bacteria and viruses
bacteria
: are microscopic organisms that are prokaryotes.
prokaryotes are divided in two two domains: the domain bacteria (eubacteria) and the domain archaea (archaebacteria)
vocabulary
- bacteria: are microscopic organisms that are prokaryotes.
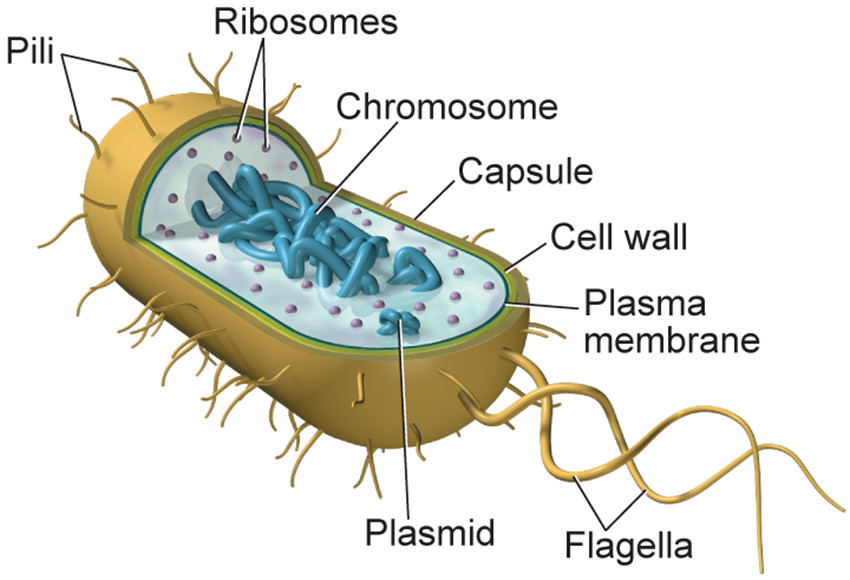
- nucleoid: a large circular chromosome in a area of the cell.
- capsule: prevents the cell from drying out and helps the cell attach to environments surfaces.
- pili: are submicroscopic, hairlike structure that are made of protein.
- binary fission: is the division of a cell in 3 genetically identical cells.
- conjugation: 2 prokaryotes attach to each other and exchange genetic information.
- endospore: when environmental condition are harsh, some times of bacteria provide a structure.

| eubacteria | archaebacteria | differences between both |
|---|---|---|
| very strong cell walls | thermoacidophiles live in hot, acidic environments | the cell wall of the eubacteria contain peptidoglycan but the archaebacteria do not |
| contain peptidoglycan | halophiles live in very salty environments | the 2 groups of organisms have different lipids in their plasma membranes |
| some have a second cell wall | methanogens cannot live in the presence of oxygen | different ribosomal proteins and RNA |
prokaryote structure
prokaryotes are microscopic, unicellular organisms.
they have some characteristics of all cells, such as DNA and ribosomes.
Lack a nuclear membrane and other membrane- bound organelles.
identifying prokaryotes
shape:
- spherical= cocci
- rod-shaped= bacilli
- spiral-shaped= spirochetes
| cocci | bacilli | spirochetes |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
cell walls
- eubacterial cells have peptidoglycan
- dyes added to the bacteria identify those with those without an outer layer of lipid.
movement
a. prokaryotic flagella are made of filaments
b. flagella help prokaryotes to move toward material that they need to survive
reproduction of prokaryotes
- binary fission: the division of a cell int 2 genetically identical cells.
- conjugation: 2 prokaryotes attach to each other and exchange genetic information.
phototrophs +
carry out photosynthesis in a similar manner as plants
chemoautotrophs
break down and release inorganic compounds that contain nitrogen or sulfur
aerobes and anaerobes
obligate aerobes are bacteria that require oxygen to grow
anaerobic bacteria do not use oxygen for growth or metabolism.
survival of bacteria
endospores: are resistant to harsh environments and might be able to survive extreme heat, extreme cold, dehydration, and larger amounts of ultraviolets radiation.
ecology of bacteria
nutrient cycling and nitrogen fixation
bacteria are decomposers, returning vital nutrients to the environment.
nitrogen-fixing bacteria live in a symbiotic relationship in the root nodules of plants such as soybeans, clover, and alfalfa.
normal flora: most of the bacteria that live in or on you are harmless.
disease-causing bacteria
- a small percentage of bacteria cause disease.
- bacteria multiply quickly at the site of infection
- bacteria secrete a toxin.
viruses (def + characteristics)
a nonliving strand of genetic material within a protein coat
no organelles to take in nutrients or use energy
cannot make proteins
cannot move
cannot replicate on their own
most viruses range in size from 5 to 300 nanometers.

virus origin
- viruses came from parts of cells
- genetic material of viruses are similar to cellular genes
viral infection
- in order to replicate, a virus must enter a host cell.
- the virus attaches to the host cell suing specific receptor on the plasma membrane.
- many viruses cannot be transmitted between different species.
