Topic 4 - Extracting Metals and Equilibria
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
Write the metals reactivity series from most to least reactive.
Potassium (K), Sodium (Na), Lithium (Li), Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), Aluminium (Al), Carbon (C), Zinc (Zn), Iron (Fe), Hydrogen (H), Copper (Cu), Silver (Ag), Gold (Au).
How are metals arranged in the reactivity series?
From most to least reactive.
Is copper more or less reactive than hydrogen?
Less.
Is sodium more or less reactive than potassium?
Less.
Is potassium more or less reactive than sodium?
More.
Are more reactive metals more or less resistant to corrosion?
Less.
Are less reactive metals more or less resistant to corrosion?
More.
Which metals are most easily oxidised?
More reactive metals.
Which metals are less easily oxidised?
Less reactive metals.
Are more or less reactive metals more likely to form cations?
More.
Are more or less reactive metals less likely to form cations?
Less.
A metal easily loses electrons to form cations. What does those suggest about its reactivity?
Very reactive.
A metal struggles to lose electrons to form cations. What does those suggest about its reactivity?
Unreactive.
A metal is easily oxidised. What does those suggest about its reactivity?
Very reactive.
A metal is not easily oxidised. What does those suggest about its reactivity?
Unreactive.
Why do elements high up in the reactivity series form cations easily?
They’re more likely to react with acid and water.
How is a metals relative resistance to oxidation related to its position in the reactivity series?
Oxidation is the loss of electrons.
Metals that are lower in the reactivity are less reactive which means they are less likely to form cations so more resistant to oxidation.
Metals that are higher in the reactivity are more reactive which means they are more likely to form cations so less resistant to oxidation.
A metal and acid react vigorously. What does this mean?
Reaction is rapid and vigorous.
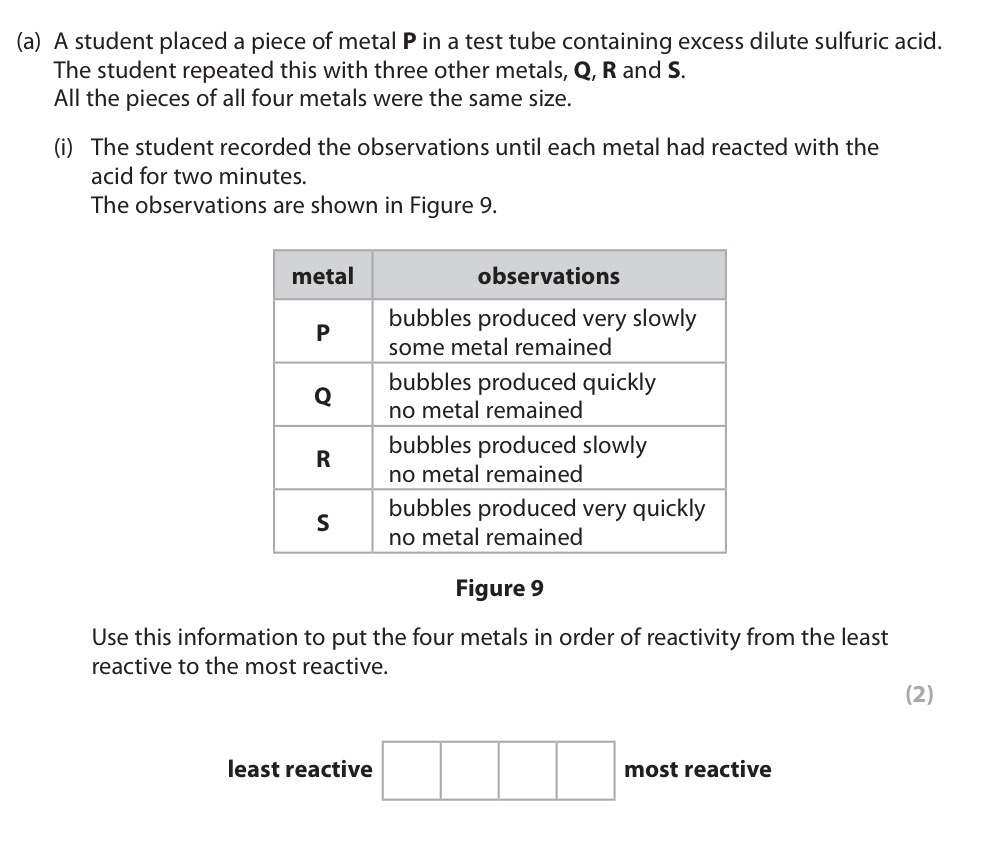
P, R, Q and S.
What is the general equation for a metal reacting with an acid?
Metal + Acid → Salt + Hydrogen
Only metals above which metal will react with dilute acid?
Hydrogen.
What do only metals above hydrogen in the reactivity series react with?
Dilute acids.
What is formed when an acid and metal react?
Salt and hydrogen.
Which two reactants react to form salt and hydrogen?
Metal and acid.
What is a salt?
An ionic compound produced when a metal reacts with an acid.
What is the general equation for a metal reacting with water?
Metal + Water → Metal Hydoxide + Hydrogen
What are the products when a metal reacts with water?
Metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Which reactants must react to form a metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas?
Metal and water.
If a metal reacts with cold water, what does it suggest about the reactivity of the metal?
Metal is very reactive as only the most reactive metals can react with water.
Does magnesium react with cold water vigorously or slowly?
Slowly.
Does potassium react with cold water vigorously or slowly?
Vigorously.
A metal reacts with oxygen but not water or acid. What does this suggest about the metals reactivity?
Not very reactive as most metals react with oxygen but only the most reactive react with water/acid.
Name a metal which will not react with water, acid or oxygen. Why?
Gold because it is extremely unreactive.
If a metal reacts with water, what does this suggest about this reactivity?
Very reactive.
If a metal reacts with acid, what does this suggest about this reactivity?
Quite reactive.
What are the products when a metal reacts with steam?
Metal oxide and hydrogen.
What is a displacement reaction?
When a more reactive substance takes the place of a less reactive one.
What is the reactivity of a substance determined by?
Tendency to lose electrons or form cations.
Is reactivity determined by tendency to lose or gain electrons?
Lose.
Is reactivity determined by tendency to form cations or anions?
Cations.
What is observed when a more reactive metal displeases a less reactive one from a solution?
The less reactive metal coats the surface or falls out as a solid.
Can magnesium displace copper from a copper sulfate solution? Why?
Yes because magnesium is more reactive.
What would you expect to observe when magnesium is added to copper sulfate solution?
Copper sulfate solution is blue.
Magnesium is more reactive than copper so when added, blue solution decolourises/blue colour of solution fades.
Copper forms at the bottom of the beaker.
In a displacement reaction, which element is oxidised and loses electrons?
More reactive.
In a displacement reaction, which element is reduced and gains electrons?
Less reactive.
Why can a displacement reaction be called a REDOX reaction?
A redox reaction is when reduction and oxidation are taking place at the same time.
In a displacement reaction, the more reactive metal atoms lose electrons to form ions. This is oxidation.
In a displacement reaction, the less reactive metal atoms gains electrons to form the element. This is reduction.
What is oxidation?
Loss of electrons and gain of oxygen.
What is reduction?
Gain of electrons and loss of oxygen.
What determines how a metal is extracted?
Position of the metal in the reactivity series.
Where are most metals extracted from?
From ores found in the Earth’s crust.
What are metal ores?
Rocks that contain enough of the metal to make it worthwhile extracting the metal.
Which metals are found in the earth’s crust as uncombined elements?
Unreactive metals.
Which metals are found in the earth’s crust as combined elements?
Reactive metals.
Some ores contain metals chemically combined with oxygen. What process must be carried out to extract the metal?
Reduction using carbon.
How are metals that are less reactive than carbon extracted from their ores?
Reduction and heating using carbon.
How are metals that are more reactive than carbon extracted from their ores?
Electrolysis.
How can metals be extracted from their ores?
Less reactive metals: Reduction and heating with carbon.
More reactive metals: Electrolysis.
How would you extract iron from its ore?
Iron is less reactive than carbon so can be extracted by reduction with carbon.
Explain the process of extracting a metal less reactive than carbon from its ore.
Carried out in a blast surface.
Metal is reduced and loses oxygen but gains electrons.
Carbon is oxidised and gains oxygen but loses electrons.
When extracting a metal with carbon, does the metal undergo reduction or oxidation?
Reduction.
How would you extract aliminium from its ore?
Aliminium is more reactive than carbon so electrolysis is used.
Explain the process of extracting a metal less reactive than carbon from its ore.
Metal is manufactured by the electrolysis of a melted compound.
Metal is discharged at the cathode and non metal at the anode.
How can aliminium be extracted from its ore?
Aliminium is more reactive than carbon so electrolysis must be used.
Molten ore undergoes electrolysis.
Metal is discharged at the cathode and non metal at the anode.
Why is aluminium dissolved in molten cryolite before being extracted from aluminium oxide?
It has a very high melting point so by dissolving it, an electrolyte with a lower melting point is reduced which reduces usage and cost.
How are metals that are higher than carbon in the reactivity series extracted?
Electrolysis.
Which metals must be extracted by electrolysis?
Any metals higher up in the reactivity series than carbon.
Predict the method that will have to be used to extract calcium from its ore.
Electrolysis.
Why is electrolysis not used to extract all metals?
It is expensive as a large amount of energy is required so metals that are less reactive than carbon has extracted using carbon.

Pick A, B, C or D.
C.
Which metals can be found as pure/native metals? Why?
Platinum, gold and silver because they are unreactive.
What are low grade ores?
Ores that only contain small amounts of metal.
State two metals that have ores that are becoming less available.
Copper and nickel.
Define: Phytomining
A process used to absorb metals from the soil.
How can plants be used as an alternative metal extraction method?
Phytomining.
Plants are grown in areas with metals in the soil.
The plants take up metals through their roots as they grow and concentrate them in their shoots and leaves.
These plants are harvested, dried and burned and the metals are removed through ash.
The ash contains metal compounds that can be extracted in electrolysis or displacement reactions.
How are the metals removed from the ash after phytomining?
Plants containing the metals are harvested, dried and burned.
During phytomining, plants that contain metals are harvested, dried and burned. How can the metals be extracted from the ash?
Displacement and electrolysis.
Describe how growing plants can result in the photomining of copper.
Plants absorb copper ions from the soil to their leaves/shoots.
These parts of the plant can then be dried, burned and harvested in a furnace and removed through ash.
The ash contains metal compounds that can be extracted in electrolysis or displacement reactions.
Define: Leachate
Acidic solution containing significant quantities of metal ions.
Define: Bioleaching
Technique using bacteria to extract metals from metal ores.
How can bacteria be used as an alternative metal extraction method?
Bioleaching.
Some bacteria absorb metal compounds and breakdown the ores by absorbing energy from bonds between atoms in compounds.
These produce acidic solutions called leachates, containing the metals.
Scrap iron is used to remove the metal from the leachate.
What is bioleaching often used to extract metals from?
Sulfides.
State two advantages of using bioleaching and phytomining to extract metals from ores.
They can be used to extract metals from low grade ores and avoids significant environmental damage.
State three disadvantages of using bioleaching and phytomining to extract metals from ores.
Only suitable for low grade ores with smaller quantities of metals.
Slow processes.
Require displacement or electrolysis for the final step.
What is the environmental impact of mining and extraction?
Destruction of habitats.
What are the advantages of recycling metals?
Economically beneficial because recycling metals is cheaper than extraction methods like electrolysis which is expensive.
Prevents need for mining and extraction of new metals, which are damaging to the environment and ecosystems.
Less waste produced so less landfill sites which take up space and pollute the surroundings.
More sustainable by not using up finite resources like burning fossil fuels.
Recycling process provides employment.
Less greenhouse gases produced, reducing global warming.
What are the disadvantages of recycling metals?
Materials must be sorted beforehand which requires energy and labour.
May not be the same quality as the original.
Workers and vehicles need to be organised and maintained as materials must be collected and transported. This requires fuel and energy.
How can iron be recycled?
With waste steel by adding both to a blast surface.
How does recycling impact the use of fossil fuels?
Use is reduced.
Is it more energy efficient to extract materials or melt and re-mould them?
Extract materials.
Does it cost more energy to extract new metals or recycle them?
Recycling them due to the energy used in collecting, transporting, storing and recycling them.
What is a life cycle assessment?
Analysis of the overall environmental impact that a product may have throughout its lifetime.
What are the four stages of the life cycle assessment?
Choice of raw materials.
Manufacturing.
Usage.
Disposal.
What different factors does a life cycle assessment of a product consider?
Extraction and processing of raw materials.
Manufacturing.
Usage of product.
Disposal.
What may be evaluated in extraction and processing of raw materials during life assessments?
Metals must be mined and extracted from their ores which requires energy and can cause pollution. Deforestation also must occur to clear space for mining which damages habitats and further contributes to pollution.
Raw materials often come from crude oil, a non renewable resource, and supplies are limited. Obtaining crude oil requires energy and may cause pollution.
What may be evaluated in the manufacture during life assessments?
Disposal of waste products could be dangerous but others may be able to be recycled for use.
Factories may lead to land being cleared, damaging habitats.
Process may require water. This polluted water must be disposed of carefully and cannot be put back into the environment.
Use of fossil fuels for machinery and transport damages the environment.
What may be evaluated in the usage during life assessments?
Paint gives off toxic fumes.
Burning fuels releases greenhouse gases.
Fertilisers may leach into streams to damage ecosystems.
What may be evaluated in the disposal during life assessments?
Uses up space at landfill sites, which can pollute the Earth.
Products may be incinerated (burnt), causing air pollution.
Recycled.
What are two disposal options for metals?
Recycled or stored at landfill.
Will a car or bicycle have a less damaging impact on the environment?
A bicycle.
Is iron a renewable or non renewable resource?
Non renewable.