Higher Physics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
Scalar
A quantity that can be described by magnitude alone
2
New cards
Vector
A quantity that can be described by magnitude and direction
3
New cards
Acceleration
Change in velocity per unit time
4
New cards
3 equations of motion
1. v=u+at
2. s=it+1/2at^2
3. v^2=u^2+2as
2. s=it+1/2at^2
3. v^2=u^2+2as
5
New cards
Projectiles at a vertical angle
Vv=vsin0
6
New cards
Projectiles at a Horizontal Angle
Vh=vcos0
7
New cards
SUVAT
S= Displacement (m)
U= Initial Speed (ms^-1)
V= Final Speed (ms^-1)
A= Acceleration (ms^-2)
T= Time (s)
U= Initial Speed (ms^-1)
V= Final Speed (ms^-1)
A= Acceleration (ms^-2)
T= Time (s)
8
New cards
Newton's 1st Law of Motion
An object will remain at rest or travel in a straight line at a constant velocity if the forces acting on it are balanced
9
New cards
Newton's 2nd Law of Motion
Fun= Ma
If an object experiences an unbalanced force, the object will accelerate in the opposite direction to which the forces applied
If an object experiences an unbalanced force, the object will accelerate in the opposite direction to which the forces applied
10
New cards
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion
For every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force
11
New cards
Accelerating up in an elevator
Up: +
Accelerating: +
Reading(N) = W+F (Weight+Force)
Accelerating: +
Reading(N) = W+F (Weight+Force)
12
New cards
Decelerating up in an elevator
Up: +
Decelerating: -
Reading(N) = W-F (Weight-Force)
Decelerating: -
Reading(N) = W-F (Weight-Force)
13
New cards
Accelerating Down in an elevator
Down: -
Accelerating: +
Reading(N) = W-F (Weight-Force)
Accelerating: +
Reading(N) = W-F (Weight-Force)
14
New cards
Decelerating Down in an elevator
Down: -
Decelerating: -
Reading(N)=W+F (Weight+Force)
Decelerating: -
Reading(N)=W+F (Weight+Force)
15
New cards
tension
T=ma (Tension=mass x Acceleration)
16
New cards
Magnitude of force exerted on one block by another
F=ma rearranged to a=F/m then Force of Block A on Block B= ma
17
New cards
momentum equation
P=mv (momentum = mass x velocity)
18
New cards
Two masses collide and stick together
(m1u1)+(m2u2)=(m1+m2)v
19
New cards
Two masses collide & move apart with different velocities after the collision
(m1u1)+(m2u2)=(m1v1)+(m2v2)
20
New cards
An explosion: one mass explodes into two seperate masses which move off separately with different velocities
mu=(m1v1)+(m2v2)
21
New cards
elastic & Inelastic Collision calculation
Total Ek before Collision = (1/2m1u1^2)+(1/2m2u2^2)
Total Ek after collision= (1/2m1v1^2)+(1/2m2v2^2)
Total Ek after collision= (1/2m1v1^2)+(1/2m2v2^2)
22
New cards
Impulse equation
F=ma
F= m(v-u)/t
F= m change in v/t
Ft= change in (mv)
F= m(v-u)/t
F= m change in v/t
Ft= change in (mv)
23
New cards
Force time graphs
The area under a force-time graph is the impulse / change in direction, impulse is equal to the area under a force time graph
24
New cards
Airbags
An airbag slows the passenger speed to zero with little to no damage. To do this it needs to increase the time over which the change in speed (and momentum happens)
25
New cards
Crumple Zones
Crumple zones increase the time it takes for a vehicle to stop in the event of a crash, this reduces the force experienced by the driver and occupants on impact. Seatbelts also help with this
26
New cards
Galilean Invariance
The laws of physics are the same whether moving at a constant speed or at rest
27
New cards
Universal Law of Gravitation equation
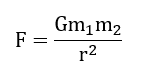
28
New cards
Universal Law of Gravitation
29
New cards