Clin 2 Rachels Part
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
what is early intervention
state based
rehab services for qualifying infants and toddlers
what age is early intervention for
less than 3 years old
focus of early intervention
helping children reach developmental milestones!
some common diagnoses are premature birth or medical conditions that will result in a developmental dealy
what is school based intervention
built into education system in individualised education plans
must be greater than 3 yo up to 21 yo
varied levels of supervision and equipment needs..
goal of school based intervention
helping children participate to the best of their abilities in the classroom and at school
common diagnoses: cerebral palsy, down syndrome, genetic conditions (these also apply to early intervention)
acute care
where is this and what populations
in the hospital
pediatric and adult
varied clinical presentation
- dif diagnoses and ages
- and varied abilities (dependent to independant)
many specialized units within this (neuro, trauma, ortho, cardiac, gen med)
acute care focuses on
functional mobility and planning for discharge from the hospital
what type of equipment is used here
- the same in SNF
variety!
wheelchairs
loftstrand and ax crutches
tilt table
cane
hoyer lift
can adults go to childrens hospitals?
yes
often ones that had a childhood disability that you want to keep seeing same physician
lot of super specific diagnosis..
Inpatient Rehabilitation
when do people go here
for intensive therapy following acute care stay
have to tolerate 3 hours of therapy a day
need to have comprehensive needs to qualify PT OT SLP
- neuro, ortho, trauma..
what variety do you see
adult and pediatric
independent to dependent
goal of inpatient rehab
maximizing independent and return to PLOF
skilled nursing facility
when do patients go here
after acute care stay
- and when not able to tolerate the 3hrs of IPR
comprehensive needs
variety of assistance here again
what do patients need to qualify SNF
3 night stay in the hospital
focus of SNF
maximizing independent and return to PLOF
- same as IPR
- acute care is more functional, planning for discharge
- LTC preventing more impairments, educating
- outpatient dif
long term care
who is this for
individuals who may never return home
- so assist level very high
goal of LTC
prevent secondary impairments and education for families
- pediatric and adult here
outpatient who is this for
individual in community
pediatric and adult
low assist levels typically
equipment is WC, lofstrand and ax crutches, canes
focus of outpatient
optimize functional mobility and independence
which patient care setting do you not see pediatrics?
skilled nursing facility
T/F all patient care setting you will see a range independent to dependent patients
false!
LTC
- typically only higher assist levels (mod to max)
simple outpatient
- typically lower end of assist (ind to mod)
FIM = functional independence measure
how many levels
and what are they
FIM 1 = total assistance
FIM 2 = maximal assistance
FIM 3 = moderate assistance
FIM 4 = minimal (contact) assistance
- CGA variation..
FIM 5 = standby assist
FIM 6 = modified indepedence
FIM 7 = complete independence
FIM 1, 2, 3
FIM 1 total = less than 25% effort
FIM 2 max = less than 50%, at least 25%
FIM 3 mod = less than 75%, at least 50%
FIM 4,5
FIM 4 = min = at least 75% effort
- can assume all body weight, needs guidance
FIM5 SBA = needs cueing or coaxing
CGA = variation - pt needs occasional contact for balance/ dynamic stablity
FIM 6, 7
FIM 6 mod ind = uses AD but ind w that
FIM 7 complete ind = all tasks without modification
what AD is the best for safety?
front wheeled walker
which crutches are better for long term use?
loftstrand
- little to no risk of impingement
- esp w ataxia or neuro condition
what can be used to transfer max assist pts
hoyer lift

what is a tilt table used for
circulation, cognition, muscle activation, proprioception
- typically for patients w severe injuries
esp used if pt laying down for a long time
weight bearing good for bone health
when choosing the right AD
consider (3)
amount of support needed
motor and cognitive function of pt
WB status of patient
what kinda pts are canes good for
minimal balance or stability impairments
- cannot be used to reduce weight bearing through a LE
what is a rollator good for
patients with endurance impairments
community ambulators
- not good for WB restrictions or balance issues
ex: COPD
front wheeled walker can reduce/eliminate WB through a LE?
yes
- this is best for patients w balance, strength, and mobility impairments
when to use a junior/ped walker
ped patients
pts under 5'2"
when to use a bariatric walker
wider pts
>350 lbs
non-bariatric but extra wide walkers
pts who need a wider device but less than 350 lbs
hemiwalker is best for
hemiplegic pts after a stroke
picture about picking walker/cane
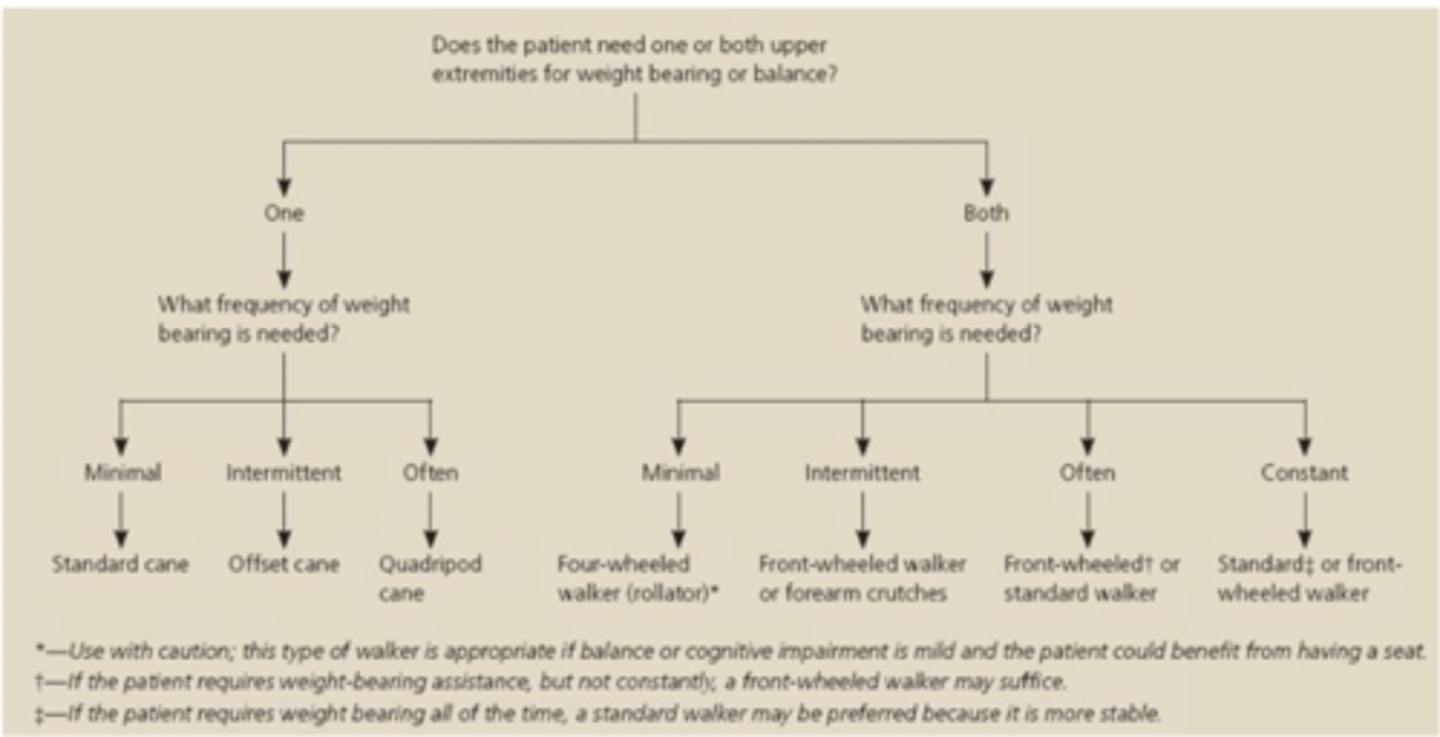
keys to good body mechanics (2)
neutral spine
keep pt within your COM
- again always using counterweight, not lifting
T/F if possible, you should assist pt on affected side
yes
- cane should be on unaffected side
when possible, have pt tranfer to their BLANK side
strong
where to be for stairs
behind going up
in front going down
- going down can depend if major height difference
posterior approach hip precautions post THR
no hip flexion past 90
no adduction past neutral
no IR
so watch sitting, dont cross legs, dont point toe in.
anterior approach hip precautions post THR
no extreme extension
w ER
lateral approach hip precautions post THR
no hip flexion past 90
no adduction past neutral
no IR
+ no active hip abudction
ALWAYS VERIFY W SURGEON ORDERS
sternal precautions
No pushing, pulling, lifting more than 5-10
dont reach behind your body or above your head w both arms
- use a pillow to brace incision site
back precautions
BLT
No Bending, Lifting, Twisting
WBS
name em
non weight bearing
toe touch WB
partial WB
WB as tolerated
full WB
non wieght bearing
no weight onto limb
toe touch WB
toes can rest on the ground for balance, but not for weight bearing
partial weight bearing
percentage needs to be defined by surgeon
WBAT
pain/comfort guide WB
- THR, TKR
difference of hemiplegia and hemiparesis
hemiplegia is complete or severe loss of motor function
hemiparesis is milder/partial
plegia = paralysis
be sensitive in communication - people are going through moments of trauma
(especially acute care and subacute...)
how would you handle a bariatric walker
or gait belt
im going to get equipment that will be a better fit for you
gait belt: going to put this on you for your safety
patient centered care
patients and families are BLANK with the provider and the care team
partners
- we are experts of movement, not someone elses life
4 core concepts of patient centered care
respect and dignity
- pts should have autonomy
information sharing
- ensure pts informed of their medical info
participation
- they should participate in process
collaboration
- communicate!
participation
should patients participate in decision making process and treatment?
shift from what model?
yes they should!
we are shifting from paternalist model
what is key for patient centered care and shared decision making
communication!
studies show pts want to be listened do, want the truth, risks, options, want choices
ICF was created when and by who
2001
by WHO - world health organization
this is the framework for describing and organizing information on function and disability
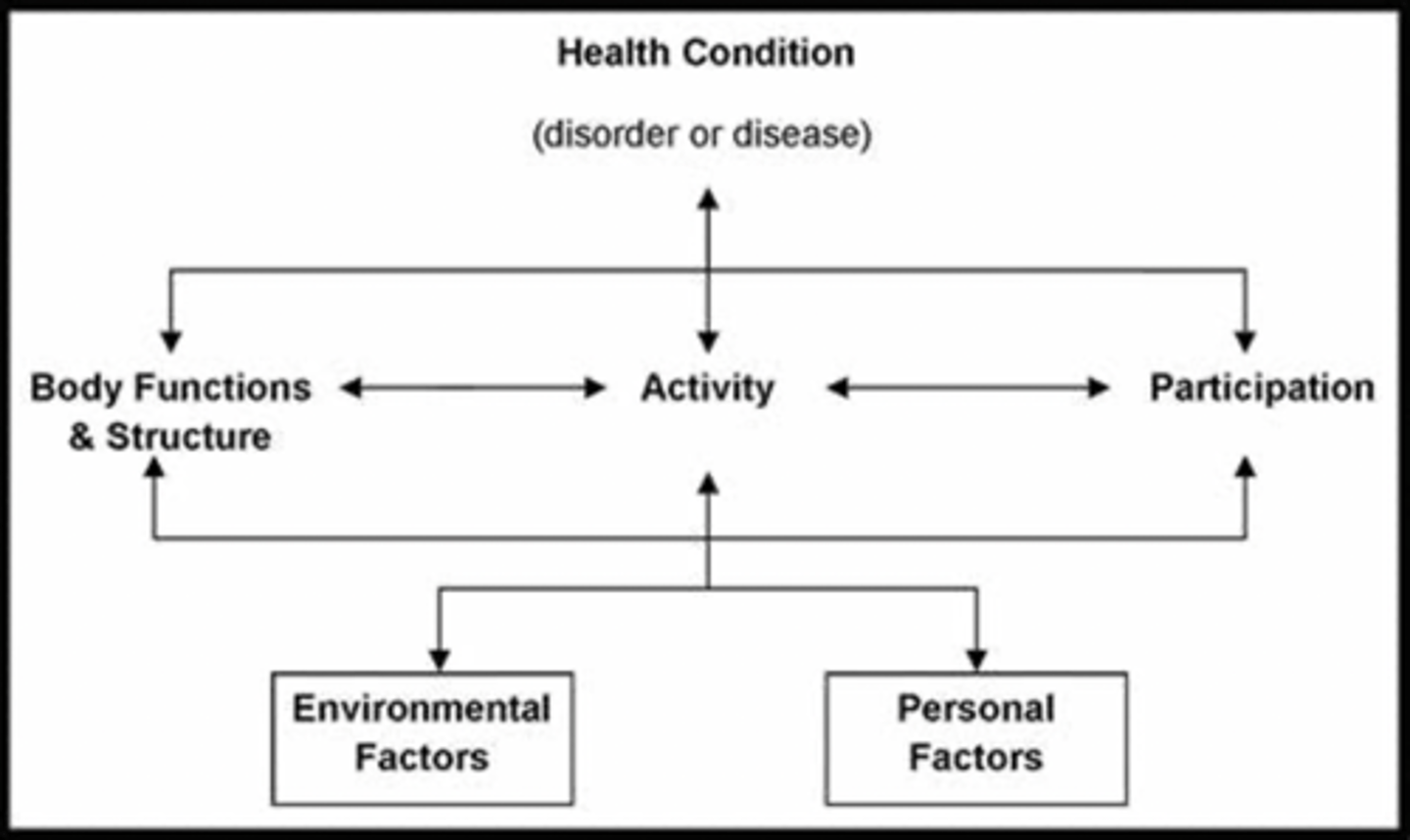
adaption of the ICF for peds is
F words
Function
Family
Fitness
Fun
Friends
Future

health condition/medical diagnosis
specific!
- neuro related diagnoses
- orthopredic related diagnosis
example: stroke, broken bone, deconditioning
which ICF is how disability is experienced by the individual?
- demographic information
personal factors
like age, gender, motivation
which ICF is the environment in which the person is carrying out ADLs
environmental factors
here we consider stairs, accessibility..
which ICF is body level
example: strength, balance, endurance..
body functions and structure
which ICF is individual level
the "ings" of life
activites
- sitting, standing, walking, running, talking, writing
if pt is in the ICU for a while, sitting up for how long can be pretty difficult
15 minutes
- be mindful of this with cardiac chairs
from acute care therapists often recommend a freq of PT after discharge which helps determine what type of PT facility
what are these
2-3 d/wk = HH outpatient
5-7 d/wk = SNF/IPR
- we don't recommend destinations bc insurance..
what is the AM-PAC
Activity Measure for Post Acute Care
helpds determine whether is is safe to return home
cutoff of 18 for discharge locations (6 is total dependence)
how to use WB status to determine AD
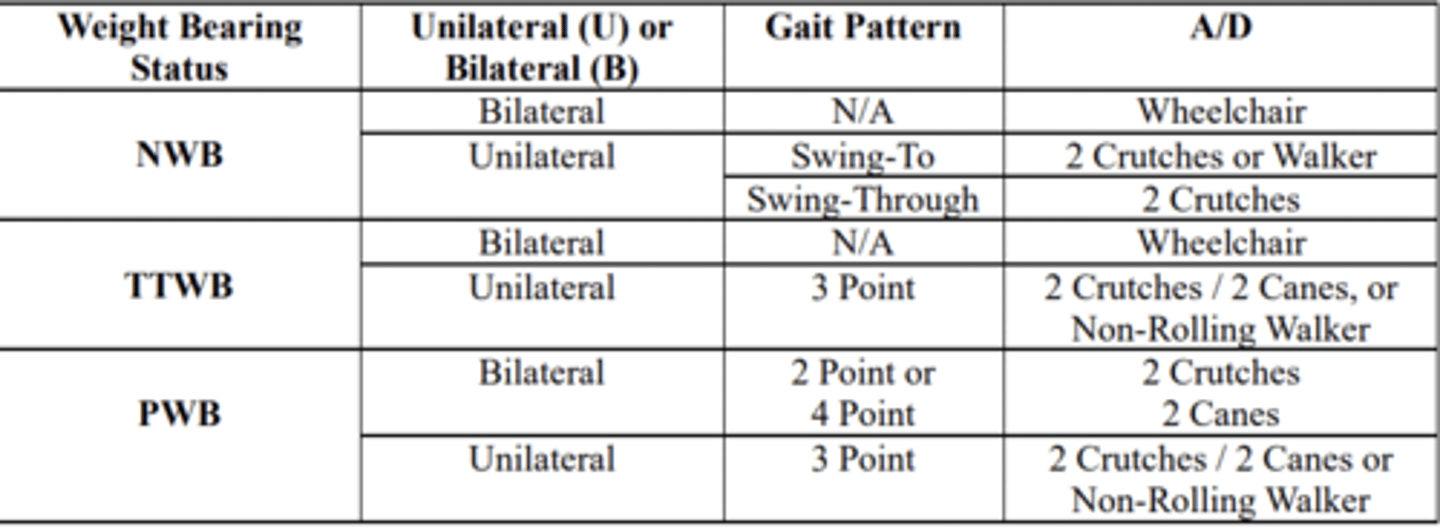
bilateral NWB
gait pattern?
AD?
N/A - no gait pattern.. not walking
AD: wheelchair
unilateral NWB
gait pattern
AD
gait pattern: swing to or swing through
AD: 2 crutches or walker for swing to
2 crutches for swing through
TTWB bilateral
gait pattern
AD
gait pattern: N/A.. not walking
AD: wheelchair
unilateral TTWB
gait pattern
AD
gait pattern: 3 point
AD: 2 crutches, walker
bilateral PWB
gait pattern
AD
gait pattern: 2 point or 4 point
AD: 2 crutches
unilateral PWB
gait pattern
AD
gait pattern: 3 point
AD: 2 crutches or walker