ID1 Exam 1
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Before antimicrobials what was the main killer of the human race?
Infectious diseases
What is the rate of death due to infectious diseases today?
1/2
What are the 3 characteristics used to describe the world of microorganisms?
Unseen, undiscovered, dominant
Rank the sizes of the following from largest to smallest: viruses, bacteria, human cells, protozoa
Protozoa > human cells > bacteria > viruses
What are some reasons that bacteria are the dominant life form on Earth?
Live in every biosphere, most diverse organisms, influence evolution, great in numbers, began life, and have many life sustaining functions such as O2 production and nutrient cycling
Why is it difficult to culture species of bacteria?
Many species are codependent on each other with many consuming the excretions of others as food sources
SATA In what way can bacteria be considered the dominant form of life on Earth?
Bacteria are composed of eukaryotic cells
Bacteria are the most abundant organisms on Earth
Bacterial activity has influences the evolution of other organisms
Bacteria inhabit all parts of the biosphere
Bacteria demonstrate the greatest species diversity
2,3,4,5
What are the nonliving microbials to focus on in this class
Prions, viruses
What is the genetic code for prions?
Proteins
What is the genetic code for viruses?
DNA or RNA
How do we classify bacteria?
Thickness of cell walls as determined by gram staining
What type of gram stain does a thin wall bacteria lead to?
Gram -
What type of gram stain does a thick wall bacteria lead to?
Gram +
What are the 4 eukaryotic kingdoms that microbes exist in?
Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animale
How are protists classified?
Photosynthesizing (protozoa), non-photosynthesizing
Define magnification
Ratio of the size of an image to the size of an object
What is used to achieve magnification of specimens?
Series of lenses
How is total magnification calculated based on the lenses?
Total magnification = Magnification of each of the lenses multiplied by each other
100x= (10x)*(10x)
How is magnification calculated based on relative sizes?
Magnification = image size/actual size
(220mm/2.3mm=9.6x)
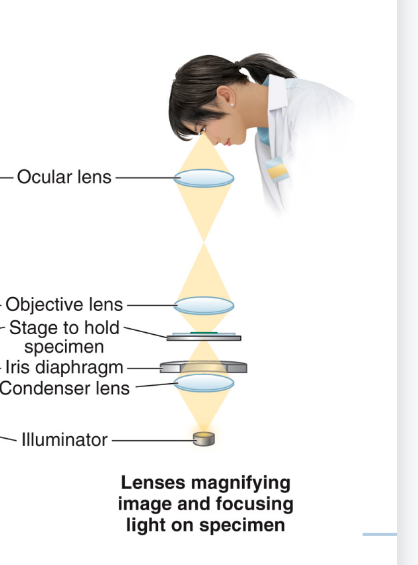
What type of microscope is this displaying?
Bright light microscope
Define resolution
the degree to which is microscope is able to produce separate images of lines that are very close together; a measure of the sharpness of an image
How is resolving power calculated?
l/(2*NA) [l= wavelength of light, NA= numerical aperture of lens]
Define numerical aperture
A measure of light refraction, proportional to the refractive index of the medium in which light is traveling in
True or false. Light with a greater wavelength would produce a greater resolution of an image.
False. l/(2*NA)
How can the numerical aperture be increased
Using immersion oil as it has a greater refractive index than are which limits the refraction of light, improving the resolution
SATA Which of the following influences the resolving power of a microscope?
The wavelength of light
The refractive index of the medium through which the light is traveling
The numerical aperture of the lens
The intensity of light
1,2,3
What are some disadvantages to bright-field miscropy?
Limitations on magnification and resolution, thin prep of specimen, staining is often required to improve contrast
What is bright-field microscopy used for?
Examining bacterial morphology or external structures or identifying eukaryotic pathogens and gram identification
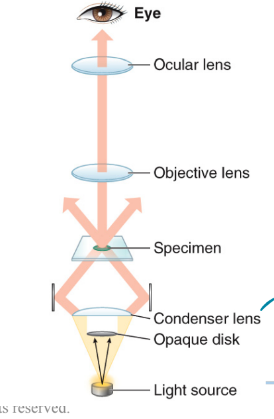
What type of microscope is this?
Dark-field microscopy
What are some advantages to dark-field miscroscopy?
No staining required, able to visualize live and very thin organisms
How does dark-field microscopy work?
Light comes at an angle around an opaque disk which is reflected through condenser lenses and into the objective lens, making the image appear light
What are some advantages to fluorescence microscopy?
Fluorescent molecules can be made to only bind to specific proteins, highlights items too small to see
What is an example of a clinical application of fluorescence microscopy?
Identification of neurons infected with rabies virus
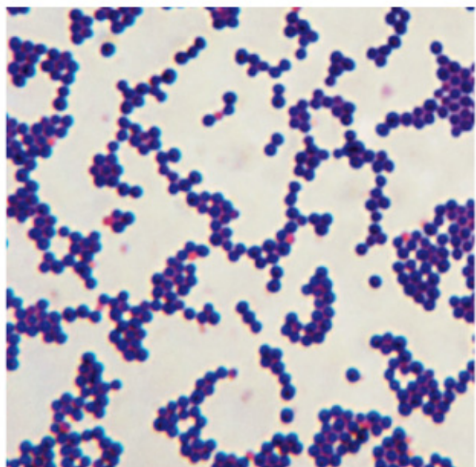
What type of microscope was used to view this image?
Bright-field microscope
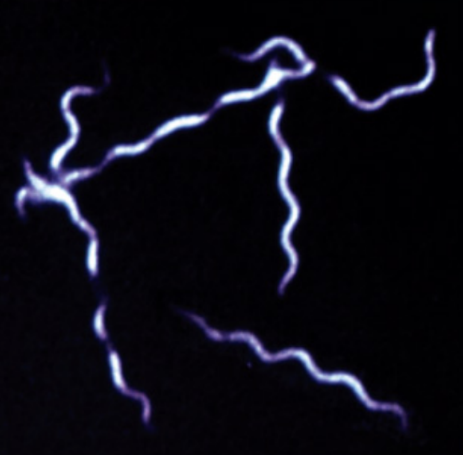
What type of microscope was used to capture this image?
Dark-field microscope
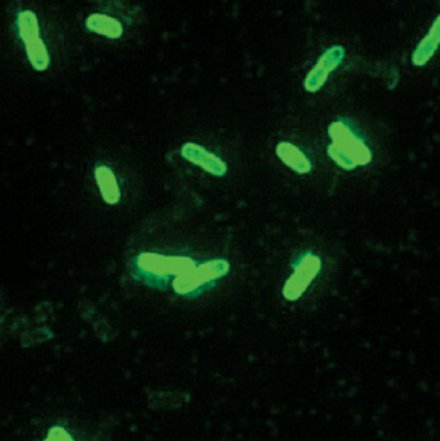
What type of microscope was used to capture this image?
Fluorescence microscope
Define smear for light microscopy
A suspension of a bacterial sample is spread on a slide with an inoculating loop then air dried
Define fixation for light microscopy
Process of adhering bacterial cells to a slide by coagulating carbohydrates and proteins to glass surface via heat or chemical methods
Describe a basic (pH) stain
Stain is positively charged at a neutral pH and binds to negatively charged proteins in addition to DNA
Describe acidic stains
Negatively charged at neutral pH, since bacterial surfaces tend to be negatively charged, the stain is repelled leaving a stained background and the cells themselves unstained (negative staining)`
Describe a differential stain
Use of multiple des to allow for differentiation of one microbe to another such as gram staining
What is the order of dyes and solutions used for gram staining?
Crystal violet, gram’s iodine, ethanol, safranin
What does crystal violet do?
Stain all bacterial cells with peptidoglycan in their walls
What does gram’s iodine do?
Interacts with crystal violet to form insoluble complexes
What does ethanol do in gram staining?
Decolorizes the stain, removing violet-iodine complexes from the bacteria with thin layers of peptidoglycan
What is safranin’s purpose?
Counterstain that colors the DNA of all the cells so they’ll appear red or purple
If a bacterium has a thick cell wall, what will the result of gram staining be? (color and + / -)
Purple, Gram +
What does it mean if a bacterium is red or pink after gram staining?
The bacterium has a thin cell wall, gram -
The _____ in a Gram stain removes the _____ from _____ cells.
EtOH; crystal violet and iodine; gram negative
EtOH; crystal violet and iodine; gram positive
iodine; crystal violet; gram negative
iodine; crystal violet; gram positive
safranin; iodine; gram negative
1
Describe acid-fast staining and how it’s used as a diagnostic tool
Process where red fuchsin is applied and heat is applied to drive the stain through specimens with a waxy wall then rinsed with an acid alcohol decolorizer, then methylene blue is applied for better visualization. This is used to diagnose diseases such as TB and leprosy where the bacteria have a thick, waxy wall
Define endospore
Resistant asexual spores that develop inside some bacteria which can help in identification and diagnosis of certain species
What type of stain is capsule staining?
Negative stain
Why would we stain flagella?
Too thin to see with a light microscope so staining helps with visualization
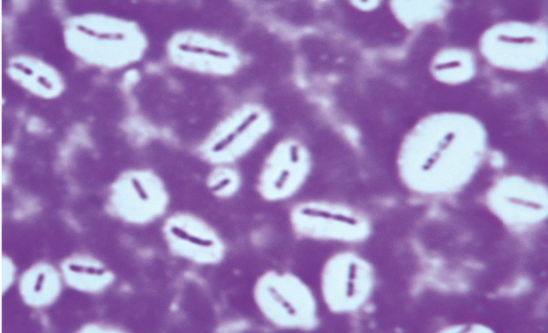
What type of stain is this?
Capsule stain
Acid fast stain
Endospore stain
Dark field microscopy
1
What are common features of prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Macromolecular structure, DNA as genetic information, DNA → RNA → protein, ATP as energy, cell membrane provides structure and function, glycolysis is the energy-yielding pathway
How is genetic information stored in a prokaryote?
In a circular chromosome or in one nucleoid
What is the difference between an 80S ribosome and a 70S ribosome?
70 S has no space between ribosome components and is present in prokaryotes, 80S is present in eukaryotes and has a gap
What is the cell wall of a prokaryote made of?
Peptidoglycan
How do prokaryotes divide?
Binary fission
SATA The key feature shared by all prokaryotic cells include
80S ribosome
True membrane-bound organelles
Replication via binary fission
Structurally complex cell wall
3,4
A _____ cell has _____ but lacks _____
Prokaryotic; a single circular chromosome; a nucleus
Eukaryotic; multiple linear chromosomes; 80S ribosomes
Prokaryotic; a complex cell wall; a cell membrane
Eukaryotic; many complex membrane-bound organelles; the ability to divide by mitosis
1
SATA How do prokaryotes help to sustain life on Earth?
Photosynthetic prokaryotes produce glucose and oxygen gas used by all other aerobic organisms
Only prokaryotes can perform nitrogen fixation
CH4 generating bacteria live within roots of legumes and other plants
Prokaryotes live in symbiotic relationships in stomachs of grazing animals to give them nutrients from plant material
1,2,4
What determines the shape of a bacterium?
Cell wall
What does a bacillus shaped bacterium look like?
Rod
What does a vibrio shaped bacterium look like?
Curved rod
What does a spirillum shaped bacterium look like?
Coil
What does a coccus shaped bacterium look like?
Sphere
What does a spirochete shaped bacterium look like?
Coiled hair (tight curl)
What does diplo- mean?
Double
What does strepto- mean?
Twisted chain
What does staphylo- mean?
Cluster
What does tetrad mean?
Group of four
What does sarcinae mean?
Bundle

Describe the shape and grouping of these bacteria
Staphylococci
Describe the shape and grouping of these bacteria (it’s 8 total spheres in a cube I forgot the picture lol)
Sarcinae cocci
SATA Which of the following are correctly matched?
Coccus: spherical-shaped
Bacillus: rod-shaped
Spirillum: helical-shaped
Spirochete: curved rod
1,2,3
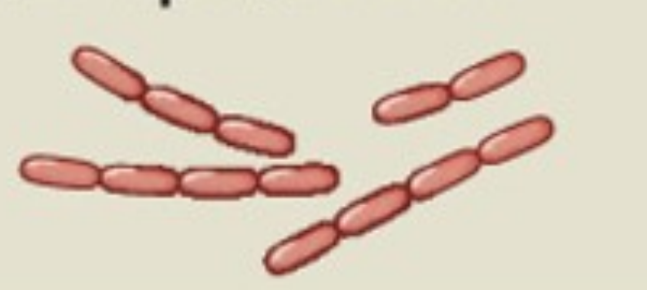
The image shown is a
Streptobacillus
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus
Sarcinae
What were three things that changed from 1900 to now that led to fewer deaths from infectious diseases?
Sanitation, vaccination, antibiotics
What are some unintended consequences of overuse of antibiotics?
Antibiotic resistance, alterations in the microbiome leading to things such as c diff
What is a hallmark sign of infection?
Fever (>100.4F)
What can create a false positive for a fever?
Malignancy, drug fever, blood transfusions, recent surgery
What can create a false negative fever?
Use of antipyretics, antimicrobial therapy, overwhelming infection
What lab value is generally a confirmation of infection?
Elevated white blood cell count (>10,000)
What is a way to zero in on where an infection may be in the body?
Where pain and inflammation is occuring
What should we do before beginning antimicrobial therapy?
Start efforts to identify the pathogen- microscopy, culture, or molecular tests
What is an issue with selecting antimicrobial therapy when it comes to pre-marketing data?
Lack of comparative trials, extremely ill patients were excluded, generally all organisms are susceptible to antibiotics
If a culture is gram postive, how will it appear under a microscope?
Blue
If a culture is gram negative, how will it appear under a microscope?
Red or pink
Define MIC
Lowest concentration of antimicrobial that prevents visible growth performed with a broth dilution
Define MBC
Lowest concentration of antibiotic that kills a bacterium
What are some situations where we should determine an MIC?
Severe infection (especially when the MIC is expected to be low), unusual resistance, uncommon organisms, unexpected treatment failure, usage of a new antibiotic that isn’t normally in a culture panel
Define antibiogram
A chart made to describe susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics for a local population (such as a hospital), used to make empiric decisions to treat infection
What’s an important thing to consider with antibiotics in terms of protein binding?
Only free drug is active
Where do most pathogens typically live if an infection is in tissue?
Extracellular fluid
How does the free drug concentration in the blood compare to the extracellular fluid concentration?
Equal
True or false. Renally eliminated antibiotics can be used to treat UTIs
False
Define bactericidal agent
An agent that kills 99% of the organism within 24 hours
Describe concentration dependent bactericidal activity
A direct relationship between antibiotic concentration and bactericidal effect
Describe time dependent bactericidal activity
Maximum suppression of an organism is achieved as long as antibiotic concentrations remain above the MIC
Define bacteriostatic
An antimicrobial that kills <99% of an organism in 24 hours; kills enough to keep growth in check