Chapter 5 - skeleton
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Arthr/o
joint
Brachi/o
Arm
Carp/o
Wrist
Cervic/o
Neck
Chondr/o
Cartilage
Cost/o
Rib
Crani/o
Cranium
Dactyl/o
Finger, toe
Kinesi/o
Movement
My/o
Muscle
Myel/o
Bone marrow
Orth/o
Straight
Os/te/o
Bone
Ped/o
Foot, child
Spondyl/o
Vertebrae
Thorac/o
Chest
Main points about the skeleton
206 Bones
Articulating framework for muscles and other tissues
Protects vital organs
Stores minerals
Makes blood cells
How many parts is the skeleton divided into?
2
what are the 2 parts called?
Axial & Appendicular
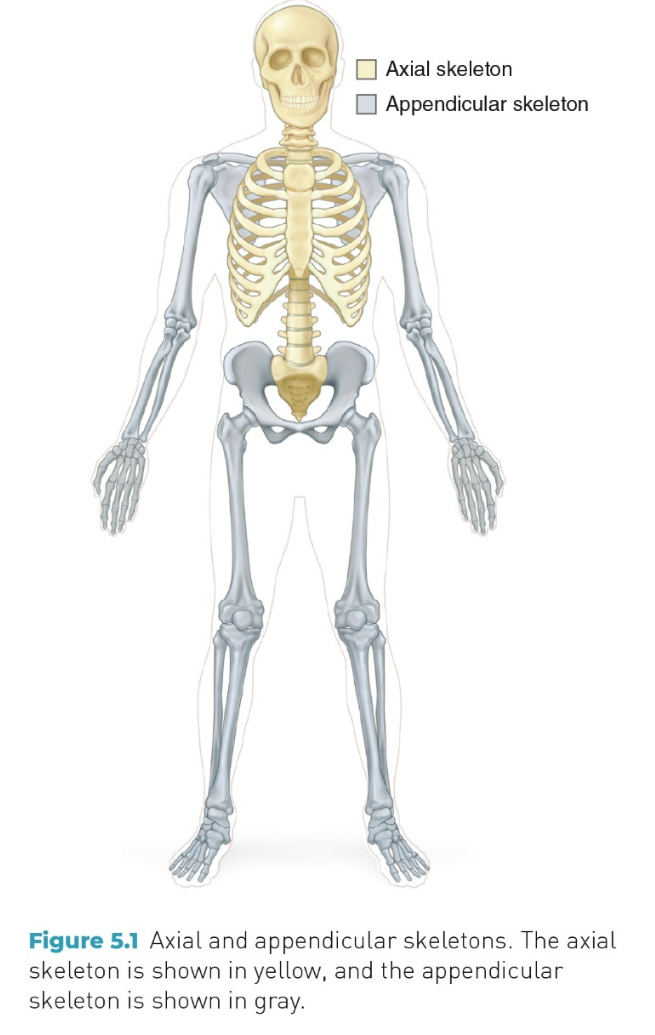
Axial
Skull
chest
spinal column
Appendicular
Arms
legs
shoulders
pelvic bones
What is the band of tissues which connect two bones together?
Ligaments
What attaches muscles to bones?
Tendons
What is the place where bones comes together?
Joints ( Articulations)
what is ossification?
The bone formations. It begins in the early fetal development where the skeleton is mainly al cartilage.
What connects tissues with mature bone cells which is called Osteocytes?
Osseous tissue
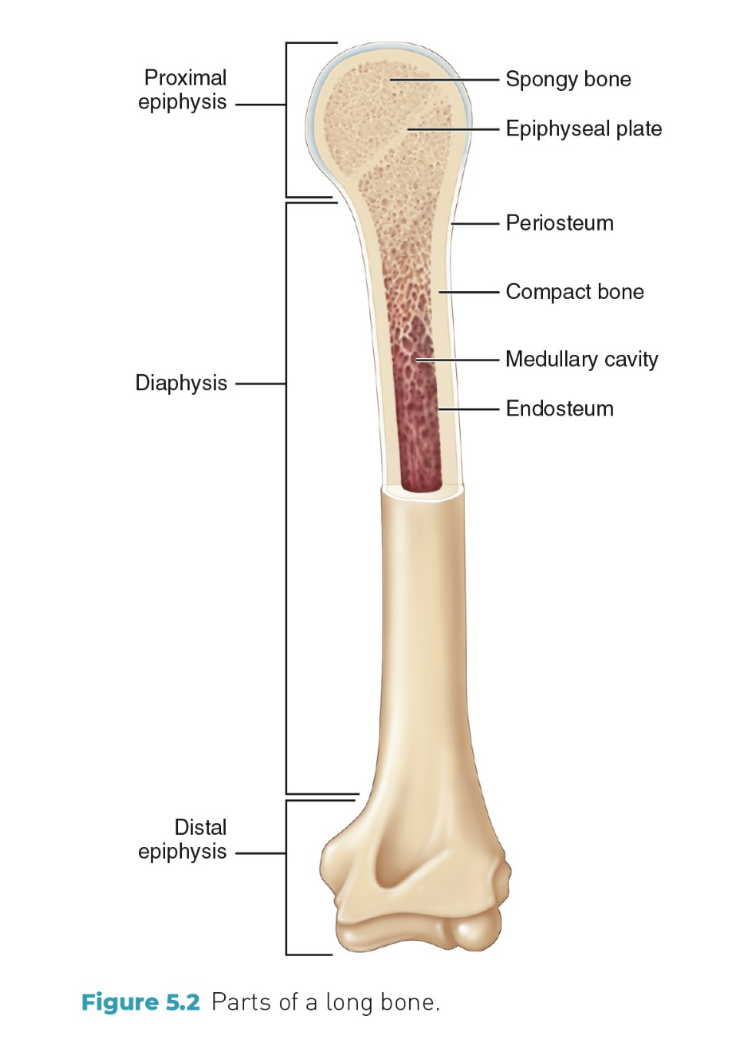
what are the different parts of the long bone?
Diaphysis
Epiphysis
Epiphyseal plate
Medullary cavity
Marrow
Diaphysis
a shaft
Epiphysis
The each end of a long bone
Epiphyseal plate
A growth area of a long bone
Medullary cavity
A cavity inside of the diaphysis
Marrow
A tissue which produces blood cells
Compact bone
Hard, dense bone which makes up diaphysis
Spongy bone
A mesh-like bone tissue which is found in the epipysis
Periosteum
A membrane which covers the bone surface
Endosteum
A inner surface of medullary cavity which is lined with a thin layer of cells
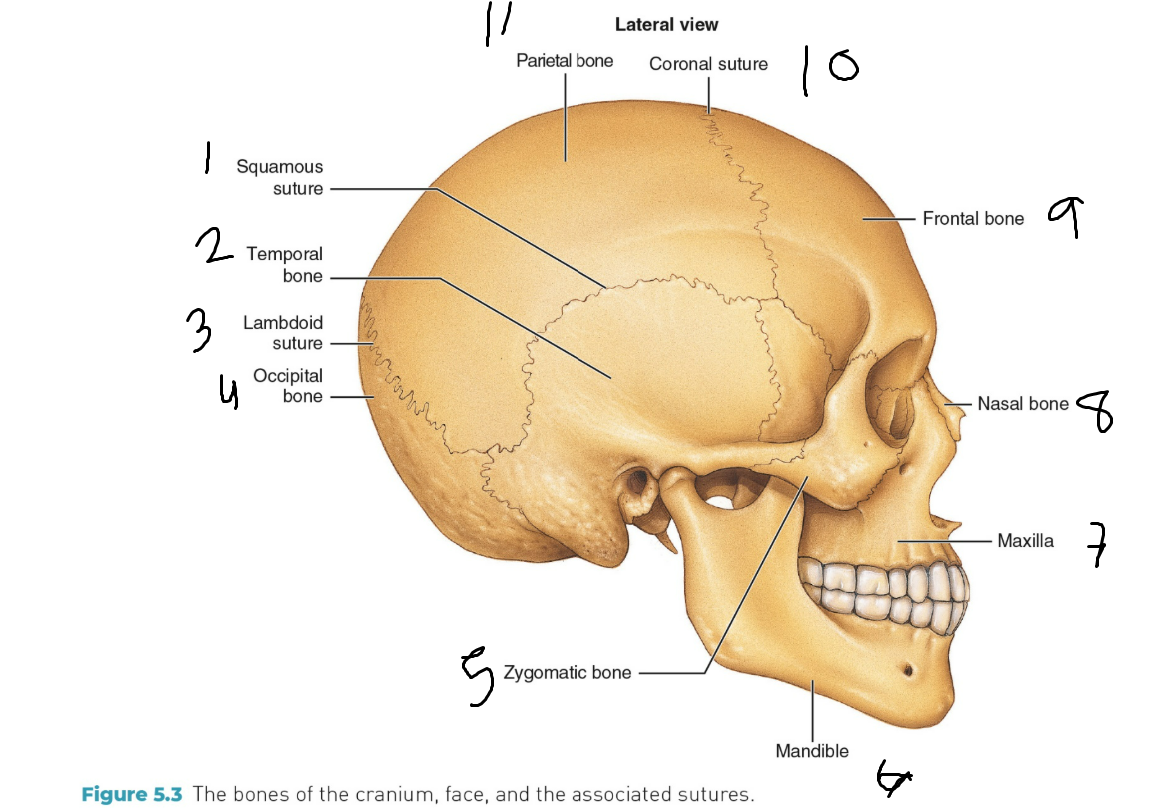
Label the terms
Main facial bones names
Nasal bone, Zygomatic bones, Maxilla, & Mandible
Nasal bone
This forms the bridge of the nose
Zygomatic bones
This forms the cheeks
Maxilla
This is the upper jaw, which is unmovable
Mandible
This is the lower jaw which IS moveable
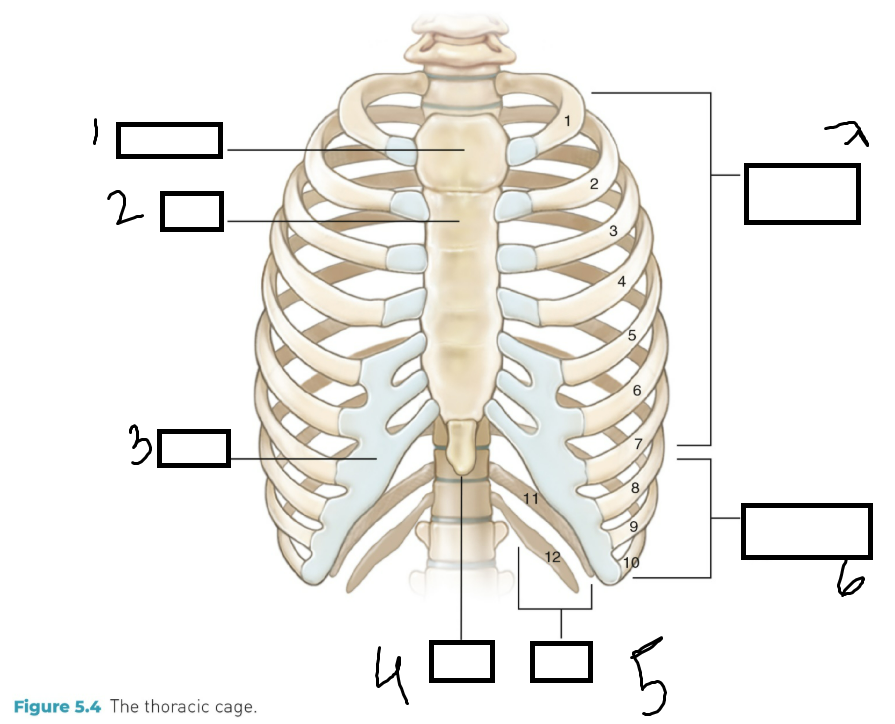
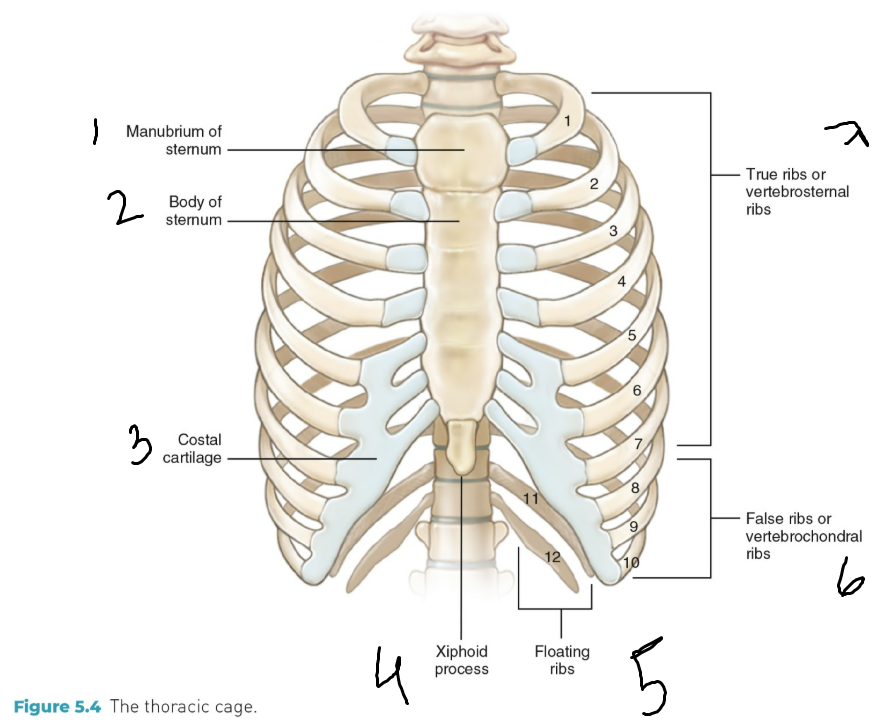
Label he parts
Thorax
Breastplate or thoracic cage and the major organs are inside the thoracic cage: heart and lungs.
How many vertabrea’s and ribs in the thorax region?
12 thoracic vertebrae, 12 ribs, costal (rib) cartilages, sternum.
How do the rib pairs attach?
They attach correspondingly numbered vertebrae (backbone)
Label the terms
Spinal column
Five sections of vertebrae
Prefix letter (C for cervical, T for thoracic, L for lumbar), followed by number indicating placement on column
7 cervical vertebrae
12 thoracic vertebrae
5 lumbar vertebrae
At the base of the spinal column are the sacrum and coccyx.
Sacrum formed by five fused sacral vertebrae.
Coccyx contains three to five fused coccygeal vertebrae