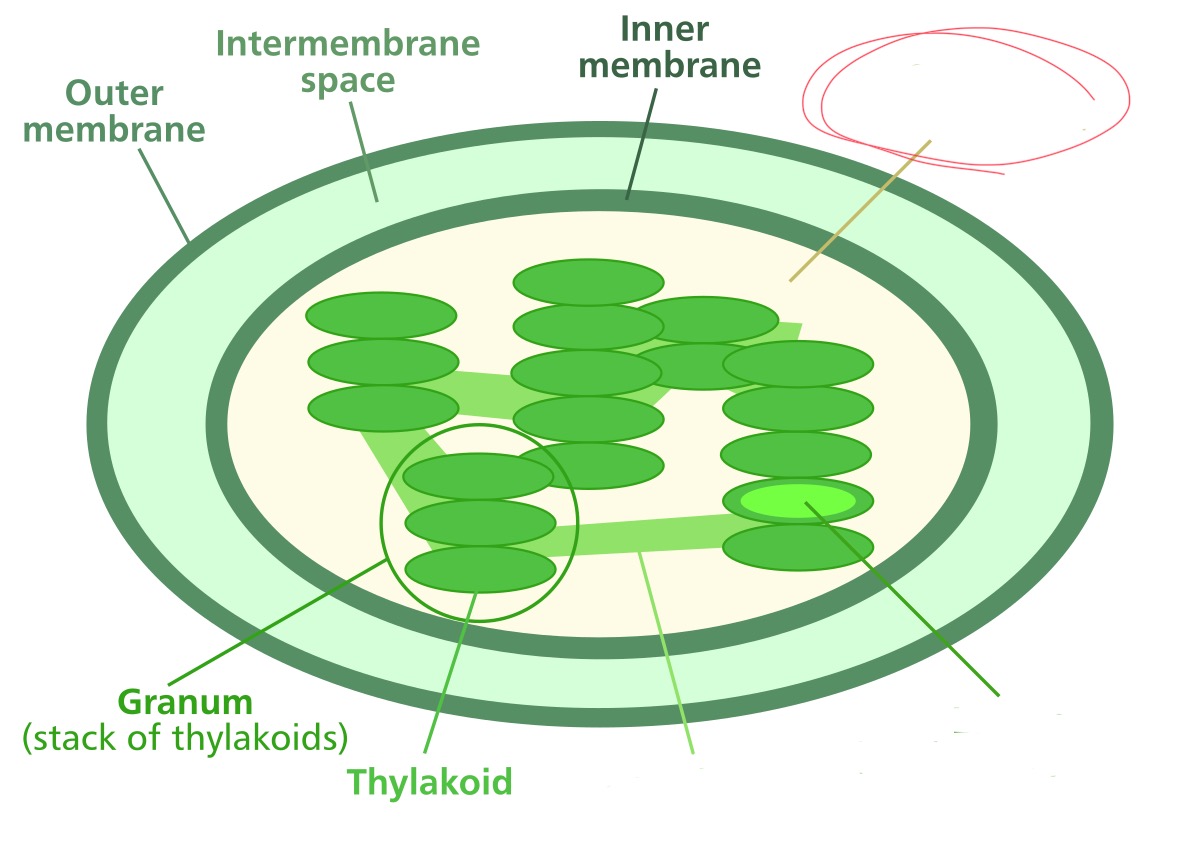
What structure is it pointing to?
stroma
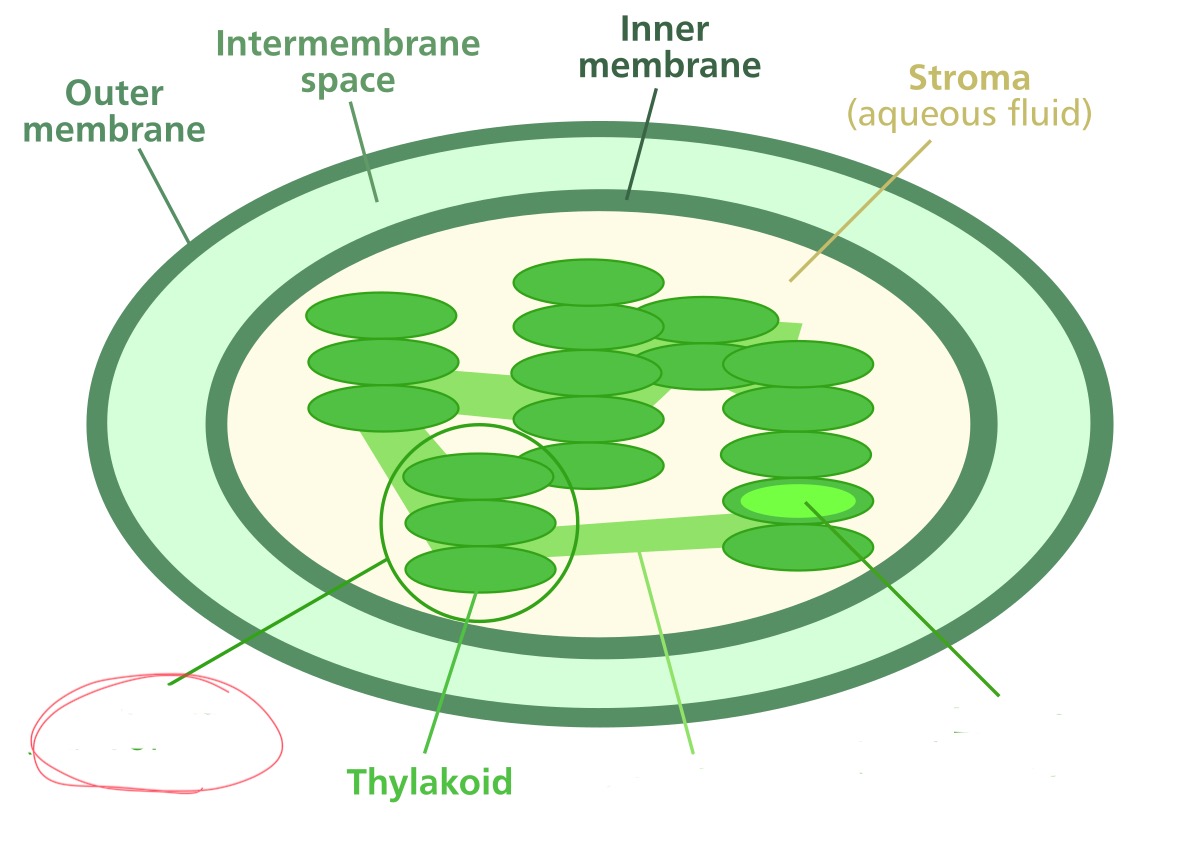
What structure is it pointing to?
granum
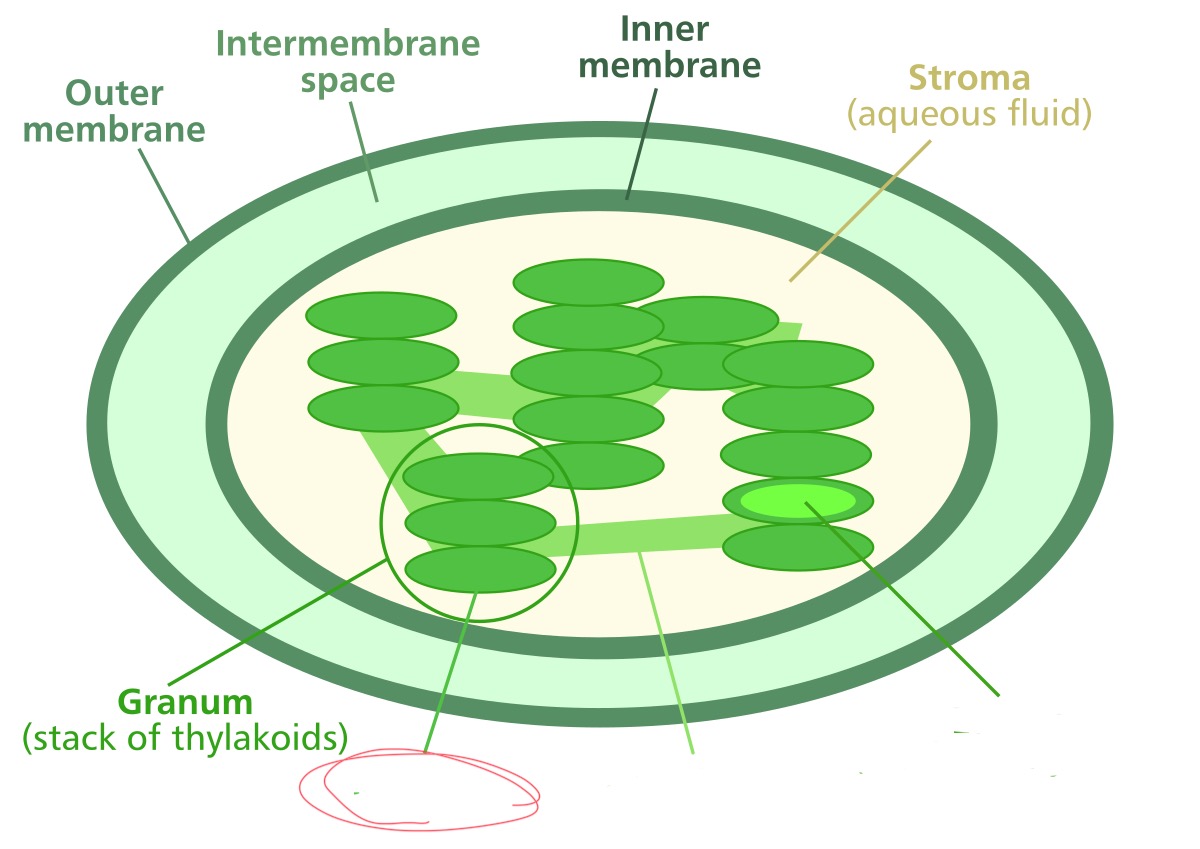
What structure is it pointing to?
thylakoid
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?
in the stroma of the chloroplast
What is an advantage of the grana structure?
since the granum are stacks, it maximizes the surface area for light harvesting and ATP synthesis
Light
made of photons of any wavelength or color of the electromagnetic spectrum
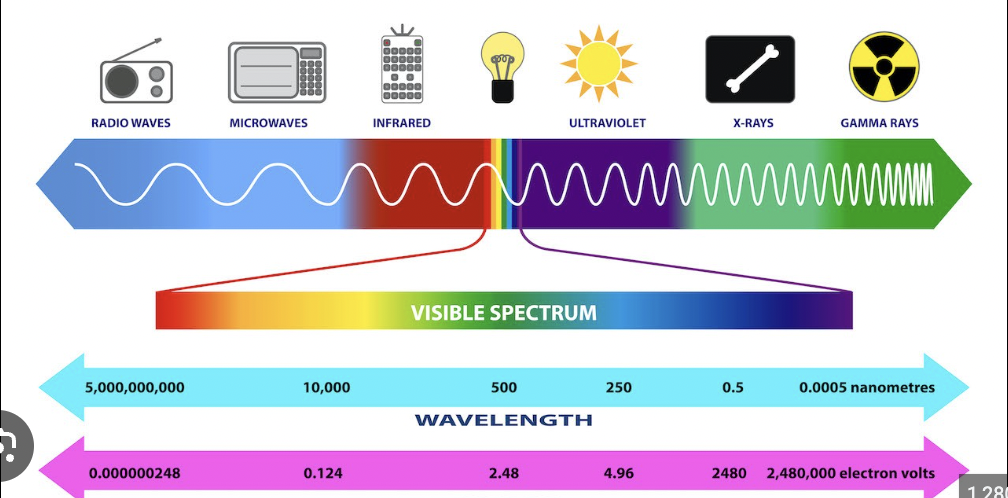
What does this image represent?
the electromagnetic spectrum
What 3 things can happen when light strikes an object?
the light can be reflected, transmitted, and/or absorbed
Which of the 3 light responses when it strikes an object can humans see?
reflected and transmitted light
Which of the 3 light responses when it strikes an object do plants use?
absorbed light
Light-dependent reactions
in the thylakoid membrane, light energy is absorbed and converted to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH
NADPH
an electron carrier, specifically a H+ carrier, in high energy/reduced state
NADP
empty carrier in low energy/oxidized state
Calvin cycle
in the stroma of the chloroplasts, energy from ATP and NADPH is used to make carbohydrates from CO2
What 3 colors of light does chlorophyll capture?
blue, violet, red light
What 2 colors of light does chlorophyll reflect?
green and yellow light
Accessory pigments
absorb wavelengths (colors) of light chlorophyll a cannot and pass the energy to chlorophyll a
What is an example of an accessory pigment?
chlorophyll b
Photosystem
one chlorophyll a molecule and all of its associated accessory pigments and electron transport system (ETS) molecules
What are the two types of photosystems named for the wavelength/color of light they absorb best?
P700/PI and P680/PII
What is the non-cyclic light reaction process?
PI and PII work simultaneously. light excites e- in PII (chlorophyll a/accessories pass e- to it) and these excited e- are sent to PI. light excites e- in chlorophyll a of PI (or accessory pigment sends excited e- to chlorophyll a) and these electrons are sent to NADP+ converting NADP+ to NADPH
In the non-cyclic light reaction, how does PII get excited e-? Where do the e- get sent to?
light excites the e- or chlorophyll a/accessories pass e- to it
In the non-cyclic light reaction, where do the excited e- in PII get sent to?
sent to PI
In the non-cyclic light reaction, how does PI get excited e-?
light excites e- in chlorophyll a of PI or an accessory pigment sends an excited e- to chlorophyll a
In the non-cyclic light reaction, where do the e- in PI get sent to?
sent to NADP+ to convert into NADPH
What is the input and output of the non-cyclic light reaction?
input: sunlight output: NADPH
In the non-cyclic light reaction, where and how are replacement e- obtained?
PII splits water molecules
In the non-cyclic light reaction, what is the reaction for obtaining replacement e-?
H2O → 2e- + 2H+ + ½ O2
In the non-cyclic light reaction, what happens to the H+ and O2 from the reaction to obtain replacement e-?
H+ produced stays in thylakoid disc interior and O2 is released as a product
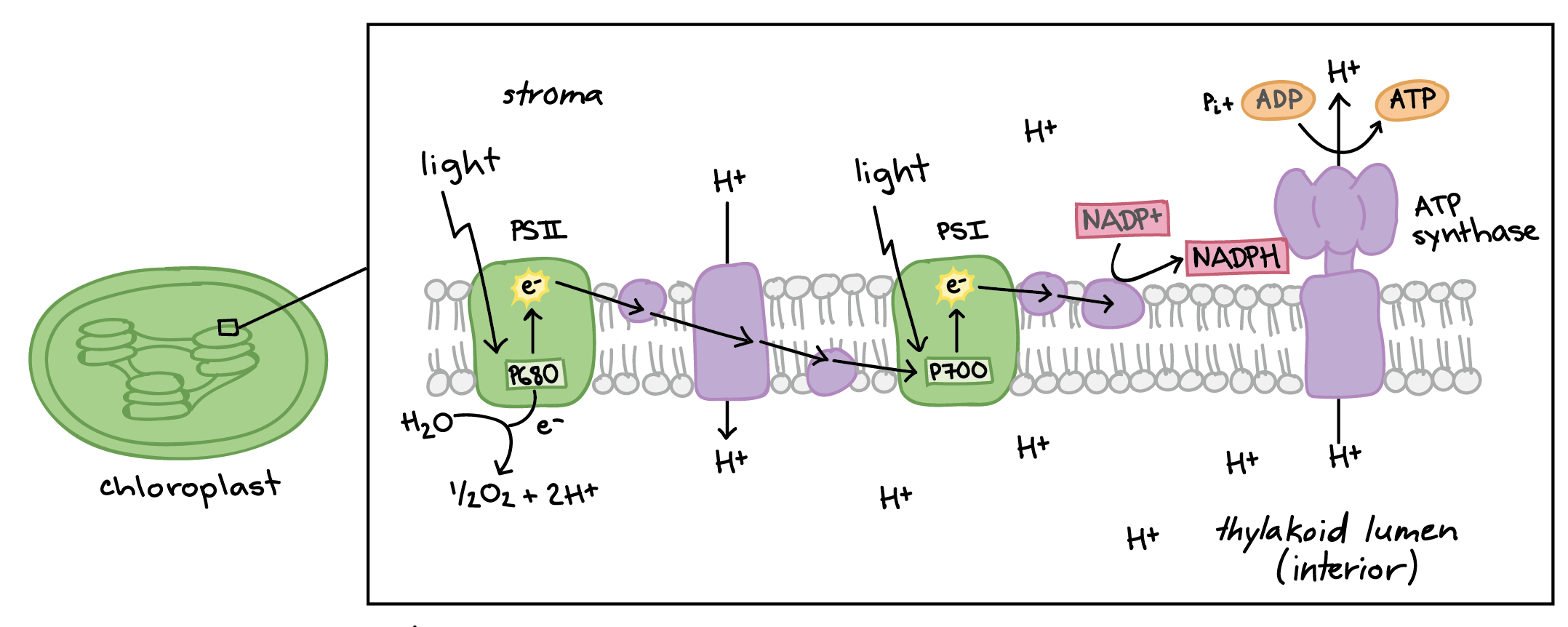
What process does this diagram show?
non-cyclic light reaction
What is the process for ATP production?
ETS pumps H+ from stroma to thylakoid interior creating a chemiosmotic gradient of concentration and charge which is a form of potential energy. H+ pass through the ATP synthase which uses the energy of their passage to force the reaction to produce ATP
How is the chemiosmotic gradient created for ATP production?
ETS system pumps H+ from stroma to thylakoid interior
For ATP production, describe the chemiosmotic gradient.
thylakoid interior has high H+ concentration from splitting water and ETS pumping. stroma has low H+ concentration from ETS pumping
In ATP production, how is energy produced to form ATP?
ATP synthase uses energy from H+ passing through to form ATP
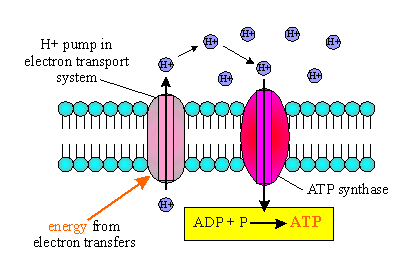
What process does this diagram show?
ATP production
What is the reaction for ATP production?
ADP + P + energy → ATP
What energy transformation was accomplished during ATP production?
H+ concentration gradient is a potential energy being converted into ATP
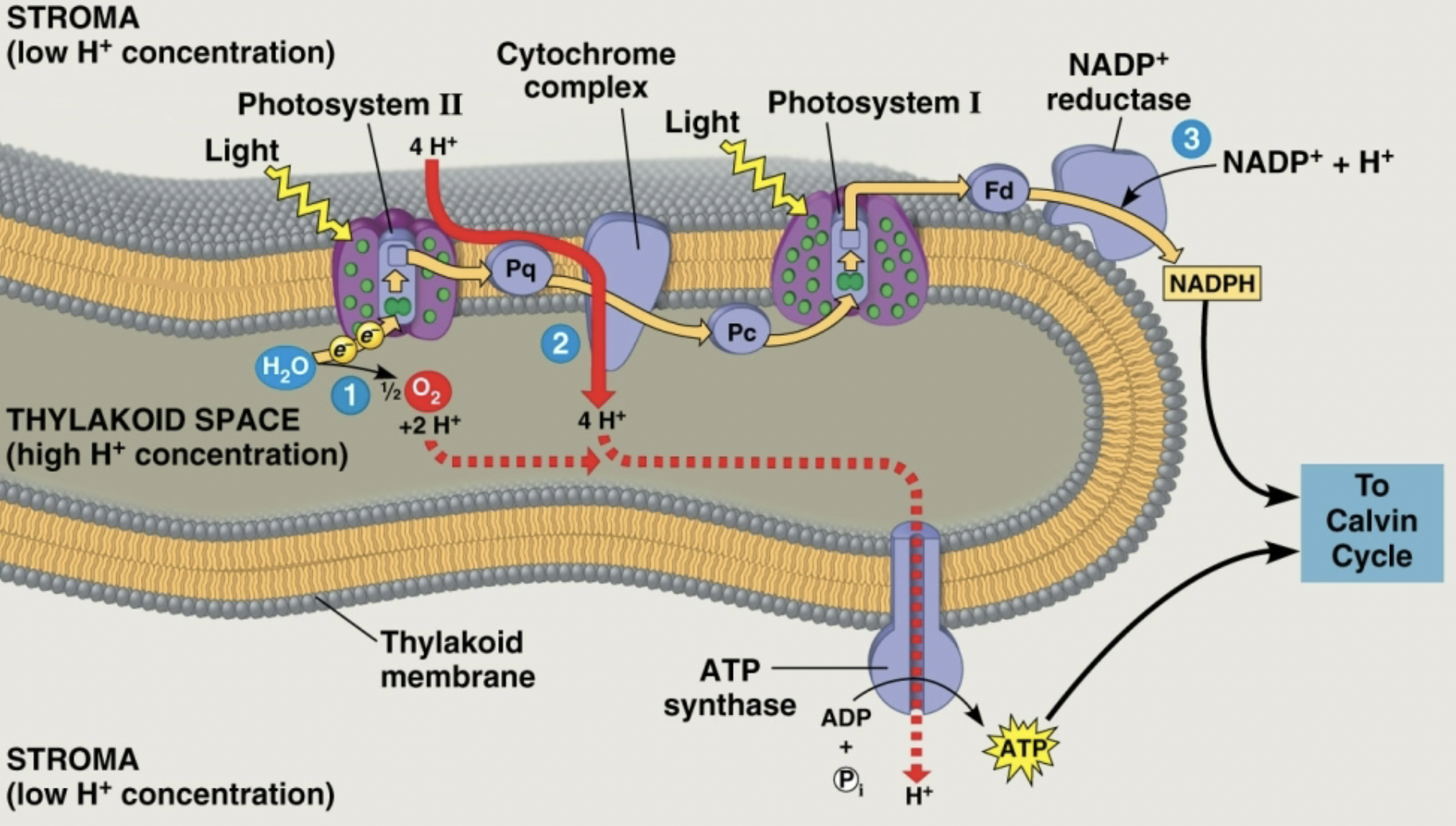
What processes does this diagram show?
non-cyclic light reaction and ATP production, more generally noncyclic electron flow
What happens during cyclic electron flow?
light excites e- in PI. these e- are sent to the beginning of ETS where they are sent back to PI. this makes ATP generation without NADPH production
What are the similarities and differences between cyclic and non-cyclic electron flow?
both have excited e- from PI. in cyclic, the excited e- are sent to the beginning of ETS to be sent back to PI. in non-cyclic, the excited e- are sent to NADP+ to convert into NADPH
What are the inputs and outputs of the cyclic electron flow?
input: sunlight output: ATP
Give a summary description of the noncyclic pathway.
light energy was used to create small energy molecules NADPH and ATP. water was needed and oxygen was produced
Which step did NADPH come from?
end of photosystem I (PI)
What was water needed for?
to split and get replacement e-
Which step did ATP come from?
H+ going through ATP synthase
Which step produced oxygen?
splitting water by photosystem II (PII)
Give a summary description of the cyclic pathway.
sunlight energy was used to create small energy molecule ATP without creating any of the molecule NADPH
What happens during the carbon fixation phase of the Calvin cycle?
CO2 combines with 5-Carbon Ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) creating a 6 Carbon molecule, catalyzed by RuBP carboxylase or Rubisco. the 6 Carbon molecule made immediately splits into 2 molecules of 3-Phosphoglycerate
What does RuBP stand for?
ribulose bisphosphate
During carbon fixation, what does CO2 combine with to form a 6 carbon molecule?
5 carbon ribulose bisphosphate
During carbon fixation, which enzymes catalyze the reaction of CO2 and 5 carbon RuBP to form a 6 carbon?
RuBP carboxylase and Rubisco
During carbon fixation, what happens to the 6 carbon molecule?
splits into two molecules of 3-Phosphoglycerate
What happens during the reduction phase of the Calvin cycle?
ATP and NADPH are used to convert 3-Phosphoglycerate to Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
What does G3P stand for?
glyceraldehyde 3-phsophate
What happens to 1/6 of G3P produced from reduction?
removed and used to make glucose, starch, amino acids, etc
What happens during the regeneration of RuBP phase of the Calvin cycle?
5/6th of the G3P produced from reduction phase is recycled to regenerate RuBP using ATP
What was the input and output of the Calvin cycle?
input: ATP, NADPH output: G3P
What are the 3 phases of the Calvin cycle?
carbon fixation 2. reduction 3. regeneration of RuBP

What process does this picture show?
Calvin cycle
What is “normal” photosynthesis known as?
C3 photosynthesis
Why is it called C3 photosynthesis?
3-Phosphoglycerate produced from CO2 fixation has 3 carbon atoms
What is the C4 pathway process?
Addition of CO2 to existing molecules by enzyme PEP carboxylase instead of Rubisco in the mesophyll cell and passing the fixed CO2 to the bundle-sheath cell
What is the purpose of the C4 pathway?
improve the use of CO2
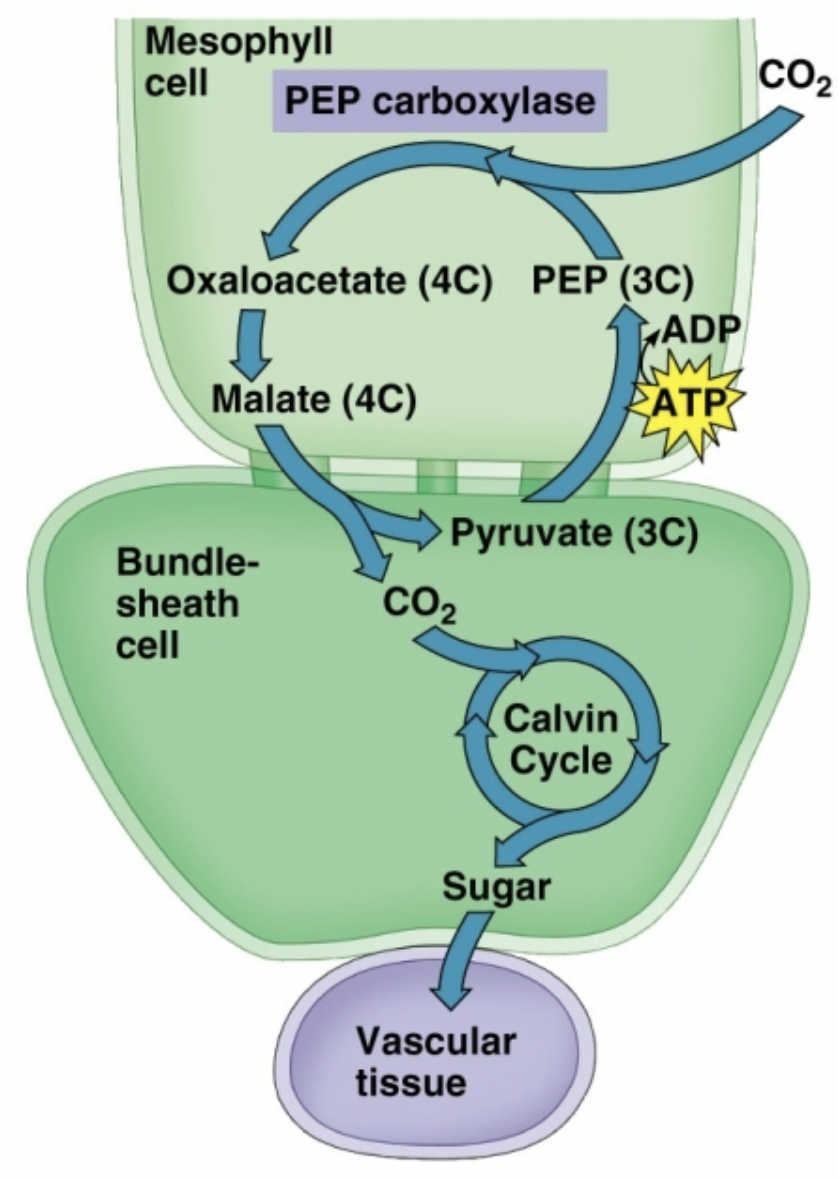
What process is shown in this picture?
C4 pathway
What is the difference between C3 and C4 plants?
C3 plants fix carbon directly into a 3 carbon molecule. C4 plants use the C4 pathway to fix CO2 into a 4 carbon molecule by PEP carboxylase in the mesophyll cells
How does adding CO2 to existing molecules by PEP carboxylase instead of Rubisco improve the use of CO2?
PEP carboxylase has a higher affinity (degree a substance combines with another) for CO2 than Rubisco
How does the fixed CO2 passed to the bundle-sheath cell improve the use of CO2?
the bundle-sheath is where the Calvin cycle takes place, so the Calvin cycle is protected from oxygen and photorespiration
Mesophyll
an outer layer of cells
Bundle-sheath
inner layer where the Calvin cycle takes place
What does CAM stand for?
Crassulacean Acid Metabolism
How is water loss prevented in CAM plants?
opening the stomata to take in CO2 and fixing CO2 at night, storing the CO2 in organic acids
During hot days, how is water loss prevented in CAM plants?
stomata are closed to conserve water and CO2 from storage is used for the Calvin cycle
If the CAM plant fixes CO2 at night, why doesn’t it just do all of photosynthesis at night?
the plant needs sunlight to perform photosyntehsis which is not available at night
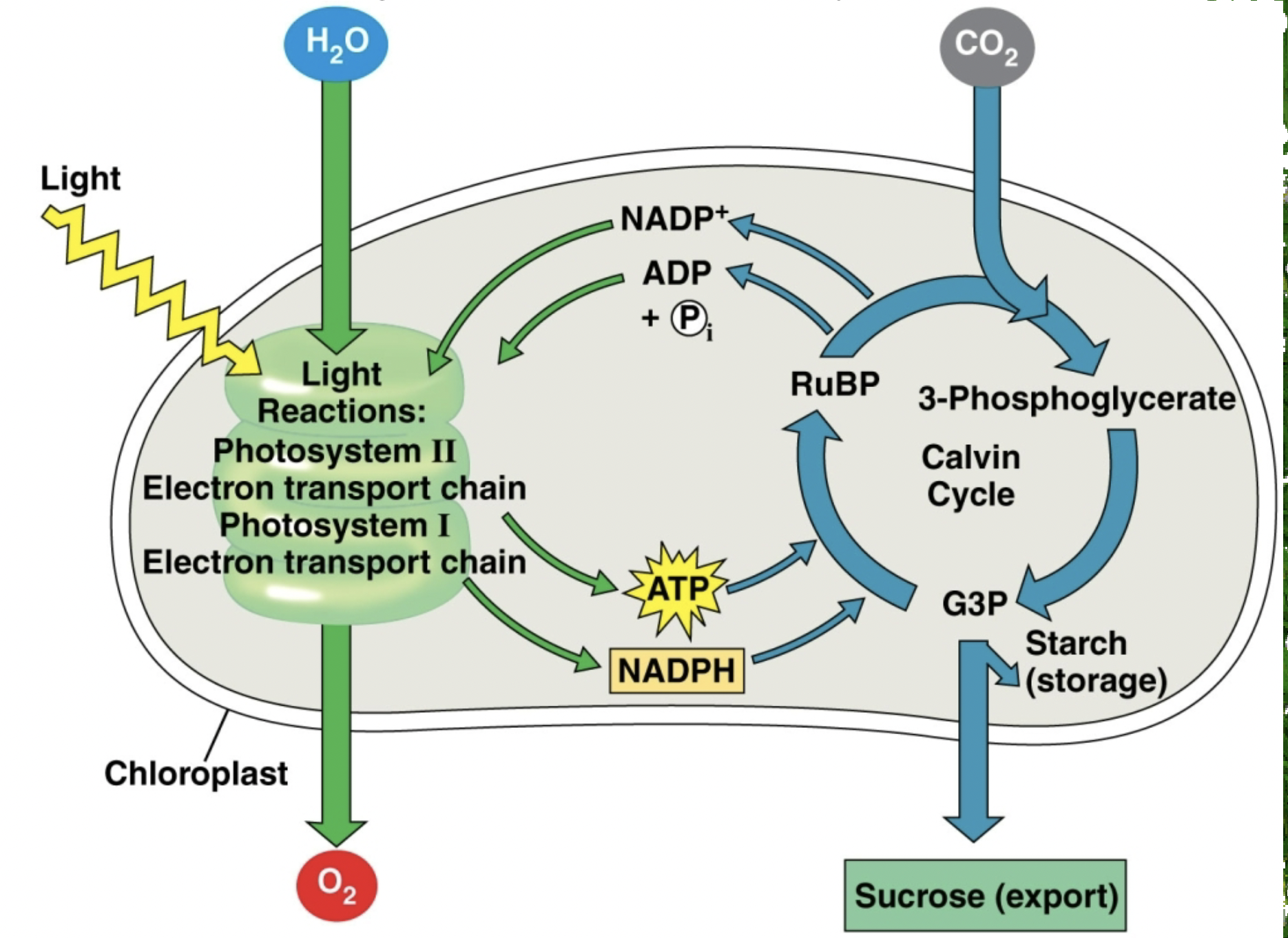
What processes does this picture show?
light reactions, calvin cycle
What processes happen during photosynthesis?
light reaction, noncyclic and cyclic electron flow, ATP production, Calvin cycle