Aircraft Control Surfaces and Components
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quiz PLTW Aerospace
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
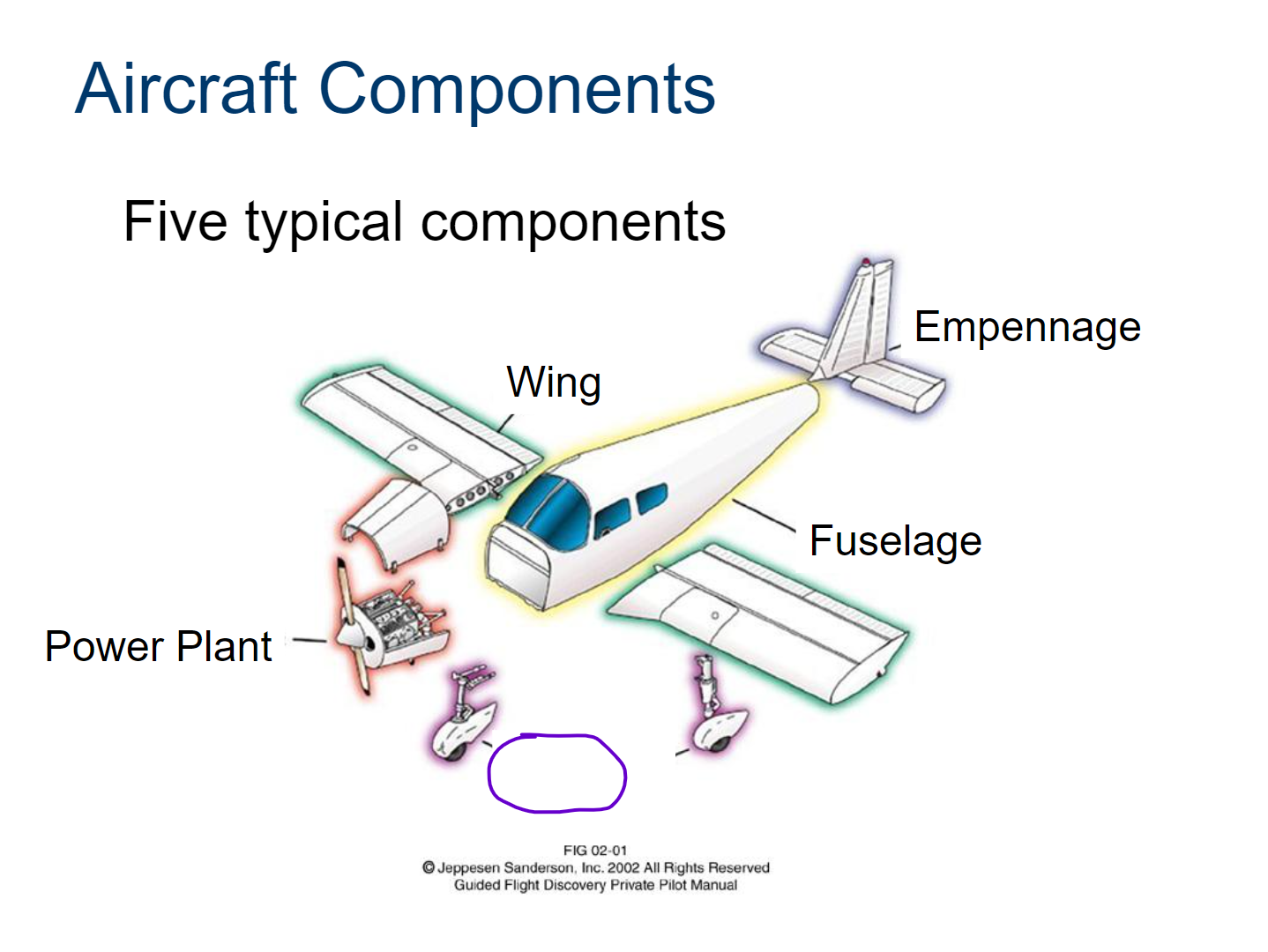
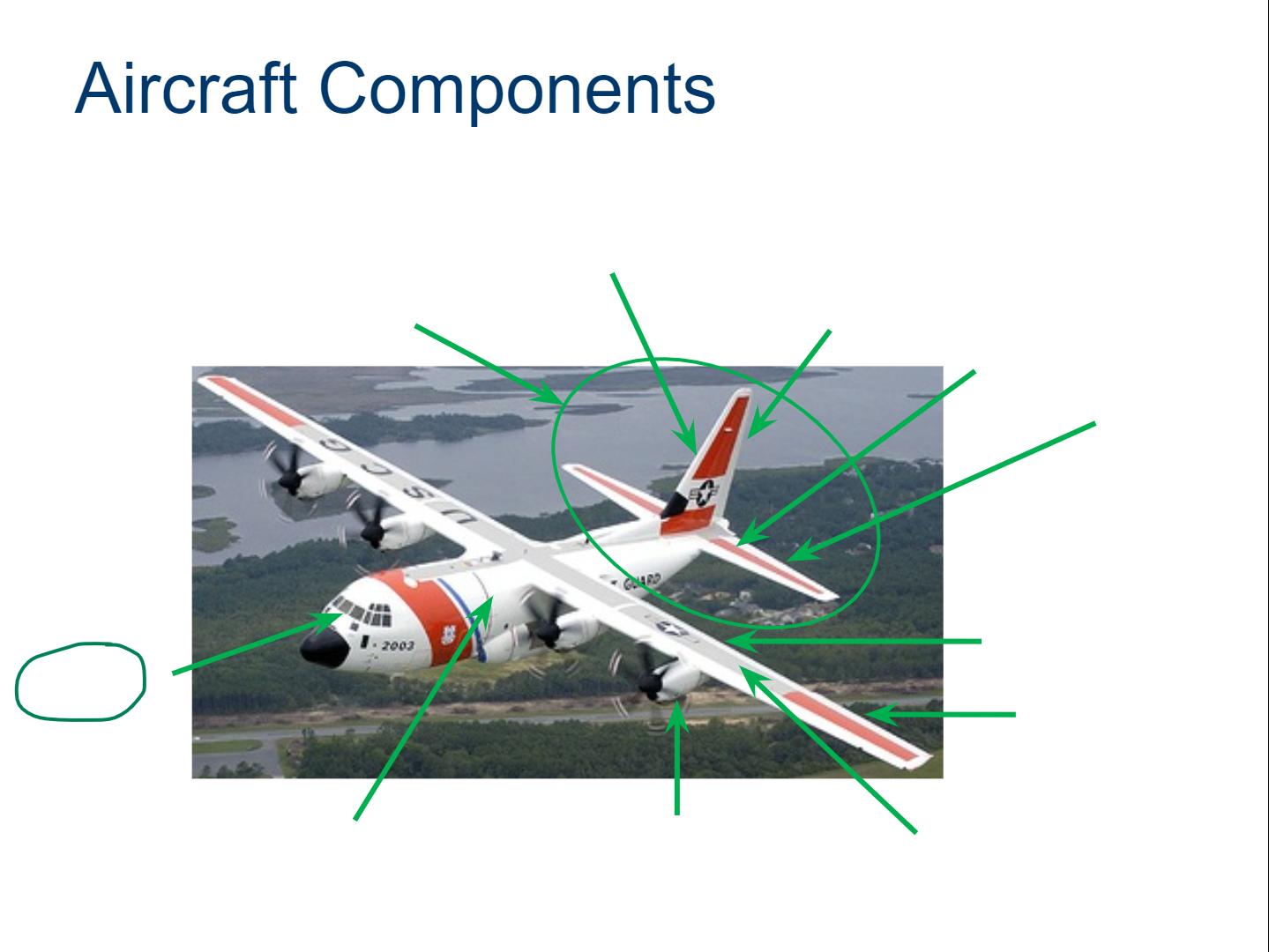
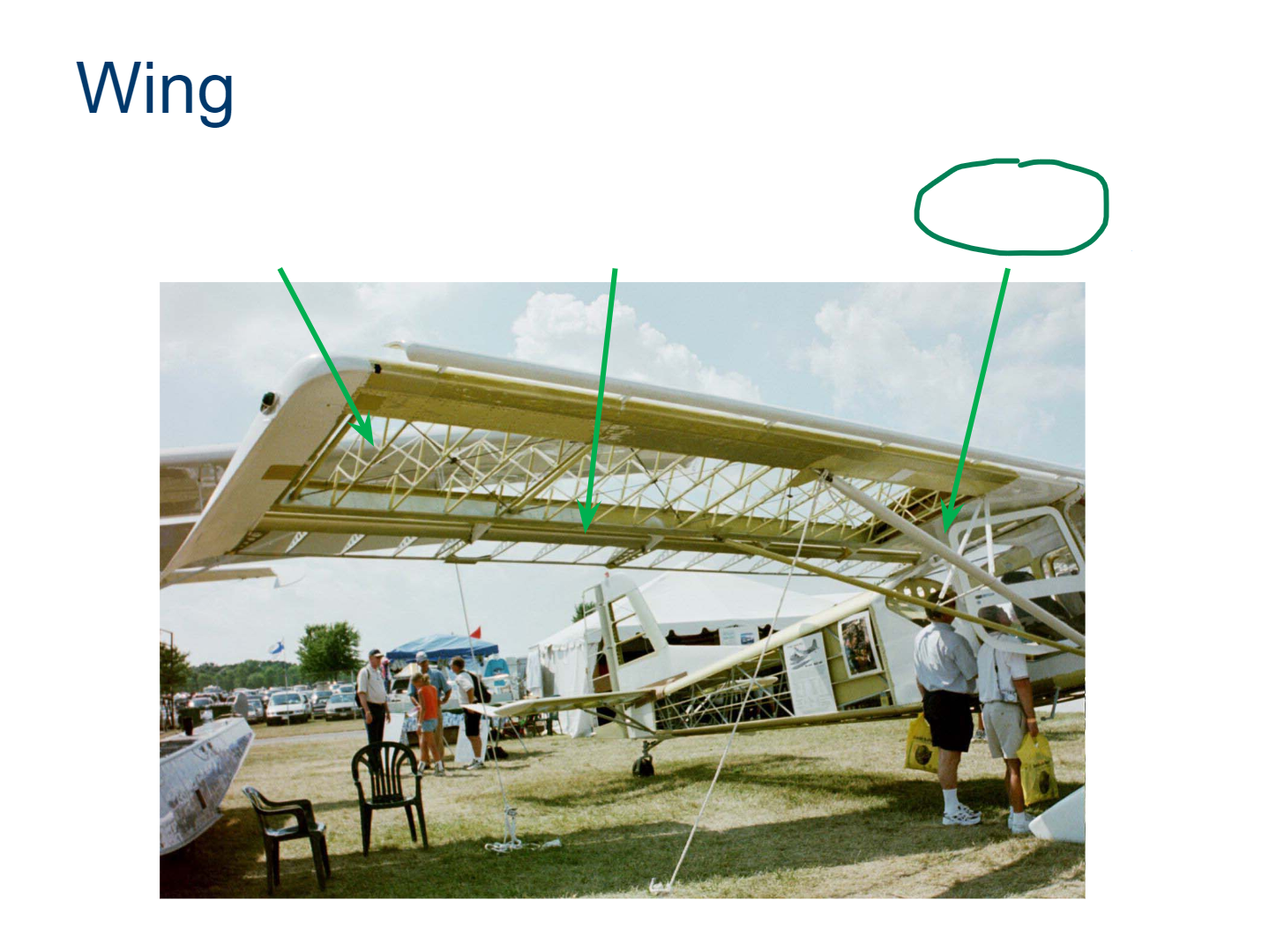
Wing

Fuselage

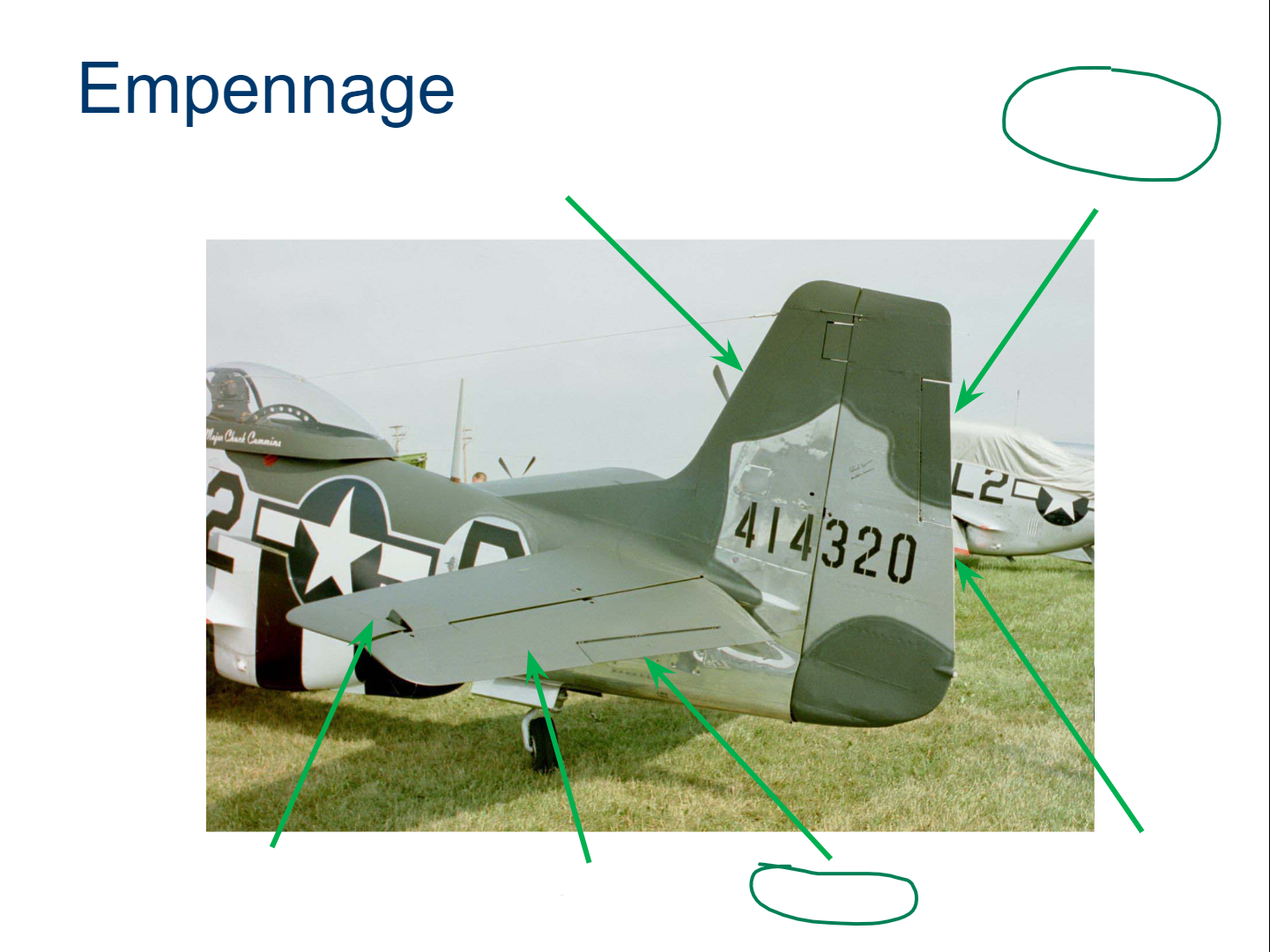
Empennage

Power Plant

Landing Gear
Vertical Stabilizer
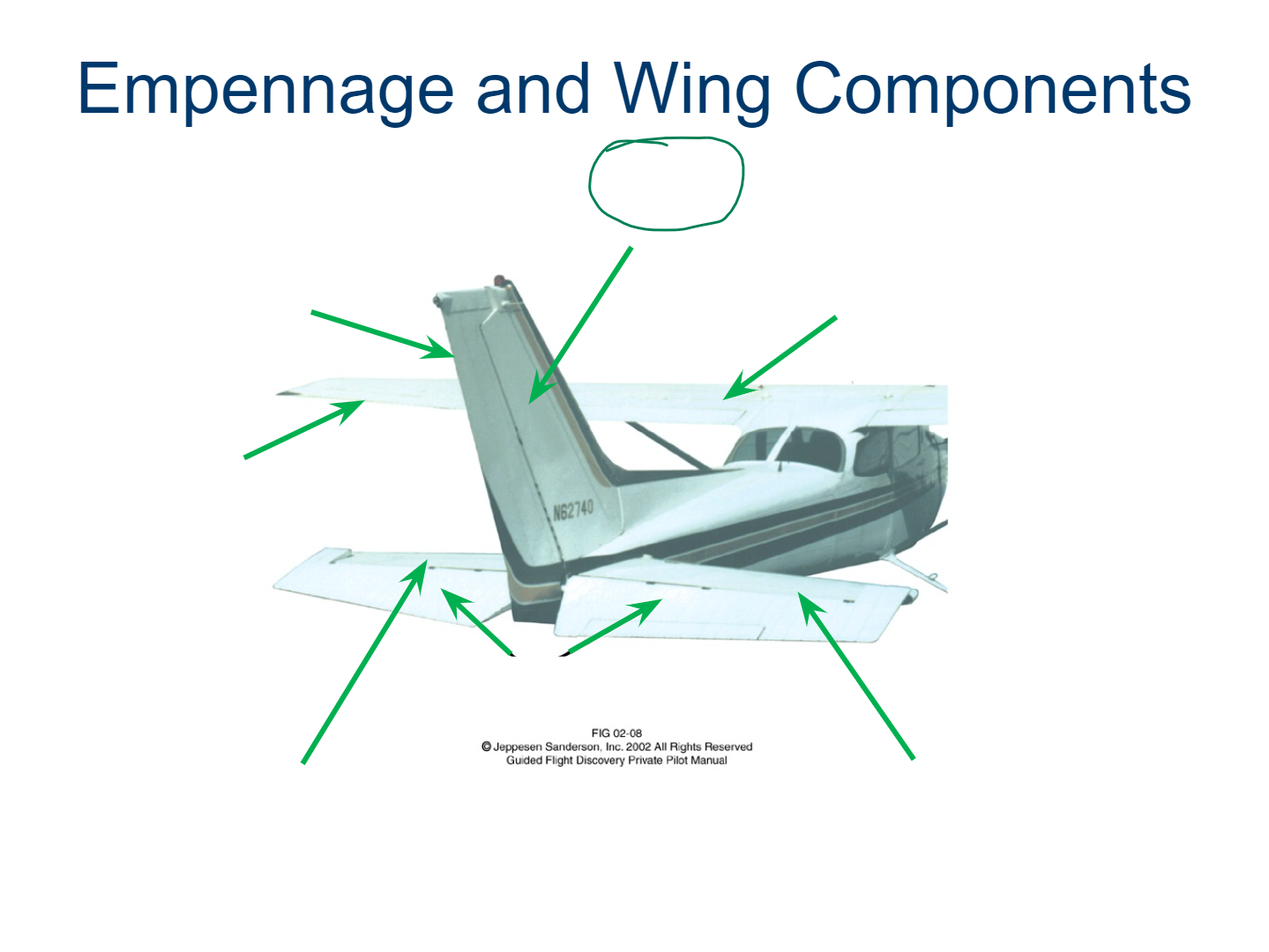
Rudder
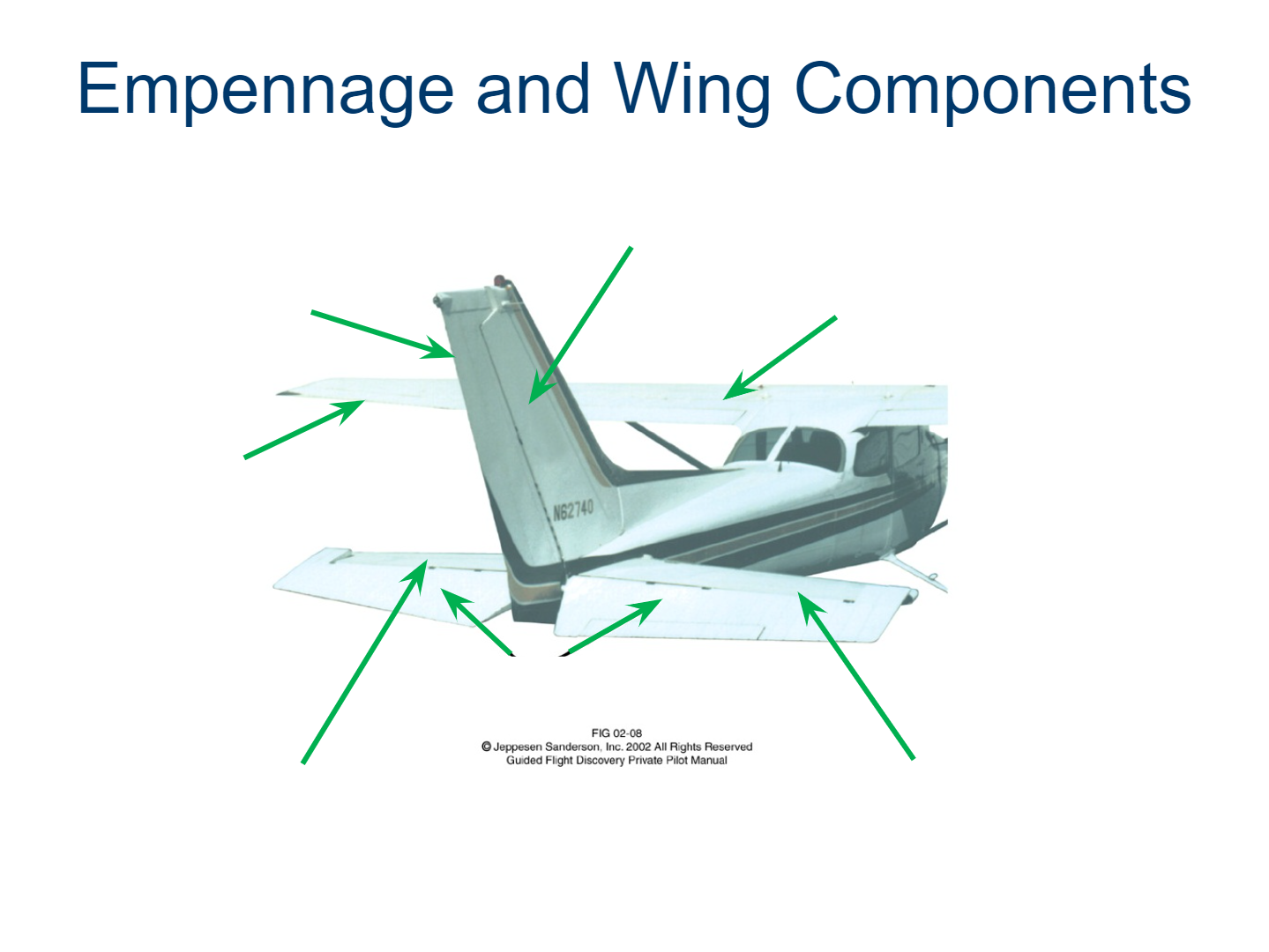
Flaps
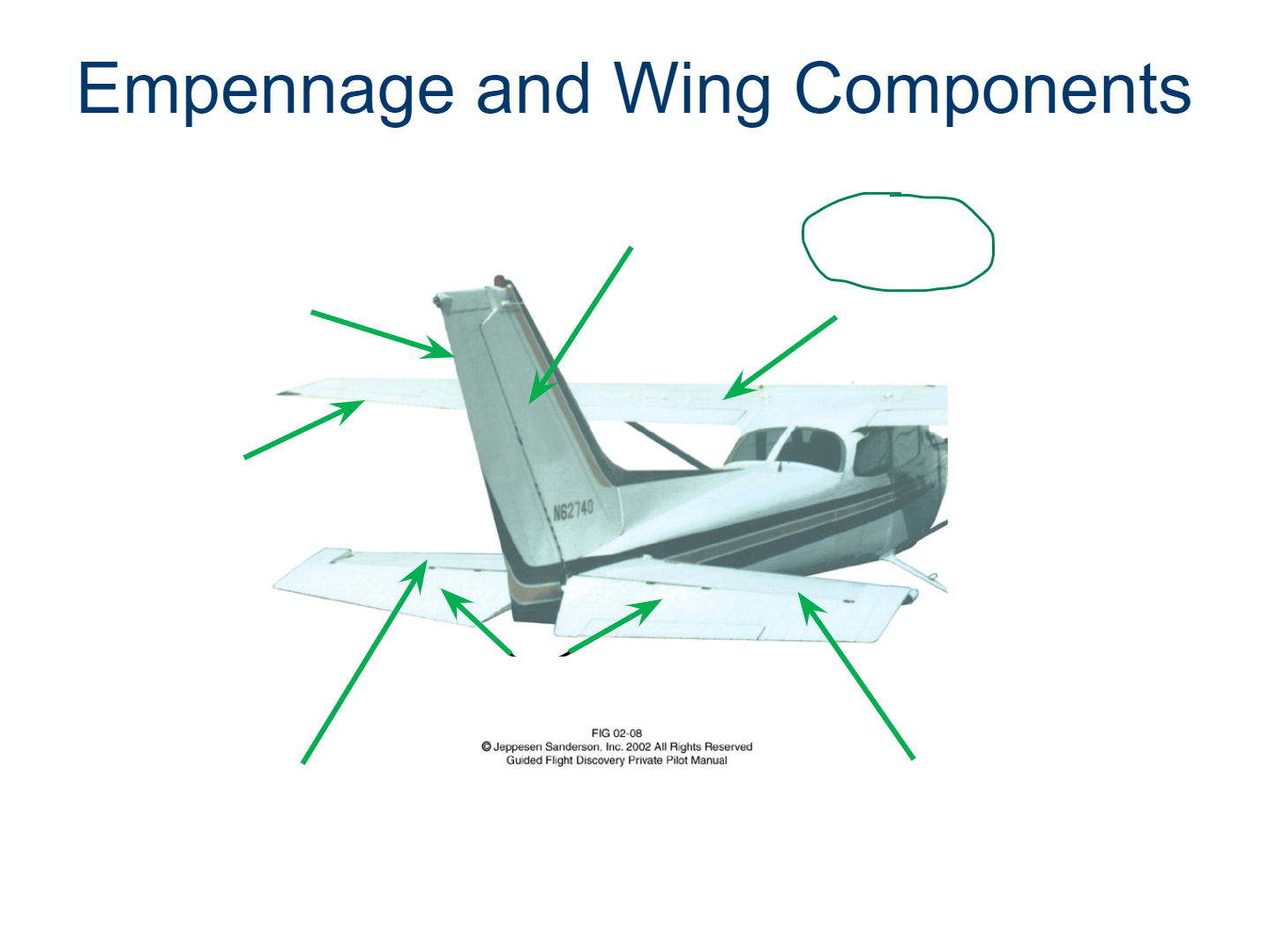
Ailerons
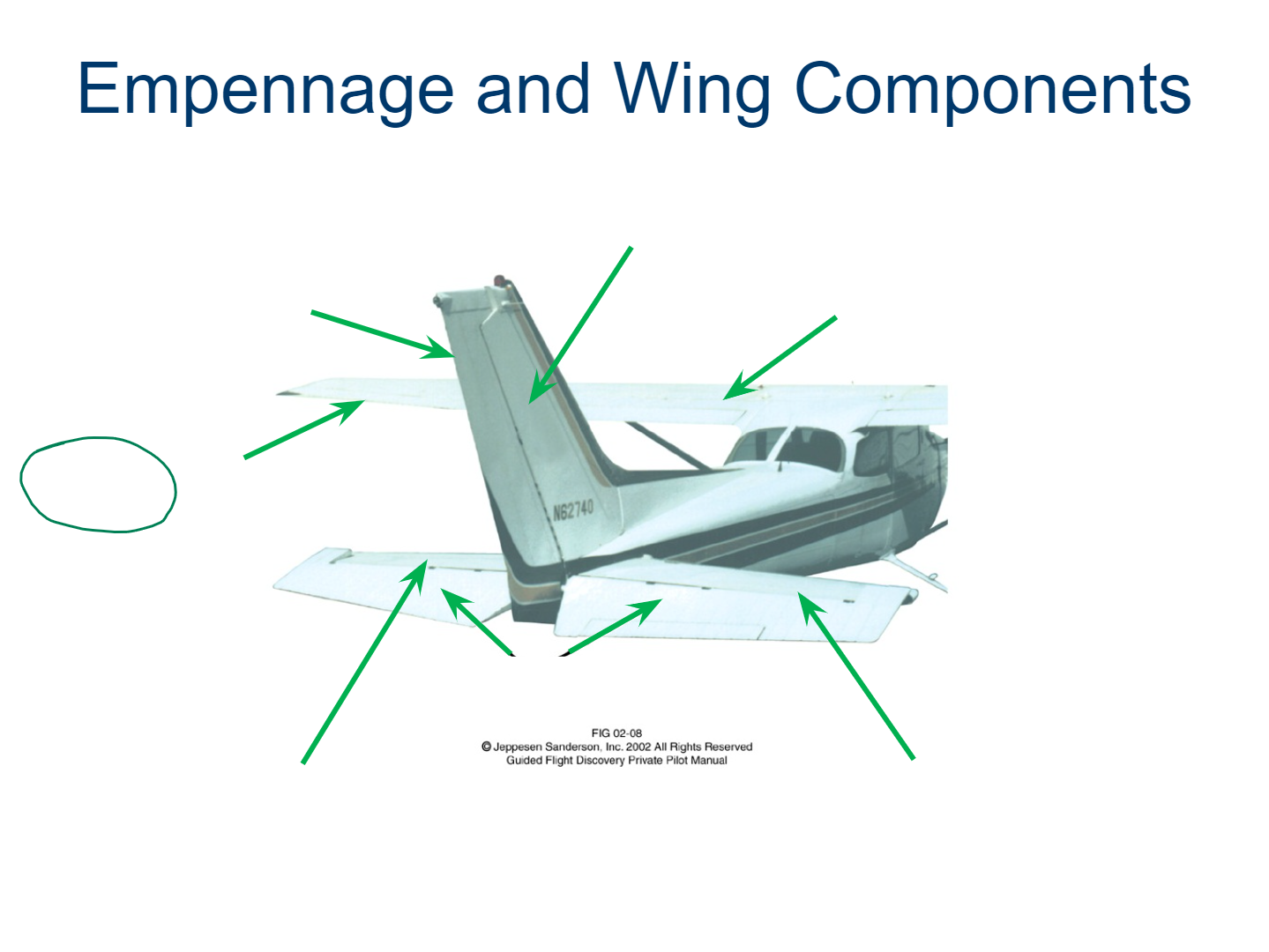
Horizontal Stabilizer
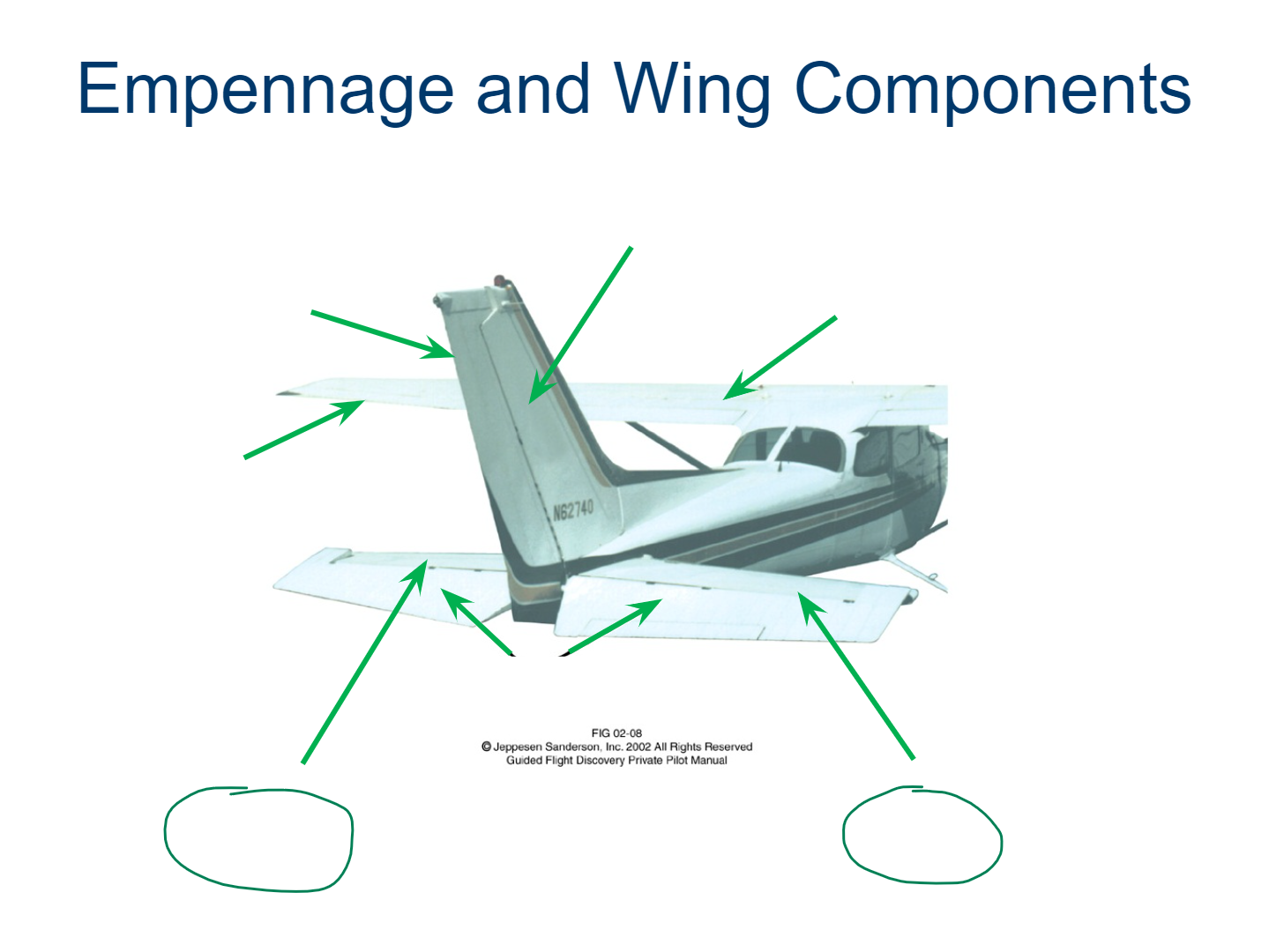
Elevator
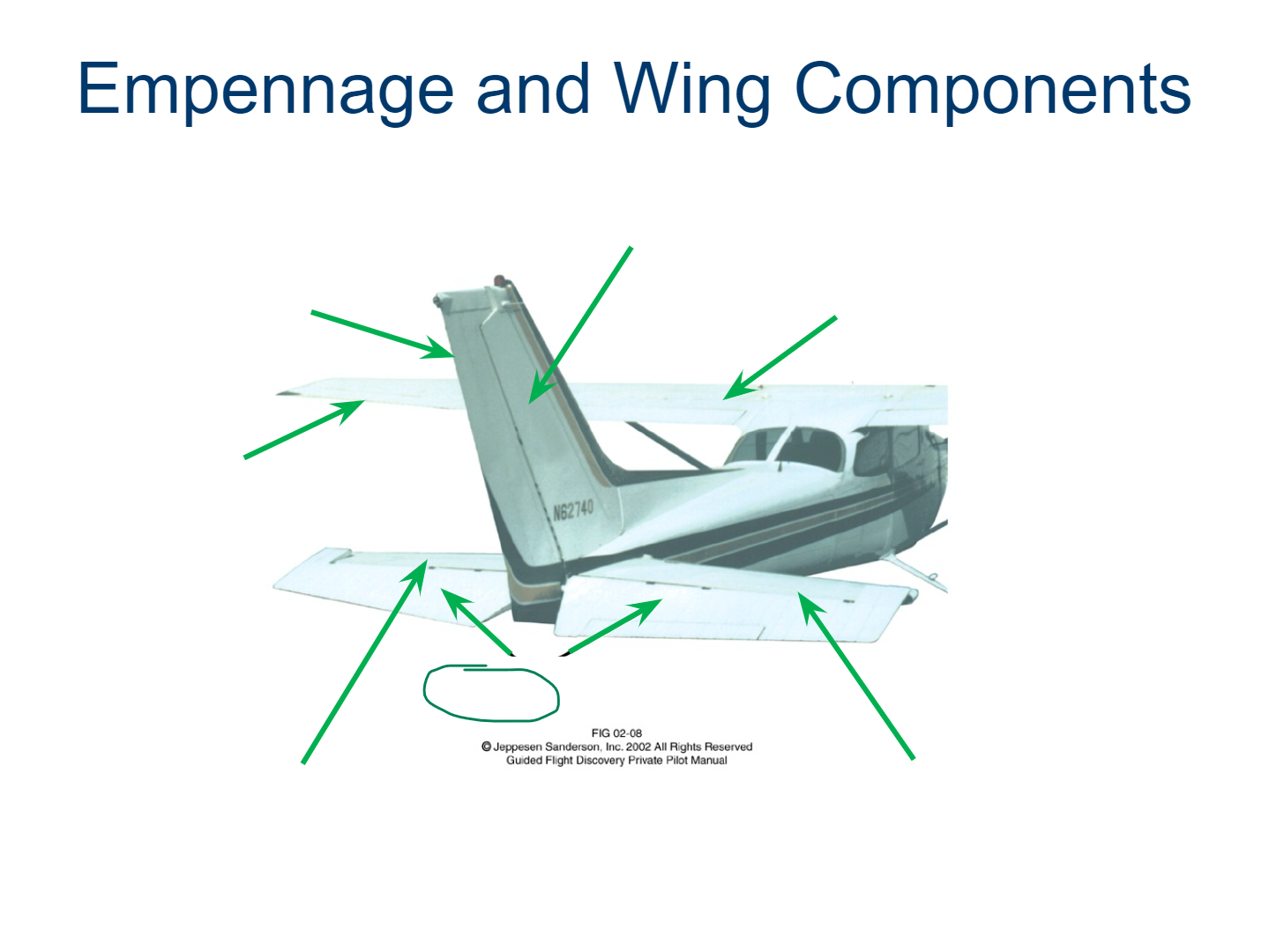
Trim Tab
Cockpit

Ribs
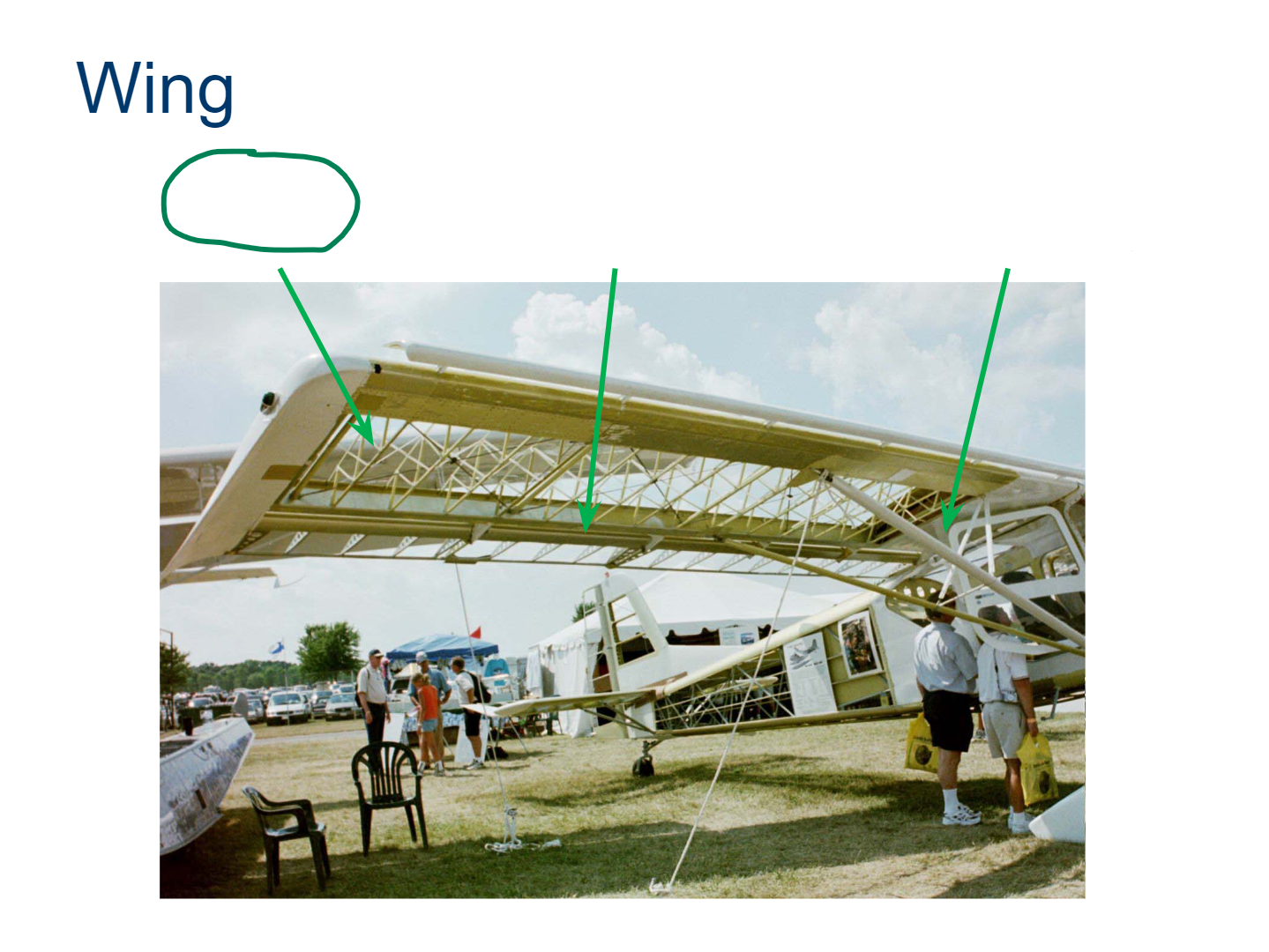

Spar
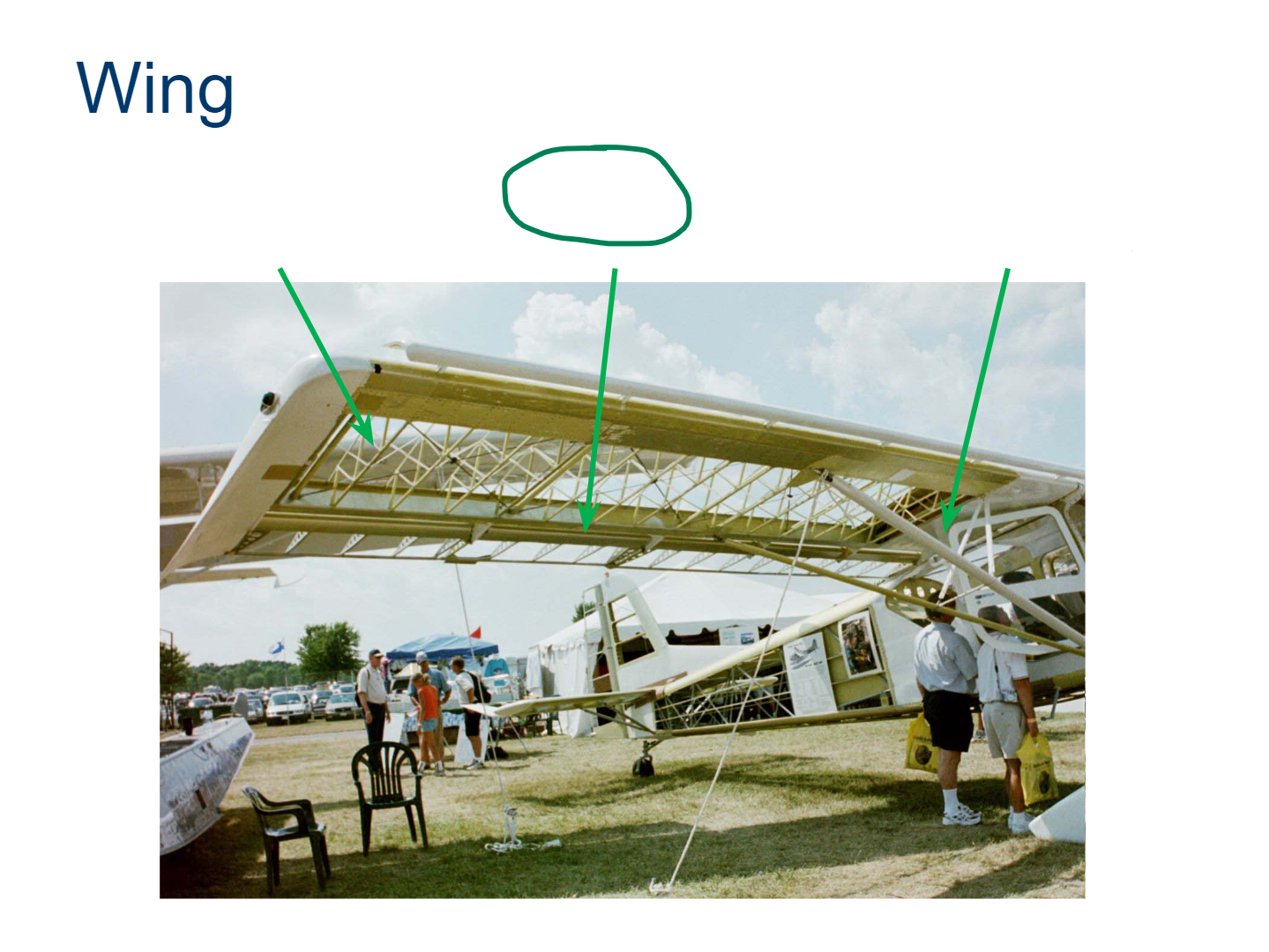

Wing Strut

Winglet
An extension of a wing tip used to limit air from recirculating from the high pressure airflow below the wing to low pressure above the wing. This recirculation induces wing tip vortices and increases drag.

Center of Gravity
Point where weight of object is balanced
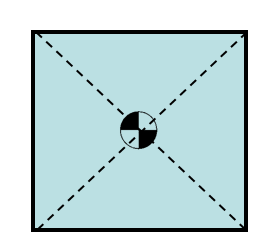
stability
Aircraft with positive _________ returns to steady flight after disturbance
•Aircraft with positive stability returns to steady flight after disturbance
•Maneuverability is an indication of an aircraft’s ability to handle the stress of maneuvers
•Controllability is an indication of an aircraft’s ability to react to pilot inputs
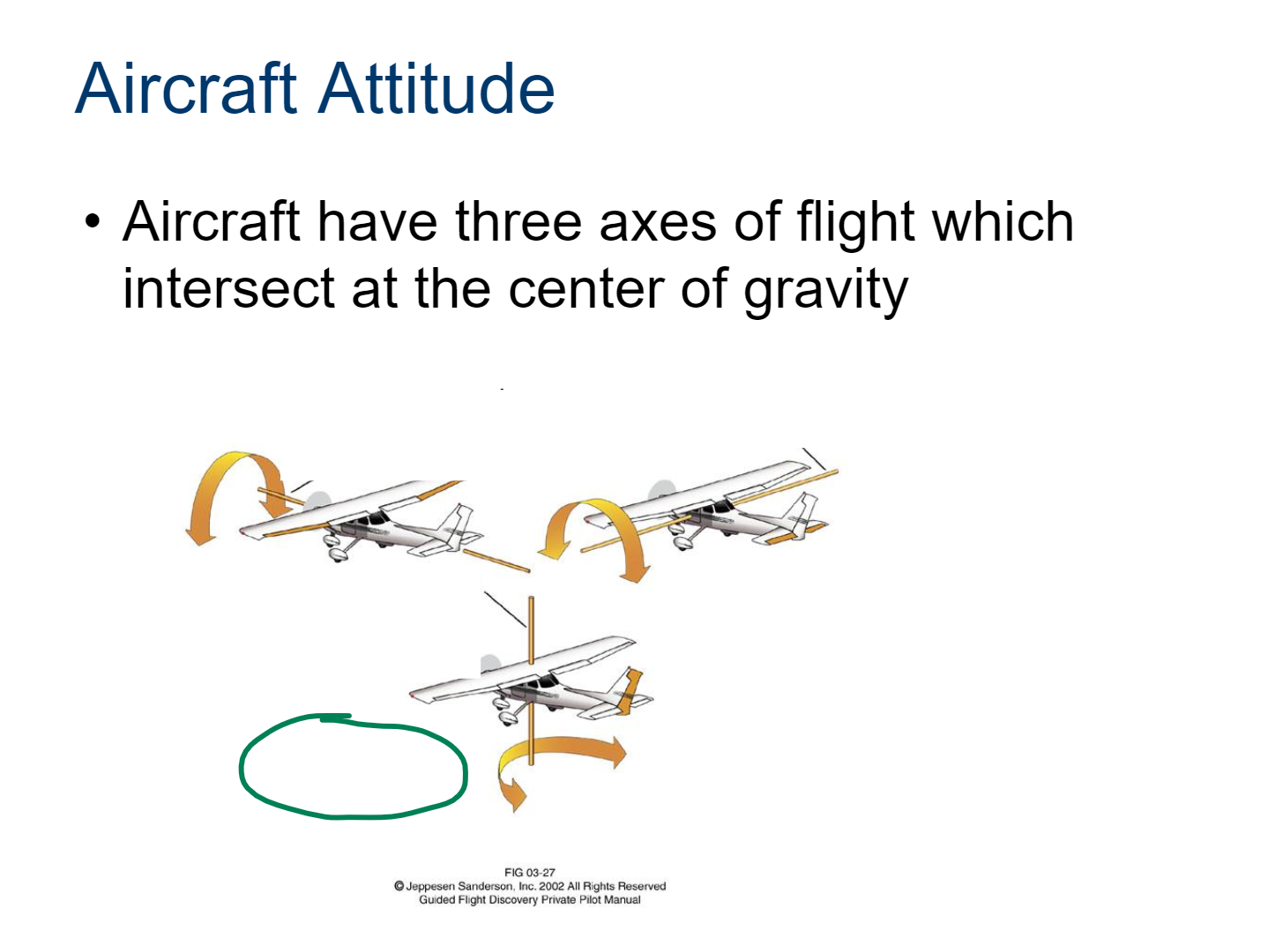
Aircraft Attitude
The orientation of an aircraft in relation to the horizon and other reference points, including pitch (nose up or down), roll (tilting left or right), and yaw (rotation left or right).
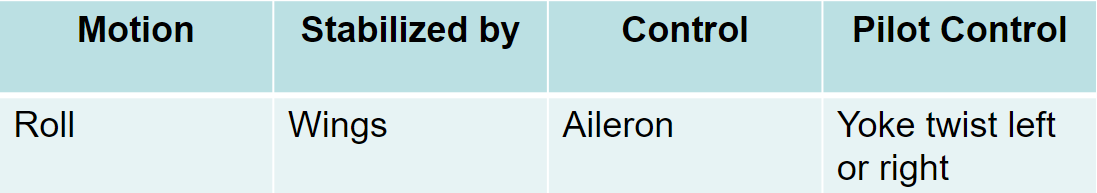
longitudinal axis
roll is controlled by the ailerons
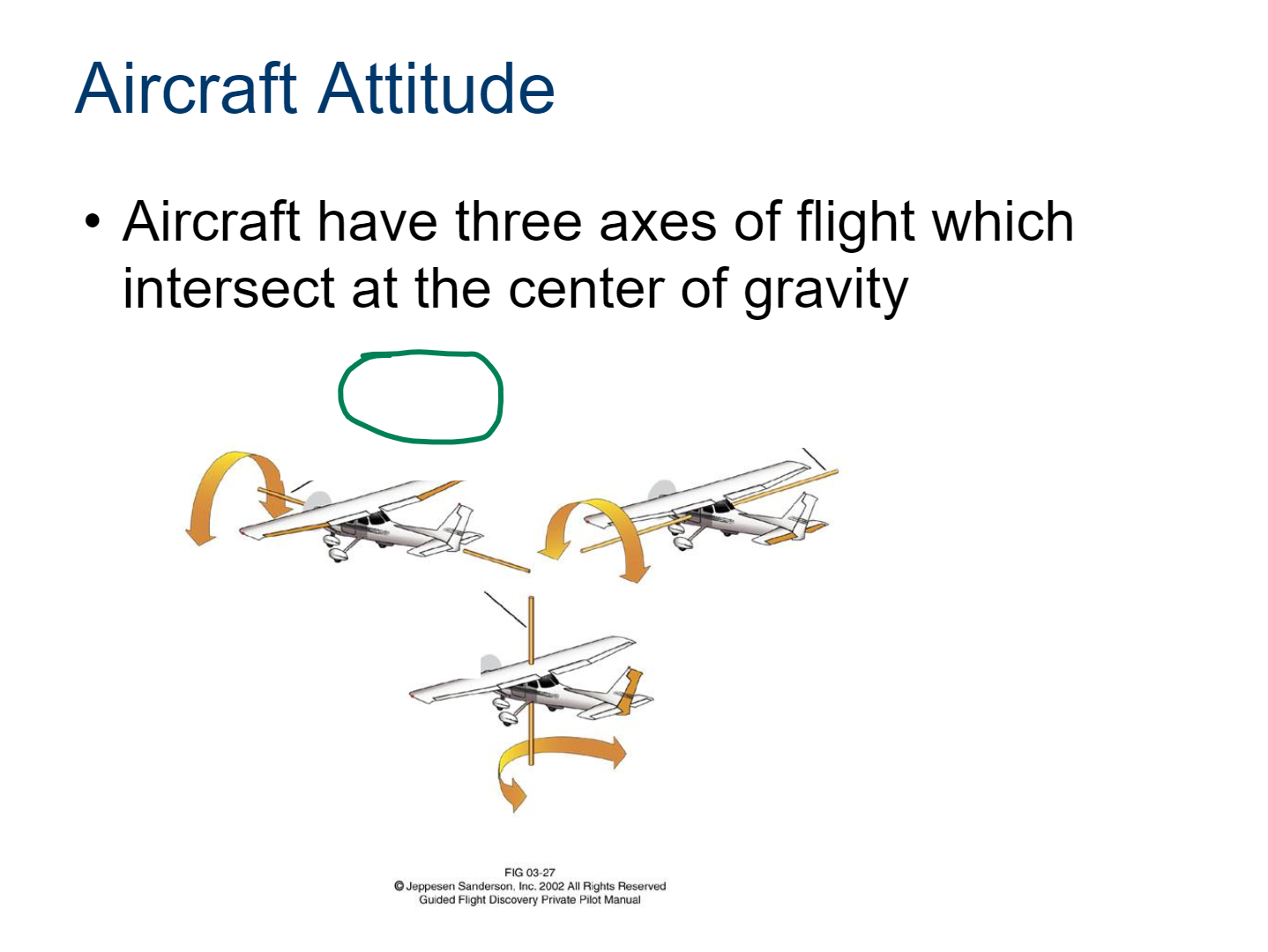
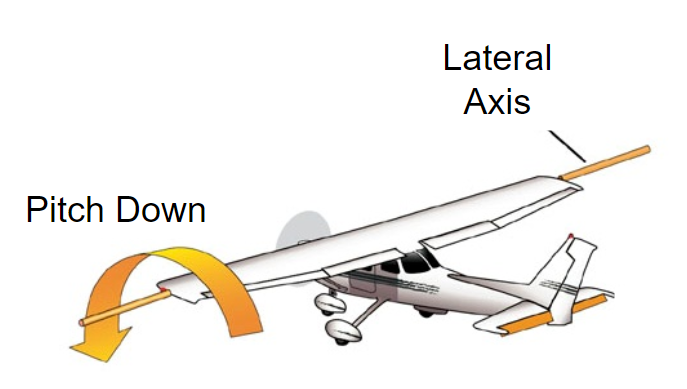
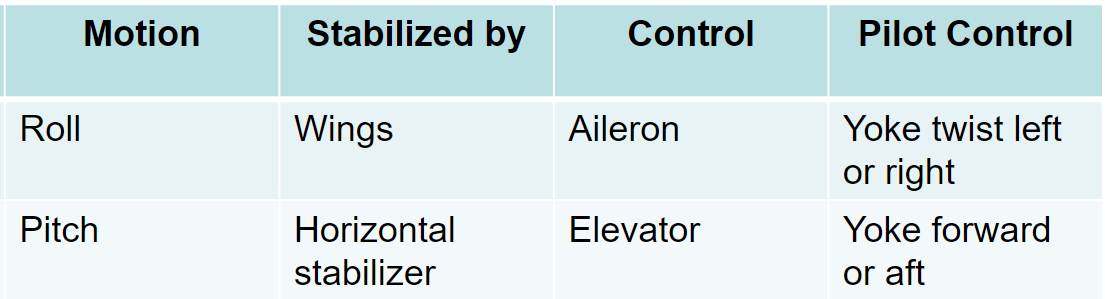
lateral axis
pitch is controlled by the elevator
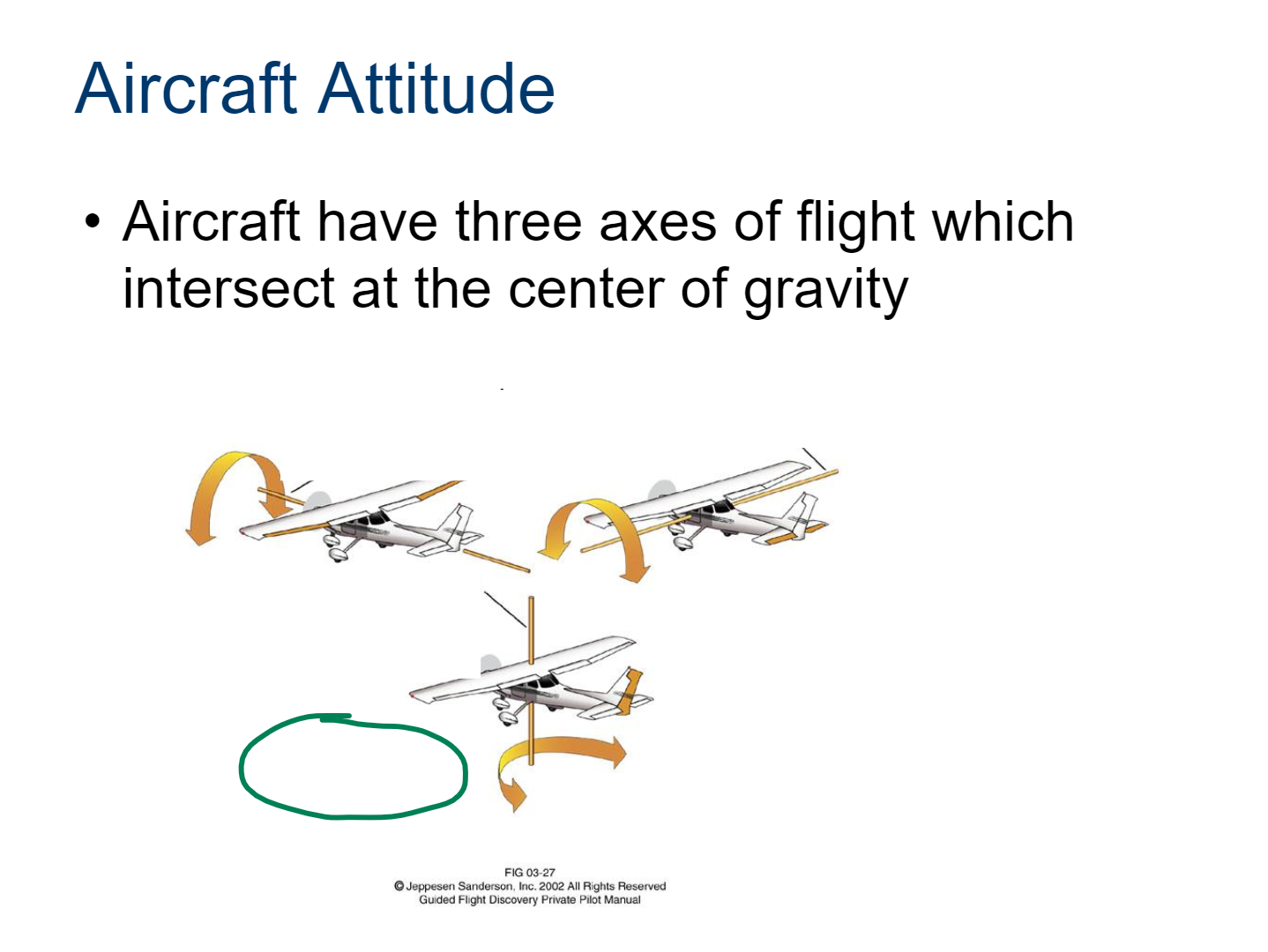
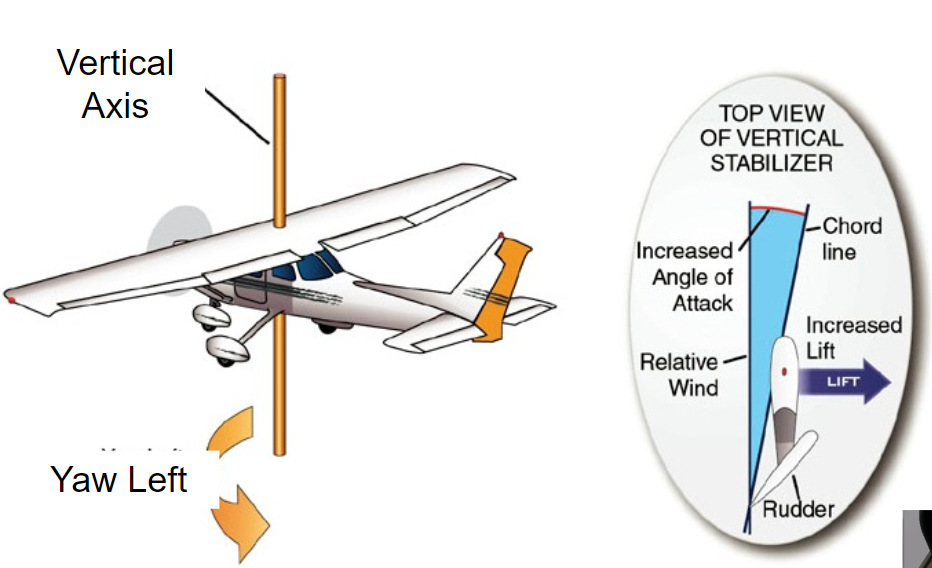
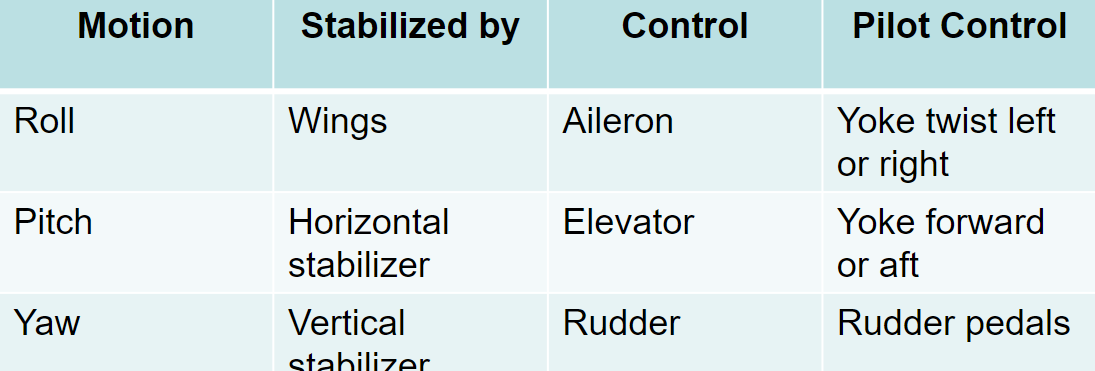
vertical axis
yaw is controlled by the rudder
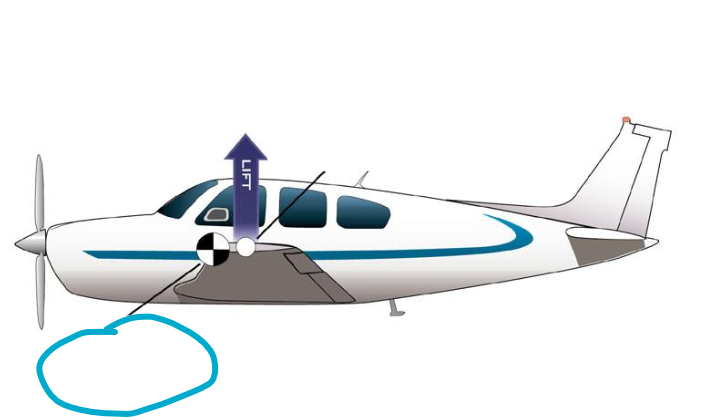
Center of Pressure
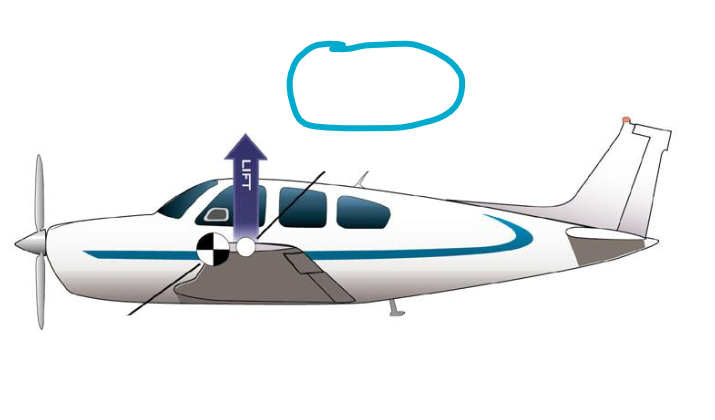
Center of Gravity

to turn left, the aircraft must roll left
right wing must raise and left wing must descend
right aileron is lowered and left aileron is raised
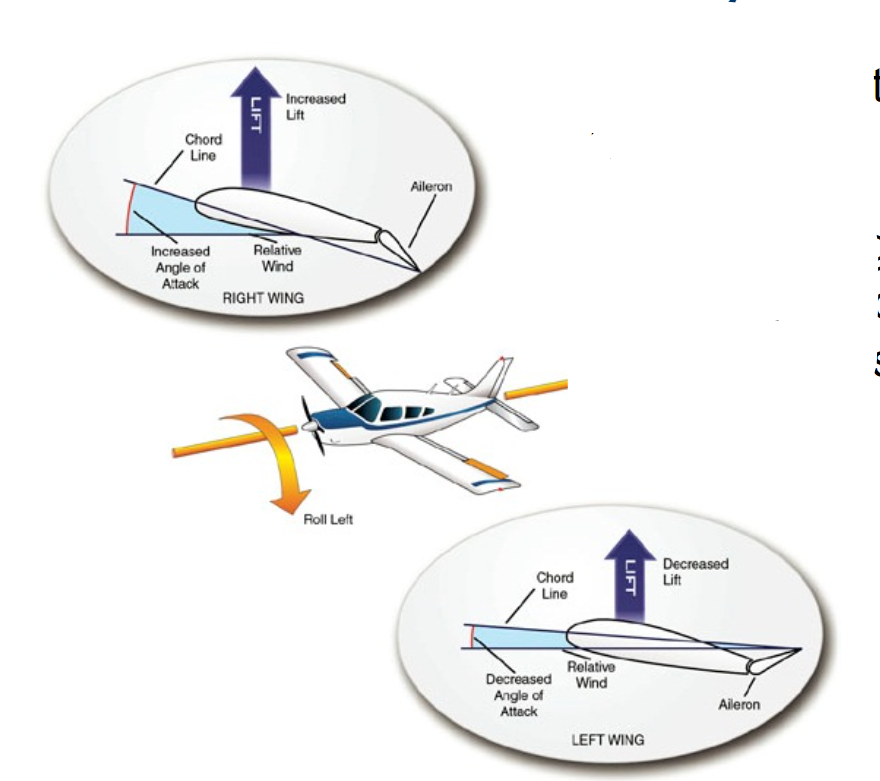
Yoke rotated left
Left and right flaps lower
Left aileron raises
Right aileron lowers
Flaps level lowered
When are flaps used?
Used during takeoff and landing to increase lift at lower airspeed. The use of _____ at cruising speed would damage the wing.
Push the yoke forward
Lower the elevator
To descent, the pilot reduces power and lowers the elevator to pitch down
what does pushing left pedal away from you do?
To yaw the aircraft nose left, the rudder must deflect left.
Longitudinal Axis
Lateral Axis
Vertical Axis
Why do airplane designs differ?
The differences more than aestheic
Consider how a design affects lift and drag and other characteristics
High Wing
generates most lift
improved pilot downward visibility
high center of gravity
pusher engine avoids introducing turbulence over wing

Mid Wing
Generates the least lift of the three

Low Wing
generates list as a median between high and mid
increased ground effect increases lift during takeoff
limited pilot downward visibility

Biplane Wing Configuration
Increased wing area generates more lift
increased wing area generates more drag

Canard Wings
provide forward center of gravity
improves pitch control
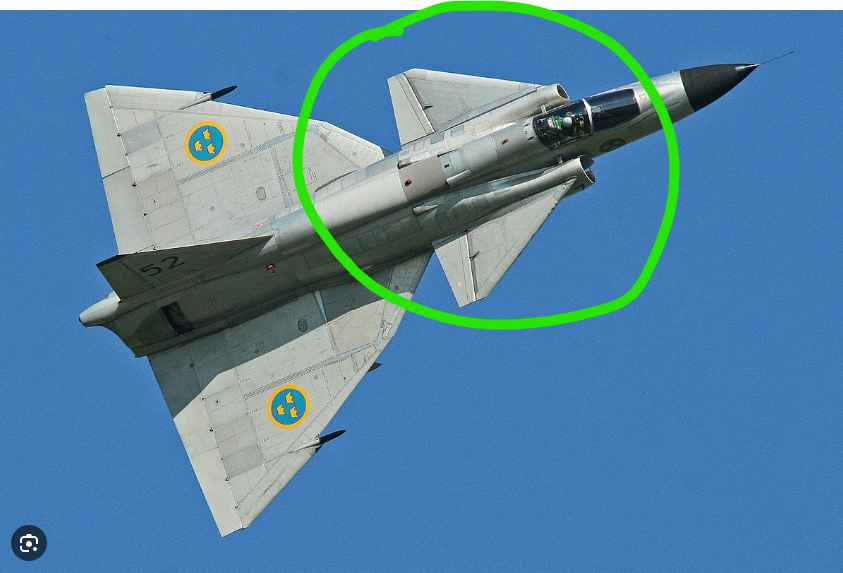

Twin vertical stabilizer
improves yaw control

Triple Verticle stabilizer
Three vertical stabilizers improve yaw control
Could be needed to compensate for the limitation of other features

V-tail
Early versions of the design made it difficult for a pilot to control yaw
Note the relative percentage of wing that is flap versus aileron.


Tractor Power Plant
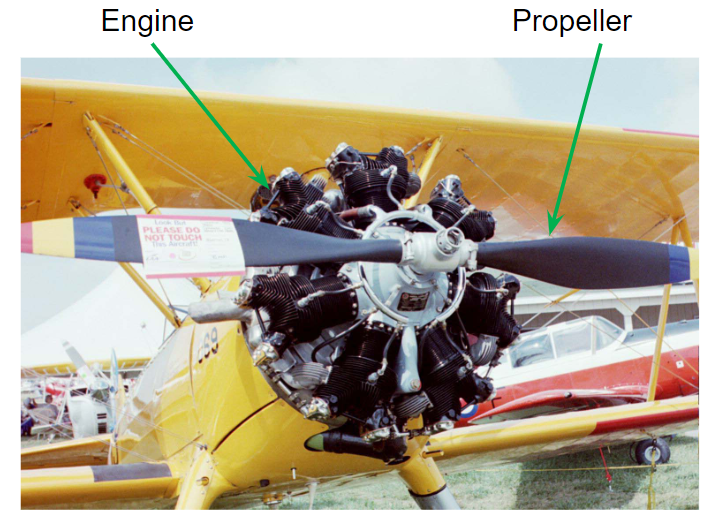

Pusher Power Plant
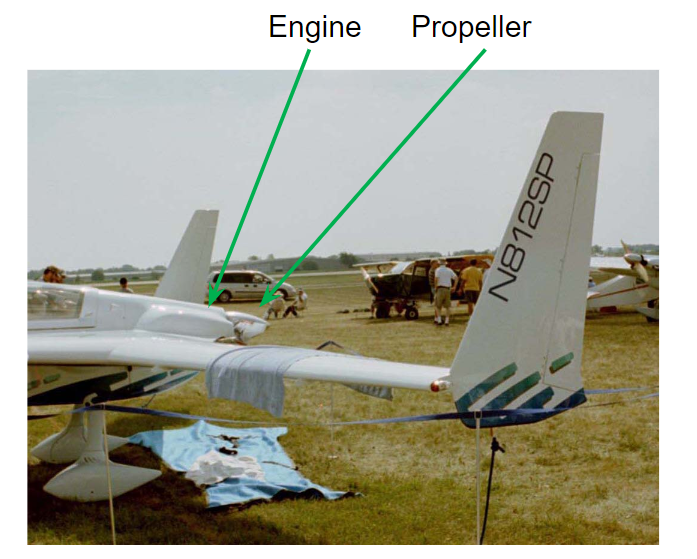

Varaible Direction Power Plant


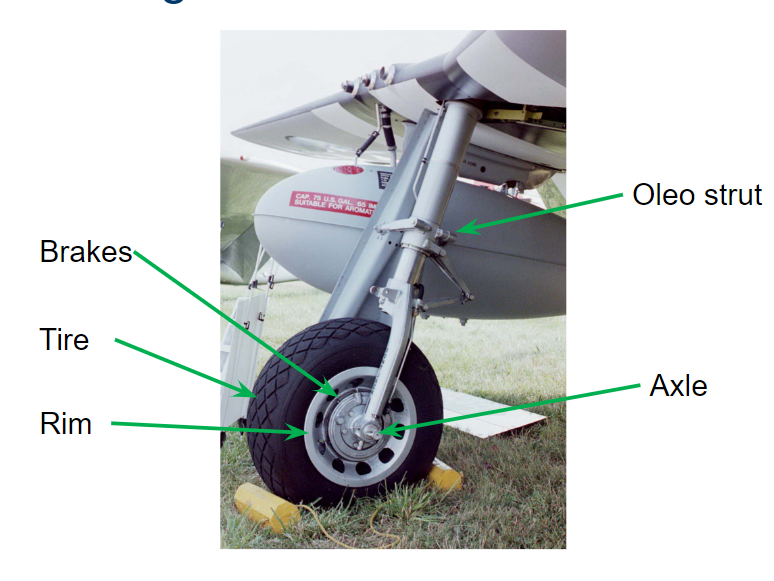
Oleo Strut


Floats
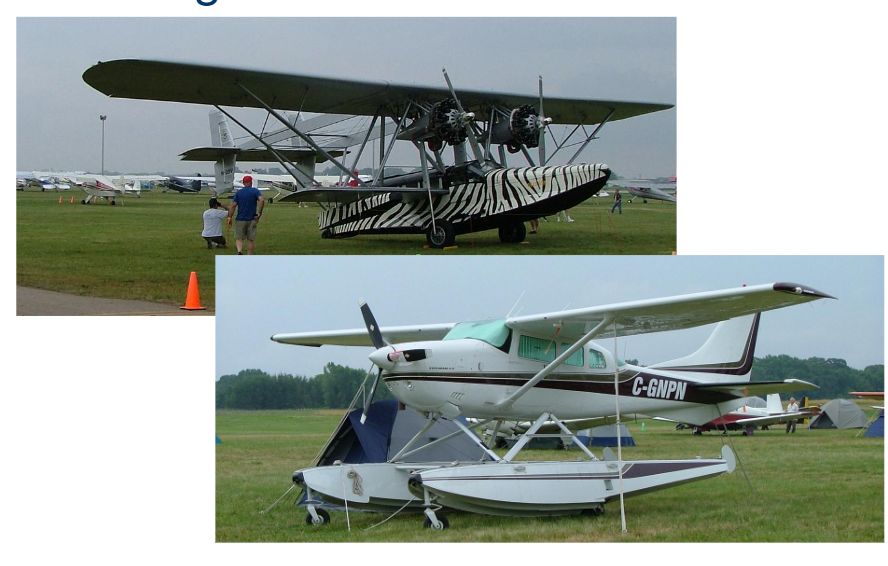


Tail dragger


Tricycle
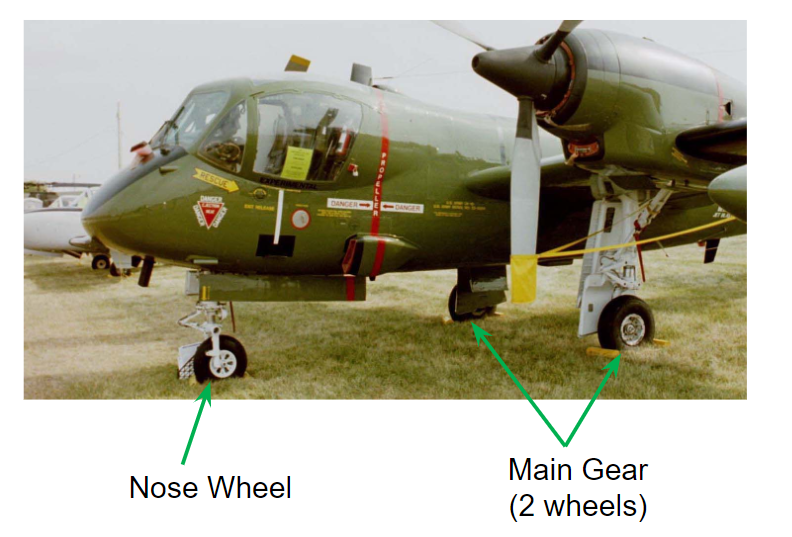

Rough field
Rough field landing gear has smaller wheels to allow large shock absorbers
Large shock absorbers
Absorb impact of a rough terrain
Propeller is above tall grass

Soft field
Soft field landing gear has large wheels to minimize sinking into terrain

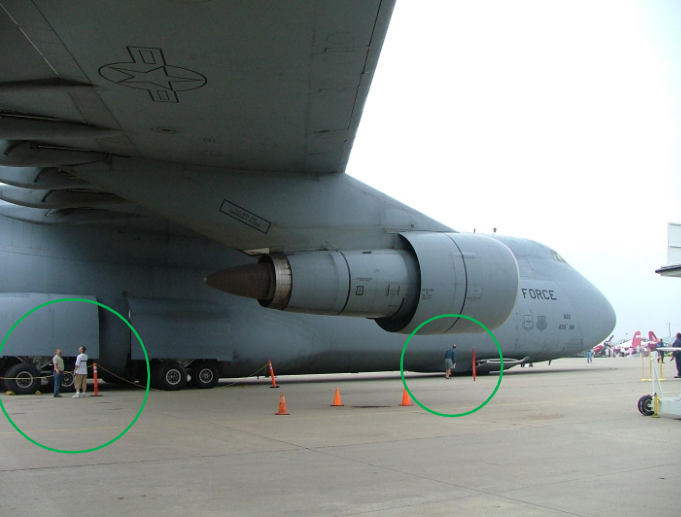
Fuselage size
Aircraft can be very large. The aircraft shown is a Lockheed C-5 Galaxy. The people shown in the image demonstrate the scale of the aircraft.

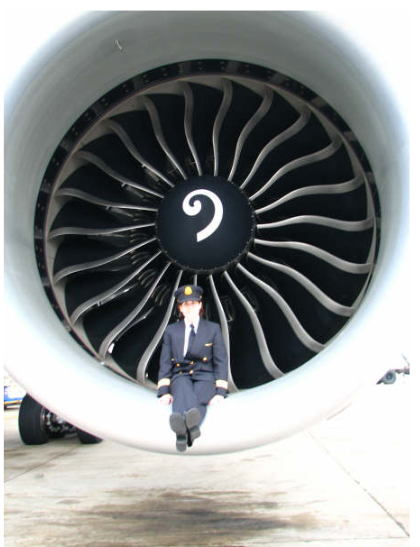
Engine Size
The Boeing 777 engine is so large that it dwarfs the pilot seated in the engine inlet.

Specialized Configuration
Aircraft may be designed or modified to perform specialty functions. This example is a Boeing 747 modified to transport a space shuttle. The image above is of the final flight of Space Shuttle Endeavour landing in Los Angeles in September, 2012.
