Grade 11 Biology Exam
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
Define biodiversity
the variety and number of different life forms on Earth
Three levels of biodiversity and what they are:
Species: variety and abundance of species in an area
Genetic: the biological variation that occurs within a species (genes)
Ecosystem: range of habitats, resident organisms, and relationships
What tool is "species" for scientists?
It allows them to categorise living things into different groups, which represents which living things are the same or different.
What can living things within a species do?
breed freely under natural conditions
Hybridization
When two species of plant or animal breed with one another
What is morphology, and why is it helpful?
The physical appearance.
It helps us classify naturally hybridised plants.
Heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food.
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food.
The 6 types of interactions between species
- Food Supply
- Protection
- Transportation
- Reproduction
- Hygiene
- Digestion
How does loss of biodiversity affect us? (4)
- Loss of food supply
- Loss of natural and potential medicines
- Disruptions of carbon intake by biogeochemical cycles
- Economic impacts on tourism and forestry
Taxonomy
The science of classifying and identifying organisms
Carl Linnaeus
- came up with genus
- came up with binomial nomenclature
- came up with DKPCOFGS
DKPCOFGS
- Dear King Philip Came Over For Good Soup
- Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Binomial nomenclature rules
- Genus is capitalized
- Species is not capitalized
- Underlined if handwritten
-Italicized if typed
- Genus can be shortened
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history of a species or group of species.
Clade
A group of species that includes the ancestor and all its descendants.
Dichotomous keys
A classification system based solely on appearances.
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. (eg. archaea and eubacteria)
Eubacteria
Another term for prokaryote, used to distinguish from archea bacteria.
What are the cause of most diseases?
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Protists
Why are microorganisms important?
They:
- recycle nutrients
- can help humans cure diseases
- autotrophs provide food for others
Similarities between Eubacteria and Archaea (4)
- Single-celled
- the organelles DON'T have membranes
- contains plasmid DNA
- found everywhere
Differences between Eubacteria and Archaea (3)
- Eubacteria tend to have more genetic information (Archae are simpler)
- Chemical differences in cell wall and cell membrane composition
- Archaea are typically extremophiles
Characteristics of Bacteria (6)
- DNA is in a single loop found in the nucleoid
- May also contain plasmids (small loop of DNA)
- scattered ribosomes
- flagella and/or pili
- cell membrane and cell wall (peptidoglycan)
- Some are surrounded by a capsule for added protection
What are the cell membrane and cell wall composed of?
Peptidoglycan: cross-links, to form a strong rigid wall
What are the three shapes of bacteria?
- Cocci (spherical)
- Bacilli (rod-shaped)
- Spirilla (spiral)
Obligate aerobe
requires oxygen (All animals are obligate aerobes)
Facultative aerobe/anaerobe
When there's oxygen they use it, and when there's not they don't need it.
Obligate anaerobe
requires the absence of oxygen
What are the two types of bacteria reproduction?
- Binary fission
- Conjugation
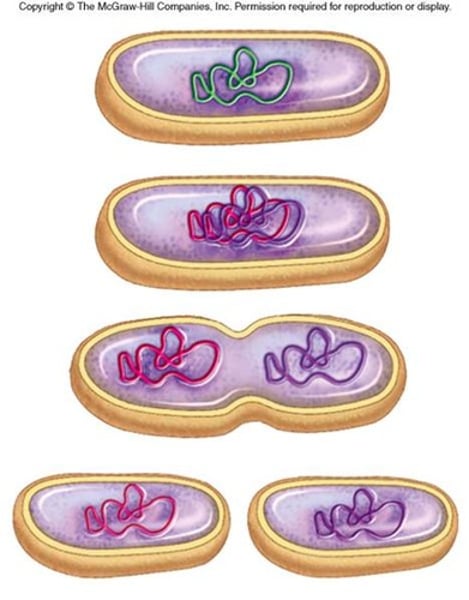
What are the four steps for Binary Fission?
Step 1 - The parent cell replicates its chromosome and plasmid DNA
Step 2 - The two strands of DNA migrate to opposite ends of the cell
Step 3 - The cytoplasm begins to separate, taking each piece of DNA in opposite directions
Step 4 - The cell wall and cell membranes form around each new cell
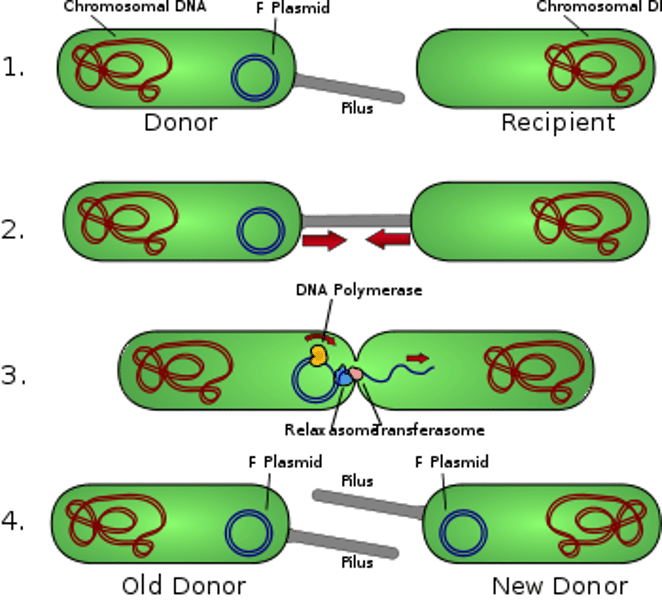
Conjugation
- considered a form of sexual reproduction
- a way that bacteria can diversify their DNA
- One bacteria passes a copy of its plasmid DNA through a pilus into another bacteria cell
What level of organisation is "Virus"
Class
Why are viruses kinda lame?
They don't have their own cellular functions, so they can't perform the basic functions that a cell can. They NEED cells to survive.
Why are viruses considered non-living? (4)
-not made out of cells
- don't grow
- can't make their own energy
- cannot reproduce on their own
Virus general structure
- A genome (a cluster of DNA or RNA)
- genome surrounded by a capsid coat made of proteins
- no cytoplasm, organelle membranes, or cell membranes
- some have a lipid envelope that encloses the virus, or glycoprotein spikes
Glycoprotein spikes
allows for attachment, fusion, and entry into host cells
Virus morphologies (4)
- helical
- polyhedral
- spherical
- complex (bacteriophage)
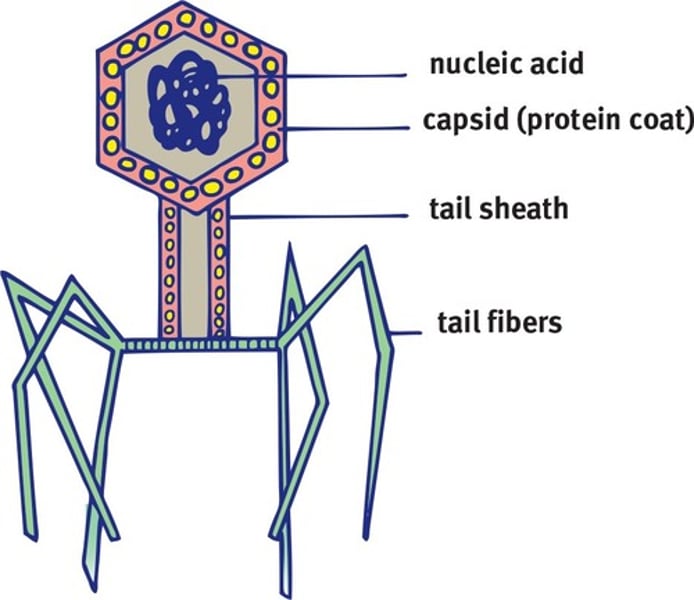
Bacteriophage structure
- A sheath and tail fibers
- Sheath: syringe; injects genetic material into bacterium
- Tail fibers: help the bacteriophage recognize and connect to the correct host cell
What do viruses do when they aren't invading?
Stay in an "inert state" (like hybernation)
The Lytic Cycle steps (5)
- Acronym A.E.R.A.L. (Ah E(l)RAL)
- Attachment
- Entry
(Lysogenic cycle)
- Replication
- Assembly
- Lysis
Extend on Lytic Cycle steps
1) Attatchment - the virus' glycoproteins bind to receptors on the surface of the host cell's membrane
2) Entry - the virus injects its genetic material (DNA or RNA) into the host cell
3) Replication - the host cell makes more viral DNA/RNA and proteins
4) Assembly - the new viruses are assembled inside the cell
5) Lysis - the cell ruptures allowing the new viruses to escape
Then repeat!
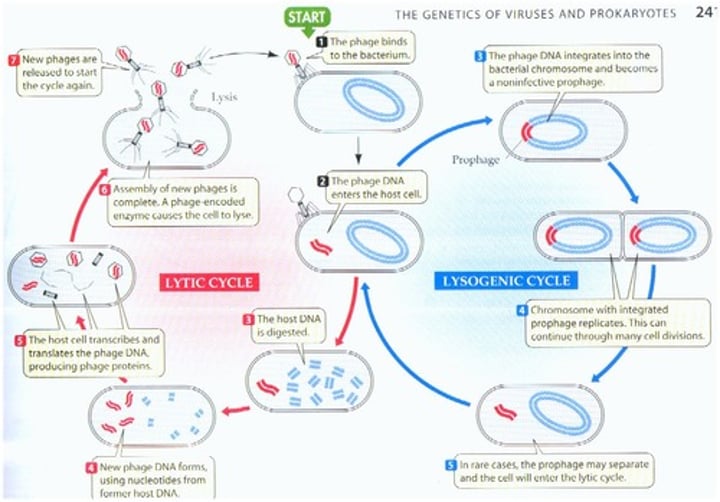
The Lysogenic Cycle
- an offshoot of the Lytic Cycle
- takes place between Entry and Replication
- Provirus' form: the virus' viral DNA will make itself a part of the host cell's DNA
- this step allows the virus to control parts of the host cell while staying dormant and eventually replicating (or slowly replicating)
What level of organisation is "Protists"?
Kingdom (protozoa)
Protists
- typically unicellular
- all eukaryotes (meaning they have cell organelles with membranes and segmented parts)
- DO NOT form tissues ( NO specialized cells)
Eukaryote
- domain
-An organism consisting of a cell or cells in which the genetic material is DNA in the form of chromosomes contained within a distinct nucleus.
- Eukaryotes include all living organisms other than the eubacteria and archaebacteria.
What're the 4 types of protist metabolism?
1) Autotrophs
2) Heterotrophs
3) Saprotrophs
4) Parasites
Autotrophic metabolism
photosynthetic (like plants)
Heterotrophic metabolism
consume other organisms (usually through phagocytosis)
Saprotrophic metabolism
eat dead things
Parasitic metabolism
obtain nutrients from host
Red tide
An algal bloom that results in the discoloration of the water
What level of organisation is "Fungi"?
Kingdom
What relationship is common between Fungi and Plants?
Symbiotic
Benifits of fungi
- Treatments (like penicillin)
- Fermentation in food using yeast
Fruiting Body
- the reproductive structure of a fungus that contains many hyphae and produces spores
- seen above ground
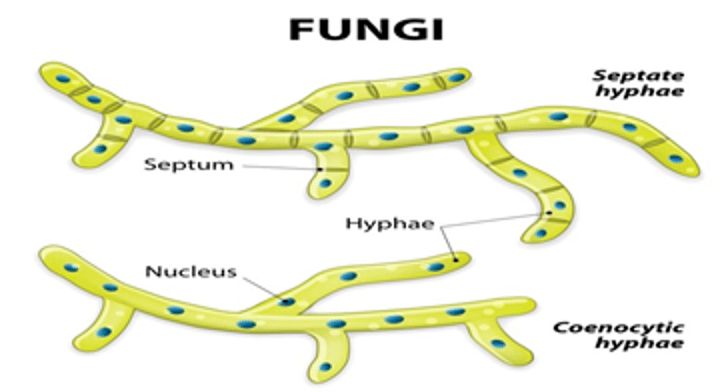
Hyphae and mycellium
Hyphae:
-microscopic tubes that allow materials to pass through and into the fungus
- underground
- what the fuzz on moldy foods is made up of
Mycellium:
- the network of hyphae
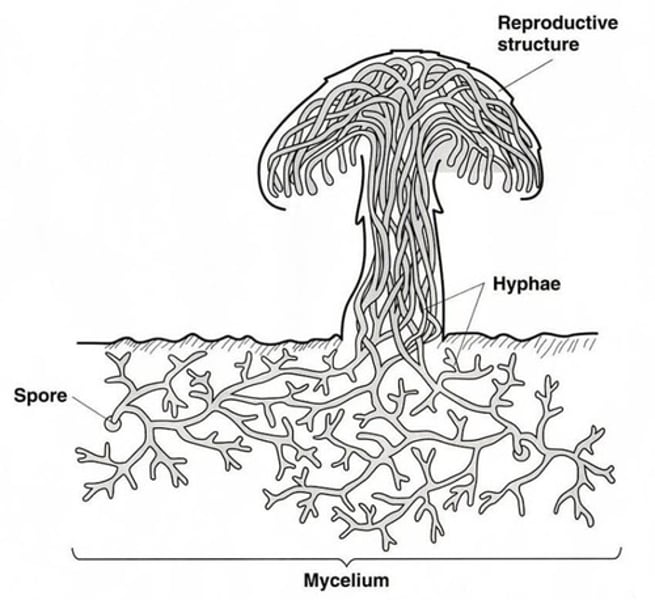
What's the one unicellular fungi?
Yeast
Fungi "septum"
The internal walls that separate the cells
2 types of fungi reproduction
Sexual and Asexual
What is the more common form of fungal reproduction?
Asexual
3 forms of asexual reproduction in Fungi
1) budding
2) fragmentation
3) spores
Budding
- A form of asexual reproduction of yeast in which a new cell grows out of the body of a parent.
- nucleus pretty much replicates itself and a new vacuole is formed in the new cell
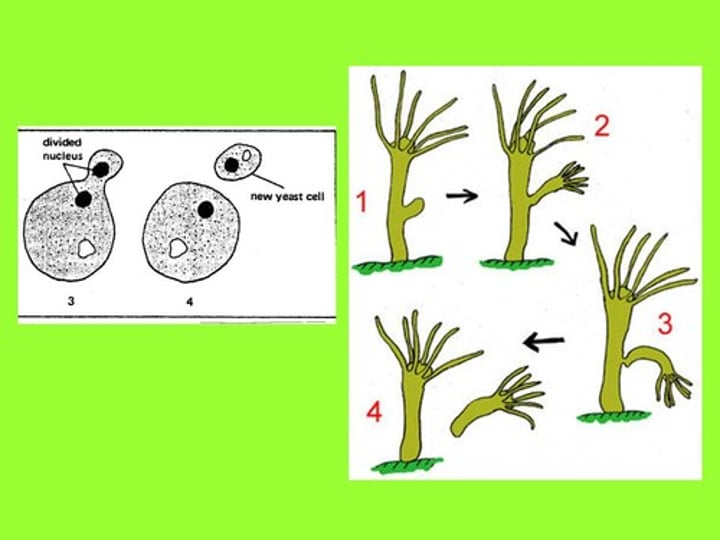
Fragmentation
A form of asexual reproduction where a single parent breaks into parts that regenerate into whole new individuals.

Spores
The fruiting body makes a spore, which drops off and begins it's own life cycle.
Fungi sexual reproduction
1) Cells are present in hyphae, and when two hyphae meet, they both release a cell and this becomes one big mycelium (called a "dikaryotic cell")
2) As the mycelium grows, it may become a mushroom cap
3) When the mushroom cap is done growing, structures called basidia are found on the gills of the cap
4) The two original cells undergo meiosis in the basidia and spores are released
What level of organisation is "Plantae" (plants)
Kingdom
What level of organisation is Animalea (animals)?
Kingdom
Animals
- multicellular
- top of the food chain
- the first animals are thought to have emerged 800 million years ago
Characteristics of animals
- multicellular
- heterotrophs
- can develop specialized cells (Ex. nerve cells)
- coelom is only found in animals (but not all animals have it)
prokaryotes
unicellular
smaller
dna in cytoplasm
no nucleus
aseuxal
eukaryotes
muti-cellular
bigger/more complex
dna in nucleus
sexual
biological species
organisms that can naturally breed + produce fertile offspring
morpholgical species
organisms that share physical features
Phylogenetic
a group of organisms that share a common ancestor, sharing unique sets of traits including DNA analysis
lithotrophs
gets energy from carbon dioxide. hydrogen sulphide and methane
organotrophs
gets energy from living organisms
phototrophs
gets energy from light
antibodies
type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria
types of vaccines
live attenated vaccines
inactive vaccines
subit vaccines - from antigens
dna vaccines
gene therapy
technique that uses a gene to treat, prevent or cure a disease or medical disorder
prions
abnormal, pathogenic agents that are tranmissble. when misfolded proteins that can infect other proteins and cause fatel neurological damage
fungi
decomposers- break down plants and animal debris
endosybiotic theory
eukaryotic cells used to be archea/bacteria then early bacteria engulfed them and instead of killing them, they used them for energy
protists
contain their own dna in a cirrular chromosome
reproduce by binary fission
cells cannot make new ones if removed
brown algae
meiosis
spore (n)
mutlicellular haploid (n)
binary fission
gametes
fertilization
zygote (2n)
mutilcellular diploid (2n)
malaria
mosquito bites a human injecting plasmodium
infects and reproudes asexually in liver
invade red blood cells
bursts red blood cells open
new mosquito bites the human and the plasmodium reproudes in the mosquito
dna
the material that makes up our genetic code, found in all living organisms. has the codes for genes and is found in the nucleus. DNA is a double helix, there are two complimentary strands
genes
tells the cells what proteins to make
base nucleotides
adenine + thymine - 2 h-bonds and guanine + cytosine - 3 h-bonds
purines
adenine and guanine
pyrimidines
cytosine and thymine
the central dogma
when the dna code becomes proteins
transcription
copies a part of dna and takes it out and it becomes rna
translation
the rna gets turned into amino acids
3 bases on rna makes one amino acid
mitosis
the division of parent cells into two daughter cells - only somatic cells
they undergo mitosis to grow, repair injury or to replace dead cells
karyotyping
an individuals complete set of chromosomes
turner syndrome
missing one sex chromosome
edwards syndrome
extra chromosome 18
supermale syndrome
extra sex chromesome, y