immu2011: t + b cells
1/267
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
268 Terms
antigen
a substance recognised by lymphocytes
foreign to body
b cells
recognise free floating or membrane bound antigen
t cells
recognise peptides on MHC molecules
MHC molecules
surface molecules presenting peptide antigens
naive t cell
t cells from thymus, not yet exposed to antigens
t cell receptor
recognises a specific pathogen antigen
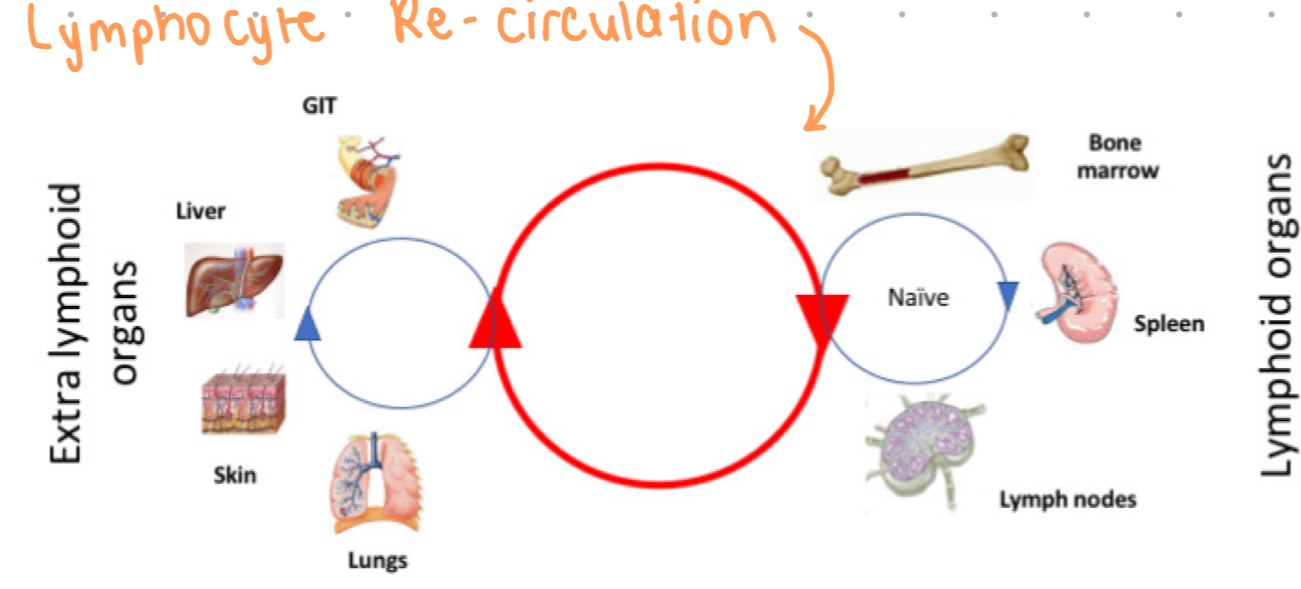
lymphocyte recirculation
movement of naive lymphocytes through lymphoid tissues
t cells re-circulate to continue to encounter foreign antigens
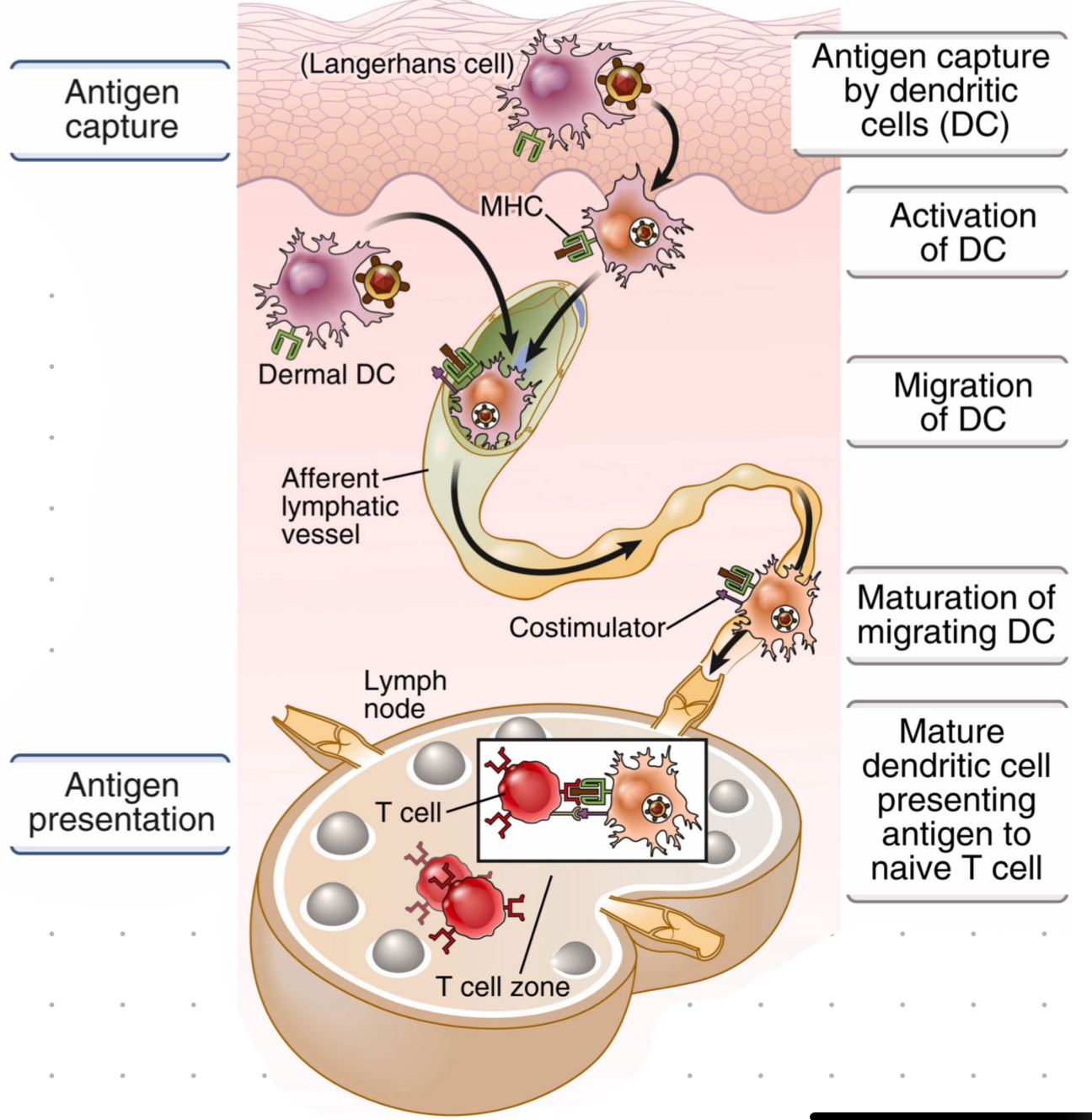
antigen encounter
bringing T cells and antigens to lymphoid tissues for interaction
maximising antigen encounter
DCs are strategically located in periphery where they capture antigens, become activated, and migrate to lymph node where they present antigen to naive T cell
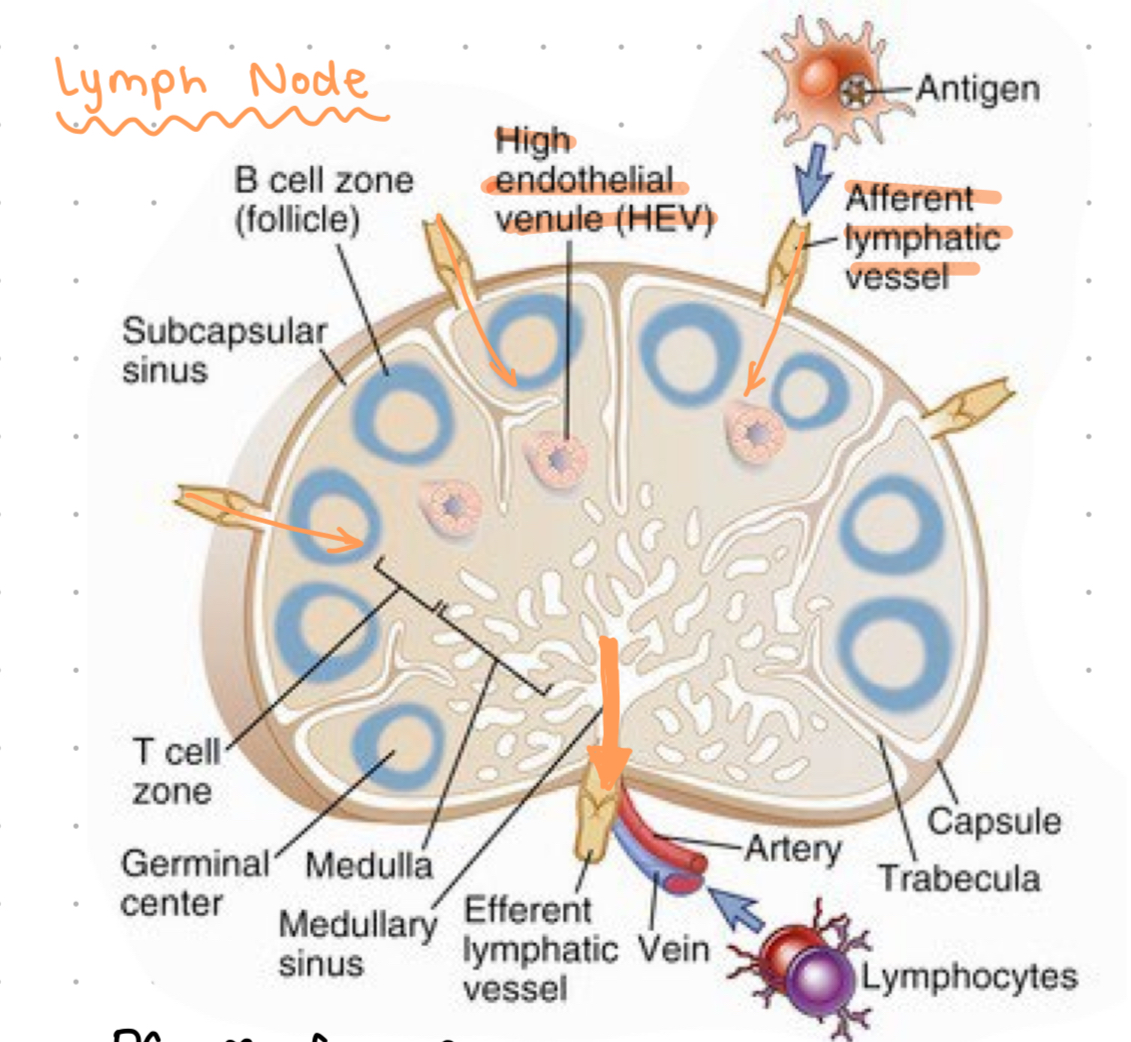
lymph node
DC travel from periphery to the _____.
HEV = specialised vessels which connect lymph to blood
only DCs can activate naive T cells
antigen processing
breaking down captured proteins into peptides for MHC presentation
afferent lymphatic vessel
where the antigen enters from periphery and is transported to the lymph node where T cell are location
DC migration
via lymphatic vessels
during transport DC become activated and mature, allowing them to present antigen to T cells
antigenic determinants
small parts of pathogen molcules which are recognized by T cell receptors, couple aa’s long
AKA epitope
antigen recognition + presentation
antigen captured (by resident cells + DCs)
DCs carry antigen to lymph node via vessels, during transport DC mature allowing them to present to T cells
antigen presentation to receptors on T cells
antigen processing
proteins broken down into smaller peptides
peptides loaded onto special surface molecules (MHC) so T cells can “see” them
epitope
amino acids recognised by T cell receptors
MHC
major histocompatibility complex
responsible for displaying antigens to T cells
HLA molecule
human leukocyte antigen, another term for MHC molecules
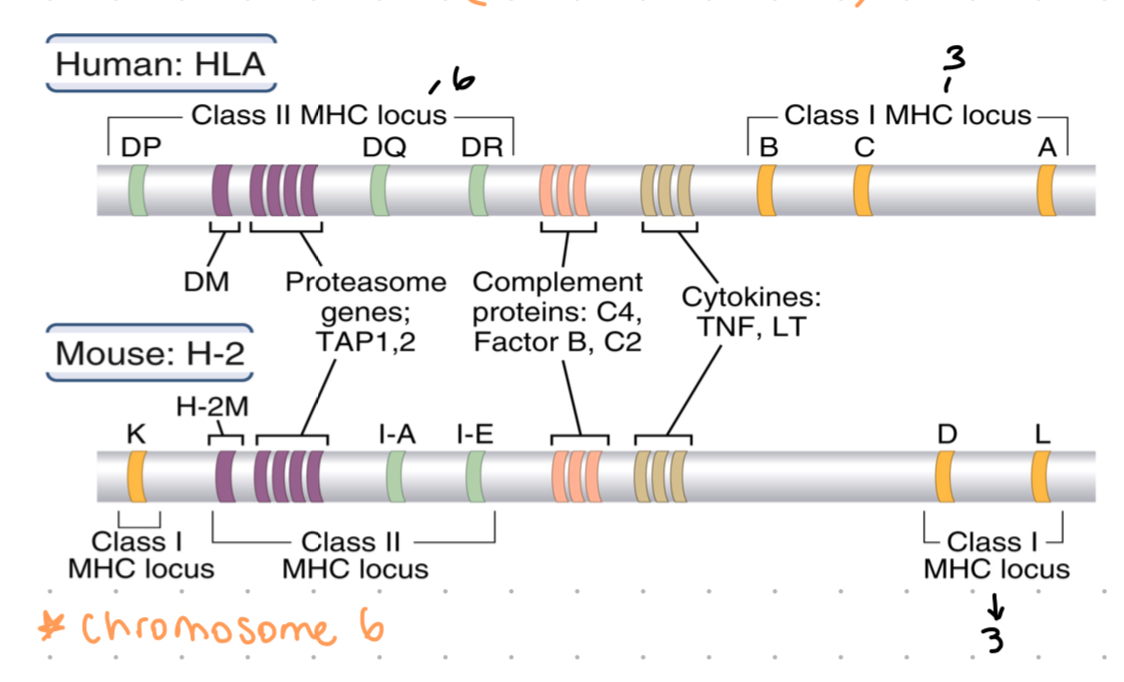
the MHC in humans, HLA genes located on chromosome 6
polymorphic
having variations between individuals, highly expressed in MHC genes
MHC class 1
expressed by all uncleared cells
presents peptides to CD8+ t cells
MHC class 2
expressed only on antigen presenting cells (eg, DC)
presents peptides to CD4+ t cells
graft acceptance
determined by MHC
identical MHC locus = acceptance
dissimilar MHC = graft rejection
expression of MHC
co dominant
for each MHC - 1 allele from each parent
3 class loci for each class 1 gene = HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C - as co-dominant, each DC expresses 6 MHC class 1 types
3 class loci for class 2 → HLA-DP, HLA-Dq, HLA-DR
peptide binding cleft
site on MHC molecules where peptides are accommodated for T cell recognition
class 1 MHC locus
HLA-A
HLA-B
HLA-C
3 loci, codominant expression = 6 molecules expressed on cell surface
class 2 MHC locus
HLA-DR
HLA-DQ
HLA-DP
3 loci, codominant expression = 6 molecules expressed on cell surface
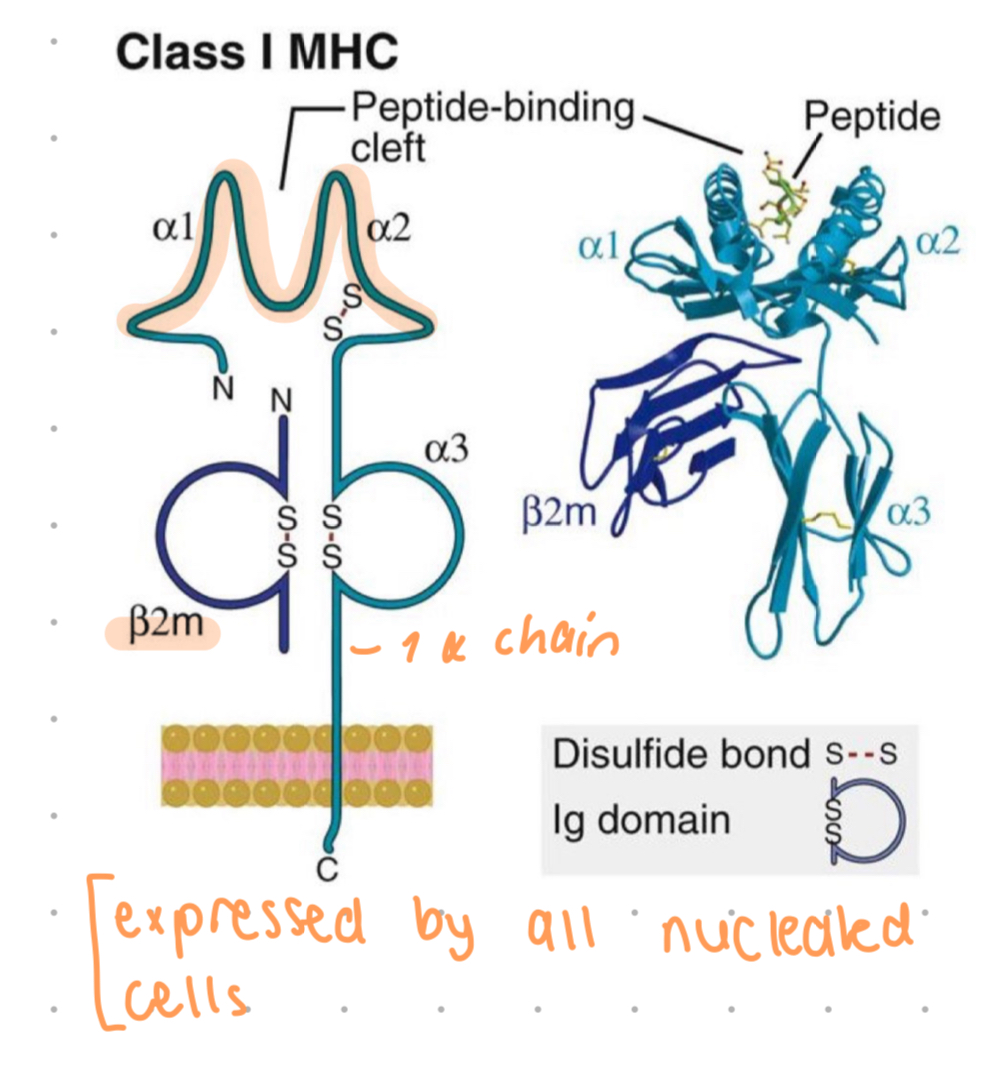
MHC class 1 structure
1 alpha chain
a1 and a2 is where polymorphic residues are, they also form a closed peptide binding cleft
cleft may accomodate aa 8-11 long
a3 is invariant, contains site for CD8+ t cells only, can only activate CD8 t cells
a chain is non-covalently associated w/ B2 microglobulin, a protein which is encoded by gene outside MHC
CD8
T cell co receptor binding to MHC class 1, restricting CD8+ t cell recognition
CD4
t cell co-receptor binding to MHC class 2, restricting CD4+ t cell recognition
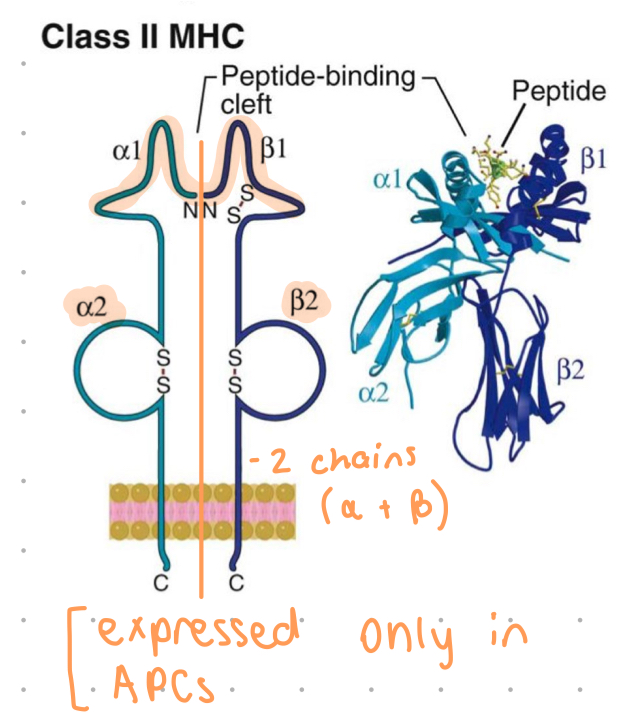
MHC class 2 structure
an alpha and beta chain
a1 and b1 = polymorphic residues, form (open conformation) binding cleft
cleft accommodates 10-30 aa’s
b2 = binding site for CD4+ only
a2 and b2 chains anchor MHC to membrane of APCs (DCs, B cells, macrophages)
antigen processing pathways
processes where MHC class 1 presents intracellular antigens while class 2 presents extracellular antigens
note - DC may express class 1 or class 2 MHC
proteasome
cellular complex degrading proteins into peptides for MHC presentation
TAP
transporter associated with moving peptides into ER for MHC loading
tapasin
molecule assisting in the correct folding of MHC class 1 in ER
phagolysosomes
vesicle formed by fusion of phagosome with lysosome, degrades molecules
CLIP
invariant chain with CLIP occupies the peptide binding cleft in newly synthesised class 2 molecules, CLiIP sequence keeps molecule stable and blocks other peptides form binding until MHC class 2 is fully synthesized
ubiquitin
tagging protein for degradation in the proteasome during MHC class 1 pathway
DM
protein in late endosomes exchanged CLOP for higher affinity peptides in class 2 pathway
novel prize for MHC
awarded to peter doherty and rolf zinkernagel for MHC resistrction work
bare lymphocyte syndrome
condition caused by TAP deficiency leading to susceptibility to infections
MHC class 1 pathway
proteins sourced from cytosol
proteins are unfolded and tagged with ubiquitin for degradation
proteasome shed the proteins into peptides - enhanced by inflammatory cytokines (TNF, IL-1)
peptides actively moved by TAP into ER
in ER class 1 molecules are synthesised - a chain (folding assisted by chaperone molecules), b2 microglobulin
newly formed class 1 MHC molecule binds to TAP via tapasin
peptides are loaded into the MHC class 1 groove
peptide loaded MHC class 1 exits to the golgi to be packaged into exocytic vesicles
presentation to CD8+ MHC class 1 restricted lymphocytes
MHC class 2 pathway
extracellular antigens (bacteria, parasites, fungi) recognised by PRR
internalised by phagocytosis into phagosome/endosomes
endosomes fuses w/ lysosome, which contains proteolytic enzymes + acidic pH
degrades proteins into peptides
AT same TIME
a and b chains of MHC 2 are being synthesised in ER
invariant chain (Ii) with CLIP occupies binding cleft in newly synthesised class 2
class 2 transported out of ER via golgi in a exocytic vesicle (brings MHC class 2 and degraded proteins together)
enzymes in the late endosomes/lysosomes also contain a class 2 MHC-like protein called DM
class 2 molecules loaded with antigen and transported to cell membrane
presentations to CD4+
humoral immunity
a type of adaptive immune response primarily involving antibodies, which are proteins produced by B cells
involves macromolecules in “humours” i.e bodily fluids secreted antibodies, complement proteins, some antimicrobial
B cell role
production of antibodies
common lymphoid progenitor
neutralise + eliminate EC microbes + microbial toxins
antibodies can’t enter cells, so IC microbes not eliminated, need cell mediated immunity
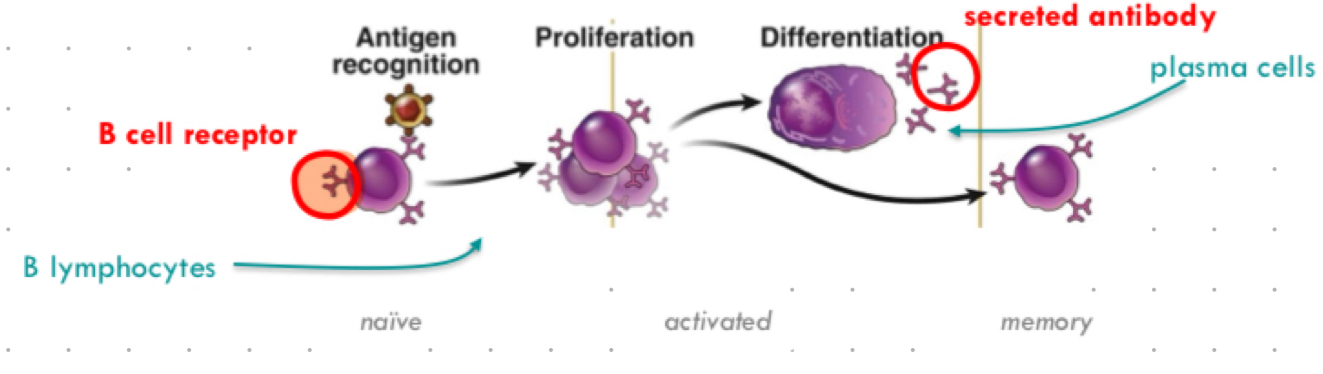
plasma cells
activated B lymphocytes producing antibodies, memory b cells
X linked agammaglobulinemia
genetic disorder affecting B cell development, causing susceptibility to infections
severe recurrent infections, particularly in response to encapsulated bacteria (b cells particularly good at eliminating these)
poor vax response - as no antibodies
vaccination response
immune systems reaction to provoke antibody production
b cell cascade of events
antigen recognition ( b cells) → proliferation (activated) → differentiation (plasma cells) → memory
b cell origin
begin life as a cell surface bound receptor (b cell receptor/BCR), also known as bound antibody
antigen specific receptors
b cells have diverse __________.
can recognise ~10^11 antigens
receptors generated by somatic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments
note - for innate cells, PRR only recognise ~1000 via germline encoded receptor
B cell receptor (BCR)
antibody precursor on b cell surface
somatic recombination
process generating diverse antigen receptors
bursa of fabricus
site of b cell development in birds
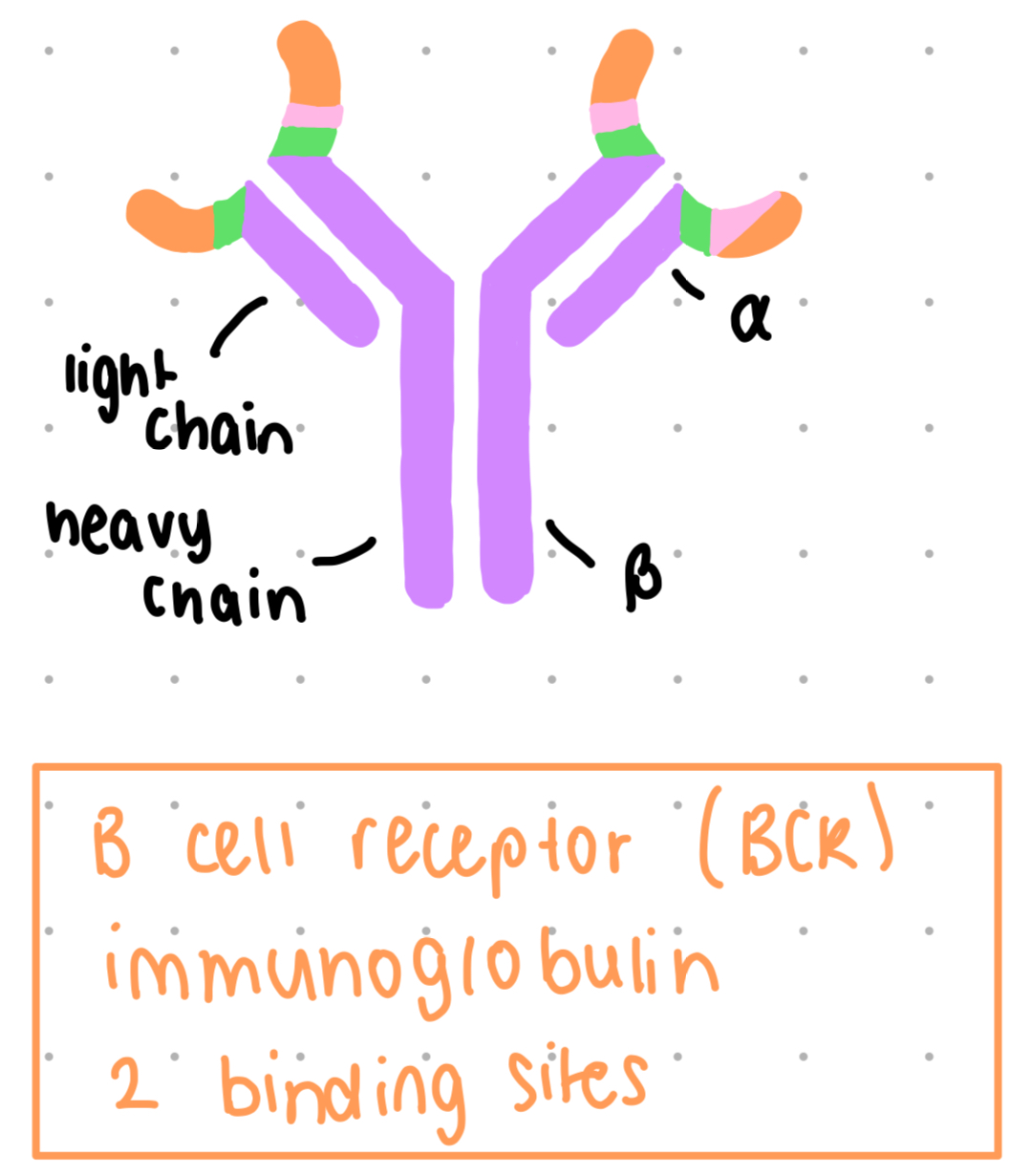
b cell receptor structure
immunoglobulin, 2 binding sites
membrane bound
constant region (purple) + variable regions (other colours)
variable region binds to antigen
~10^11 possible BCRs, space constraints dictate that frequency of cells specific for one antigen is very low (~1:100 - 1:10,000)
after activation - cells undergo clonal expansion so response is slower than innate response
TCR = t cell receptor
membrane bound
constant = purple, variable = other
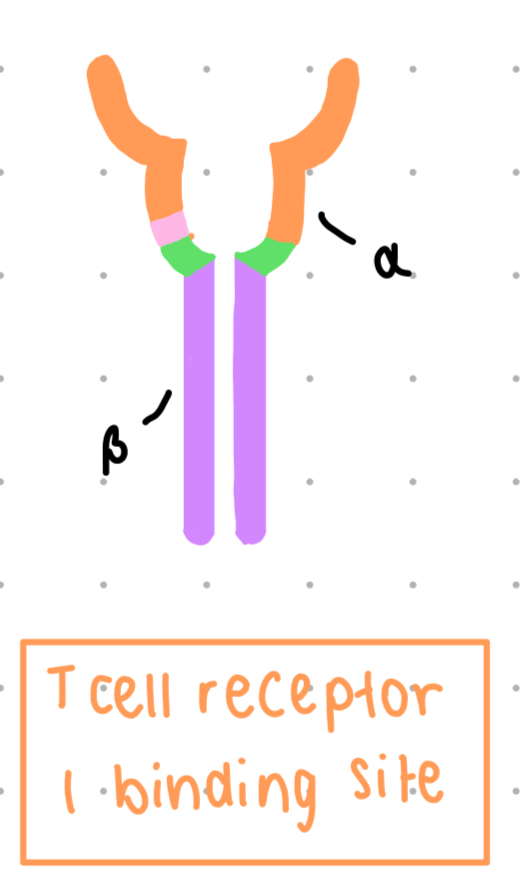
BCR vs. TCR
genetically related (similarities between heavy chain and B chain, light chain and alpha chain)
structurally and functionally unique
antigen receptors of any one cell all have one specificity
each cell expresses thousands of this one receptor on their cell surface
TCR - antigen recognition
recognise processed peptide antigen, presented by MHC molecules
linear epitopes
TCR binds to both peptide and MHC
BCR - antigen recognition
recognise ‘free’ antigens or antigens ‘delivered’ by other cells
linear + conformational epitopes
can be protein, lipids, carbs, nucleic acids (native form)
more recognition than t cells
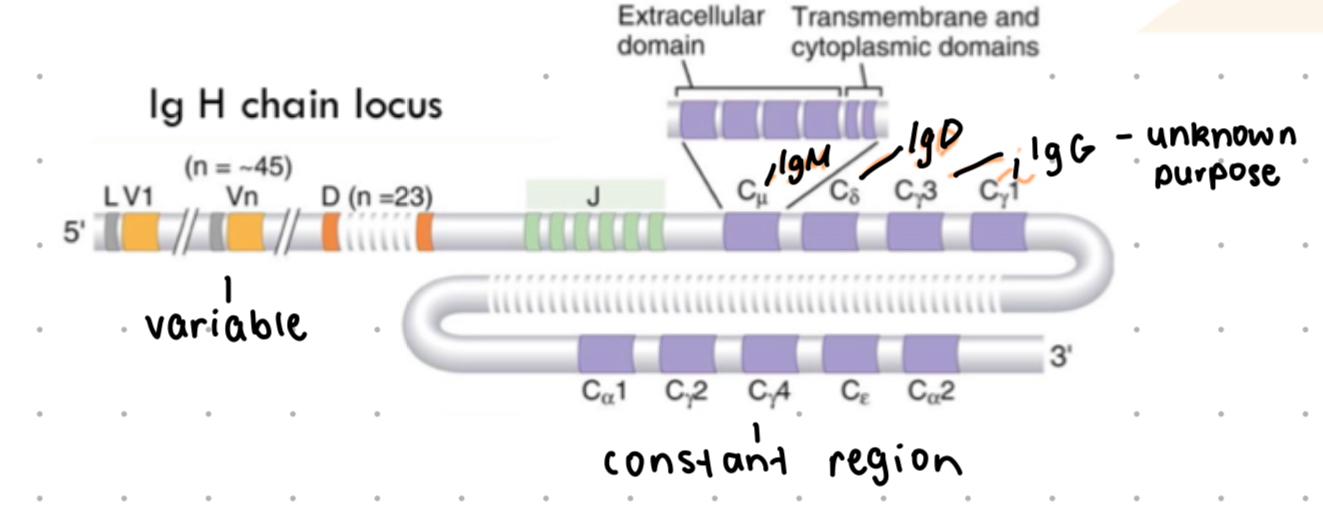
antibody isotopes
different antibody classes with distinct functions
IgG
most abundant antibody in human serum
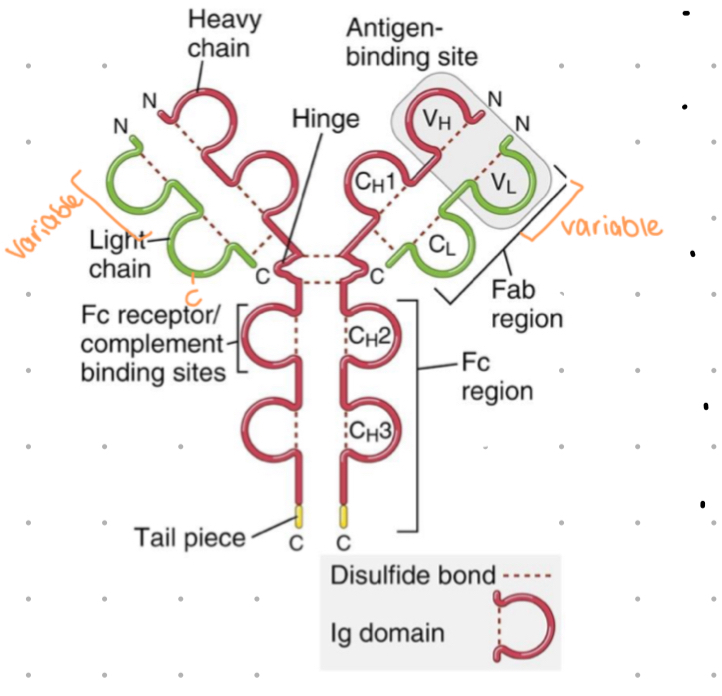
antibody structure
4 polypeptide chains assembled in Y shape
2 identical light (L) chains - approx 25 kDa
light chain = 1 variable + 1 constant domain
2 identical heavy (H) chains - approx 50kDa
1 variable + 3-4 constant domains
2 variable regions make up ‘antigen binding’ site
hinge gives flexibility - allows variable regions to come closer together or further apart to bind epitopes
papain
a protease enzyme from papaya
used to dissect antibodies
cleaves molecule into two Fab fragments and one Fc region
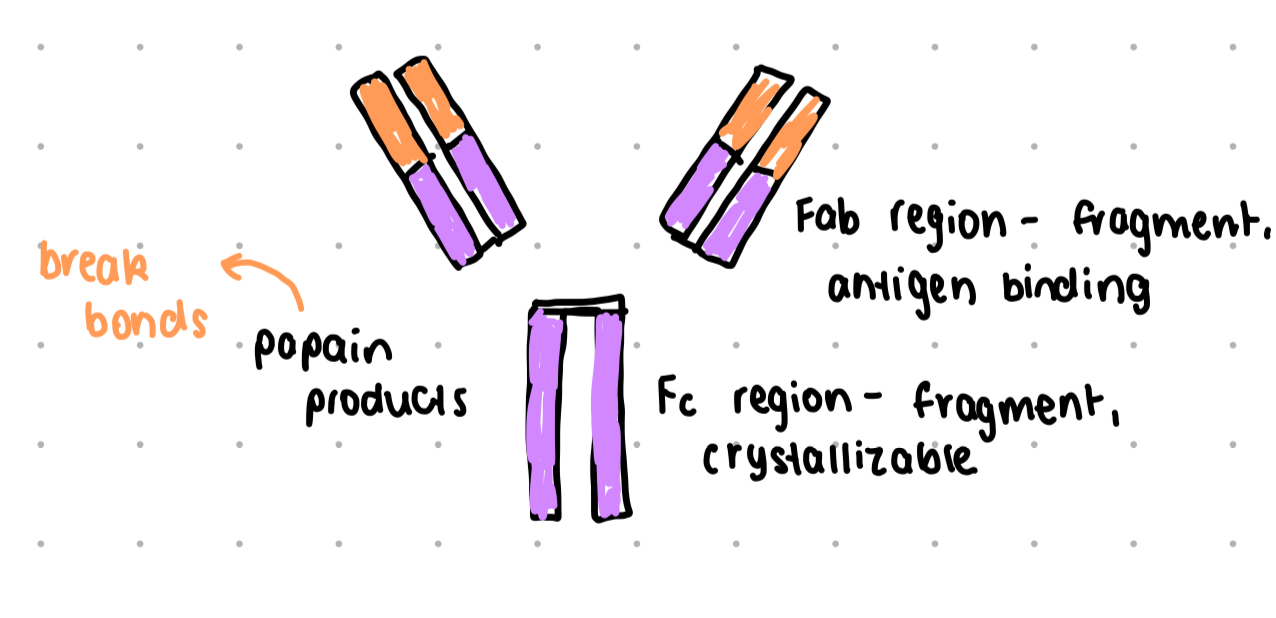
Fab region
fragment - antigen binding region
Fc region
fragment, crystallizable region, binds to cell surface receptors (Fc receptors) and some proteins of complement
IgM
original antibody isotope, always first one produced
low affinity so assemble for 10 binding sites
abundance of isotypes
IgM - ~5%, M heavy chain
IgG - ~80%
IgA - ~15%
IgE - traces
IgD - ~0.25%
class switching
requires CD4 helper T cells to switch from IgM to other antibody classes
constant domain for each isotope is the same, different isotypes have different heavy chains which creates different effector functions
neutralisation
process where antibodies bind to pathogens to prevent entry
IgM, IgG, IgA (lumen of mucosal organs) can act as neutralisers
mucosal immunity
immune defence in GI, respiratory, urogenital tracts
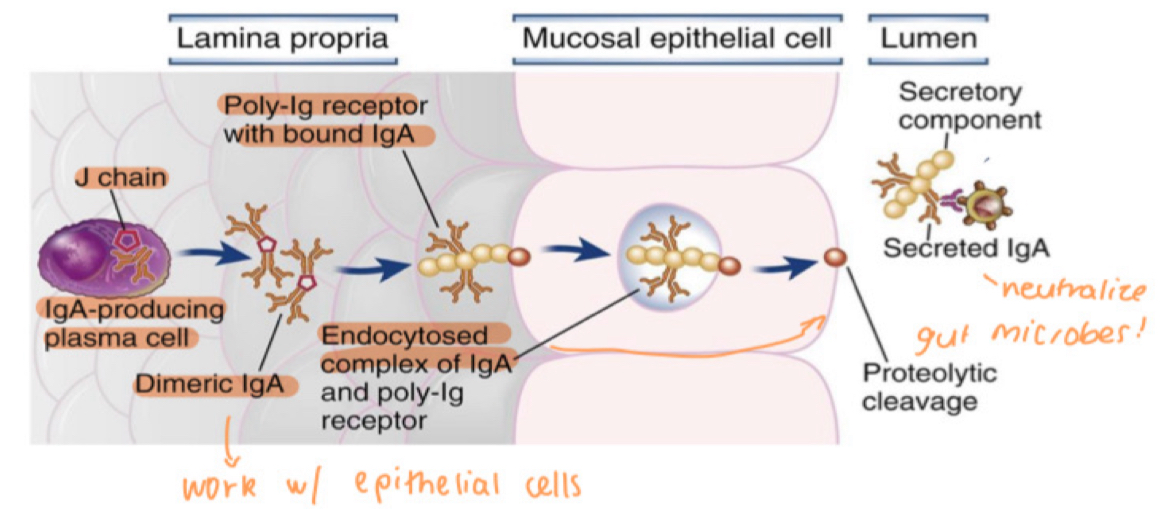
IgA antibody, diners held together with J chain
IgA binds to poly-Ig receptor
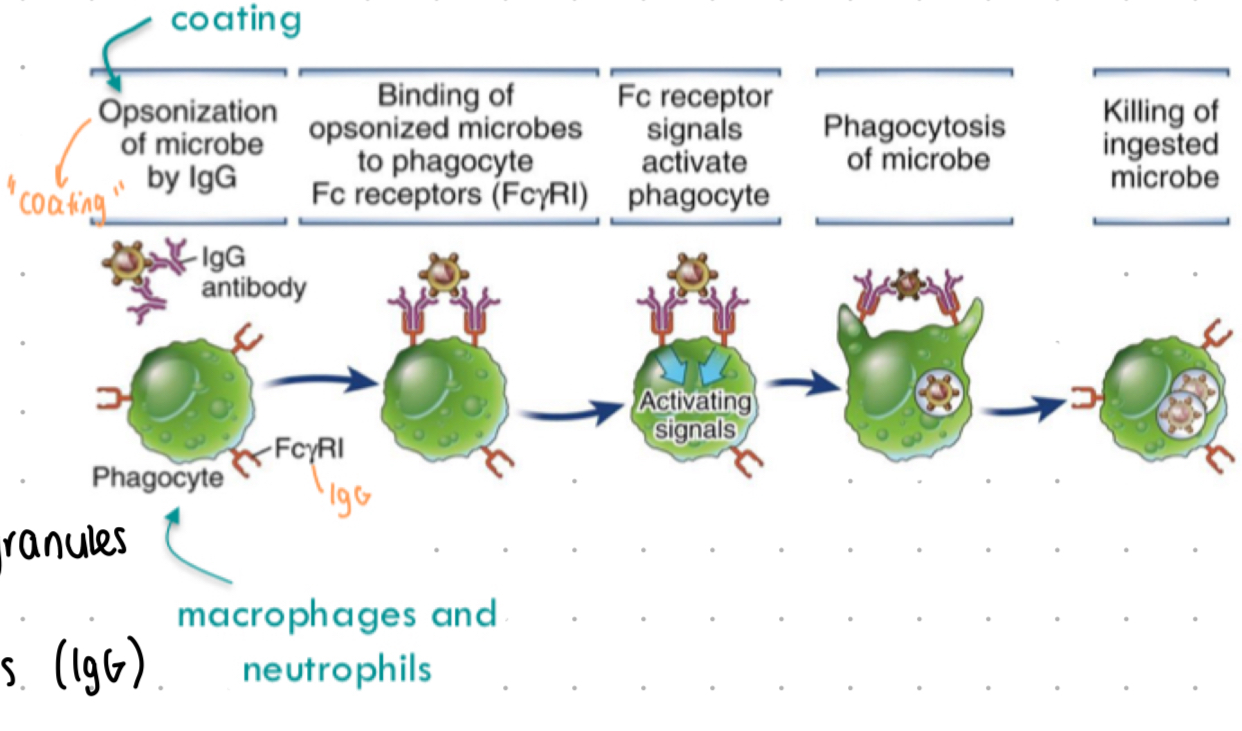
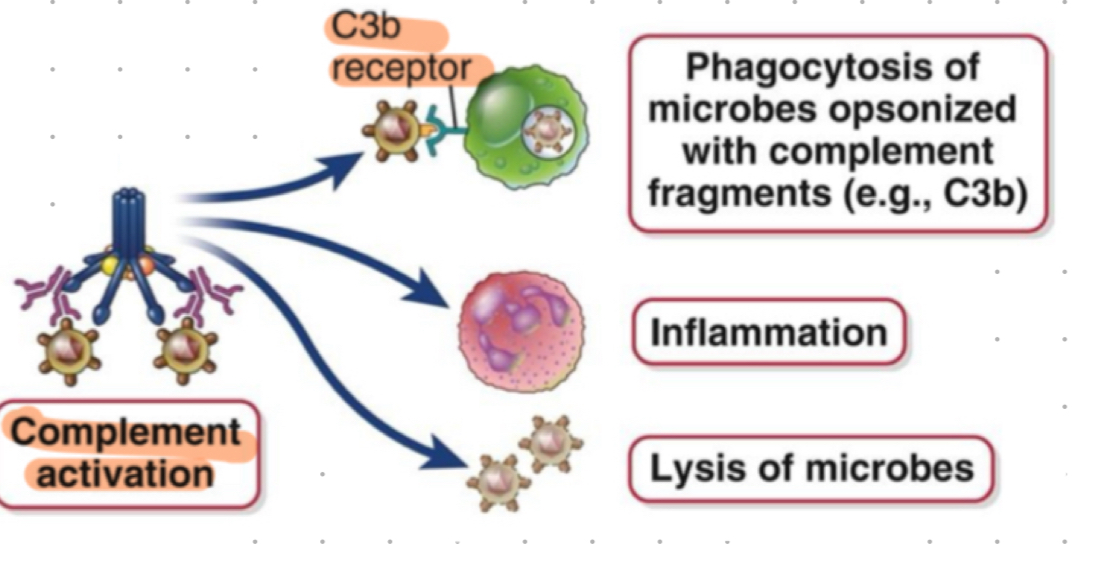
opsonisation
process of tagging pathogens for phagocytosis
IgA defence mechanisms
complex is endocytosed into epithelial cells and transported across cell (transcytosis)
released into lumen by proteolytic cleavage
then neutralises microbes + prevents their entry
opsonisation - antibodies
“antibody dependent cell phagocytosis”
IgG + IgA - Fc regions bind to Fc receptors (FcyR or FcaR) on phagocytes
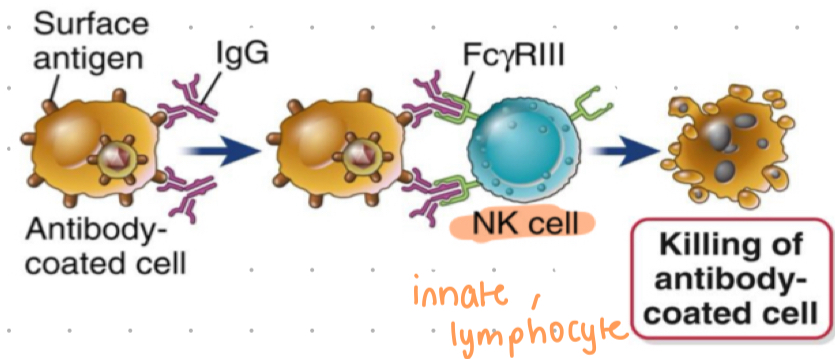
ADCC
antibody-dependant cell-mediated cytotoxicity (cell killing mechanism)
ADCC process
IgG binds to foreign antigens on surface of cells (infected cells)
NK cells express FcyR3 that engages with IgG bound cell
receptor mediated signals elicit release of granules containing toxic proteins
Fc region binds to Fc receptors on NK cells (IgG)
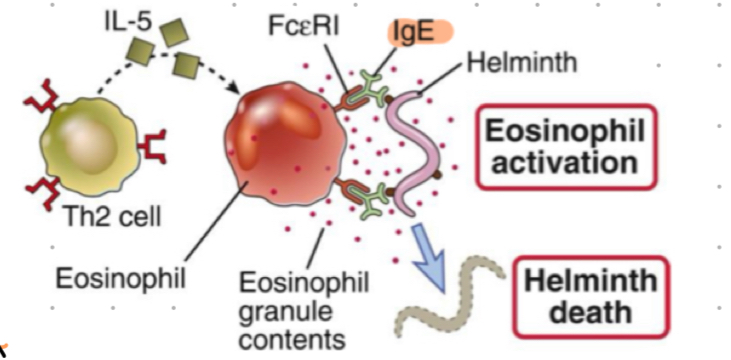
IgE
antibody involved in allergic responses and parasitic defence
activates mast cells + basophils
Antibody + Helminths
IgE combats parasites
helminth (worms) are big and cannot be phagocytosed
IgE opsonsises worms, FceRI on eosinophils binds IgE inducing eosinophil activation + release of cytoplasmic granules that kills the parasite
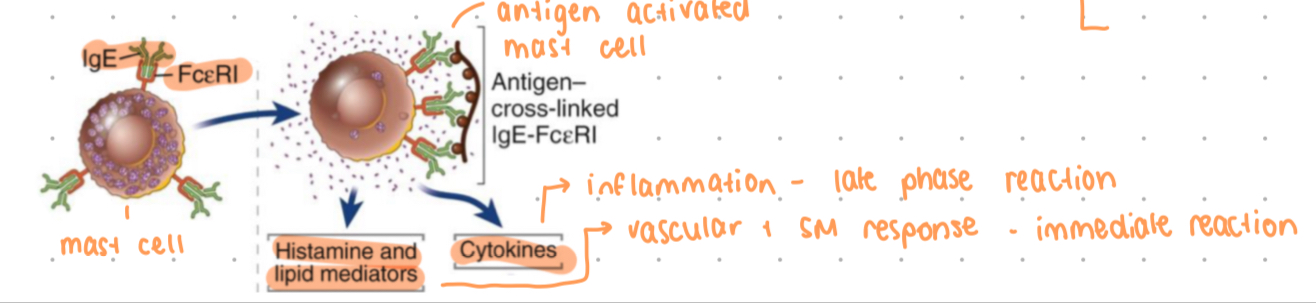
IgE role
binds to FceRI on mast cells + basophils, coating with IgE = sensization
antigen needs to bind to 2 or more FcR bound IgE to trigger cross linking of FcR + cell activation
triggers release of inflammatory mediators (histamine)
allergic responses, also physiological responses to protect from venoms + toxins
complement + antibodies
classical pathway activated by IgM + IgG antibodies
IgG1 and IgG3 most regular activators
lymphocyte development
process of B and T cell lineage commitment and receptor gene rearrangement
many selection events
selection events - lymphocyte development
process that preserves cells with useful receptors and eliminates self reactive ones
b cell development
process during which b cells develop and mature
pro b cell
cell starting point in b lymphocyte development
V(D)J recombination
process of gene segment rearrangement to create B cell receptor variability
VDJ recombinase
enzyme regulating gene rearrangement in immature B and T cells
junctional diversity
process adding random nucleotides to increase BCR diversity
positive selection
process determining if B cell receptor is functional and in frame
after all cutting and lighting of gene segments, is the VDJ segment in frame with constant region Cm segment), can it make a functional protein
no BCR = no survival signals
negative selection
process eliminating self-reactive B cells
did BCR that binds to self-antigen too strongly, if self reactive, B cells rearrange the light chain in a process called receptor editing
failing this step results in deletion
making a diverse BCR
rearrangement of gene segments by V(D)J recombination
random rearrangement of one V (variable) gene segment, one D segment (Ig H chain only) and one J gene segment to make a single V(D)J exon that will code for the variable region of the protein
introduce random nucleotides at the junctions between VDJ = junctional diversity
greatly increase diversity of receptors produced, with just VDJ = ~3×10^6 possible BCR, with JD = ~10^11 BCRs
addition of random nucleotides catalyses by TdT (lymphocyte specific enzyme)
positive + negative selection
migration to spleen as an immature B cell, differentiation into mature B cell
pro b cell BCR
Ig H chain (heavy chain)
Ig k/
pro B cell - BCR structure
Ig H locus (heavy chain) = variable region (V, D, J segments) + constant region - c
Ig K/¥ locus = variable region (V, D, J segments) + constant region (c ) - light chain
VDJ recombination - key points
ordered - D gene segment fuses to J gene segment, then V to DJ
its mediated by an enzyme only expressed in immature B and T cells - VDJ recombinase, cut DNA and bring segments close together
B1 cells
innate type of B cells
follicular B cells
major subset of B cells, responsible for antibody production
express surface bound IgM and IgD
recirculation of B cells
movement of mature (naive) B cells between lymphoid organs in search of antigens
BCR cross linking
trigger for B cell signalling upon antigen binding
b cells in lymph nodes
b cells located in follicles
T independent response
B cell response without T cell help, produces short lived plasma cells
T dependent response
B cell response requiring T cell assistance for class switching + affinity maturation
germinal centre reaction
process where B cells proliferate and undergo affinity maturation