Cell Organelles
Cell Organelles
Structures in eukaryotic cells that have specialized functions.
Main Roles of Organelles
-Cell Boundaries
-Control Cell Functions
-Energy Transformers
-Support and Locomotion
Cell Has Two Parts:
-Nucleus- Control Center of Cell
-Cytoplasm- Outside the nucleus includes most organelles and cytosol (fluid part)
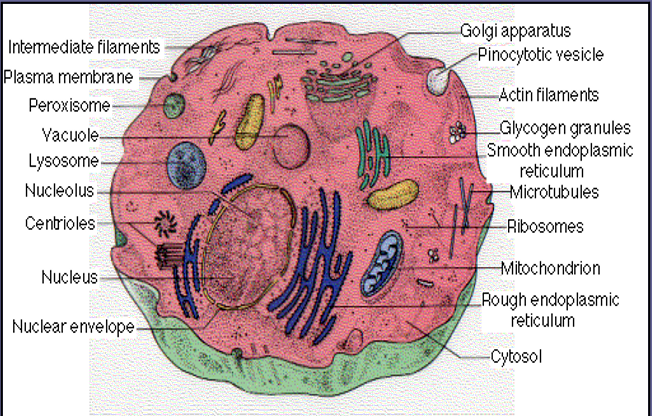
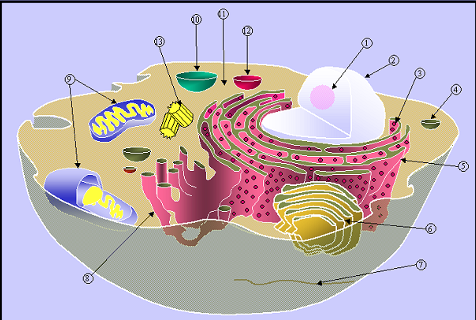
Cell Organelles and Their Functions:
Nucleus- control center of the cell; contains chromatin (chromosomes) and the nucleolus; surrounded by the nuclear envelope.
- Chromatin (Chromosomes): hereditary information (DNA)
- Nucleolus: makes ribosomes components
- Nuclear Envelope: double membrane boundary around the nucleus; contains pores.
Cytoplasm: where cell metabolism takes place; surrounded by the plasma membrane, which acts as a boundary or gateway for the cell.
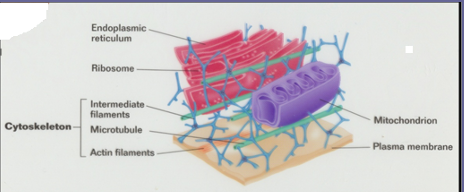
Cytoskeleton: includes microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments.
- Microtubules: structure and support of the cell; form tracks for organelles to move along
- Microfilaments (Actin): change the cell shape; contraction; movement of the cell
- Intermediate Filament: holds cell parts together in network.
Vesicles: short-term storage sacs; short-term transport
Mitochondria: cellular respiration, the powerhouse of the cell
Ribosomes: protein synthesis; free ribosomes make proteins for use inside cells (sometimes found inside the Rough ER)
Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough): folded membranes; ribosomes attached ER synthesize proteins for cell membrane and use outside the cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth): folded membranes; makes lipids
Golgi Complex: package, sort, and distribute proteins
Lysosomes: sac with digestive enzymes that hydrolyze macromolecules and used parts of the cell; “suicide sack”
Vacuole: storage sac of water, food, and waste,…
Peroxisomes: break down toxins; converts fats to carbohydrates
Centriole: made of microtubules; used in cell division in animal cells; located in the region called centrosomes
Cell Wall: structure and support of plant cell
Chloroplast: photosynthesis (make food) in plant cell
Structures for movement of cell or of materials around the cell- composed of microtubules
- Cilia: short hairlike structures
- Flagella: long whiplike tail
The Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane is a Boundary Around the Cell