1: Organisation of the Body
Science
Science — a broad field of inquiry that attempts to understand nature in rational logical manner.
Its process is active and changing as new experiments add new knowledge.
It is affected by culture and culture is affected by society.
Hypothesis — an idea formed from observations and experiments.
Experiment — series of tests of a hypothesis.
Controlled experiments — eliminated any influences or biases not being directly tested.
Theory — a hypothesis that has been supported by experiments and thus shown to have a high degree of confidence
Laws — a theory that has an unusually high level of confidence, or an observable occurrence appears to be always true.
Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy
Anatomy — study of the structure of an organism and the relationship of its part.
(Greek) — to cut apart.
Gross Anatomy — study of body parts visible to naked eye.
Microscopic Anatomy — study of body parts with a microscope
Cytology — study of cells.
Histology — study of tissues.
Developmental Anatomy — study of human growth and development.
Pathological Anatomy — study of diseased body structures.
Systemic Anatomy — study of body by systems.
Systems —groups of organs that have common function.
Physiology
Physiology — science that deals with the function of the living organism; how the body works.
(Greek): physis [nature] ; logos [study, words]
It is subdivided according to:
type of organism involved (human, plants, animals)
organisational level studied (molecular, cellular)
a specific or systemic function studied (neuro, respiratory, cardiovascular)
Language of Science and Medicine
Scientific terms are often based on Latin or Greek word parts.
International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA) — They formed a worldwide committee to publish a list of universal standard anatomical terminology.
Terminologia Anatomica (TA) — published 1998; list of gross anatomy.
Terminologia Histologica (TH) — published 2008, list of microscopic anatomy.
Avoidance of Eponyms
Eponyms — terms that are based on a person’s name.
Eustachian Tube = Auditory tube
tube connected to the middle ear.
Islets of Langerhans = Pancreatic islets
endocrine component of the pancreas.
Bowman’s capsule = Glomerular capsule
a part of the nephron that forms a cup-like sack surrounding the glomerulus.
Characteristics of Life
Criterion that might be used to define life:
Autopoiesis — a concept where living organisms self-organise or self-maintain.
Cell theory — any independent structure made up of one or more microscopic units are called cells in a living organism.
Metabolism — the whole sum of reactions that occur throughout the body within each cell and that provide the body with energy.
CHARACTERISTICS | DESCRIPTION |
Responsiveness | Ability of an organism to sense, monitor, and respond to external and internal changes. |
Conductivity | Capacity of living cells to transmit a wave of electrical disturbance from one point to another within the body. |
Growth | Organised increase in the size and number of cells, tissues, organs, and body itself. |
Respiration | Exchange of respiratory gases between an organisms and its environment. |
Digestion | Complex food products are broken down into simpler subtances that can be absorbed and used by body cells. |
Absorption | Movement of molecules through a membrane and into the body fluids for transport to cells for use. |
Secretion | Production and release of bodily substances for diverse body functions. |
Excretion | Removal of wastes from the body. |
Circulation | Movement of bodily fluids from one body area to another in a continuous basis. |
Reproduction | Formation of new individual offspring. |
Levels of Organisation
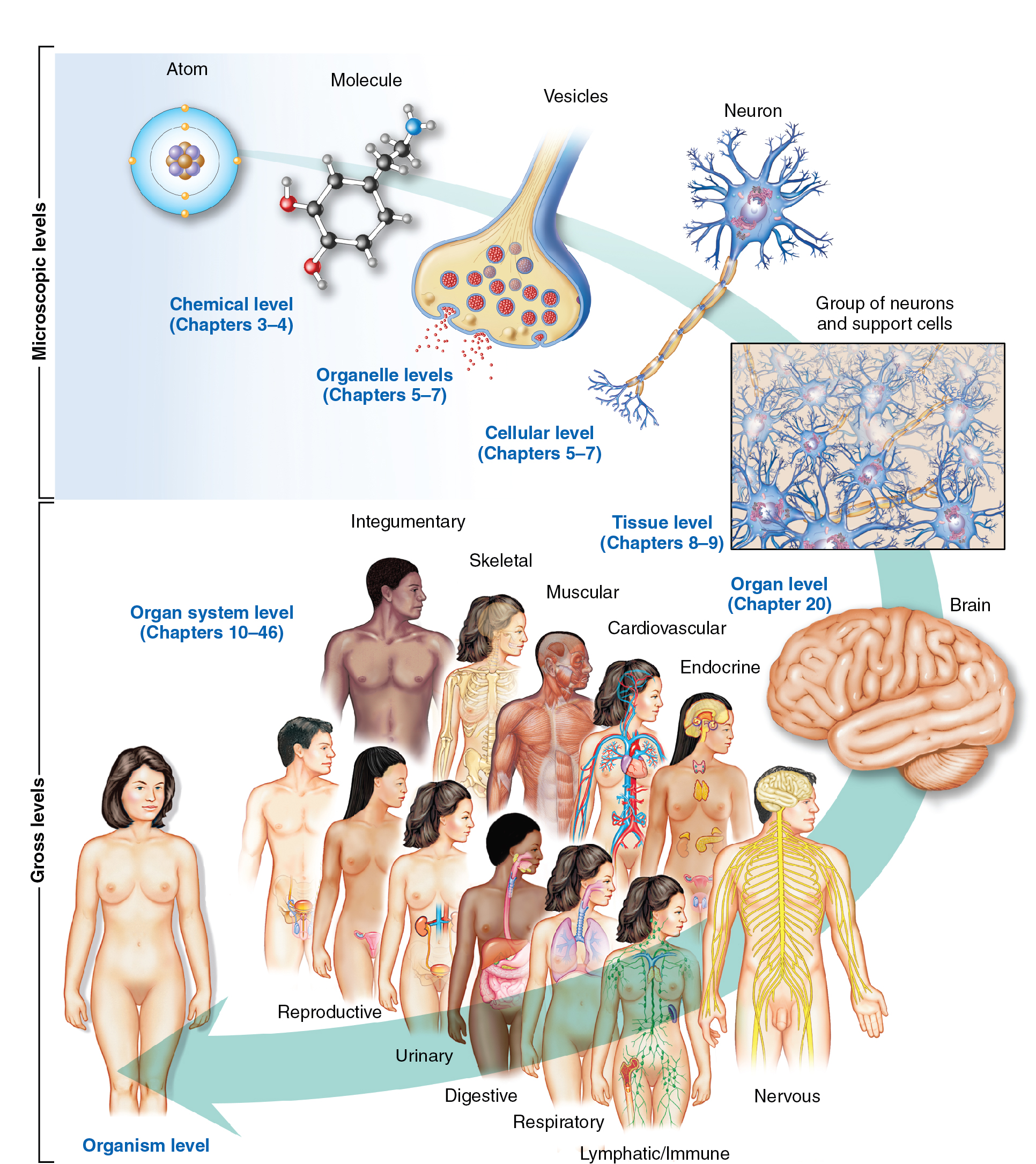
Chemical Level
Atoms — smallest unit of matter, so small they are invisible.
Molecules — combination of atoms to form larger chemical groups.
Macromolecules — combination or larger and more complex molecules.
Cytoplasm — a gel-like material made of fluids, particles, and membranes; this fills the inside of the cells.
Cellular Level
Cells — smallest and structural units that possess and exhibit the basic characteristics of a living matter.
Each cell is surrounded by membrane and characterised with single nucleus surrounded by the cytoplasm—that includes numerous organelles.
Cells specialise of differentiate to perform unique functions.
Fat cells — structurally modified to permit the storage of fats.
Cardiac muscle cells — able to contract with great force.
Organelle Level
Organelles — subunit of cells which performs specific functions within it.
Tiny organs that allow cells to live.
They cannot live outside the cell, the cell can’t survive without the organelles.
Some examples:
Mitochondria — powerhouse of the cell—which provides energy that needed by the cell.
Golgi apparatus — set of sacs that provides packaging services to the cll by storing material for future use.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) — network of channels within the cell that act as highways for movement of chemicals, and acts as sites for chemical processes.
Tissue Level
Tissue — a group of cells that all developed together from the same part of the embryo and perform a certain function.
The fabric of the body.
Four major tissues:
Epithelial Tissues — tissues that forms the covering of internal and external surfaces of the body.
Connective Tissues — tissues that supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body.
Muscle Tissues — tissues that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts.
Nervous Tissues — tissues that are the main component of the nervous system.
Organ Level
Organ — a structure made up of different kinds of tissues arranged together to perform specific functions.
Heart as an example of organ level:
Muscle and connective tissues give it shape and helps pumps blood.
Epithelial tissues lines that cavities/chambers.
Nervous tissues controls the pumping contractions.
Each organ has unique shape, size, appearance, and placement in the body—and each can be identified by the pattern of tissues that forms it.
System Level
Systems — the most complex of the organisational units; it involves varying numbers and kinds of organs and together, they perform complex functions in the body.
Major Body Systems:
Integumentary
Skeletal
Muscular
Nervous
Endocrine
Cardiovascular
Lymphatic/Immune
Respiratory
Digestive
Urinary
Reproductive
System groupings:
Musculoskeletal system
Neuromusculoskeletal system
Microbiome — a set of interacting communities of bacteria and other microorganisms that inhabit the human body; microbial systems influence normal body functions
Human microbiome — the microorganisms that live in or on a particular part of the body.
Functional Category | System | Principal Organs | Functions |
Support and movement | Integumentary | Skin | Protection, temperature regulation, sensation |
Skeletal | Bones, ligaments | Support, protectioc, movement, mineral and fat storage, blood production | |
Muscular | Muscles, tendons | Movement, posture, heat production | |
Communication, control, and integration | Nervous | Brain, nerves, spinal cords | Control, regulation, coordination of other systems, sensation, memory |
Endocrine | Pituitary gland, pancreas, adrenals | Control and regulation of other systems. | |
Transportation and defence | Cardiovascular | Heart, blood | Exchange and transport of materials |
Lymphatic | Lymph nodes, spleen, thymus | Immunity, fluid balance | |
Respiration, nutrition, and excretion | Respiratory | Lungs, trachea, nose | Gas exchange, acid-base balance |
Digestive | Stomach, intestines, liver, mouth | Breakdown and absorption of nutrients, eliminates waste | |
Urinary | Kidney, ureters, bladder | Excretion of waste, fluid and electrolyte balance, acid-base balance | |
Reproduction | Reproductive | Testes, prostate, penis Ovaries, uterus, vagina, breasts | Reproduction, continuity of genetic information, nurturing of offspring. |
Organism Level
Organism — a living thing that can function on its own.
a living thing that has an organized structure, can react to stimuli, reproduce, grow, adapt, and maintain homeostasis.
Human Body — the physical substance of the human organism, composed of living cells and extracellular materials and organized into tissues, organs, and systems.
Anatomical Position
Anatomical position — the body is in an erect, or standing, posture with the arms at the side and palms forward.
It is the reference position that gives meaning to the directional terms used to describe body parts and regions.
Bilateral symmetry — the right and left sides of the body mirror images of each other.
Only one plane can divide the body into right and left halves.
Its important feature is the balanced proportions.
Body Placement
Ipsilateral — placement of a body part meaning same side.
Contralateral — placement of a body part meaning opposite side.
Body Position
Supine — position where the body is lying face upward.
Prone — position where the body is lying face downward.
Body Cavities
Cavity — any hollow within the body or its organs.

Major Body Cavities | Areas | Parts | Organs |
Dorsal Body Cavities — In the dorsal (back) part of the body. | Cranial Cavity (above) | Space within the skull | brain |
Spinal Cavity (below) | Lies within hollow spinal canal | spinal cord | |
Ventral Body Cavities — On the ventral (front) side of the trunk. | Thoracic Cavity (above diaphragm) | Mediastinum — mid-portion of thoracic cavity. | heart, trachea, right and left bronchi, oesophagus, thymus, blood vessels, thoracic duct, other lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, nerves. |
Pleural Cavity — entire space to the sides of the mediastinum. | right and left lungs | ||
Abdominopelvic Cavity (below diaphragm) | Abdominal Cavity | liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, intestines, spleen, kidneys, ureters | |
Pelvic Cavity | urinary bladder, reproductive organs, sigmoid colon and rectum |
Membranes that line cavities
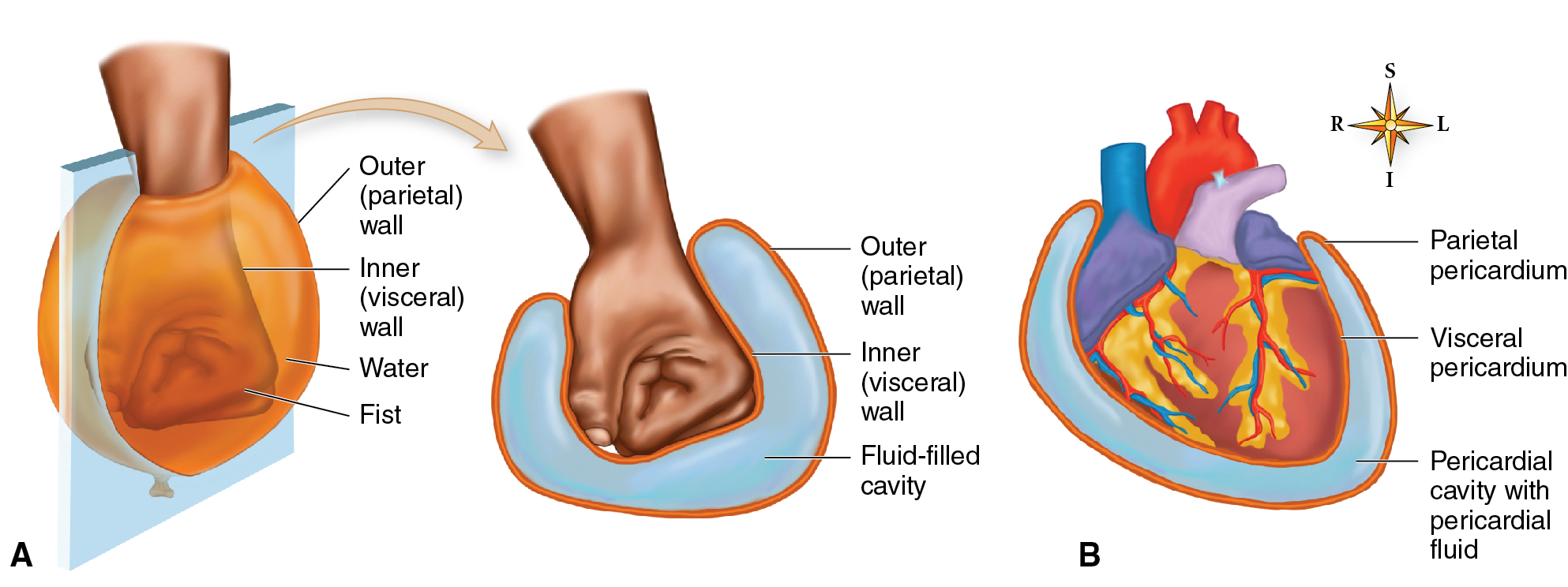
Parietal Pericardium — the outer layer that's firmly attached to your fibrous pericardium.
Visceral Pericardium — the innermost layer of pericardium; it covers heart and the roots of your great vessels.
Parietal Peritoneum — the membrane lining the inside of the abdominal cavity.
Visceral Peritoneum — the membrane that covers the organs within the abdominal cavity.
Peritoneal Cavity — the space between the two membranes in the abdomen.
Body Regions
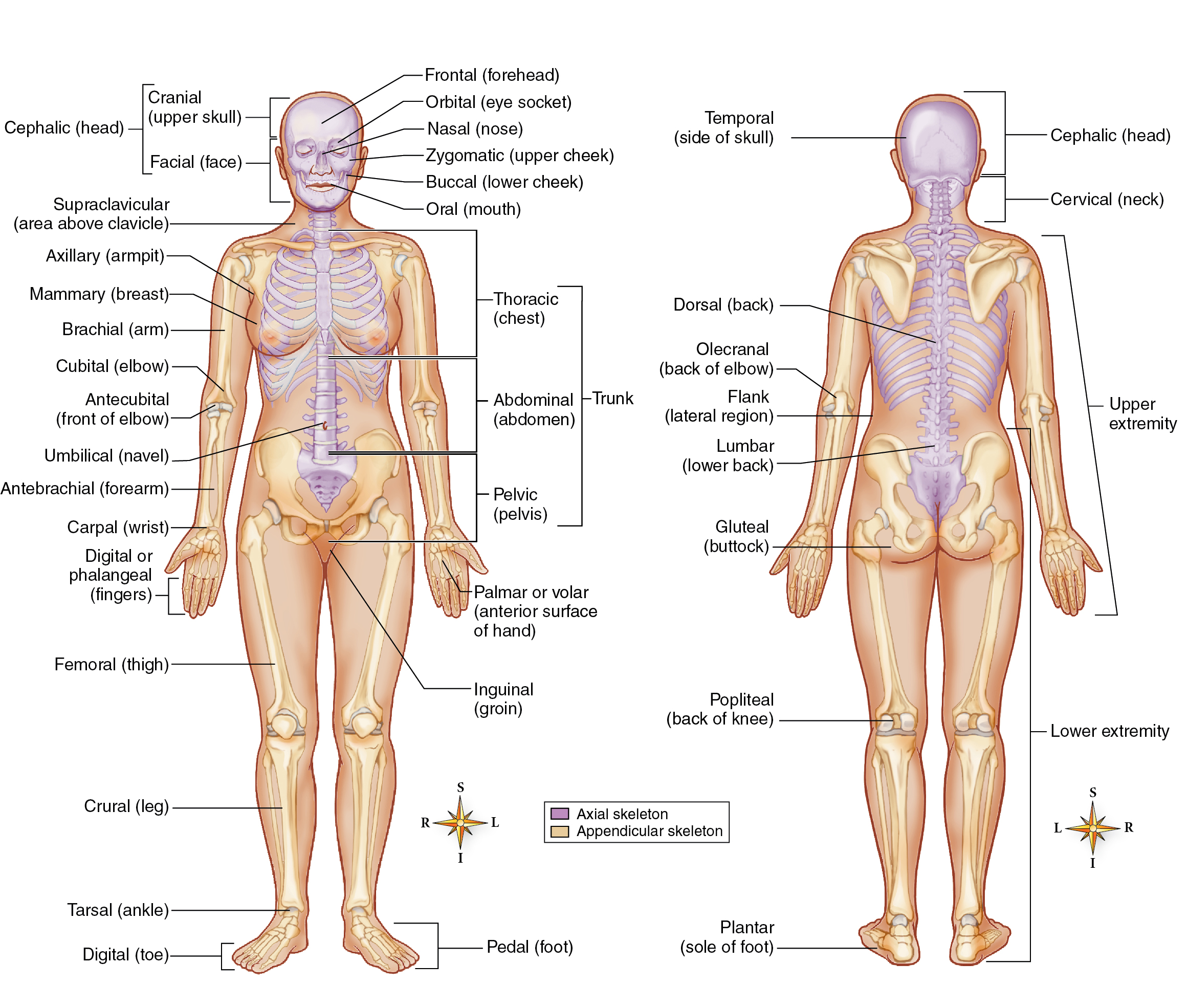
Major Subdivision of Body as a Whole
Axial Portion — portion of the body consists of the head, neck, and torso, or trunk.
Dorsal Cavities
Ventral Cavities
Appendicular Portion — portion of the body consists of the upper and lower extremities and their connections to the axial portion.
Upper extremity (limb) — shoulder, arm, forearm, wrist, and hand components
Lower extremity (limb) — hip, thigh, leg, ankle, and foot.
Latin-Based Descriptive Terms for Body Regions
BODY REGION | AREA OR EXAMPLE |
Abdominal (ab-DOM-in-al) | Anterior torso below diaphragm |
Acromial (ah-KRO-mee-al) | Shoulder |
Antebrachial (an-tee-BRAY-kee-al) | Forearm |
Antecubital (an-tee-KYOO-bi-tal) | Depressed area just in front of elbow (cubital fossa) |
Axillary (AK-si-lair-ee) | Armpit (axilla) |
Brachial (BRAY-kee-al) | Arm |
Buccal (BUK-al) | Cheek (inside) |
Calcaneal (cal-CANE-ee-al) | Heel of foot |
Carpal (KAR-pal) | Wrist |
Cephalic (se-FAL-ik) | Head |
Cervical (SER-vi-kal) | Neck |
Coxal (KOK-sal) | Hip |
Cranial (KRAY-nee-al) | Skull |
Crural (KROO-ral) | Leg |
Cubital (KYOO-bi-tal) | Elbow |
Cutaneous (kyoo-TANE-ee-us) | Skin (or body surface) |
Digital (DIJ-i-tal) | Fingers or toes |
Dorsal (DOR-sal) | Back or top |
Facial (FAY-shal) | Face |
Femoral (FEM-or-al) | Thigh |
Frontal (FRON-tal) | Forehead |
Gluteal (GLOO-tee-al) | Buttock |
Hallux (HAL-luks) | Great toe |
Inguinal (ING-gwi-nal) | Groin |
Lumbar (LUM-bar) | Lower part of back between ribs and pelvis |
Mammary (MAM-er-ee) | Breast |
Manual (MAN-yoo-al) | Hand |
Mental (MEN-tal) | Chin |
Nasal (NAY-zal) | Nose |
Navel (NAY-vel) | Area around navel, or umbilicus |
Occipital (ok-SIP-i-tal) | Back of lower part of skull |
Olecranal (o-LECK-ra-nal) | Back of elbow |
Oral (OR-al) | Mouth |
Orbital or ophthalmic (OR-bi-tal or op-THAL-mik) | Eyes |
Otic (O-tik) | Ear |
Palmar (PAHL-mar) | Palm of hand |
Patellar (pa-TELL-ar) | Front of knee |
Pedal (PEED-al) | Foot |
Pelvic (PEL-vik) | Lower portion of torso |
Perineal (pair-i-NEE-al) | Area (perineum) between anus and genitals |
Plantar (PLAN-tar) | Sole of foot |
Pollex (POL-lex) | Thumb |
Popliteal (pop-li-TEE-al) | Area behind knee |
Pubic (PYOO-bik) | Pubis |
Supraclavicular (soo-pra-cla-VIK-yoo-lar) | Area above clavicle |
Sural (SUR-al) | Calf |
Tarsal (TAR-sal) | Ankle |
Temporal (TEM-por-al) | Side of head |
Thoracic (tho-RAS-ik) | Chest |
Zygomatic (zye-go-MAT-ik) | Cheek (outside) |
Abdominopelvic regions
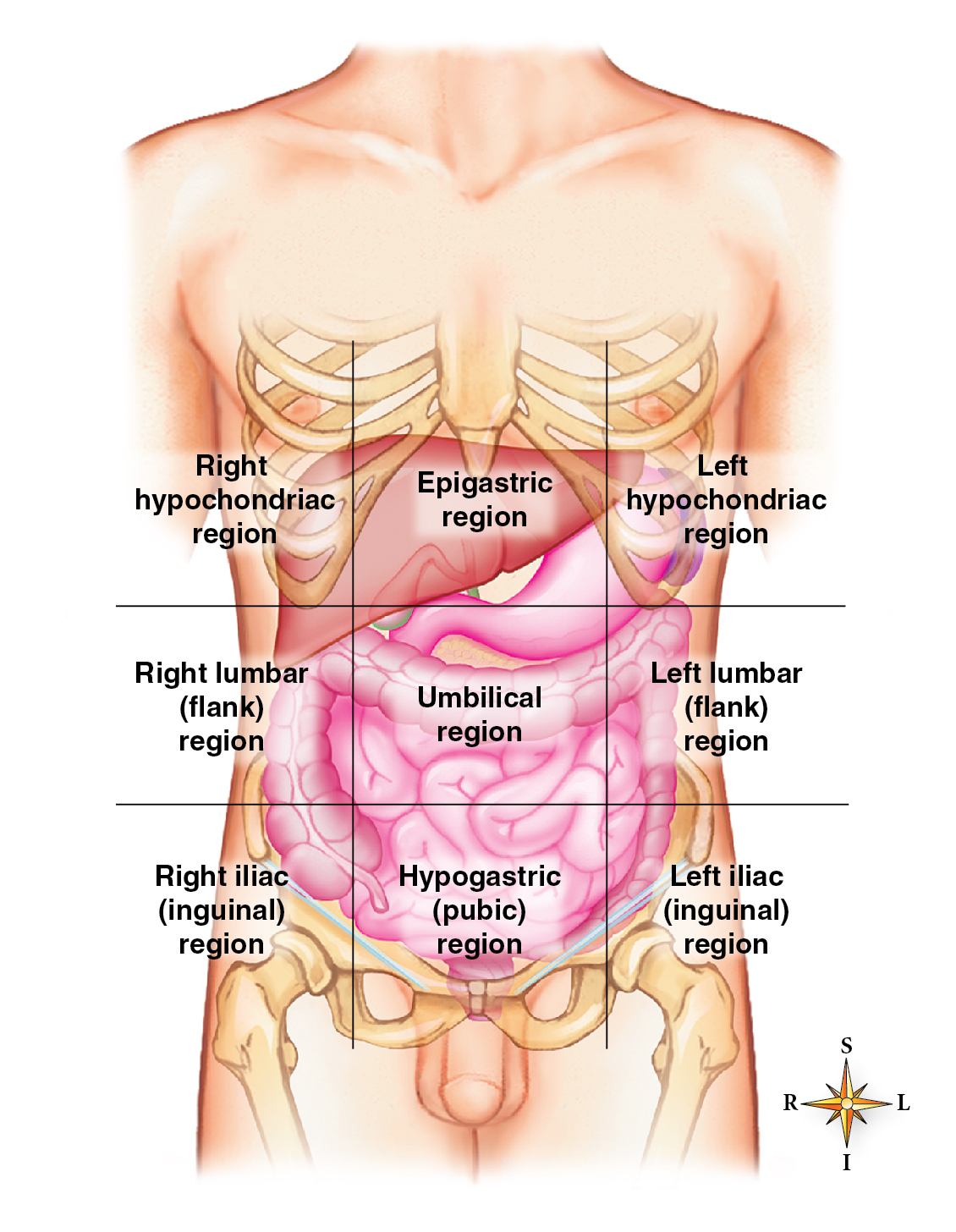
Right Region | Middle Region | Left Region | |
Upper region | Right hypochondriac region — liver, gallbladder, part of small intestine, part of ascending colon, part of transverse colon, right kidney | Epigastric region — oesophagus, stomach, liver, spleen, pancreas, right and left kidneys, right and left ureters, right and left suprarenal glands, small intestine, transverse colon is located. | Left hypochondriac region — part of stomach, top of left lobe of liver, left kidney, spleen, tail of pancreas, part of small intestine, part of transverse colon, part of descending colon. |
Middle region | Right lumbar (flank) region — inferior-most part of the right lobe liver; gallbladder; small intestine; ascending colon; part of the right kidney | Umbilical region — stomach; pancreas; small intestine; transverse colon; medial extremities of inferior poles of the right and left kidneys; right and left ureters; cisterna chyli | Left lumbar (flank) region — portion of the small intestine; part of the descending colon; part of the left kidney |
Lower region | Right iliac (inguinal) region — small intestine; sigmoid colon; rectum; urinary bladder; right and left ureters; uterus, right and left ovaries and uterine (female); ductus deferens, seminal vesicles and prostate (male) | Hypogastric (pubic) region — small intestine; vermiform appendix; cecum; ascending colon; right ovary and right uterine tube in females. | Left iliac (inguinal) region — descending colon; sigmoid colon; part of the small intestine; left ovary and the left uterine tube (female) |
Hypochondriac — “under cartilage“ ; the rib cartilage.
Epigastric — “upon the stomach“.
Iliac — hip region.
Hypogastric — “below the stomach.“
Abdominopelvic quadrants
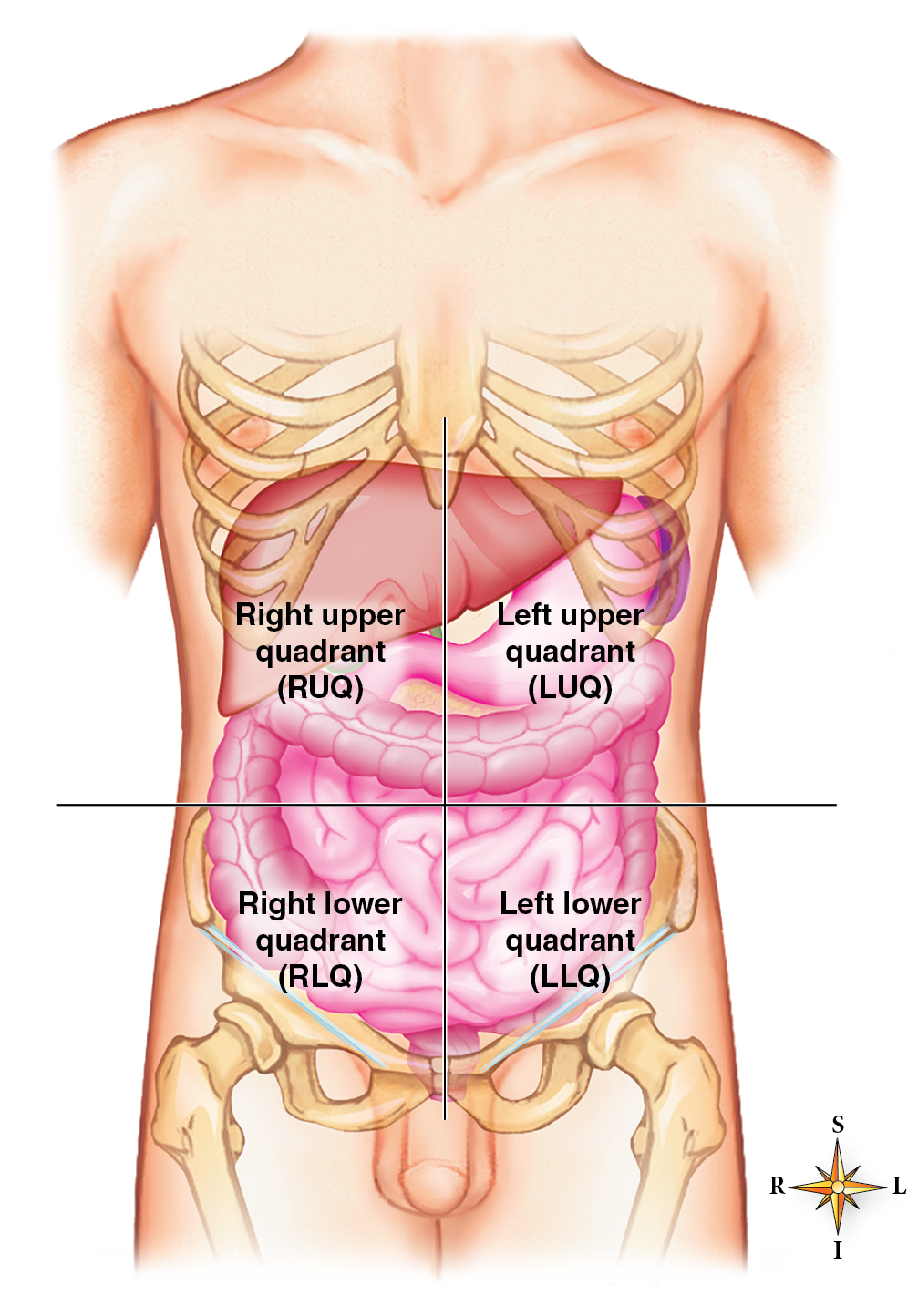
Terms used in describing body structure
Directional terms
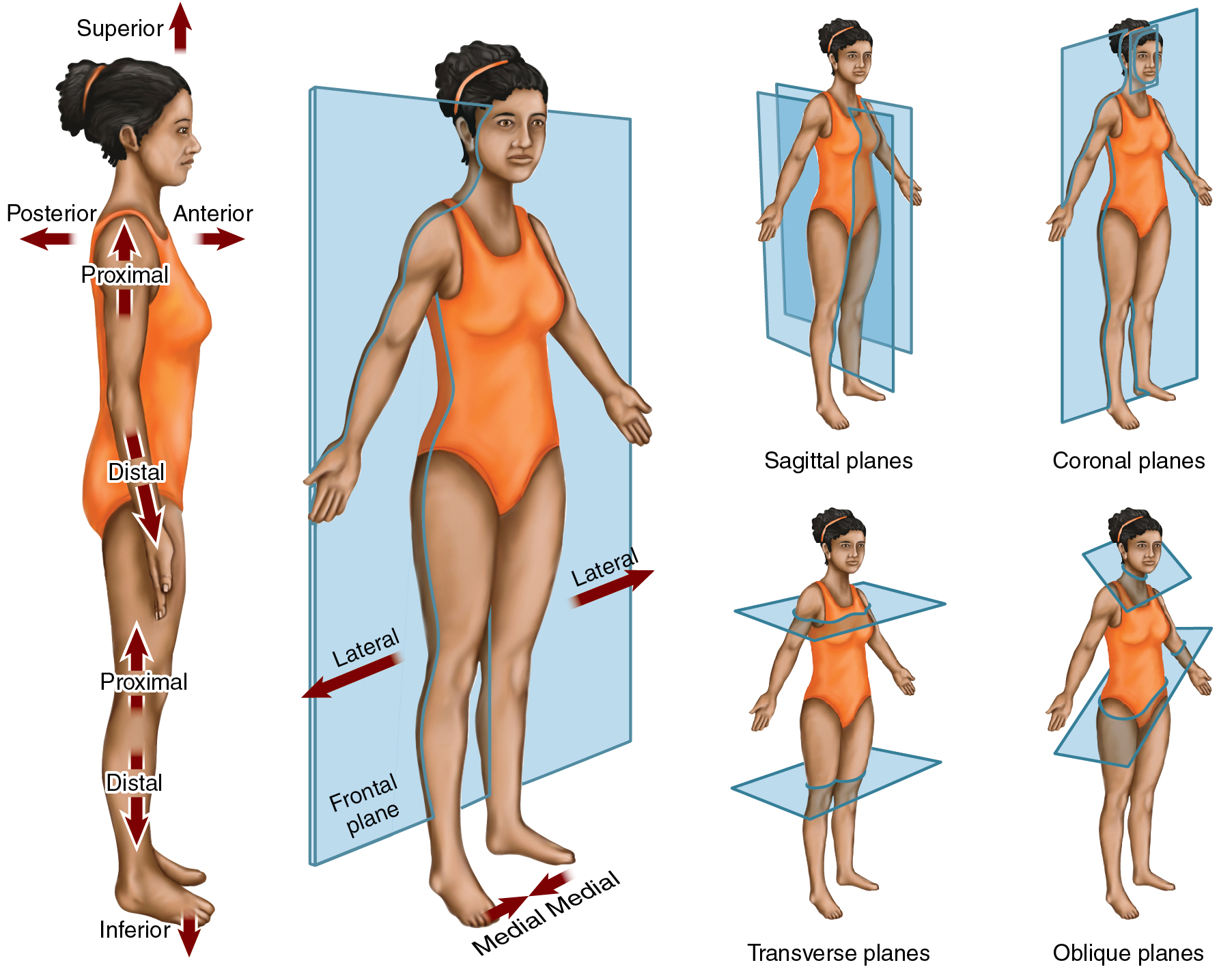
TERMS | MEANING | EXAMPLE |
Superior | toward the head upper; above | lungs are located superior to the diaphragm |
Inferior | toward the feet lower; below | stomach is located inferior to the diaphragm |
Anterior | in front of ventral | nose is on the anterior surface of the body |
Posterior | in back of dorsal | the shoulder blades are on the body’s posterior surface |
Medial | toward the midline of the body | the heart lies medial to the lungs |
Lateral | toward the side of the body; away from its midline | the lungs lie lateral to the heart |
Proximal | toward or nearest the trunk of the body, or nearest the point of origin of one of its parts | the elbow lies at the proximal end of the forearm |
Distal | away from or furthest from the trunk or the point of origin of a body part | the hand lies at the forearm’s distal end |
Superficial | nearer the surface | the skin of the arm is superficial to the muscles below it |
Deep | further away from the body surface | the bone of the upper part of the arm is deep to the muscles that surround and cover it |
Terms related to organs
Lumen — the hollow area of organs.
Luminal — of or near the lumen.
Luminal Obstruction — blockage of the respiratory airway.
Central — near the centre.
the central nervous system
Peripheral — around the boundary.
the peripheral nervous system
Medullary — an inner region or core of an organ.
medulla is the inner region of the kidney.
Cortical — an outer region or layer of an organ.
cortex is the other part of the kidney
Basal — the base or widest part of an organ.
the basal surface of the cell faces away from the lumen.
Apical — the narrow tip of an organ.
the apical surface faces the lumen of a hollow organ.
Anatomical Compass Rosette
A = Anterior | P (opposite A) = Posterior |
D = Distal | P (opposite D) = Proximal |
I = Inferior | S = Superior |
L (opposite M) = Lateral | M = Medial |
L (opposite R) = Left | R = Right |
Body planes and sections
PLANES | DESCRIPTION | SECTION |
Sagittal Planes | any lengthwise plane running from front to back and top to bottom, dividing the body or any of its parts into right and left sides | sagittal section — a flat cut made along a sagittal plane.
|
Coronal Planes (Frontal Plane) | any lengthwise plane running from side to side and top to bottom, dividing the body or any of its parts into anterior and posterior portions. | coronal/frontal section — a cut made along a coronal plane: |
Transverse Planes (Horizontal Plane) | any crosswise plane that divides the body or any of its parts into upper and lower parts. | transverse/horizontal section — a cut along any transverse plane of the body; |
Other planes and sections | cross section — a cut along a plane parallel with the short axis of an organ | |
longitudinal section — a cut along the long axis of an organ | ||
oblique section — diagonal cuts. |
Interaction of structure and function
Complementarity of structure and function
Structure determines function, and function influences the actual anatomy of an organism over time.
Anatomical structures are adapted to perform specific functions because of their unique size, shape, form, or body location.
Understanding the interaction of structure and function assists in the integration of otherwise isolated factual information.
Atrophy — the wasting away of a part of the body as we age.
reduce our ability to repair or replace worn tissues.
Developmental Processes — the changes in functions that occur during the early years.
Ageing processes — the changes the occur during the late years of life.
Gerontology — the study of ageing processes and other changes that occur in our lives as we get older.