PP3 Prelims
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Three Basic Legal Forms
Proprietorship
Partnership
Corporation
Proprietorship
owned by one person who has complete undiluted control over its decisions and destiny and personally has a legal and financial responsibility for all of the firm’s actions
Partnership
share both the ownership of the firm and liability for its acts. Each partner is liable for the business actions and obligations of all of the partners.
Corporation
the principals who form the corporation become its employees as such are eligible for employee benefit programs, which are usually the greatest advantage to be derived from incorporation.
Limited liability company/partnership (LLC/LLP).
Hybrid entities that combine the characteristics of a corporation and a partnership or sole proprietorship. Members of the company cannot be help personally liable for the company's debts or liabilities
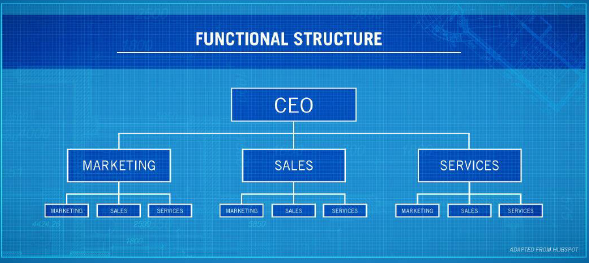
Functional Internal Organization
Separates the various functions which must be performed in the development of a project.
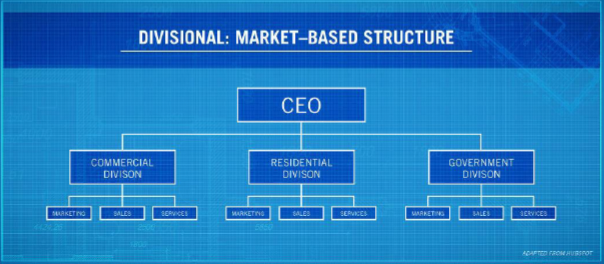
(Market Based) Internal Organization
each division essentially operates as its own company, controlling its own resources and how much money it spends on certain projects or aspects of the division.
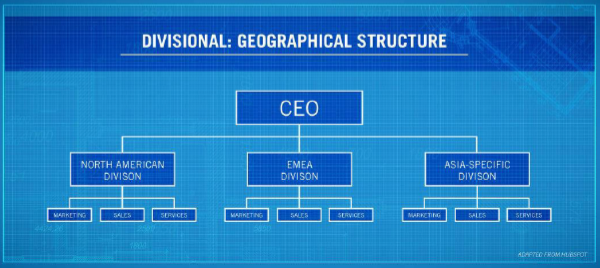
(Geographical) Internal Organization
each division essentially operates as its own company, controlling its own resources and how much money it spends on certain projects or aspects of the division.
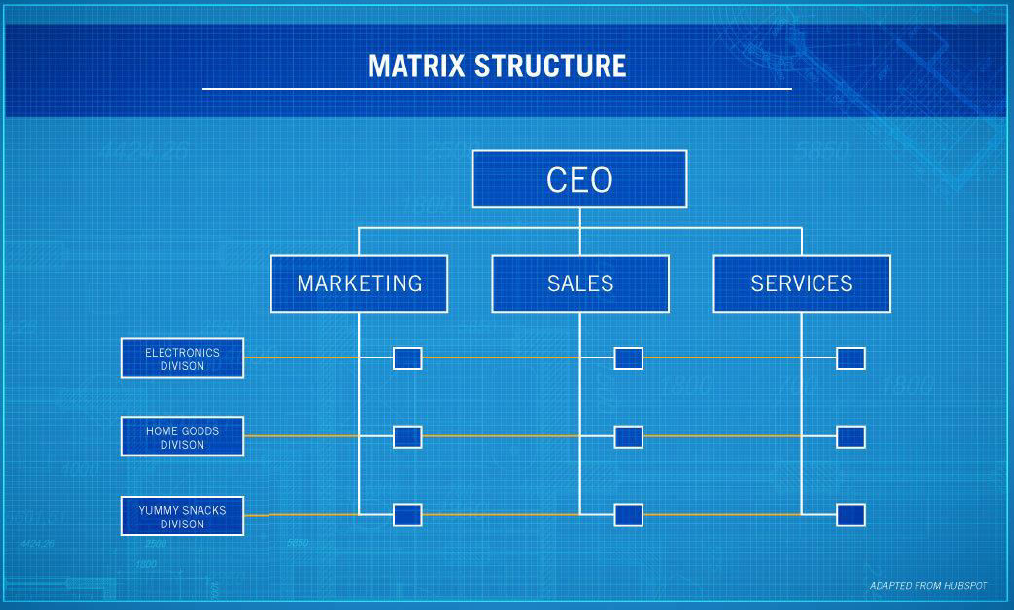
Matrix Internal Organization
A hybrid organizational structure, the matrix structure is a blend of the functional organizational structure and the projectized organizational structure. Advantages of this structure is that employees can share their knowledge across the different functional divisions, allowing for better communication
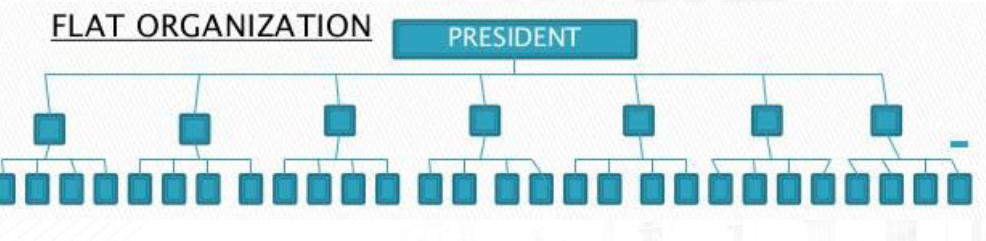
Flat Organization
allows for more decision making among the levels of an organization and, overall, flattens out the vertical appearance of a hierarchy.
Functional structure + Flat structure = flatarchy organizational structure
A management team must be able to accomplish three functions
Execute the business plan
Identify fundamental changes
Make adjustments to the plan
business plan
Written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A written plan from a marketing, financial and operational viewpoint
Labor Code of the Philippines
Presidential Decree No. 442
Department of Labor and Employment, DOLE
National government agency mandated to formulate policies, implement programs and serve as the policy coordinating arm of the Executive Branch in the field of labor and employment
National Labor Relations Commission, NLRC
A quasi-judicial body tasked to promote and maintain industrial peace by resolving labor and management disputes. Attached to the Department of Labor and Employment
Employer
A legal entity that controls and directs a worker under express or implied contract of employment and is obligated to pay the employee salary or wages in compensation.
Employee/Worker
An individual who works part-time or full-time under a contract of employment whether express or implied and has recognized rights and duties.
Employment Contract
An express or implied agreement specifying terms and conditions under which a person consents to perform duties controlled by an employer in return for an agreed upon salary.
Minimum Wage
Lowest Hourly rate an employer can pay and employee as mandated by law.
Minimum wage NCR (2021)
Php 537/day
Monthly Income = Php 537×20 = 10,740
Normal Hours of Work
The normal hours of work of an Employee shall not exceed eight (8) hours a day.
Night Shift Differential
Shall apply to work performed between 10pm to 6am.
Overtime
Work done by an employee beyond the normal hours of work.
Holidays
2x regular rate.
Termination of Employment
Termination by Employer.
Closure of Establishment and Reduction of Personnel.
Disease as ground for termination.
Termination by employee.
Retirement.
Termination by Employer
Serious misconduct or willful disobedience
Gross and habitual neglect
Fraud or willful breach by the employee
Commission of a crime or offense by the employee
Closure of Establishment and Reduction of Personnel
Installation labor-saving devices
Retrenchment to prevent losses or the closing or cessation of operation of the establishment
Disease as ground for termination
An employer may terminate the services of an employee who has been found to be suffering from any disease and whose continued employment is prohibited by law or is prejudicial to his health as well as to the health of his co-employees.
Termination by Employee
An employee may terminate without just cause the employee-employer relationship by serving a written notice on the employer at least one (1) month in advance.
Retirement
Age of sixty (60) years or more, but not beyond sixty-five (65) years which is hereby declared the compulsory retirement age,
Termination Procedure
A written notice served on the employee specifying the ground or grounds for termination. Gives employee chance to explain his side
A hearing or conference, the employee concerned, with the assistance of counsel if he so desires is given opportunity to respond to the charge, present his
evidence, or rebut the evidence presented against him.
A written notice of termination served on the employee, indicating that upon due consideration of all the circumstances, grounds have been established to justify his termination.
COLA
Cost of Living Allowance
Overtime pay
additional pay for work performed in excess of 8 hours a day.
13th Month Pay
shall at least be 1/12 of the total basic salary earned for the year by any rank - and - file employee. It should be given to t he employees not later than December 24 of every year.
retirement pay
the amount given an employee who has reached the age of 60 years for optional retirement and 65 years old for compulsory and who has served the company for at least 5 years in the service.
retirement benefits computation
Minimum retirement pay = 22.5 days x daily rate x number of years of service.
Bureau of Internal Revenue, BIR
National government agency mandated to formulate policies, implement programs and serve as the policy-coordinating arm tasked to collect taxes from the Filipino People
Gross Income
All wealth which flows into the taxpayer other than as a mere return of capital. All income derived from whatever source
Taxable Income
Gross Income less the allowable deductions
Income Tax
tax on a person's income, emoluments, profits arising from property, practice of profession, conduct of trade or business
Gross Income
totaly salary a person earns before taxes
amount an individal or business makes before deductions
Net income
amount an individual or business makes after costs and deduction
take-home income a person earns after taxes
Persons required to File Income Tax Returns
Resident citizens receiving income from sources within or outside the Philippines
Non-resident citizens receiving income from sources within the Philippines
Aliens, whether resident or not, receiving income from sources within the Philippines
Basic Personal Expenses
a mandatory deduction allowed to individual citizens in the Philippines regardless of status at the amount of 50,000.00Php
Additional personal exemptions
a mandatory deduction of 25,000Php for each qualified dependent child up to a maximum of 4 children with a maximum amount of 100,000Php
Withholding Tax on Compensation
Tax withheld from individuals receiving purely compensation income.
Companies required to File Income Tax Returns
Corporation shall include partnerships, no matter how created or organized.
Domestic corporations receiving income from sources within and outside the Philippines
Foreign corporations receiving income from sources within the Philippines
Estates and trusts engaged in trade or business
Corporate Tax Rate
both for domestic and resident foreign corporations is 30% based on net taxable income. Prepared by Certified Public Accountants
Pag-IBIG (PD 1530)
Pagtutulungan sa Kinabukasas: Ikaw, Bangko, Industria, at Gobyerno
Pag-IBIG
an answer to the need for a national savings program and an affordable shelter financing for the Filipino worker
Two (2) modes of applying for a Pag-IBIG housing loan
Developer-Assisted - the developer assists the member in his/her housing loan application;
Retail - the member applies directly to the Fund.
Developer-Assisted
the developer assists the member in his/her housing loan application;
Retail
the member applies directly to the Fund.
Housing loan program grants opportunities to Pag-IBIG Fund members to avail of housing loans:
Purchase of a fully developed lot not exceeding 1,000 square meters,
Purchase of a residential house and lot, townhouse or condominium unit, inclusive of a parking slot;
Construction or completion of a residential unit on a lot owned by the member;
Home improvement, i.e. any alteration in an existing residential unit intended by a homeowner
Refinancing of an existing mortgage with an institution acceptable to the Fund.
SSS
Social Security System
SSS
To provide meaningful protection to members and their beneficiaries against the hazards of disability, sickness, maternity, old age, death, and other contingencies resulting in loss of income or financial burden.
Sickness Benefit (SSS Benefit)
a daily cash allowance paid for the number of days a member is unable to work due to sickness or injury
Maternity Benefit (SSS Benefit)
daily cash allowance granted to a female member who was unable to work due to childbirth or miscarriage.
Retirement Benefit (SSS Benefit)
a cash benefit either in monthly pension or lump sum paid to a member who can no longer work due to old age.
Disability Benefit (SSS Benefit)
takes into account the medical management of illnesses and injuries and their corresponding impairment ratings
Death Benefit (SSS Benefit)
a cash benefit either in monthly pension or lump sum paid to the beneficiaries of a deceased member
Funeral Benefit (SSS Benefit)
a cash benefit given to whoever pays the burial expenses of the deceased member or pensioner.
PhilHealth
established to provide health insurance coverage and ensure affordable, acceptable, available and accessible health care services for all citizens of the Philippines
Members in the Formal Economy
This member category includes those with formal contracts and fixed terms of employment including workers in the government and private sector, whose premium contribution payments are equally shared by the employee and the employer.
Members in the Informal Economy
This member category includes a wide range of individuals and sectors ranging from the self-earning to migrant workers.
Indigent Members
persons who have no visible means of income, or whose income is insufficient for family subsistence
Sponsored Members
This category includes members whose contributions are being paid for by another individual, government agencies, or private entities
Lifetime Members
This category is for members who have reached the age of retirement under the law and have paid at least 120 monthly premium contributions.
Senior Citizens
This category is for those who are 60 years old and above and are not currently covered by any of the existing membership categories of PhilHealth.
PhilHealth Premium Contribution
PhP200.00 to PhP875.00
Employee share represents half of the total monthly premium while the other half is shouldered by the Employer
GSIS
Government Service Insurance System
GSIS
A government-owned and controlled corporation (GOCC) of the Philippines.
Created by Commonwealth Act
No. 186 and Republic Act No.
8291 (GSIS Act of 1997)
GSIS members
entitled to various social security benefits, such as life insurance, separation or retirement, and disability benefits.
Civil Code
the product of the codification of private law in the Philippines.
it ensures that every person shall respect the dignity, personality, privacy and peace of mind of his neighbors and other persons
establishes the difference between public law and private law
Preliminary Title (The Civil Code Sum of Parts)
States the title, effects and applications of law
Book I: Persons & Family Relations (The Civil Code Sum of Parts)
Persons, marriage and conjugal rights, legal separations and annulments, and other family obligations by relation
Book II: Property & Property Rights (The Civil Code Sum of Parts)
Classes of property and terms of possession (items)
Book III: Ownership (The Civil Code Sum of Parts)
Servitude, modes of acquiring ownership & succession/ inheritance laws
Book IV: Obligations & Contracts (The Civil Code Sum of Parts)
Laws and nature of obligations held to by written contracts and supporting documents
The engineer or architect who drew up the plans and specifications for a building is liable for damages if within [BLANK] from the completion of the structure,
fifteen years
INTELECTUAL PROPERTY CODE OF THE PHILIPPINES
Republic Act No. 8293
Ownership of Copyright
copyright shall belong to the author of the work
case of works of joint authorship (Ownership of Copyright)
coauthors shall be the original owners of the copyrighT
a work of joint authorship consists of parts that can be used separately (Ownership of Copyright)
the author of each part shall be the original owner of the copyright in the part that he has created;
(Ownership of Copyright)
In the case of work created by an author during and in the course of his employment, the copyright shall belong to:
The employee, if the creation of the object of copyright is not a part of his regular duties even if the employee uses the time, facilities and materials of the employer
The employer, if the work is the result of the performance of his regularly-assigned duties, unless there is an agreement, expressed or implied, to the contrary
a work commissioned by a person (Ownership of Copyright)
the person who so commissioned the work shall have ownership of the work, but the copyright thereto shall remain with the creator
RA 61111
PHILIPPINE MEDICAL CARE PLAN