Nursing fundamental Final Review
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/291
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
292 Terms
1
New cards
Health is a state of complete _____, _______*, and ___*_____ well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity__
physical, mental and social well-being
2
New cards
Wellness is a dynamic state of heath in which an individual actively progresses ______________________, ahcieving an optimal balance ebtween internal and external environments
progresses towards a higher level of functioning
3
New cards
health promotion are activities that help persons ____ __or__ ____ their present level of health and reduce their risk of developing certain diseases
maintain or enhance
4
New cards
disease is___ __or__ ___ of biological or phycological processes
malfunctioning or maladaptation
5
New cards
QSEN strides for
patient centered nursing care
6
New cards
Person centered care has what 6 values
promoting respect, honoring choice, promoting positive well-being, supporting independence, improves quality of life, and empowers recipient of care
7
New cards
Patient safety is the ____ __and ____ of patient injuries of adverse events__ ______ of health care delivery
avoidance and prevention
resulting from the processes
resulting from the processes
8
New cards
Adverse event is an __ __caused by__ ______________ that delays discharge and/or results in disability
adverse event
9
New cards
types of data
subjective (symptom) and objective (sign)
10
New cards
sources of data for assessment
primary sources and secondary sources
11
New cards
types of physical assessment
inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation
12
New cards
what is the regular order of assessment? what about for abdominal
for regular assessments its
inspection → palpation → percussion → and auscultation
but in abdominal assessments' its
inspection → auscultation → percussion → and palpation
inspection → palpation → percussion → and auscultation
but in abdominal assessments' its
inspection → auscultation → percussion → and palpation
13
New cards
When inspecting …
concentrated watching. Involves looking, listening, and smelling for unexpected findings when interreacting with patients
identify degree of distress, provide private conditions with adequate lighting and exposure. Look for size, shape, color, symmetry, position, and abnormalities
identify degree of distress, provide private conditions with adequate lighting and exposure. Look for size, shape, color, symmetry, position, and abnormalities
14
New cards
when palpating
use touch to gather info. Using parts of the hand to detect different characteristics of the skin, organs, glands, blood vessels, and thorax. Hands should be warm, with short fingernails. Technique should be slow, gentle, and systematic. Palpating tender areas last, start with light palpation and end with deep palpation
15
New cards
percussion is
tapping the body with fingertips to produce a vibration to determine location, size, and density of structures
16
New cards
when auscultating
listen to sounds produced by the body such as lungs, heart, blood vessels, and abdomen using our ears and stethoscope. We are assessing for frequency, loudness, quality, and duration
17
New cards
when considering cultural sensitivity
respect differences and avoid stereotyping. Consider health beliefs, use of alternative therapies, nutrition habits, relationships with family, and comfort with physical closeness
18
New cards
colonization occurs with the present and growth of microorganisms within a host but ___________ or damage
without tissue invasion
19
New cards
infection is the __ __of a susceptible host by a pathogen or microorganism__ _____________
invasion
resulting in disease
resulting in disease
20
New cards
assessment of infection risk include
age, lifestyle, occupation, nutritional status, travel history, stress, procedures, and disease
21
New cards
chain of infection
reservoir, infectious agent, susceptible host, portal of entry way in, mode of transmission, portal of exit way out, and reservoir
22
New cards
medical asepsis
clean technique to reduce the number and transmission of disease causing microorganisms after they leave the body, but doesn’t necessarily eliminate them
23
New cards
universal precautions
to prevent the transmission of bloodborne pathogens from exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials. Avoiding bloodborne pathogens from bodily fluids
24
New cards
standard precautions
to prevent and control infections and its spread to all persons. Based on the principle that all blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions, nonintact skin, and mucous membranes may contain transmissible infectious agents
25
New cards
key elements of standard precautions
hand hygiene, use of PPE, safe injection practices, equipment handling, and respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette
26
New cards
when should u wash your hands
when hands are visibly dirty, after known or suspected exposure to C diff or other infectious __diarrhea__ during norovirus outbreaks. After exposure to bacillus anthracis is suspected or proven, before eating, and after using a restroom
27
New cards
use hand sanitizer for
everything else when washing hands are not needed
28
New cards
PPE includes
gloves, gown, mask or respirator, and goggles or faceshield
29
New cards
To don PPE, what is the order
gown → mask or respiratory → goggles or faceshield → gloves
30
New cards
to take of PPE what is the order
gloves → goggles of face shield → gown → mask or respirator
31
New cards
contact precautions
direct patient or environmental contact
32
New cards
droplet precautions
respiratory tract transmission over short distances
33
New cards
airborne precautions
remains in the air, infective over time and distances
34
New cards
protective environment
limited patient population
35
New cards
levels of communication
intrapersonal, interpersonal, small group, public, electronic
36
New cards
four phases of nursing patient relationship
preinteractions, orientation, working, and termination
37
New cards
Active listening means being ____ to what a patients is saying both ____ and _____
Active listening means being **attentive** to what a patients is saying both **verbally** and **nonverbally**
38
New cards
SOLER in active listening
sit facing the patient
open position
lean towards the patient
eye contact
relax
open position
lean towards the patient
eye contact
relax
39
New cards
Empathy is the ability to ______ and accept another person’s ________ accurately perceive feelings, and communicate the understanding to the other person
Empathy is the ability to understand and **accept** another person’s **reality** accurately perceive feelings, and communicate the understanding to the other person
40
New cards
_________ is one of the most potent and personal forms of communication
touch
41
New cards
types of communication barriers
cant speak clearly, cognitive impaired, hard of hearing or deaf, vision loss, unresponsive or does not speak english
42
New cards
aphasia
injury to speech center in the cerebral cortex. lost their ability to understand or express speech as a result of brain damage
43
New cards
dysarthria
weak, slow moving, or non moving muscles of the mouth
44
New cards
In the interview stage of history
gathering subjective data to obtain information and built report. Its to record a complete health history
45
New cards
three phases of the interiew
introductory, working, and closure
46
New cards
during the health history you collect
Biographical data, sources of history, reasons for seeking care/chief complain, history of present illness, past health, family history, review of systems, functional assessment, perception of health
47
New cards
PQRSTU
provocation/palliation
quality and or quantity
region or radiation
severity scale
timing onset, duration, frequency
Understand patients perception and/or unable to do
quality and or quantity
region or radiation
severity scale
timing onset, duration, frequency
Understand patients perception and/or unable to do
48
New cards
provocation or palliation
what brings it on? what were you doing when you first noticed it, what makes it better? worse?
49
New cards
quality and/or quantity
How does it look, feel, or sound? How intense/severe is it
50
New cards
Region and/or radiation
Where is it? Does it spread anywhere else
51
New cards
Severity scale
How bad is it (1-10 scale)? Is it getting better, worse, or staying the same
52
New cards
timing onset, duration, frequency
onset - exactly when did it first occur? Duration - How long did it last? Frequency - How often does it occur
53
New cards
Understand patients perception and/or unable to do
What do you think it means? What are you not able to do as a result
54
New cards
vital signs include
blood pressure, temperature, pulse, respiration, oxygen saturation, and pain
55
New cards
when to measure vital signs
on admission to a healthcare facility, when assessing a patient during home care visits, in a hospital on a routine schedule'
before, during, after medications and treatments or procedures
before, during, and after nursing interventions influencing a vital sign
when a patients general condition changes
when a patient reports nonspecific symptoms of physical distress
before, during, after medications and treatments or procedures
before, during, and after nursing interventions influencing a vital sign
when a patients general condition changes
when a patient reports nonspecific symptoms of physical distress
56
New cards
factors affecting body temp
age, exercise, hormonal level, environment, circadian rhythm, temperature alterations
57
New cards
temperature measurement sites
oral, axillary, rectal, tympanic, and temporal
58
New cards
average temperature ranges
normal: 36 - 38 C (96.8 - 100.4 F)
average oral/tympanic: 37 C (98.6 F)
average rectal: 37.5 (99.4)
average axillary: 36.6 C (97.6)
average oral/tympanic: 37 C (98.6 F)
average rectal: 37.5 (99.4)
average axillary: 36.6 C (97.6)
59
New cards
factors that can influence pulse
exercise, temperature. emotions, medications, postural changes, pulmonary conditions, hemorrhage
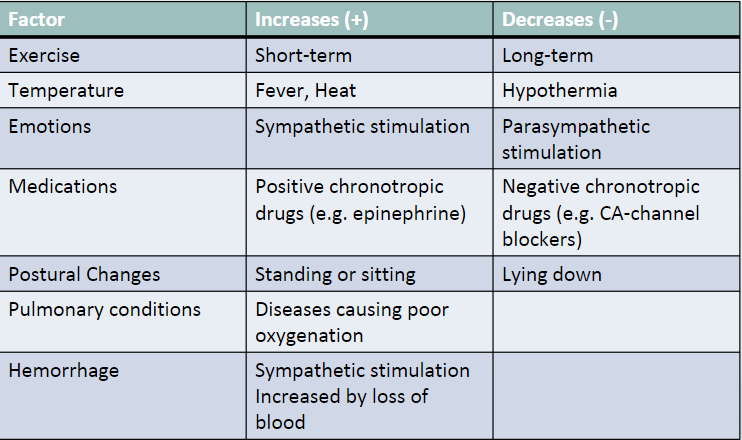
60
New cards
tachycardia, eucardia, and bradycardia
tachycardia: >100 bpm
eucardia: 60-100 bpm
bradycardia:
eucardia: 60-100 bpm
bradycardia:
61
New cards
when assessing radial pulse check for what elements
rate, rhythm, strength/amplitute, and equality
62
New cards
other than radial you can measure pulse using
apical pulse. listening at 5th ICS, mid-clavicular line. Check for rate and rhythm, (not strength)
63
New cards
ventilation
the movement of gases in an d and out of the lungs
64
New cards
diffusion
the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli and the red blood cells
65
New cards
perfusion
the distribution of red blood cells to and from the pulmonary capillaries
66
New cards
mechanics of breathing
inspiration is an active process. expiration is a passive process
67
New cards
factors affecting breathing
exercise, acute pain, anxiety, smoking, body positions, medications, neurological injury, and hemoglobin function
68
New cards
respiration ranges
tachypnea > 20 per minute
eupnea: 12-20 per minute
bradypnea:
eupnea: 12-20 per minute
bradypnea:
69
New cards
respiration assessment should include
rate, depth, rhythm, and effort
70
New cards
blood pressure is when
the **force exerted on the walls of any artery** by the pulsing blood under pressure from the heart. The peak of the maximum pressure when ejection occurs is the **systolic** pressure. **Diastolic** is the minimal pressure exerted against the arterial walls at all times
71
New cards
an increase or decrease in any of these factors can affect blood pressure
cardiac output, peripheral resistance, blood volume, viscosity, elasticity
72
New cards
factors that influence blood pressure
age, stress, ethnicity, gender, daily variation, medications, activity and weight, and smoking
73
New cards
normal blood pressure value
less than 120/80
74
New cards
abnormal blood pressure ranges
elevated/hypertension: >120 /
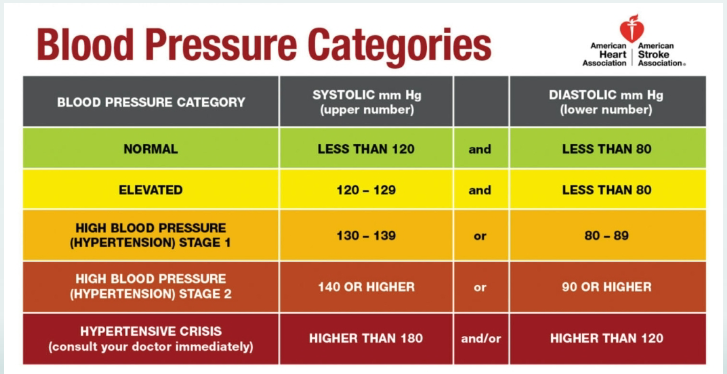
75
New cards
common errors in BP measurement
taking BP when person is anxious, smoking/caffeine, position of arm above heart, position of arm below heart, wrong cuff size, cuff wrapped too loose, failure to wait 1-2 minutes before repeating BP, arm not supported
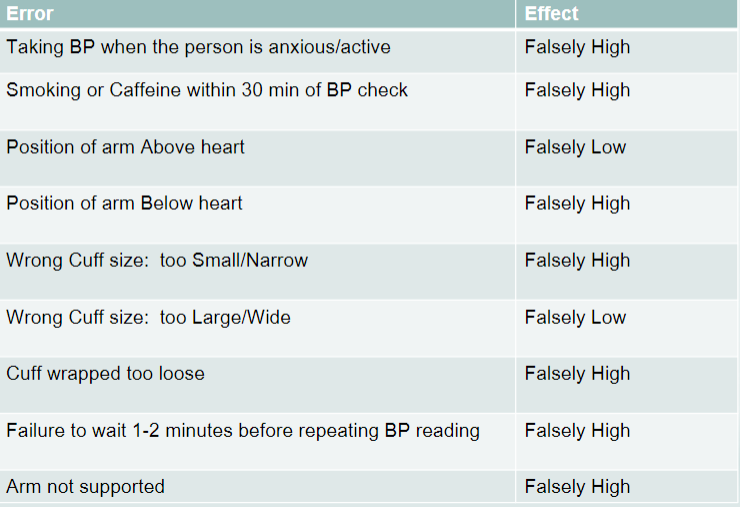
76
New cards
korotkoff sounds
sounds heard over an artery distal to the blood pressure cuff when the cuff is deflated
77
New cards
auscultatory gap
gap in between the first and second Korotkoff sounds. Causes underestimation of SBP or overestimation of DBP. be sure to inflate the cuff high enough to hear the true SBP before gap and avoid this by using the palpatory method before auscultatory method
78
New cards
when is electronic blood pressure not appropraite
hypertension, hypotension, irregular heart rhythm, peripheral vascular obstruction, shivering, seizures, excessive tremors. and inability to participate
79
New cards
avoid taking Bp when
patient is on hemodialysis with a AV shunt, has had a mastectomy, has a central venous/PICC lines, has an open wound
80
New cards
documenting BP
blood pressure value, site used
81
New cards
oxygen saturation evaluates
diffusion and perfusion. the percent of hemoglobin that is bound with oxygen in the arteries is the percent of saturation of hemoglobin
82
New cards
normal SPO2 value
93 - 100%
83
New cards
documentation of SPO2
measured value, flow rate of oxygen, and method of oxygen delivery device
84
New cards
factors affecting SPO2 measurement
patient motion, nail polish, and artificial nails
85
New cards
general survey is a
brief study of the whole persons **general health state** and obvious **physical characteristics**. Provides an **overall** impression and includes **objective** parameters that apply to the **whole** body including physical appearance, body structure, and mobility
86
New cards
general survey includes what factors
gender and race, age, signs of distress, body type/stature, posture, gait, body movements, nutritional status, hygiene and grooming, dress, body odor, affect and mood, speech, signs of abuse, substance abuse, and height and weight
87
New cards
psychological assessement
evaluation of one’s mental health and social well-being in a collection of subjective data
88
New cards
what to assess and tools you can use in a psychological assessment
psychiatric and psychological history - PHQ2 or 9: GAD
medications
history of dug or alcohol use - CAGE, AUDIT -C
violence risk: suicide, intimate partner violence : ASQ, HITS
coping skills
attitude beliefs
medications
history of dug or alcohol use - CAGE, AUDIT -C
violence risk: suicide, intimate partner violence : ASQ, HITS
coping skills
attitude beliefs
89
New cards
factors of a social health assessment
social, family, employment, dedication, and developmental history, legal trouble, financial situation and culture
90
New cards
factors of acute pain
short term(
91
New cards
chronic pain
lasting 6 months or longer, malignant/non-malignant
92
New cards
three types of pain scales
numeric rating scale, verbal descriptor scale, and face pain scale revised
93
New cards
pain >7 you should
assess Q and R.
A: how would you describe your pain
R: show me where it hurts. does it stay there or does it spread somewhere else
then immediately report the QRS of pain to your nurse or clinical instructor
A: how would you describe your pain
R: show me where it hurts. does it stay there or does it spread somewhere else
then immediately report the QRS of pain to your nurse or clinical instructor
94
New cards
pain 1-6
assess PQRSTU mnemonic. Ask at what level would you like your pain to be when moving around? then report to your nurse, clinical faculty your patient’s response
95
New cards
PAINAD
pain assessment in advanced dementia. use numeric rating scale or verbal descriptor scale
96
New cards
acute pain behaviors
autonomic and protective responses
guarding, grimacing, vocalizations (moaning, agitation, restlessness, stillness)
diaphoresis
changes in vital signs
guarding, grimacing, vocalizations (moaning, agitation, restlessness, stillness)
diaphoresis
changes in vital signs
97
New cards
chronic pain bhaviors
adaptation has occurred so more variability
bracing, rubbing, diminished activity, sighing, and change in activity
bracing, rubbing, diminished activity, sighing, and change in activity
98
New cards
Falls are a common cause of ______ and ________
hip fractures and traumatic brain injury
99
New cards
non-modifiable risk factors for fall
age, sex, race/ethnicity, history of fall
100
New cards
modifiable health factors for fall prevention
difficulties with gait and balance, lower extremity weakness, adverse drug events and polypharmacy, vitamin D deficiency, orthostatic hypotension visual impairment, foot issues or improper footwear, and home hazards