Modules 4-6
1/339
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
340 Terms
What are the three major muscle types?
cardiac muscles
smooth muscles
skeletal msucles
What are the 3 levels of skeletal muscle organization, from largest to smallest subunit? Describe their key points
Muscle → whole muscle is made up of individual muscle fibres which run the ENTIRE length of the muscle
Muscle fibre → run parallel to each other → surrounded by connective tissues → multinucleated, with a very large number of mitochondria
Myofibrils → the cell is divided along its length into discrete contractile units
what is another name for a single muscle cell?
a muscle fibre
describe the side view of a Myofibril
Pattern of light and dark bands (gives striated pattern)
describe the cross sectional view of a Myofibril
highly organized pattern of thick filaments and thin filaments
What are thin filaments made of?
actin
What are thick filaments made of?
myosin
is an I band of a myofibril light or dark?
light
is an A band of a myofibril light or dark?
dark
What is an A band of a myofibril?
a dark band made up of stacked thick and thin filaments
what is an I band of a myofibril?
portion of the myrofibril where the thin filaments don’t extend into the A band
what is the H zone of a myofibril?
slightly lighter portion of the A band, containing only protiens that hold the thick filaments (myosin) in a stack
What is the M line of a myofibril?
proteins that hold the thick filaments together in a stack
what is the Z line of the myofibril?
a verticle line in the middle of the I band
what does the distance from one Z line to the next represent?
a sarcomere - functional unit of skeletal muscle
How is muscle length increased in muscle growth?
new sarcomeres are added onto the ends
what kind of protein is myosin?
motor protein
what does myosin do with the use of ATP?
moves along actin filaments
what does each molecule of myosin consist of?
2 subunits forming a dimer
what proteins make up thin filaments?
actin, troponin and tropomyosin
what are actin filaments made up of?
individual spherical actin molecules that come together to forma double helix structure
what is tropomyosin? what’s its role in thin filaments?
thin double helix protein
lies end to end along the actin helix structure
regulatory protein, prevents interactions of actin and myosin
what is troponin? what is its role in thin filaments?
regulatory protein complex made of 3 polypeptides
one binds to actin, one binds to tropomyosin and the other binds to Ca2+
what does the “power stroke” refer to?
the interaction between myosin and actin, leading to a shortening of the sarcomere
what are the steps of the cross-bridge cycle?
binding - myosin cross-bridge binds to actin molecule
power stroke - the myosin head bends, pulling the thin filament inward
detachment - cross-bridge detaches at the end of power stroke and returns to original conformation
binding - cross bridge binds to more dista; actin, and the cycle repeats
where does the body get the energy to shorten the sarcomere from?
excitation-contraction coupling
conversion of electrical signals into actual contraction
what are the 2 membrane structures that help transmit signals to muscular fibres?
sarcoplasmic reticulum
T-tubules
what is a sarcoplasmic reticulum?
membranous structure that runs parallel to muscle fibres
storage site for Ca²+
how does the T tubule transmit a depolarization wave to the SR?
The SR forms sacs adjacent to T-tubules
dihydropyridine receptors lie on the surface of T-tubules
touching the Dihy- receptors are the ryanodine receptors on the SR
when the dihydropyridine receptors sense the depolarization wace, they influence the ryanodine receptors to undergo a conformational change. - Ca²+ enters the cytoplasm
what is a dihydropyridine receptor?
voltage sensor that senses the wave of excitation at it travels down T-tubules
what are ryanodine receptors?
receptors on the SR that are a form of Ca²+ channel
what ion serves as the primary trigger for muscles to contract?
Ca²+
why can’t contraction take place in a relaxed muscle?
because tropomyosin and troponin are blocking the myosin binding site on the actin molecules, preventing cross-bridge formation
what causes muscle relaxation?
decreased nerve activity at the neuromuscular junction
what is acetylcholinesterase?
enzyme that causes rapid hydrolysis of acetylcholine
what is happening in the SR when a muscle is relaxed?
Ca²+ ATPase pumps the calcium back into the SR for when its needed again.
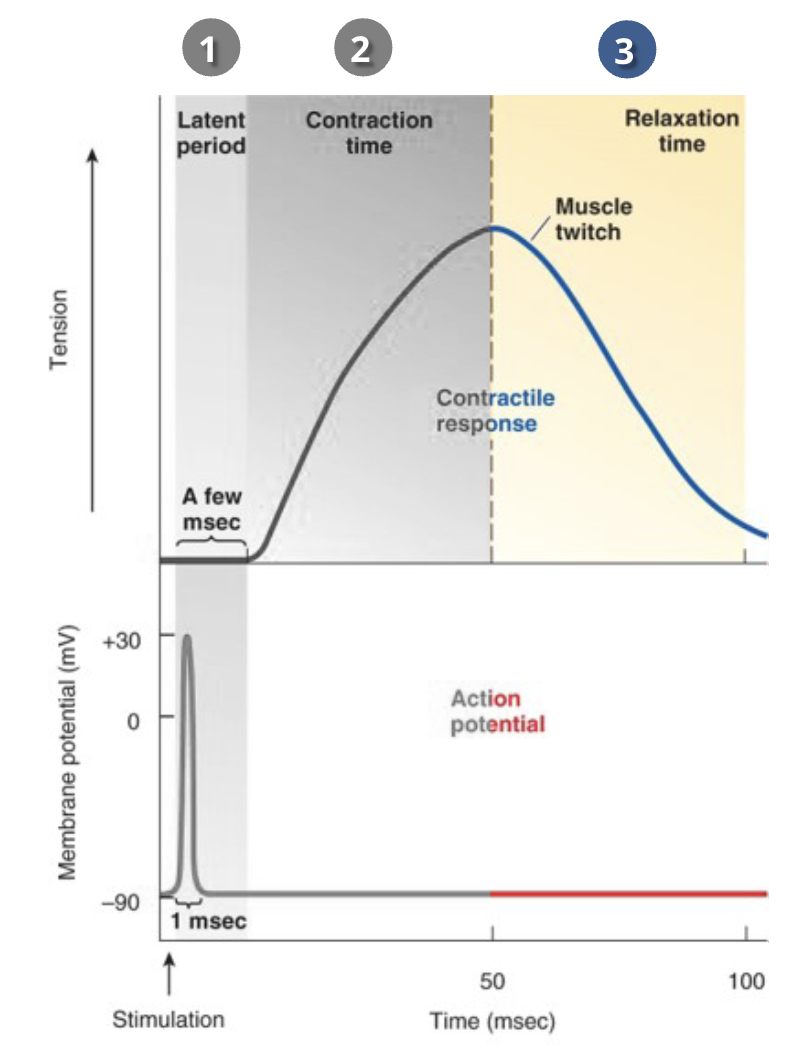
what are the 3 steps to the temporal relationship between the action potential and the mechanical action in muscles?
latent period
delay before contraction actually starts - when cross-bridge cycling is beginning
Contraction time
it takes time for the actin filaments to slide along the myosin
Relaxation time
ends when all Ca²+ is removed.
what is considered as the basic unit of muscle contraction?
a twitch - contraction of a single fibre
what are the two ways in which the body gets more muscle fibres to twitch?
motor unit recruitment
increasing frequency of stimulation
what is a motor unit?
a motor neuron branches out and innervates multiple muscle fibres - when that motor neuron is activated, all of its fibres contract
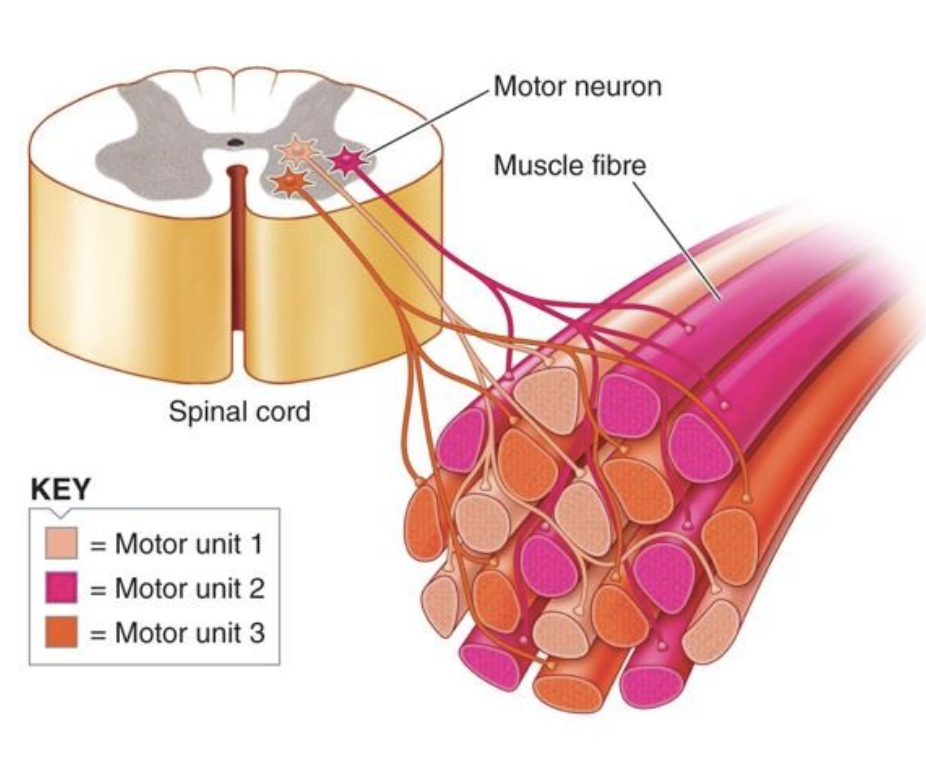
are the muscle fibres of a motor unit adjacent?
no
how does the body prevent fatigue during a sustained contraction?
the body can selectively rotate the activation of motor units
how does the body overcome the fact that skeletal muscle action potentials are relatively short, when it wants to sustain contraction?
the membrane potential quickly recovers to undergo another action potential
if a muscle fibre is restimulated after it has completely relaxed….
the second twitch has the same magnitude compared to the first
if a muscle fibre is restimulated before it has completely relaxed…
twitch summation occurs
if a muscle fibre is stimulated so rapidly that the twitches overlap…
tetanic contraction occurs
what are the two kinds of tetanic contraction? which is the stronger one?
unfused
muscle fibres do not completely relax before the next stimulation
fused (tetanus) (strongest)
no relaxation of the muscle fibres between stimuli
what determines the amount of tension that can be generated by a muscle at tetanus?
length of the muscle at the onset of contraction
explain the length-tension relationship for a less than optimal length muscle
as the fibre length is shortened, thin filaments overlap → decreases efficiency of contraction, and tension
occurs at about 70% of resting muscle length
explain the length-tension relationship for an optimal length muscle
maximal number of cross-bridge binding sites are available for cross-bridge binding
can achieve maximal contraction
explain the length-tension relationship for a greater than optimal length muscle
less overlap of thick and thin filaments → less cross-bridges are available → less tension can develop
what are the common athletic muscular injuries?
Contusion - muscle is subject to sudden, heavy, extrinsic compressive force
strain - muscle fibres are exposed to an excessive force caused by intrinsic tension
laceration - deep cut or tear if the musclew
how are muscle contractions categorized at the level of the motor unit?
isotonic
muscle tension remains constant as it changes length (bicep curl)
isometric
muscle fibre tension increases as it remains at the same length (isometric holds)
how are muscle contractions categorized at the level of the whole muscle?
concentric dynamic contractions
tension while the muscle shortens
eccentric dynamic contractions
tension while the muscle lengthens
what are the 3 ways in which ATP is important in the contraction-relaxation process of skeletal muscle?
splitting of ATP to provide energy for power stroke
binding of new ATP to myosin head to release the cross-bridge
Active transport of Ca²+ back into SR
what are the 2 major types of fatigue?
central fatigue
CNS decreases its activation of motor neurons
muscle fatigue
reduces contractile activity before all ATP runs out → prevents rigor mortis
what are possible reasons for muscular fatigue to occur? how do they cause fatigue?
local accumulation of ADP and Pi from ATP hydrolysis
when ATP metabolite concentrations get too high, they interfere with cross-bridge cycling
accumulation of lactic acid
inhibits the enzymes of glycolysis, reducing ATP production
accumulation of extracellular K+
without ATP, the Na-K pump can’t function → membrane depolarization
glycogen depletion
muscle glycogen stores can become depleted
are all of the muscle fibres in one motor unit the same?
yes
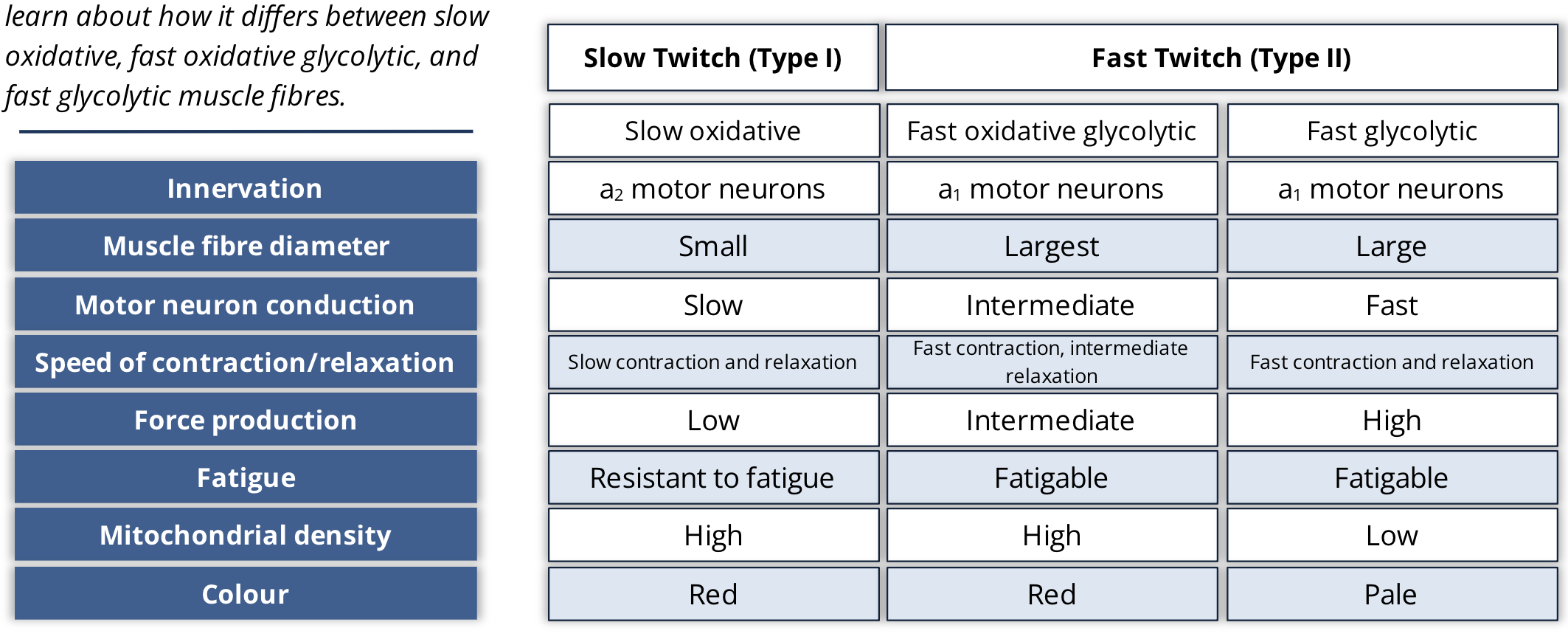
what are the 2 classifications of muscle fibres?
fast twitch muscle fibres (Type 2)
Slow twitch muscle fibres (Type 1)
what are the slow twitch muscle fibres speed of contraction
slow rate
what are slow twitch fibres innervated by?
a2 motor neurons
how do a2 and a1 motor neurons compare to eachother?
A2 are smaller than A1
A2 have lower activation threshold than A1
A2 have slower conduction speeds than A1
what are the metabolic properties of a slow twitch muscle fibre?
produce their ATP by aerobic process
what are fast twitch muscle fibres speed of contraction?
fast
what are fast twitch muscle fibres innervated by?
a1 motor neurons
what are the metabolic properties of fast twitch muscle fibres?
Fast oxidative glycolysis fibres produce ATP by aerobic and anaerobic metabolism
Fast glycolic fibres produce ATP by anaerobic means
what determines the colour of muscle fibres?
how fast they produce their energy
a muscle that is dense in mitochondria and myoglobin content is going to be what colour?
red
muscles that are less dense in mitochondria and myoglobin content are going to be what colour?
white
what colour is a fast glycolytic fibre?
white
what colour is a slow oxidative fibre?
red
what colour is a fast oxidative glycolytic fibre?
red

fill in the table
what are the 2 kinds of muscle receptors responsible for proprioception?
muscle spindles
golgi tendon organs
what do muscle spindles do?
they monitor changes in muscle length and play a key role in stretch reflexes
what do golgi tendon organs do?
primary purpose is to respond to changes in muscle tension
where are golgi tendon organs found?
at the junction of tendons and muscle fibres
how do golgi tendon organs respond to muscular stretch and contraction?
muscle fibre contracts → tension pulls on tendons
the stretch activates the afferent fibres in the tendons → stronger pull on the tendon = higher rate of firing in the golgi tendon organ afferents
what’s an intrafusal fibre?
a fibre found among extrafusal fibres, but only the ends of intrafusal fibres are contractile, not the middle
what’s an extrafusal fibre?
a regular muscle fibre
what are the 3 different levels of input involved in motor control?
afferent neurons
spinal reflexes
maintain posture
primary motor cortex
mediate fine voluntary movements of body parts
brain stem
regulates overall body posture
what are the 3 kinds of muscle?
skeletal
smooth
cardiac
where are smooth muscle cells found?
in the walls of hollow organs and tubes
where are cardiac muscle cells found?
the heart
do skeletal muscles have sarcomeres?
yes
do smooth muscle have sarcomeres?
no
what are the different filament types that participate in contraction of smooth muscle?
thick myosin filaments
longer than the skeletal ones
thin actin filaments
contain tropomyosin but not troponin
intermediate filaments
support the cytoskeletal framework
how are thick and thin filaments oriented in smooth muscle?
at angles, anchored by dense bodies
what does troponin do in skeletal muscle?
blocks cross-bridge formation until Ca²+ is present
what are the steps for myosin cross-bridge activation in smooth muscle?
during excitation, Ca²+ enters the smooth muscle cell and binds to calmodulin
Ca²+ -calmodulin complex binds to and activates myosin light chain kinase
once activated, the kinase phosphorylates myosin light chain, which allows the myosin cross-bridge to bind to actin
what is calmodulin?
calcium messenger protein
what is myosin light chain?
a protein associated with the myosin head. Aids in cross-bridge formation
do smooth muscle cells have T-tubules and Sarcoplasmic reticulum?
no t tubules
very little SR
what are the 2 ways in which smooth muscle cells receive calcium for muscle contraction?
Ca2+ entry from the ECF
Ca²+ release from the SR
how does smooth muscle receive Ca²+ from the ECF?
voltage gated dihydropyridine receptors function as Ca²+ channels
→ if the cell depolarizes enough, the channels open
how does smooth muscle receive calcium from the SR?
once Ca²+ enters, it can activate calmodulin OR it can stimulate the SR to release Ca²+ through CIRC
where is single unit smooth muscle predominantly found?
hollow organs
where is multiunit smooth muscle contraction predominantly found?
large blood vessels, small airways
is single unit smooth muscle contraction myogenic or neurogenic? what does that mean?
myogenic - self excitable and does not require nerve stimulation
is multiunit smooth muscle contraction neurogenic or myogenic? What does that mean?
neurogenic - innervated by nerves to contract