Developmental psych 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I am literally losing my mind whilst I study it- Cheers!
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
1
New cards
Development
life long, multidirectional. Systematic changes and continuities in individuals between conception and death “womb to tomb”
2
New cards
Conceptualizing
Prenatal Period- conception to birth
infancy- first two years of life
Preschool period-2-5 years
Middle childhood- 6-10
adolescence- 10-18
emerging adulthood-18-25
early adulthood- 25-40
middle adulthood-40-65
late adulthood- 65 or older
Age range IS approximate. This is _________ the life span
\
infancy- first two years of life
Preschool period-2-5 years
Middle childhood- 6-10
adolescence- 10-18
emerging adulthood-18-25
early adulthood- 25-40
middle adulthood-40-65
late adulthood- 65 or older
Age range IS approximate. This is _________ the life span
\
3
New cards
emerging adulthood
Transitional period between adolescents and full-fledged adulthood that extends from 18 to 25 sometimes as late as 29
4
New cards
Five factors of Emerging adulthood
Identity exploration- finding who you are.
instability- frequent changes in where you live, work, love.
self-focus- little to no responsibilities for others
feeling in-between
feeling of possibilities
instability- frequent changes in where you live, work, love.
self-focus- little to no responsibilities for others
feeling in-between
feeling of possibilities
5
New cards
historical
periods in history have shaped how we behave. children of 17th century Europe and north America were seen as little adults lawfully. laws were passed to ban child labor and schooling was made compulsory and separated youth from adults. This is how _______ influence behavior
6
New cards
Culture
Gender, race and other significant characteristics mean different things in different (______) .__ Different (____) can put children on different development pathways.
This is how _____ Influence behavior.
This is how _____ Influence behavior.
7
New cards
age grade
What status, race, privileges, and responsibilities for that age. U.S are adults when they turn 18. Japan has a ritual at 20
8
New cards
Subcultural
African, Hispanic, native, Muslim, Asian, and European American individuals have a very different developmental experience. They could be from low or high SES. This is how _____ influence behaviors
9
New cards
Historical trends
______ like jobs becoming more complex and requiring higher education have led to the new stage Emerging adult.
10
New cards
cultural
Not everyone has the same age grade. people of certain ages are subjected to different norms. This is the _____ influence on who will experience emerging adulthood.
11
New cards
Socioeconomic status
Some do not have the money to go to college and find themselves. This is the ______ influence on who will experience emerging adulthood.
12
New cards
Gender
Women may not feel like everything is possible due to inequality. This is the _____ influence on who will experience emerging adulthood.
13
New cards
Education
Only 8% of the world go to college. Because of this, they jump into adulthood. This is the _____ influence on who will experience emerging adulthood.
14
New cards
Characteristic
People who are W.E.I.R.D, people who are able to go to college, people with high SES have the _____ of people who will most likely experience emerging adulthood.
15
New cards
Arnett and Mitra
surveyed a large sampling of 18–60-year-olds on the five emerging adult theories. They found that both emerging adults agreed with the theories, but so did a large number of older adults. this is important because older age groups may not be as distinctive to emerging adults as previously thought.
16
New cards
Extreme positions
An _____ on the nature-nature issue is that if development is due to soley one or the other.
17
New cards
Ethnocentrism
evaluation of other cultures according to preconceptions or originating in the standards and customs of one's own culture.
18
New cards
W.E.I.R.D
____ are problematic because they are used to generailzed the entire popualtion when not every one is ____
19
New cards
Position
developmental scientist today take the ____ that both nature and nurture is involved.
20
New cards
Schizophrenia
the study on _____ was conducted to see if nature or nurture influence development. It showed that healthy homes= less chance and disturbed homes= Higher chance, showing that both nature and nurture are important
21
New cards
Life span Development
How we change and grow from conception to death is the science of _____
22
New cards
Key assumptions
the 7_____ of Baltes’s modern life span perspective are
__Lifelong process__
__Multidirectional__- development happens
__Lifelong process__
__Multidirectional__- development happens
23
New cards
developmental issues
Major ______ are
Continuity-Discontinuity- gradual or abrupt
Nature-Nurture- inborn or environmental
Universalist-context specific everyone or certain people.
Continuity-Discontinuity- gradual or abrupt
Nature-Nurture- inborn or environmental
Universalist-context specific everyone or certain people.
24
New cards
Theoretical perspectives
Major_____ are
__Learning theories__- Watson, skinner, Pavlov.
Development → learned associations
__Cognitive development__- Piaget
Children construct more advanced modes of thinking.
__System theory__ Bronfenbrenner’s system,
1 microsystem - immediate environment 2. mesosystem- induvial observing people in their microsystem 3 exosystem- social environment and governmental forces. 4 macrosystem subculture and culture
__Learning theories__- Watson, skinner, Pavlov.
Development → learned associations
__Cognitive development__- Piaget
Children construct more advanced modes of thinking.
__System theory__ Bronfenbrenner’s system,
1 microsystem - immediate environment 2. mesosystem- induvial observing people in their microsystem 3 exosystem- social environment and governmental forces. 4 macrosystem subculture and culture
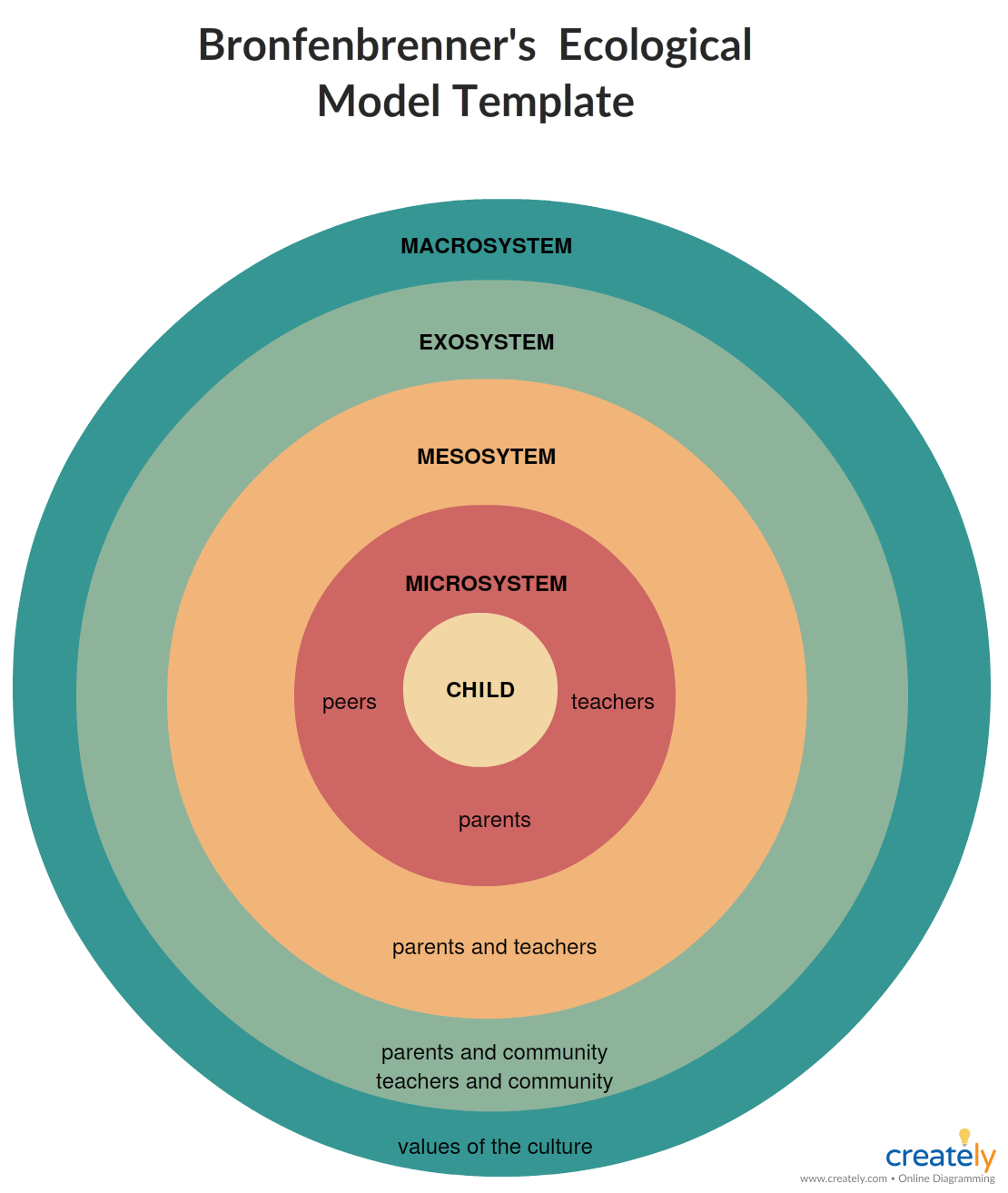
25
New cards
Piaget, Erikson, Freud
\------ ------ and ------ Takes on the three major themes or issues in developmental psych
Discontinuity
universalist
Nature vs nurture
Discontinuity
universalist
Nature vs nurture
26
New cards
Bandura, skinner, Watson
\------ ------ and ----- Takes on the three major themes or issues in developmental psych
Continuity
Context
Nurture
Continuity
Context
Nurture
27
New cards
Bronfenbrenner
\------ Takes on the three major themes or issues in developmental psych
nature AND nurture
continuity
context
nature AND nurture
continuity
context
28
New cards
Psychoanalytic theories
\-----------
strengths: calls attention to the unconscious processes and motivations
Weakness: not falsifiable, difficult to test
strengths: calls attention to the unconscious processes and motivations
Weakness: not falsifiable, difficult to test
29
New cards
Learning theories
\----------
strengths: can be observed.
weakness: depends on individual (not general)
strengths: can be observed.
weakness: depends on individual (not general)
30
New cards
System theories
\--------
strengths: can be applied to everyone
strengths: can be applied to everyone
31
New cards
Cognitive- development
\---------
strengths: Show how children develop and think
strengths: Show how children develop and think
32
New cards
Mamie Clark
\------- was the second black person and first black women to graduate with a Ph. D at Columbia. experiment on white and black dolls
33
New cards
scientific method
a belief that investigations should allow facts, their systematic observations or data, to determine the merits of true thinking.
34
New cards
Good Hypothesis
“People who eat chocolate will score higher on a measure of happiness than people who do not eat chocolate” is an example of a -------
35
New cards
representative sample
subject populations that seek to accurately reflect the characteristics of a larger group
36
New cards
General research designs
Cross section designs- assessing people of different age groups or cohorts.
Longitude design- one cohort of individual is assessed repeatedly over time.
case study: in depth examination of an induvial
experimental method- manipulation
correlations- how they depend on one another
Longitude design- one cohort of individual is assessed repeatedly over time.
case study: in depth examination of an induvial
experimental method- manipulation
correlations- how they depend on one another
37
New cards
correlation coefficient
can range from -1.00 to +1.00 positive correlations move in the same direction, negative opposite.
38
New cards
four ethical procedures
consent, confidentiality, debriefed
39
New cards
correlation studies
\------ dont have IV
40
New cards
Random assignment
when you take the random sample and divide them up into random groups based on nothing
41
New cards
Random sample
random people for a study