Cell Division & Molecular: IB content
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Mother Cell
The original cell that is divided to produce daughter cells originate. Also called the parent cell
Cleavage furrows
The region that pinches an animal cell during cytokinesis
Cell plate
The new cell wall that is built to split up a replicated plant cell in cytokinesis
Contractile actin & myosin proteins
The ring that pinches an animal cell during cytokinesis.
the ring is made of the former
The former is made of the latter
Vesicles for division
These carry additional cell membrane and cell wall parts to build the cell plate
Anuculeate cells
Cells without a nucleus
Elongated DNA
Another term for chromatin
Condensation
The process where loose DNA is packaged into chromosomes
Histones
The proteins DNA supercoils around during cell replication
Supercoiling
A ± value that represents how tightly wound packaged DNA is. Most DNA is slightly -.
+ : over-winding
- : under-winding
Microtubules
Structural hollow tubes that form the cytoskeleton of a cell, giving it structure and forming the spindle fibers
Microtubule motors
Proteins that transport all kinds of cargo along microtubules (it’s the cvnty walking protein from the memes)
Down-syndrome
A genetic disorder with an additional 21 chromosome caused by non-disjunction. Called trisomy-21
Recombinant chromatids
The term for chromatids having undergone the crossing over
Proliferation for growth
Fancy term for the fact that cells replicate so the organism can grow
Biosynthesis of cell components
When cells produce molecules (lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) to carry out their functions and build structures
Cyclins
A group of proteins that control the cell’s progression through the cell cycle.
They bind to CDKs so they can act as enzymes
CDKs
Cyclin-dependent protein kinases.
When bound to cyclins, they can act as enzymes for the cell cycle, telling the cell to proceed to the next stage of interphase
Checkpoints
The points in the cell cycle where CDKs are activated
Proto-oncogenes
A cell that has the potential to become an oncogene
Oncogenes
A section of genes that can mutate the become cancerous by causing cells to divide more frequently than they should
Tumour suppressor genes (TSGs)
Code for proteins that regulate the cell cycle and prevent cells from becoming cancerous
Metastasis
A pathogen or tumour that has spread from its original location to another location on the organism
Benign
Cells are forming a tumour but they’re not spreading to the rest of the body
Malignant
If the cells rupture the organ they’re in and spread to the rest of the body
1° tumor
One that occurs at the original site of the cancer
2° tumor
One that has spread from the original site to a new one
Mitotic index
The ratio of cells undergoing mitosis over the amount of cells
Chimpanzee chromosome #
Diploid cells: 48
Haploid cells: 24
Karyotyping
A test to map the genes of a cell
Karyograms
A visual representation of a cells chromosomes arranged in a standard format
Genomes
All the genetic information in a cell
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms
Where a single nucleotide differs in at least 1% of the population.
Personalized medicine
AKA precision medicine, when medical professionals use the known genetic sequence of their patients to help prescribe more effective treatments
Parthenogenesis
Females reproducing asexually
Covalently bonded atoms
a strong bond between two or more non-metal elements
In DNA, molecules within the strands are this, and hydrogen bonds connect the bases
Nucleotide
One building block of DNA
Contains:
a phosphate group
A deoxyribose sugar
A nitrogenous base (A, T, C, or G)
Nucleosomes
During cell replication, a DNA packaging unit comprised of ~146 base pairs around 8 round histones and held by one long histone
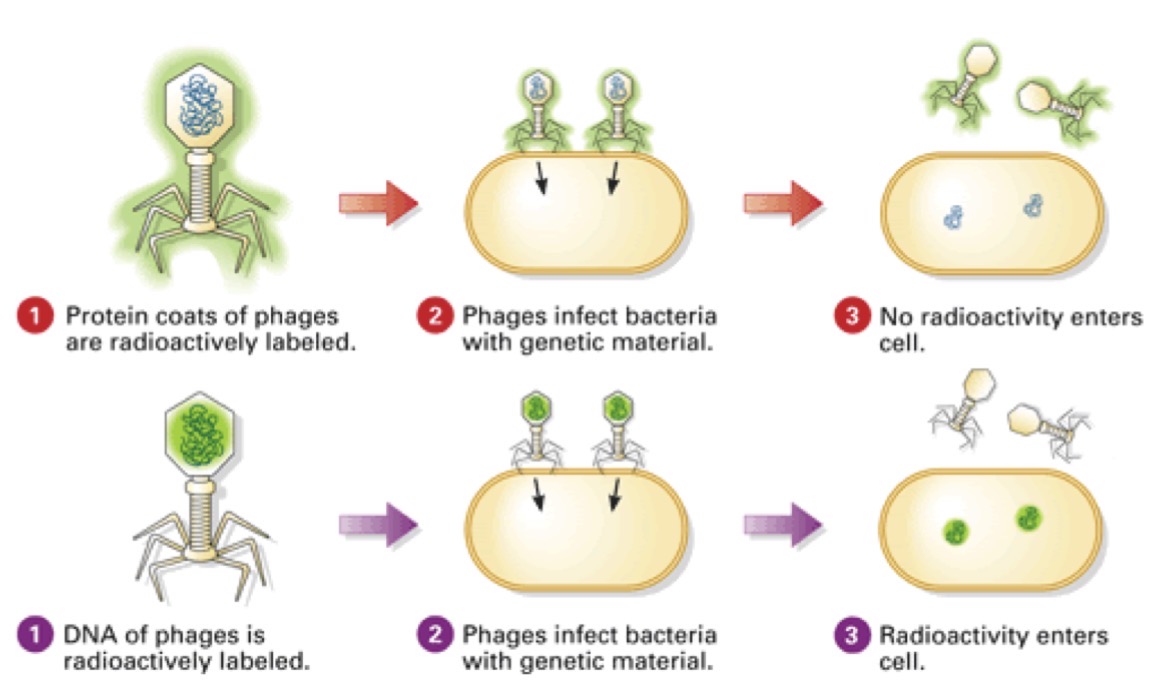
Hershey-Chase
An experiment that proved DNA is the genetic material being inserted by viruses during infection using radioactvity
Chargaff’s Rule
DNA contains equal amounts of A & T, and equal amounts of C & G
“Problem of induction”
A philosophical problem, that questions the justification for our belief in future events based off past observations. We cannot logically prove the future will resemble the past.
“Certainty of falsification”
A philosophical concept; things can only be seen as true so long as it has not been proven false, and every scientific law we observe holds a disclaimer that it will only be a law so long as we haven’t found proof of its falsity.
Tetra-nucleotide hypothesis
Suggested that nucleic acids were composed of the repeating sequence of four nucleotides with equal amounts of each of the four bases ATCG
this theory led scientists to believe DNA was too simple to hold genetic material, instead believing proteins were the source.
70s Ribosomes
The smaller than eukaryotes ribosomes found in prokaryotes (bacteria, archaea), mitochondria and chloroplasts
Naked Circular DNA
Prokaryotes have a continuous loop of DNA without histones
Polymers of nucleotides
Think about the breakdown of those individual words
DNA and RNA
Helicase
The enzyme responsible for unwinding and unzipping DNA
DNA polymerase I
removes RNA primers
Fills those gaps with DNA nucleotides
Repairs damaged DNA
Slow
DNA polymerase III
Main replication enzyme
Synthesizes new DNA strands
Completes long stretches very quick
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
A lab technique using a thermocycler machine to make many copies of a small amount of DNA
Taq DNA polymerase
a polymerase from a bacterium found in hot springs (withstands heat), one of the components to run a PCR
Gel electrophoresis
A lab technique used to separate DNA fragments to identify its origin. Enzymes chop up DNA so that it can be put into an electrical chamber that separates them into wells.
How we can do paternity tests
Continuous vs. Discontinuous replication of the strands
leading strand vs lagging strand
DNA proofreading
Done by the DNA polymerases
RNA polymerase
The enzyme that opens up DNA for the creation of mRNA and synthesizes mRNA
Degeneracy
For each amino acid, there may be more than one codon
Universality
With a few exceptions, all life shares the same genetic code
Small vs. Large ribosome subunit
Small: mRNA bonds to this
Large: where the tRNA and their proteins come in
Elongation
The Taq polymerase catalyst the building of new DNA strands by extending the primers
5’ to 3’ transcription
During the formation of mRNA, the 5’ end of the mRNA is synthesized
3’ to 5’ translation
During the formation of proteins, the mRNA is read from the 3’ end to the 5’ end
Telomeres
Useless ends of chromosomes that exist to protect the actual important stuff from famage
Genes for rRNAs
found in the DNA of all cells
transcribed to form rRNA molecules and the proteins made form ribosomes
Genes for tRNAs
transcribed from DNA to form tRNA
Splicing
Process of removing sections of introns from primary mRNA to make sure its ready.
5’ caps
Protective strand on the 5’ end of mRNA
Helps move the mRNA from nucleus to ribosome
Helps ribosomes attach to mRNA
3’ polyA tails
Protective strand on the 3’ end of mRNA
Helps move the mRNA from nucleus to ribosome
Helps mRNA be efficiently translated into proteins
Stabilize mRNA transcripts
To make sure mRNA doesn’t degrade:
5’ caps
Poly-A tail
RNA binding proteins
A binding sites for tRNA on the ribosomes
The first binding site
holds the the tRNA carrying the next amino acid to be added to the polypeptide chain
P binding sites for tRNA on the ribosomes
Second binding site
Holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain
E binding sites for tRNA on the ribosomes
Third binding site
Discharges the tRNA that has lost its amino acid
Pre-proinsulin vs. Proinsulin vs. Insulin
In order, these three things are what forms the final product
Through a process of removing a signal peptide it 1 becomes 2
2 is exposed to enzymes that break peptide bonds to form 3, which is pretty small.
Proteasomes
The cellular organelle that breaks down marked (damaged or unused) proteins into amino acids
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
When a genetic sequence is altered by one letter only
Chemical mutagens
When exposure to certain chemicals damages genetic material
Mutagenic forms of radiation
when exposure to radioactivity causes bases in genetic material to rearranged
Commercial genetic tests
Tests run to detect genetic mutations, find ancestry and paternity
(Not always 100% accurate)
Gene knockout
When we render a gene inoperable in to see what happens to learn what it’s responsible for
Inoperative
Unable to carry out its normal function
CRISPR
A process the can perform cut, copy and paste with any gene
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (the mini sections that are this things namesake)
Still novel, with some ethical issues, but it has potential to fix genetic disorders
Enzyme Cas9
Works as DNA scissors in the CRISPR process
Gene editing
A process done to modify genetic sequences, often for improvement
Conserved sequences in genes
DNA stretch that has changed very little of over evolutionary time
Highly conserved sequences in genes
DNA sequences that is nearly identical across many species
Promoters
A region of DNA that determines which strand will be the template
On any gene, the promoter is always on the same strand
A short sequence of bases that is not transcribed
Enhancers
Tells the DNA when a genetic sequence should be expressed
Transcription factors
Proteins that regulate gene expression by promoting or inhibiting the binding of RNA polymerase to DNA
Nucleases
Enzymes that break down nuclear acids by hydrolysis the bonds between the nucleotides
Degradation of mRNA
A process to destroy mRNA that is unnecessary
Epigenesis
The process that results in the formation of organs and specialized tissue from a single undifferentiated cell.
Genome
All the genetic information of an organism
Transcriptome
All the RNA that a cell makes for its specific region
Proteome
The entire set of proteins that is or can be expressed by a cell, tissue or organism
DNA Methylation
The process by which a methyl group is added to a DNA nucleotide
Epigenetic tags
A methyl group that flags part of the DNA, sometimes making certain parts of the DNA unable to be expressed
if on the cytosine in the DNA of a promoter, the rest of the gene can’t be read
Histone modification
Chemical changes to these proteins that alter chromatin structure and regulate gene transcription
Alteration of methyl tags
Adding or removing these on DNA or histones to regulate gene expression without changing the DNA sequence
Tigons/ligers
Male tiger + female lion = smaller hybrid
Male lion + female tiger = enormous hybrid
Monozygotic twins
Another term for identical twins
Tryptophan in bacteria
Acts as a corepressor that binds to the trp repressor protein, enabling it to inhibit transcription of the trp operon