Ch 24 - Free Trade and Protectionism
- Free trade: international trade (imports and exports) without government restrictions
- Trade of goods and services without trade barriers
- Protectionism:
- Protection of domestic industries against foreign competition
- Government restrictions are placed on the imports of foreign competitors (tariffs, quotas and subsidies)
Arguments for protectionism:
- Protecting domestic employment
- Protecting the economy from low cost labour
- Protecting the economy from low cost labour
- Protecting an infant (sunrise) industry
To conclude:
- Protectionism raises prices to the consumers and producers of the input
- Less choice for consumers
- Competition would diminish and domestic firms would become inefficient
- Reduced economic growth
- Comparative advantage is distorted leading to inefficient use of world resources
Types of protectionism:
Tariff : a tax that is charged on an imported good. Any tax will cause suppliers to supply less
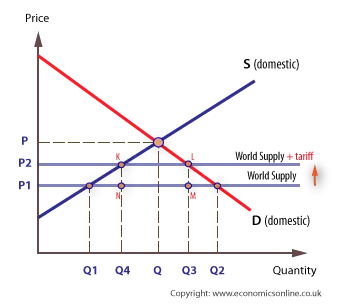
If wheat (example) is not purchased there is a deadweight loss of welfare
There is a deadweight loss of welfare
There is inefficiency of domestic products and a loss of world efficiency
Subsidy: an amount of money paid by the government to a form per unit of output
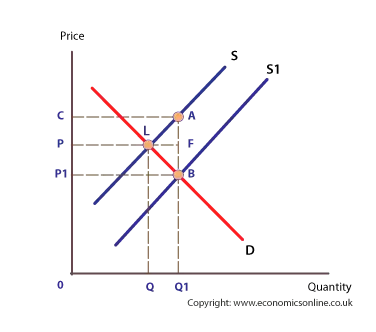
- Government is giving the subsidy to the fir to make it more competitive
- Domestic supply curve will shift downward reducing the price
- Consumers are indirectly affected by the government’s use of tax revenues to find the subsidy
- Could lead to higher taxes and is an opportunity cost, governments could spend taxes on other things
Quotas: physical limit on the number of value of goods that can be imported to a country
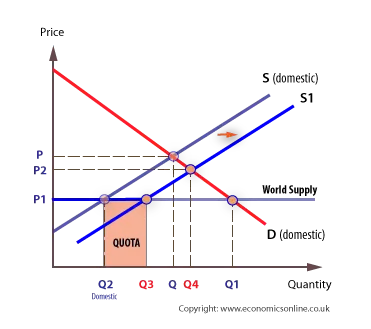
- Excess demand of Q3Q2, prices begin to rise
- As price rises, imports are not allowed to supply more
- Domestic products begin to enter the market attracted by the high price of wheat
Voluntary export restraints:
- Agreements between exporting and importing countries in which the exporting country agrees to limit the quality of exports of a specific good below a certain level
Administrative barriers:
- When goods are imported there are always administrative processes
Health, safety, and environmental standards:
- When restrictions are put on the type of goods that can sold in the domestic market
- Embargoes: complete ban on imports
- National embargoes: marketing campaigns to encourage people to buy domestic goods