The reproductive system
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What are Gamete ?
haploid cell
What Is the Male gamete?
spermatozoa
What is the Female gamete?
oocyte or ovum
What is the Pelvic floor
internal wall of skeletal muscle that separates the pelvic cavity and the perineum
Pelvic roof
formed by parietal peritoneum
Parietal peritoneum
lining of abdominal cavity and firmly attached to walls
Perineum
inferior to pelvic floor, situated between the proximal parts of lower limbs
Peritoneal cavity
space between visceral and parietal cavity
what are the layers of the uterus wall ?
Perimetrium (outer)
Myometrium (middle)
Endometrium (internal
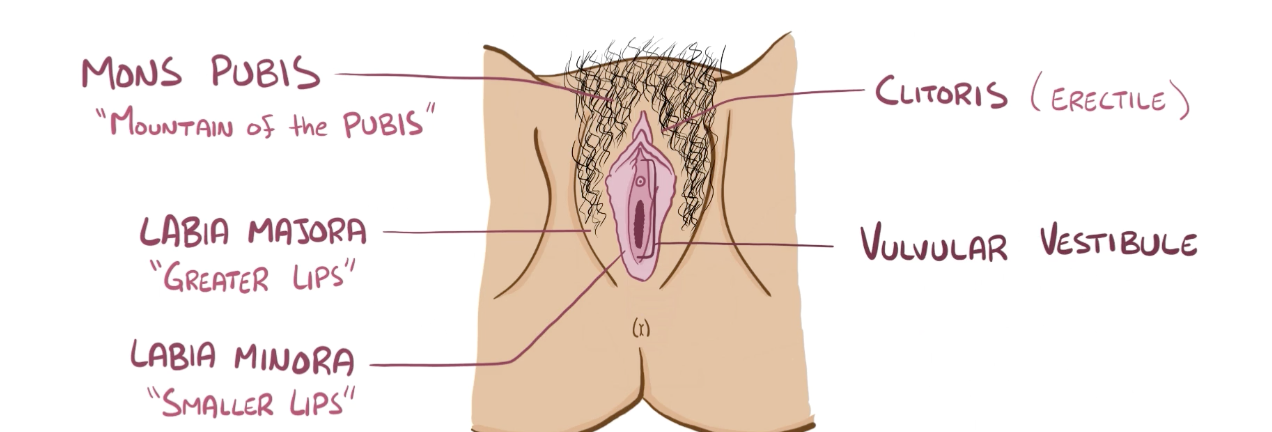
Name the structure in red
Labia majora
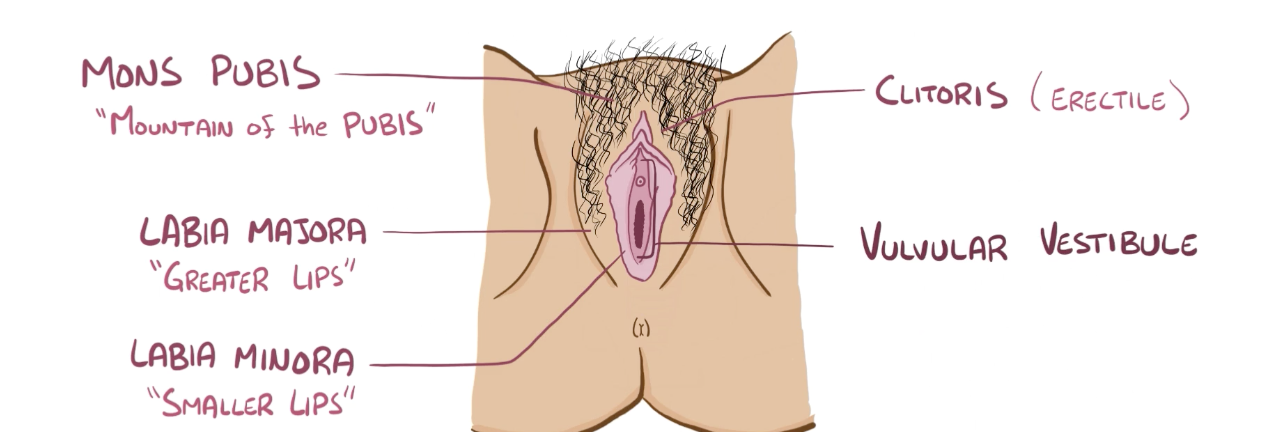
Name the structure in red
Clitoris
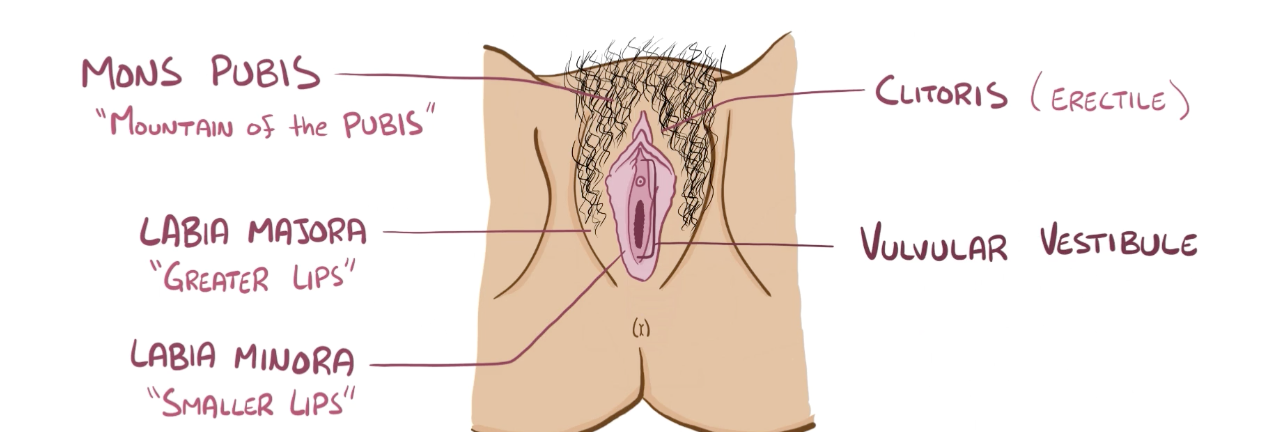
Name the structure in red
Valvular vestibule
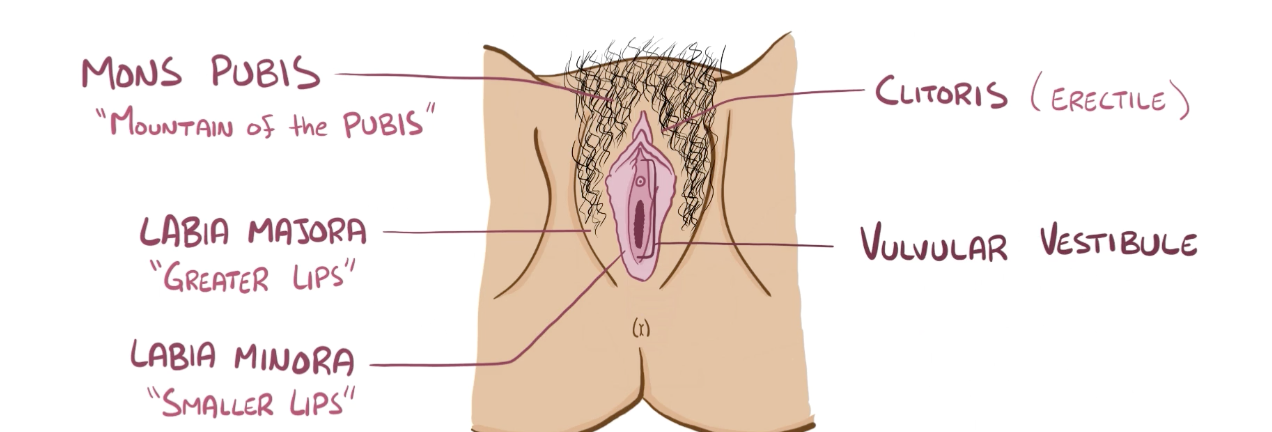
Name the structure in red
Mons pubis
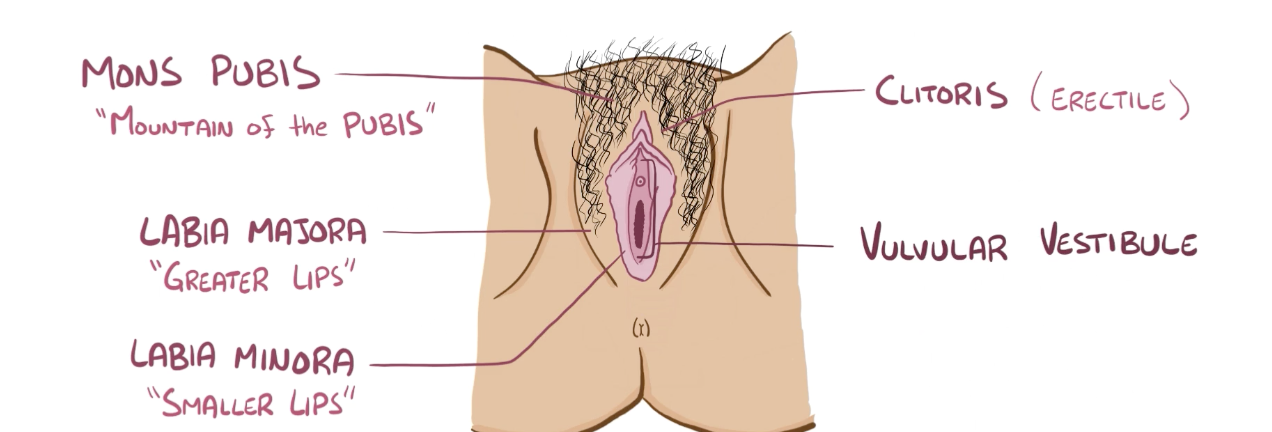
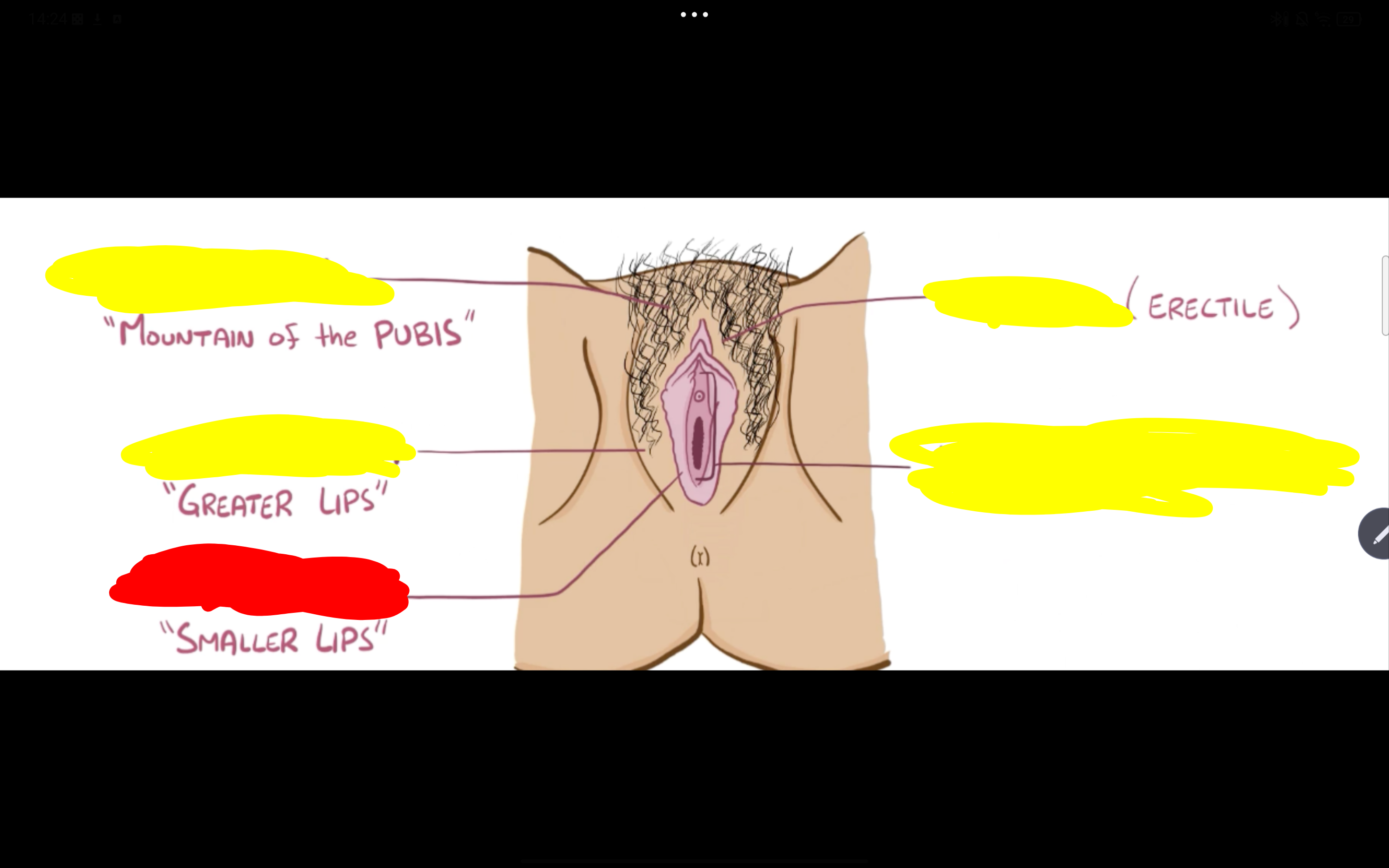
Name the structure in red
Labia minora
Anterflexed
uterus tipped anteriorly relative to the axis of the cervix
Anteverted
cervix tipped anteriorly relative to the axis of the vagina
Rectouterine pouch (of Douglas)
Double folding of the peritoneum between the rectum and the posterior wall of the uterus
Most inferior part of the peritoneal cavity in an upright female patient
Utero-vesicle pouch
Double folding of peritoneum between the anterior surface of the uterus and the bladder
Characteristics of the Ovaries
located laterally in the pelvic cavity
Develops on the posterior abdominal wall and move onto the lateral wall of the pelvis
Secrete oestrogen and progesterone in response to pituitary hormones
What arteries supply the uterus ?
Iliac artery provides blood to the uterus
Ovulation
Ova released from ovaries into peritoneal cavity
Ovum gathered by fimbriae into infundibulum of uterine tube
Ovum moved along uterine tube by cilia until it reaches the uterus
Menstruation
During menstruation, an unfertilised ovum is expelled by contractions of the myometrium
where does Fertilisation usually occurs ?
usually occurs in the ampulla
where does Implantataion usually occurs ?
usually occurs in the body of the uterus
Ectopic pregnancy
fertilised ovum implants outside of the uterine cavity
What are the external organs of the male reproductive system?
Penis
Scrotum→ testes
What are the internal organs of the male reproductive system?
System of ducts→ sperm travels → ejaculation
Accessory sex glands→ vas deferens, prostate gland, seminal glands, penis
Rectrovesical pouch
Double folding of peritoneum located between the rectum and the bladder
It is the lowest part of the peritoneum wall when a patient is
what Is the Development of the testes?
During development, the testis originate on the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity
By birth they have descended into the scrotum through the anterior abdominal wall
Route of Sperm from Testes to Urethra
Seminiferous tubules → rete testis → head of the epidermis → vas deferens
Vas deferens → seminal gland → ejaculatory duct → urethra
what does the Spermatic cord contains?
Vas deferens
Testicular artery
Pampiniform plexus of veins
Pathway for sperm ejaculation
Sperm travel from testes → vas deferens (in spermatic cord).
Spermatic cord passes through anterior abdominal wall to reach pelvic cavity.
Vas deferens joins duct of seminal gland → forms ejaculatory duct.
Right & left ejaculatory ducts unite inside prostate → open into urethra.
Urethra exits body at external urethral meatus (penis).
Torsion of the testis
Twisting of the spermatic cord
Disrupts blood supply - severe pain, danger of necrosis
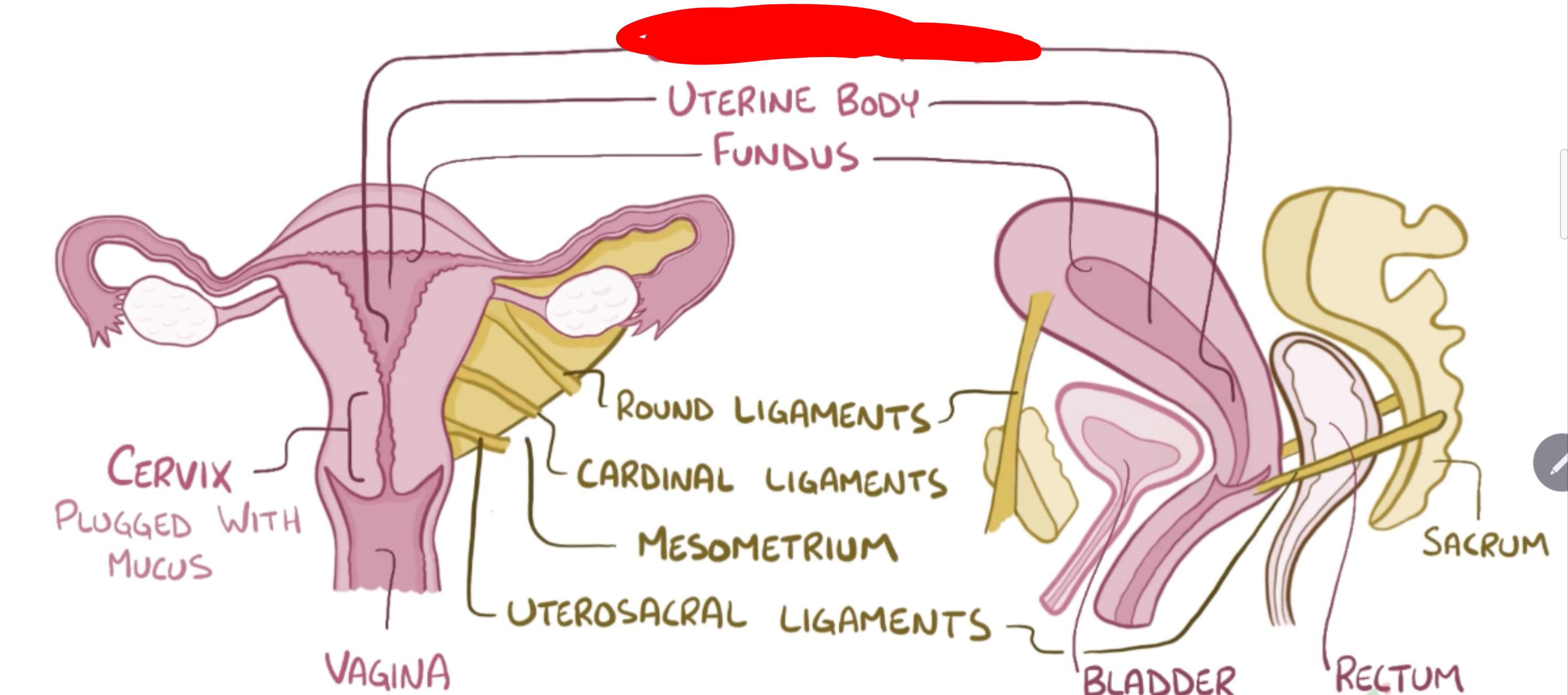
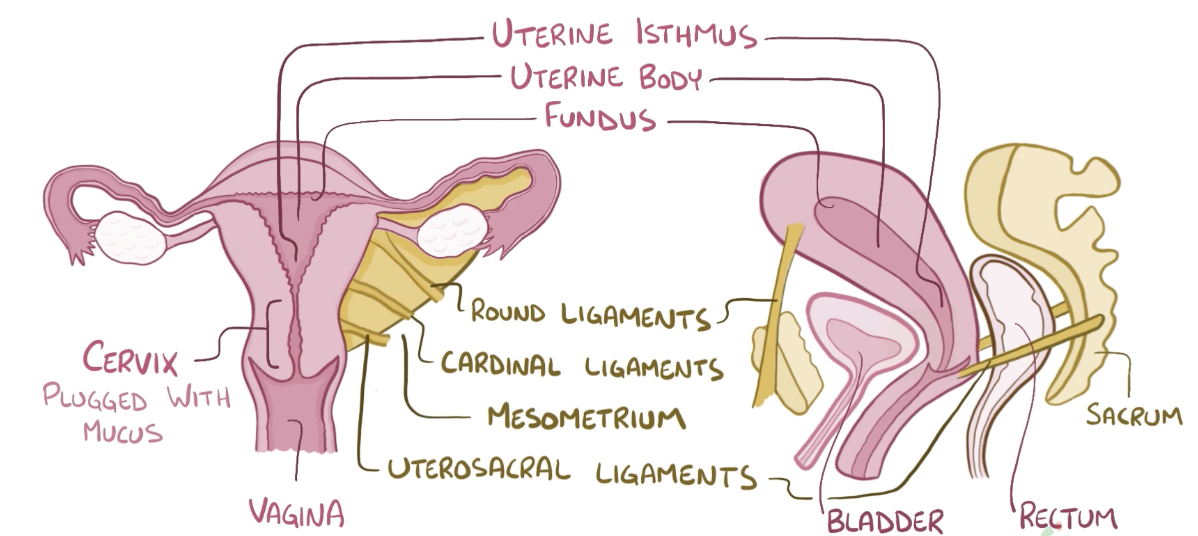
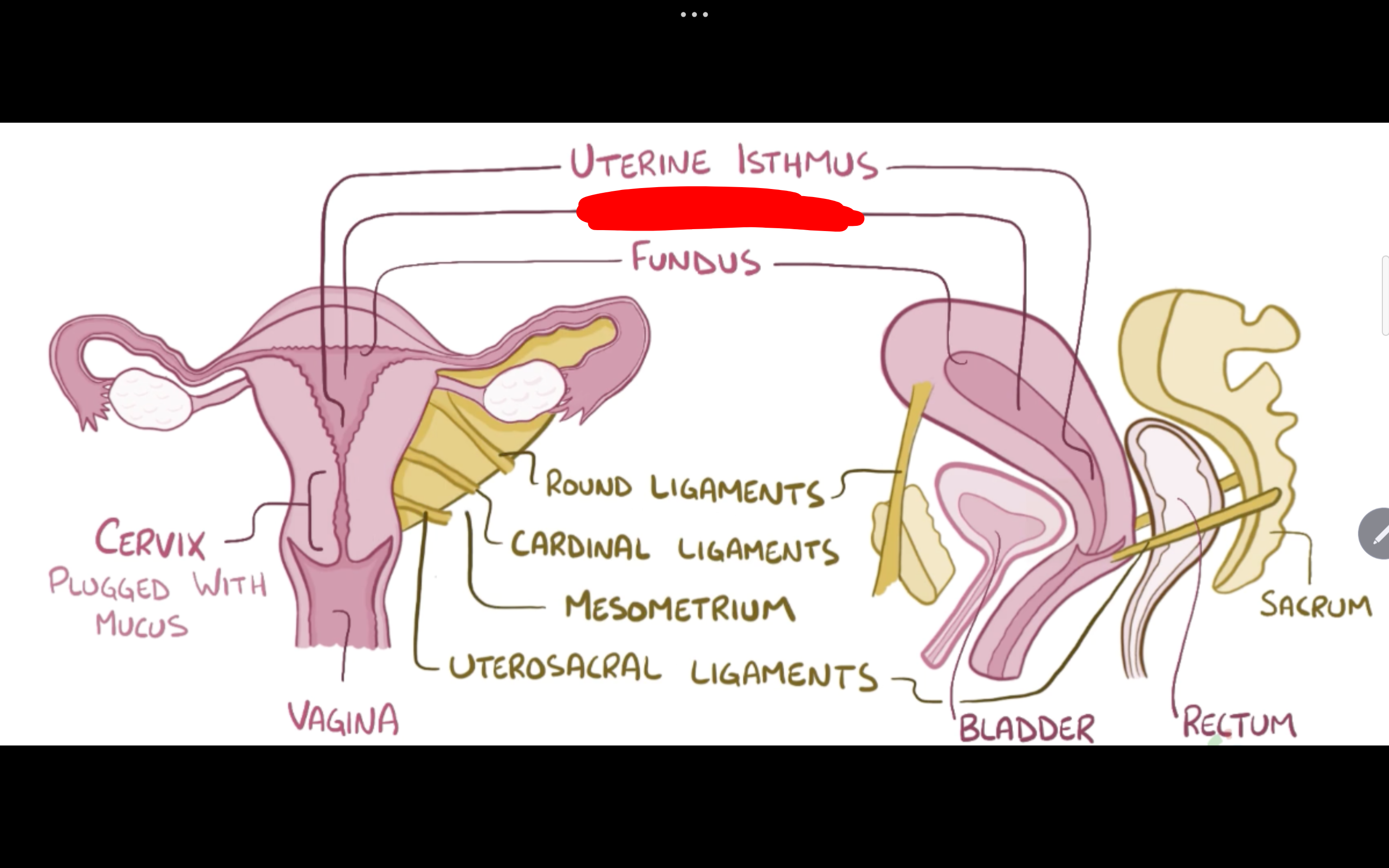
Name the structure in red
Uterine isthmus
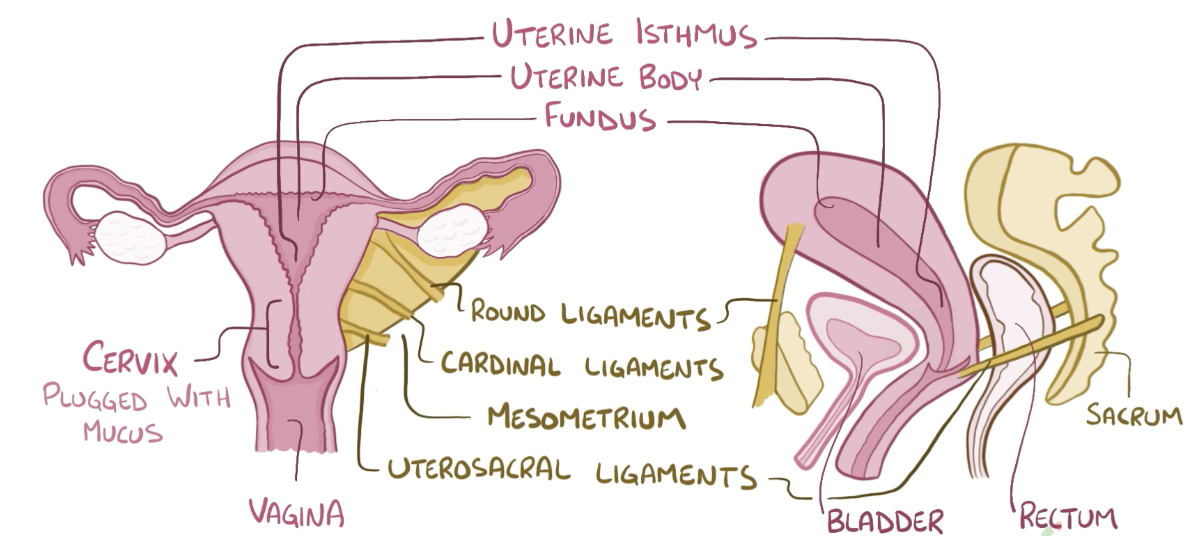
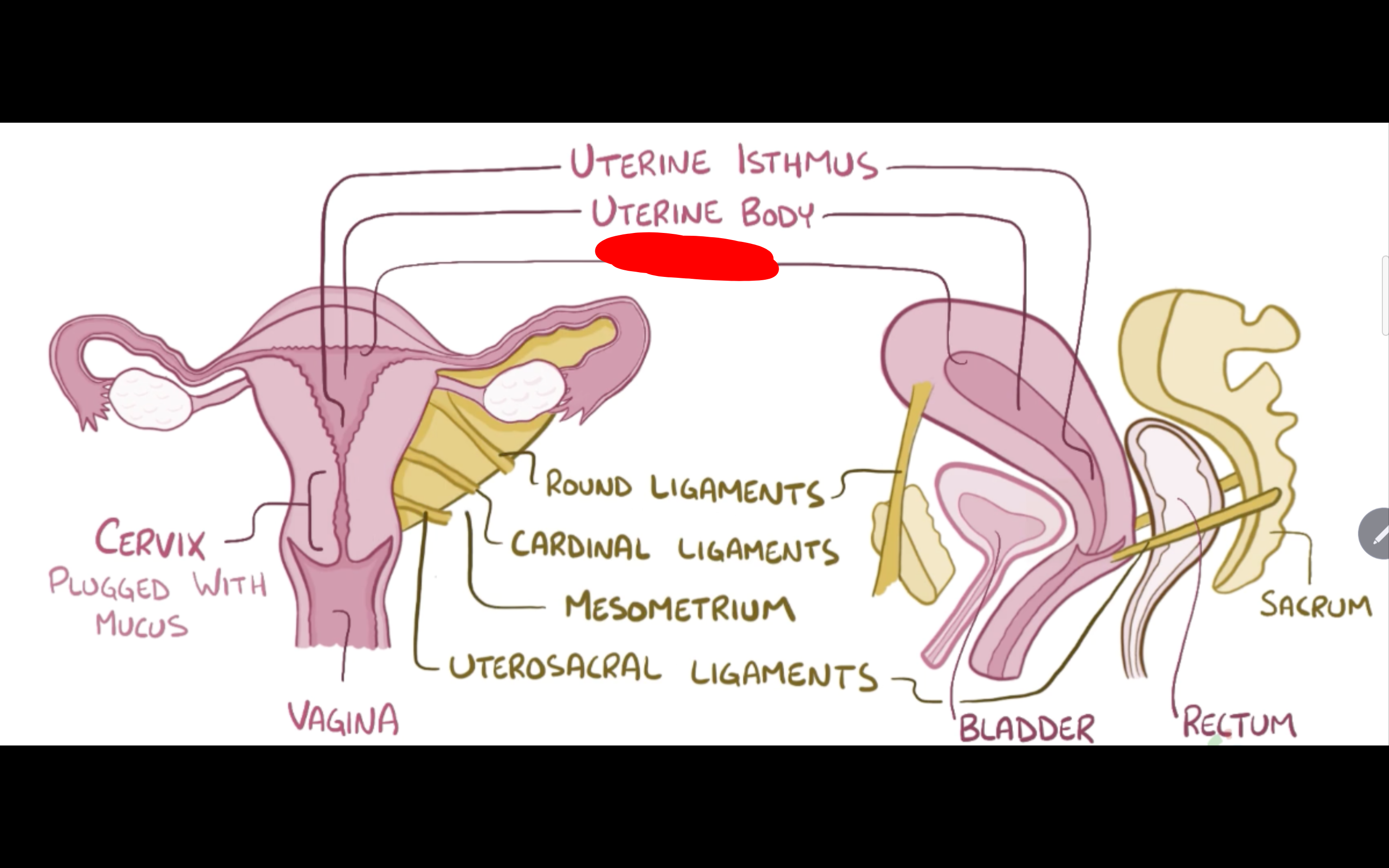
Name the structure in red
Uterine body
Name the structure in red
Fundus
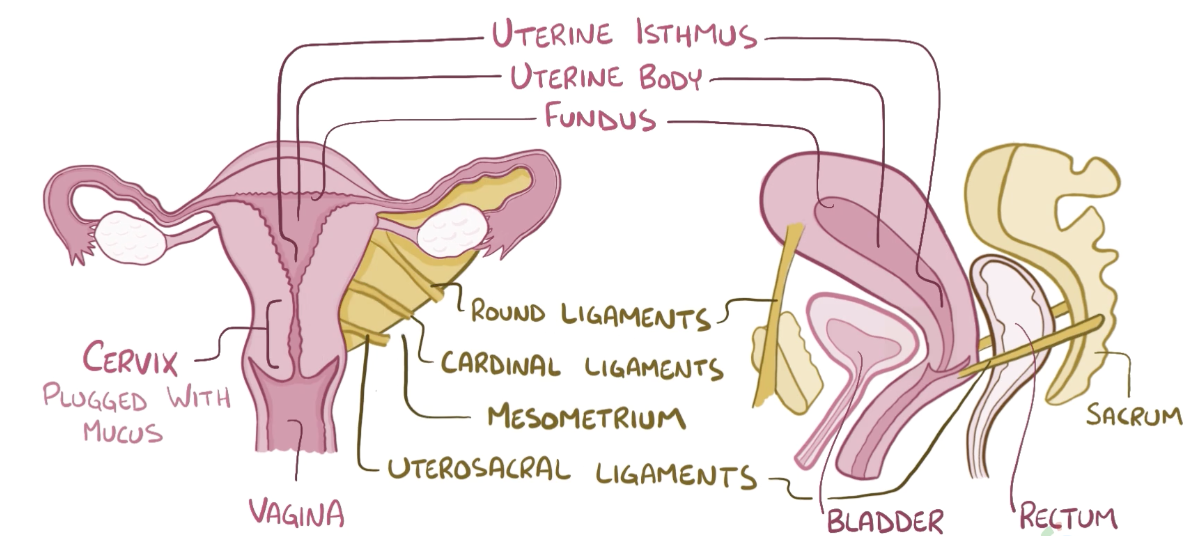
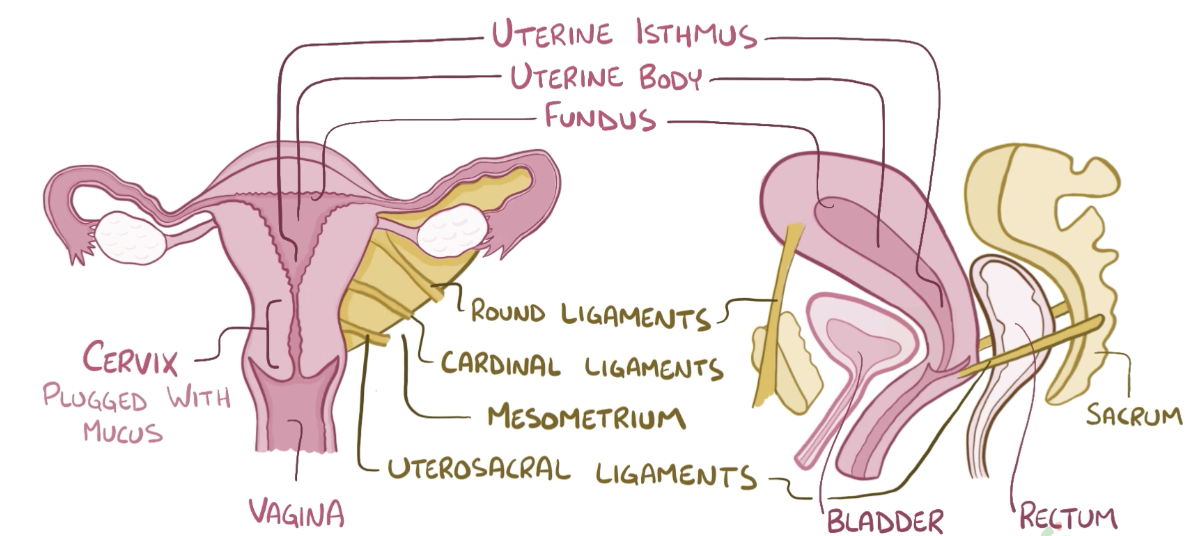
Name the structure in red
Round ligaments
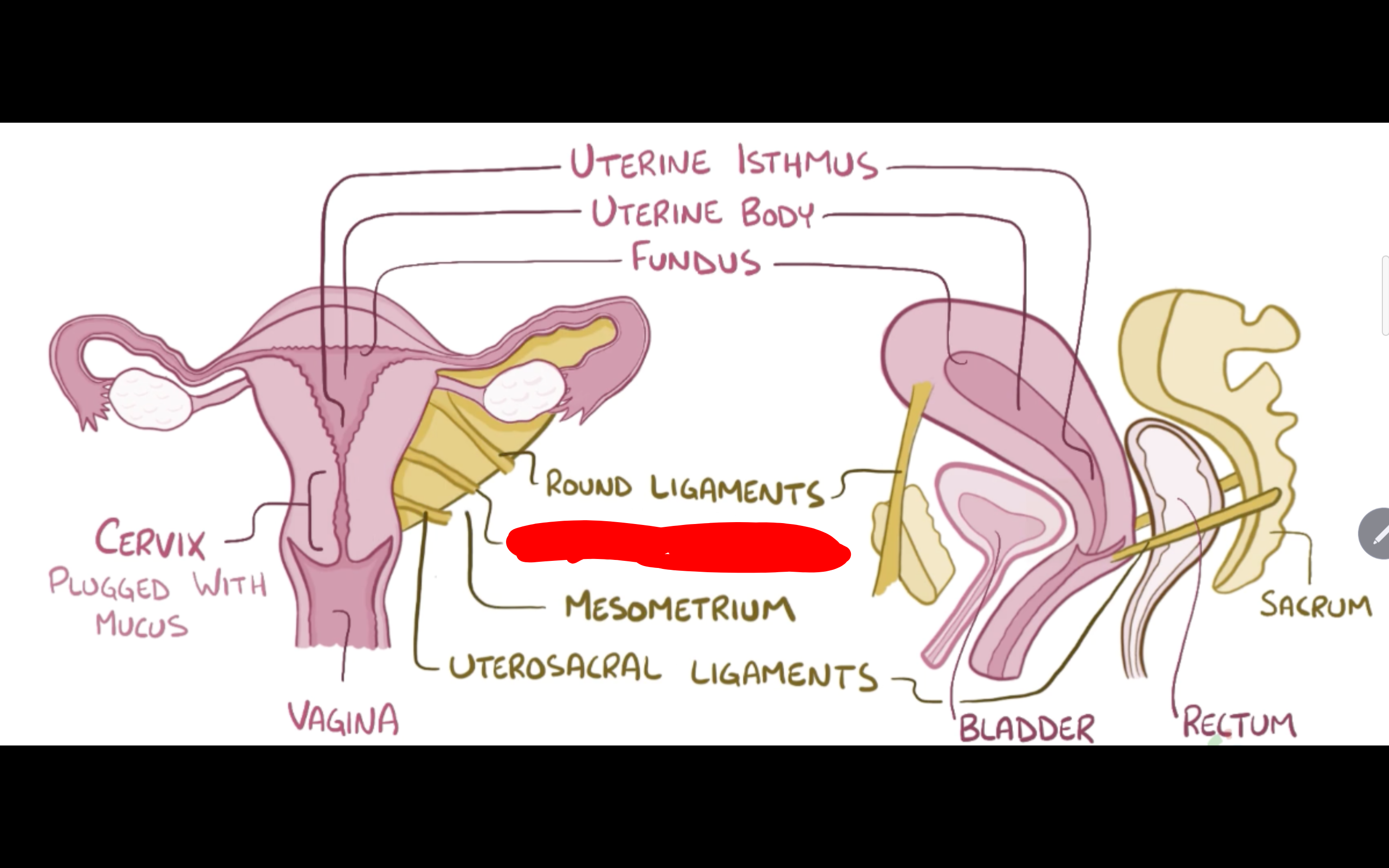
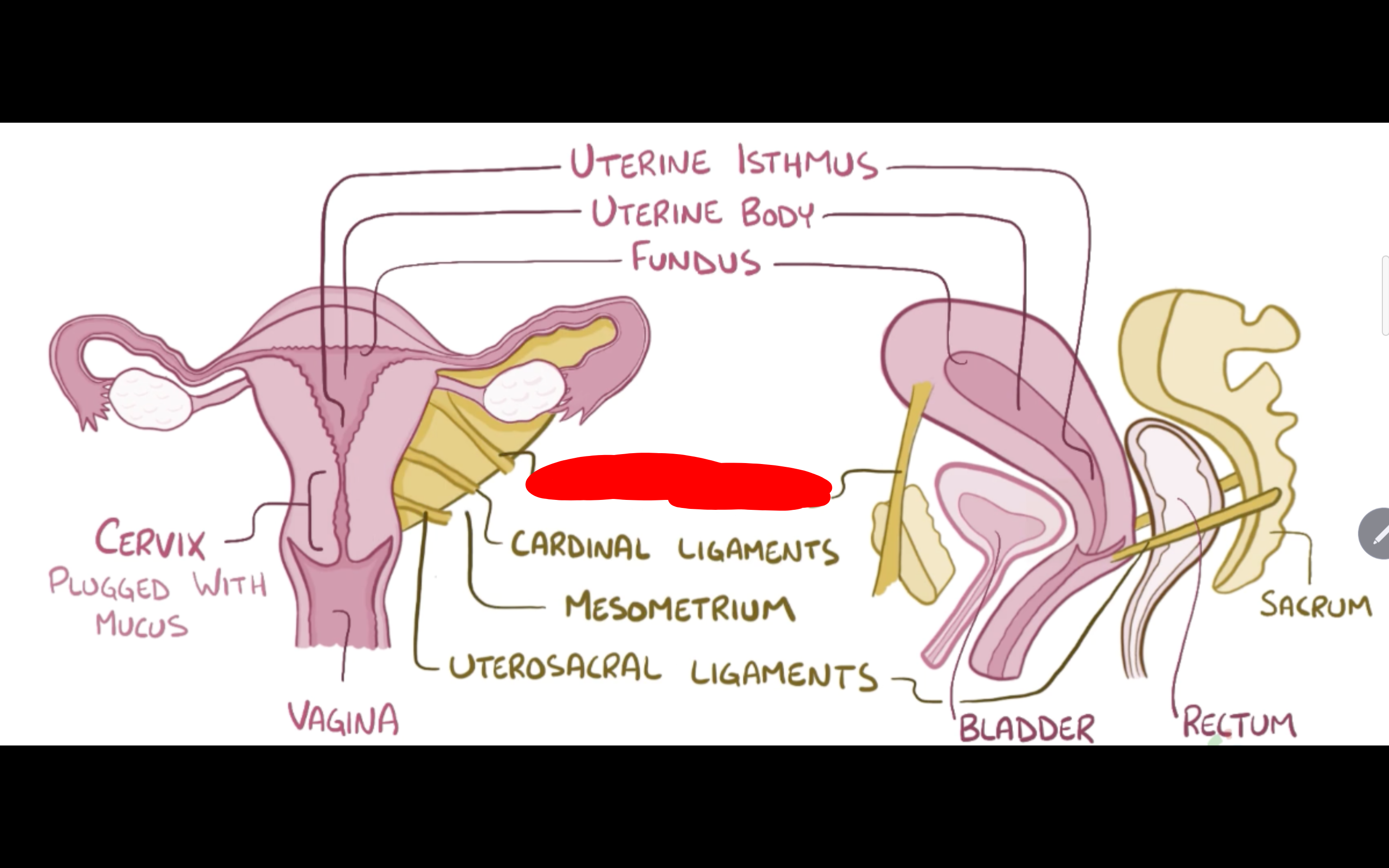
Name the structure in red
Cardinal Ligaments
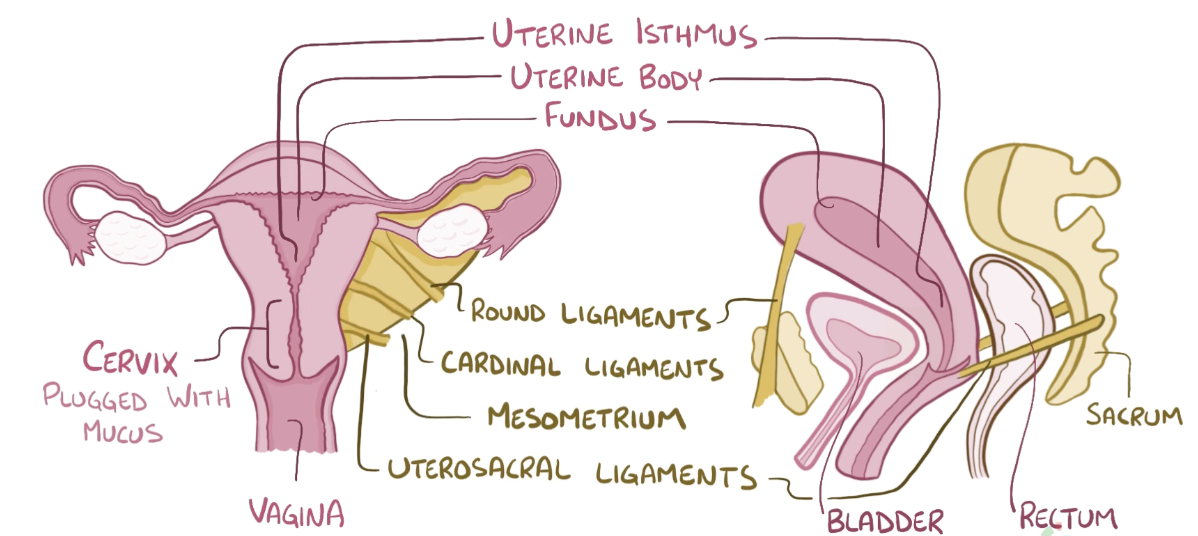
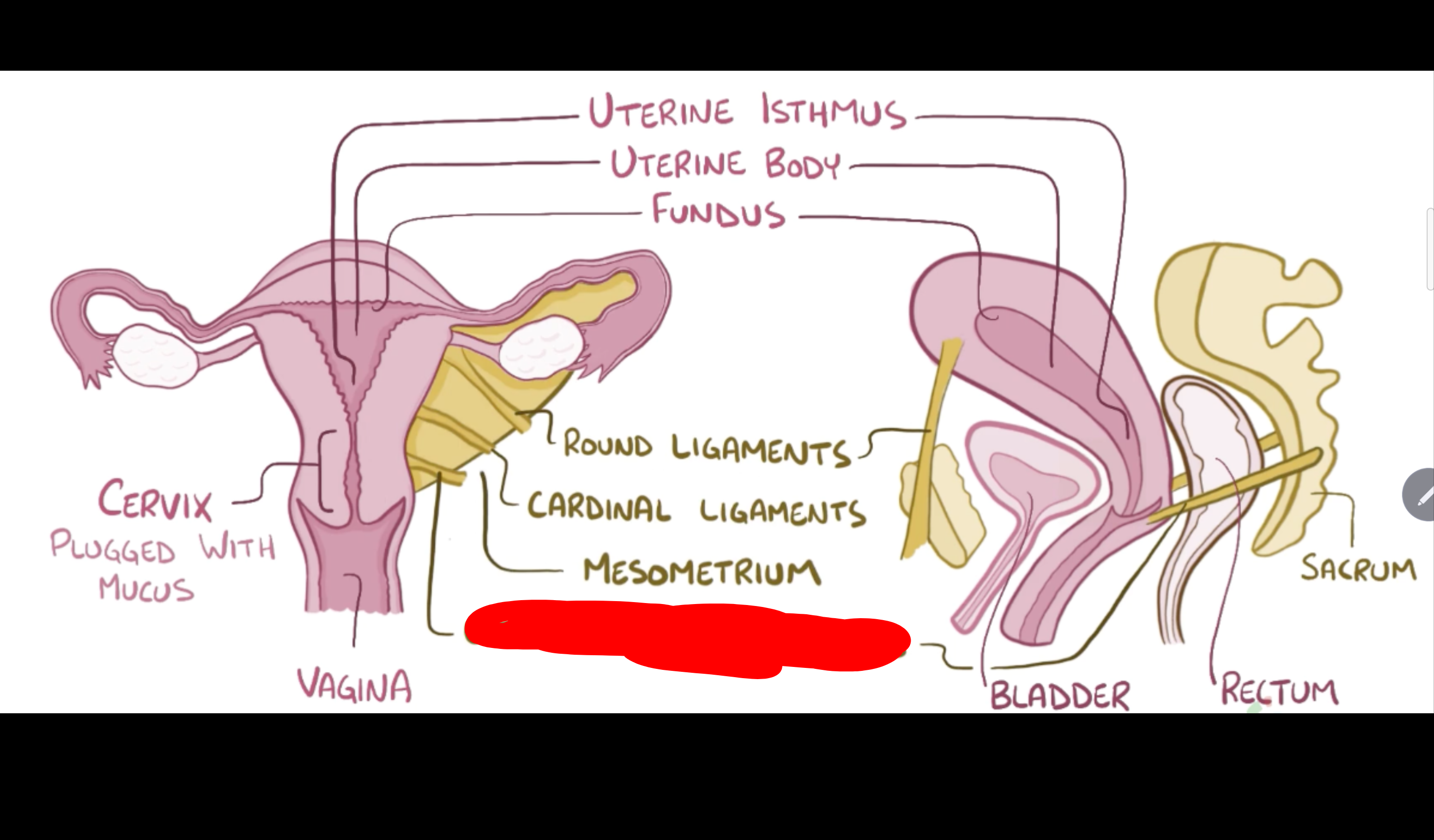
Name the structure in red
Mesometrium
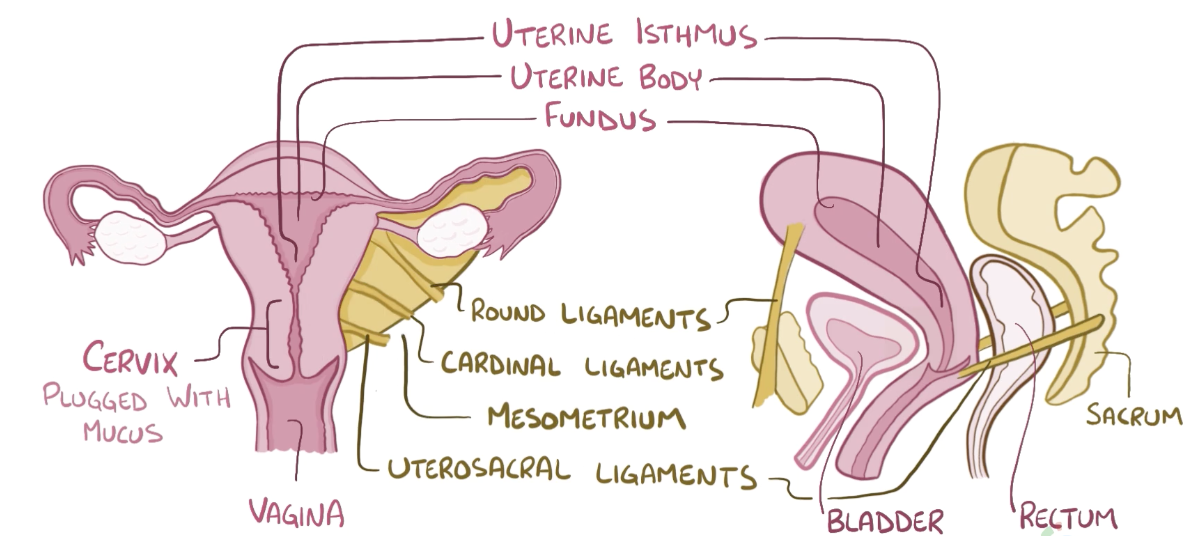
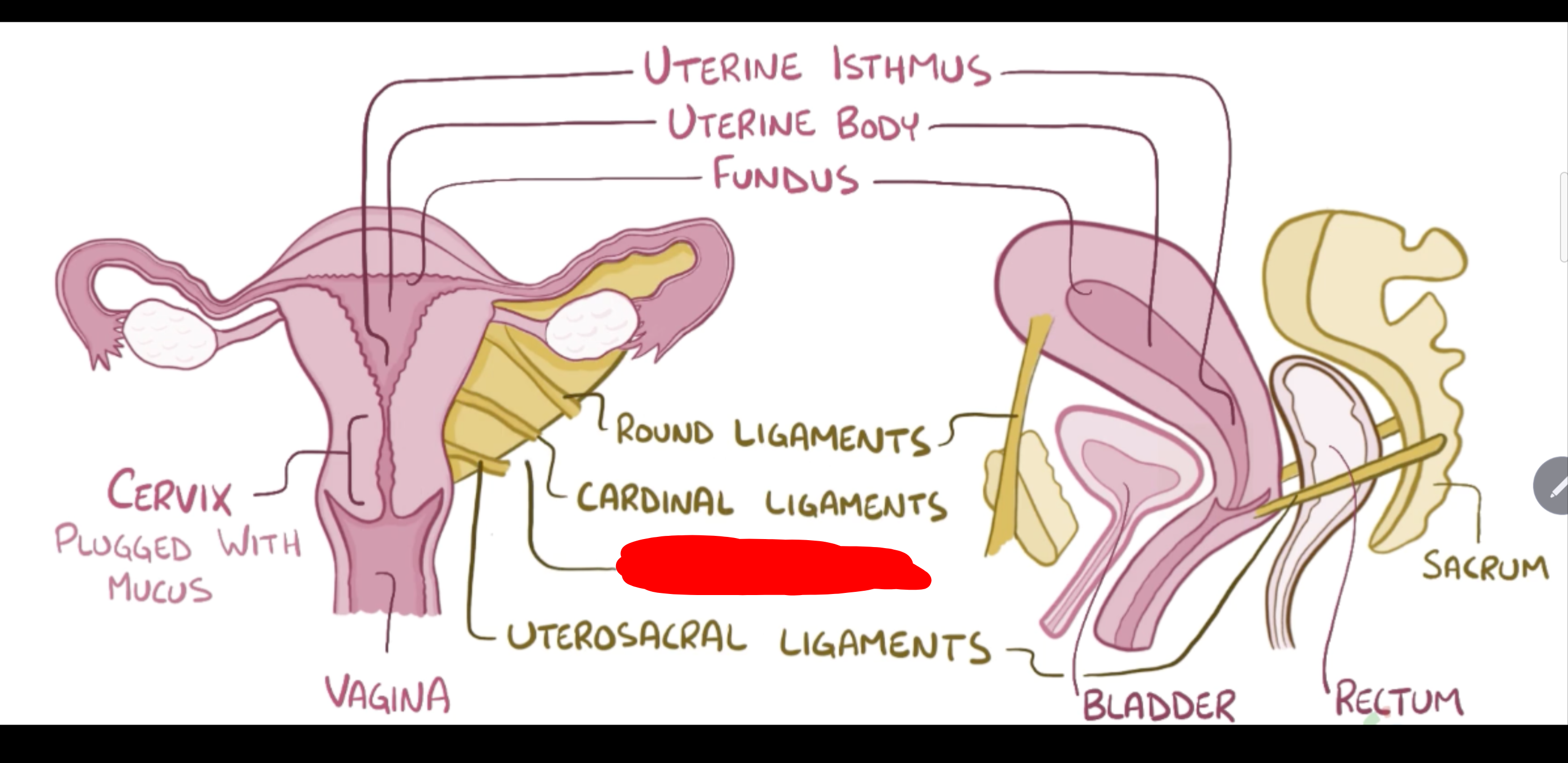
Name the structure in red
Uterosacral ligaments
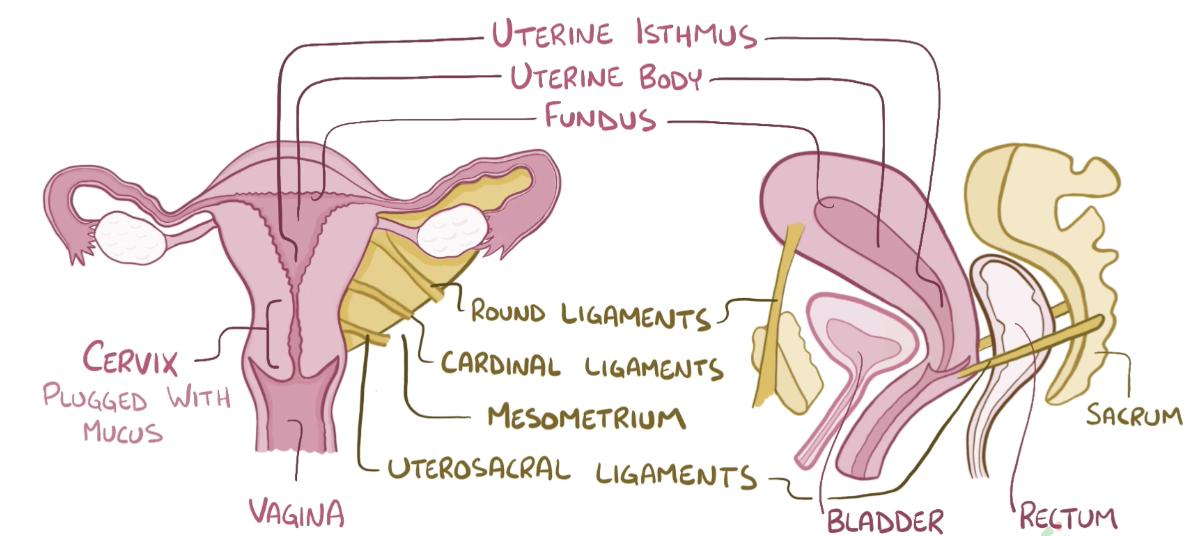
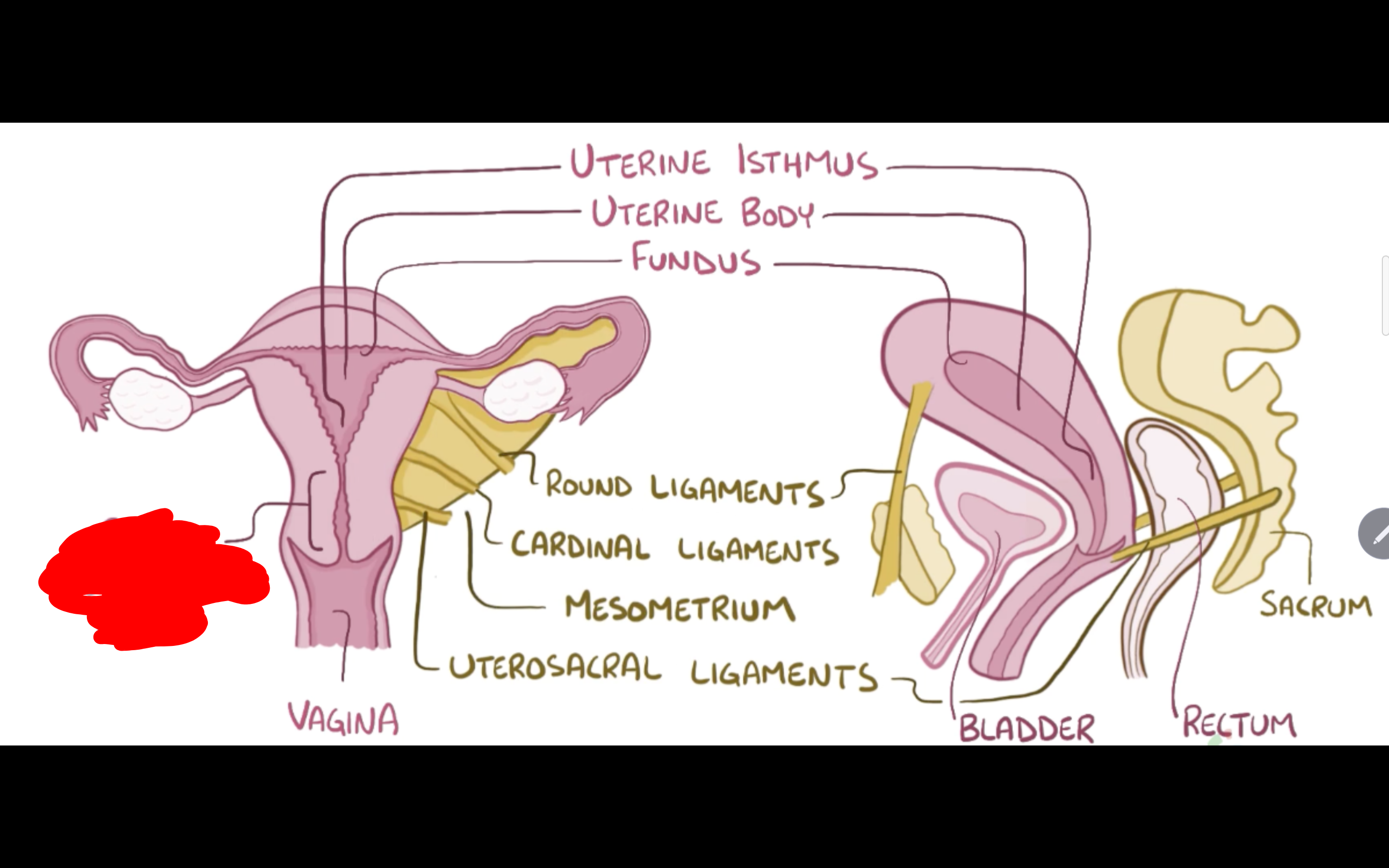
Name the structure in red
Cervix
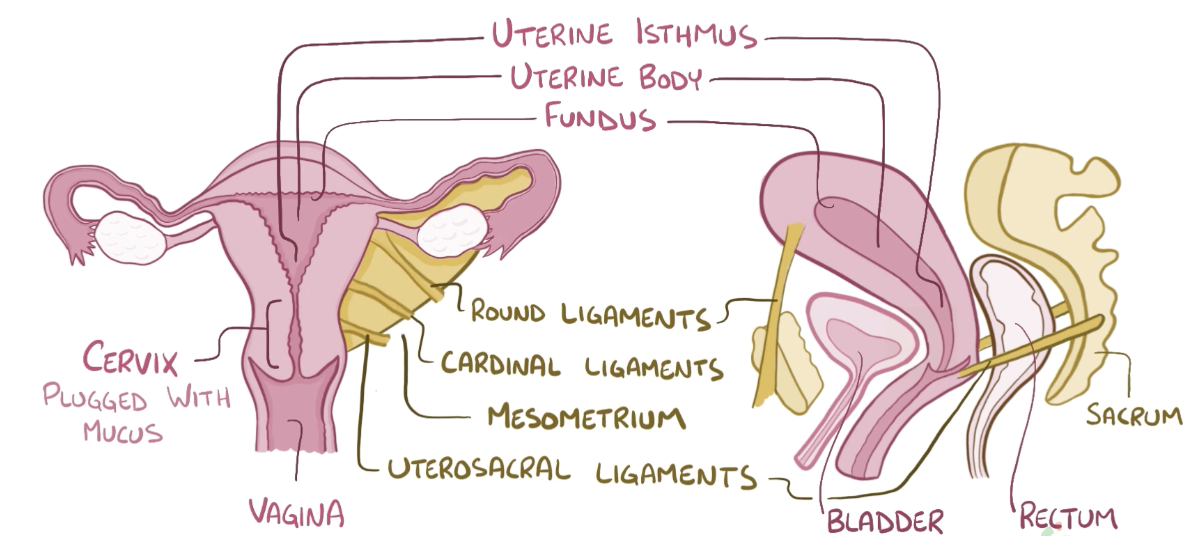
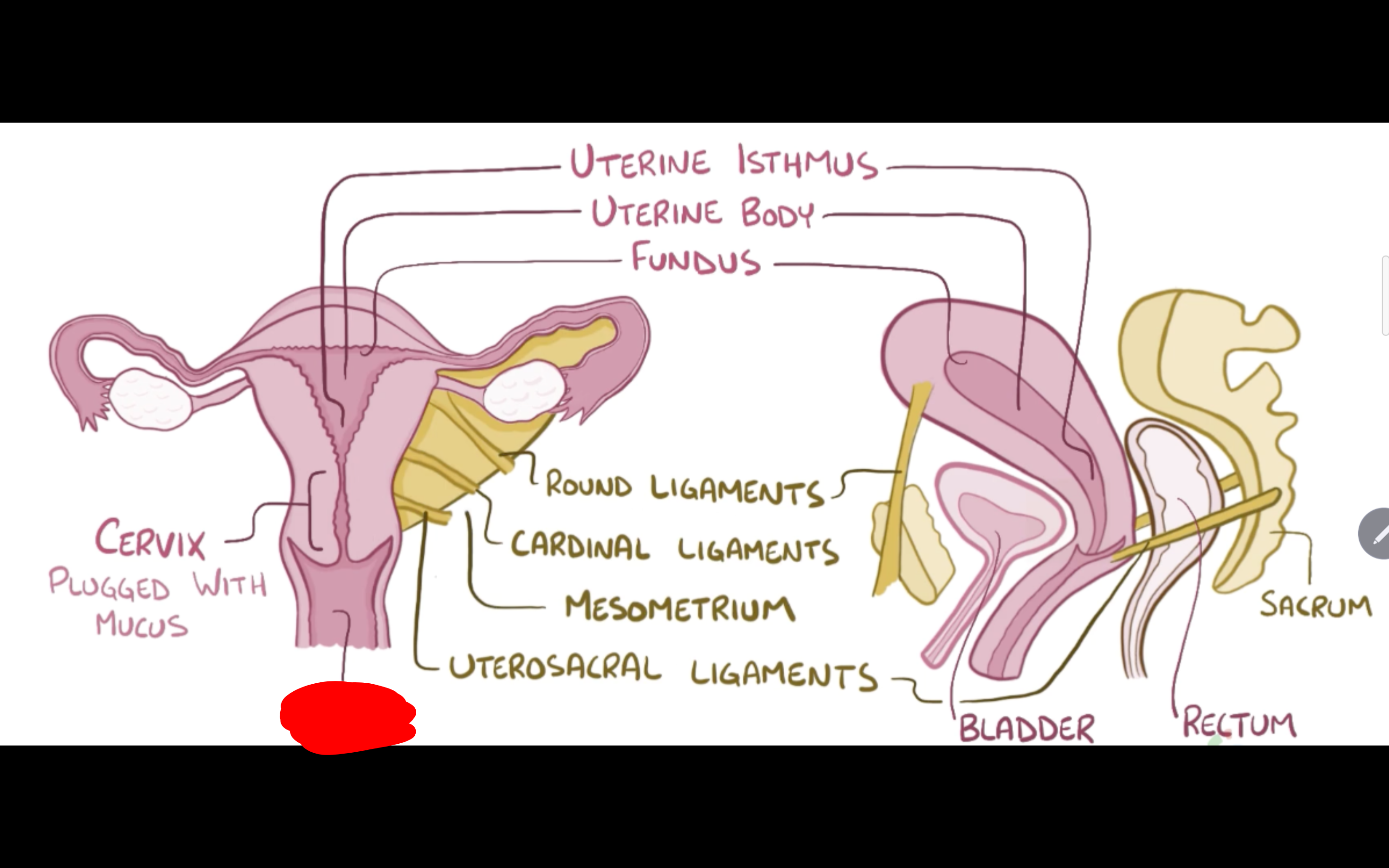
Name the structure in red
Vagina
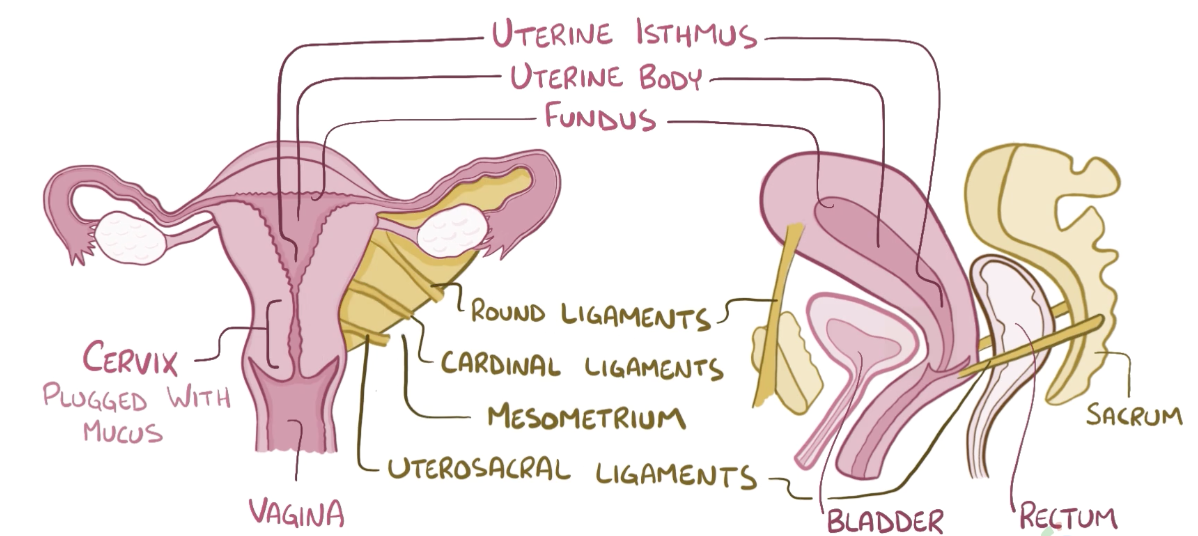
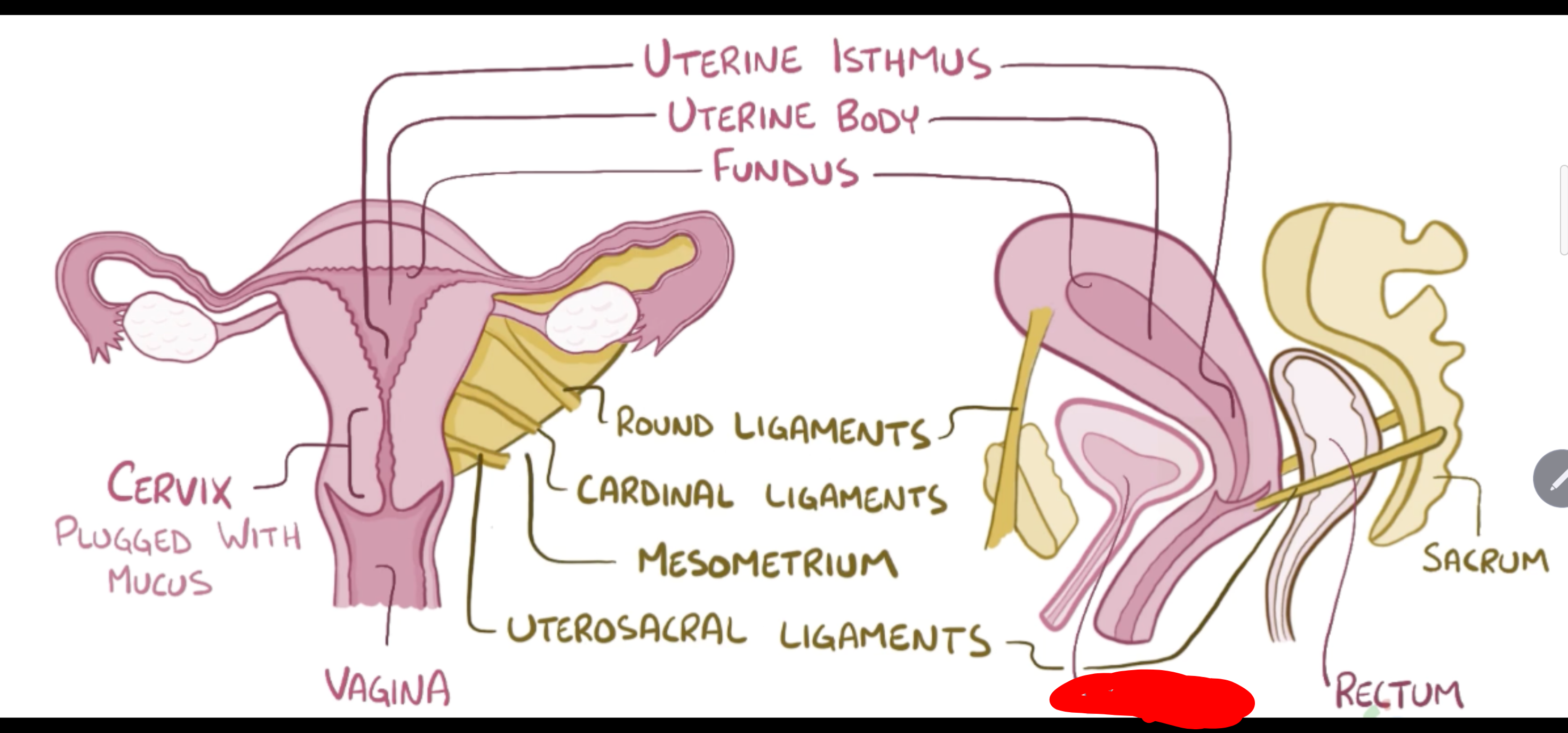
Name the structure in red
Bladder
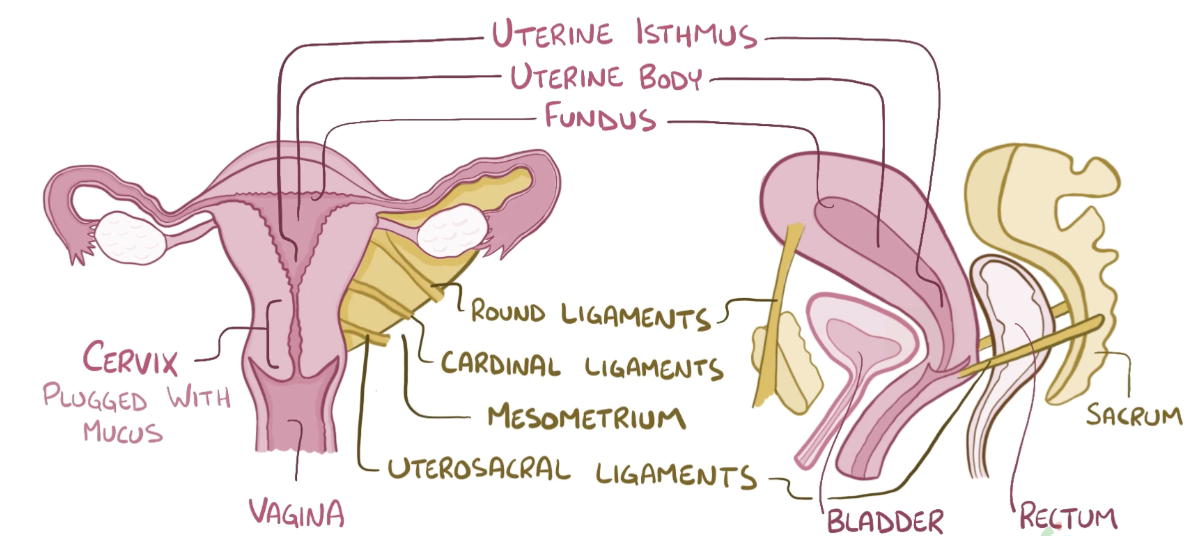
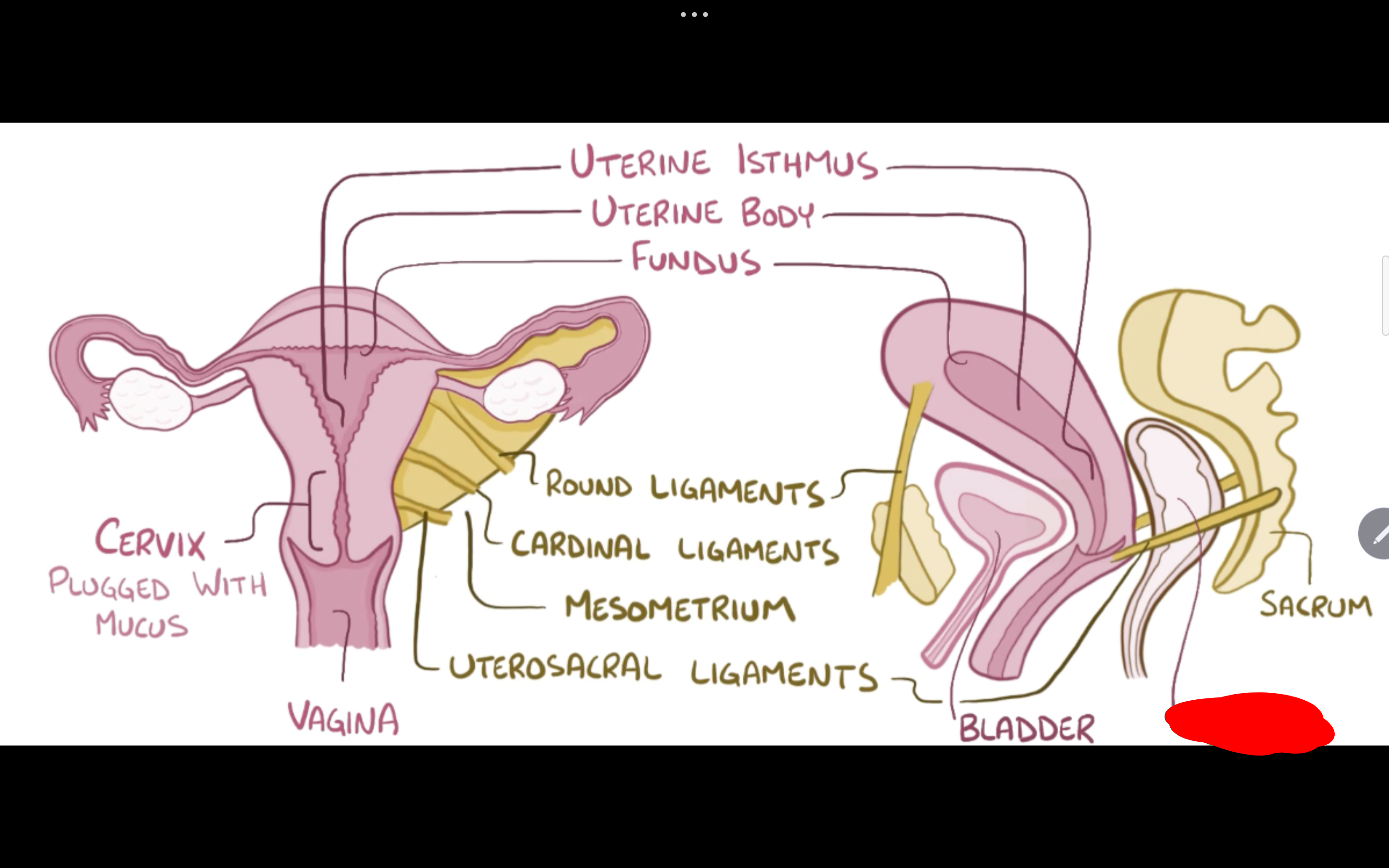
Name the structure in red
Rectum
Name the structure in red
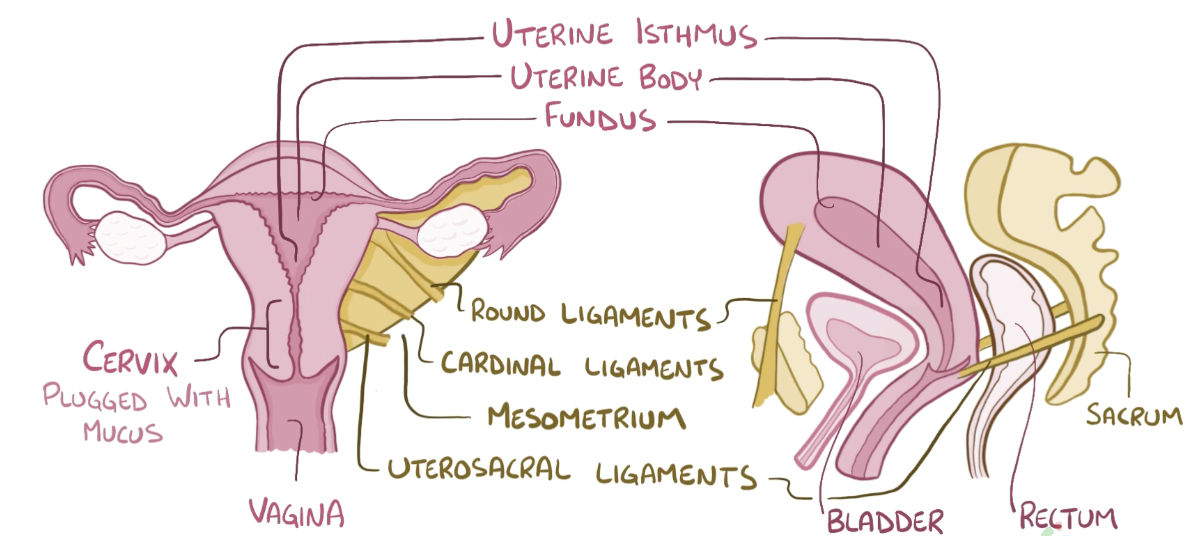
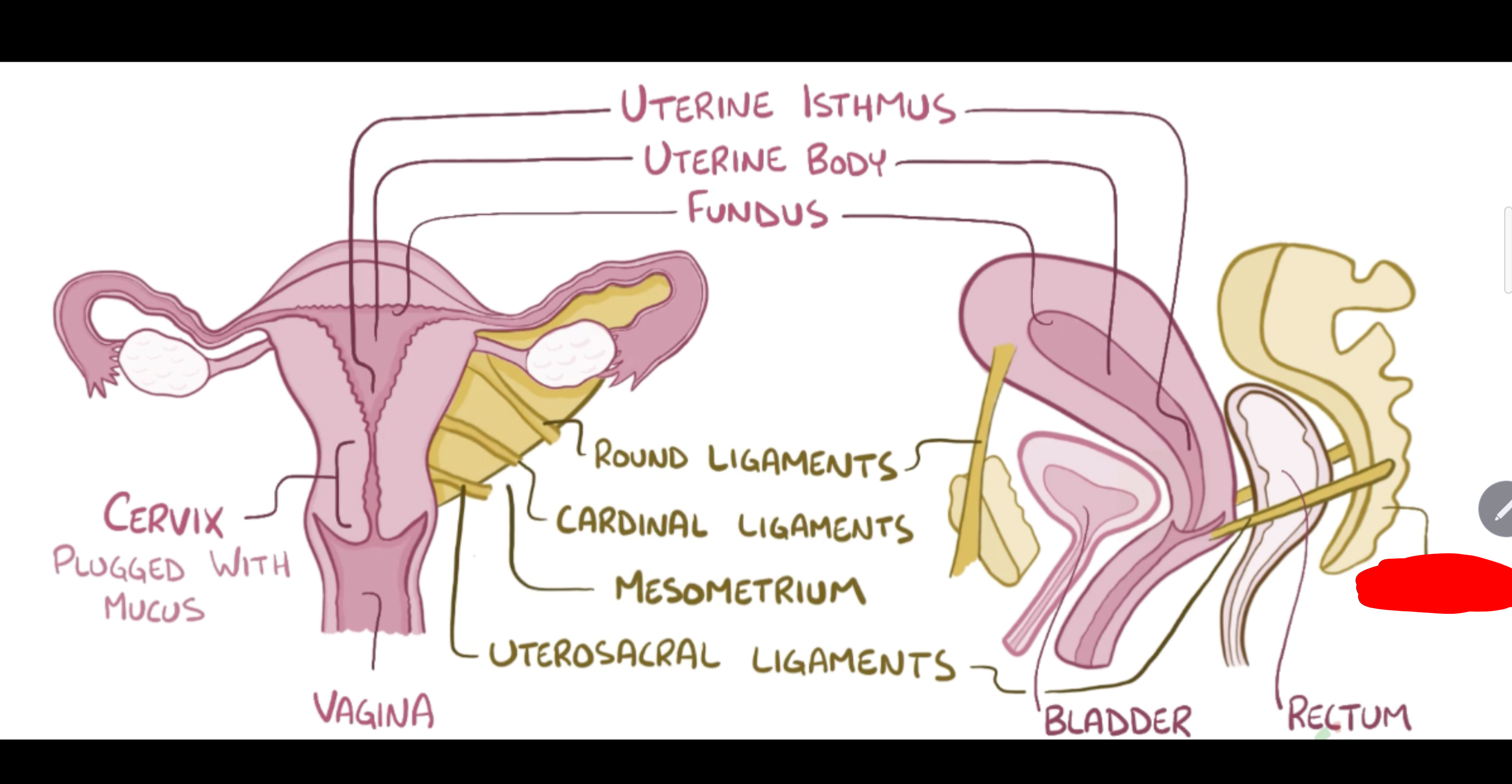
Sacrum
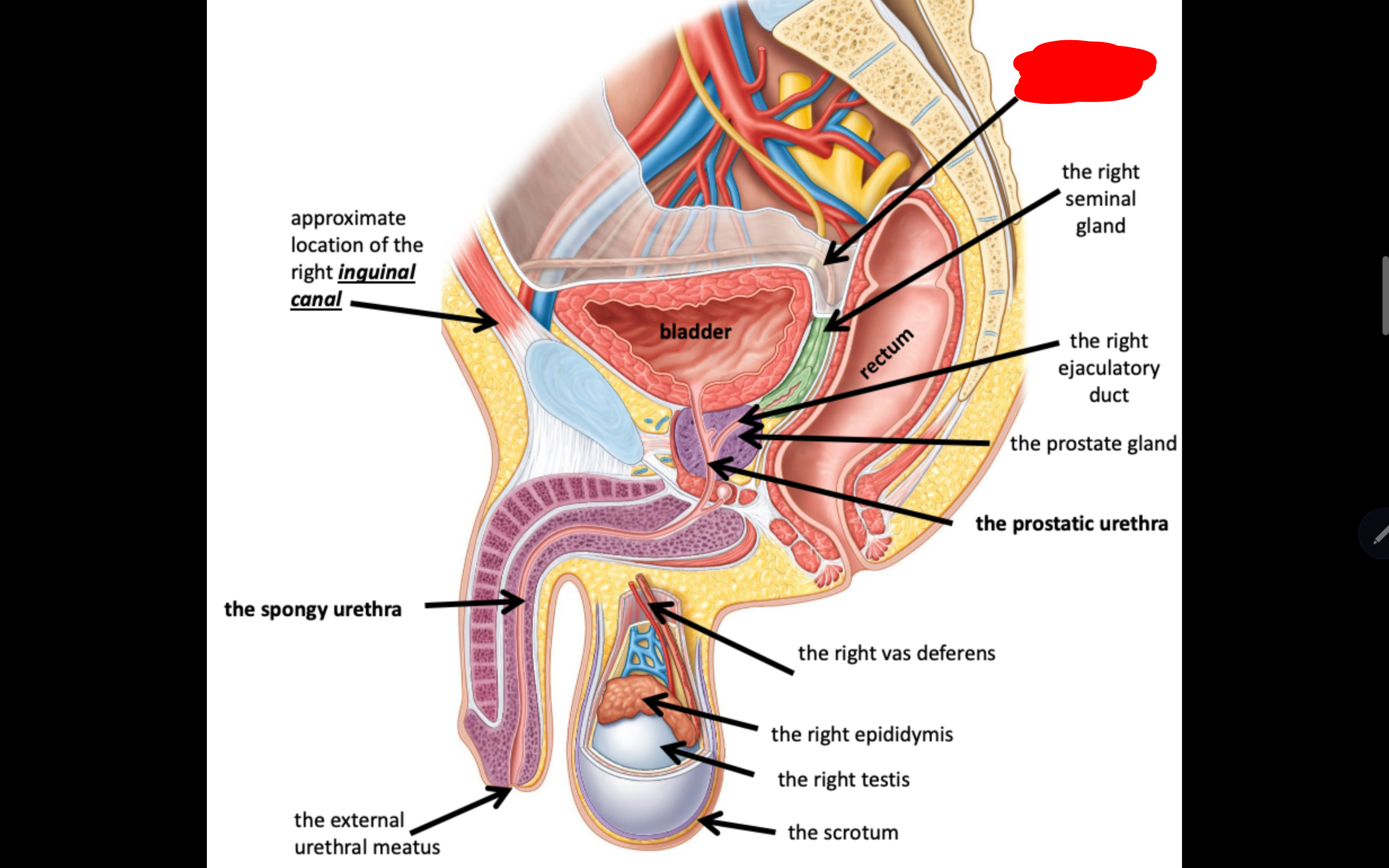
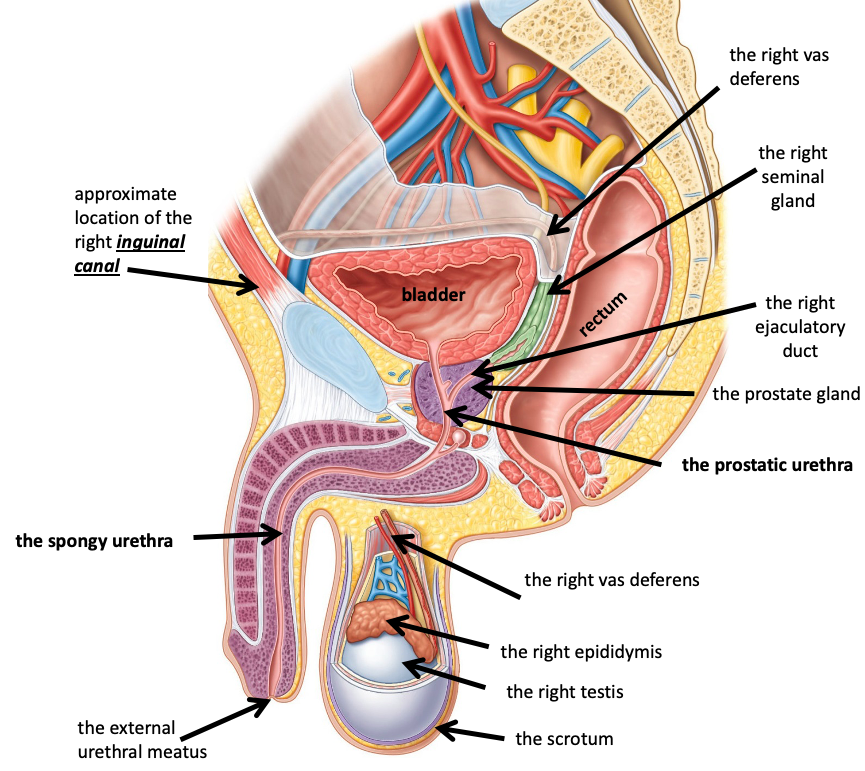
Name the structure in red
The right van deferens
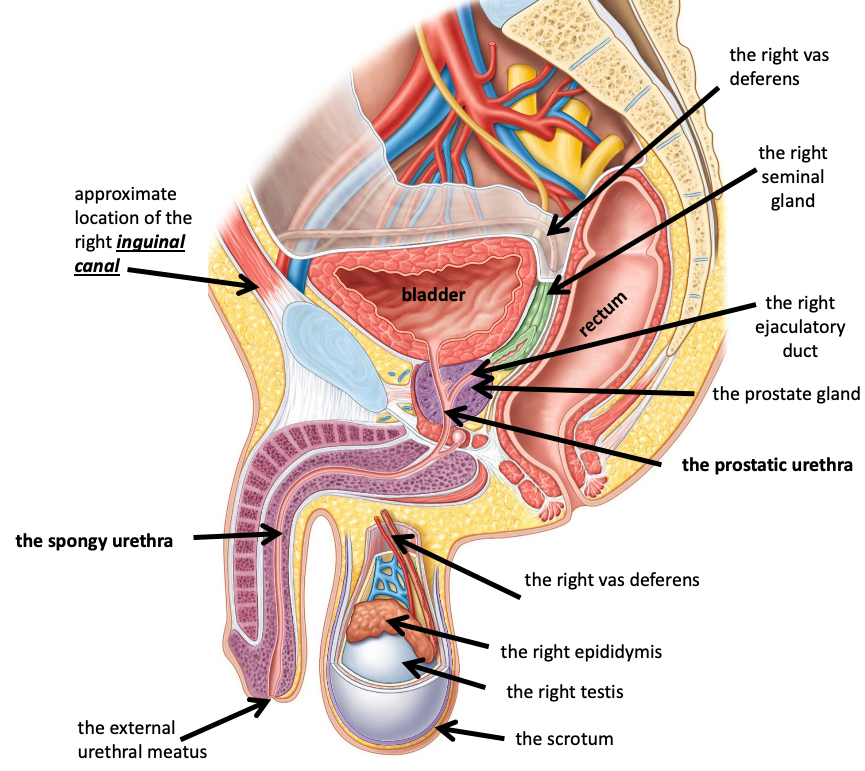
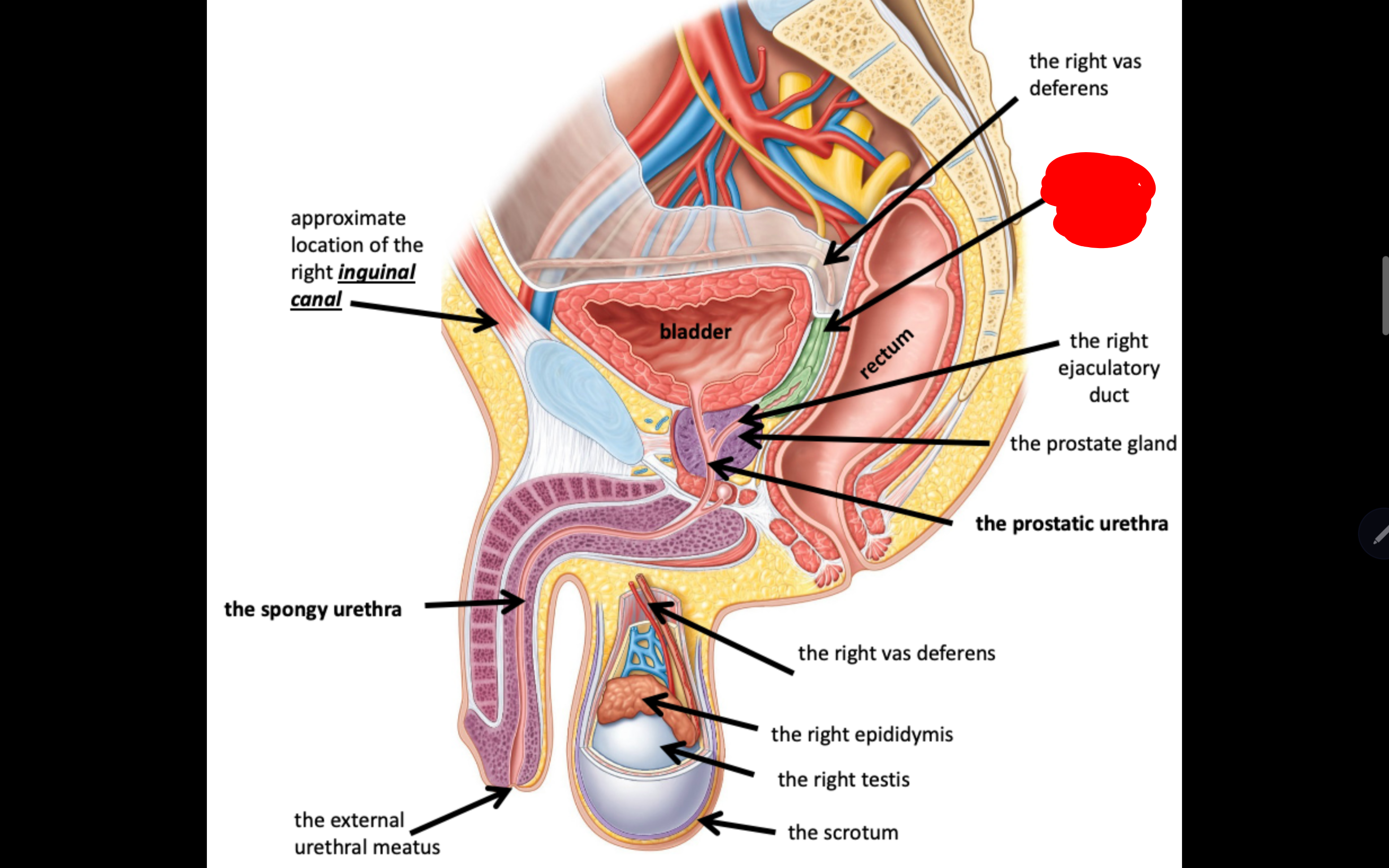
Name the structure in red
The right seminar gland
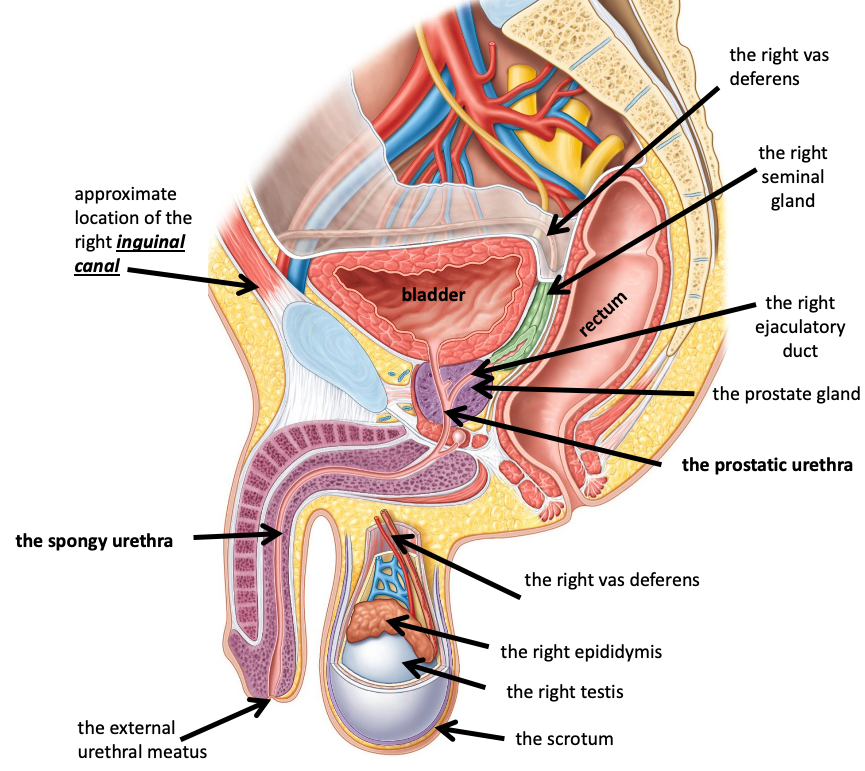
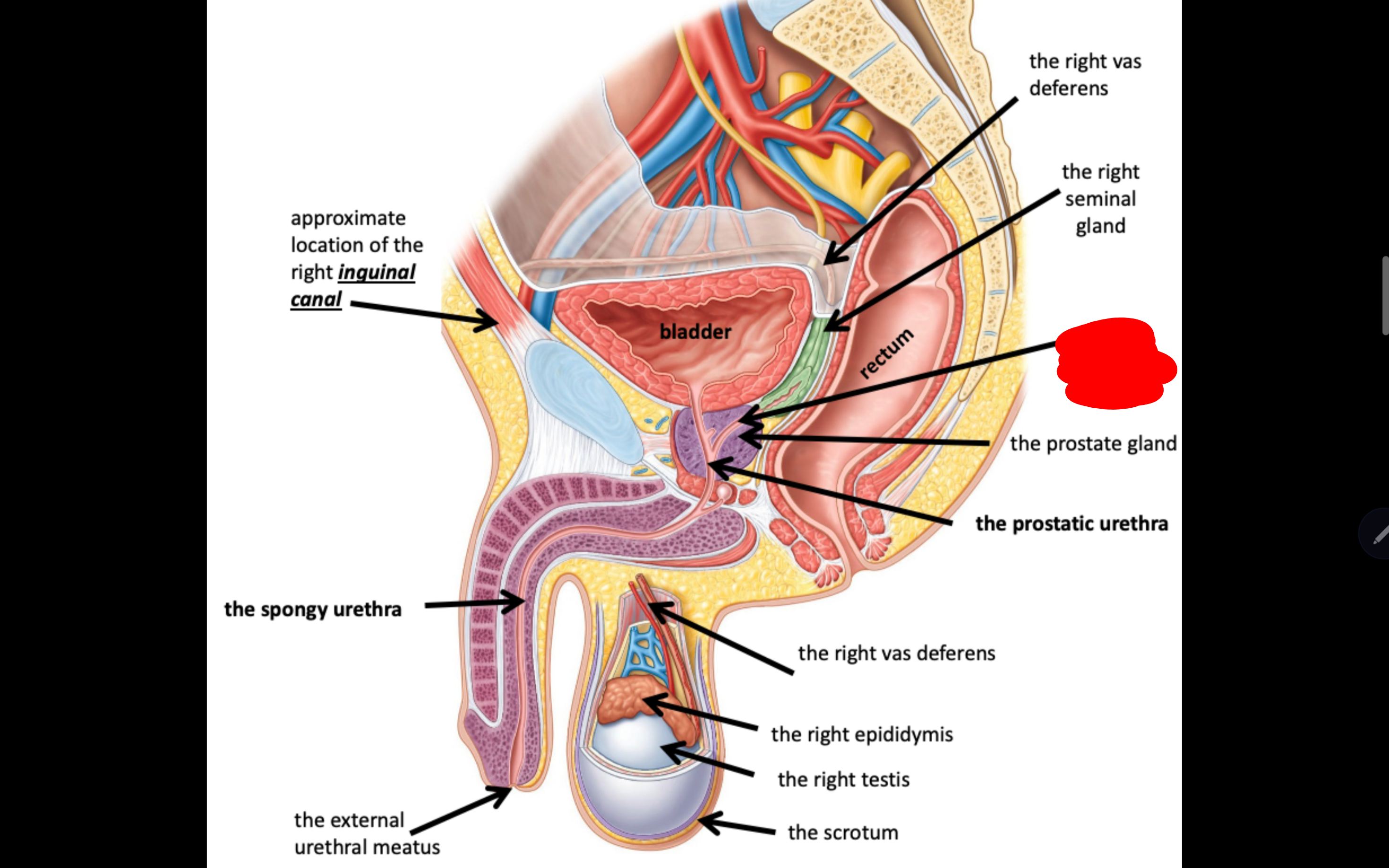
Name the structure in red
The right ejaculatory duct
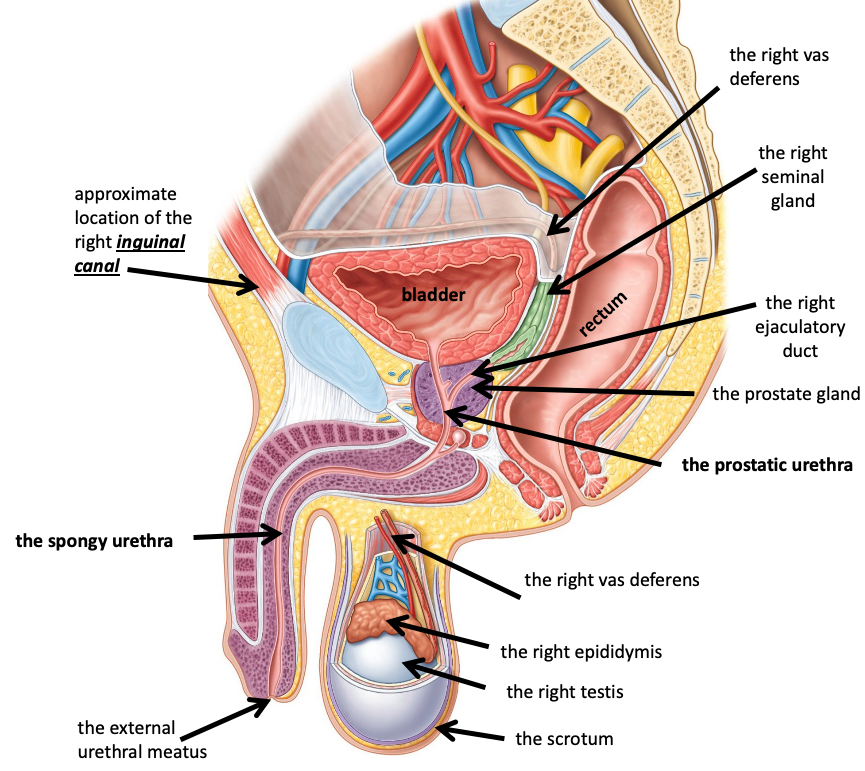
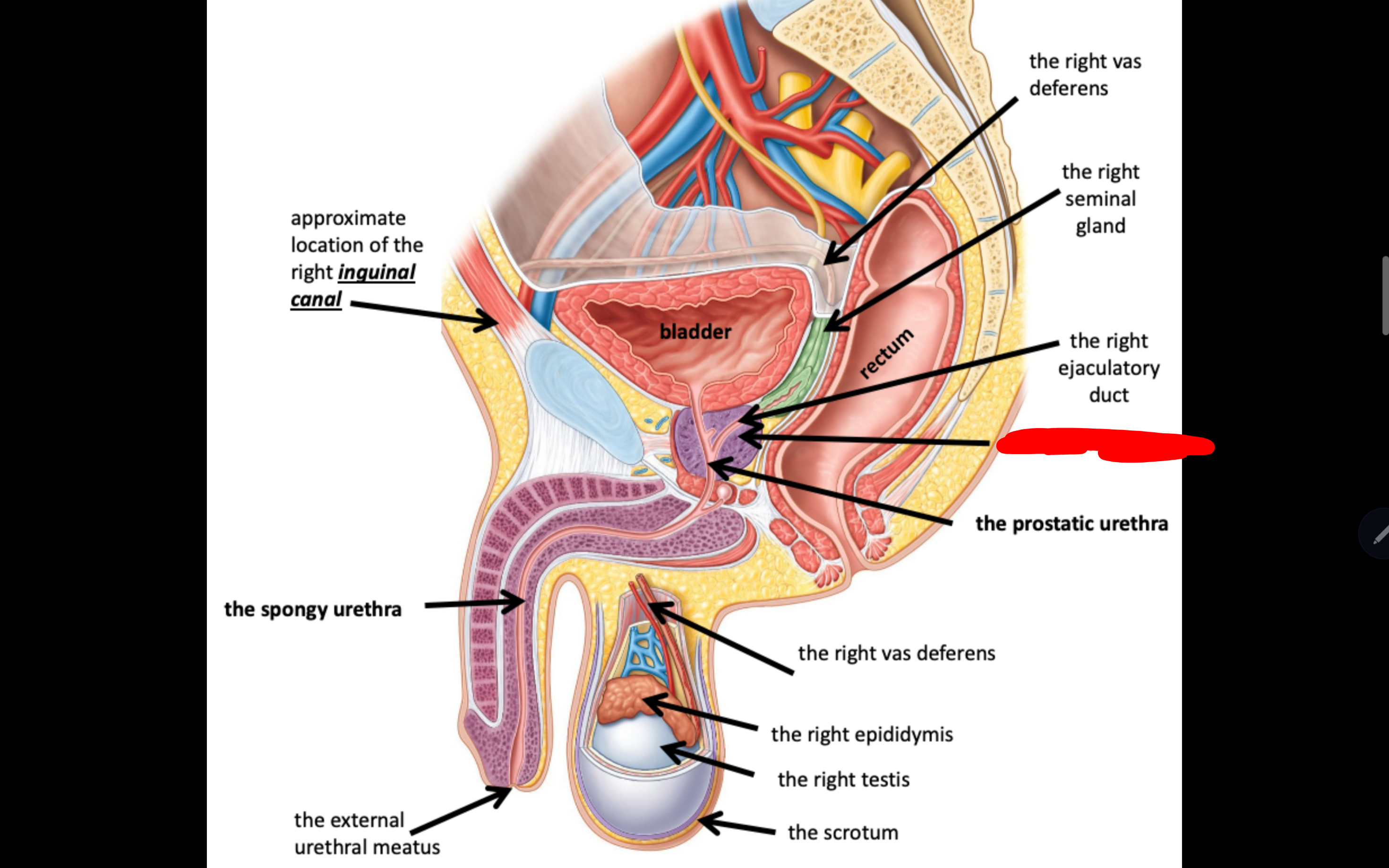
Name the structure in red
The prostate gland
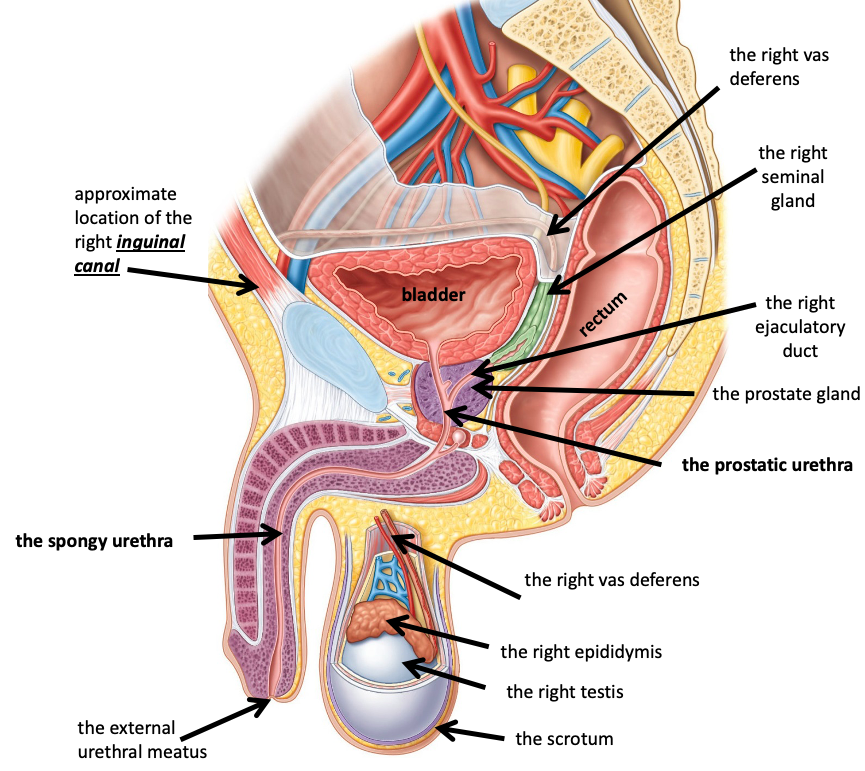
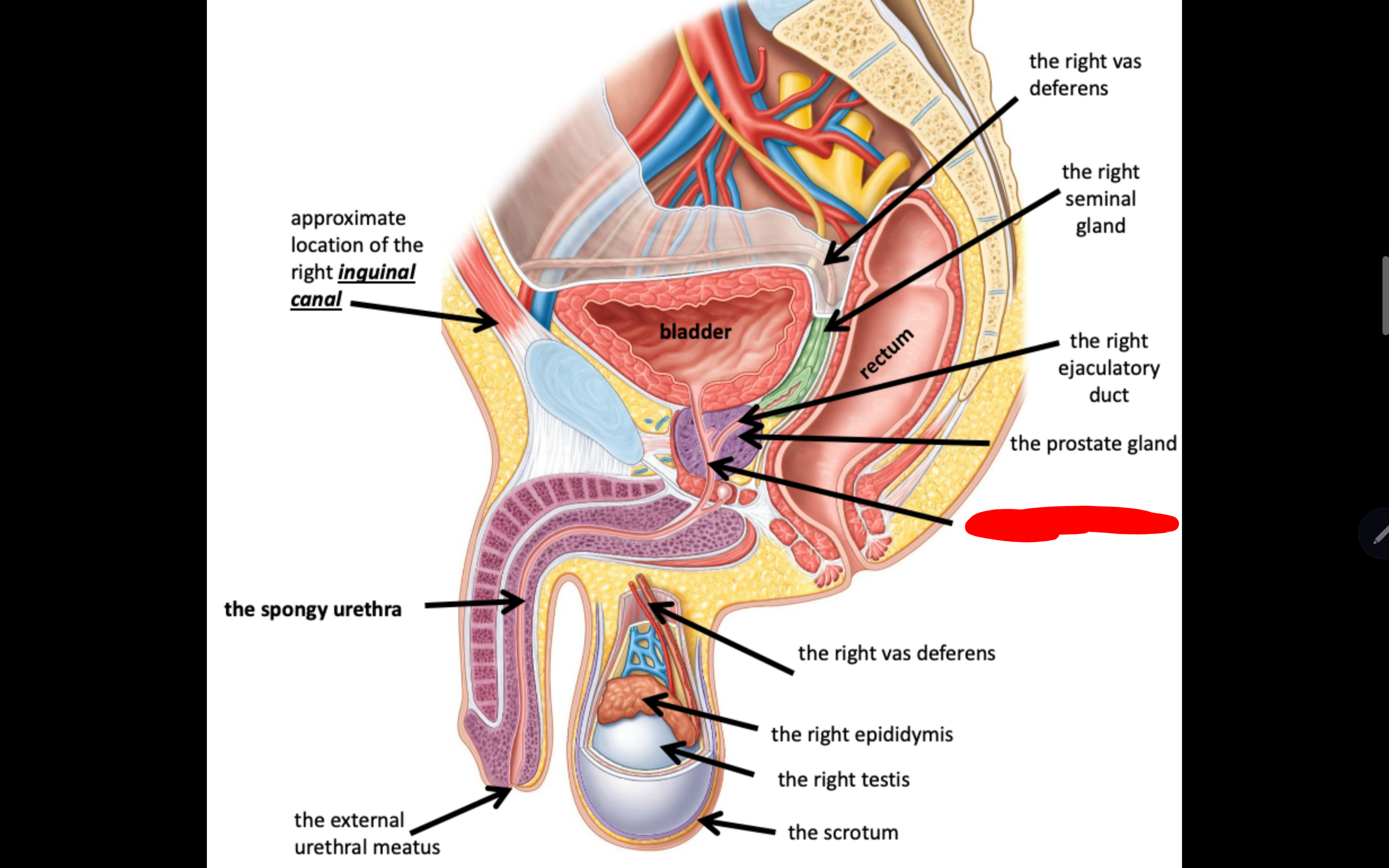
Name the structure in red
The prostatic urethra
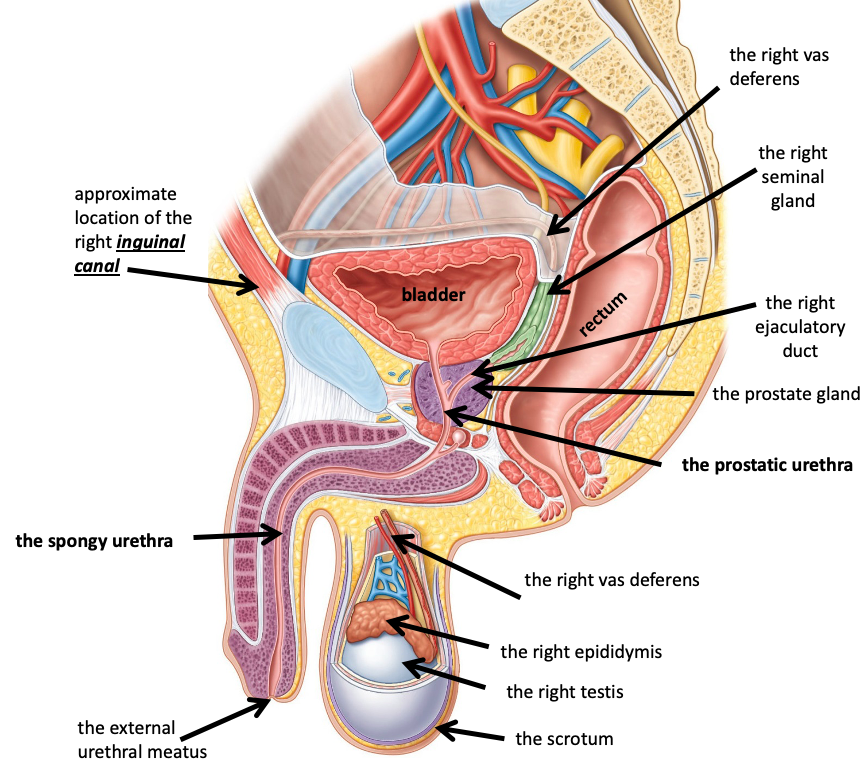
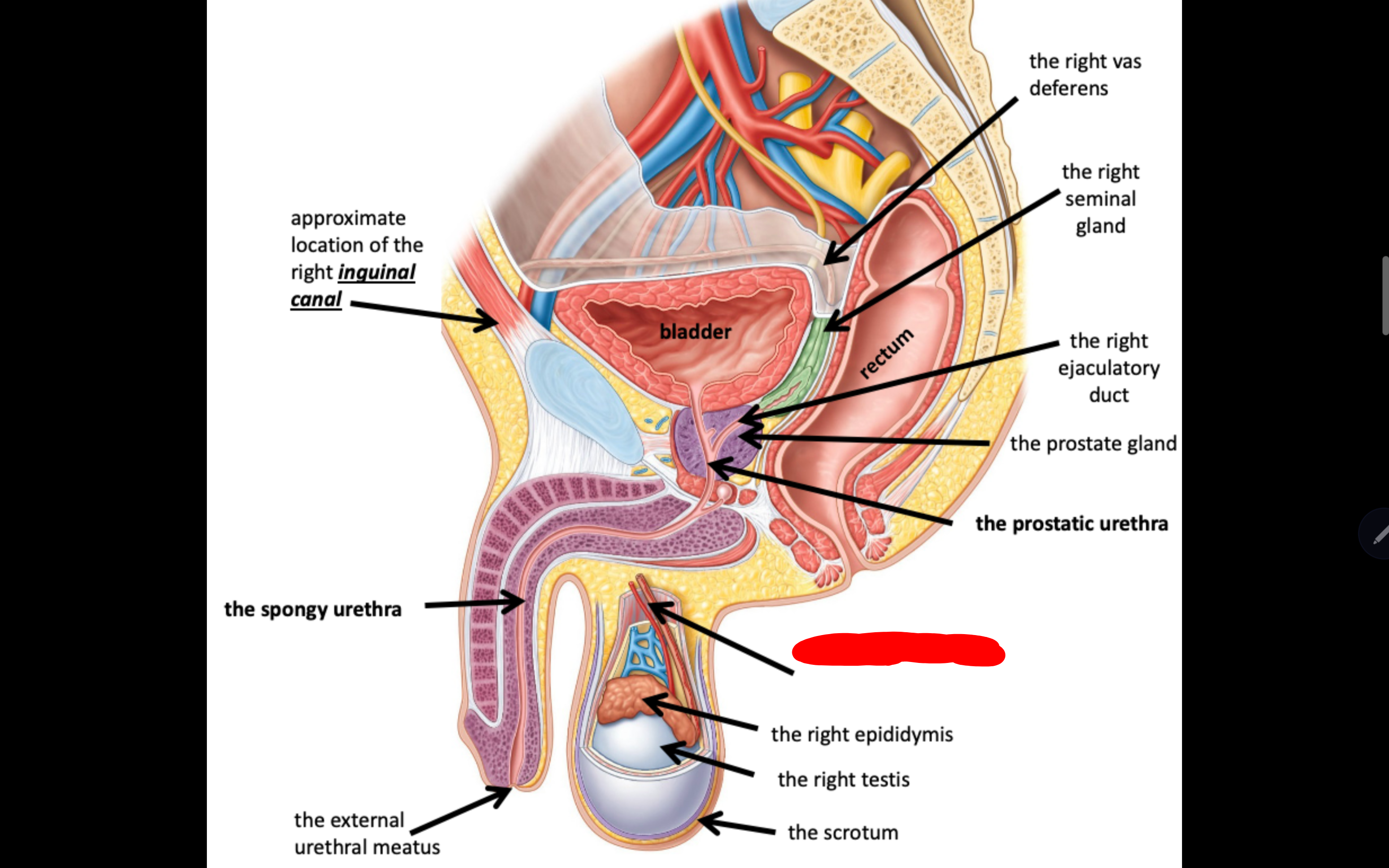
Name the structure in red
The right van deferens
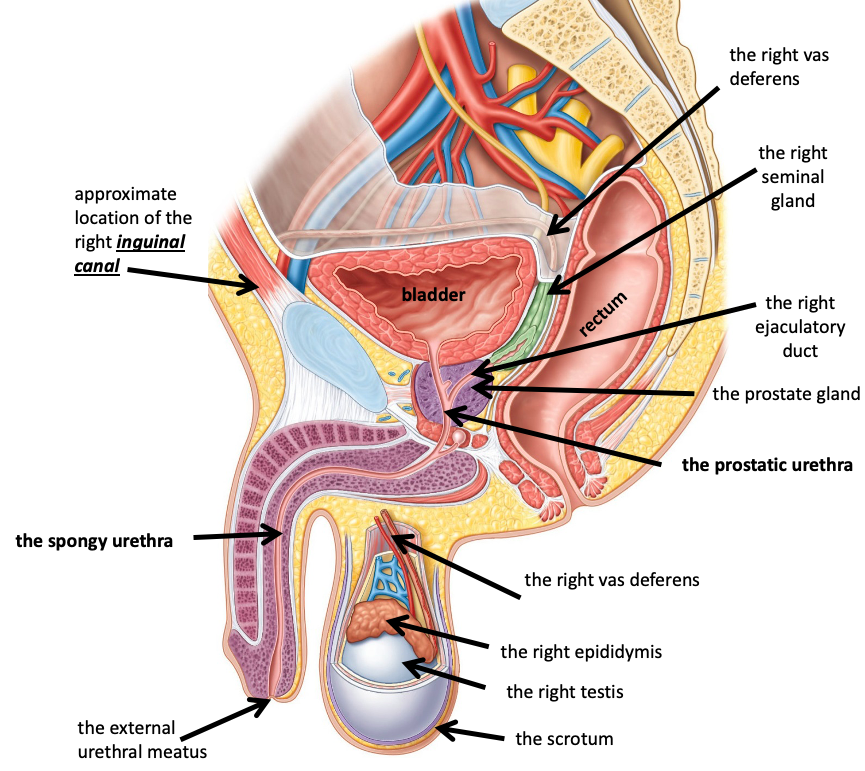
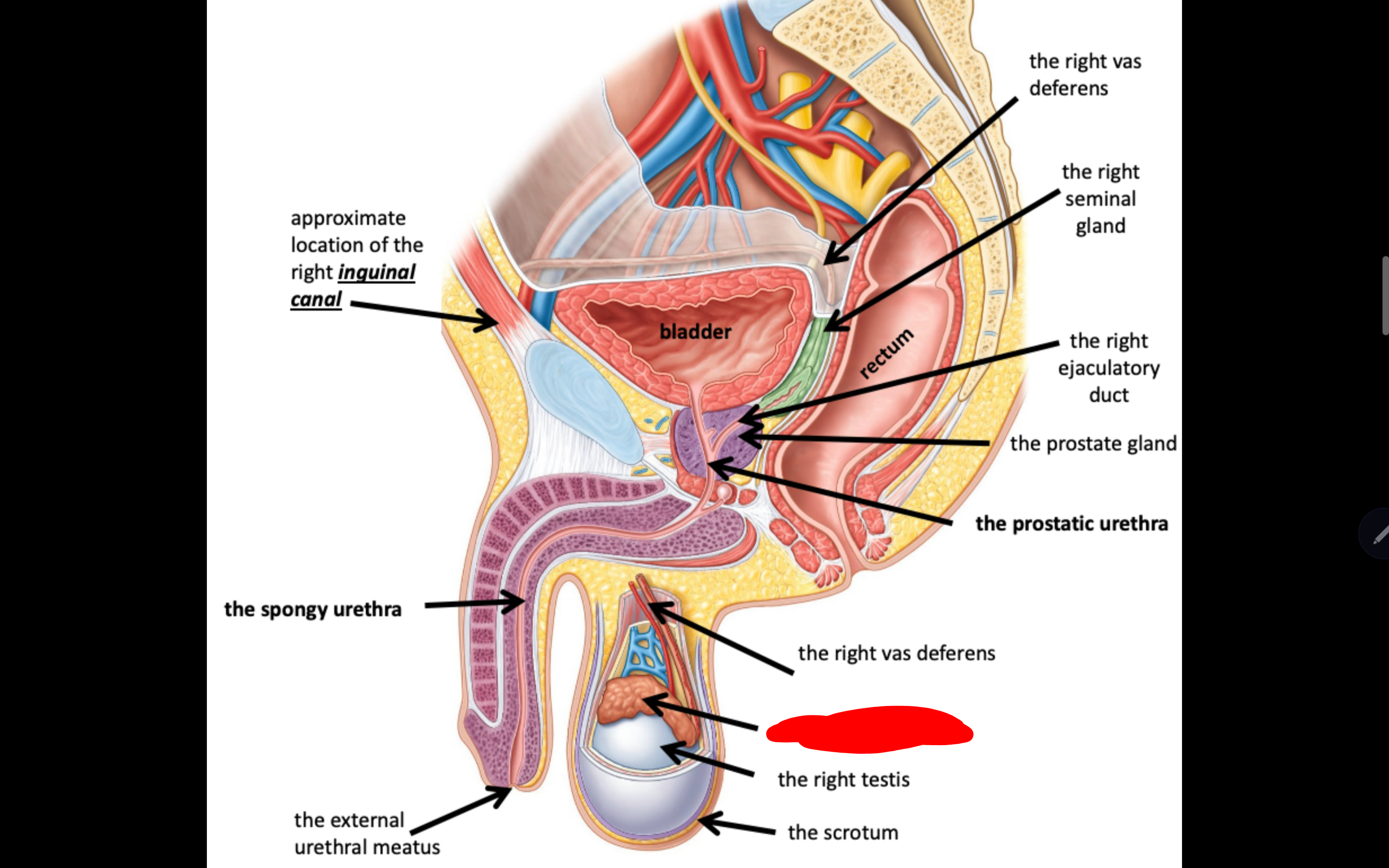
Name the structure in red
The right epididymis
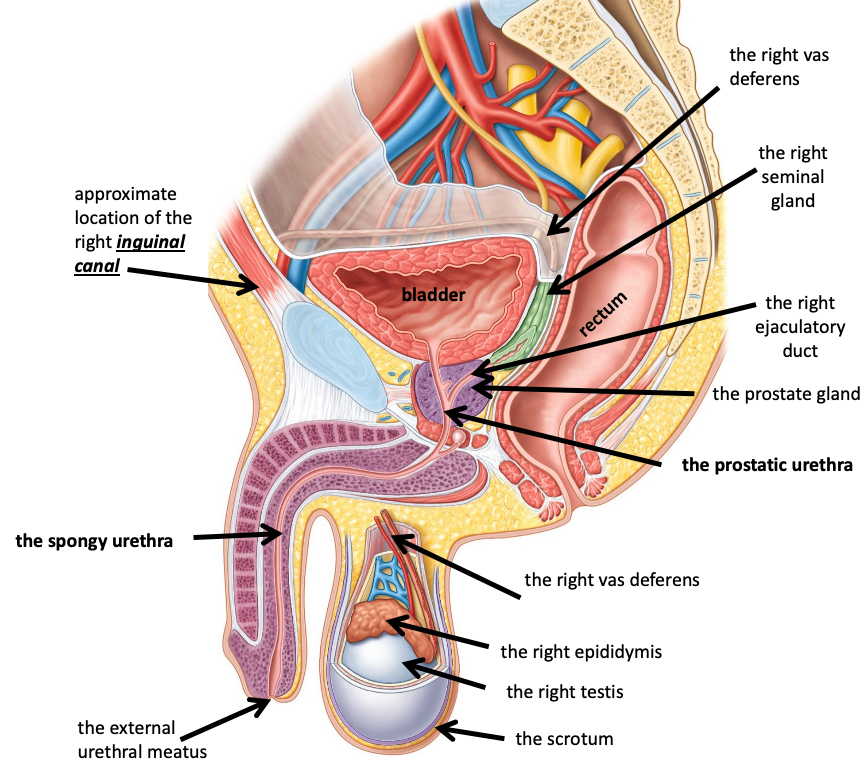
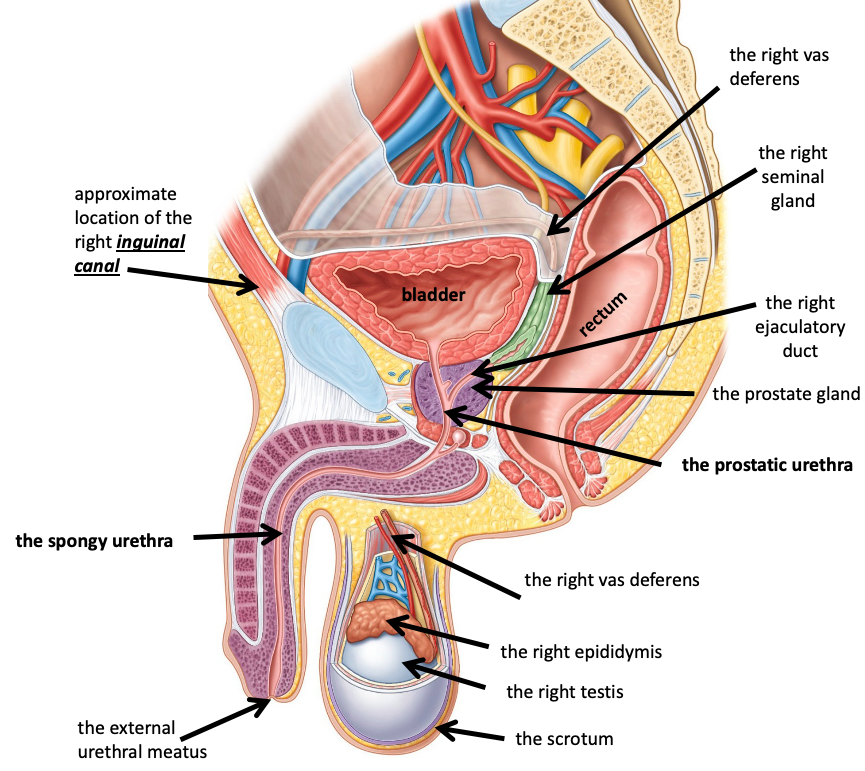
Name the structure in red
the right testis
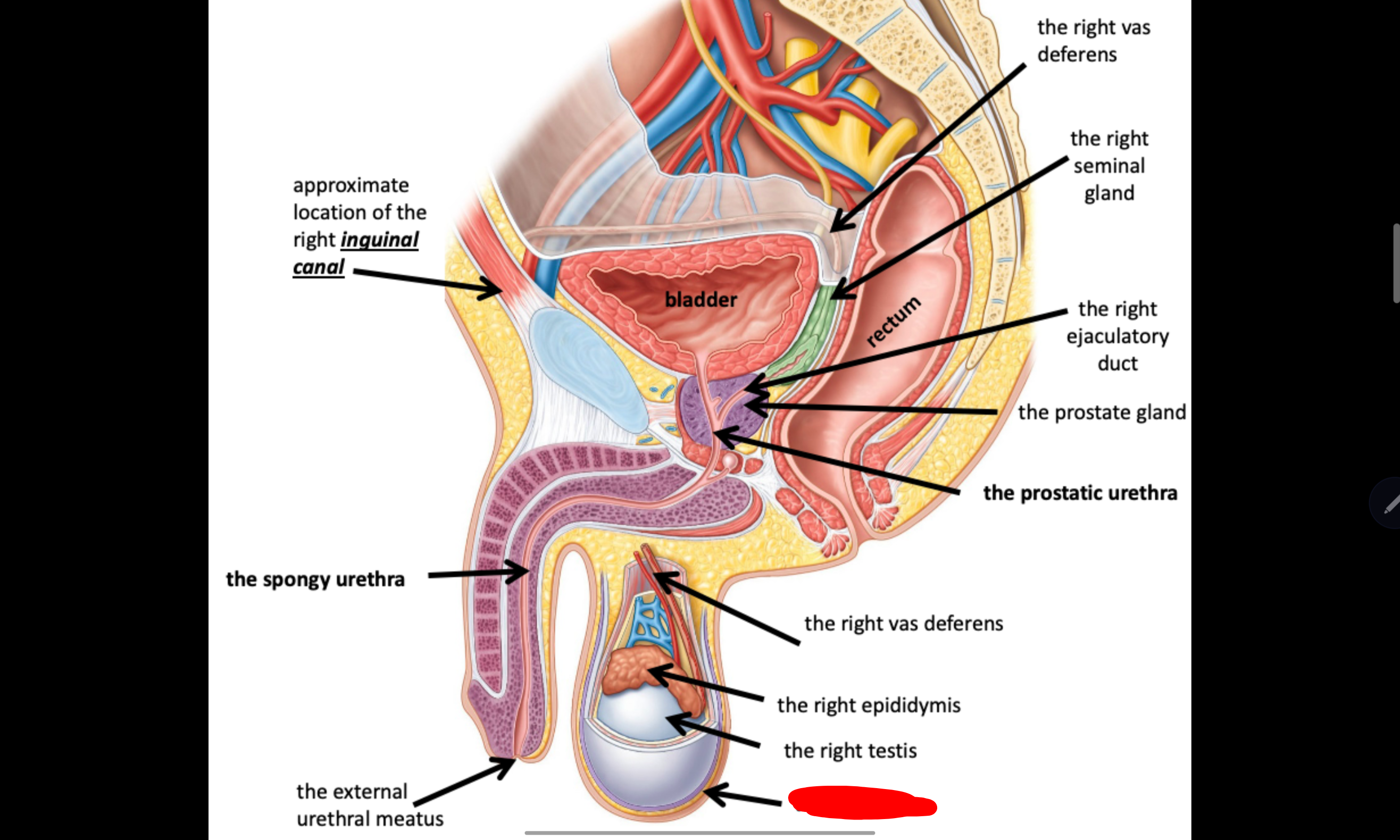
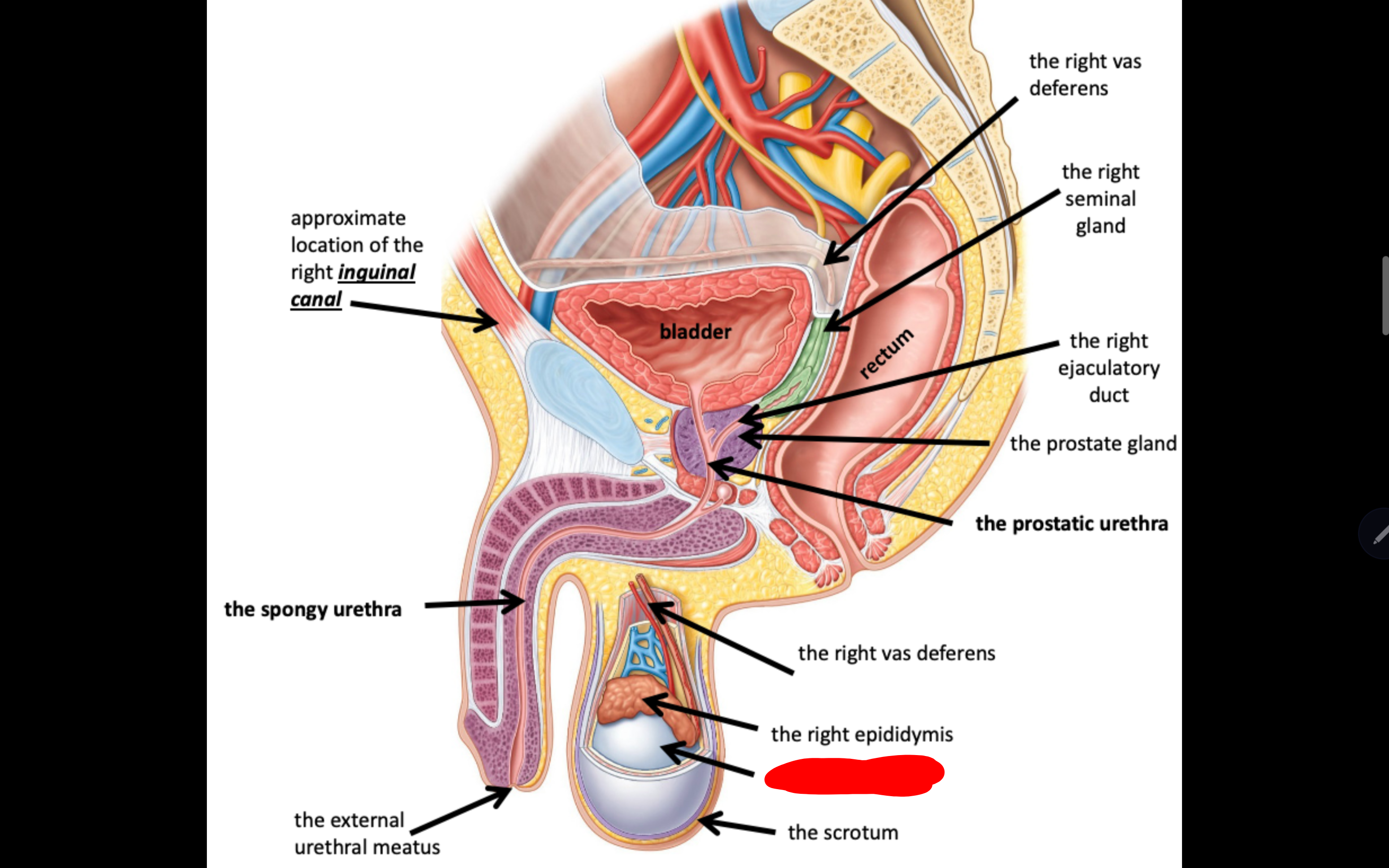
Name the structure in red
The scrotum
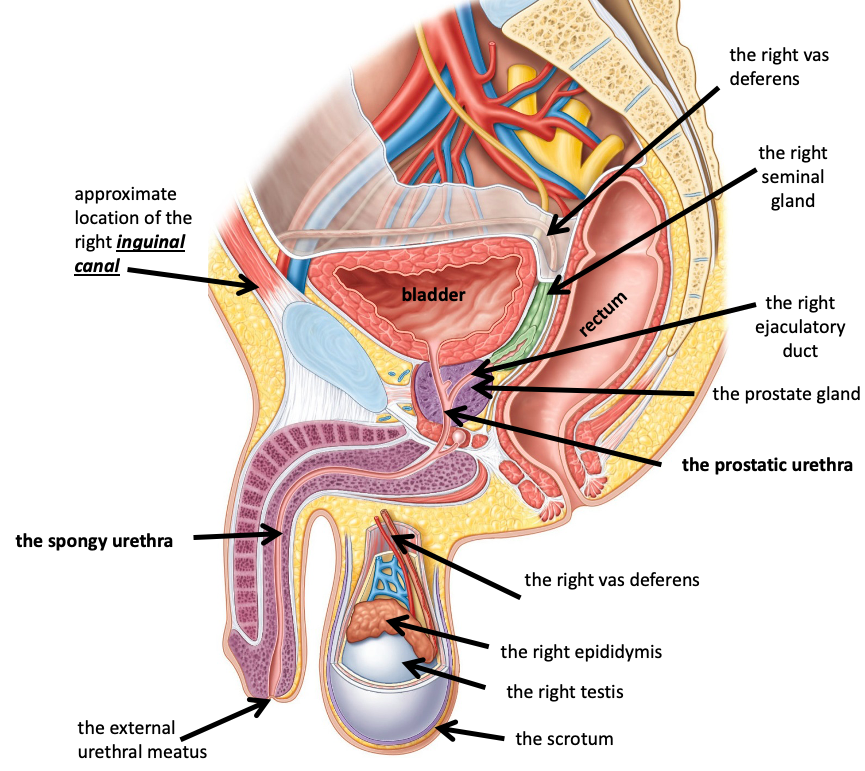
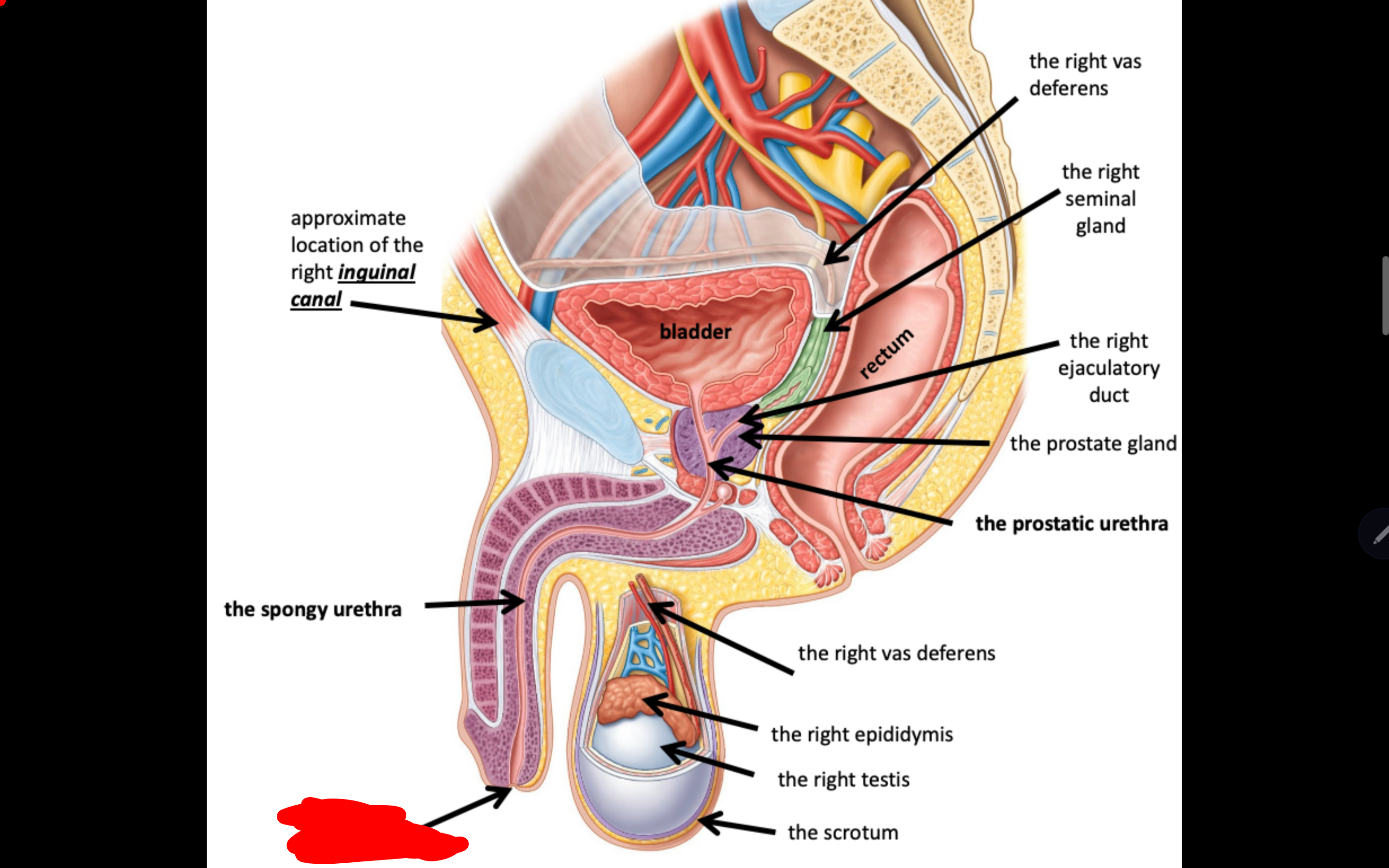
Name the structure in red
The external urethral meatus
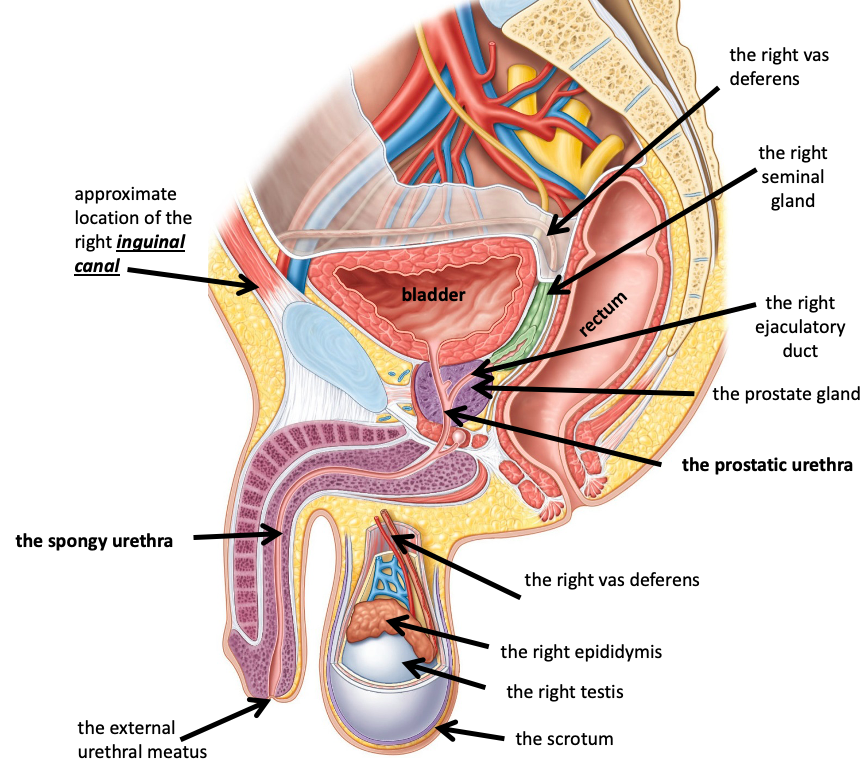
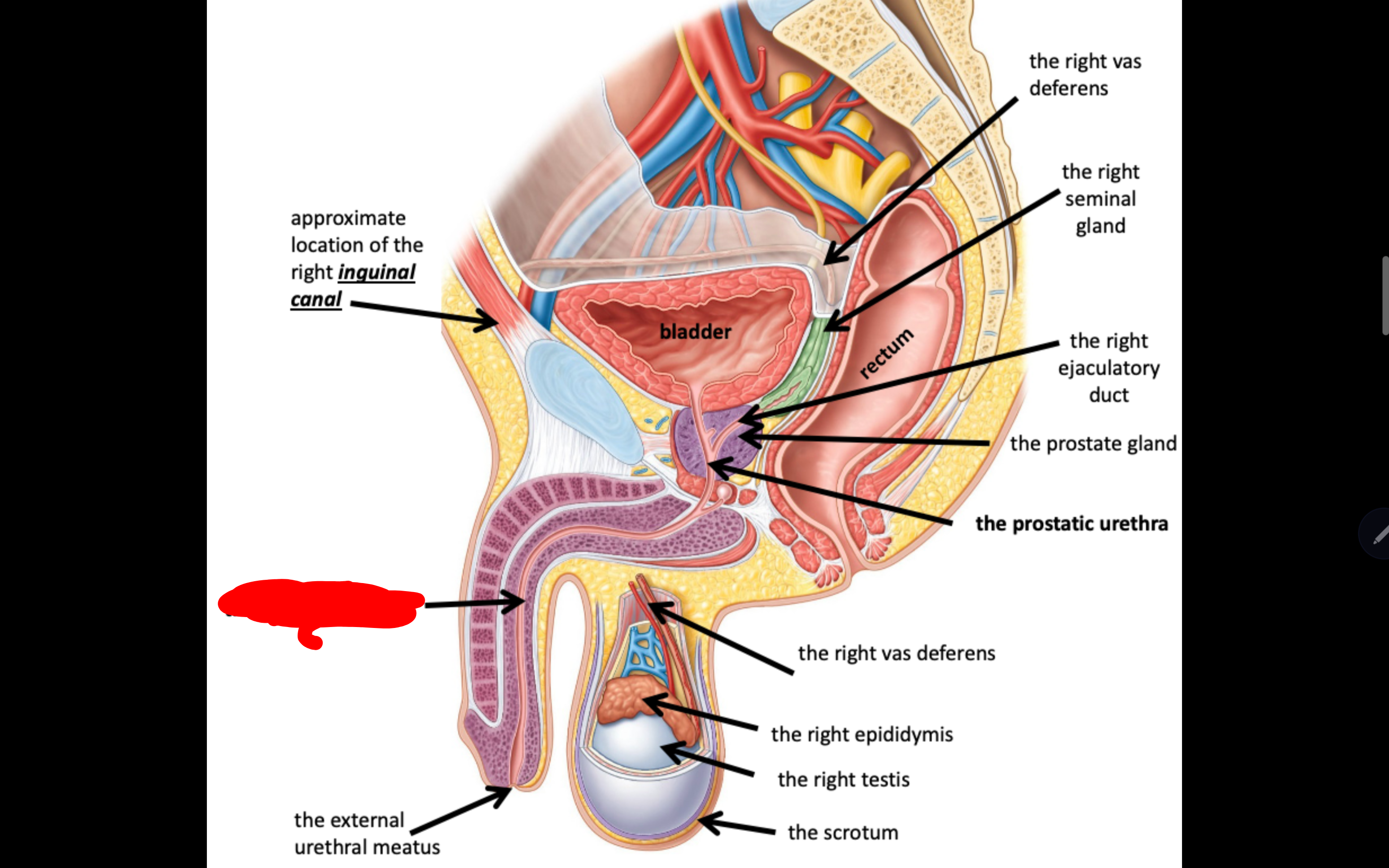
Name the structure in red
The spongy urethra
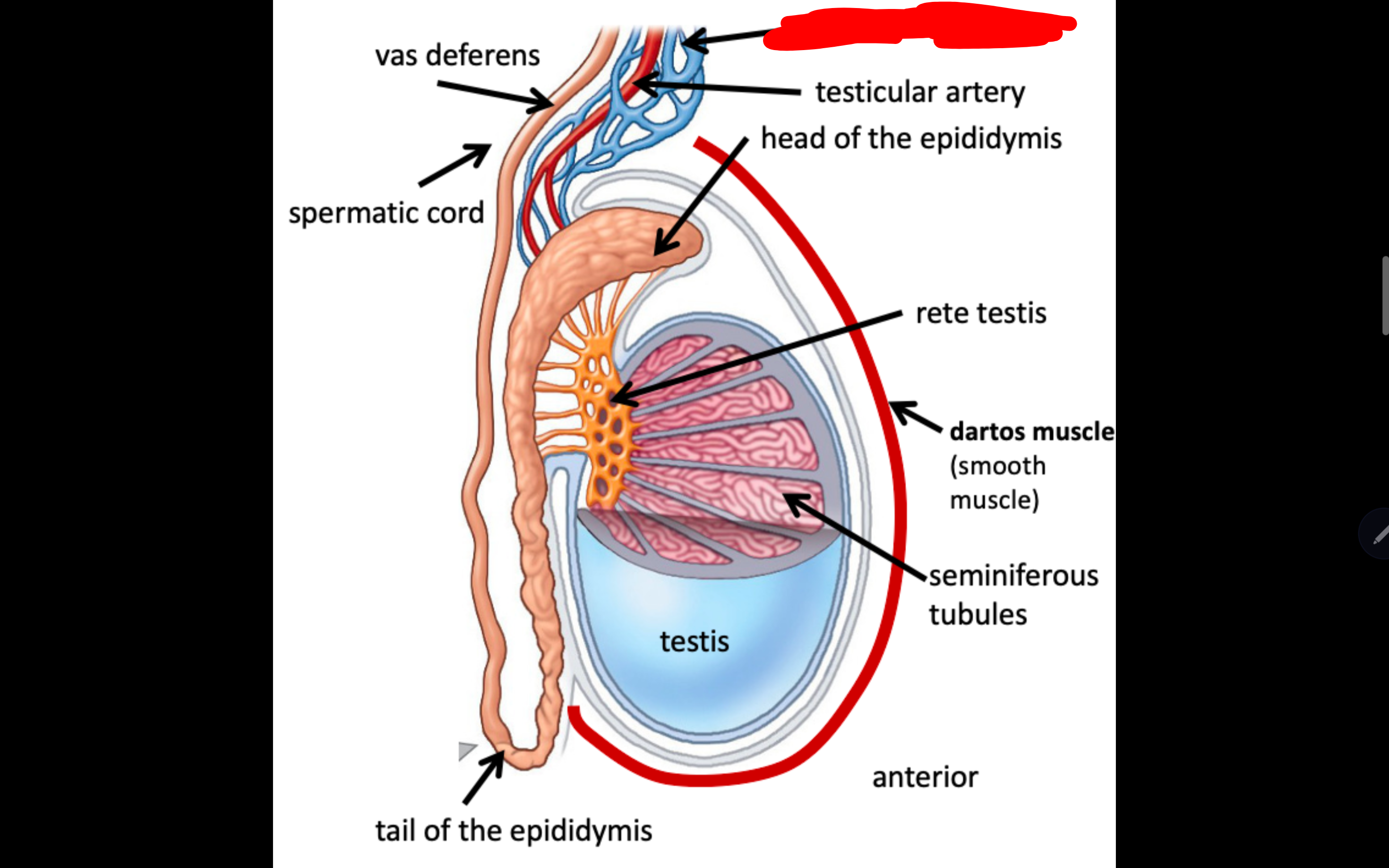
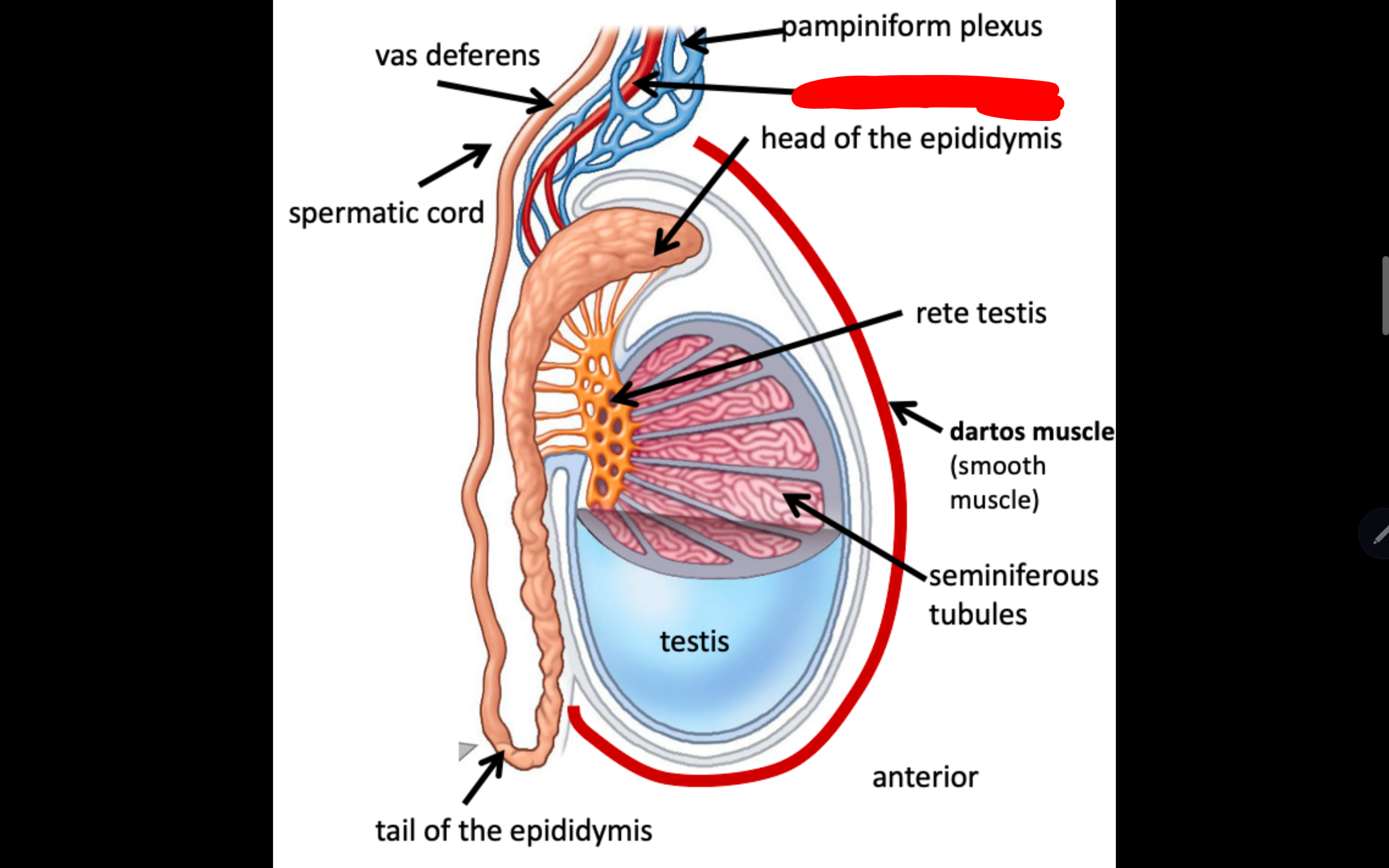
Name the structure in red
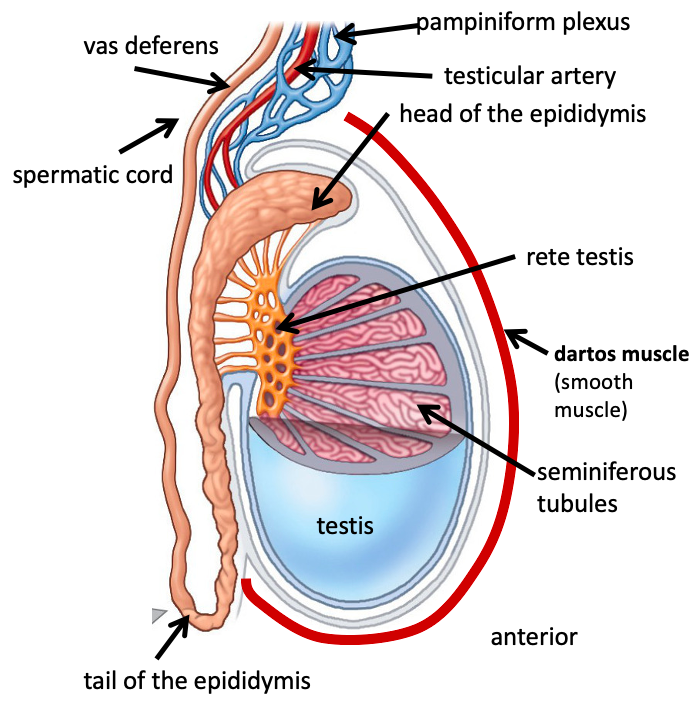
Pampiniform plexus
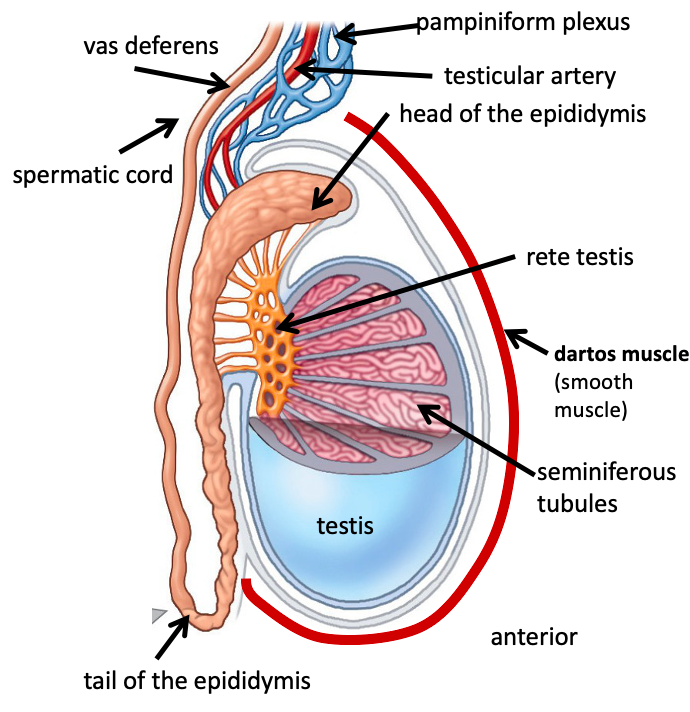
Name the structure in red
Testicular artery
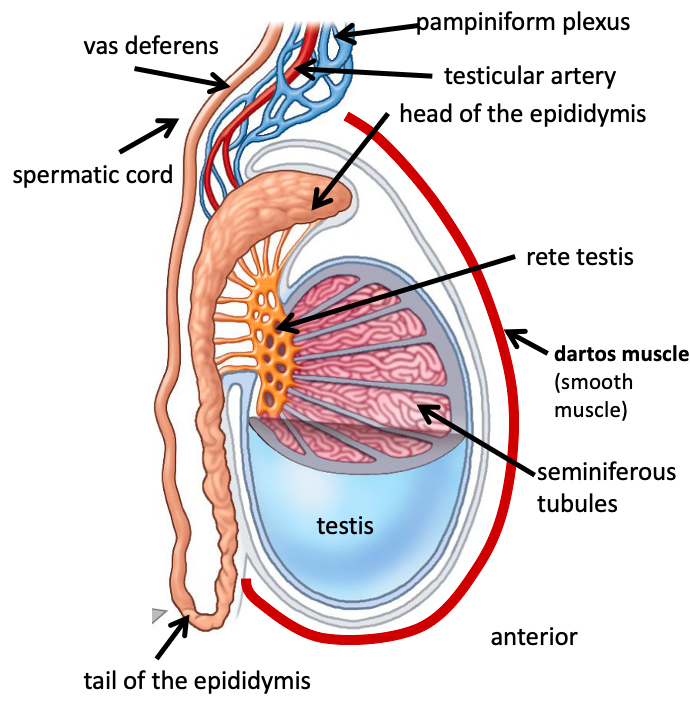
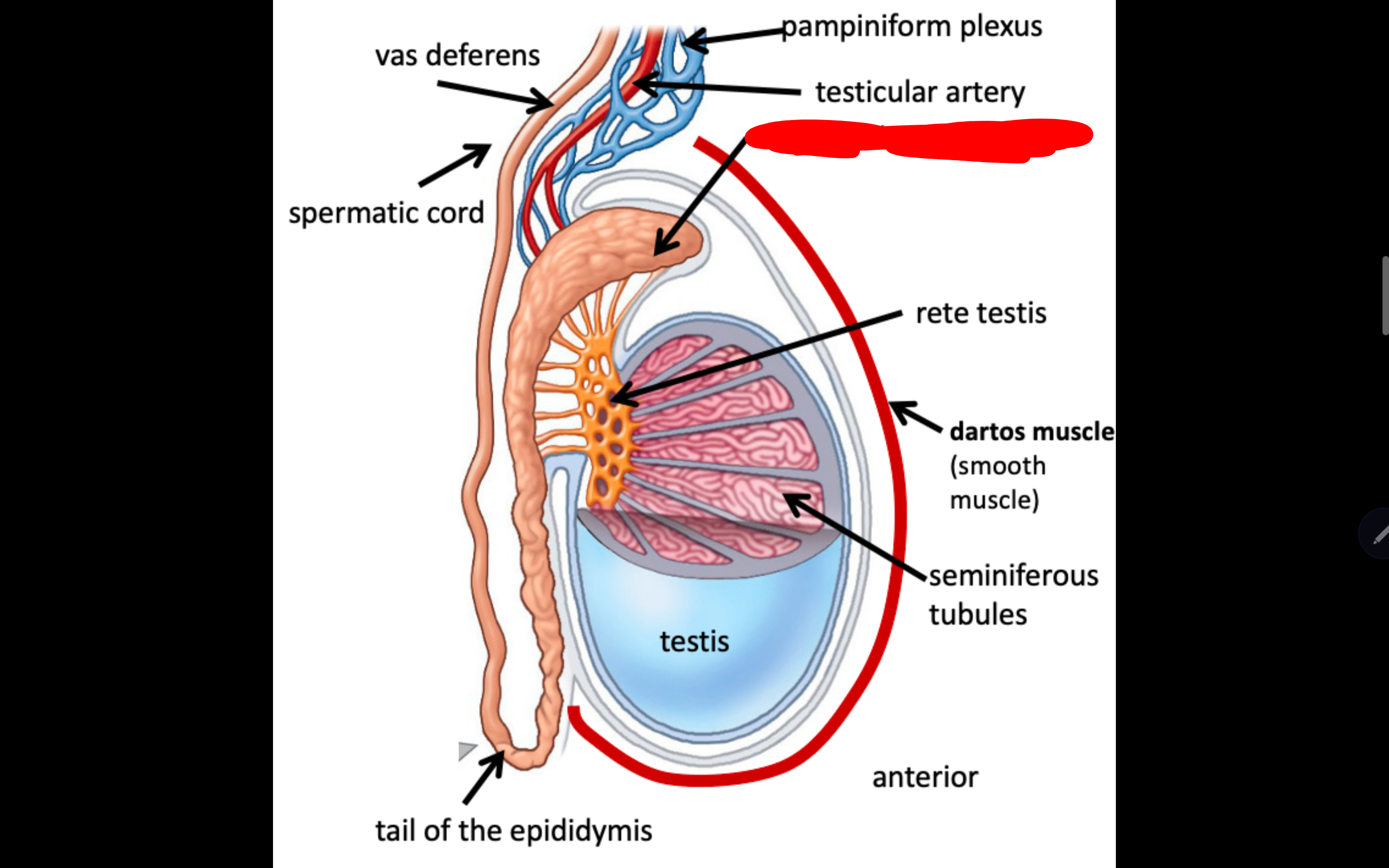
Name the structure in red
Heard of the epididymis
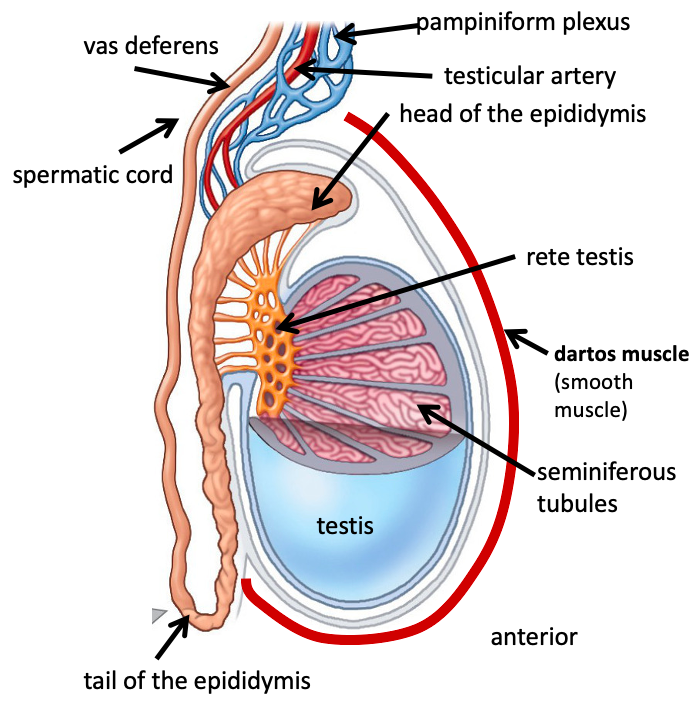
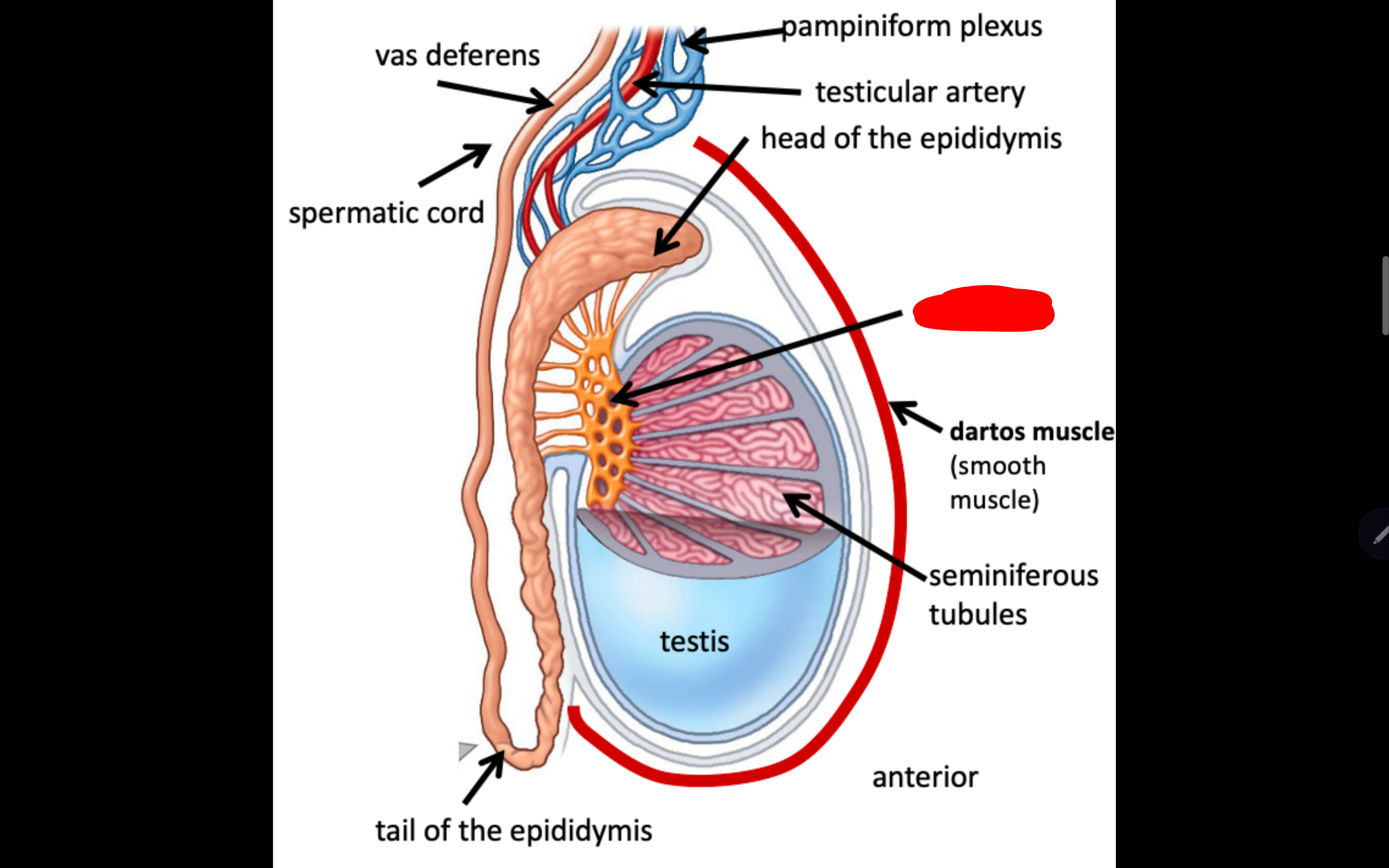
Name the structure in red
Rete testis
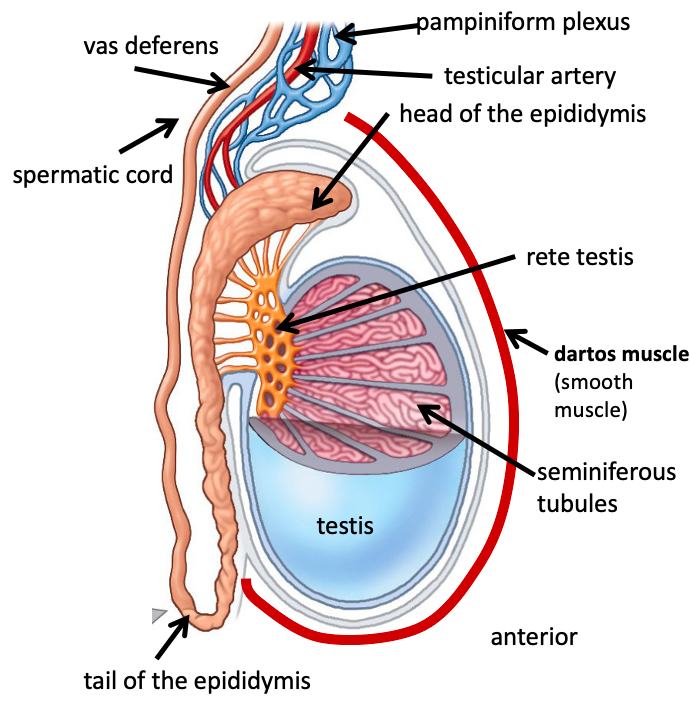
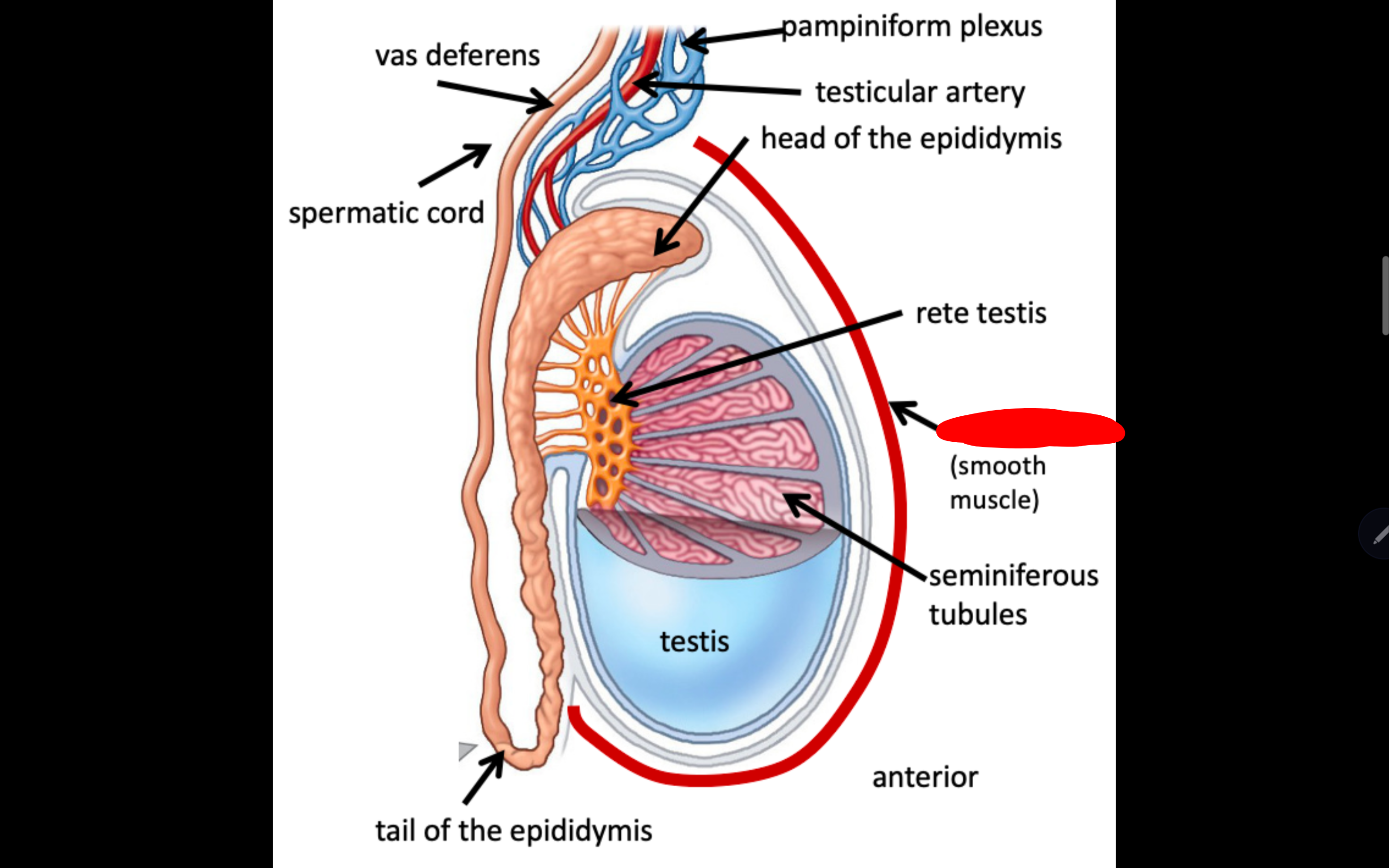
Name the structure in red
Dartos muscle
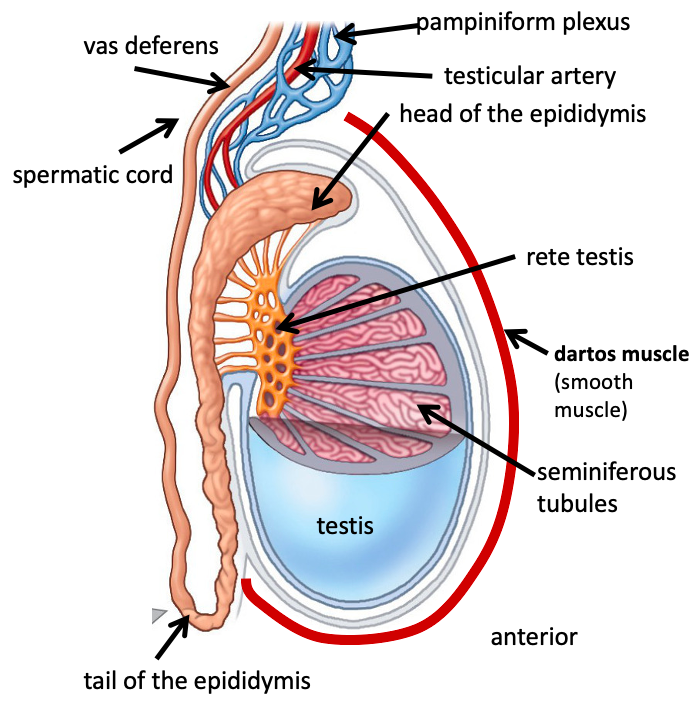
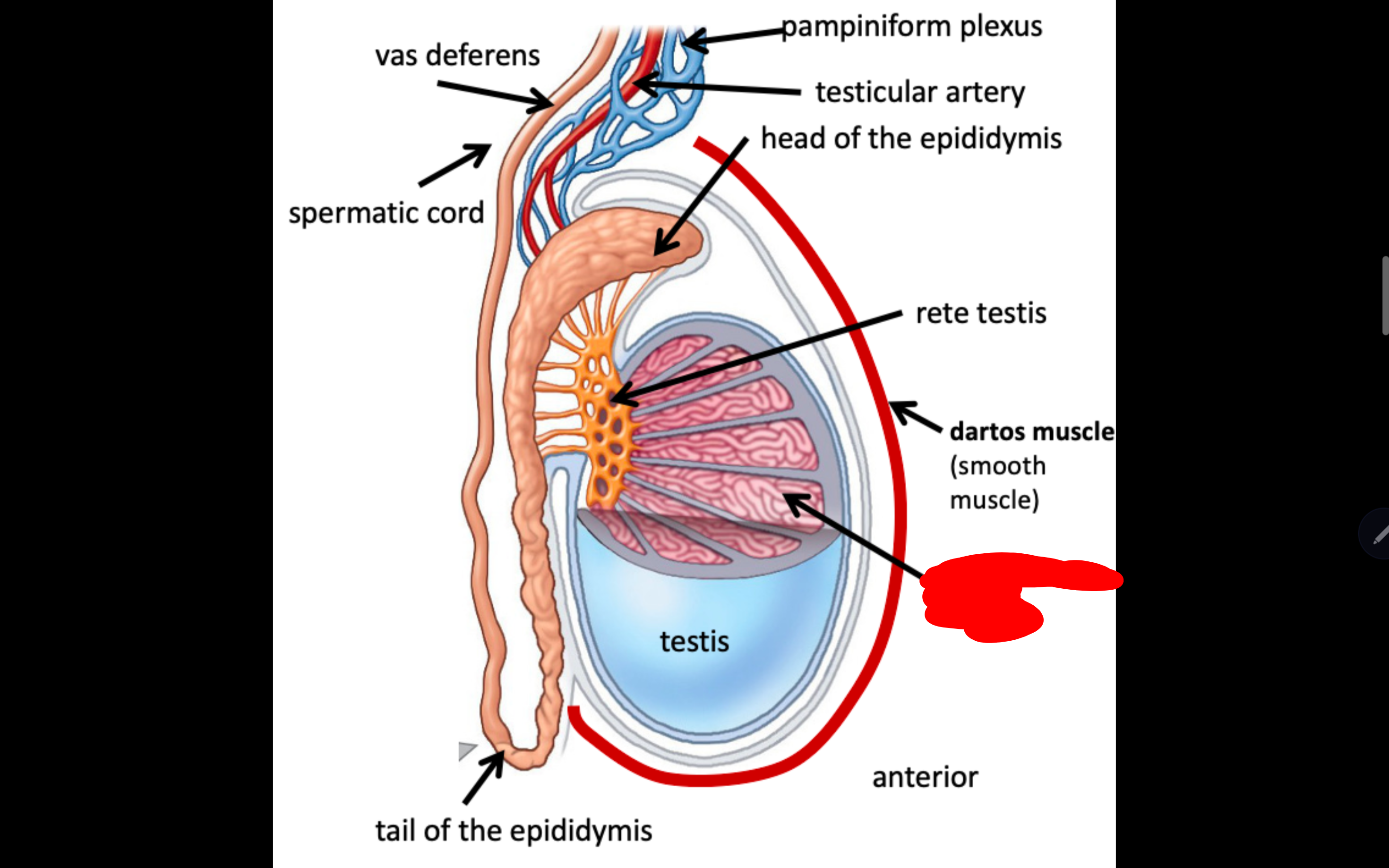
Name the structure in red
seminiferous tubules
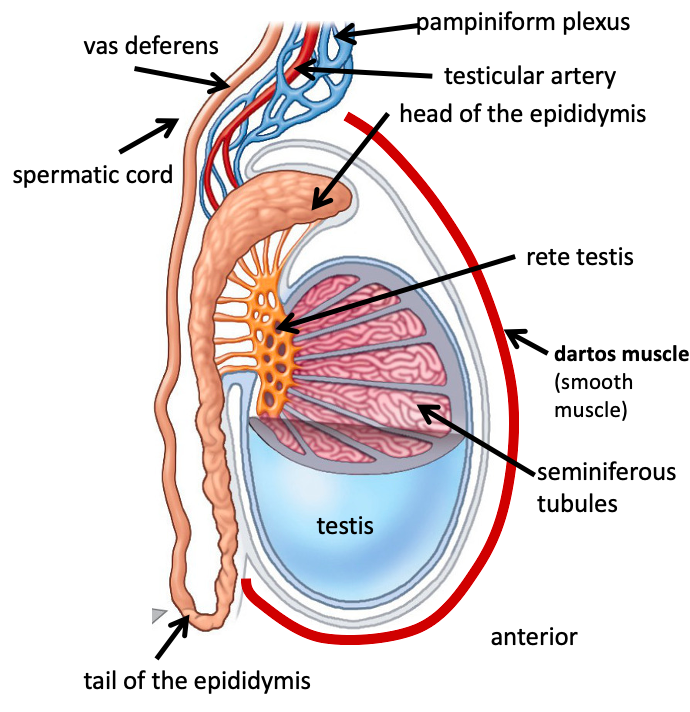
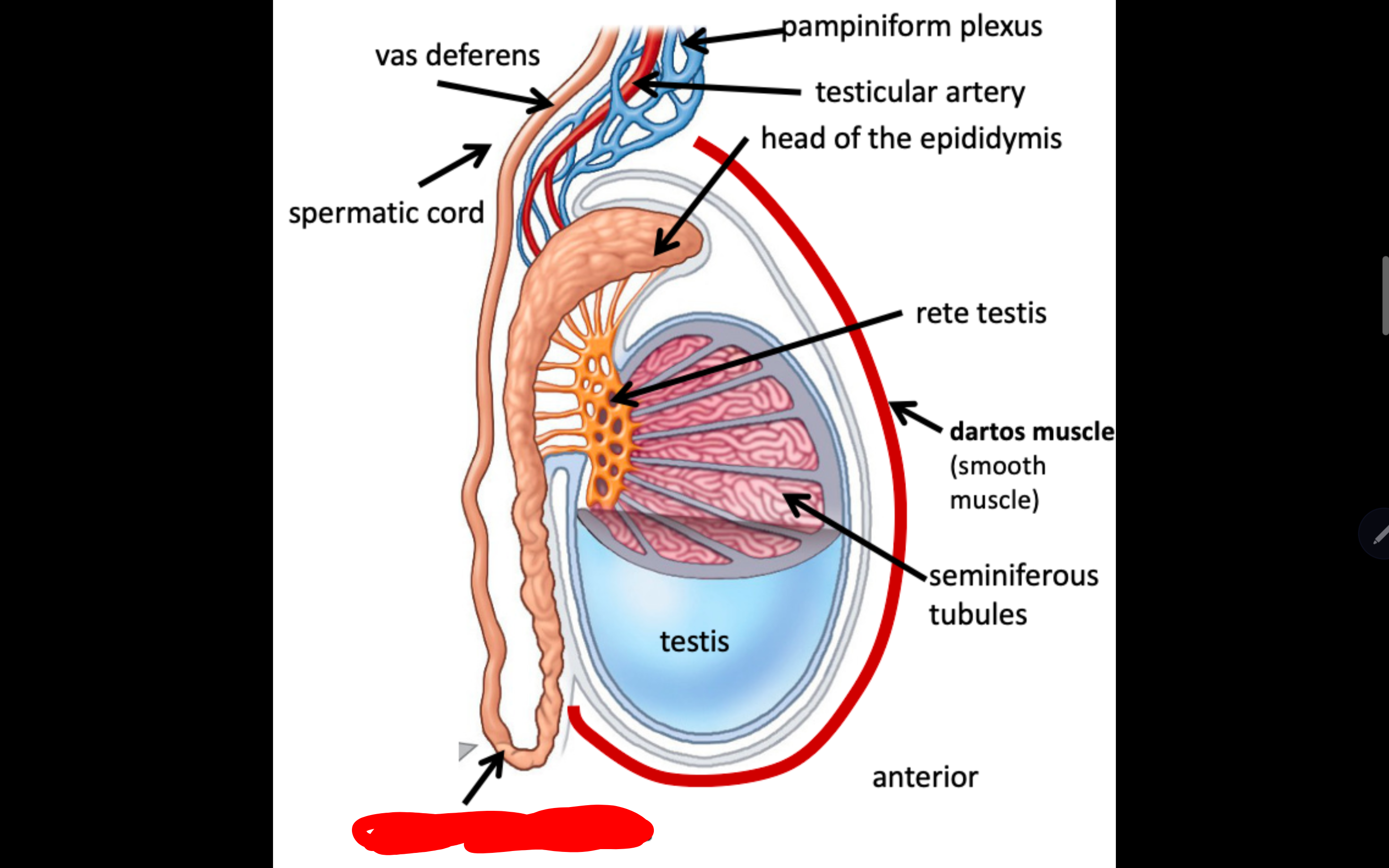
Name the structure in red
Tail of the epididymis
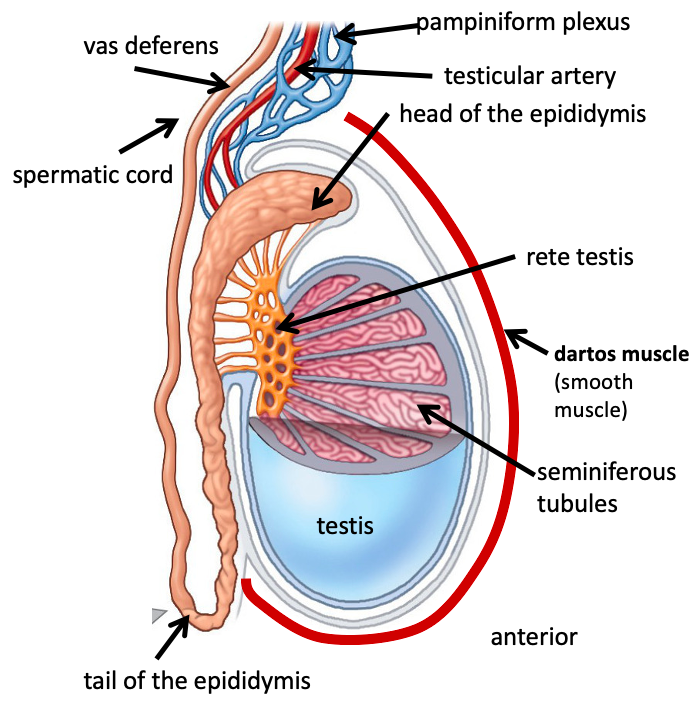
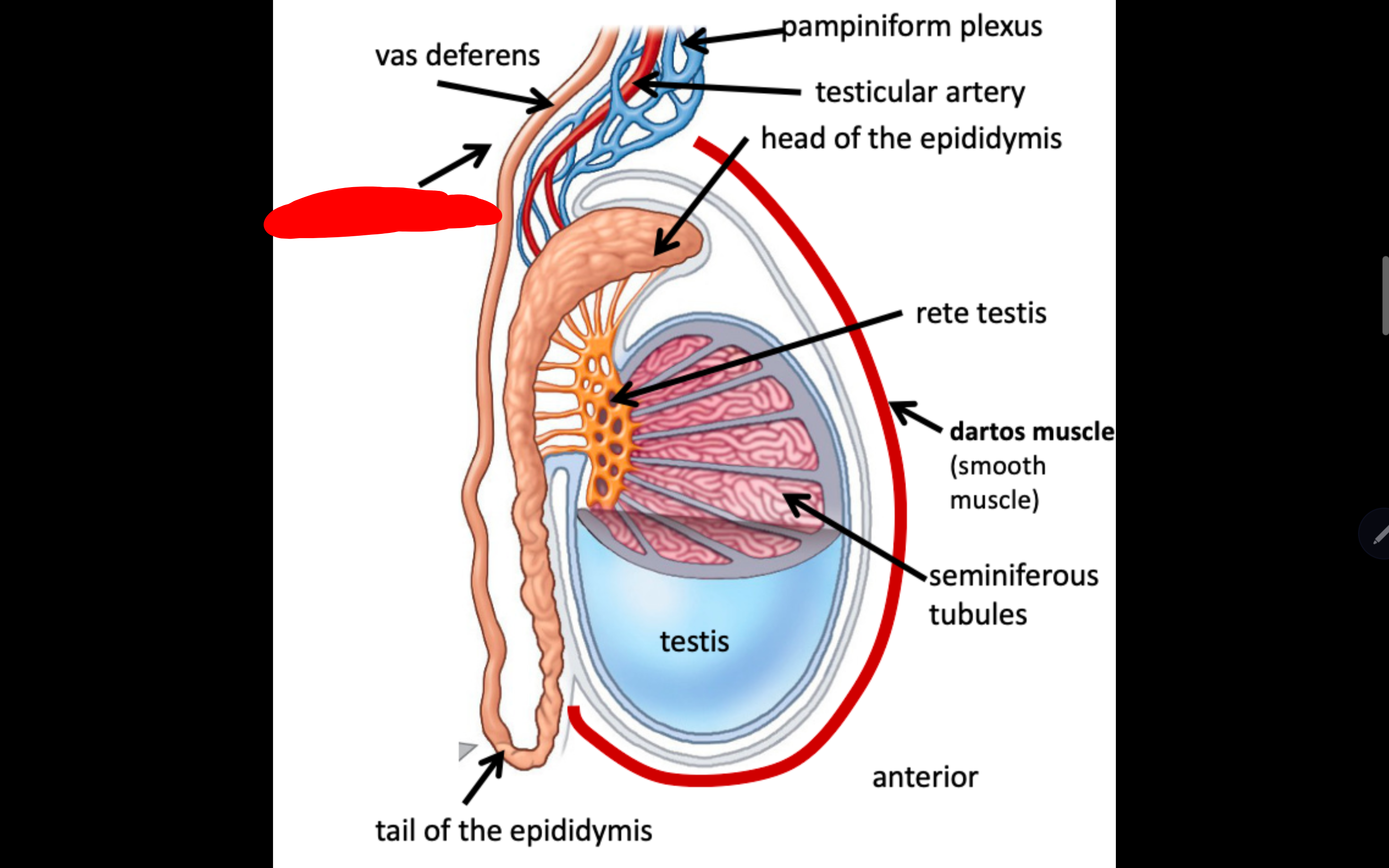
Name the structure in red
spermatic cord
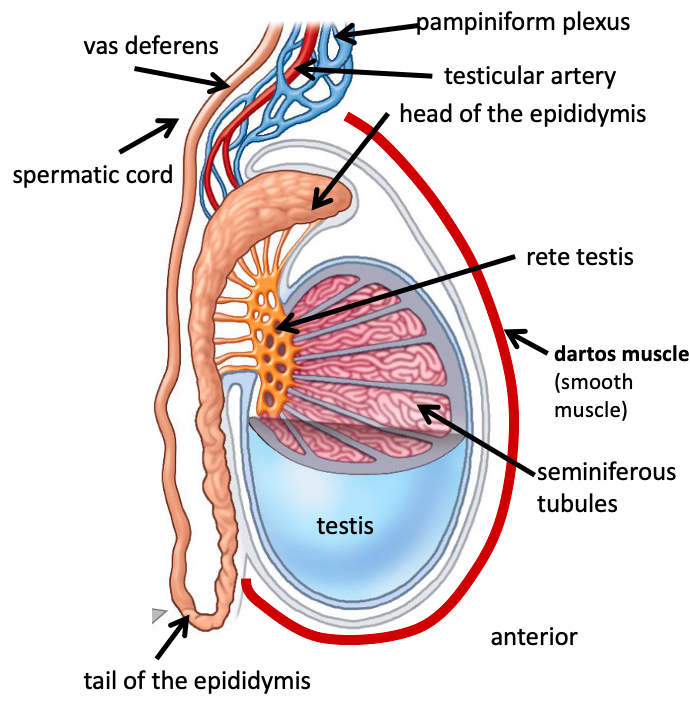
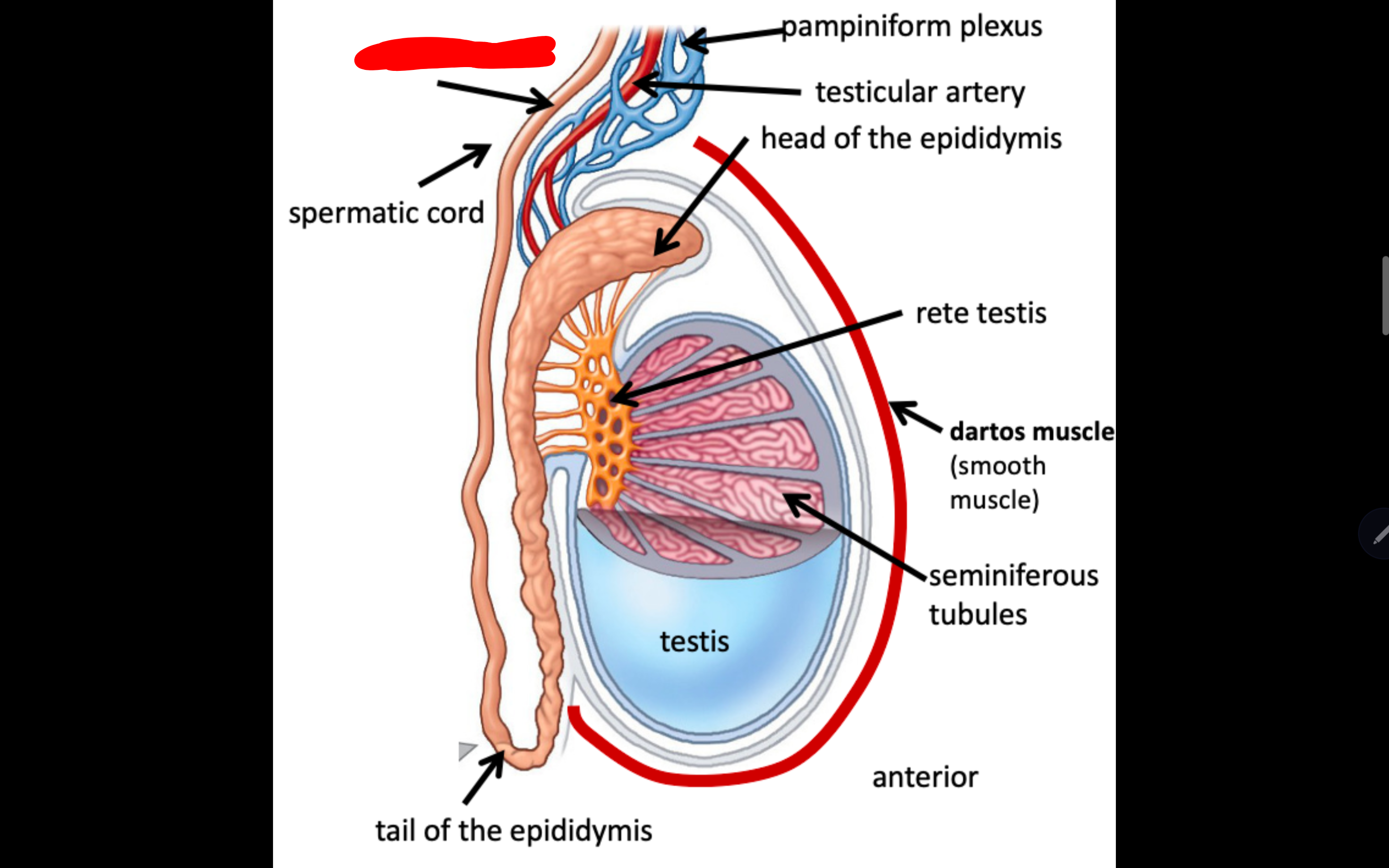
Name the structure in red
Vas deferens