Bio: Chap 3 - The Biosphere
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
ecology is…
the study of interactions amount organisms & their physical environment
the biosphere includes:
the combined portion of living & non-living aspects of planet earth
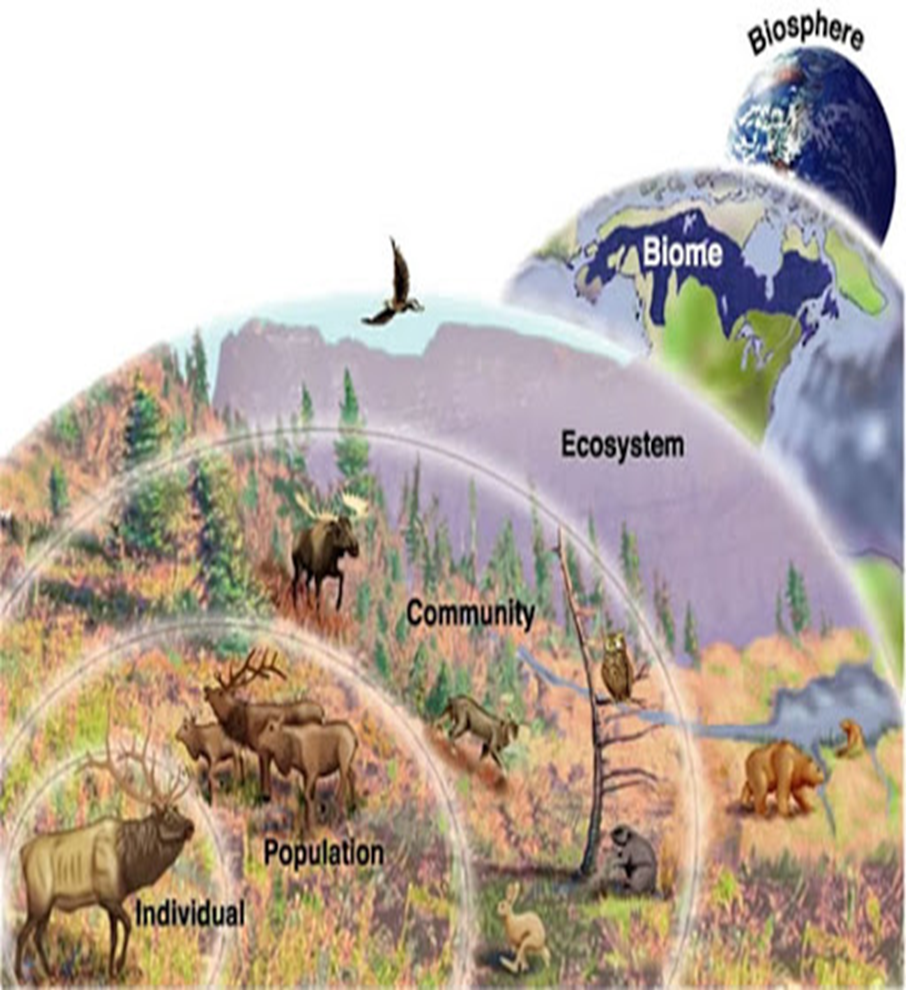
species
a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce offspring
population
a group of a particular species living in the same area
community
different population living in the same area
ecosystem!!
all living & non-living factors combined
term to remember?
SPaCE BB
biome
group of ecosystems with the same climate
observation
counting the number of koala bears in a specific location using satellites or radio tags
experimentation
growing plants using different fertilizers in a greenhouse
modeling
illustrating a food web to show feeding relationships among organisms in an ecosystem
biotic
living
abiotic
non-living
autotrophs
can store energy in forms that is useful & available to other organisms that eat them. they utilize photosynthesis and chemosynthesis
what do autotrophs eat
photosynthesis (make their own food)
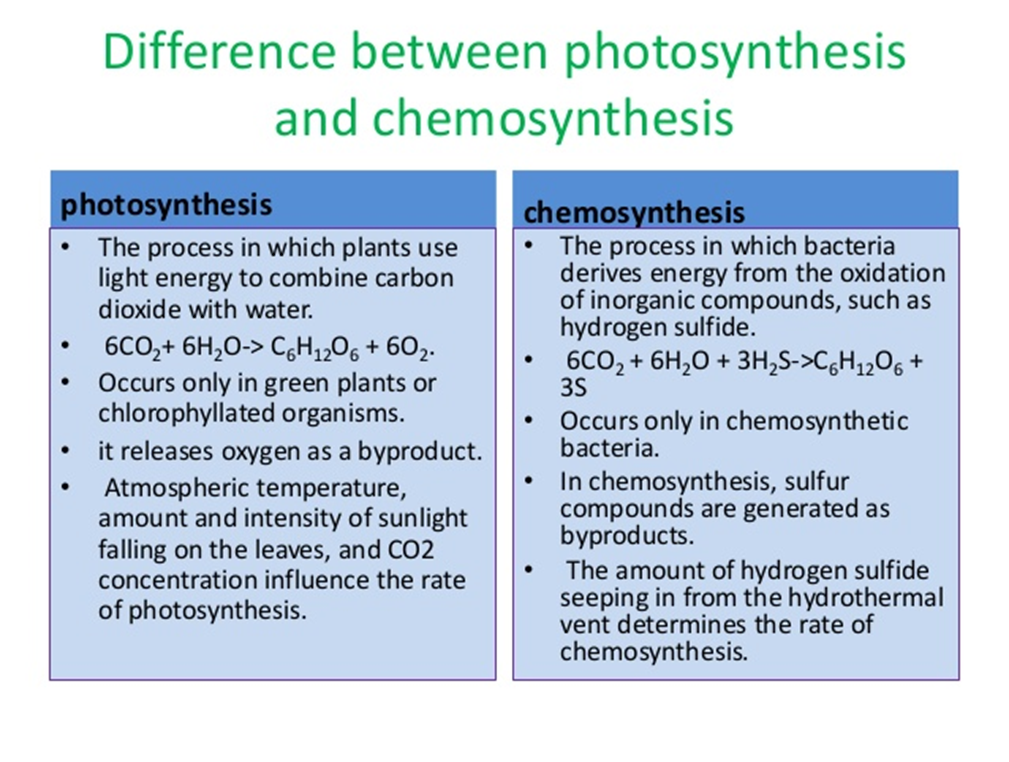
photosynthesis
the process in which plants use light energy to combine carbon dioxide with water
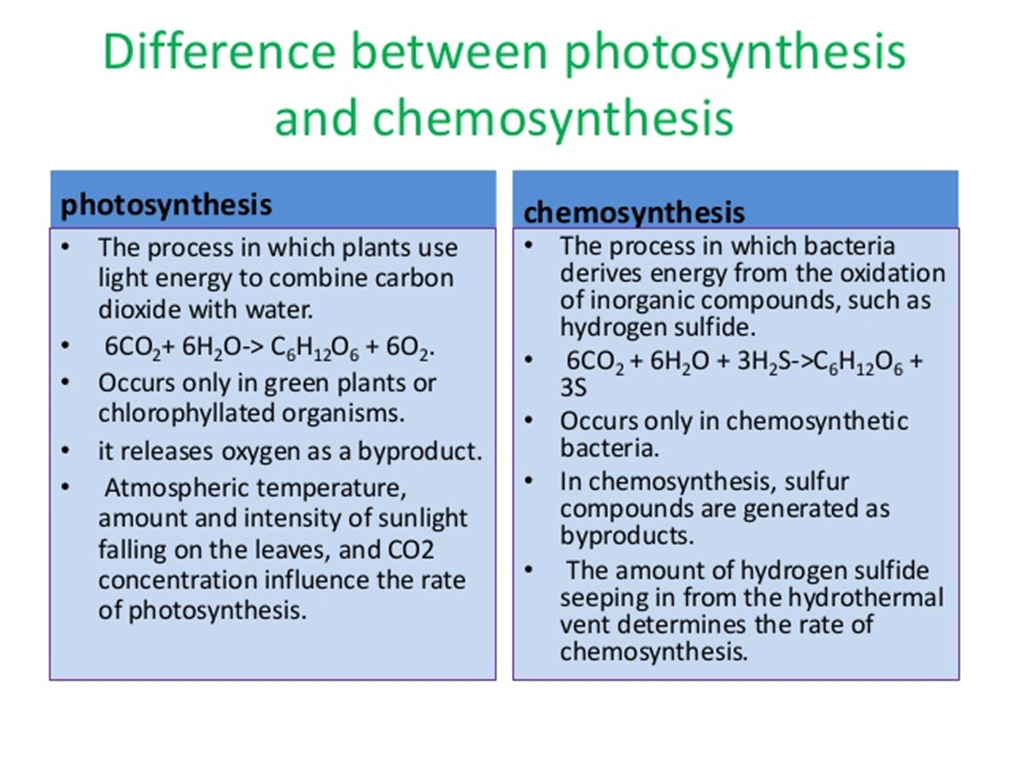
chemosynthesis
the process in which bacteria derives energy form the oxidation of inorganic compounds, such as hydrogen sulfide.
consumer
an organism that gets its energy by eating other organisms
consumer: - heterotroph
(gets energy directly from the sun)
ex: all other organisms except autotrophs
six types of consumers and what each one eats?
carnivore: meat eater
herbivores: eats plant matter
omnivores: eat meat/plants
scavengers: do not hunt but eat dead things they find
decomposers: break don organic matter (dead plants / animals)
detritivores: eat dead remains
decomposers
like bacteria and fungi, chemically break down organic matter and produce detritus
detritivores
eat the remains of dead animals and plants.

living things in our world are connected to other ______________ in a variety of ways.
organisms
the branch of biology called ________ is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and their____________, including relationships between living and _____________ things.
ecology, environments, nonliving
all living things on earth can be found in the _______________, the portion of Earth that supports life.
biosphere
the biosphere extends form high in the _____________ to the bottom of the ocean.
atmosphere
many different environments can be found in the biosphere. all living organisms found in the environment are called _____________ ____________
biotic factors
nonliving parts of an enviorment are called _________ ____________ .
abiotic factors
Whales, trees, and ____________ are biotic factors.
humans
ocean currents, temperature, and ________ are abiotic factors.
soil
a group of organism of one species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time
population
a collection of interesting populations
ecosystem
interactions among the populations and abiotic factors in a community
competition
occurs between organisms when resources are scarce
community
a terrestrial ecosystem
forest
which level of organization contains all the organisms of ONE species that live in a certain area?
population
what is the highest level of organization studied by ecologists?
biosphere
a group of populations / includes animals of different species living together ex. a pond with all of its many species of creatures living together in one location
community
nutrient
chemical substances needed to sustain life like water and minerals (carbon, phosphorus, nitrogen)
food chains/web continually recycle nutrients
plat a vital role in all ecosystems; build tissue and carry out essential life functions

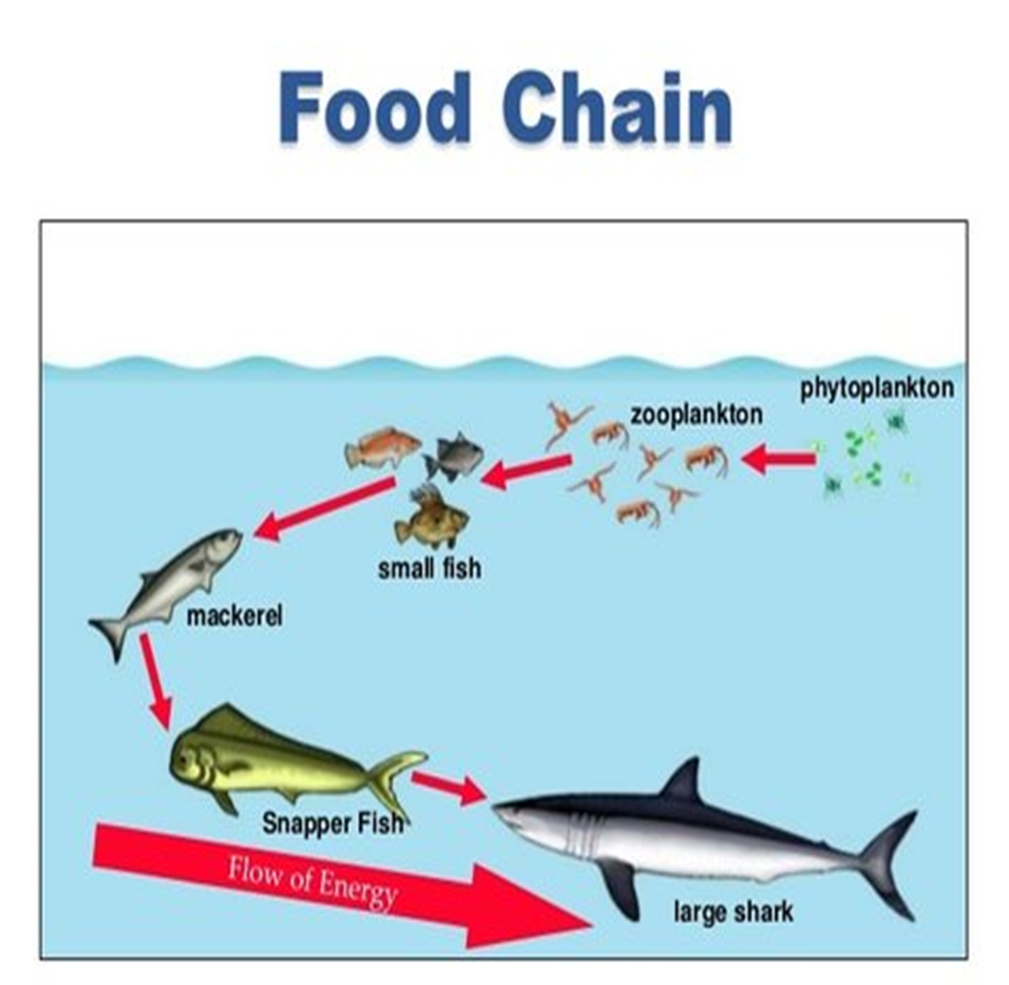
food chain
series of feeding steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
the sun is not always shown but it is the main, source of energy
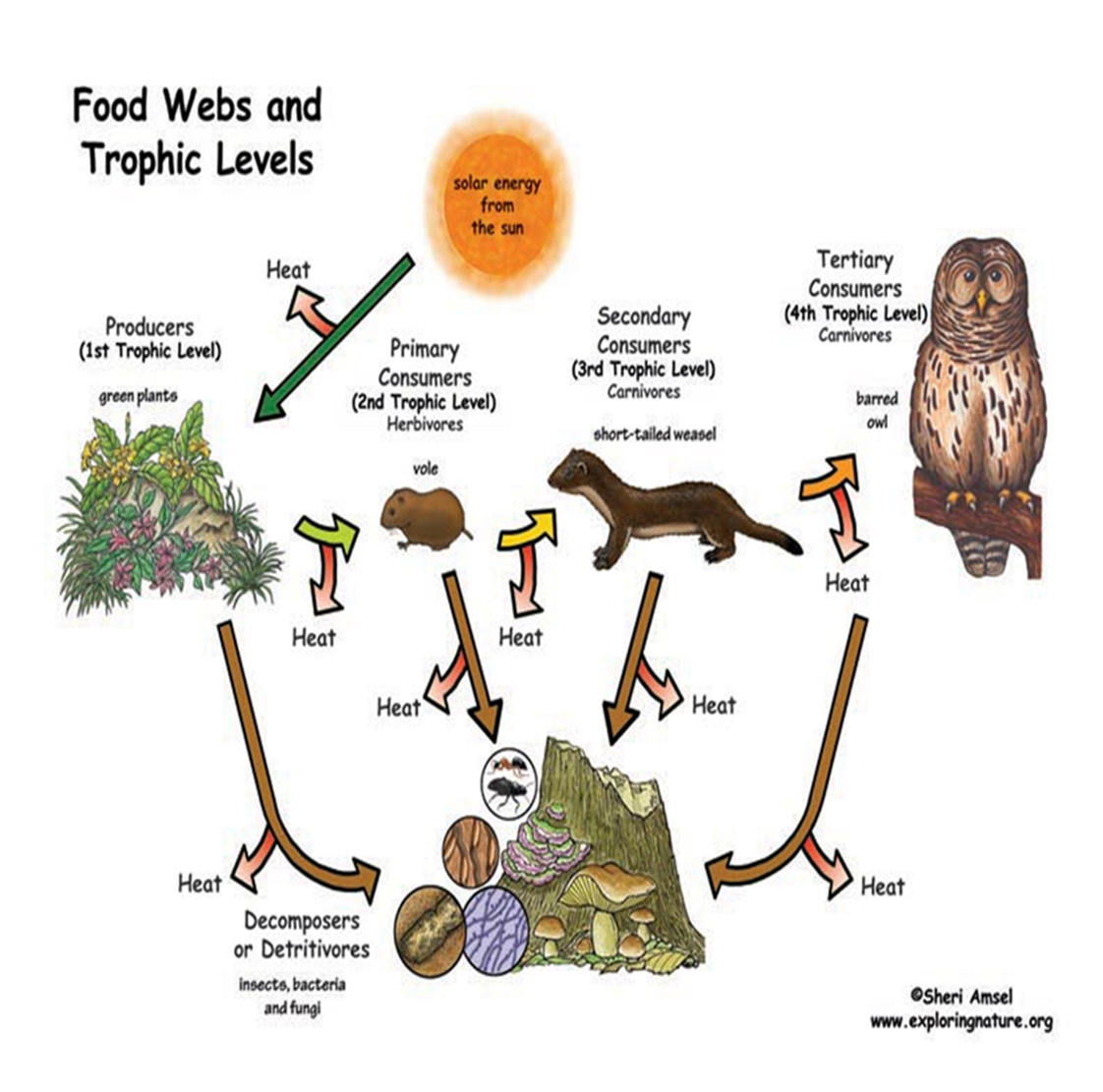
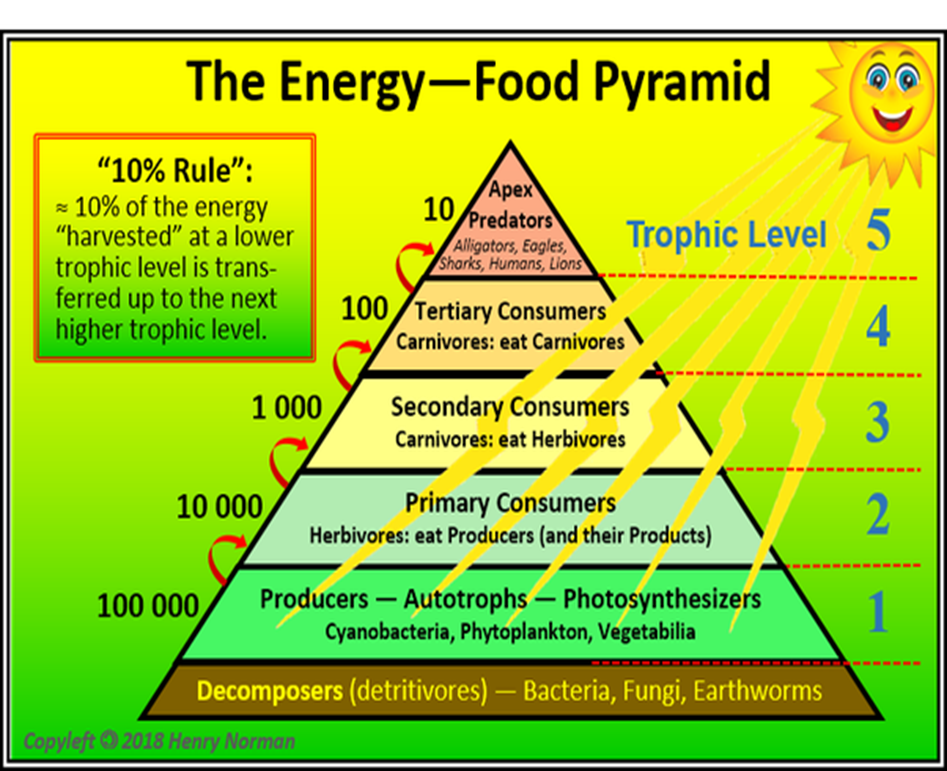
trophic levels
each step in a food chain that shows the transfer of energy.
cannot contain more organisms than there is energy to support
energy flows in one direction and that is away from the sun

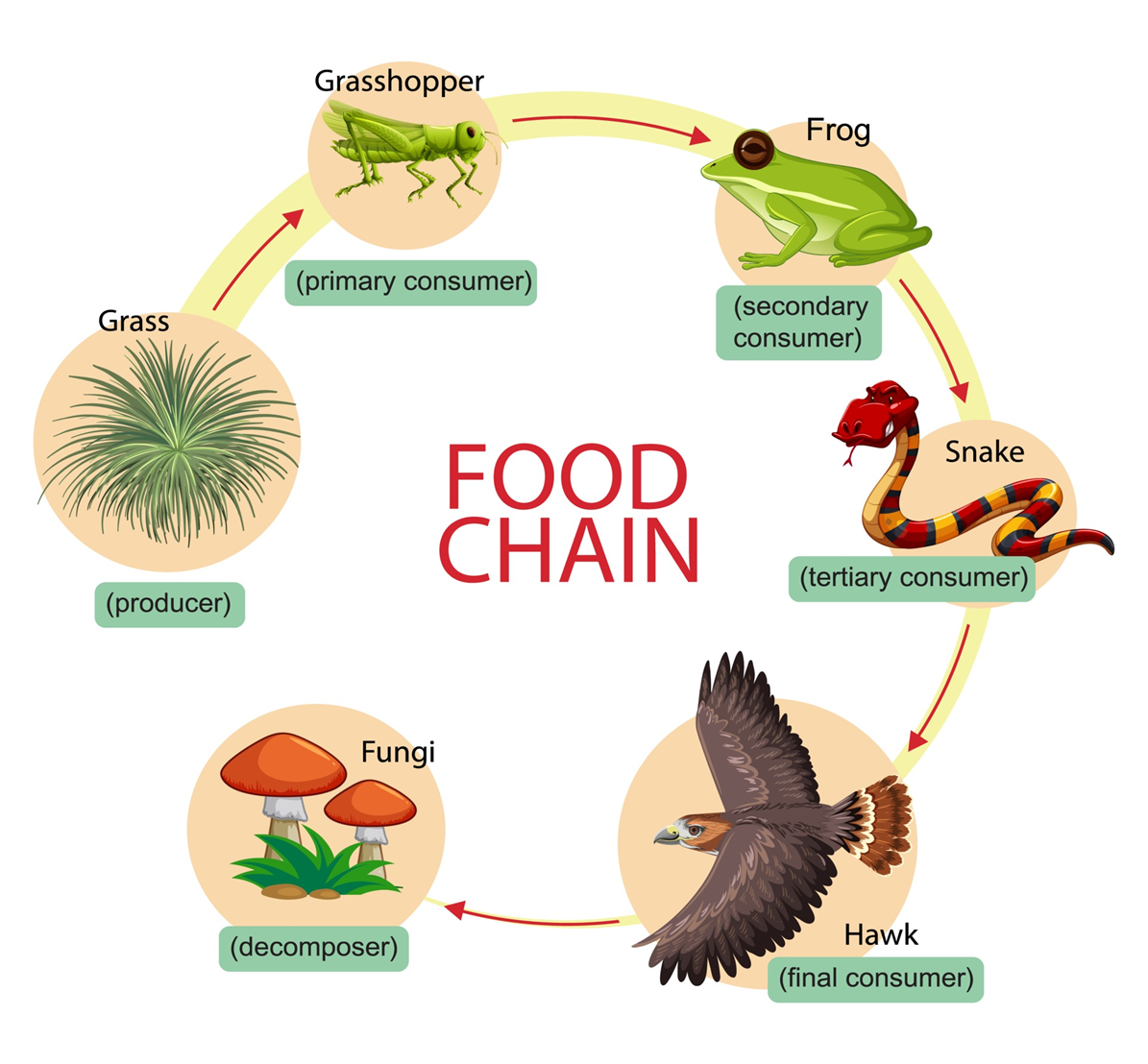
Where is energy greater, at the grasshopper level or the snake level and why?
the grasshopper because they are the primary consumers, & also more heat
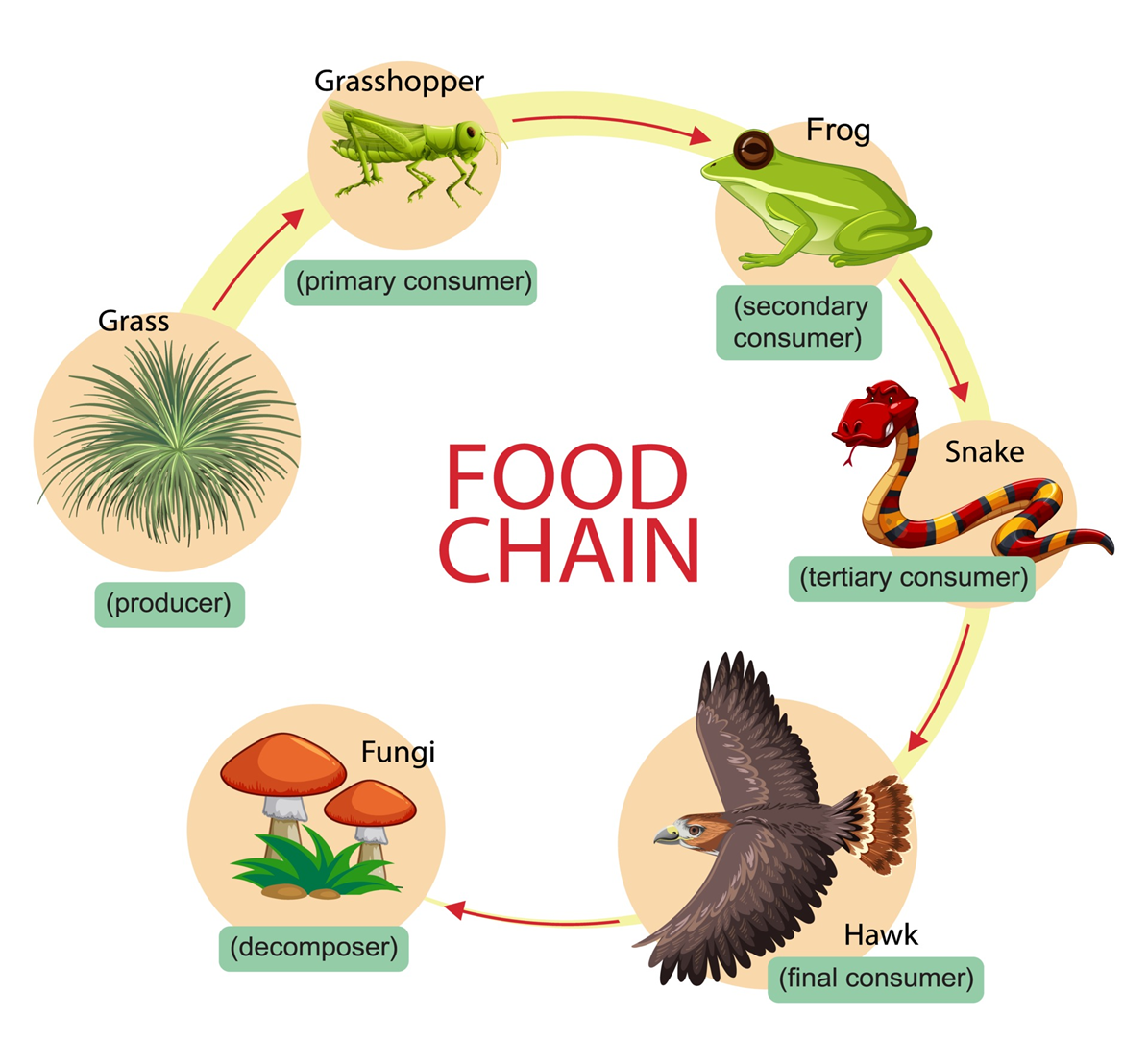
Who is the top level carnivore?
the hawk (final consumer)
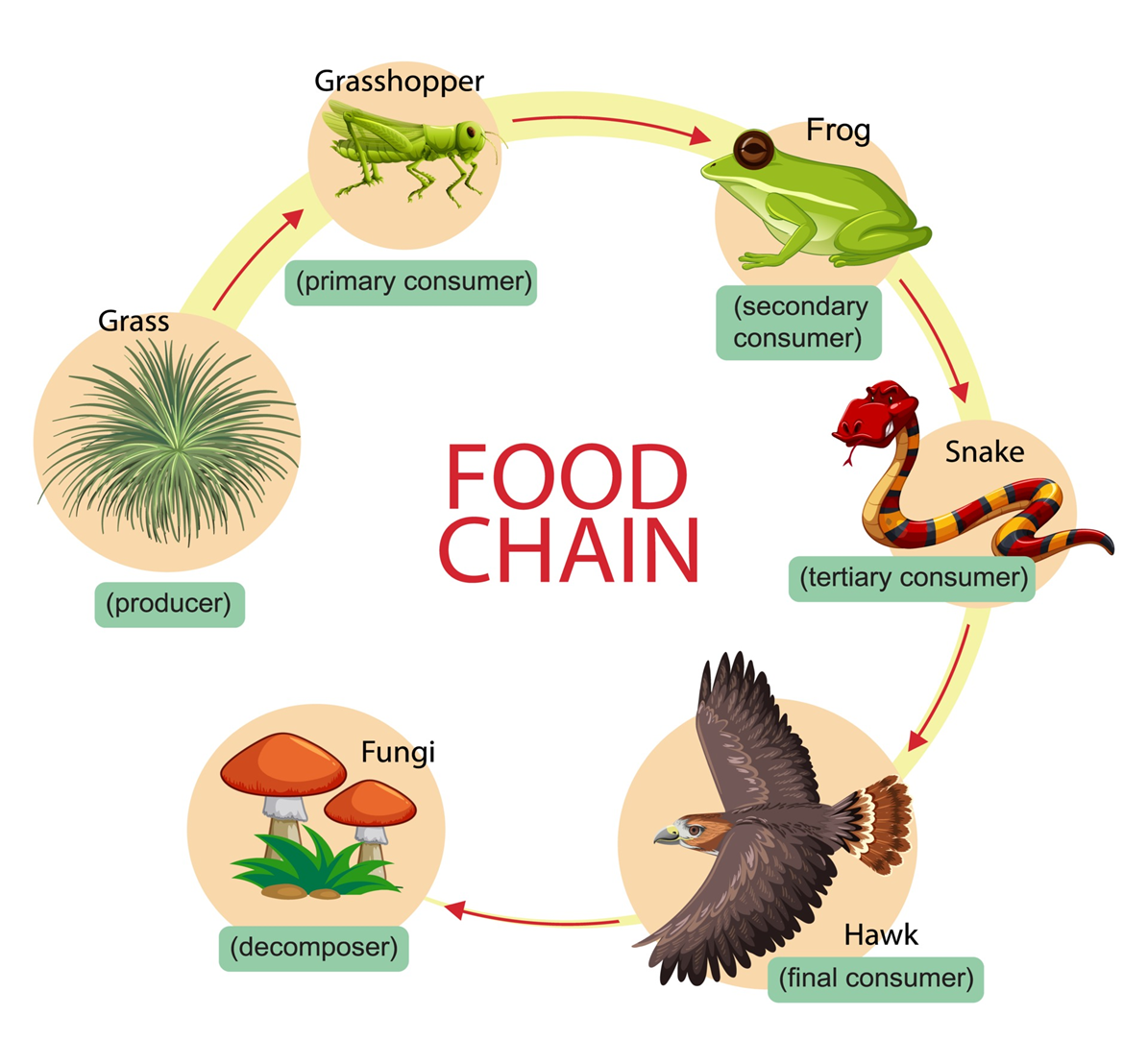
Who is the herbivore?
the grasshopper (its eating plants)
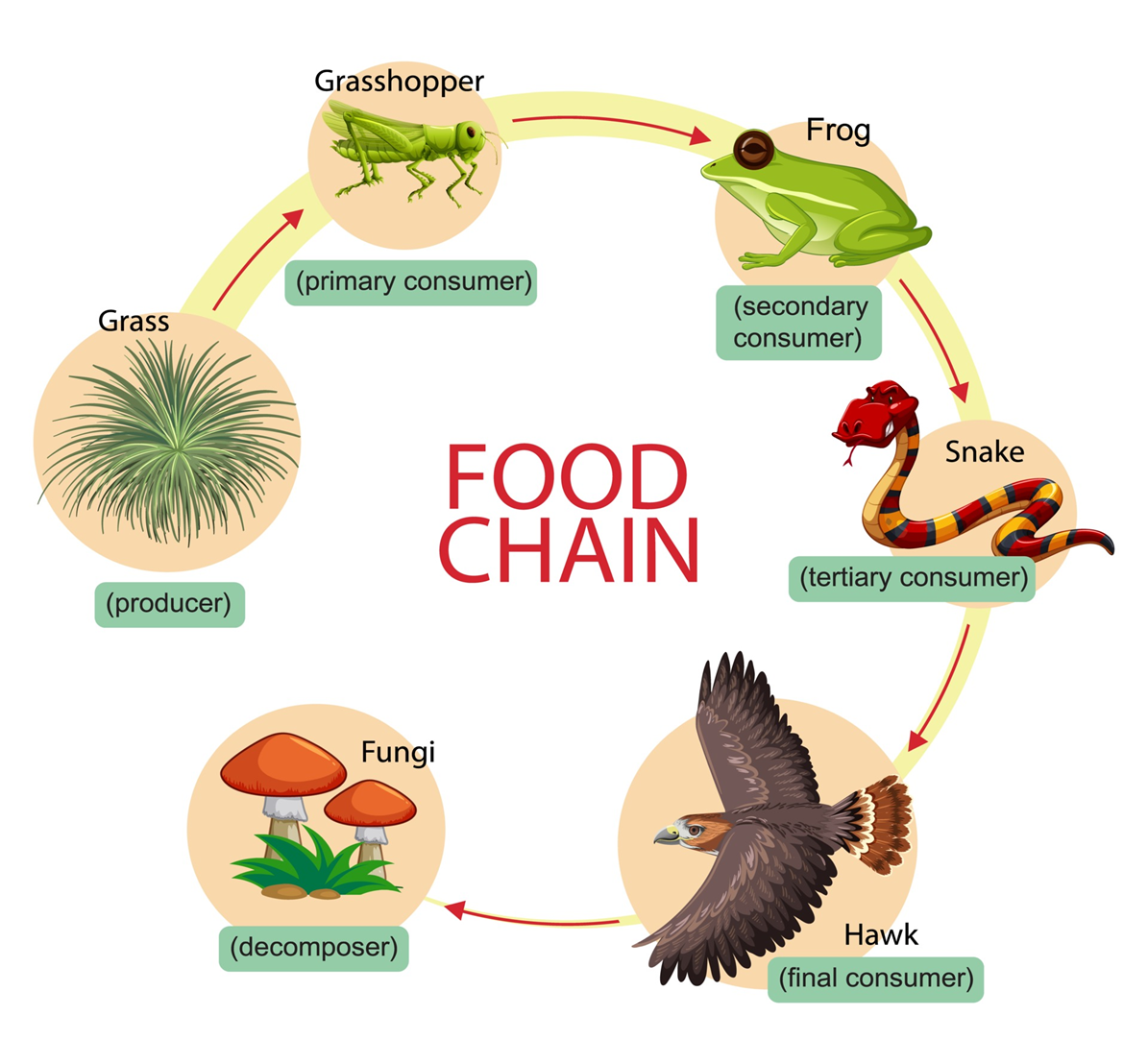
How many steps away is the frog from the sun?
3 trophic levels
What trophic level is the hawk?
5th trophic level
10% rule
only 10% of the energy stored in an organism is passed to the next organism on the next trophic level
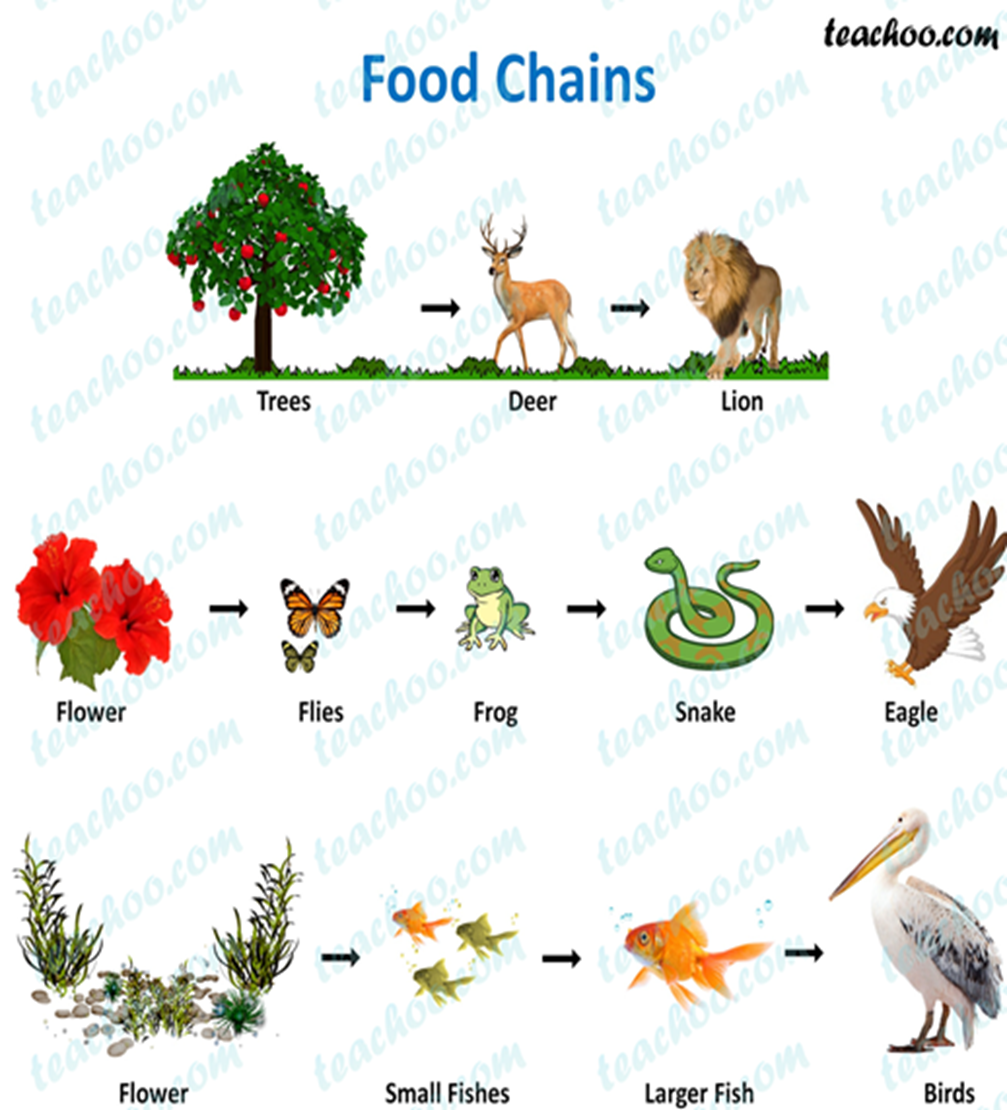
life processes
movement, digestion, reproduction, metabolism, respiration…
the REST is eliminated as HEAT
food webs
interconnected food chains that show all feeding relationships in an ecosystem
phytoplankton
plant-like aquatic microorganisms found in marine and fresh water (plants)
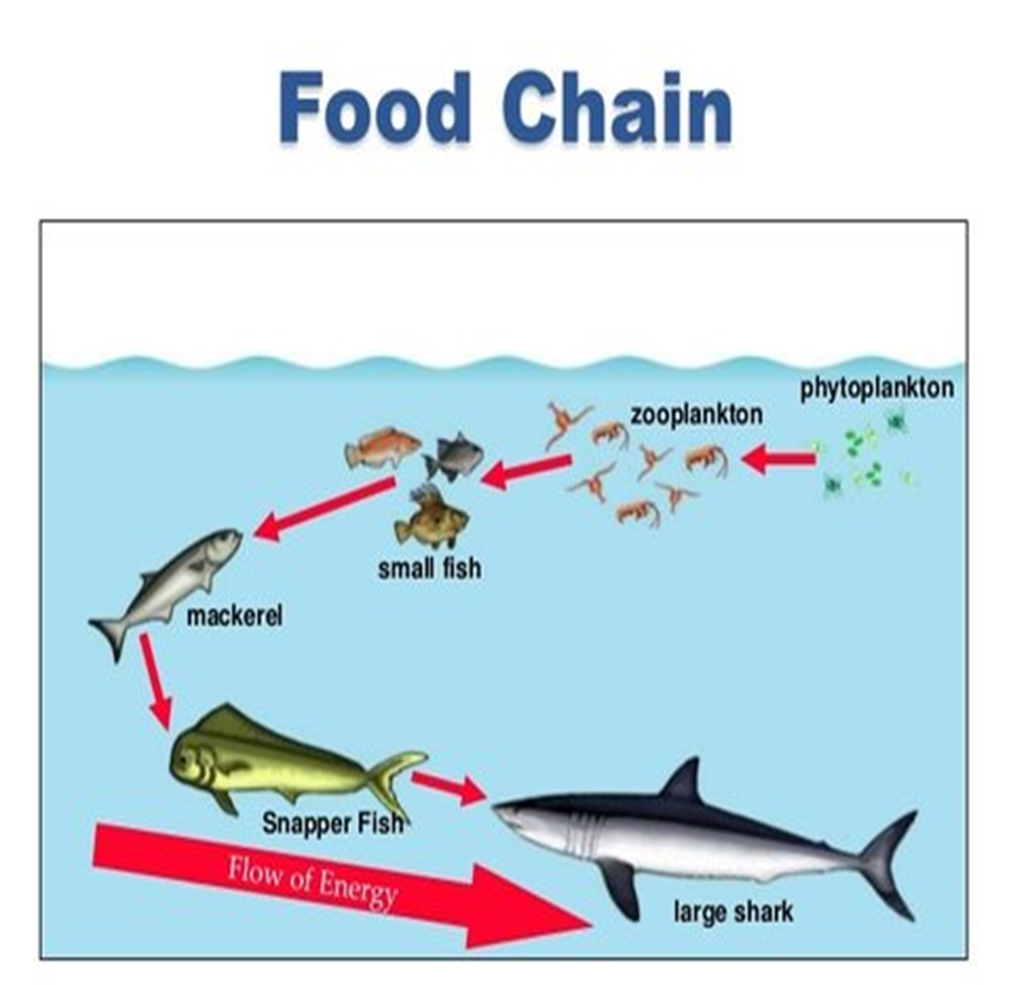
zooplankton
aquatic animal-like organisms & the larval stages of other life forms (animal!)
energy pyramids
shows relative amounts of energy available at each trophic level
biomass pyramid
shows the relative or total amount of living organic matter at eat trophic level
pyramid of numbers
shows the relative number of individuals living at each trophic level
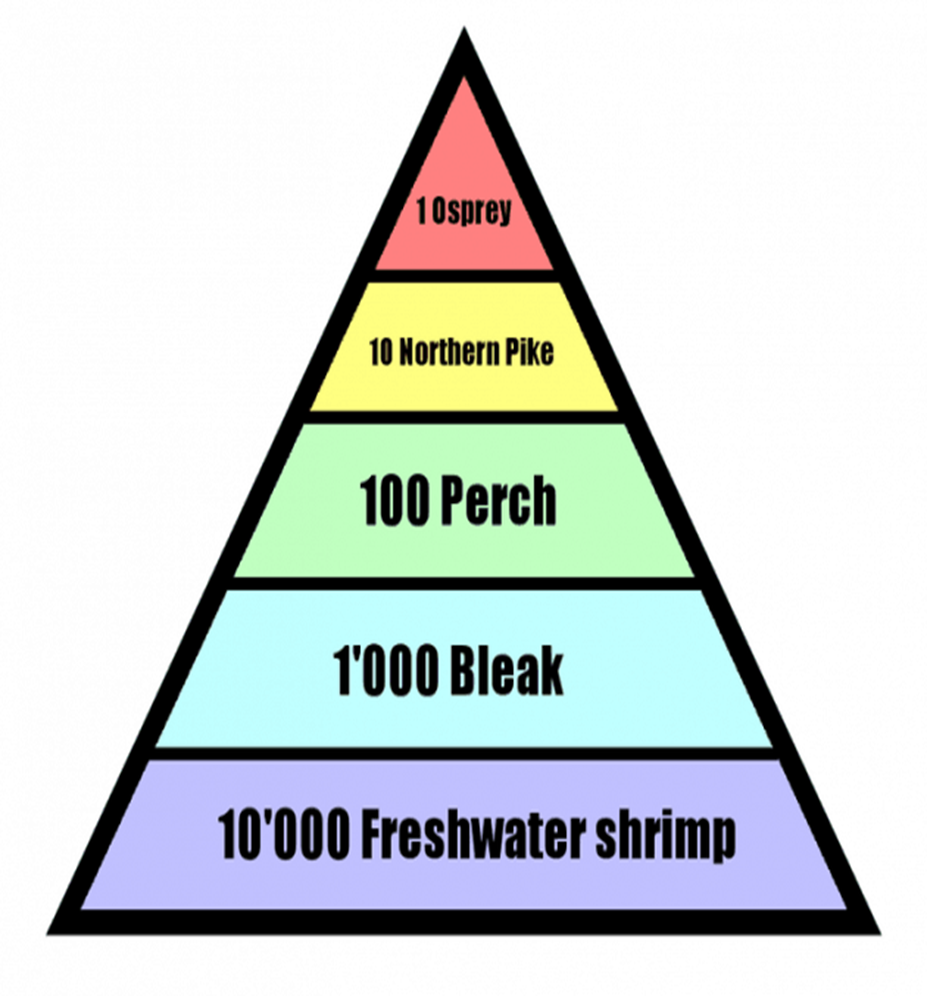
ecological pyramids
show the relative amount of biomass, numbers or energy contained within each trophic level in a food chain/web