AP Art History Works - unfinished
1/249
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Medium, vocab & style, content, date, location/artist, context/function
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
250 Terms
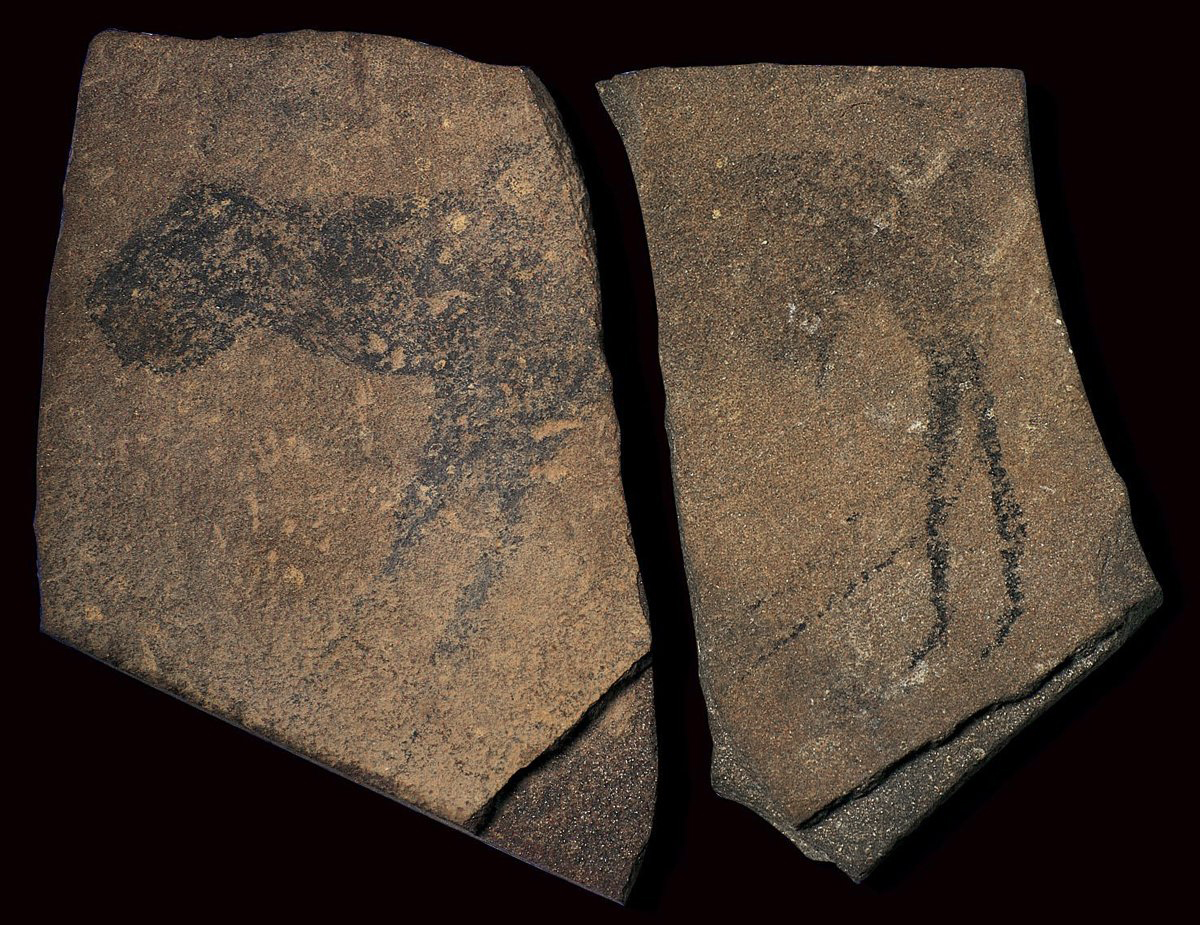

Apollo 11 Stones
Made of charcoal, ochre, and white
Depicts a half-antelope half-human
Cracked in two
Found in Western Africa in 1969-1972
From 25,500-25,300 BCE
Small and portable, likely spiritual
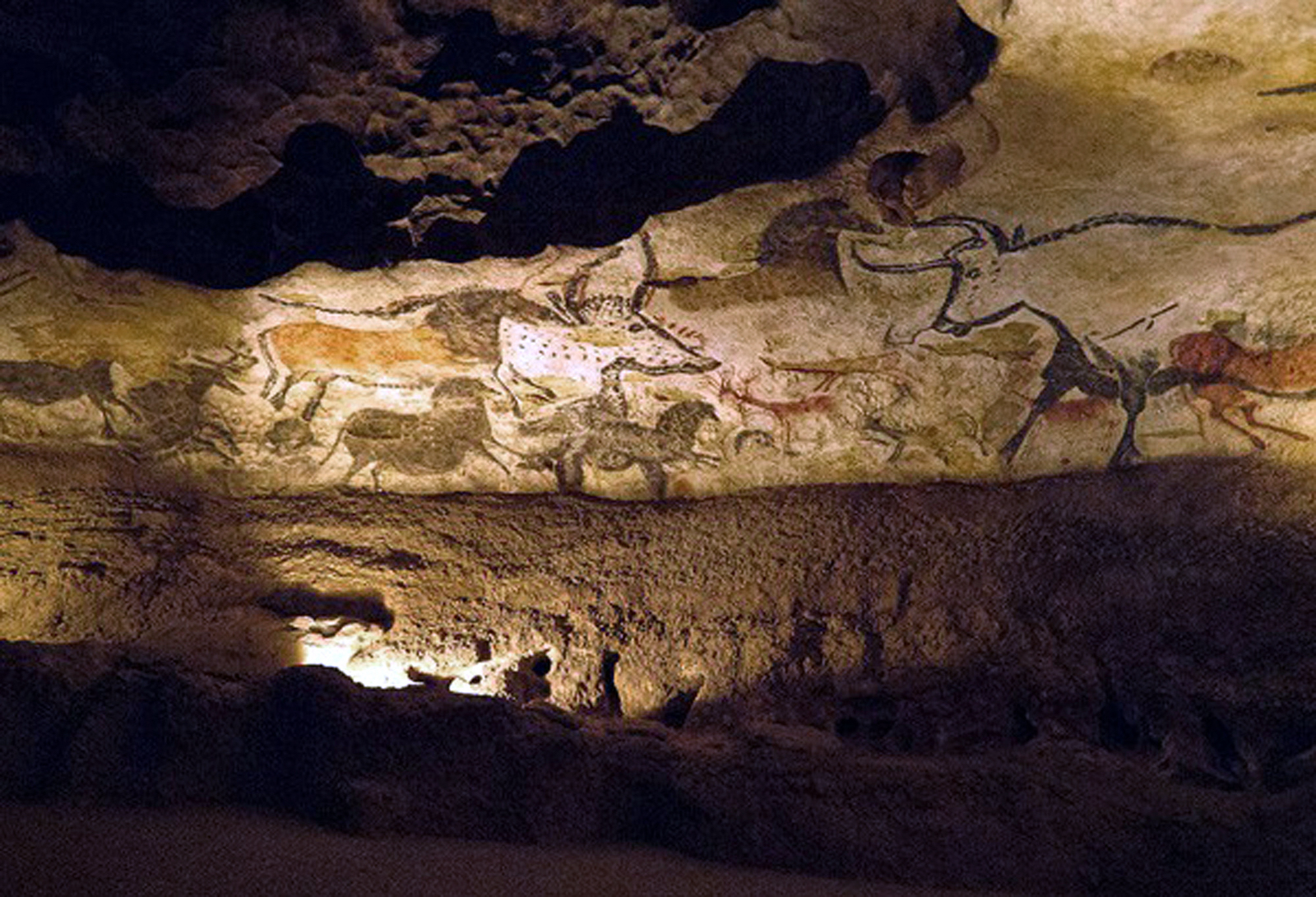

Great Hall of the Bulls - Lascaux Cave
Made of ochre and many pigments
Depicts bulls, horses, bears, and other large animals
Overlapping pictures, hierarchy of scale, twisted perspective
Found in Lascaux Cave, France, a site with around 6,000 other animals depicted on cave ceilings and walls
From around 15,000 BCE
Likely spiritual connections and for artistic purposes

Camelid Sacrum in the Shape of a Canine
Made of sacrum bone from a camelid animal, carved by tools and human hand, finished with polish
Depicts a canine mammal’s skull
Symmetrical, round carvings
Found in Tequixquiac, Mexico, 40 feet under ground
From around 14,000 BCE
Small, likely sacred fertility item, possibl
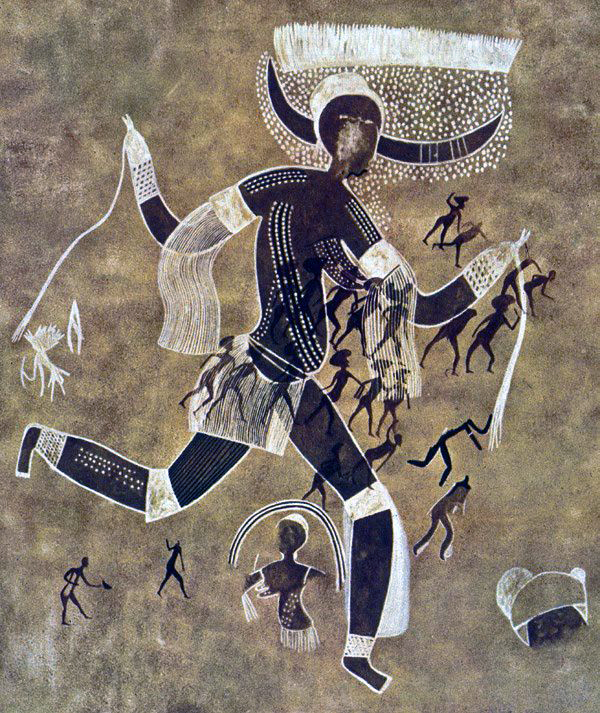

Running Horned Woman
Made of charcoals, ochre, and red pigments, wet sponges used to enhance pigments
Depicts a therianthrope woman running, dressed in fancy clothing, shows people going about daily lives
Twisted perspective, hierarchy of scale, scarification on her body, no face
Found in Tecili Niger, Algeria, in a cave
6,000-4,000 BCE
Likely depicting a Goddess, possibly a fertility celebration
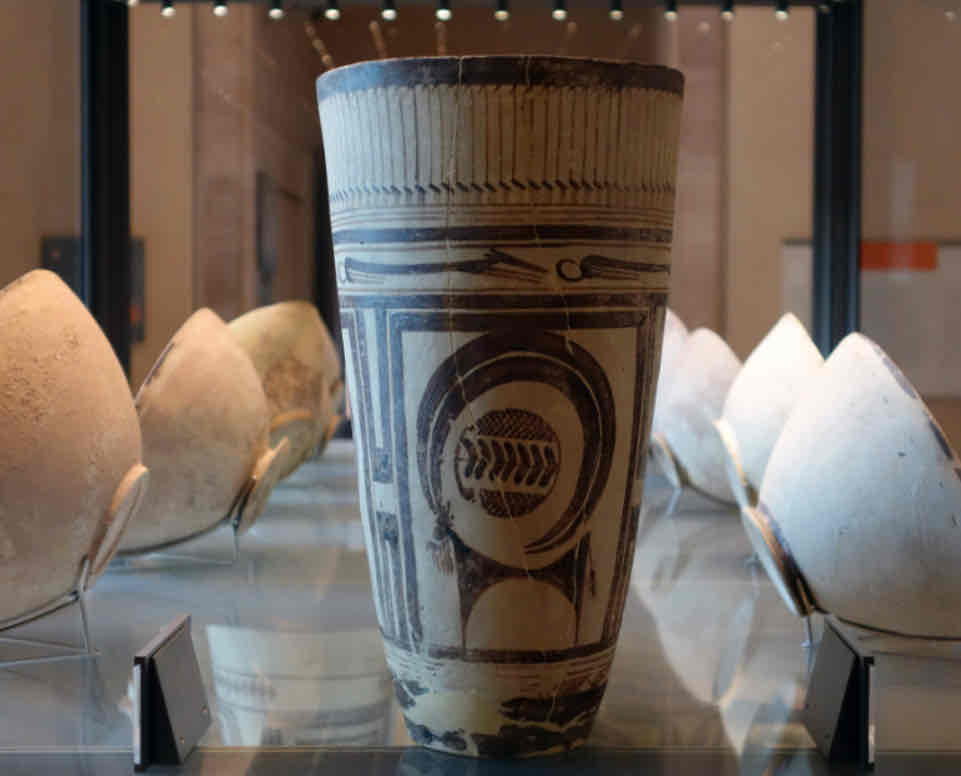

Bushel with Ibex Motifs
Made of clay and paint (slow wheel? hand-painted)
Depicts a Mountain Goat (Ibex), dogs, and birds, framed with decorations, grains shown in the middle
Bodies of animals are distorted, hierarchy of scale, register: broken composition
Found in Susu Iran, area had been occupied for 5,000 years, found in a burial site underneath a temple
4,200 BCE
Used for burial ceremonies, could also symbolize new life, pottery shows the civilization was settled and had free-time
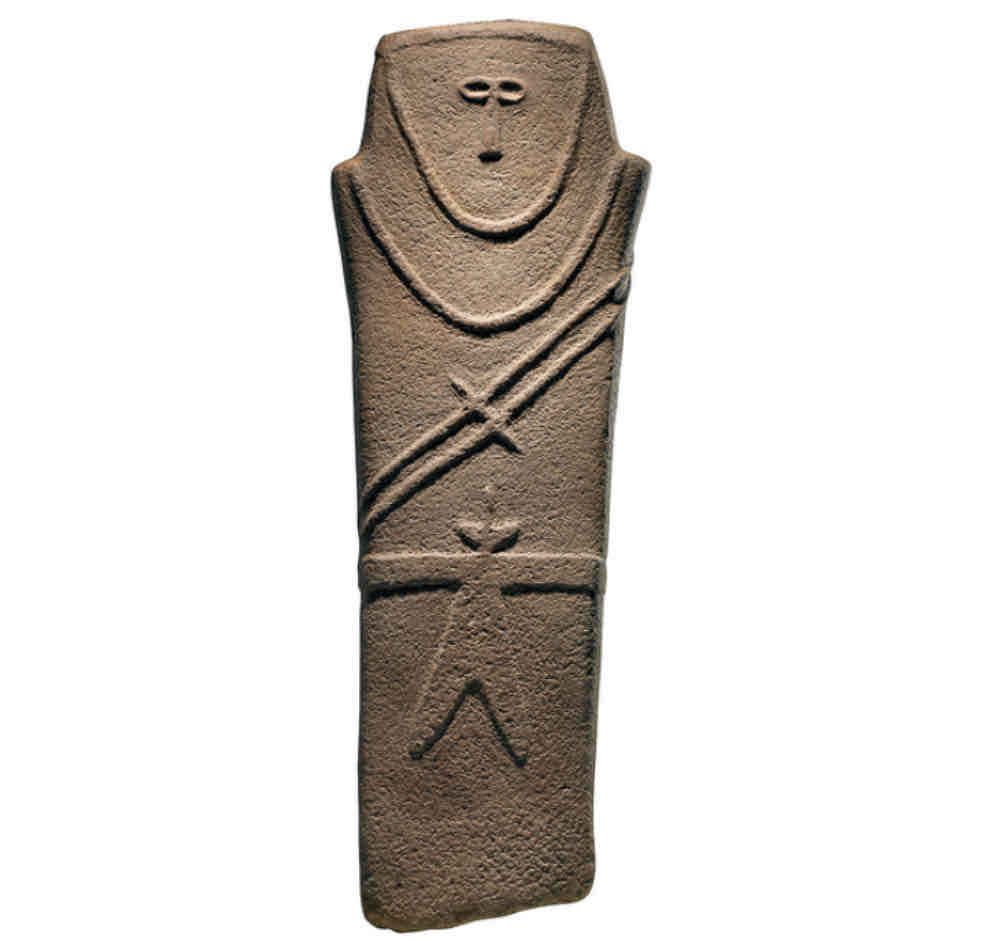

Anthropomorphic Stele
Carved into a flat, vertical stone, 3D, both sides are carved, 3’
Depicts a male figure with warrior-like accessories
Human characteristics are vague, geometrically stylized
Found in Ha’il, Saudi Arabia in a burial site, pre-Islam Arabia
6000-4000 BCE
Used as a grave marker, shows developed tool usage
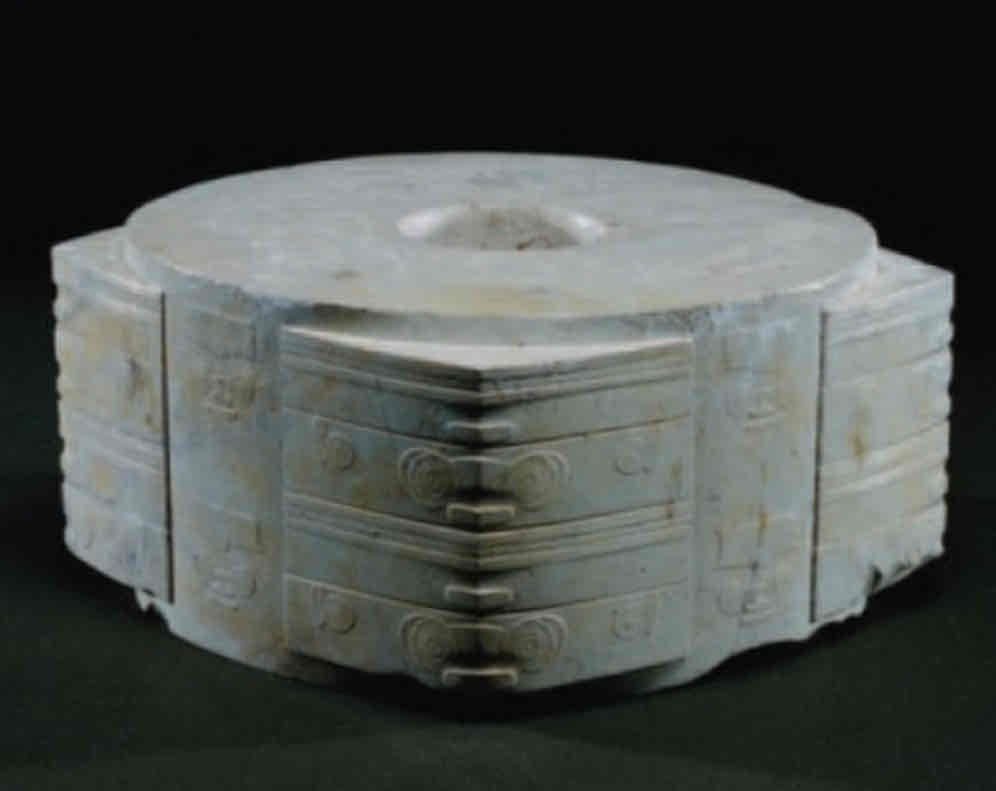

Jade Cong
Carved Cong into a piece of jade jadeite, hollow center
Depicts Taotie, mythical Chinese creature, geometric patterns
Taoties had big eyes and no jaw, vaguely represented
Found in Liangzhu, China, in burials and grave sites
2500 BCE
Used as a symbol of wealth, represented death, shows skill of carving and using jade
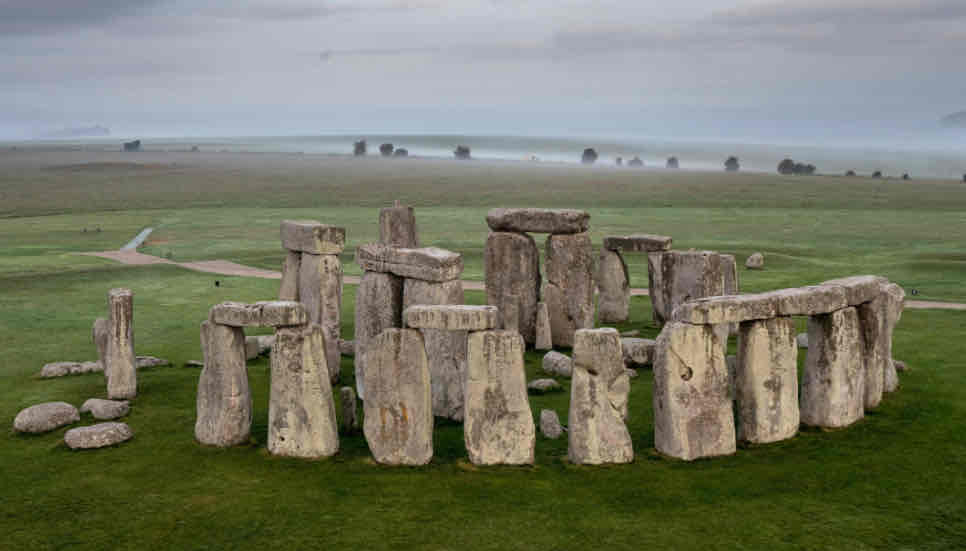

Stonehenge
Arranged stones in a henge formation, large Sarsen stones, smaller bluestones
Megalith
Posts and lintels, triliths, all in a circular formation
Found in Salisbury Plain, England
3000-1500 BCE
Used as a solar calendar, trilithon horseshoe frames the Sun on the Summer Solstice, could be used in rituals to worship the Sun
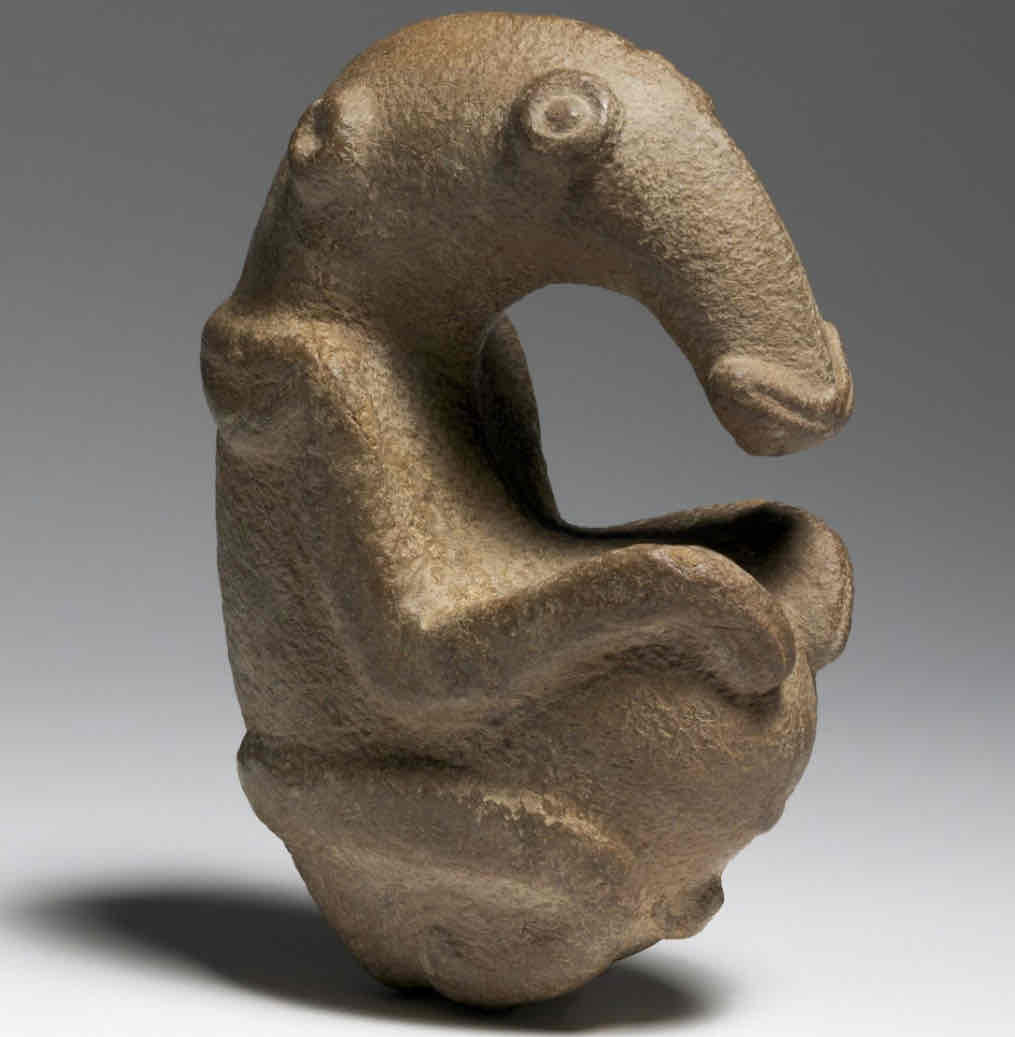

Ambum Stone
Carved Graywacke stone, smooth surface, 8”, shiny patina finish
In the shape of an unknown creature, anteater or echidna?
Detailed, proves talent with stone tools, strong material
Found in Enga, Western Himalayas
1500 BCE
Could be spiritual, means of protection, or promotion of fertility, used to grind herbs in a mortar and pestle
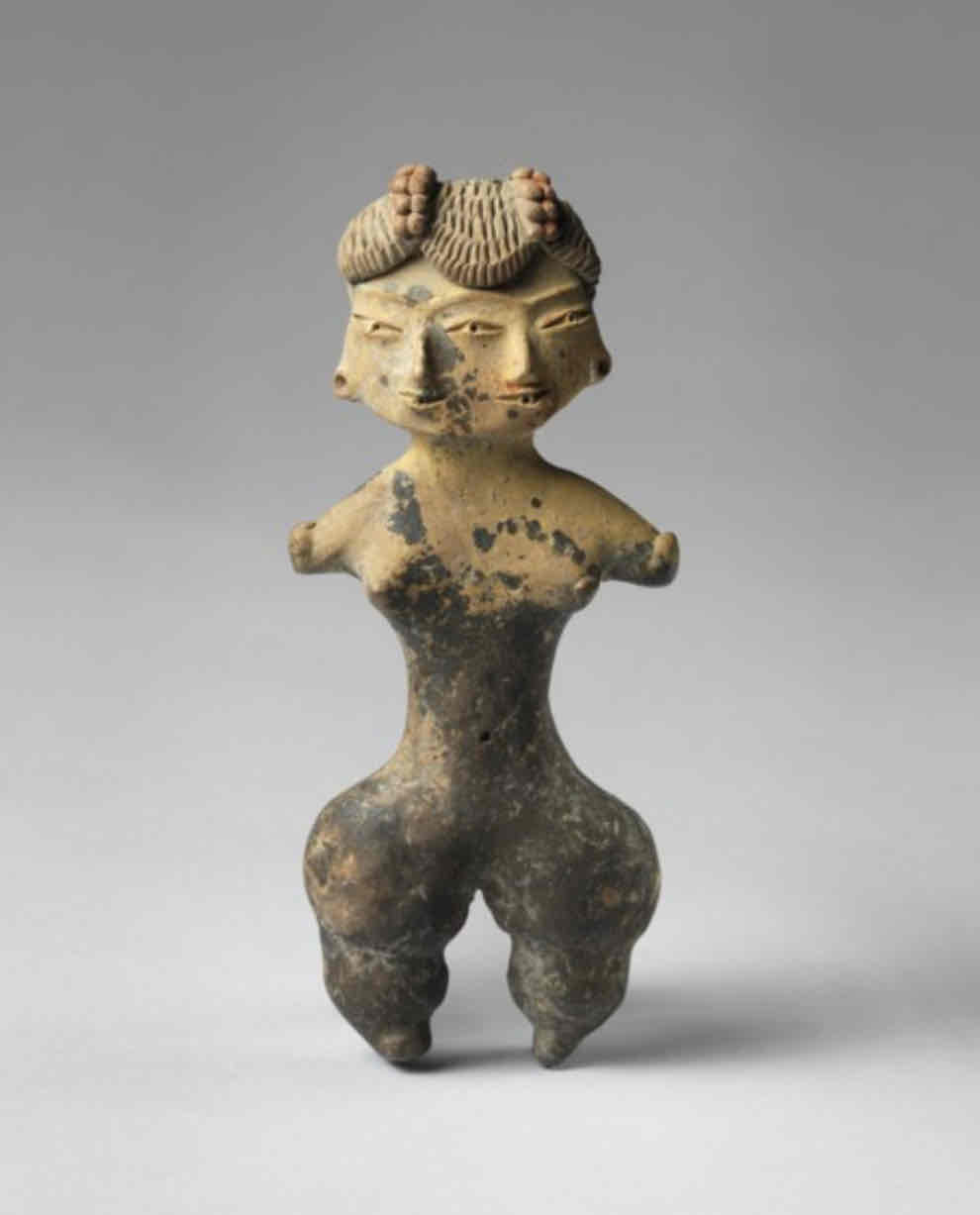

Tlatilco Figure
Made of ceramics, 4” tall, reds, yellows, and blacks, rolled stamped designs, incisions
In the shape of a woman, hips are emphasized, sharp eyes and a slight smile, two faces and one body
Shows the duality motif, detailed hair, obvious female shape
Found in the Valley of Mexico, Tlatilco
1200-900 BCE
Two faces could represent life and death, birth defects, twins, found in burial sites under present-day Mexico City
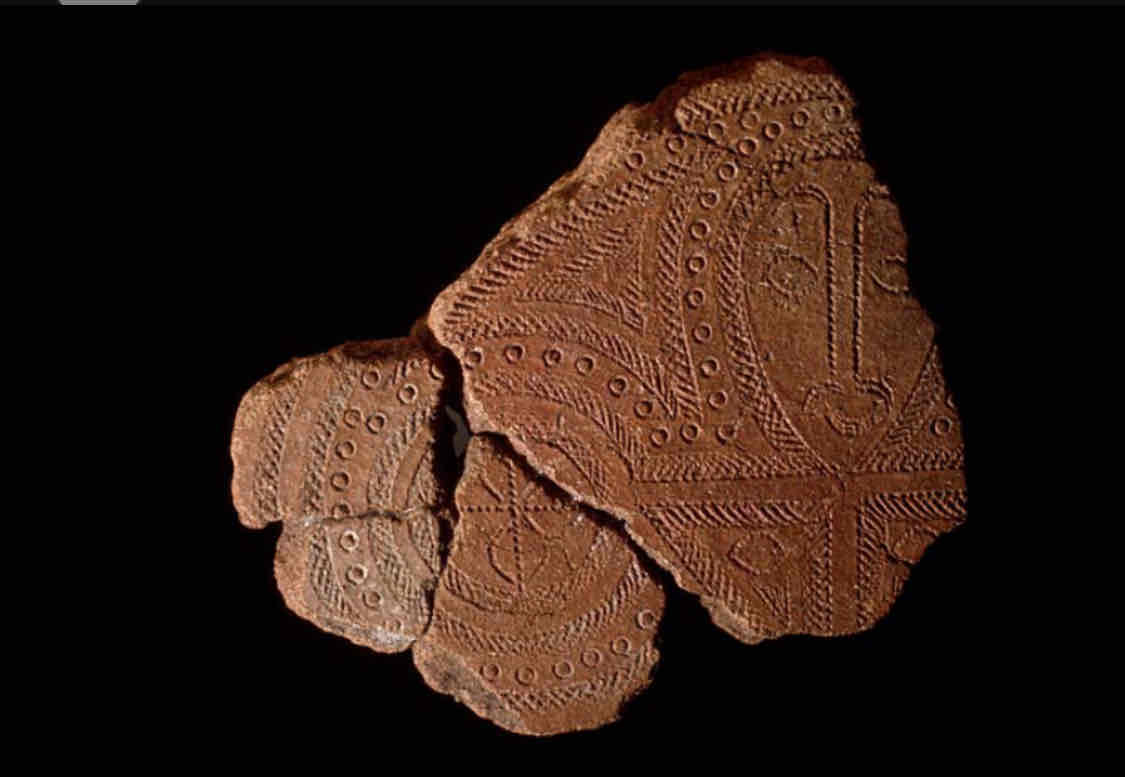

Lapita Terracota Fragments
Made of clay and sand, cracked, stamped and incised designs, hand shaped
Vaguely shows a human face, geometric intricate patterns
Intricate patterns that were important to Lapita culture, could be depicting sea and trade routs
Found across Polynesian, Micronesian, and Melanesian islands, but are from the Lapita people from the Santa Cruz islands
1000 BCE
Could be used to serve food, used in trade or travel, shows what tools were used, represents the seafaring nature of the Lapita people
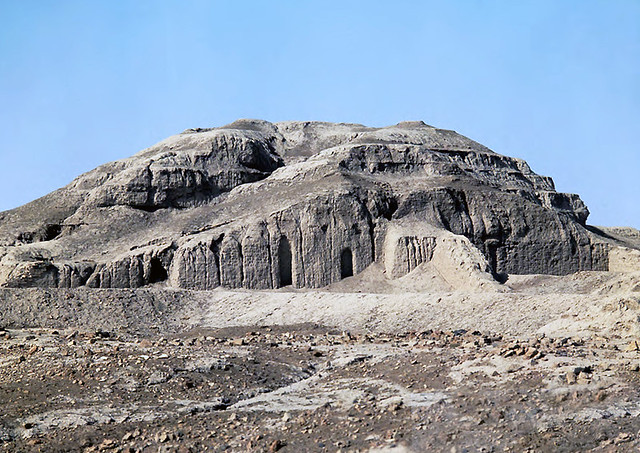

White Temple and its Ziggurat
Made of mud brick and Bitumen for waterproofing and white cedar
Elevated two stories on top of a ziggurat
The temple was made for the sky god, Anu
Found in the city of Uruk in Sumer, modern day Iraq, lion and leopard bones found beneath the temple buried
3500-3000 BCE
The Sumerian king went here to speak to Anu, shows the theocratic government of the time

Statues of Votive Figures
Carved into gypsum or limestone
1’-2’ tall, figure in the round, ringed beard, hierarchies of scale, negative space between legs and arms
All were positioned to be praying, wide eyes to represent constant wakefulness for the gods, clothed, inscriptions of the person’s name who is represented
Found in the square temple at Eshnunna in Sumer
2700 BCE
Created by artisans payed by people who wanted a place to pray in the temple, since average citizens weren’t allowed in
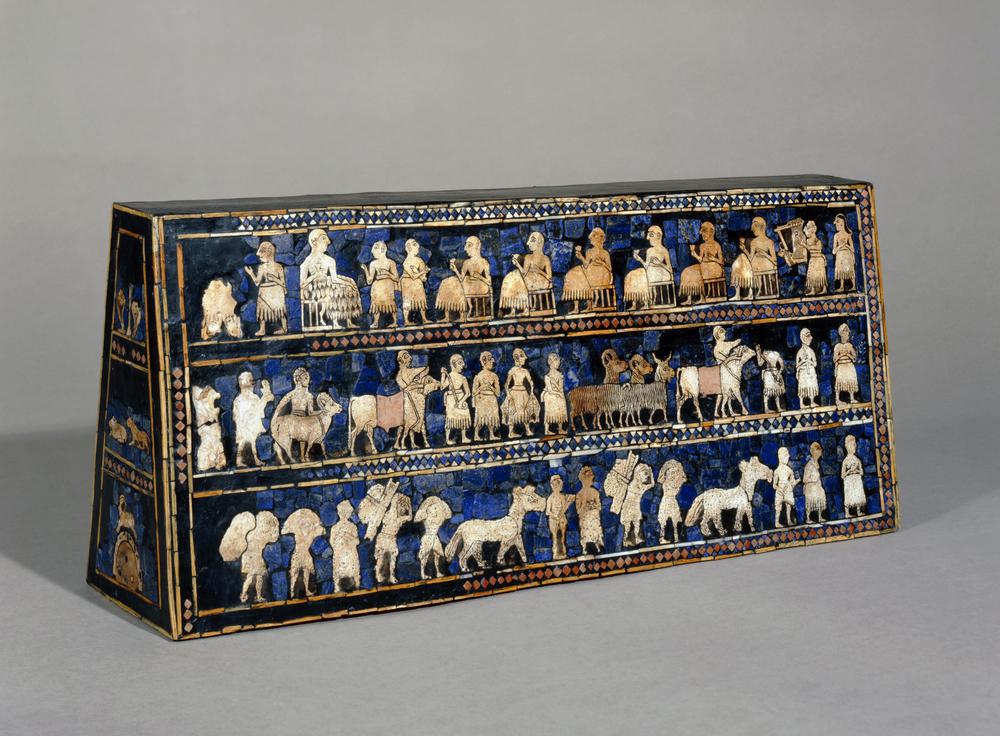

Standard of Ur
Made of expensive imported materials, lapis lazuli for the blue mosaic laid into a carved wooden base
3 registers, two sides, hierarchy of scale, twisted perspective, 20” long
One side was a part scene, the other side depicts war, new inventions like the wheel are shown, shows settled and organized societies, wealthy people in the top register, poor people in the bottom
Found in the royal tombs of Ur in Mesopotamia, modern day Iraq
2600-2400 BCE
Purpose is unknown, found buried with other lavish items, could have been used to carry items, could be a war celebration
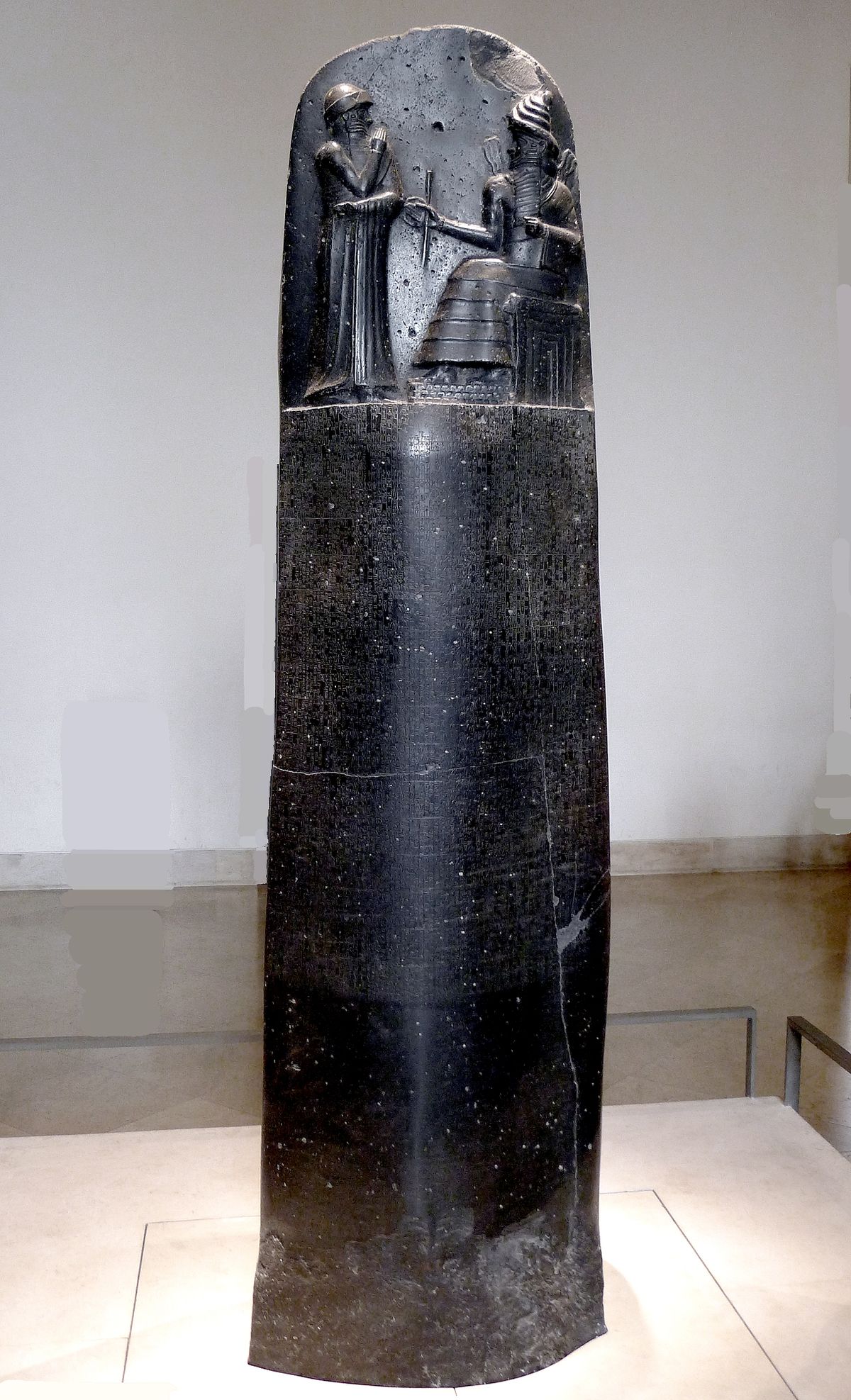

Code of Hammurabi
Carved into basalt steel, stele
Foreshortening to create depth, low-relief, hierarchy of scale, stylized people, composite view with body facing front, face to the side
Depicts the god of justice, Shamash, talking to the Babylonian King, Hammurabi, handing over keys to lead, Shamash has lightning bolts, a measuring rod, coiled rope, and full beard
Found in the city of Susa, Iran, but is originally from Babylonia
1792-1750 BCE
300 lines of cuneiform text in Akkadian laid out rules for governing Babylonia, and is an early example of justice and legality

Lamassu
Carved from stone
Therian, human face, body of a bull, eagle wings, mythological lamassu motif, 14’ tall, symmetry
Depicts the Lamassu creature, from the front they are stationary and two feet are visible, from the side they are walking and four feet are visible, inscription between the legs warns of damnation to anyone who harms the Assyrian king'
Found in the Citadel of Sargon II, Iraq
720-705 BCE
Supported the citadel gates (7 gates total), made to guard and warn those who came near, Assyrians were very paranoid

Apadana (Audience Hall) Darius & Xerxes
Made with clay bricks and carved stone pillars
Elaborate building complex, hypostyle with 72 columns, 65’ tall, cosmopolitan and organized
Building complex on the top of a plateau, relief sculptures depicting Persian processions delivering gifts to a king, columns decorated with animals and symbols
Persepolis, Persia, modern day Iran
520-465 BCE
Served as a gathering hall for Persepolis, could fit 10,000 people, used for receptions and festivals, built so it could overlook the area and be marveled at, shows the power of the empire and the people’s loyalty to the king
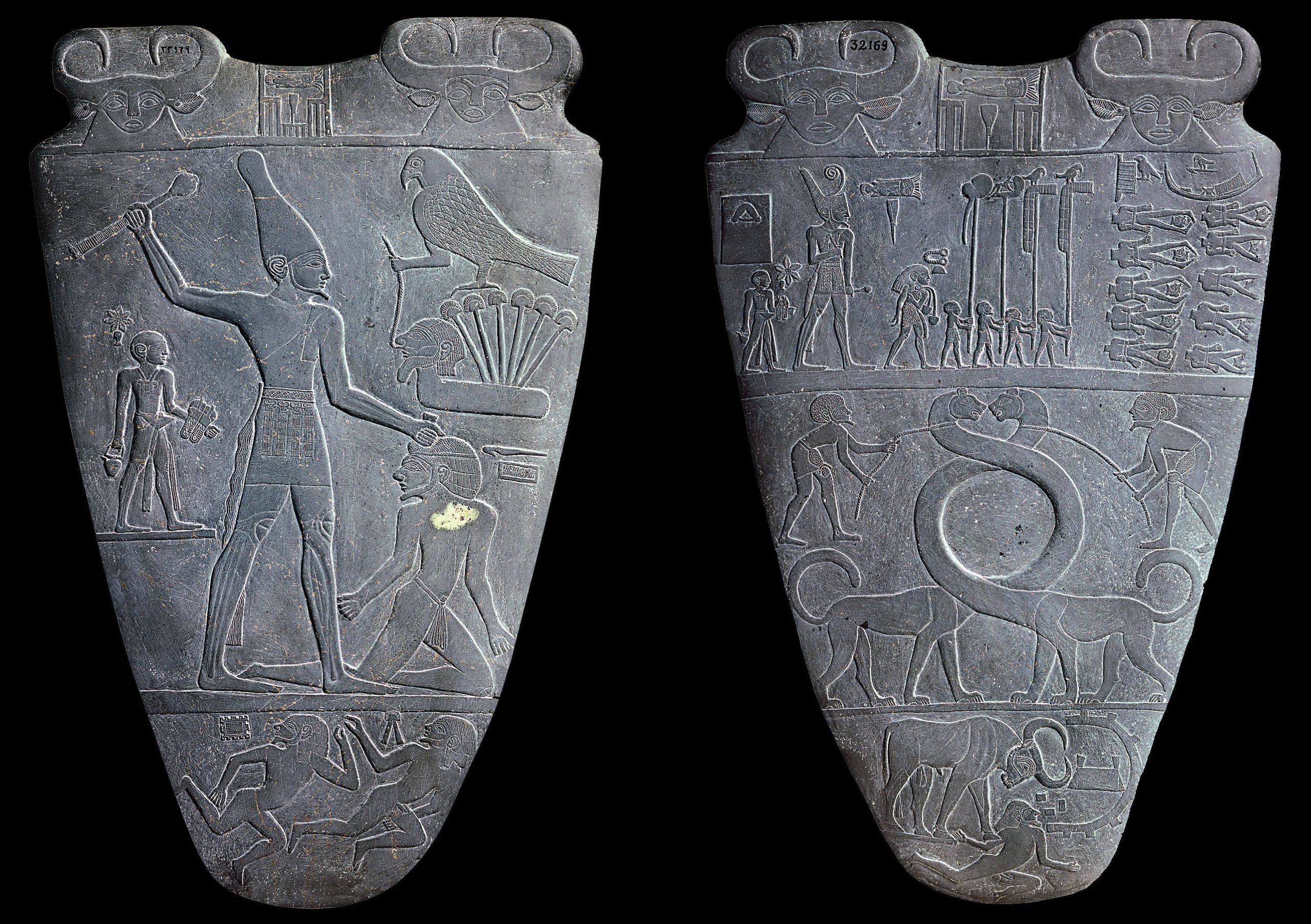

Palette of King Narmer
Carved into Greywacke stone
Continuous narrative, twisted perspective, hierarchy of scale, 2’ tall, 2 sided, separated with register lines,
Depicts events in the reign of King Narmer, shows upper and lower Egypt, shows dead bodies, foes, serpapod myth, Falcon God Horus, sandal barers
Predynastic Egypt, temple of Hierakonpolis
3,000-2,920 BCE
Items in this shape were used as makeup palettes, typically just for black eye makeup, this palette was simply comemmorative for King Narmer
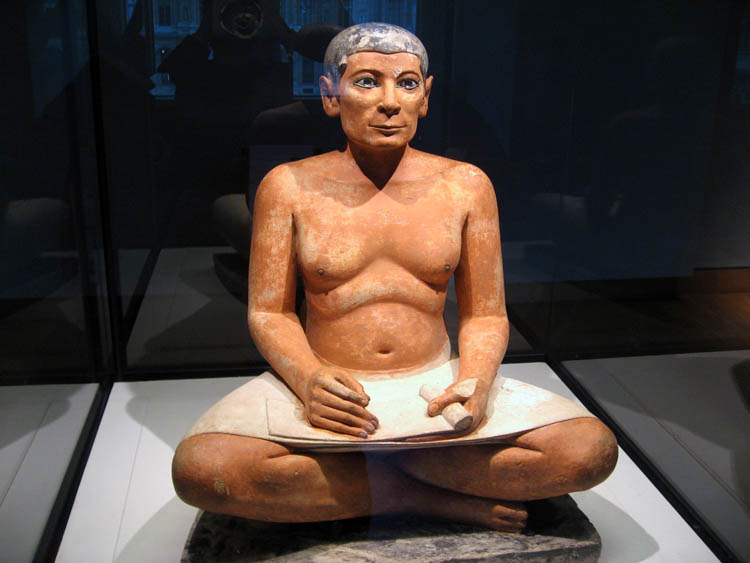

Seated Scribe
Carved and painted limestone, glass eyes, wooden nipples
1.5’ tall, realistic, idealized
Depicts an ideal scribe and a realistic person of the time
Saqqara, Egypt
2620-2500 BCE
Accompanied a burial, found in a tomb to accompany someone of high-ranking status, giving them a scribe to follow them into the afterlife

Great Pyramids and Sphinx
Carved into white limestone, pyramids are topped with gold, sphinx was painted red
Khufu is 480’ and has two chambers and several boat pits, Menkaure is 213’ with a complex interior with decorations, Khafre is 448’ on a 33’ plateau, lines up with stars and directions, sphinx is 66’, therian - pharaoh head on lion body
The pyramids are white and topped with gold to represent the soul going up, the sphinx is bright red to stand out in the dessert and honor cats, sphinx has purposeful pieces taken out of its face
Giza, Egypt
2550-2490 BCE
Modeled after ben-ben, symbol of the cult of Ra (sun), likely built to honor pharaohs and display their greatness
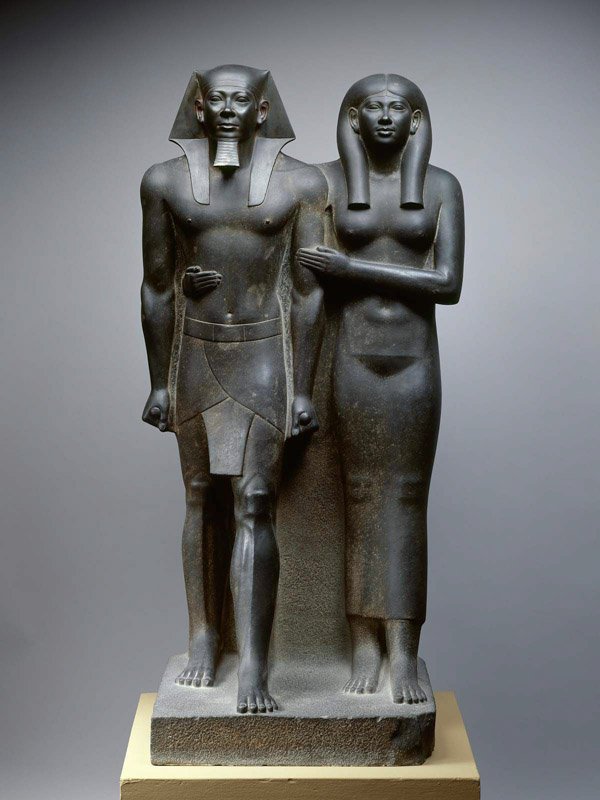

King Menkaure and Queen
Carved into Greywacke
Male and female figures, idealized, standing in pharaoh pose, originally painted
The figures show a man and a woman being gentle and affectionate, dressed in high class clothing and stylized hair, calm and happy expression
Giza, Egypt
2490-2472 BCE
No significant hierarchy of scale shows them being depicted as equal, likely created to show the King’s more personal side, vessel for the human spirit
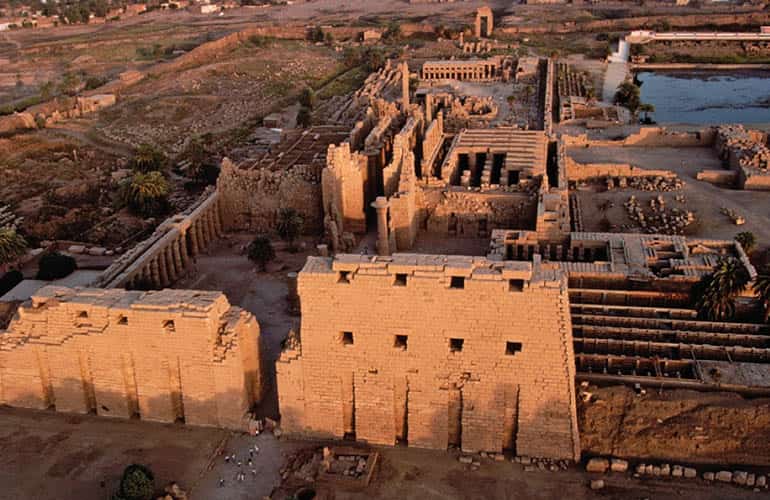

Temple of Amun-Ra
Made of sandstone and mud bricks
Building complex featuring a hypostyle hall, clerestory windows, tons of columns
One of the largest religious complexes, reliefs that were once painted
Kamak, Egypt
1550-1250
Created as a religious center to worship Amun, Ra, and other gods, gods would come here and receive offerings from priests, represents the primeval waters of creation
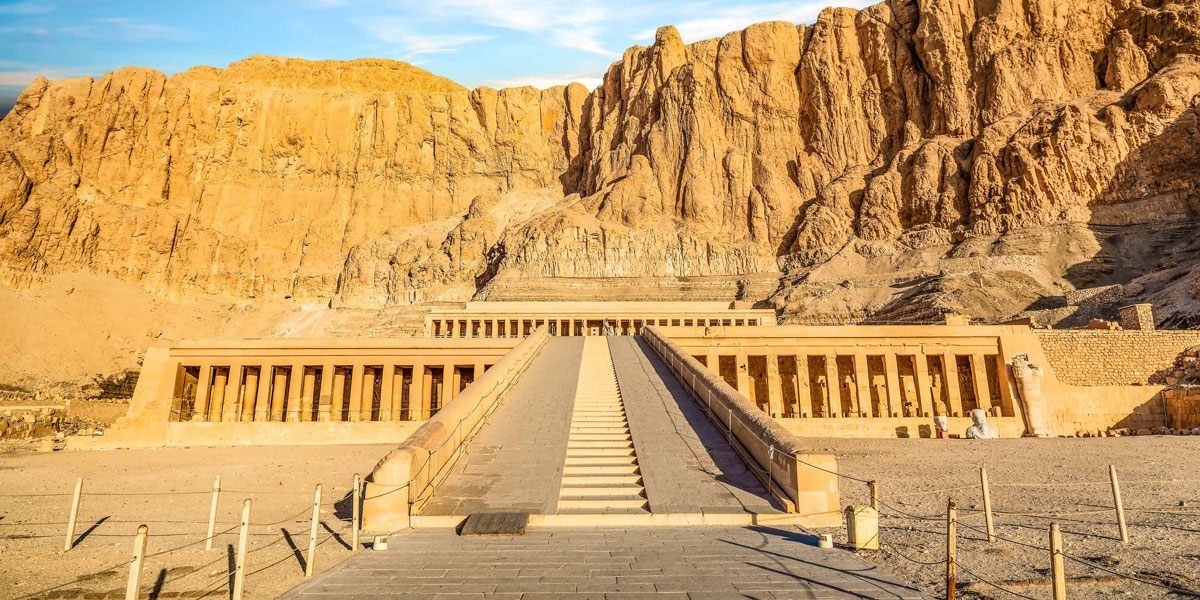

Mortuary Tomb of Hatshepsut
Built from sandstone and red granite
Carved into a cliffside, columned terraces, ramps, 200 granite statues, 10 granite red statues 9’ tall
Elaborate gardens, lines up with Sun on the solstice, elaborate reliefs to show Hatshepsut’s reign
Near the Valley of Kings, Luxor, Egypt
1473-1458 BCE
Created to honor Queen Hatshepsut, the only female leader of ancient Egypt, she was controversial of her time and often depicted herself as male for respect, her relative tried to have her erased from history, but this temple proves her reign

Akhenaten, Nefertiti, 3 Daughters
Limestone
Relief, smooth contours, slaw jaws, thin limbs, androgynous bodies, relaxed expressions, Amama Period
Depicts a domestic scene between Akhenaten, Nefertiti, and 3 daughters, the Ankh symbol of life pointed toward them, affectionate scene, Aten god depicted giving off light
1353-1335 BCE
Egypt
Meant to normalize the new Amama Period art style to the public, Akhenaten shifted the state religion to declare Aten as the new and only god, shifted the art style and moved the capital from Thebes to Amama, found in a house, likely used as a decoration

Innermost Coffin of Tutankhamen
Gold, enamel, semi-precious stones, lapis lazuli
Stylized human face, vulture and winged snake motifs
6’ long, 500 lbs, two goddesses are etched into the lid, back is inscribed with spells from the Book of the Dead, 130 walking stickers were found with it, 1 of 3 coffins
1323 BCE
Egypt
Tombs were ritualistic and guided a soul into the afterlife, preserved bodies very well, coffins showed off wealth

Last Judgement of Hu-Nefer
Painted on papyrus
Register lines, twisted perspective, composite pose, continuous narrative, onc symbol of eternal life, hieroglyphs to tell the narrative
Shows Hu-Nefer being led through the the halls of demons and proclaiming innocence, then Anubis leading him to present his heart on the scale against the ostrich feather, Ammit eats the heart if it’s not pure
1275 BCE
Egypt
From the Book of the Dead that tells the stories of the afterlife and death process, Egyptians believed that the scariest part of life was if your heart wasn’t pure and you ceased to exist, the afterlife and purity of heart were very valued

Athenian Agora
Marble
Bouleuterion Chamber, Tholos emergency Senator meeting center, Stoas (walkways with columns and walls), Agora (outdoor plaza, governmental and sacred), Archaic-Hellenistic Greece
Plaza with several different separated locations, at the base of the acropolis
600-150 BCE
Athens, Greece
Held the Panathenaic Festival to celebrate Athena and dedicate a Peplos robe to her, political center to support Democracy, temples dedicated to Gods/Goddesses

Anavysos Kouros
Marble with paint, carved with iron tools
Patterned hair, archaic smile, pharaoh pose influence, kouros (male youth), idealized
Depicts an ideal young boy, has an inscription for his death
530 BCE
Athens, Greece
Marks a grave or acts as an offering/representation for a god

Peplos Kore
Marble with paint
Stylized hair, archaic smile, kore (female youth sculptures), static pose (goddess theory?)
Depicts a young woman of no known identity, clothed, found buried in 3 pieces, possibly damaged from a Persian siege, left arm is missing but she likely held something to identify her as a goddess, peplos shawl, snatched waist (adorns Athena), likely wore a star crown
530 BCE
Athens, Greece
Marked a grave/altar, meant to honor a goddess or depict a well-respected young woman

Niobides Krater
Red clay, white painted highlights, pottery wheel, polished
Overlapping figures, naturalized and fluid poses, contrapposto pose, isocephalism (no real ground)
One side depicts the murder of Niobe’s children by several gods after Niobe praised her children too much, other side is celebratory and honoring Heracles
460-450 BCE
Found in Italy, from Greece, shows trade
Used as a vessel for mixing wine and water, since water wasn’t safe to drink it was better to mix it with wine
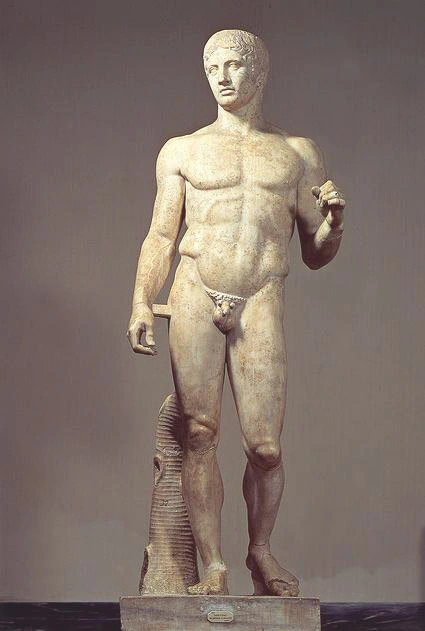

Doryphoros (spear barer)
Marble, original in bronze
Contrapposto, idealized with 7 heads proportion, firm stance, stoic expression, transition between rigid Archaic style and Classical humanized style
Depicts an ideal man’s physique, likely held a spear and shield, has a support beam for his leg
450-440 BCE
Greece, made by Polykleitos
This sculpture would inspire classical work and early American work, this figure was very influential in his appearance, found in a gym, used as a good luck charm

Acropolis
Marble
Center point of city, stood above Athenian Agora
447-410 BCE
Athens, Greece, likely made by Ikintos & Kallikrates
Taken over by Persians and future rulers
Temple of Athena Nike:
Ionic columns, frieze depicting marathon events, amphiprostyle with four columns in front and back
Entrance of Acropolis, honored Nike, the goddess of victory, commemorative for Greek’s victory over Persians, covered with images of Nike such as the frieze relief of her adjusting her sandal - shows her humanized, balanced, with wet drapery, and taking her shoes off before she enters the temple
Parthenon
Idealized proportions, illusion to appear straight from below, Doric and Ionic columns
Once housed 40’ Athena statue of gold and ivory, pediment and frieze sculptures for Athena and depictions of Greek battles, curved floor to avoid rain buildup, Plaque of Ergastines who presented the peplus cloth to Athena statue, Isocephalism (heads on the same level), meant to be seen from below so it used deeper carvings, Helius, Horses, and Dioysis - Elgin Marbles, triangle composition, originally on a pediment, uses contrapposto and wet drapery, depicts the birth of Athena from Zeus’s head as other gods observe


Grave Stele of Hegeso
Marble and paint
Hierachy of scale, wet drapery, pillars and pediment
Hegeso is looking at jewlery that was presented to her, everyday life setting
410 BCE
Greece
Made for Kallimachos, depicts Hegeso looking at her dowry since she never married while she was alive, grave marker
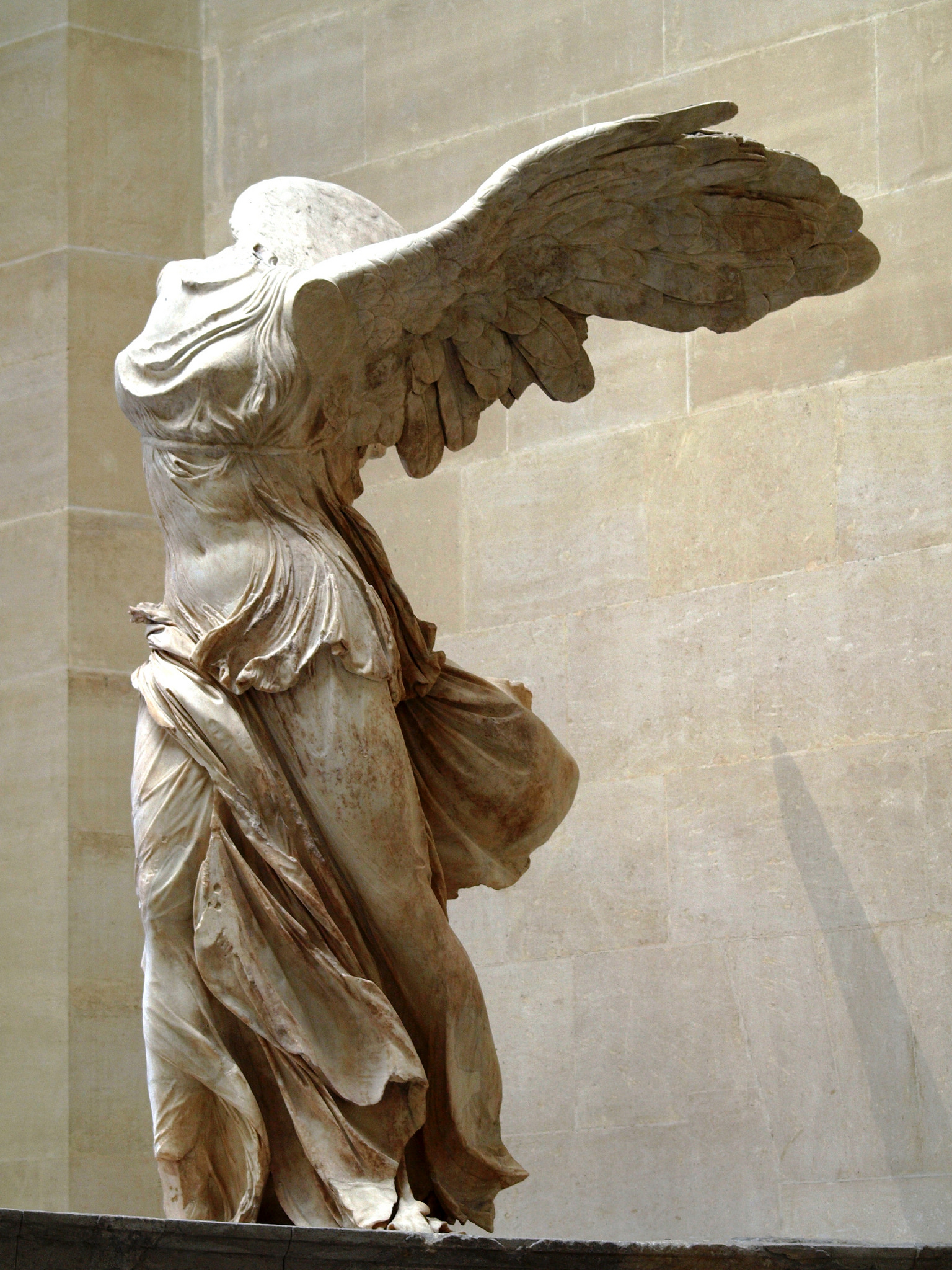

Winged Victory (Nike) of Samothrace
Marble
Contrapposto, twisted torso, fluidity and movement, dramatic negative space, wet drapery
Over 9’ tall, Nike standing up against wind currents, missing her head and arms, very damaged and reconstructed over time
190 BCE
Sanctuary of Great Gods, Greece
Made to stand on the bow of a ship, poised in a fountain, faced out toward the coast, likely to guide maritime missions
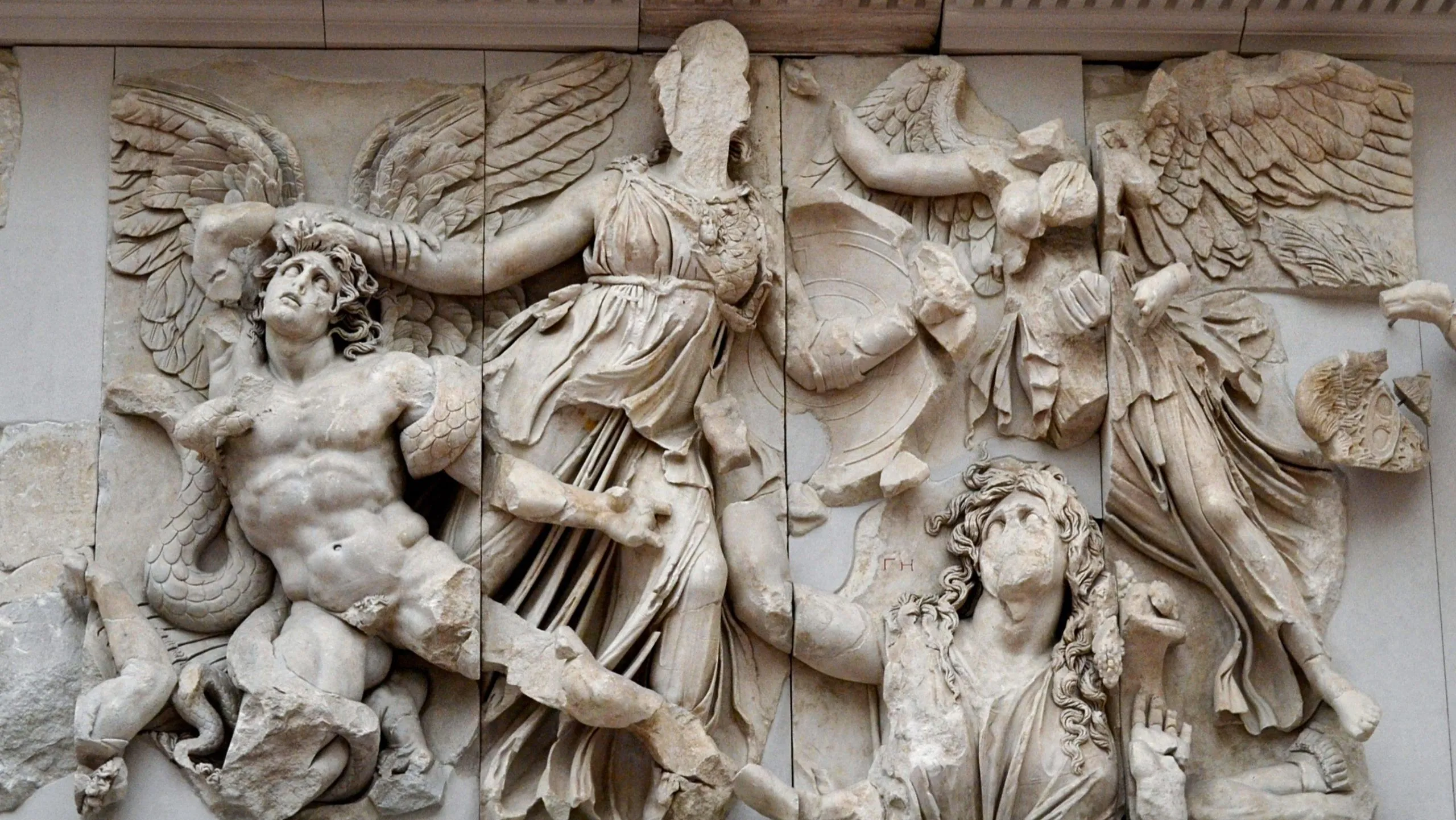

Great Altar of Zeus & Athena
Marble
Ionic columns, high reliefs, Hellenistic expressions
Massive stairs up to a platform, 8’ x 400’ low frieze depicting Gods conquering the giants who were trying to control Earth, Athena grabs a giant while Nike crowns her, Giants express a lot of pain and anguish, parallels the battles of Greeks against Persians and Gauls
175 BCE
Pergamon, Asia minor, Turkey
Made to honor victories of the Greek Gods, specifically Zeus and Athena


Alexander Mosaic
Mosaic, thousands of tiles
Foreshortening, multiple angles, emphasis through highlighting, rounded figures, tonal gradation, overlapping figures
Depicts the Battle of Issus, Alexander the Great defeats the Persians, King Darius retreats from the fight, Alexander is calm and focused while Darius is horrified as one of his men is impaled
100 BCE
House of Faun, Pompeii
Made to model a Greek mural that had been burned, depicted Alexander the Great is a very powerful way, made as decoration
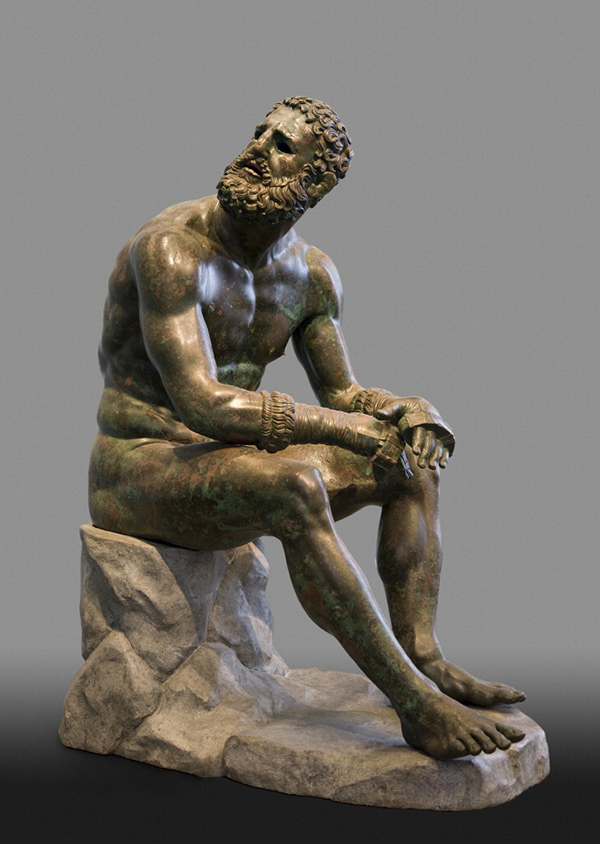

Seated Boxer
Bronze - rare since most bronze sculptures were melted down
Hellenistic exaggerated expression, negative space, aged
Depicts a boxer after his defeat, bloody and wounded, looking up at his opponent, wearing leather thong gloves, slumped
100 BCE
Found in a gym, Greece
Typically served as a good luck charm to feel before working out

Temple of Minerva & Sculpture of Apollo
Mud brick, tufa, and wood for the temple, terracotta sculpture
Influences from Archaic Greece, Doric temples with bases (tuscan capitals), contrapposto, archaic smile, idealized
Temple was raised on a podium and had three entrances leading to a small room, temples were placed on the roof
Veii, Italy, from Etruria, likely made by Vulcan of Veii
510-500 BCE
Temple has decayed over time, was made to honor gods such as Apollo


Sarcophagus of the Spouses
Terracota
Triclinium, ostrich egg to symbolize after life, made in two pieces
Depicts a married couple reclining and eating together at a banquet
Cerveteri, Italy
520 BCE
Made to honor the married couple and hold their remains , showed them as happy to portray the afterlife as more cheerful

Tomb of the Triclinium
Tufa (porous, limestone-like rock) and fresco paintings
Tricliniums were often depicted, circles that symbolized the circle of life, geometric shape motifs
Depicts lively and joyous scenes like reclining on triclinium (banquet couches), instruments, rural settings, a lot of geometric patterns, men were painted darker than women
Tarquinia, Italy
480-470 BCE
Served as a tomb for the Etruscans, funerary services were joyful rather than somber, many tombs were painted similarly

House of the Vetti
Cut stone and fresco paintings, marble fountains
4th Pompeiian style with borders and depth illusions, Peristyle halls and gardens, 100m², open atrium area with a skylight, narrow entrance
Wealthy and showy house owned by two brothers to display their money through elaborate decorations
Pompeii, Italy
300-200 BCE
Pompeii was stinky, so no exterior windows were used, only skylights provided light, completely preserved from ash, the house provides information about Pompeii and the Imperial Rome area

Head of a Roman Patrician
Marble
Verism, Hellenistic exaggeration, idealized
Shows a bust of an ideal Senator from the Rome Republic, subject was likely young but depicted old and wrinkly to be assumed wise
Rome
75-50 BCE
Busts were commissioned for families to keep as proof of lineage and to brag about their relations to noble and powerful people

Augustus (Octavian) of Prima Porta
Marble - original in bronze
Contrapposto, crater’s pose
Shows the first ruler of the Roman Empire, Octavian, and Cupid baby riding a dolphin by his feet
From Prima Porta, Rome
20 CE
Octavian is depicted as very powerful, barefoot because he’s standing on sacred ground, wearing a toga and a decorated breastplate with symbols showing his achievements and power
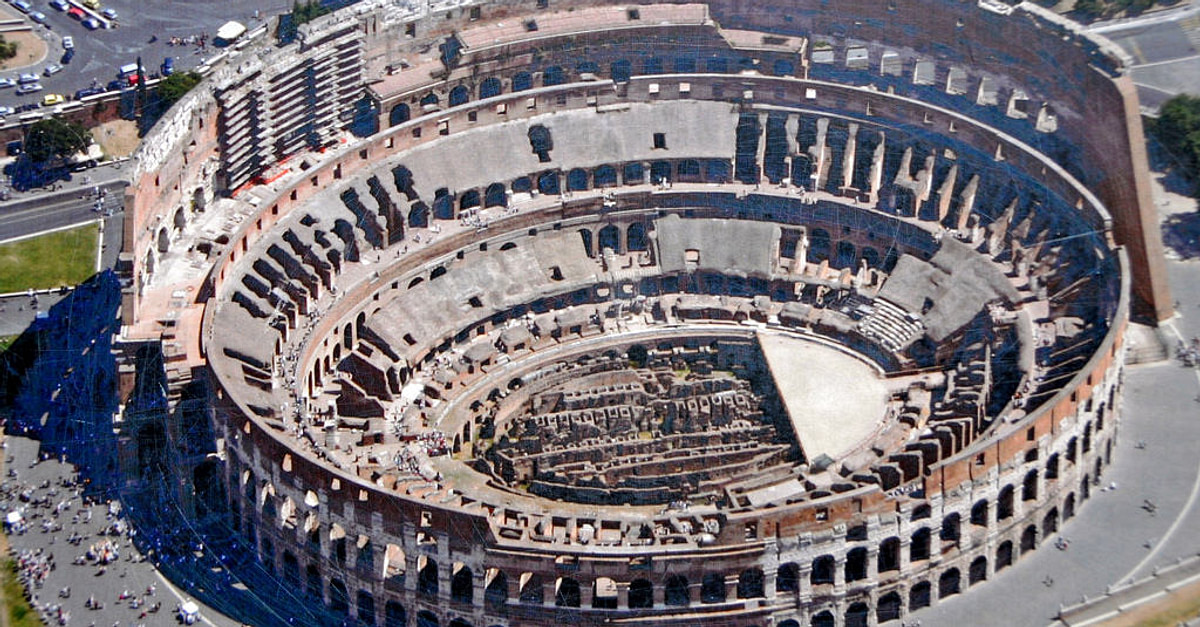

Colosseum (Flavian Ampitheater)
Stone and concrete, originally marble
Arches, barrel and groin valuts, doric, ionic, and corinthian columns
80 entrances, 3 tiers, modeled after Greek architecture, built to hold 50,000 people, subterranean vaults to hold prisoners and wild animals, canvas roof to shield from the Sun
Rome, Italy, Imperial Rome
72-80 CE
Used to host spectacles, battle re-enactments, gladiator fights, wild beast fights, executions, would sometimes fill with water for naval re-enactments, higher class people at the bottom, lower class people at the top
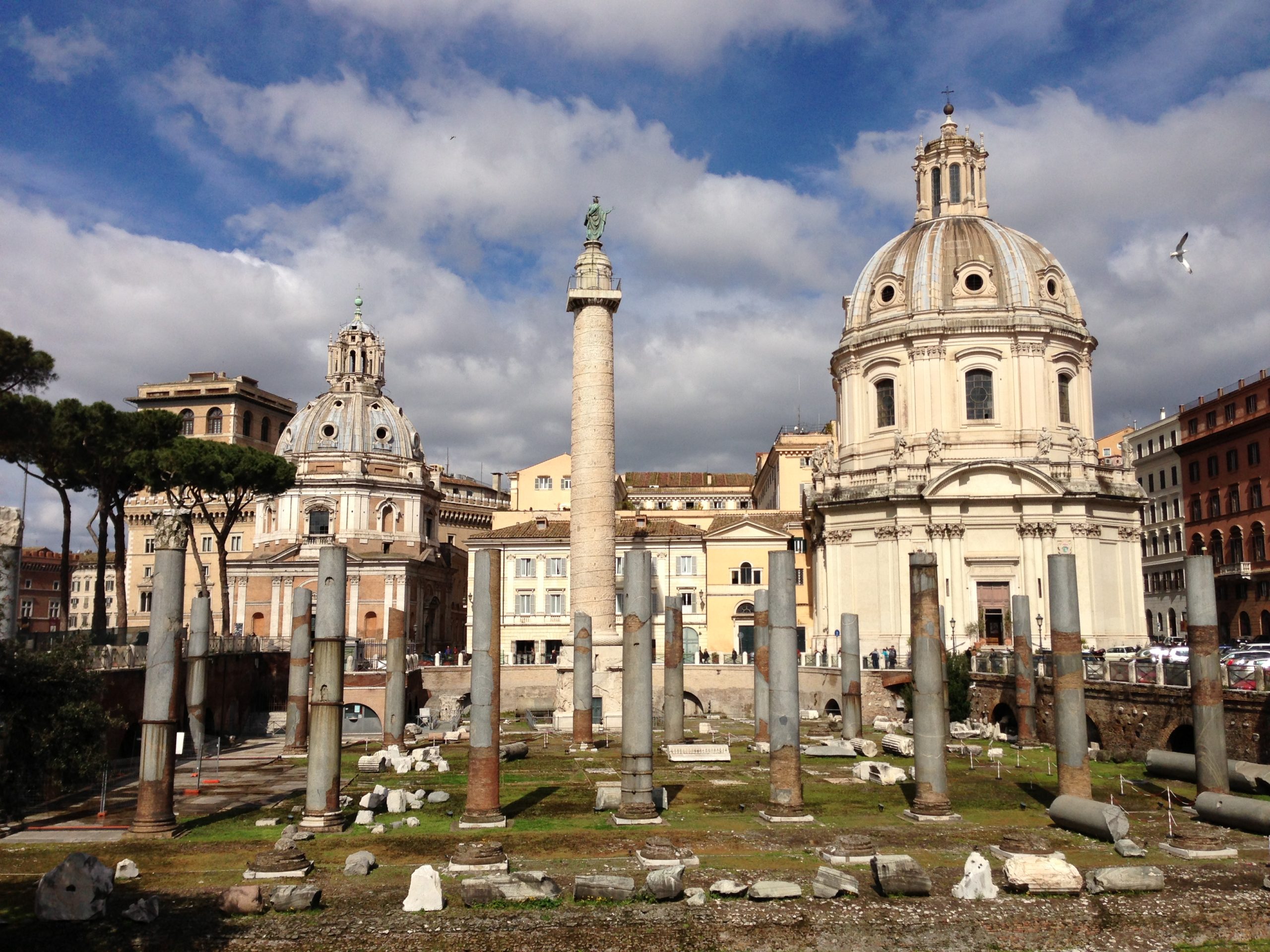

Forum of Trajan
Brick and concrete
Continuous narrative (column of Trajan), clerestory windows (Basilica Ulpia), groin and barrel vaults (Market of Trajan)
Forum has a ceremonial entrance and large statue of Trajan, and marble columns, Basilica Ulpia was a massive columned, roofed structure that inspired a lot of early churches, Column of Trajan is a spiral staircase with 625’ relief and is 125’, with 2,500 figures and 150 scenes, a lot of detail, Market of Trajan is a collection of 150 shops, public works offices, multiple levels and floors
Rome, Italy
110 CE
Main square was used for ritual business and civil meet-ups like Senator meetings, Column of Trajan as used to show Roman battles and honor Trajan, also being a grave marker, the Market of Trajan was a market and office center, and the entire forum was used to show Roman stability and display power and wealth under Trajan leadership
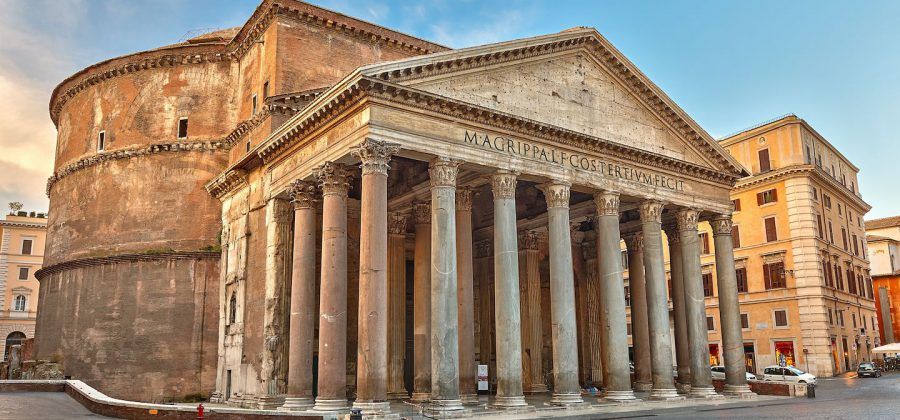

The Pantheon
Concrete with stone facing
Greek facade elements, coffers - concentric squares to reduce ceiling’s weight, cupula - hemispherical dome, 20’ thick, thickness decreases with height, oculus - 27’ hole in the ceiling to add light, columns, pediment, frieze
Ornately decorated, tiled floors, painted ceiling with spots for statue of gods and deified emperors, huge dome
Rome, Italy
118-125 CE
Was used as a place for Catholic worship and burial place for Italian Kings, heavily influential in the Italian Renaissance
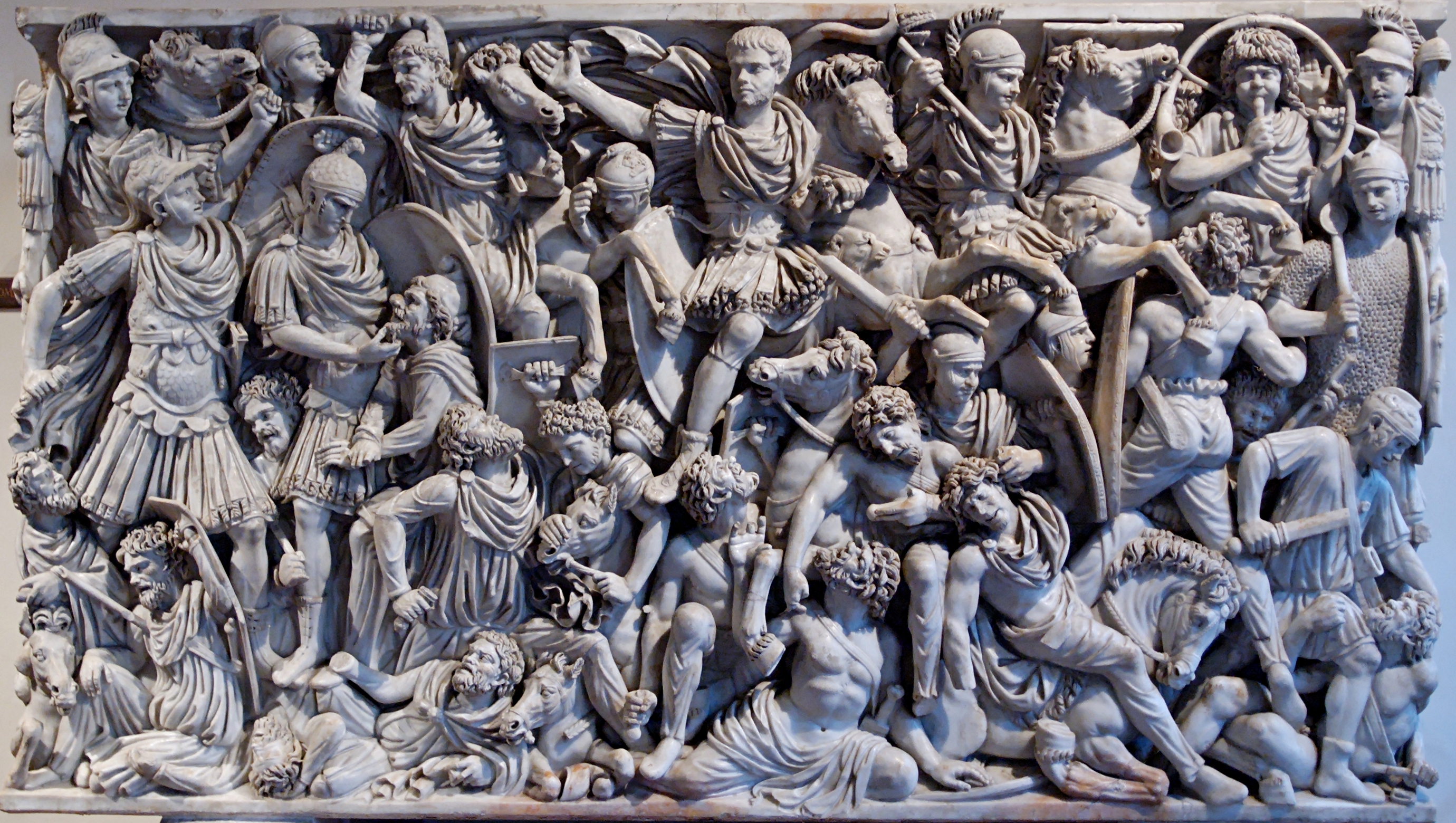

Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus
Marble
Horror Vacui - extremely crowded with confusion and chaos of battle, Orator’s pose, very high relief
Depicts Romans(shaven, armored, holding weapons, and Celts (bearded, unarmed), no consistent proportion or perspective
Late Imperial Rome, Italy
250 CE
Shows the conquest and subjugation of the time, displays the struggle to maintain power as the Roman Empire fell
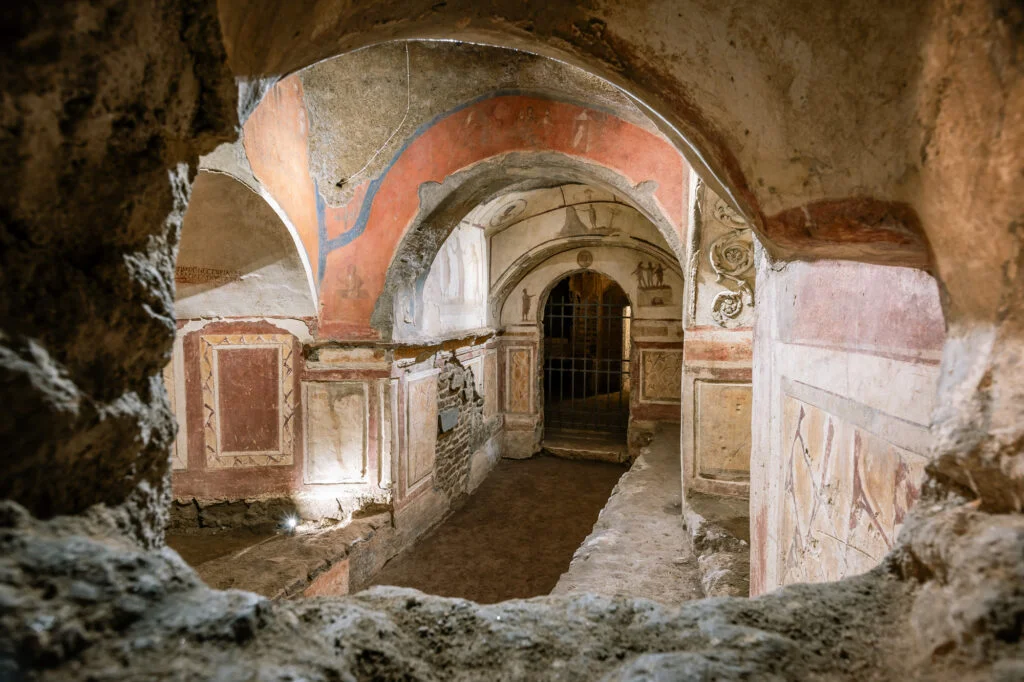

Catacomb of Priscilla
Stone and dirt?
Tufa and fresco, extended hundreds of miles, Greek inscriptions, Pompeiian style, Roman influence, low-resource paint materials, narrative paintings
Orant Fresco depicts Christ (possibly first depiction) in a pastoral scene with doves and other peace symbols, Old testament stories like Abraham sacrificing Isaac and Jonah and the whale, the Good Shepherd Fresco shows a good Christian in an orator’s pose
Rome, Italy
200-400 CE
The catacombs were a place for Christians to hide from persecution, made in honor of Priscilla, the wife of a martyr who donated the land, tombs were held in small niches (coculi) for the poor, and ornate chapels (cubicula) for the rich
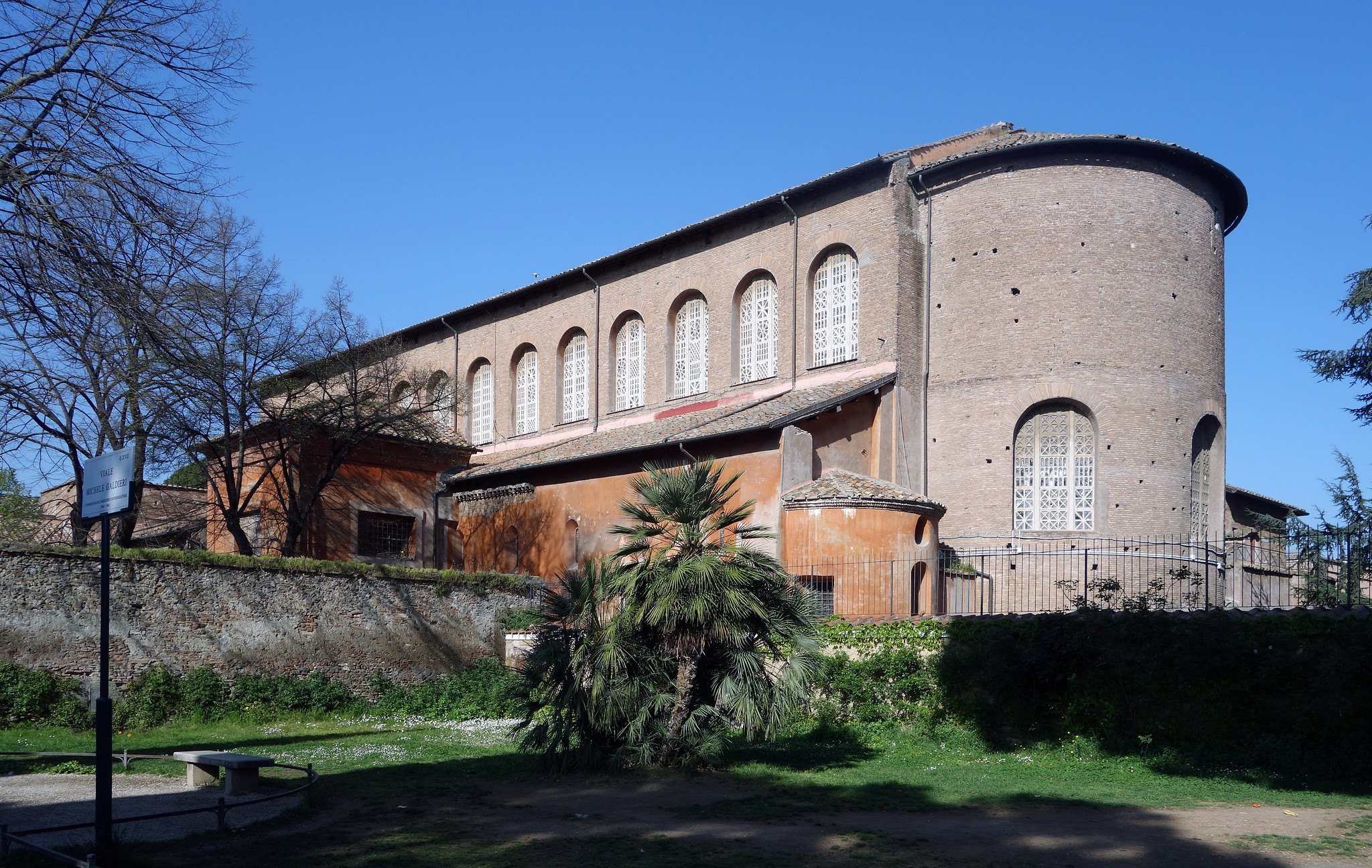

Santa Sabina
Brick, stone, wooden roof
Spolia (recycling of artwork/building), former Roman basilica, coffered ceiling to support weight, concentric octagons, corinthian columns, clerestory windows, archave (repeated arches), Eucharist (bread and wine) motif
A basic exterior once covered in mosaic, with a wide interior ornately decorated to
Rome, Italy
422-432 CE
Supported a wide congregation of men in the center and women along the sides, light and airy interior, a lot of light because it symbolizes divinity
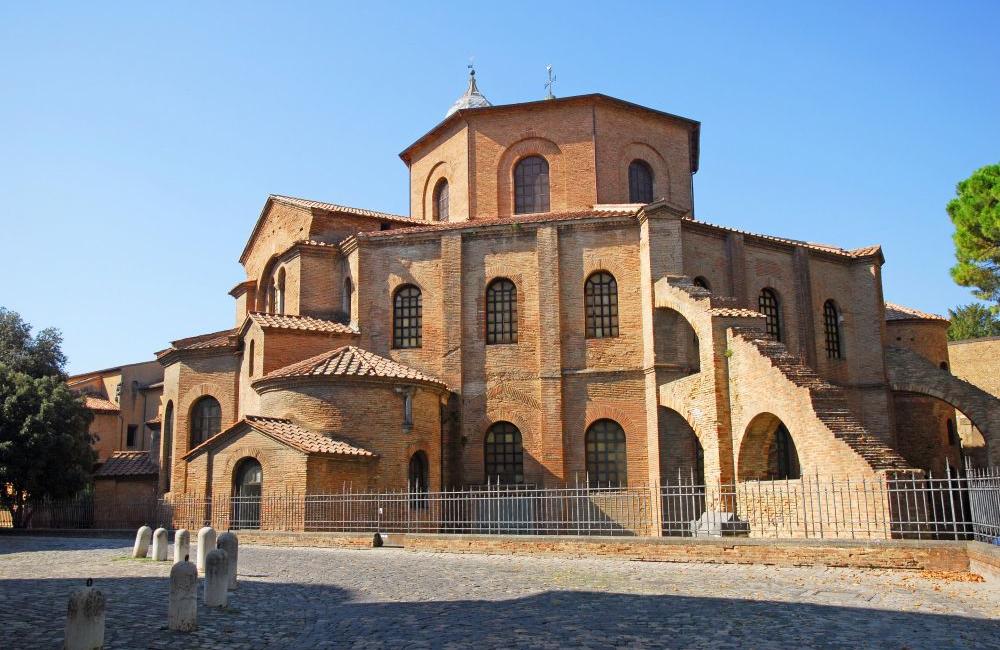

Basilica of San Vitale
Brick, marble, and stone
Octagonal and central plans, Roman domes and mosaics, Byzantine columns, capitals, flying buttresses, airy interior
Ornate interior, shrine for the spot Saint Vitalis was martyred
526-547 CE
Ravenna, Italy
Commissioned by Justinian to show his power, place of worship
Mosaics:
Justinian & Attendants
Military on the left, church clergy on the right, Justinian in the middle, idolized Justinian, symmetrical, standardized faces, overlapping feet, Justinian wearing Tyrian purple, symbol of high royalty
Theodora & Attendants
Asymmetrical suggesting Theodora is not central in her power, chalice for mass, heavy ornaments of jewelry, purple robes

Vienna Genesis
Pigment on cow skin vellum, tyrian purple and silver text
Soft figures, foreshortening, contrapposto, shallow settings, continuous narrative
Narratives to tell stories from the bible
700 CE
Syria?
Earliest surviving copy of the bible, shows society in transition from classical to Christian medieval
Jacob Wrestling an Angel
ground lines creating almost register lines, Roman architecture/columns, Byzantine figures with flattened figures and heavy clothing
Rebecca and Eliezar at the Well
Personification of water, Water Goddess, continuous narrative of Rebecca giving water to camels
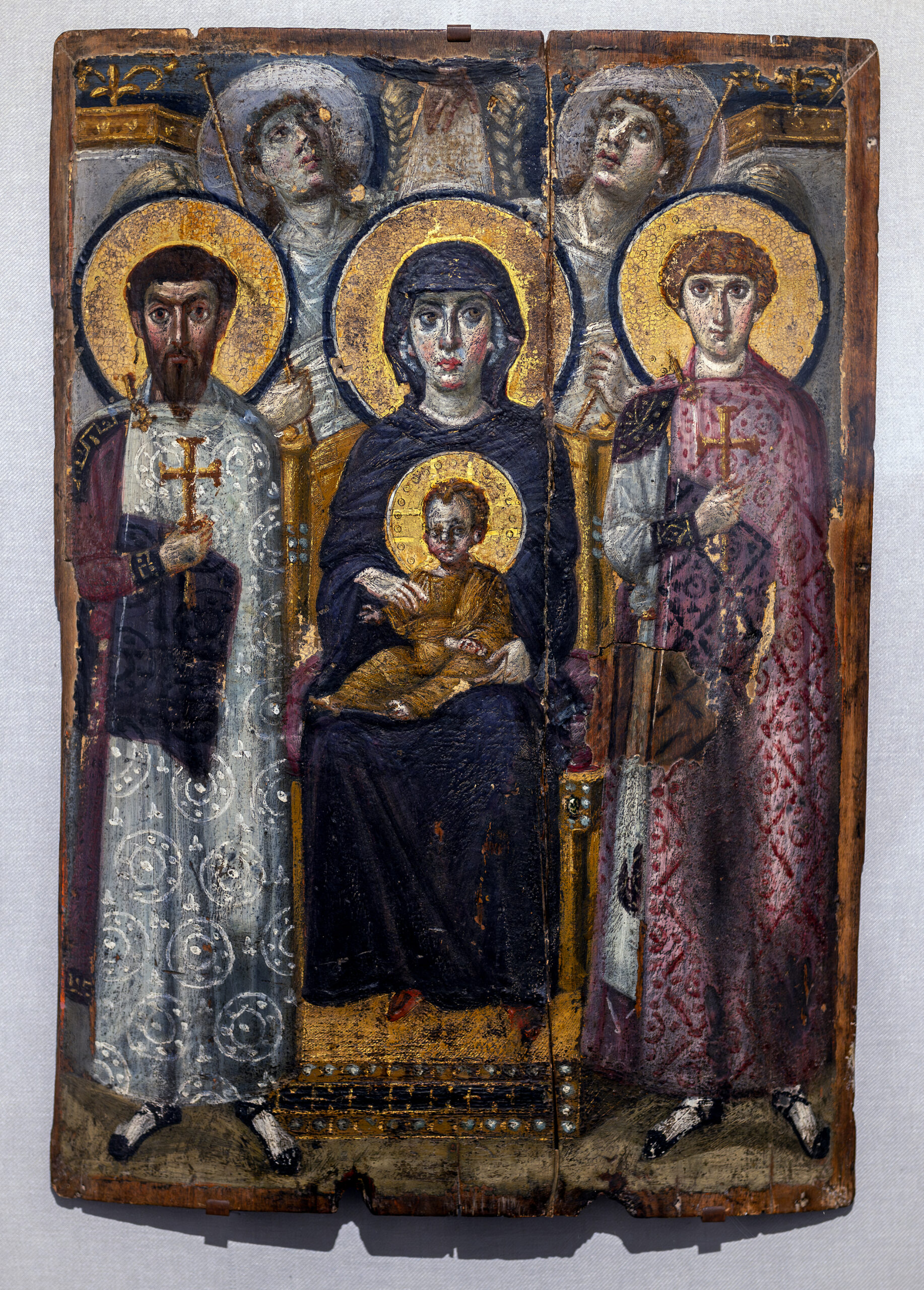

Virgin (Theotokos) and Child Between the Saints Theodore and George
Encaustic on wood
Icons, halos for divinity, stiff and front-facing, classical faces, symmetrical composition, heavy drapery and weird feet, flattened proportions, stylized, different styles showing more than one person worked on it, old man Jesus to show his wisdom
Painting depicting the Virgin Mary and Saints surrounding baby Jesus, God’s hand and angels depicted in the back, warrior saints
700-800 CE
Sinai, Egypt
Created to display and honor the divinity of Mary and Jesus
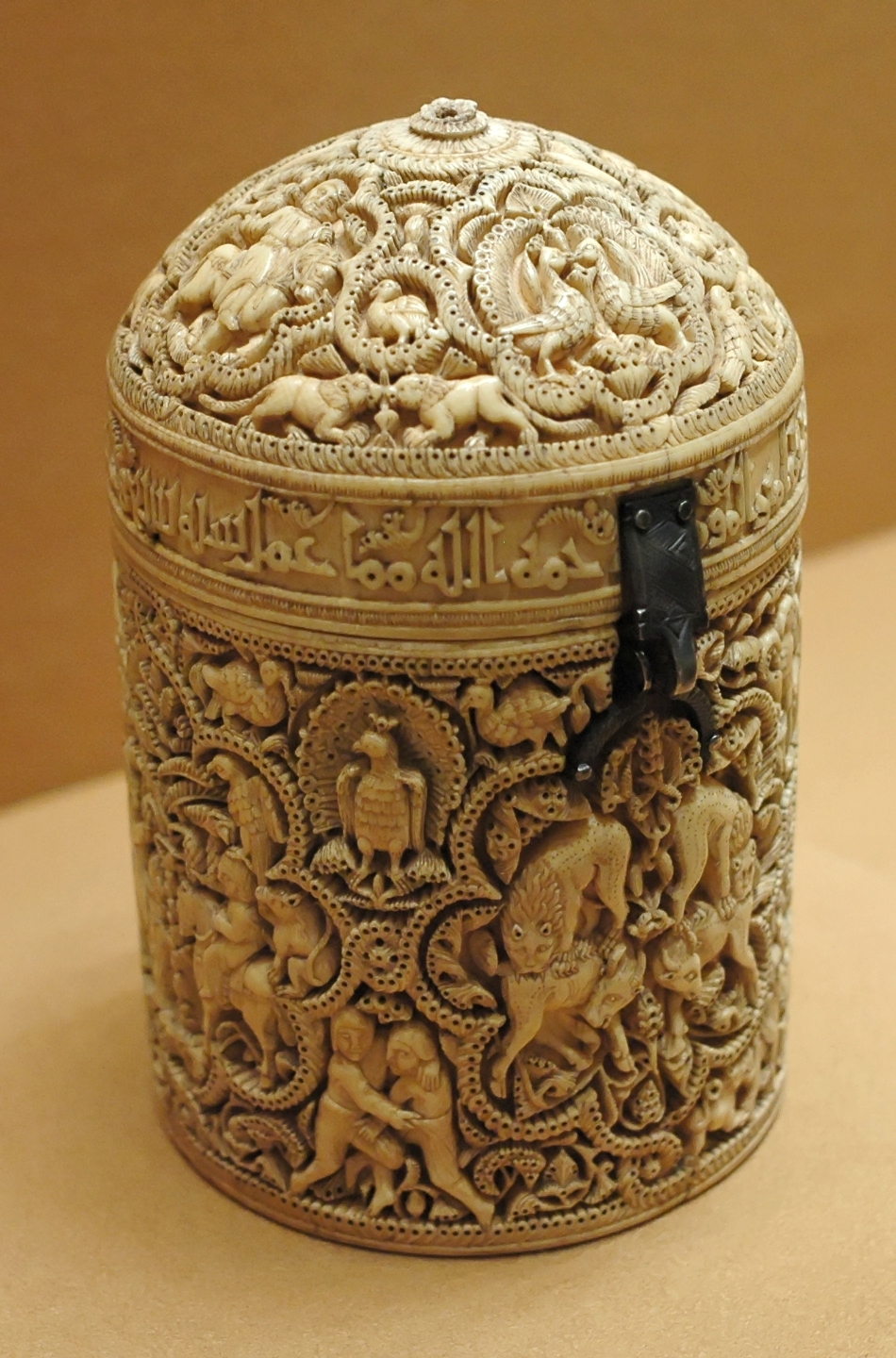

Pyxis of al-Mughira
Carved ivory
Horror Vacui
Kuffic script, depictions of people. geometric and floral motif patterns
968 CE
Muslim Spain, Ummayad Caliphate
Created as a gift to a caliph’s son, vessel for perfumes and aromatics, secular work, durable, high-status
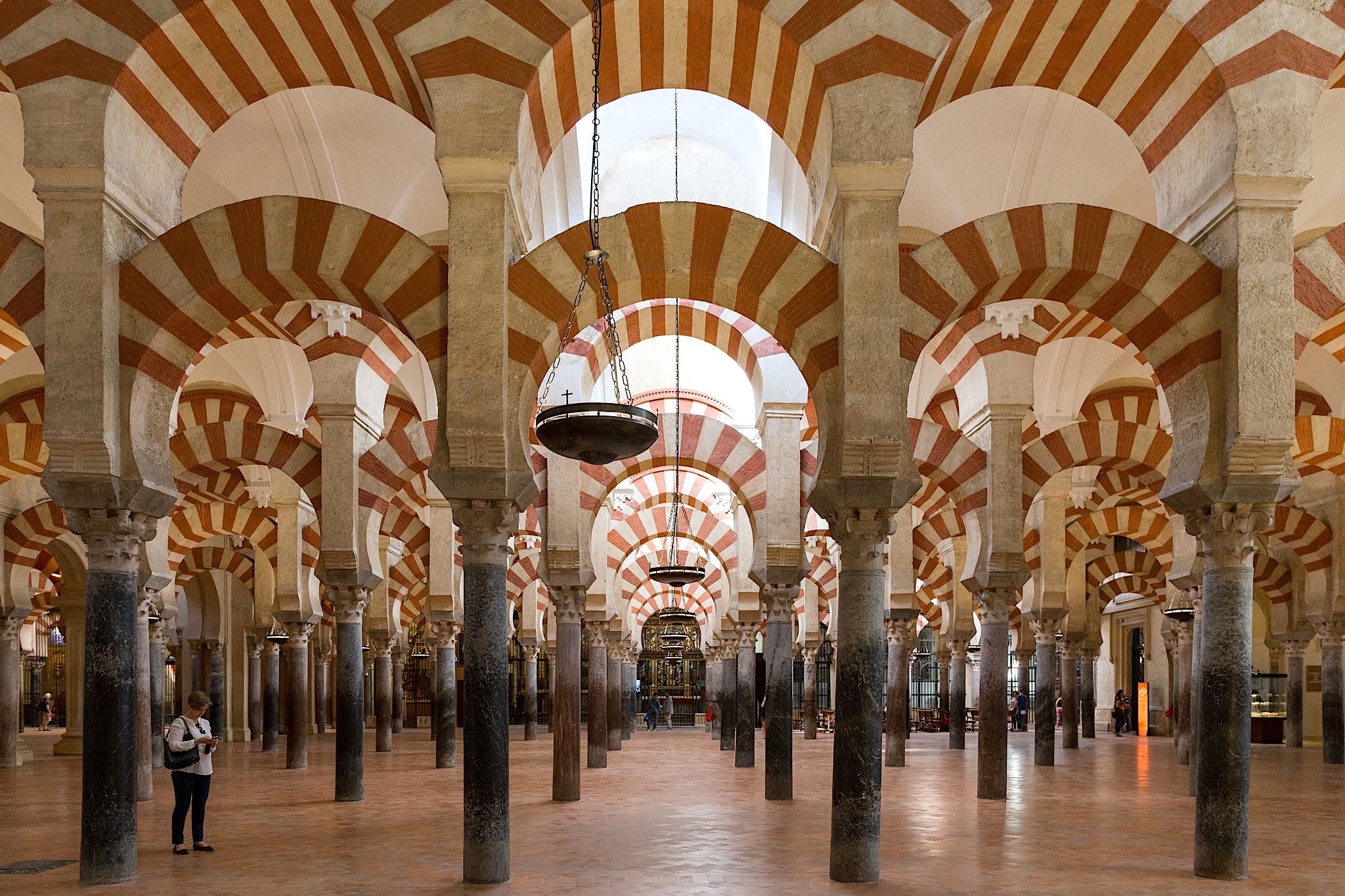

Mosque of Cordoba
Stone Masonry
Hypostyle, spolia, ancient Roman columns, repetition, dome supported by elaborate squinches
Mihrab pointing toward Damascus, Kufic calligraphy on the walls
785 CE
Umayyad Caliphate, Spain, Visigoth rule
Built over a church, oranges planted in Sahn (courtyard) to remind the prince of Saudi Arabia, powerful and ornate
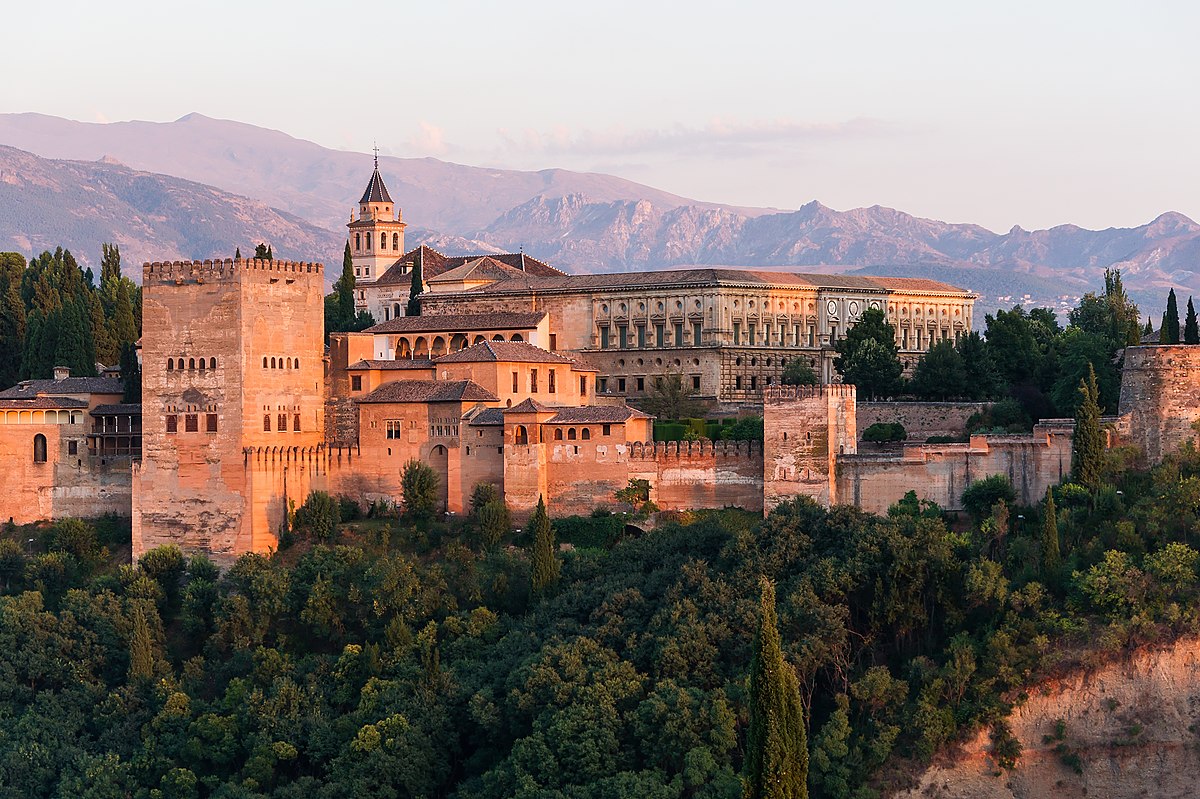

Alhombra
Whitewashed adobe stucco, wood, tile, paint
Incredibly detailed - Hall of the Sisters ornately decorated with repetition and muqarnas (carved brackets), and Court of the Lions with a central fountain, thin columns, and intricate carvings
Gardens, fountains, courtyards, three separate palaces, Alcazabra are barracks for guards, Medina is the residence and workplace for court officials, “Only God is victorious” written over 9,000 times
1238-1358 CE
Granada, Spain, Nasrid Dynasty, developed by future societies
Built as a palace for royalty, workplace, developed by different caliphates, eventually housed Ferdinand and Isabella
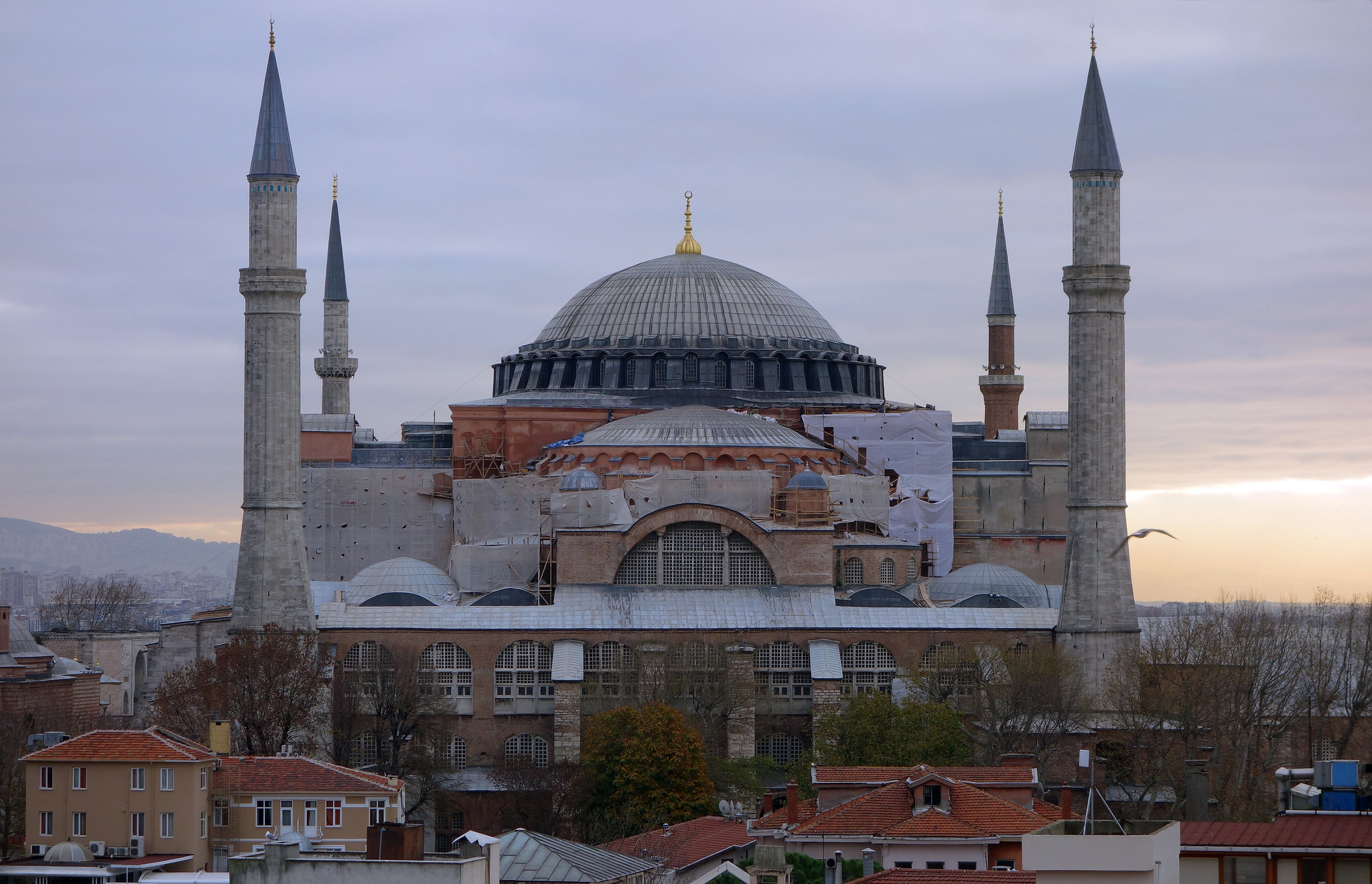

Hagia Sophia
Brick, ceramic, stone, mosaic
Domes and pendentives, central and axial church plans, Greek and Roman column influences, illusion that dome is flying
Walls covered in gold and mosaic, rebuilt after suffering fires and damages
532-537 CE
Constantinople (now Istanbul), Turkey
Largest capital under the Byzantine, religious and political center, believed to have healing powers, originally Christian under Justinian, now Muslim

Mosque of Selim II
Brick and stone
Central plan, inspired by the Hagia Sophia
Contained libraries, schools, government buildings, open and big mosque
1570 CE
Edirne, Turkey
Commissioned by Selim, Ottoman Empire, built to surpass all built before it and impress Western European travellers
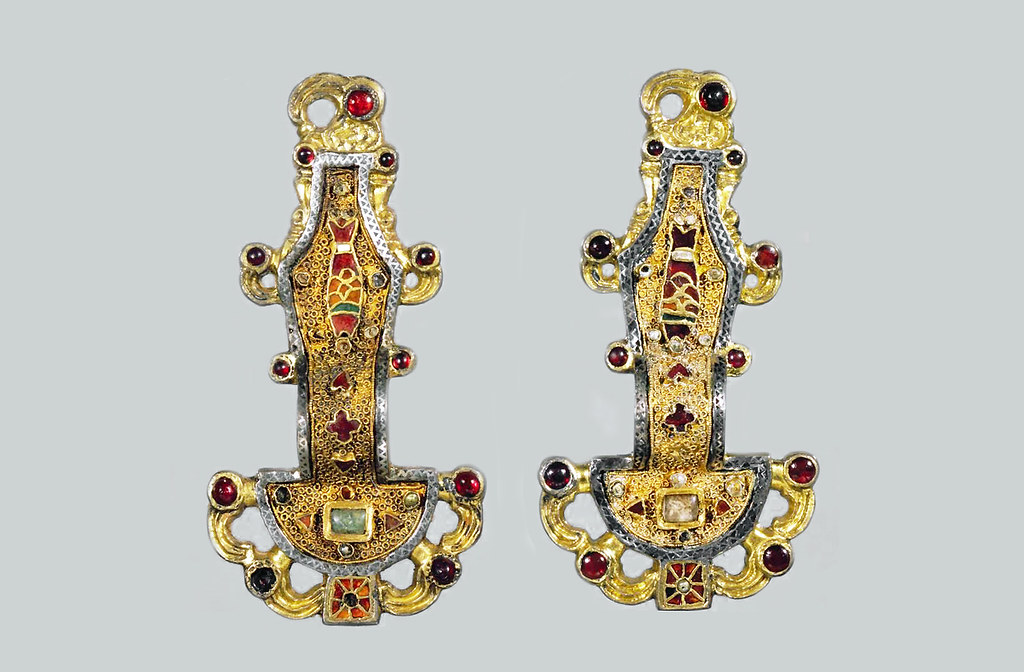

Merovingian Looped Fibulae
Silver gilt, semi-precious stones, glass mosaics, garret inlays, Chasing (patterns created by hammering)
Zoomorphic, Cloisonne (partitioning, stones laid in), Ichthys - early underground Christian motif
550 CE
Merovingian Dynasty, France
Made to pin garments and clothes, popularized in the Roman Empire, meant to show off wealth
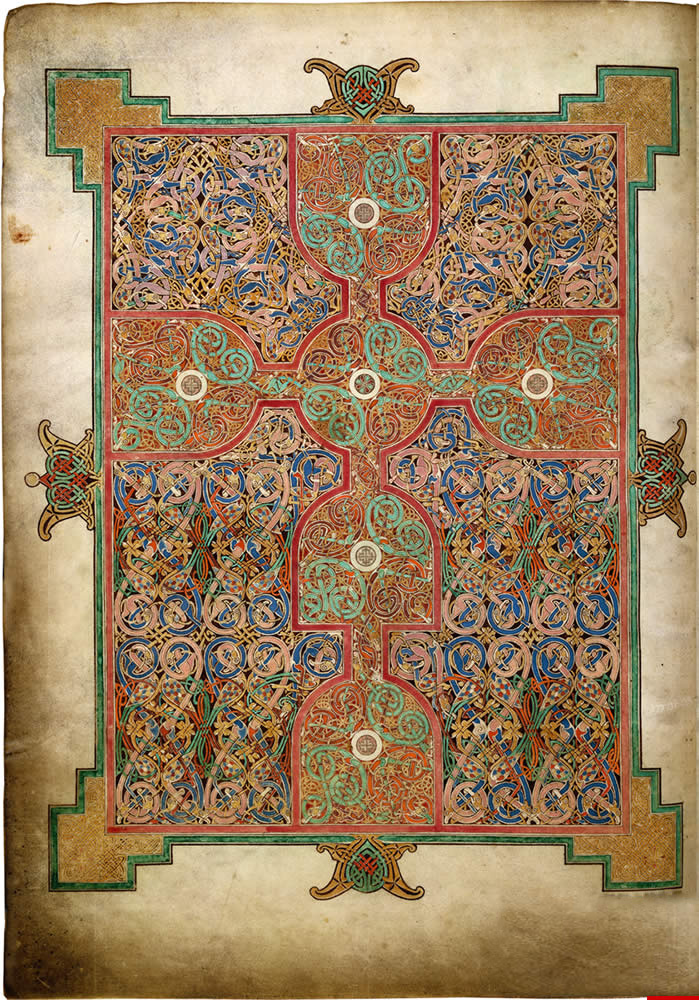

The Book of Lindisfarne
Ink, pigment, gold on vellum
Stylized, Hibero-Saxon art, illuminated manuscript, Latin text, animal style (interlaced complex animals)
Oldest surviving manuscript of the Gospel, has a colophon used to tell exactly who contributed to the manuscript and what they did
700 CE
England
Meant to tell the stories of Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John, primarily through pictures and patterns, English was added 250 years later so more people could read it
Carpet page of St. Matthew
horror vacui, knotted dog-headed snakes and long necked birds, symmetrical and balanced, Celtic and Christian influence, background shows a cross
Saint Luke Portrait
image vitul (traditional symbol of St. Luke), Hagios Lucas, beard to show status, purple to show royalty
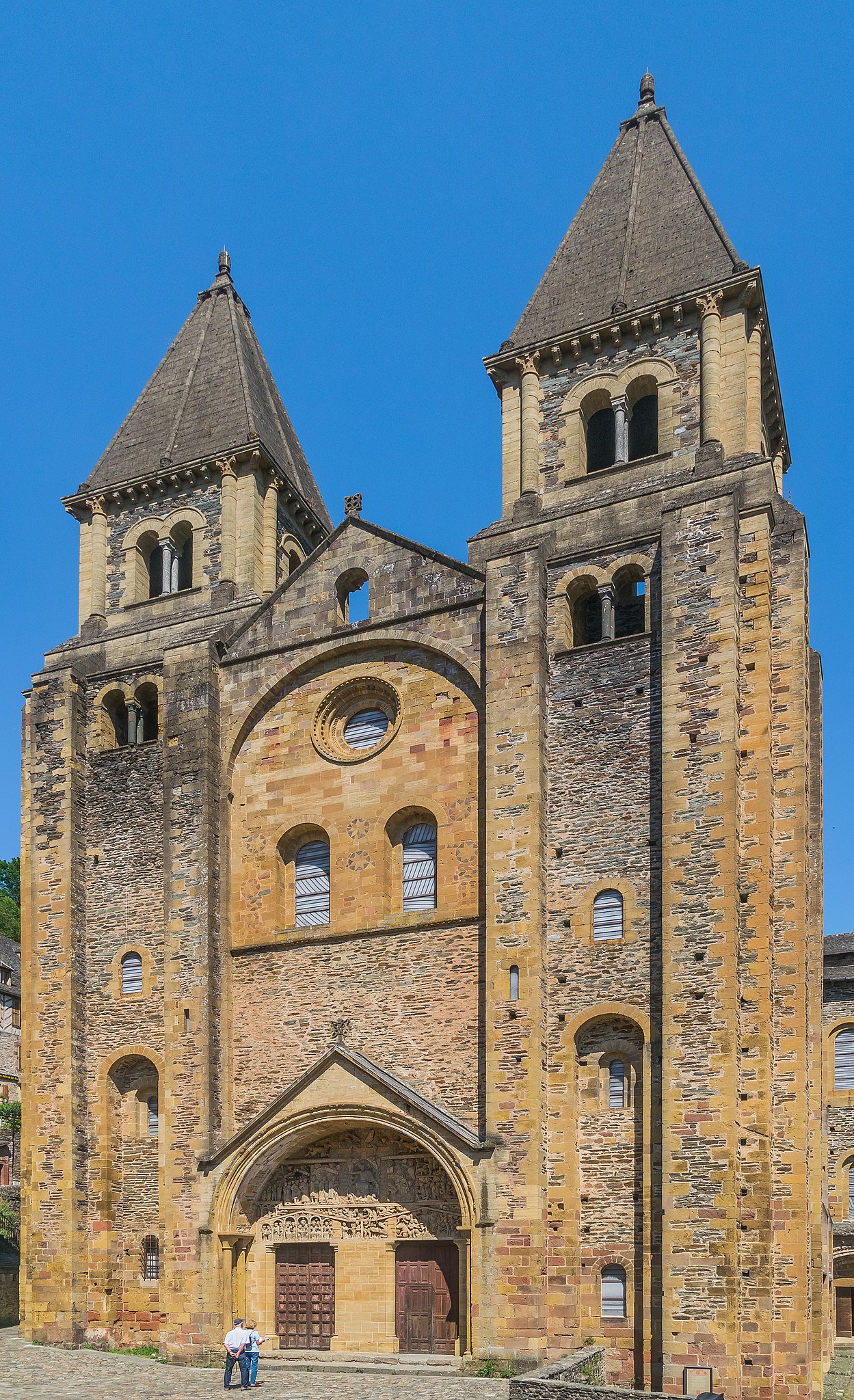

Church of Sainte-Foy
Stone
Cruciform (cross-shaped) ground plan, clerestory windows, barrel vaults, columns from Rome, Campanile wall summons people to prayer
Large, elaborate cathedral with multiple entrances, two turrets, three chapels
1050-1130 CE
Conques, France, on the route to Santiago de Compostelo
Made for a lot of people to congregate within, housed the reliquary statue of Sainte-Foy, easy to control crowds with the floor plan, attracts people on pilgrimage
Tympanum of the Last Judgement
Semi-circular stone above the door, shows Christ as a judge gesturing to those going to Heaven vs. Hell, hierarchy of scale, registers, flattened figures, heavy drapery, painted stone, serves as a warning to Christians
Reliquary Statue of Sainte-Foy
Gold, metals and gems, wood base, holds Foy’s head, a young girl who was martyred for refusing a Pagan ritual, added to over time by patrons, has enlarged hands and a head
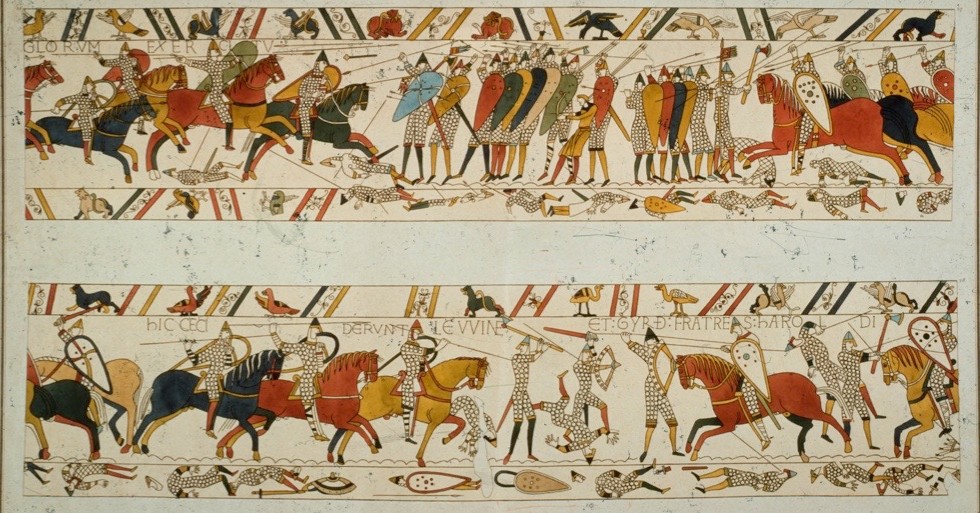

The Bayeux Tapestry
Embroidered linen
continuous narrative, flattened, little perspective/detail, natural background, limited palettes, top & bottom borders, registers
Everyday scenes, fantastical creatures, 230’ long, 600 people and 75 scenes
1066-1080 CE
Bayeux, France
Made to depict William the Conqueror’s conquest of England, Battle of Hastings, commissioned by William’shalf-brother, the Bishop of Odo, likely designed by a man and then made by a woman

Chartres Chapel
Limestone and stained glass
Originally Romanesque, rebuilt with Gothic influences, North side is Romanesque, South side is Gothic, rib vault ceiling, jambfigures of saints/apostles in the doorjambs, elaborate timpanums of the life of Mary, naturalistic and soft features
Two spindrels (left is Romanesque, right is Gothic), enlarged choir space, elaborate stained-glass windows with expensive pigments
1145-1155 CE
Chartres, France
Hosted elaborate and huge ceremonies, dedicated to Mary, held the Saint Ann reliquary (Mary’s mom), and tunic of the Virgin Mary from when she gave birth to Jesus (Santa Camisia)
Notre Dame de la Bella Verriere
Stained glass windows to let in divine light, undamaged in original fire, shows Mary crowned as queen of Heaven with Jesus in her lap, large images of saints up high, lang and laborous process to create it, narrative for those who couldn’t read, glass made, cut, painted

Moralized Bible
Pigments on vellum
Illuminated manuscript, registers, bright colors
Illustrates the bible line by line, depicts “good” Christian characters and “bad” foreign characters
13th century
France and Spain
Gives a modernized version of old biblical stories, illustrates the bible and provides relevant commentary, colors and compositions are meant to emulate stained glass windows, very expensive, created for the Blanche of Castille and her son, Louis IX
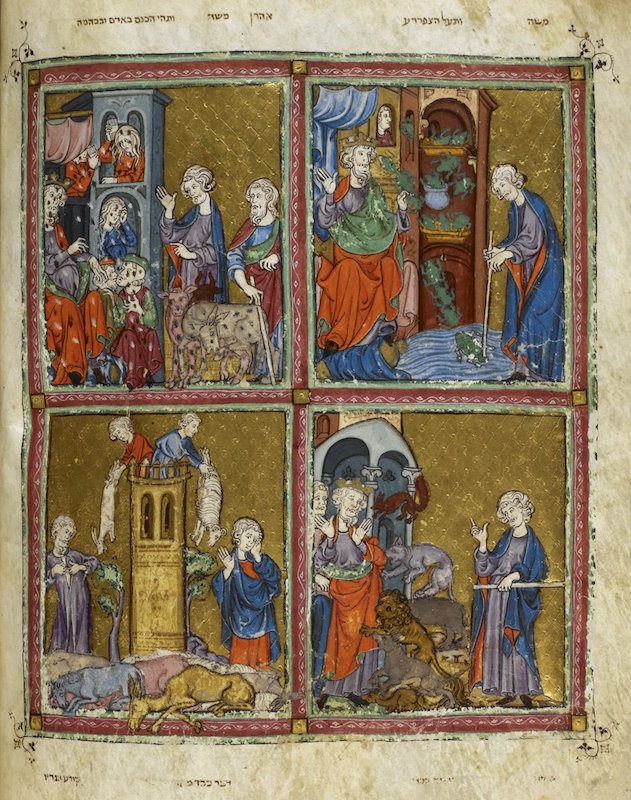

Golden Haggadah
Pigments on vellum
Heavy Christian stylistic elements, heavy drapery, enlarged heads and hands, long bodies, contemporary settings and architecture
Depicts the Passover story, showing the exodus and plagues, read right to left
1320 CE
Medieval Spain
Commissioned by wealthy Jewish patrons, used for celebrating Passover as it guides Seders
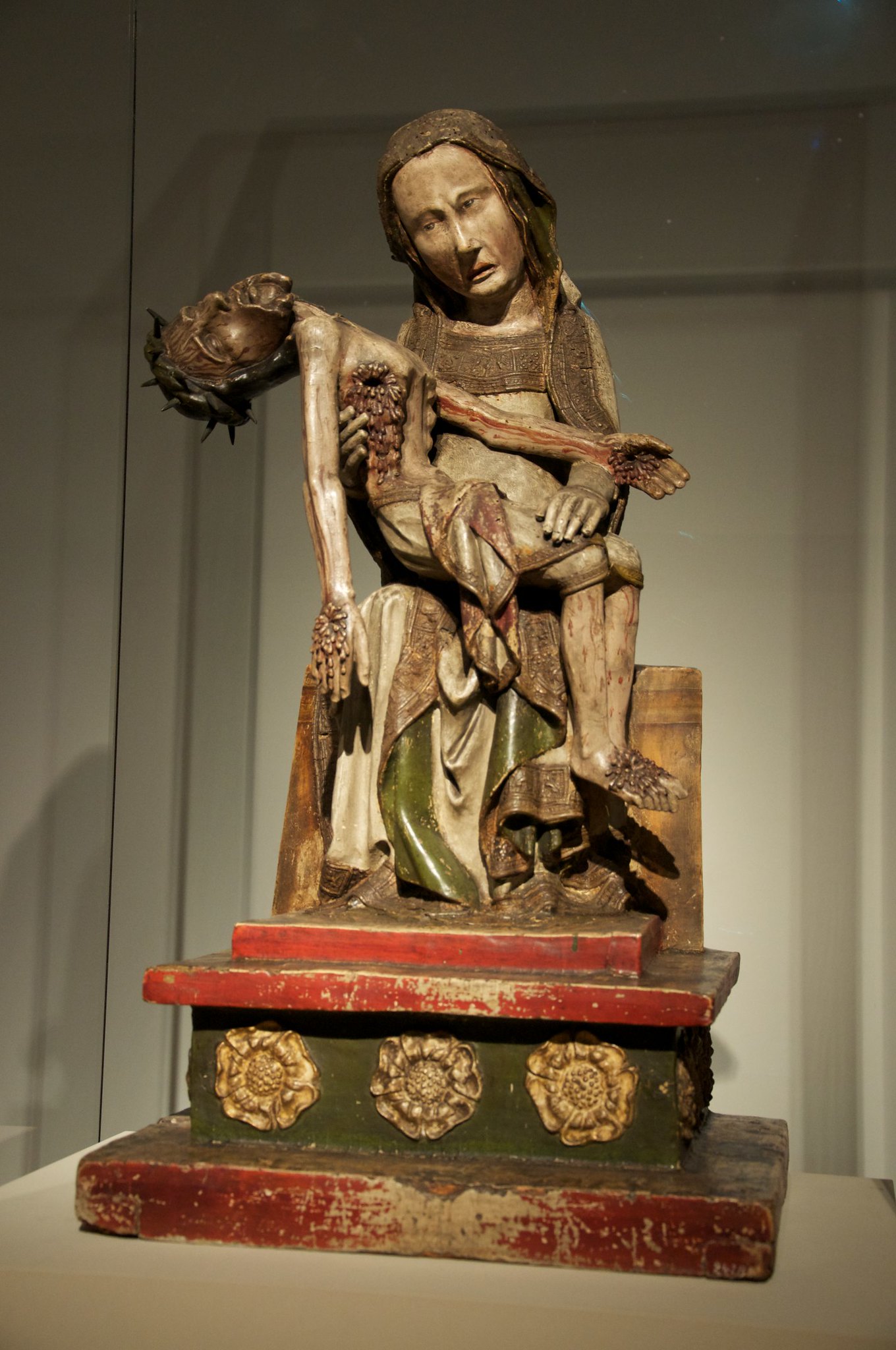

Rottgen Pieta
Wood and paint
Andactshild (made for private decoration, not worship), humanized Jesus, stigmata to show injuries, warped proportions
Shows the pieta scene of Mary holding Jesus’s lifeless body over her legs, Jesus is skinny and emaciated, has thorns on his head and wounds all over his body
1300 CE
Germany
Made to humanize Jesus and depict him suffering, as opposed to previous depictions always showing him as strong, Jesus’s misery resonated with the European people who were suffering due to political turmoil and the plague

Arena (Scrovegni) Chapel
Brick and fresco
Trompe l’oeil: painting to resemble marble
Chapel built over a Roman arena, part of the Scrovegni Chapel, excessive ultramarine usage, very spacious interior, bland exterior, elaborate paintings on the walls
1303
Famous painter: Giotto, Padua, Italy
Commissioned by Enrico Scrovegni to atone for his father’s economic sins and beg Jesus and God for forgiveness by painting Christian narratives all over the interior walls
Lamentation Scene
Depicts figures surrounding Mary and a lifeless Jesus, uses foreshortening, depth, and back-facing people which is a major breakthrough and shows Giotto’s experimentation with perspective, Jesus is not in the center like he normally is

Adam and Eve
Engraving
Contrapposto, classical sculpture influence, idealized proportions
Depicts Adam and Eve in the Garden of Eden, a scene from Genesis where Eve eats the fruit from the Tree of Knowledge, surrounded by animals including the snake, has the artists signature
1504
Germany, Altrecht Dürer
The animals represent the four humors: cat-choleric, rabbit-sanguine, ox-phlegmatic, elk-melancholic, goat represents evil, mouse represents male weakness, parrot represents cleverness and mary giving birth

The Allegory of Law and Grace
Woodcut and letterpress, recreation of a painting
Protestant influences, bisected with a tree
Depicts the Last Judgement and Law, Moses and the ten commandments, and a skeleton and satan chasing a man into hell on the left, and a figure bathing in Jesus’s blood, and Jesus also emerging from his tomb on the right
1530
Germany, Lucas Cranach the Elder
The left represents Catholicism and Judaism, emphasizing the gospel and damnation through too much focus on money rather than devotion to God, the left represents Protestantism and being led to salvation through honoring the achievements of God
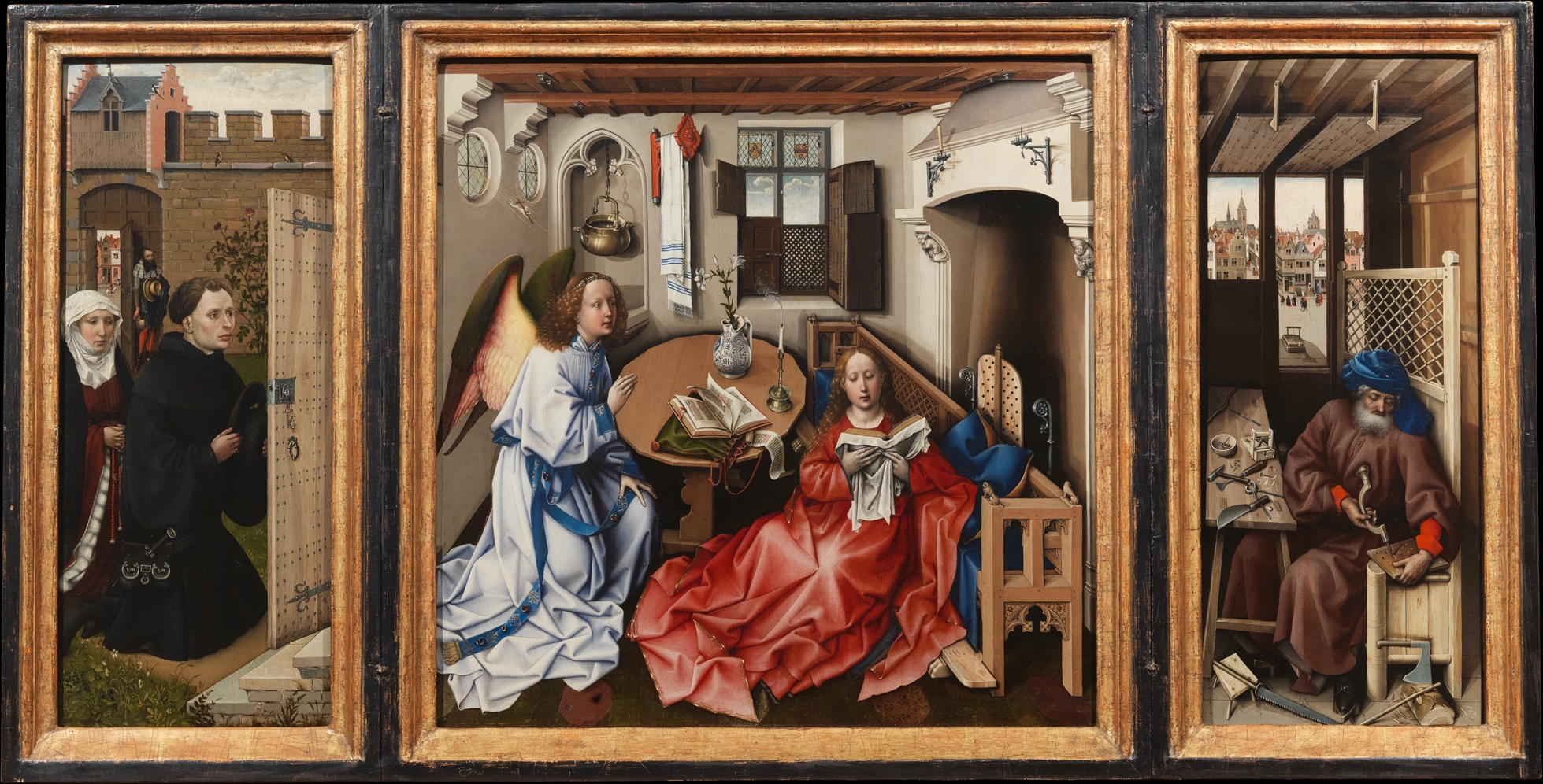

Merode Alterpiece - Annunciation
Oil on oak panel
Triptych, awkward perspective, humanized
Depicts the scene of Mary learning from the angel Gabriel that she will be the mother of God’s son, first picture are the patrons of the painting on the outside of the building, in the middle are Mary and Gabriel in a domestic setting, and on the right is Joseph in a carpentry workshop
1427-1428
Netherlands, Robert Campin
A small figure flies toward Mary, holding a cross to represent the Holy Spirit, the guard walls around the house represent Mary’s chastity, the fireplace is the entrance to Hell, the three flowers are the Holy Trinity, the wood items Joseph makes are Satan traps, everything was symbolism because Christianity couldn’t be depicted
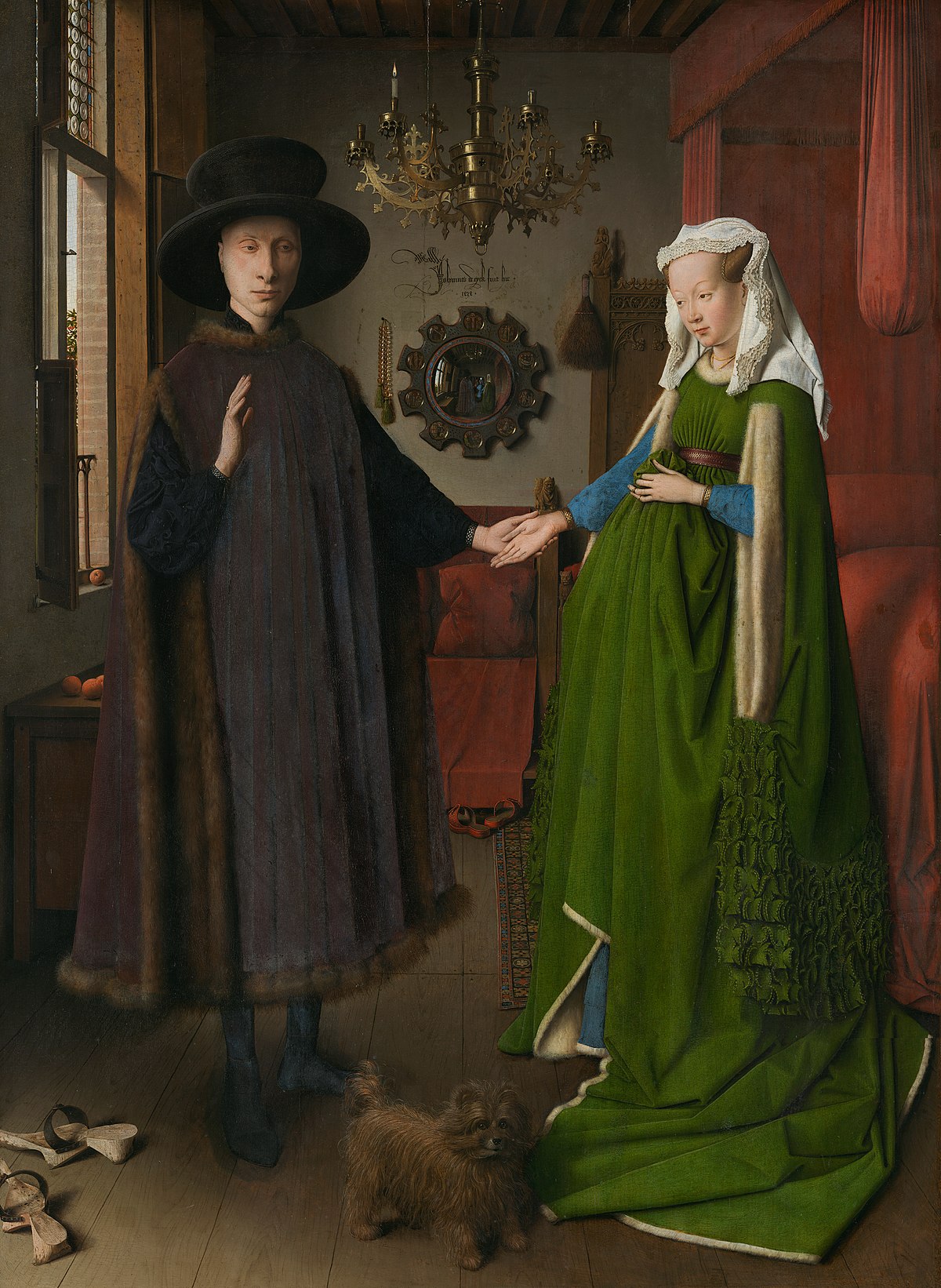

The Arnolfini Portrait
Oil on wood
Signature, Christian symbolism
Depicts a couple that has just married or possibly a memorial portrait, they stand in a room in front of a mirror
1434
Belgium, Jan Van Eyck
The elaborate fabrics and lace represent wealth, the single candle represents God’s presence, the dog represents fidelity, the roundrels in the back show biblical scenes, oranges must have been imported, praying St. Margaret of fertility on the bed, the man is near the window to show his role as a worker, the woman is by the bed to show her domestic role, the shoes are taken off to show they’re on holy ground, people shown in the mirror behind them
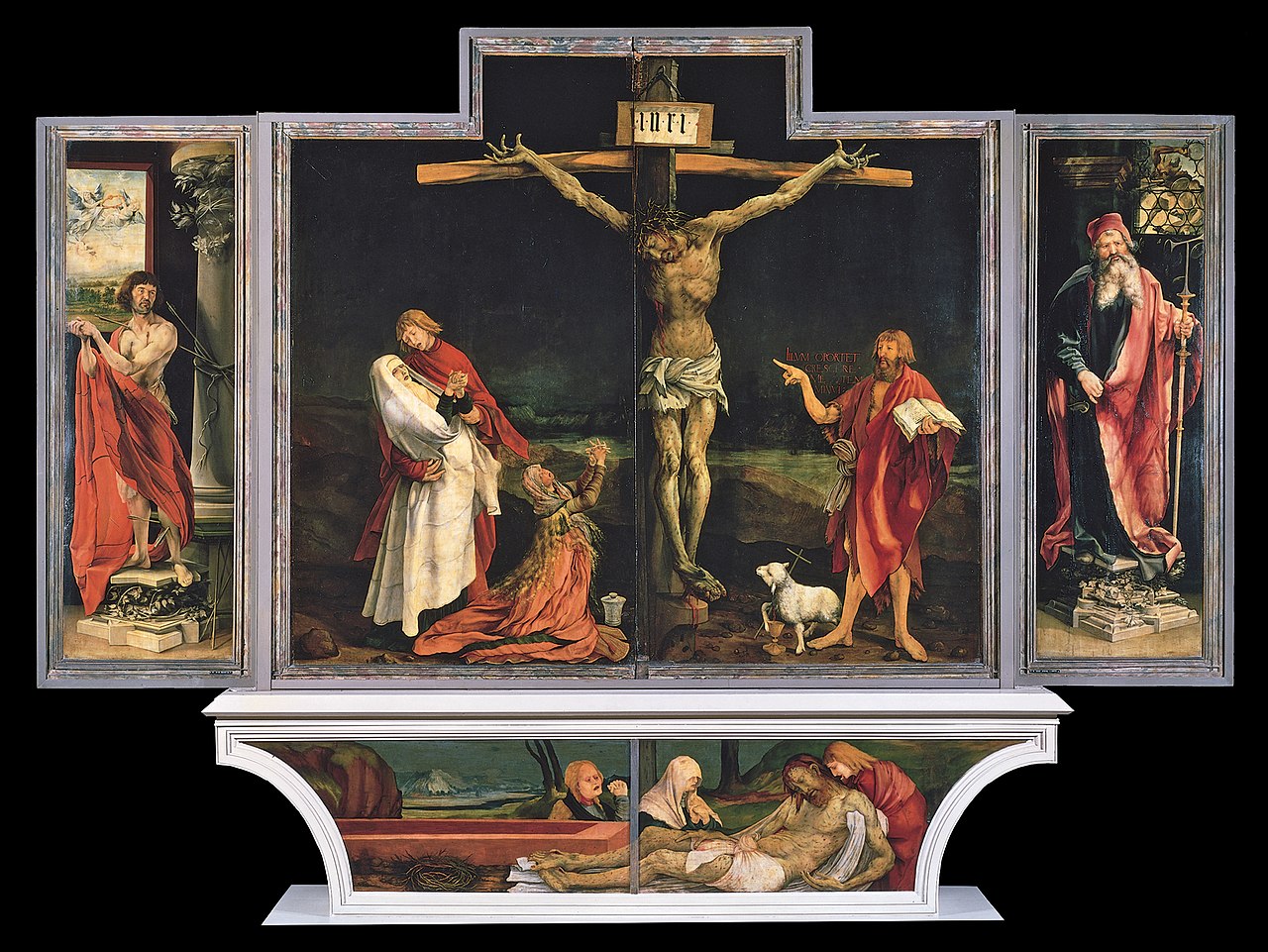
The Isenheim Altarpiece
Oil on wood
Registers, separated scenes, movable parts
11’ high, 1st panel shows Jesus suffering ergotism, 2nd panel showing Marian symbols and the resurrection, 3rd panel showing St. Anthony desert sojourn and temptation, predella (base) is the deposition and lamentation, the back is highlights of Christ’s life
1512-1516
Germany, Matthias Grünewald
Served as a decoration in a hospital for ergotism, a fungal skin disease, Jesus was shown suffering it to sympathize with the patients, Jesus’s resurrection showed he was freed from the suffering, instilled hope in the patients and encouraged faith
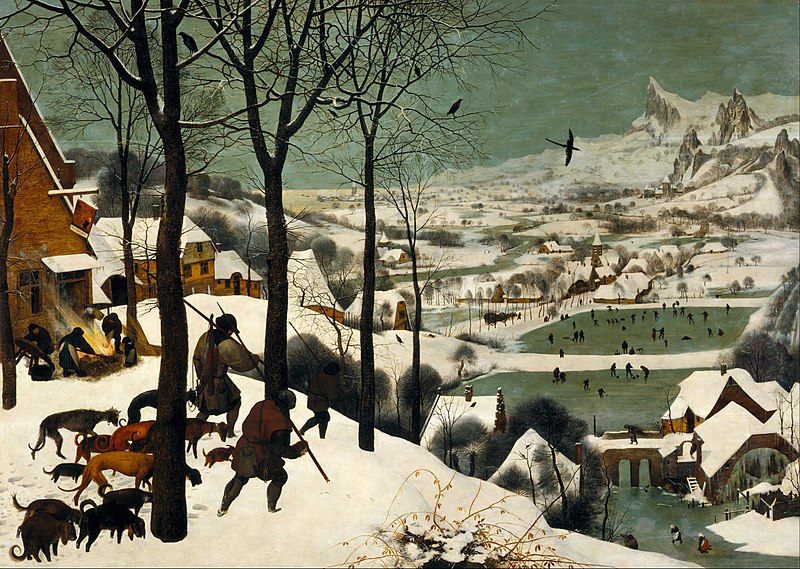

Hunters in the Snow
Oil on wood panel
Atmospheric perspective, landscape, anonymous people, part of a series, sharp, unblended colors
Shows a group of hunters overlooking a community scene in the winter, people on ice and many houses below the hill wher e the hunters stand
1565
Germany, Peter Bruegel the Elder
Meant to represent the good and bad parts of the season, good being the community and winter activities, bad being the hunters inability to catch anything, high horizon line so the viewer’s eye wanders around the painting

Pazzi Chapel
Masonry
Two parallel vaults, dome in center, Oculus, round windows at dome base, pilasters (fake columns attached to walls), roundrels, pendentives, terracota tiles with blues and grays
Chapel attached to Santa Croce church
1423
Florence, Italy, Filippo Brunelleschi (famous architect)
Commissioned by the wealthy Brunelleschi family, meeting house for monks, place for personal worship and devotion, resembles the Pantheon
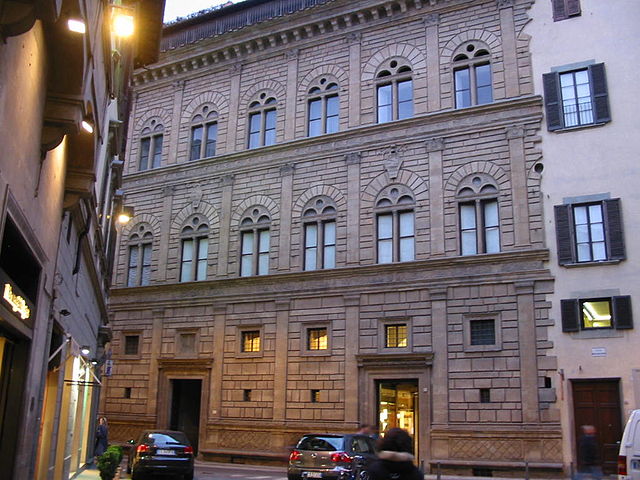

Palazzo Rocellai
Stone, masonry
Pilasters, different type on each floor, Tuscan, Ionic, Corinthian, square windows, arches, open atrium (similar to House of the Vetti), friezes with Ruccelai sails
House taking up an entire block in the city, lavish building with three floors
1450
Florence, Italy, Leon Baltista Alberti (famous architect)
Made to resemble to colosseum, 1st floor business, 2nd and 3rd floors are private quarters, order, harmony, and geometric grace
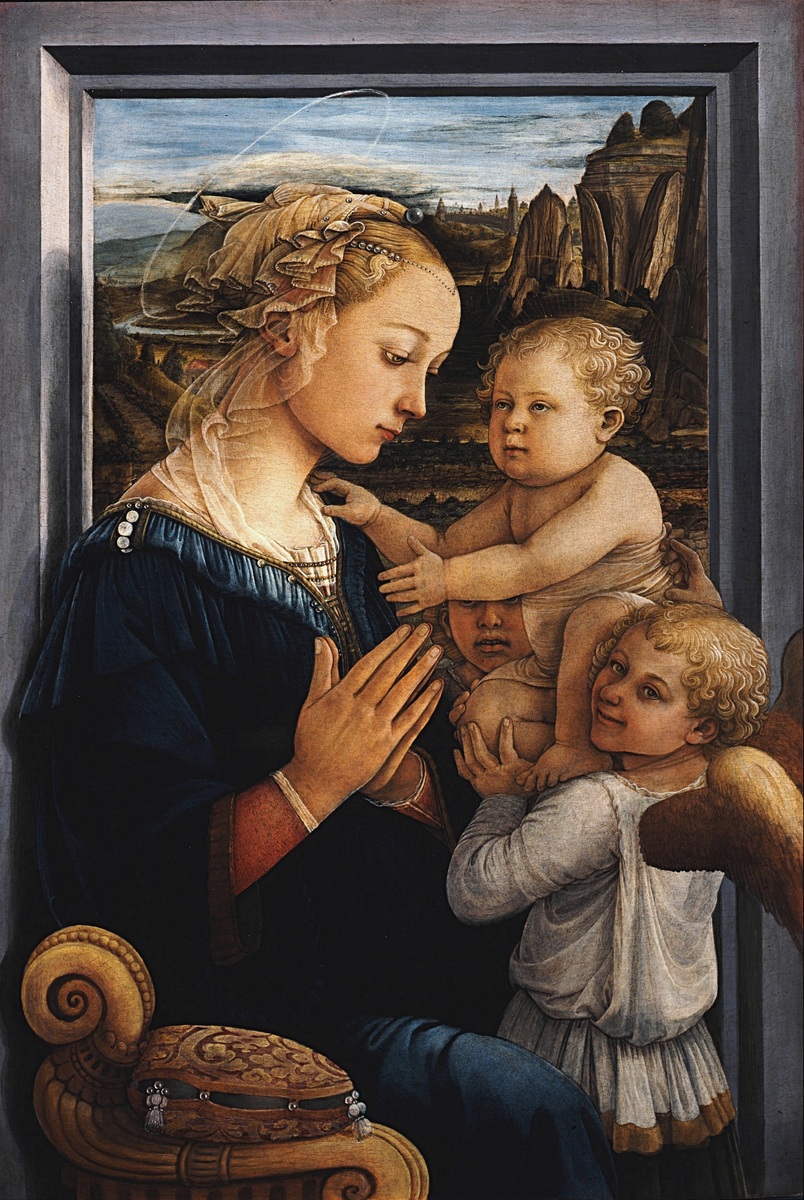

Madonna and Child with Two Angels
Tempera on wood
Window and frame illusion (trompe l’oeil), landscape, humanistic
Mary and baby Jesus depicted, two angels holding up Jesus, Mary is solemn and praying, landscape in background, slight halo over Mary
1465
Florence, Italy, Fra Filipo Lippi
Playful Jesus to look like a kid not an old man, both young and realistic, pearls and pillows represent Mary’s immaculate conception, city on the left to represent Jerusalem, rock formations meant to resemble a church
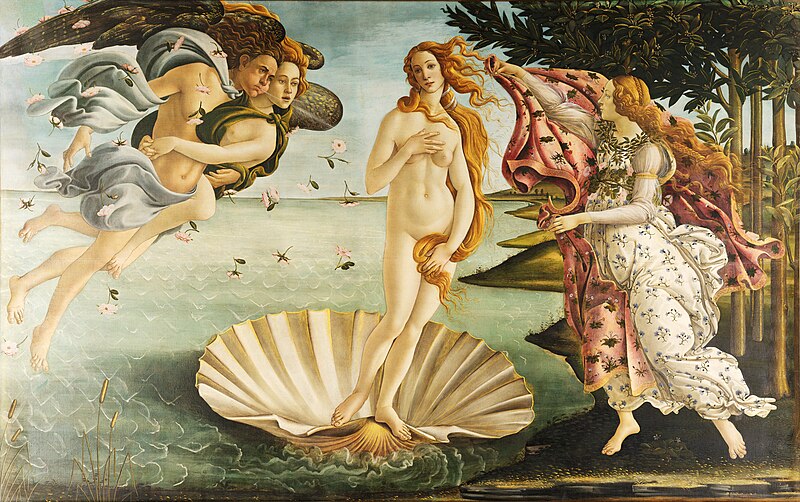

The Birth of Venus
Tempera on canvas
Contrapposto, departure from Christian imagery with female nudity, revival of Greek goddesses, flat background and lack of perspective
Shows Venus being born from the sea, west winds and a nymph to her left
1485
Sandro Botticelli
The roses represent the chaos of love, Venus represents love and also modesty, shows her birth
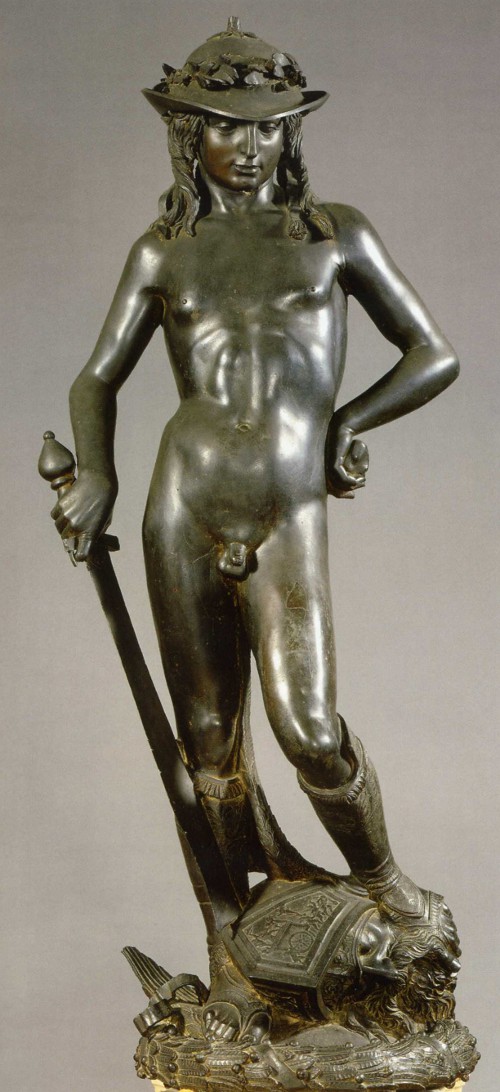

David
Bronze casting (revival from Rome!)
Roman influence, somewhat androgynous, exaggerated contrapposto
Shows David after he killed Goliath, standing in a sassy pose, Goliath’s head under his foot, holding a sword
1440-1460
Florence, Italy, Donatello
Likely made for the Medici palace, shows him proud, but also shows modesty from the downcast eyes, hat is in a renaissance design
The Last Supper
Tempera and oil (they don’t mix, it’s falling apart)
Fresco, linear perspective, vanishing point on Jesus, attempt of chiaroscuro (sharp contrasts between dark and light), individualized, dynamic poses, arcadian setting (ideal) background, grouping of threes, eucharist motif of bread and wine,
Shows Jesus and the 12 apostles at the last supper before the crucifixion, directly after Jesus says “one of you will betray me”
1494-1498
Milano, Italy, Leonardo Da Vinci
Jesus and Judas reaching for the same bowl represents the eminent betrayal, groupings of 3 represents the Holy trinity and becomes a trend, commissioned for a refectory (dining hall) over where monks eat

The Sistine Chapel
Frescoes
Complicated arrangements, emphasis on anatomy, dramatic gestures, large figures, dynamic, narratives from the Old Testament, ignudi (random naked men), idealized figures
Ceiling and backwall frescoes, depicted scenes from the Old Testament, some Pagan stories, Greco-Roman symbols and figures, acorn motifs (crest of Pope Julius II)
1508-1512, then 1536-1541
Vatican City, Michelangelo (Botticelli and Pereguino also contributed)
New popes are elected in the chapel, Michelangelo is commissioned by Pope Julius II who he hates, Michelangelo was gay so he conflicted with the church, did his last fresco extremely late out of spite
Notable frescoes:
Creation of Adam
God is in a cross section of the brain, is he made up?
Delphic Sybil
Pagan, one of 5 sybils/prophetesses (fortune tellers fore-telling the coming of Christ)
premonition and prophecy were common christian themes
Greco-Roman figure inspiration, paranoid, male model was used, biblical beauty, Greek turban, contrapposto, humanism, knowledge of anatomy
The Flood (The Deluge)
story of Noah, survivors clinging to mountaintops as the arc is built in the background
dramatic range of emotions, varied expressions and poses, clumped figures
igundi in the four corners
atmospheric perspective, unbalanced
Altar Wall Frescoes
mannerist era
end of Michelangelo’s life
The last judgement
horror vacui
Top Banner: crucifixion, Mid 1: heaven around Jesus, Mid 2: some people rise, some descend, Bottom: dead rising, shows entrance to Hell
reflective of the chaos and disunity
a lot of creative liberties, buff Jesus with no beard???, crazy weather, naked people
draperies painted on after Michelangelo’s death
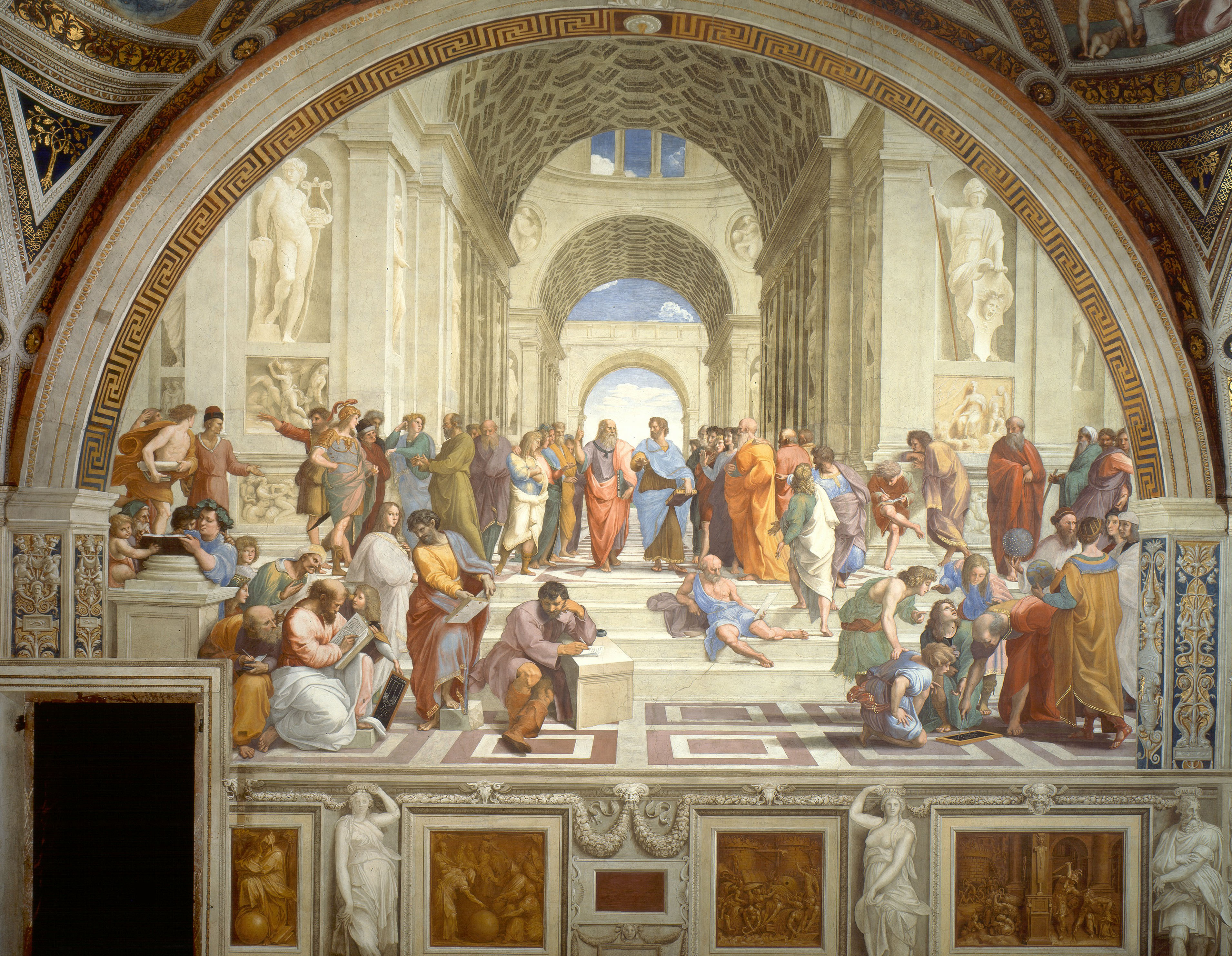

The School of Athens
Fresco
Linear perspective, classical architectural designs, arches, statues, columns, clear, open light setting
Depicts Ancient Greek philosophers among modern philosophers on the same level
1509-1511
Apostolic Palace, Vatican City, Raphael
Commissioned for Pope Julius II’s library, hung over the philosophy section to represent the books, showed modern connections to past beliefs, gestures and clothing represent the philosopher’s views
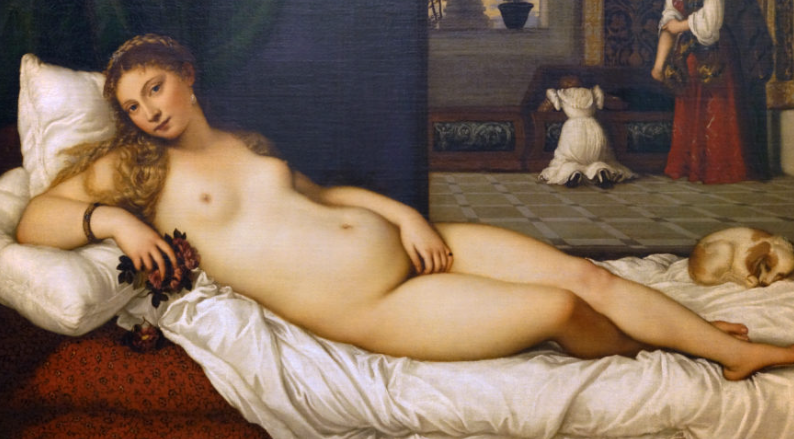

Venus of Urbino
Oil on canvas, vermillion and ultramarine blues (from Silk Road
Chiaroscuro, softer manner, arcadian setting, recling female nude trend, sfumato
Depicts a nude woman laying on a bed, facing the viewer, seductive gaze, covering in between her legs with her hands, holding roses, a dog lay by her feet, a maid and child doing laundry in the back
1538
Venice, Italy, Titian
Commissioned by a husband for his new wife, meant to show how his wife should be, modest, dog represents loyalty, roses represent love and sensuality, women doing chores in the back to show how she should work for him
Entombment of Christ
Oil on wood
Circular composition, mannerist, ragdoll effect with limbs, weightlessness, inaccurate proportions, crouched and twisted composition, flattened 3D space, inconsistent light/shadows, no ground line or linear perspective, acidic colors
Depicts a group of people in the scene following Jesus’s removal from the cross as his dead body is held and his followers cry out
1525-1528
Florence, Italy, Jacopo de Pontormo
Represents the chaos of society in the mannerist era, placed in an altarpiece in a chapel
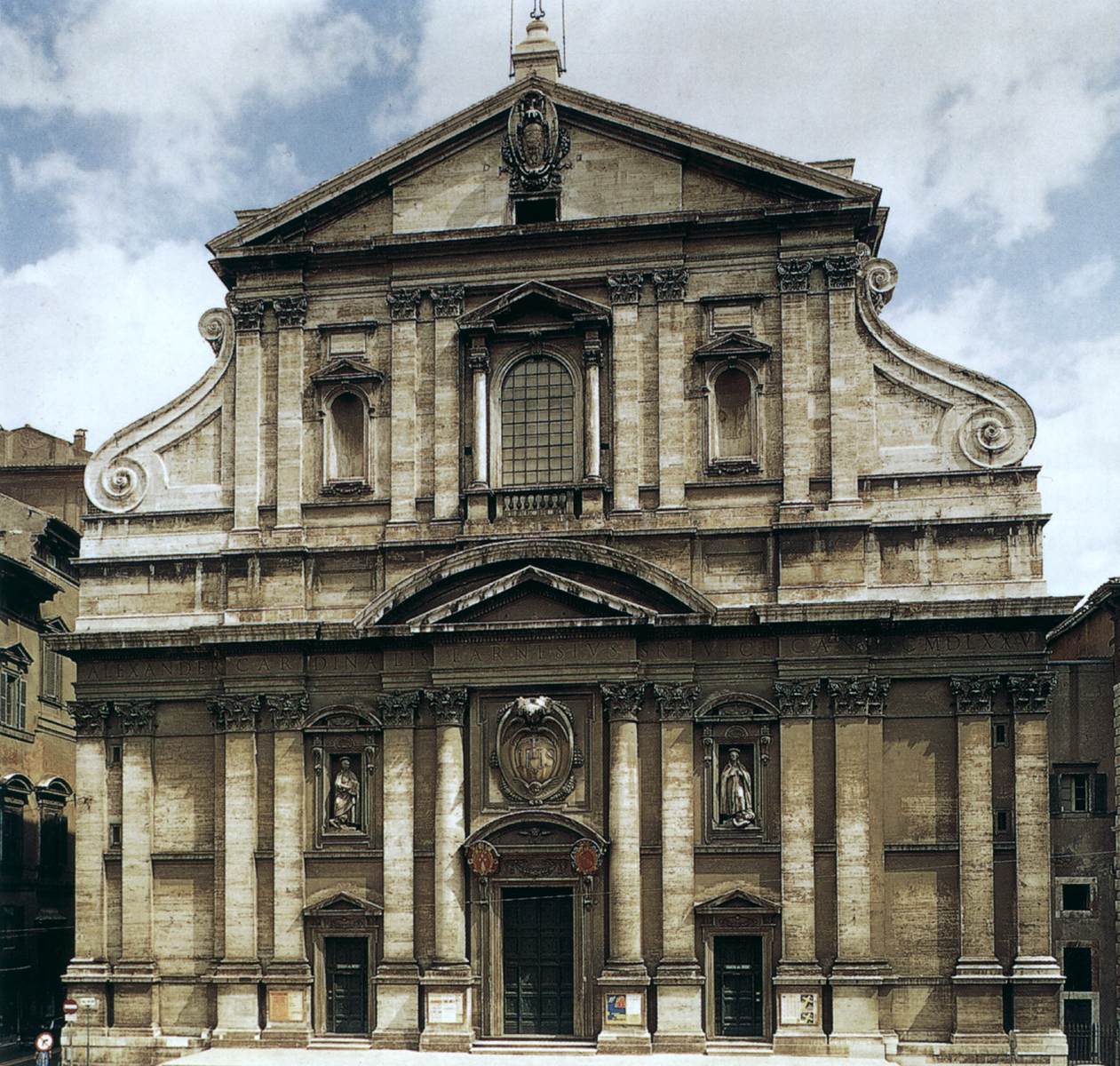

Facade of Il Jesu
Brick and marble
Classical architecture, mannerist exterior, ionic pilasters, timpanums, framing niches
Church building, white
1575-1584
Rome, Italy, Giacomo della Porta
Marks a transition between mannerist and baroque styles, mother church of Jesuit orders, Jesuits were priests that opposed the reformation
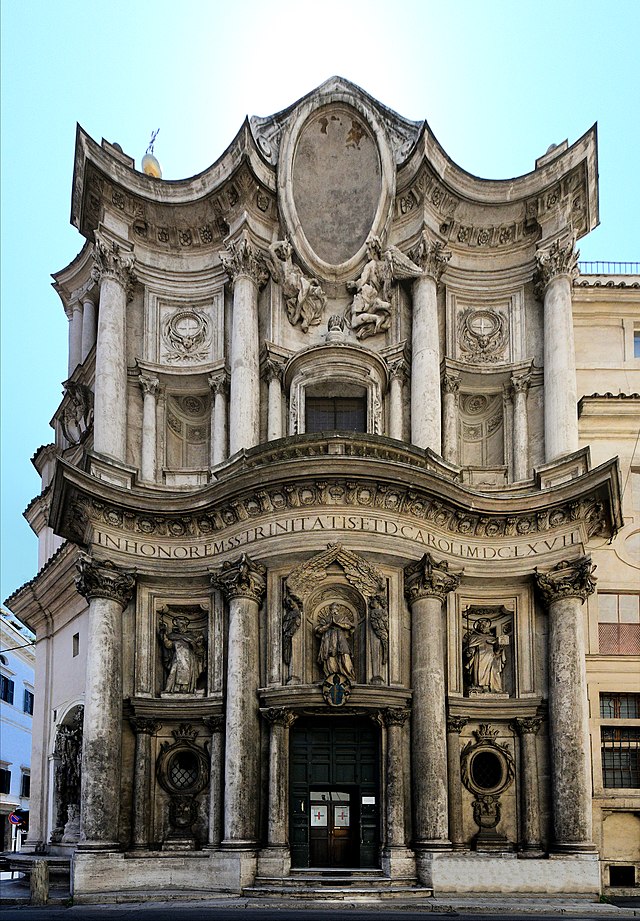

San Carlo alle Quattro Fontane
Stone and stucco (inexpensive and malleable material for building)
Retrofitted into a smaller space, baroque, soft corners, coffered oval dome ceiling, corinthian columns, niches, floating dome effect, modified central plan
Irregularly shaped chapel to fit a small space on the street, in a square with four fountains, highly decorated, wavy exterior, white and gold trims
1638-1646
Rome, Italy, Francesco Borromini
Small, but a major symbol of baroque architecture, small monastery for monks
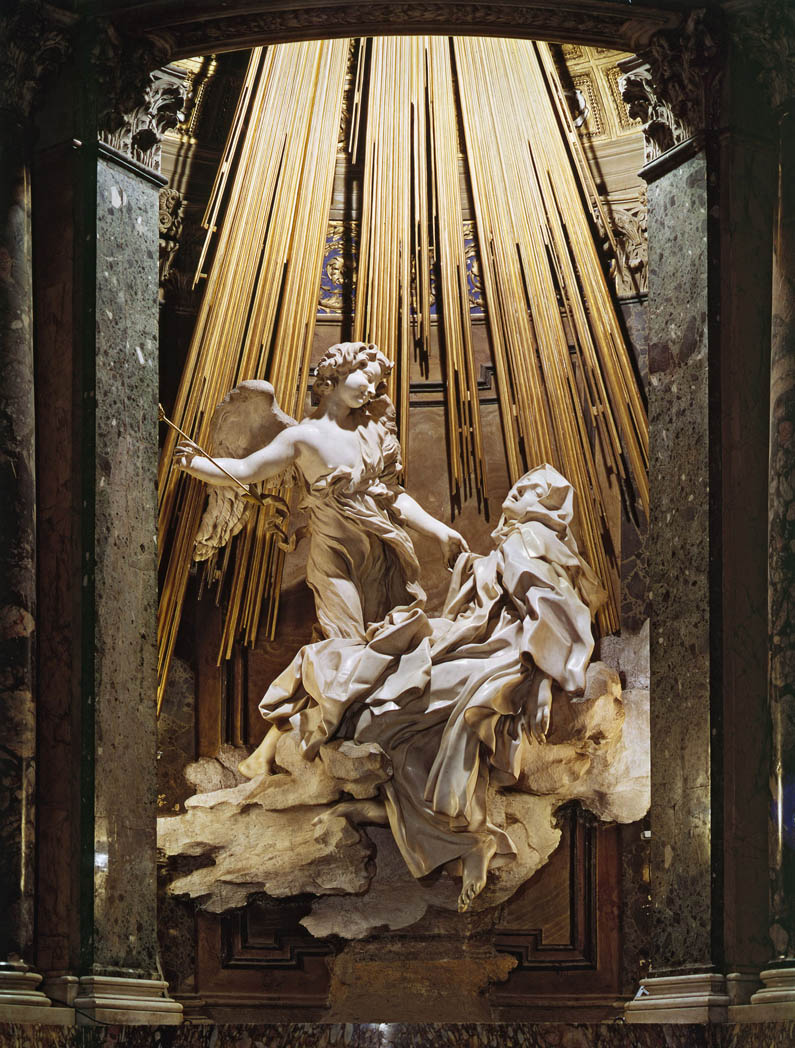

Ecstasy of Saint Teresa
Marble, stucco and gilt bronze chapel
Tenebrism, warm glow against dark chapel, classical inspiration, dramatized
Depicts Sainte Teresa getting stabbed in the “heart” by an angel and experiencing a lot of satisfaction and sensual pleasure, theatre boxes with patrons surround the statue, theatre stage is set up
1647-1652
Cornaro Chapel, Rome, Italy, Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Bernini was very interested in theatre, inspiration is taken from Saint Teresa’s diary, Teresa was obsessed with God’s love and would hurt herself to recreate the pain Jesus felt

The Palace of Versailles
Masonry, stone, wood, iron, gold leaf, marble and bronze sculptures
700+ rooms
Elaborate palace designed around Louis XIV’s room, architecture meant to look like sunrays off of the central bedroom, included a chapel, dozens of court apartments, living spaces for servants and staff, opera house, gardens and greenery
1631-18th century
Right outside of Paris, France, Louis Le Vau & Jules Hardouin-Marsart, Andre le Notre
Built to house Louis XIV and honor his achievements, as well as show off his lavish lifestyle, gardens would be the staple of modern landscaping, showed major gap between lower and upper French people (what would they end up doing about it?)
Hall of Mirrors
240’ corridor
Barrel vaults
Ceiling paintings to show Louis’ achievements
Lined with large, expensive glass panels
Held court events and receptions, very showy
Marble Courtyard
Elaborate and more ornate than the front
Covered in gold leaf
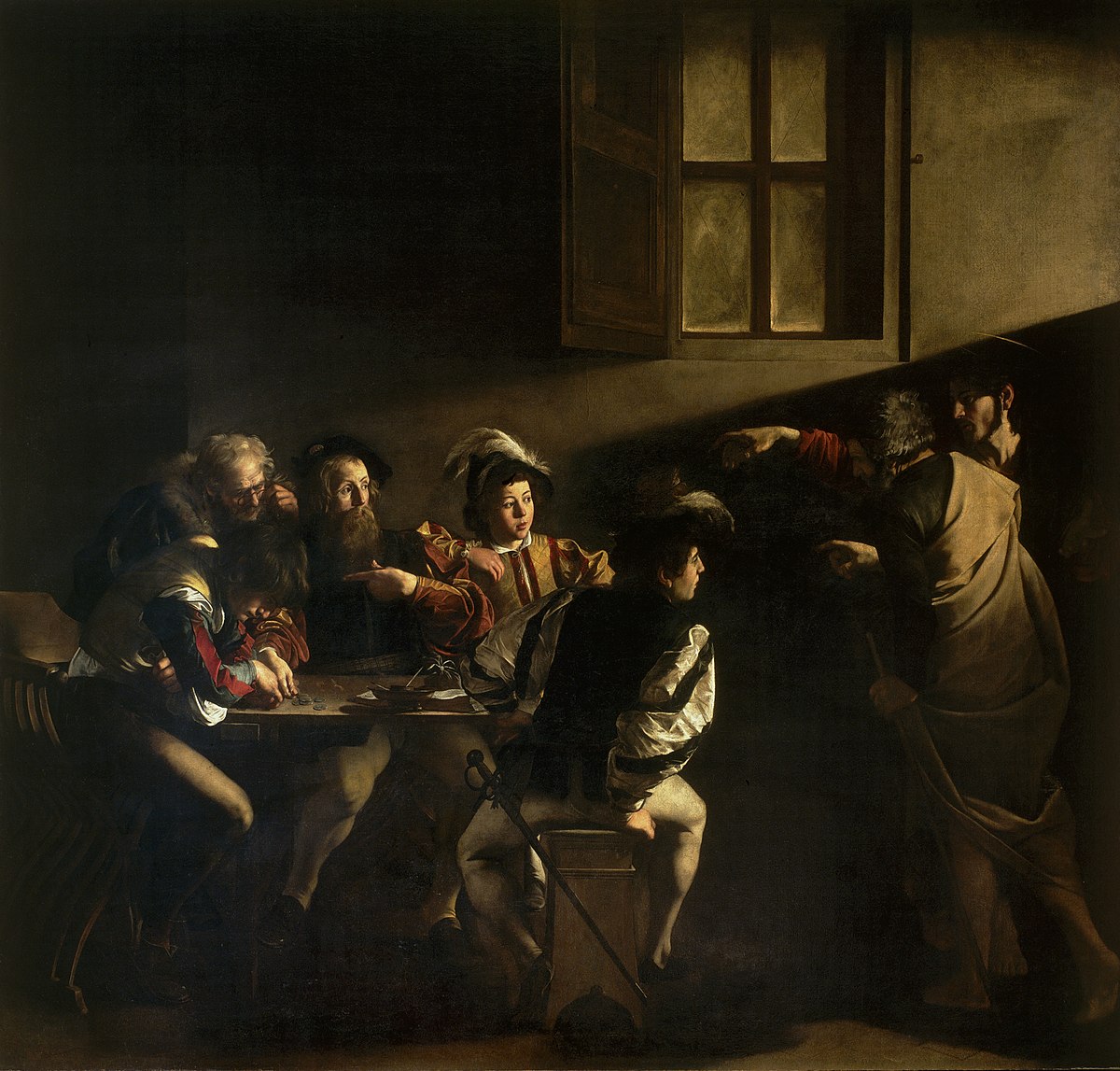

The Calling of Saint Matthew
Oil on canvas
Crowded figures, Baroque style clothing, tenebrism
Depicts people inside a tavern, counting money, looking sketchy, Jesus with a faint halo points at Matthew, who points at himself, a light source points and illuminates Saint Matthew
1600
Rome, Italy, Caravaggio
Meant to show average people could turn away from sin and be saved, shows Matthew getting called out for his shady behavior and turning toward Jesus, Caravaggio was alternative and controversial for his time, he showed the darker sides of Christianity, one of 3 paintings made to show St. Matthew’s life

Triumph in the Name of Jesus
Stucco and fresco
Foreshortening to make figures appear coming down toward the viewer, 3D illusion, trompe-l’oeil di sotto in sú (from below to above), painted shadows, bright lights
Depicts damned being cast into Hell, angels ascend
1661-1679
Il Gesu, Rome, Giovanni Battista Gaulli
Dramatic because of Bernini influence, showed damned falling into the chapel below, Jesus monogram of IHS

Las Meninas
Oil on canvas
Tenebrism, atmospheric perspective, dense bottom and a lot of negative space at the top, asymmetrical composition, candid moment, 10’ x 9’
Depicts Infanta Margharita of Spain in the center, surrounded by a dog, two dwarves, her servants, nuns and clergy, her parents (either in a mirror or in a painting on the wall), and the painter himself working on a painting beside them
1656
Madrid, Spain, Diego Velasquez
Infanta Margharita was a member of the Habsburg family who were severely inbred but very wealthy, Velasquez worked as their court painter and was commissioned to paint them in pretty clothing and make them look more attractive than they were, the dwarves on the side were used for entertainment
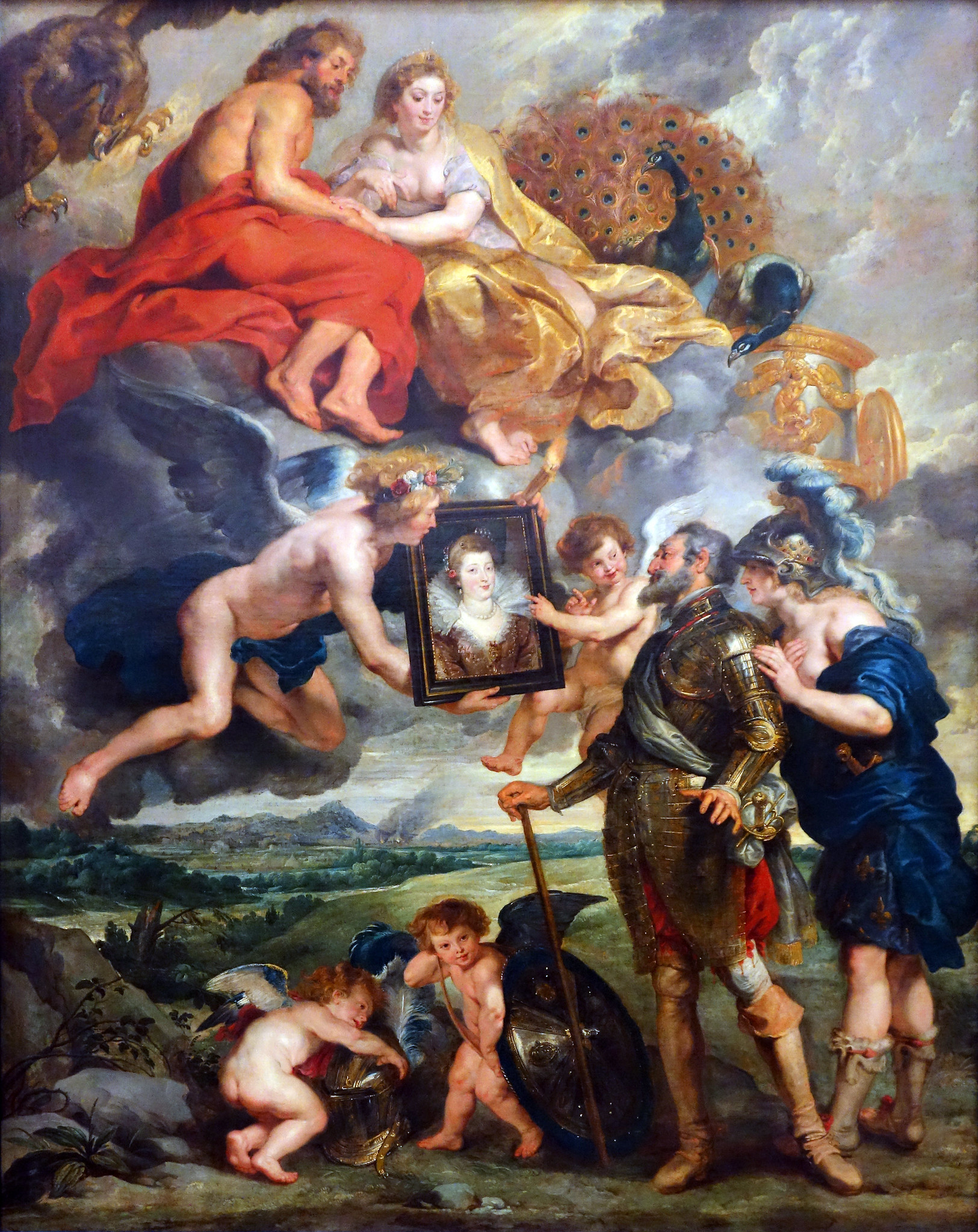

Henry IV Receives the Portrait of Marie de Medici
Oil on canvas
Roman and Christian figures
Shows the scene of Henry IV receiving the portrait of Marie de Medici whom he would marry, Juno and Jupiter, Cupid and Hymen, a woman with masculine features, cherubs
1625
Peter Paul Ruben
One of 21 paintings of Marie de Medici’s life, a lot of her life was made up, Henry IV didn’t even like her or attend the wedding, he was very unfaithful to her, Juno and Jupiter symbolize unity even though they were unfaithful to each other, Cupid and Hymen represent love, the woman behind Henry represents France urging him to choose love over war, helmet and shield are being cast aside

Self Portrait with Saskia
Etching/sketch
Northern European Baroque intimacy and quietness, preliminary art, non-contemporary clothes
Depicts Rembrandt with his wife sitting next to each other, both staring at the viewer, Rembrandt’s signature on the top corner
1636
Leiden, Netherlands, Rembrandt
Personal, intimate sketch not meant for public view, shows a private and domestic moment between Rembrandt and his wife Saskia
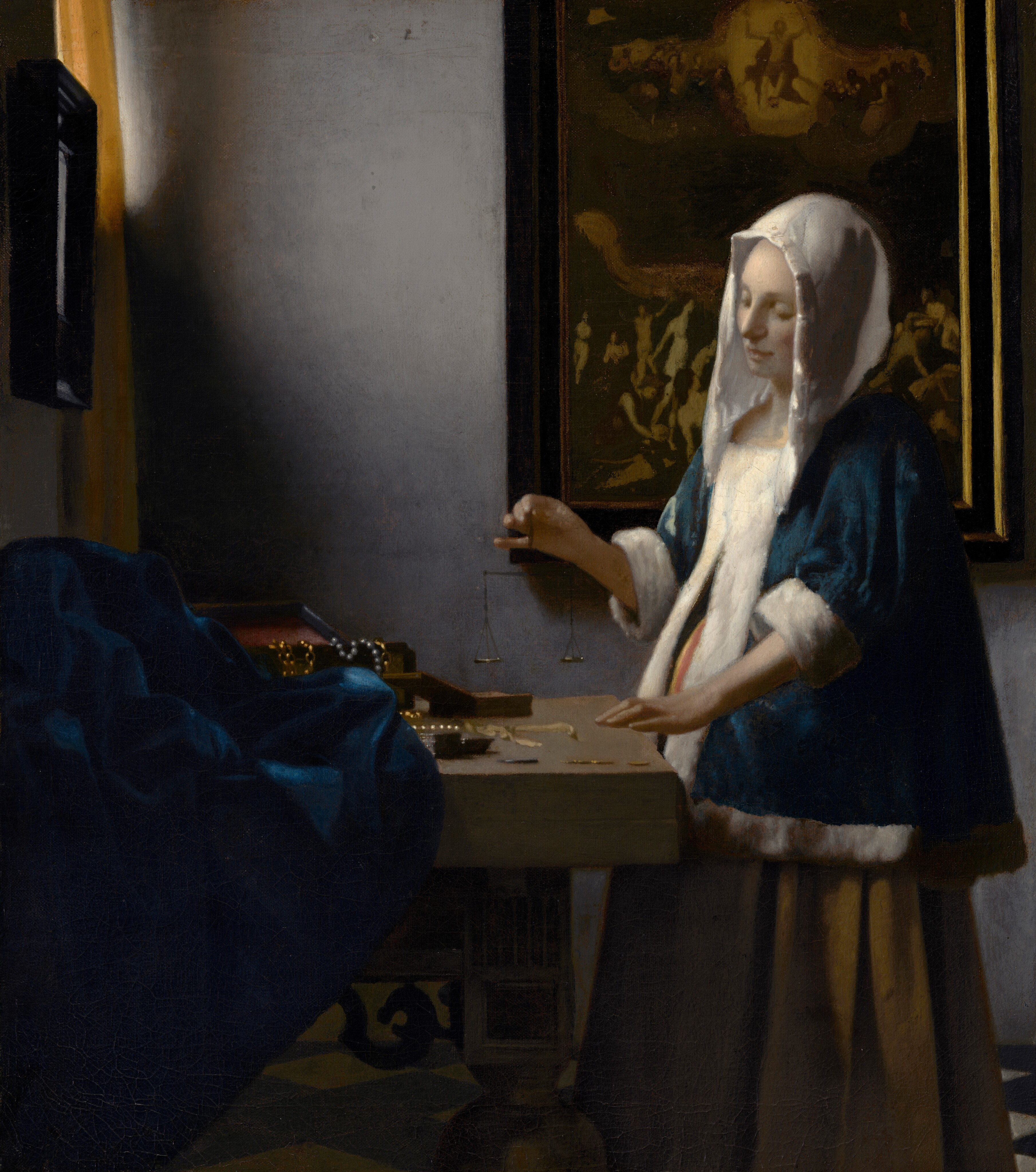

Woman Holding a Balance
Oil on canvas
Intimate, sparsely illuminated space, tenebrism, clear and highly rendered textures, balance, Northern Baroque influence, dark and muted colors, vanitas theme of falling beauty and brevity of life
Depicts a young woman holding a balance on a table, the window slightly illuminates her, gold on the table, Last Judgement painting behind her
1664
Netherlands, Johannes Vermeer
Balance of wealth and piety, center of the balance is in the exact center of the painting, balance represents judging along with the painting
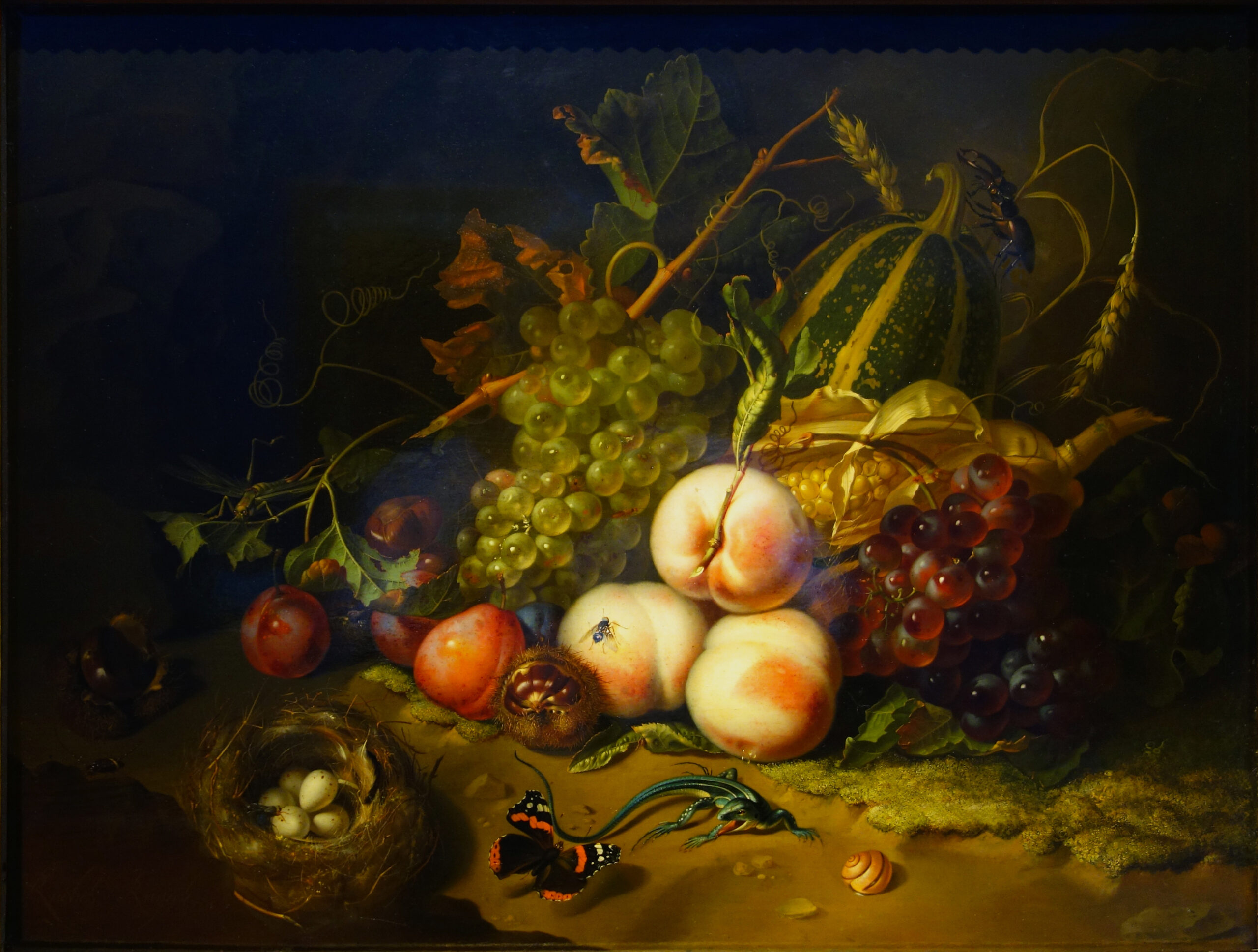

Fruits and Insects
Oil on wood
Tenebrism, still life, creative liberties, dramatic lights, vanitas motif, asymmetrical
Shows various fruits and vegetables arranged on a table surrounded by brightly colored bugs, very vibrant contrasted against a dark background
1711
Netherlands, Rachel Rusych
Grapes and wheat symbolize the eucharist, the fly eating away at the fruit symbolizing the vanitas theme, this was created for personal decoration, Rusych had the opportunity to be an artist since she could study off of her dad who was a botanist and studied anatomy, many female artists lacked this opportunity since they couldn’t be alone with men for art lessons

Frontispiece of the Codex Mendoza
Pigment on paper
Registers, eagle and cactus motif
Depicts daily life and battle scenes of the Aztecs, founding of Tenochtitlan, conquests, leaders, shows nine founders and one priest doing blood-letting, X for the intersection of two waterways
1542
Native artists, Aztec Empire, Modern day Mexico city
Commissioned for Antonio de Mendoza, viceroy of New Spain, meant to show Charles IV what Aztec life was like, food to show their agricultural prosperity, eagle landing on cactus was their sign to settle that land for the Aztecs, part of a codex (book) of tributes to the Aztecs
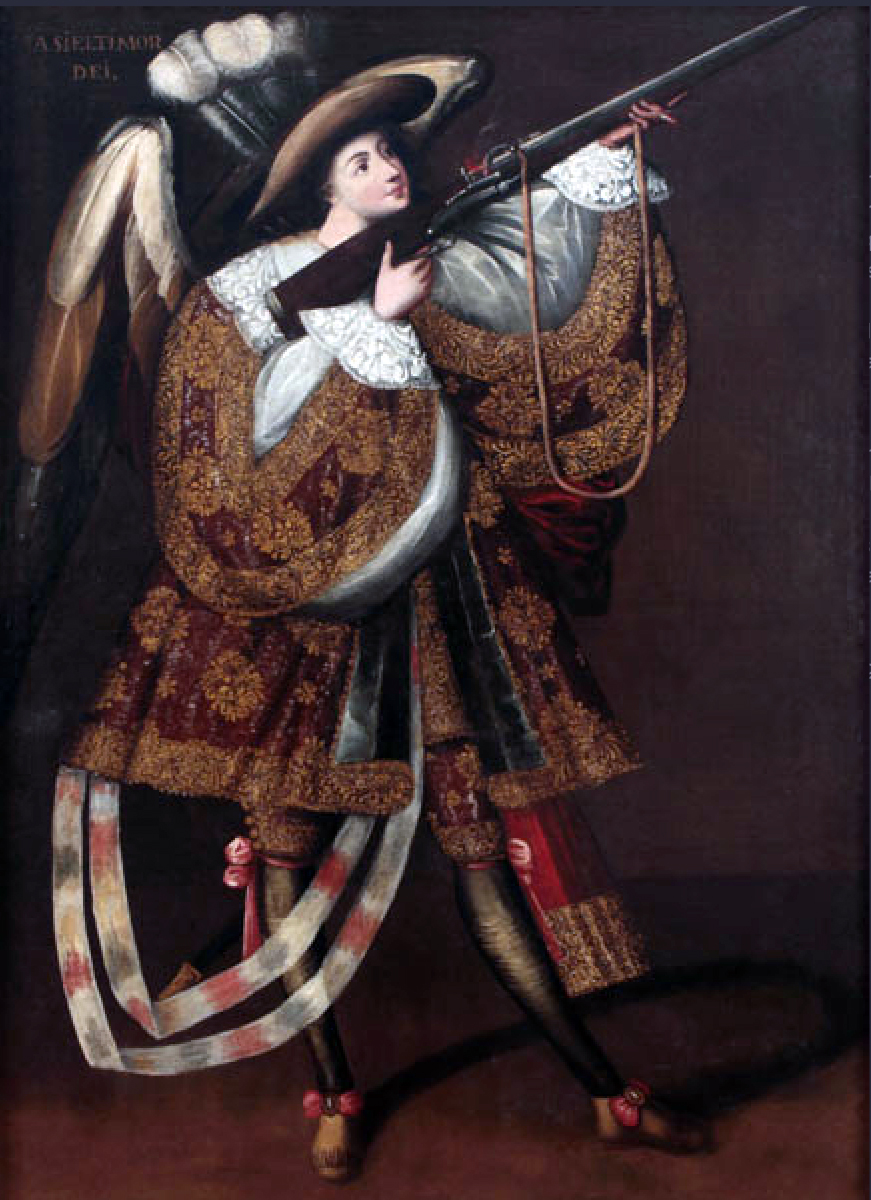

Angel with Arquebus, Asiel Timer Dei
Oil on canvas
Secret depiction of angels (-siel means angel), Mannerist and Baroque influence from clothing and dramatic pose, influence of pre-columbian Aztec winged figures, Spanish aristocratic clothing, gold threads
Shows a subtle angel with lavish Spanish clothing and elongated features pointing a gun upwards
1680
Andes region, Master of Calamarca
Angel depiction was banned since 1550, so depictions were subtle now, shows Spanish and native influence in art, celestial, aristocratic, and military combination, guardian figure
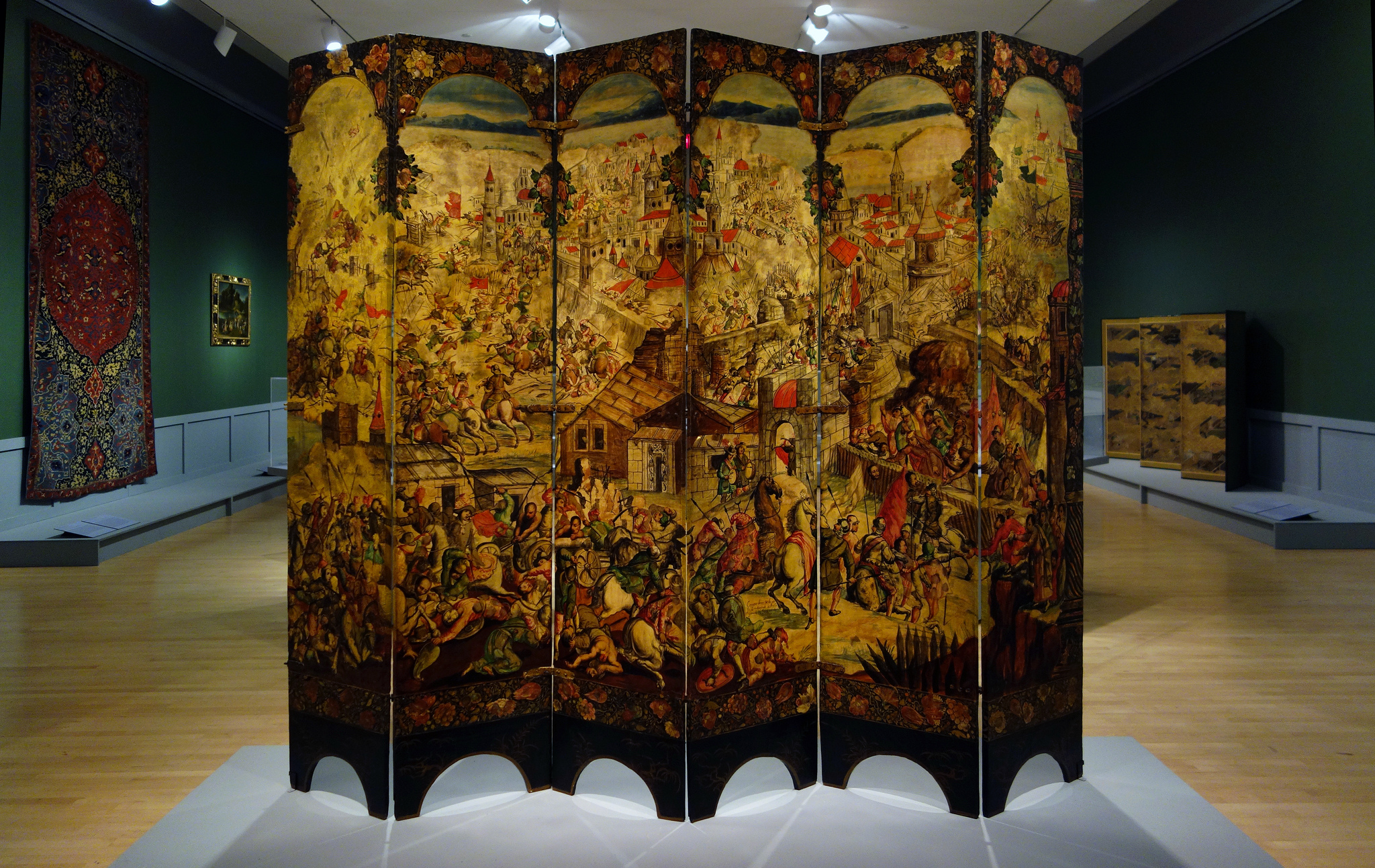

Screen with the Siege of Belgrade and Hunting Scenes
Tempera and resin on wood, inlaid with mother-of-pearl (encorchadas)
Folding, free-standing biombos, encorchadas inspired by Asian work, hierarchy of scale, bug red pigments
One side shows a war scene and the Habsburg family victory, the other side is less chaotic and shows a hunting scene, pastoral setting for private viewers
1697-1701
Modern-day Mexico, circle of the Gonzolez family
Shows Japan influence coming to the New World, inspirations from Asian lacquer work, honors the Habsburg family, created as a room divider, separated male and female audiences

Virgin of Guadelupe
Oil on canvas on wood, mother-of-pearl inlay
Roundrels, econchadas, eagle and cactus motif
Shows the Guadelupe event where Juan Diego encounters Mary on a hill where an Aztec shrine is, roses bloom everywhere, he goes to tell the archbishop, roses fall out of his tunic and Mary’s image appears, and he follows Mary’s orders to build Mary a shrine on that hill
1698
Spain, Miguel Gonzalez
Used as a symbol of aid and guidance in Mexican culture, very iconic, always depicted standing on a crescent moon held up by angels, illuminated by sun rays, 12 star crown, dark skin depiction made her appreciated by the Mexicans, created for export and reverence
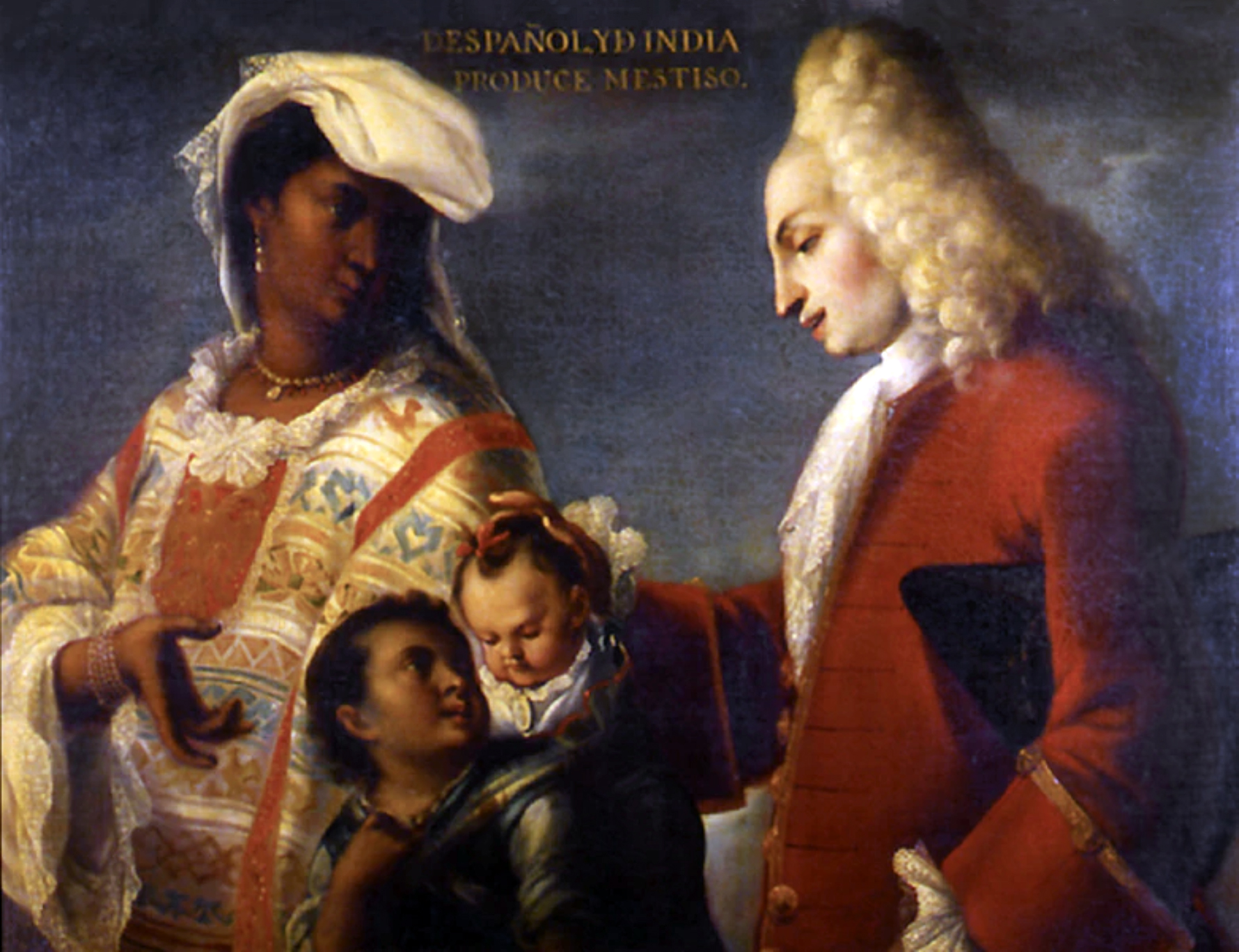

Spaniard and Indian Produce a Mestizo
Oil on canvas
Casta painting, informal and stereotypical
Shows a white Spaniard and a native woman and their mixed child against a dark background
1715
New Spain, Juan Rodriguez
Part of a series of 16 paintings showing what New Spain was like to Old Spain, the paintings illustrated the caste system which held white couples at the top and enslaved people at the bottom, mestizo children were stereotyped as humble, quiet, and simple, inspired by racist Enlightenment thinking that statues was based off biological race

Portrait of Sor Juana Ines dela Cruz
Oil on canvas
Symbols of wealth and intelligence, escudo (framed oval painting)
Shows Sister Ines in her library reading and wearing religious clothes
1750
Mexico, Miguel Cabrera
Shows Sister Ines, who became a nun to avoid marriage, published and read books, primarily theatre and poetry, very intelligent and taught other girls in the New World, headdress to show her nun habit, painted from her self portrait, purchased by admirers after her death
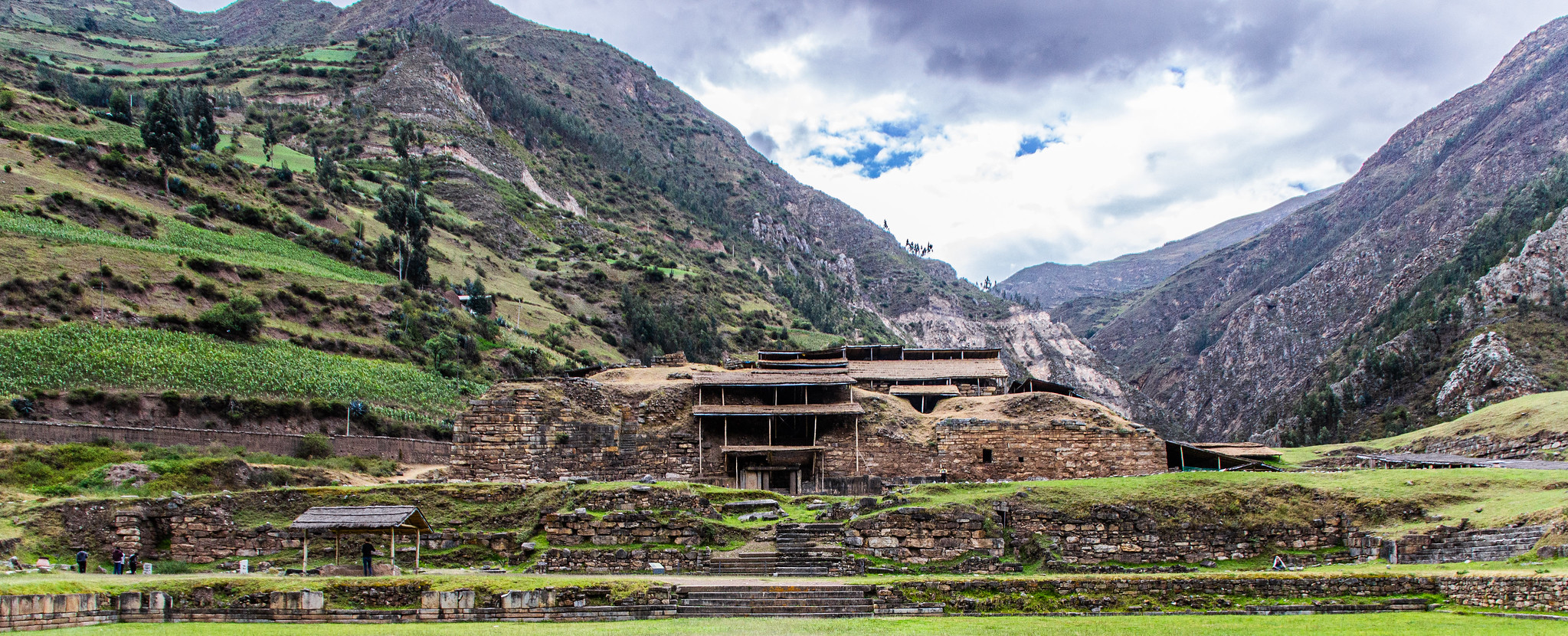

Chavin de Huantar
Stone and granite
Sides aligning with four cardinal directions, break in the Andes mountains, pilgrimage point
200’ tall, 10,000’ above sea level, two main buildings, old and new temple, sunken plazas for gatherings, flanked a river
900-200 BCE
Northern Highlands River, Peru, Chavin Empire
Powerful center, influential pilgrimage point
Lanzon Spear Lintel
-contains a hidden entrance in the old temple, with over a mile of tunnels underground
-acoustics used to project words of the gods
-lanzon spear is likely the patron deity
-15’ tall, blade shaped, low relief
-resembles a digging tool used for highland agriculture
-figure looks up and down connecting heaven and earth, cut on forehead to allow bloodletting and liquid offerings
-figure with human and animal features, jaguar face, snake head, claws, anthropomorphic
Nose Ornament
-worn by men and women
-gold alloy
-snake heads looking
-high status, indicates wealth or spiritual transformation
Granite Stone
-contour rivalry
-found in a stairway
-jaguar heads and snakes