Cell: The Unit of Life
What is a cell?
- Unicellular organisms are capable of:
- independent existence
- performing the essential functions of life.
- Anything less than a complete structure of a cell does not ensure independent living.
- Hence, the cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
- ^^Anton Von Leeuwenhoek^^ first saw and described a live cell.
- ^^Robert Brown^^ later discovered the nucleus.
- The invention of the microscope and its improvement leading to the electron microscope revealed all the structural details of the cell.
Cell Theory:
- In 1838, ^^Matthias Schleiden, a German botanist^^, examined a large number of plants and observed that all plants are composed of different kinds of cells which form the tissues of the plant.
- At about the same time, ^^Theodore Schwann (1839), a British Zoologist,^^ studied different types of animal cells and reported that cells had a thin outer layer which is today known as the ‘plasma membrane’.
- He also concluded, based on his studies on plant tissues, that ^^the presence of cell walls is a unique character of the plant cells.^^
- On the basis of this, Schwann proposed the hypothesis that the ^^bodies of animals and plants are composed of cells and products of cells.^^
- Schleiden and Schwann together formulated the cell theory.
- This theory, however, ^^did not explain how new cells were formed.^^
- ^^Rudolf Virchow (1855)^^ first explained that ^^cells divided and new cells are formed from pre-existing cells^^ (Omnis cellula-e cellula).
- He modified the hypothesis of Schleiden and Schwann to give the cell theory a final shape.
- Cell theory as understood today is
- all living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells.
- all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
An Overview of Cell
Inside each cell is a dense membrane-bound structure called the nucleus.
- This nucleus contains the chromosomes which in turn ^^contain the genetic material, DNA.^^
Cells that have membrane-bound nuclei are called eukaryotic whereas cells that lack a membrane-bound nucleus are prokaryotic.
- In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, a ^^semi-fluid matrix called cytoplasm occupies the volume of the cell.^^
The cytoplasm is the ^^main arena of cellular activities^^ in both plant and animal cells.
- Various chemical reactions occur in it to keep the cell in its ‘living state’.
Besides the nucleus, the eukaryotic cells have other membrane-bound distinct structures called organelles like the ^^endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the Golgi complex, lysosomes, mitochondria, microbodies, and vacuoles.^^
The prokaryotic cells ^^lack such membrane-bound organelles.^^
- Ribosomes are ^^non-membrane bound organelles found in all cells – both eukaryotic as well as prokaryotic.^^
- Within the cell, ribosomes are found not only in the cytoplasm but also within the two organelles – chloroplasts (in plants) and mitochondria and on rough ER.
- Animal cells contain another ^^non-membrane bound organelle called centrosome which helps in cell division.^^
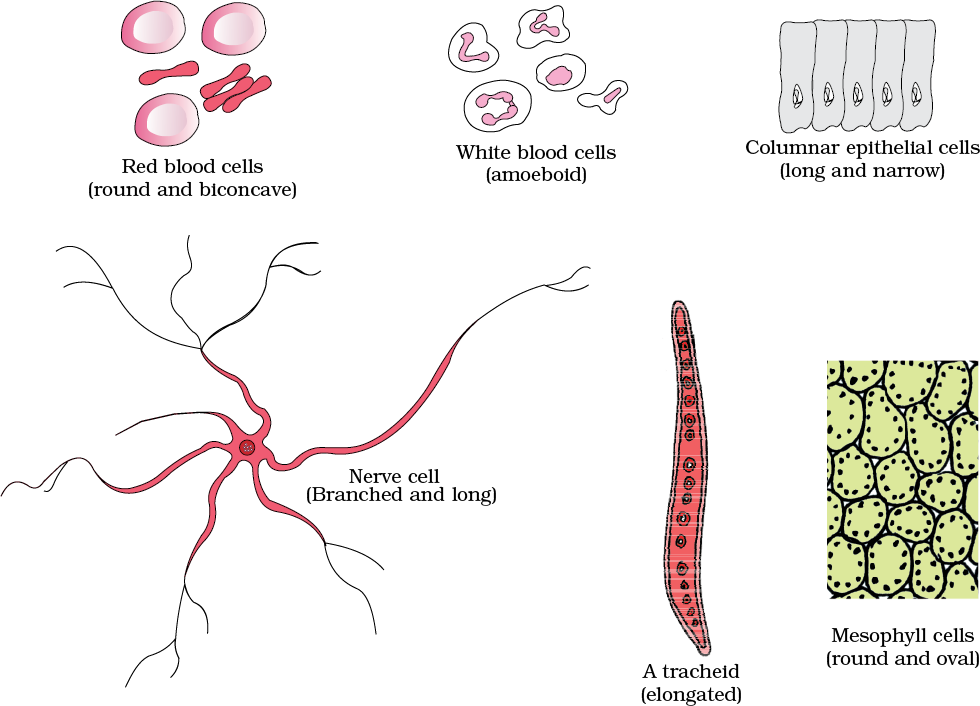
Cells differ greatly in size, shape, and activities.
- For example:
- Mycoplasmas, the ^^smallest cells^^, are only 0.3 µm in length while bacteria could be 3 to 5 µm.
- The ^^largest isolated single cell^^ is the egg of an ostrich.
- Among multicellular organisms, human red blood cells are about 7.0 µm in diameter.
- ^^Nerve cells are some of the longest cells^^.
- Cells also vary greatly in their shape.
- They may be disc-like, polygonal, columnar, cuboid, thread-like, or even irregular.
- The shape of the cell may vary with the function they perform.
Prokaryotic Cell:
- The prokaryotic cells are represented by bacteria, blue-green algae, mycoplasma, and PPLO (Pleuro Pneumonia Like Organisms).
- They are generally smaller and multiply more rapidly than eukaryotic cells.
- They may vary greatly in shape and size.
- The four basic shapes of bacteria are
- bacillus (rod-like)
- coccus (spherical)
- vibrio (comma-shaped)
- spirillum (spiral).
- The organization of the prokaryotic cell is fundamentally similar even though prokaryotes exhibit a wide variety of shapes and functions.
- All prokaryotes have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane ^^except in mycoplasma.^^
- The fluid matrix filling the cell is the cytoplasm.
- There is ^^no well-defined nucleus.^^
- The genetic material is basically naked, not enveloped by a nuclear membrane.
- In addition to the ^^genomic DNA (the single chromosome/circular DNA), many bacteria have small circular DNA outside the genomic DNA.^^
- This smaller DNA are called plasmids.
- The plasmid DNA confers certain unique phenotypic characters to such bacteria.
- One such characteristic is resistance to antibiotics.
- Plasmid DNA is used to monitor bacterial transformation with foreign DNA.
- The nuclear membrane is found in eukaryotes.
- No organelles, like the ones in eukaryotes, are found in prokaryotic cells ^^except for ribosomes.^^
- Prokaryotes have something unique in the form of inclusions.
- A specialized differentiated form of the cell membrane called ^^mesosome^^ ^^is the characteristic of prokaryotes.^^
- They are essentially ^^infoldings of the cell membranes^^.
Cell Envelope and its Modifications:
- Most prokaryotic cells, particularly bacterial cells, have a chemically complex cell envelope.
- The cell envelope consists of a tightly bound three-layered structure i.e.,
- the outermost glycocalyx
- the cell wall
- the plasma membrane
- Although each layer of the envelope performs a distinct function, they act together as a ^^single protective unit.^^
- Bacteria can be classified into two groups on the basis of the differences in the cell envelopes and the manner in which they respond to the ^^staining procedure^^ developed by Gram viz.,
- those that take up the gram stain are Gram-positive
- the others that do not are called Gram-negative bacteria.
- Glycocalyx differs in composition and thickness among different bacteria.
- It could be a ^^loose sheath^^ called the slime layer in some, while in others it may be ^^thick and tough^^, called the capsule.
- The cell wall determines the shape of the cell and provides strong structural support to prevent the bacterium from bursting or collapsing.
- The plasma membrane is selectively permeable in nature and interacts with the outside world.
- This membrane is similar structurally to that of the eukaryotes.
- A special membranous structure is a mesosome which is formed by the extensions of the plasma membrane into the cell.
- These extensions are in the form of vesicles, tubules, and lamellae.
- They help with cell wall formation, DNA replication, and distribution to daughter cells.
- They also help in respiration, and secretion processes, to increase the surface area of the plasma membrane and enzymatic content.
- In some prokaryotes like cyanobacteria, there are other membranous extensions into the cytoplasm called chromatophores which contain pigments.
- Bacterial cells may be motile or non-motile.
- If motile, they have thin filamentous extensions from their cell wall called flagella.
- Bacteria show a range in the number and arrangement of flagella.
- The bacterial flagellum is composed of three parts – filament, hook, and basal body.
- The filament is the longest portion and extends from the cell surface to the outside.
- Besides flagella, Pili and Fimbriae are also surface structures of the bacteria but do not play a role in motility.
- The pili are ^^elongated tubular structures made of a special protein.^^
- The fimbriae are ^^small bristle-like fibers sprouting out of the cell.^^
- Some bacteria are known to help attach bacteria to rocks in streams and also to the host tissues.
Ribosomes and Inclusion Bodies:
- In prokaryotes, ribosomes are associated with the plasma membrane of the cell.
- They are about 15 nm by 20 nm in size and are made of two subunits - ^^50S and 30S units which when present together form^^ 70S prokaryotic ribosomes.
- Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis.
- Several ribosomes may attach to a single mRNA and form a chain called polyribosomes or polysome.
- The ribosomes of a polysome ^^translate the mRNA into proteins.^^
- Inclusion bodies: ^^Reserve material in prokaryotic cells are stored in the cytoplasm in the form of inclusion bodies.^^
- These are not bound by any membrane system and lie free in the cytoplasm,
- Examples: phosphate granules, cyanophycean granules, and glycogen granules.
- Gas vacuoles are found in blue-green and purple and green photosynthetic bacteria.
Eukaryotic Cell:
The eukaryotes include all ^^protists, plants, animals, and fungi.^^
- In eukaryotic cells, there is extensive compartmentalization of cytoplasm through the presence of membrane-bound organelles.
- ^^Eukaryotic cells possess an organized nucleus with a nuclear envelope.^^
- In addition, eukaryotic cells have a variety of complex locomotory and cytoskeletal structures.
- Their genetic material is organized into chromosomes.
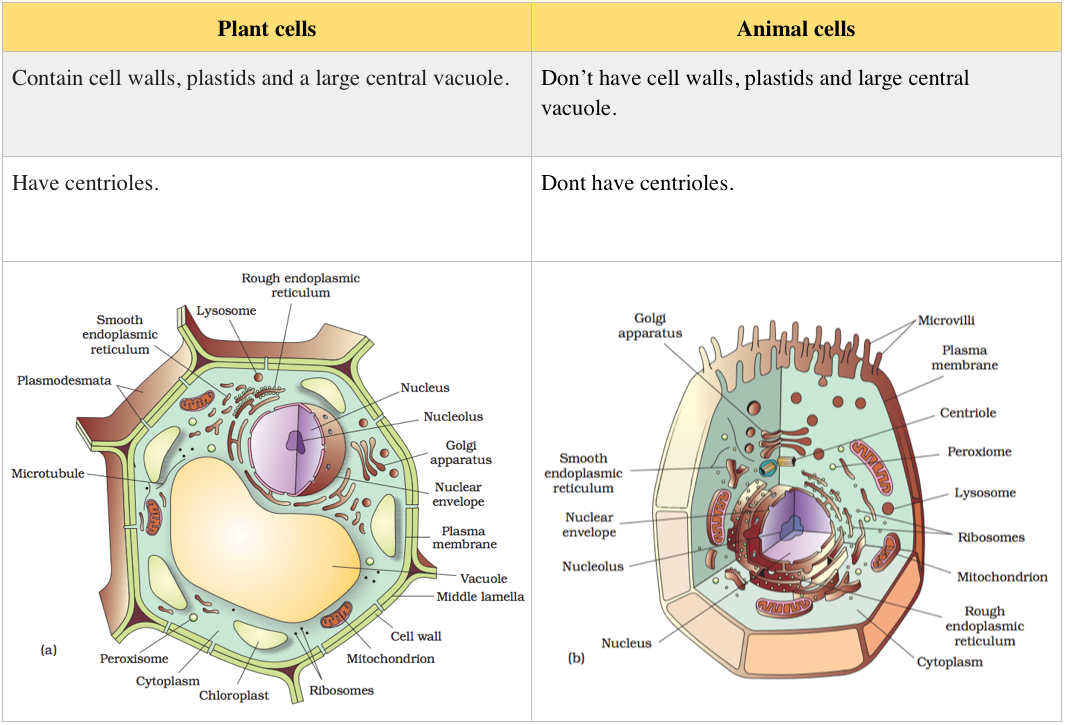
- All eukaryotic cells are not identical.
- Plant and animal cells are different as the ^^former possess cell walls, plastids, and a large central vacuole which are absent in animal cells.^^
- On the other hand, ^^animal cells have centrioles which are absent in almost all plant cells.^^
Cell Membrane:
Chemical studies on the cell membrane, especially in ^^human red blood cells (RBCs),^^ enabled scientists to deduce the possible structure of the plasma membrane.
- These studies showed that the cell membrane is mainly composed of lipids and proteins.
The major lipids are ^^phospholipids that are arranged in a bilayer.^^
- Also, the lipids are arranged within the membrane with the polar head towards the outer sides and the hydrophobic tails towards the inner part.
- This ensures that the nonpolar tail of saturated hydrocarbons is protected from the aqueous environment.
- In addition to ^^phospholipids membrane also contains cholesterol^^.
- Later, biochemical investigation clearly revealed that ^^the cell membranes also possess protein and carbohydrates.^^
- The ^^ratio of protein and lipid varies considerably in different cell types.^^
- In human beings, the membrane of the erythrocyte has approximately ^^52 percent protein and 40 percent lipids.^^
- Depending on the ease of extraction, membrane proteins can be classified as integral and peripheral.
- ^^Peripheral proteins lie on the surface of the membrane while the integral proteins are partially or totally buried in the membrane.^^
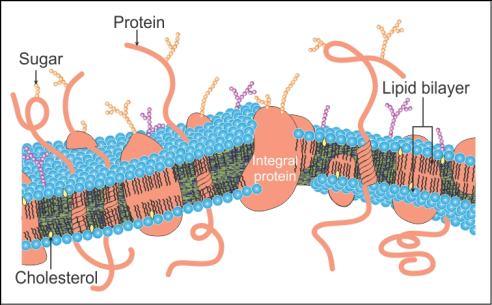
An improved model of the structure of cell membranes was proposed by Singer and Nicolson (1972) widely accepted as a fluid mosaic model.
- According to this, the quasi-fluid nature of lipids enables lateral movement of proteins within the overall bilayer.
- This ability to move within the membrane is measured as its fluidity.
- The fluid nature of the membrane is also important from the point of view of ^^functions like cell growth, formation of intercellular junctions, secretion, endocytosis, cell division, etc.^^
- One of the most important functions of the ^^plasma membrane is the transport of molecules across it.^^
- The membrane is selectively permeable to some molecules present on either side of it.
- Many molecules can move briefly across the membrane without any requirement of energy and this is called passive transport.
- Neutral solutes may move across the membrane by the process of simple diffusion along the concentration gradient, i.e., from higher concentration to lower.
- Water may also move across this membrane from higher to lower concentrations.
- The movement of water by diffusion is called osmosis.
- As the polar molecules cannot pass through the nonpolar lipid bilayer, they require a carrier protein of the membrane to facilitate their transport across the membrane.
- A few ions or molecules are transported across the membrane against their concentration gradient, i.e., from lower to higher concentration.
- Such a means of transport is an energy-dependent process, in which ATP is utilized and is called active transport, ^^e.g., Na+/K+ Pump.^^
Cell Wall:
- Cell wall not only gives ^^shape to the cell and protects the cell from mechanical damage and infection, it also helps in cell-to-cell interaction and provides barrier^^ to undesirable macromolecules.
- Algae have cell wall, made of ^^cellulose, galactans, mannans and minerals like calcium carbonate^^, while in other plants it consists of ^^cellulose, hemicellulose, pectins and proteins^^.
- The cell wall of a young plant cell, the primary wall is ^^capable of growth, which gradually diminishes as the cell matures and the secondary wall is formed on the inner (towards membrane) side^^ of the cell.
- The middle lamella is a layer mainly of ^^calcium pectate^^ which holds or glues the different neighbouring cells together.
- The cell wall and middle lamellae may be traversed by plasmodesmata which ^^connect the cytoplasm of neighbouring cells.^^
Endomembrane System:
- While each of the membranous organelles is distinct in terms of its structure and function, many of these are considered together as an endomembrane system because their functions are coordinated.
- The endomembrane system include ^^endoplasmic reticulum (ER), golgi complex, lysosomes and vacuoles.^^
- Since the functions of the ^^mitochondria, chloroplast and peroxisomes are not coordinated^^ with the above components, these are not considered as part of the endomembrane system.
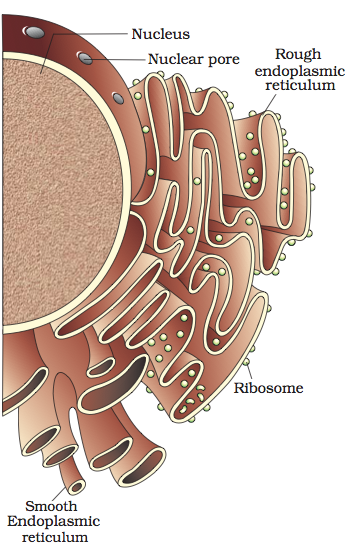
Endoplasmic Reticulum:
Electron microscopic studies of eukaryotic cells reveal the presence of a network or reticulum of tiny tubular structures scattered in the cytoplasm that is called the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- Hence, ER divides the intracellular space into two distinct compartments, i.e., luminal (inside ER) and extra luminal (cytoplasm) compartments.
- The ER often shows ribosomes attached to their outer surface.
- The endoplasmic reticulun bearing ribosomes on their surface is called rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).
- RER is frequently observed in the cells actively involved in ^^protein synthesis and secretion.^^
- They are extensive and continuous with the ^^outer membrane of the nucleus.^^
- In the absence of ribosomes they appear smooth and are called smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER).
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is the major site for ^^synthesis of lipid.^^
- In animal cells ^^lipid-like steroidal hormones are synthesised in SER.^^
Golgi Apparatus:
^^Camillo Golgi (1898) first observed densely stained reticular structures near the nucleus.^^
- These were later named Golgi bodies after him.
- They consist of many ^^flat, disc-shaped sacs or cisternae^^ of 0.5µm to 1.0µm diameter.
- These are stacked parallel to each other.
- ^^Varied number of cisternae are present in a Golgi complex.^^
- The Golgi cisternae are concentrically arranged near the nucleus with distinct convex cis or the forming face and concave trans or the maturing face.
- The cis and the trans faces of the organelle are entirely different, but interconnected.
- The golgi apparatus principally ^^performs the function of packaging materials, to be delivered either to the intra-cellular targets or secreted outside the cell.^^
- Materials to be packaged in the ^^form of vesicles^^ from the ER fuse with the cis face of the golgi apparatus and move towards the maturing face.
- This explains, why the golgi apparatus remains in close association with the endoplasmic reticulum.
- A ^^number of proteins synthesised by ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum are modified in the cisternae^^ of the golgi apparatus before they are released from its trans face.
- ^^Golgi apparatus is the important site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids.^^

Lysosomes:
- These are ^^membrane bound vesicular structures formed by the process of packaging in the golgi apparatus.^^
- The isolated lysosomal vesicles have been found to be very rich in almost all types of hydrolytic enzymes (hydrolases – lipases, proteases, carbohydrases) optimally active at the acidic pH.
- These ^^enzymes are capable of digesting carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids.^^
Vacuoles:
- The vacuole is the ^^membrane-bound space found in the cytoplasm.^^
- It contains water, sap, excretory product and other materials not useful for the cell.
- The vacuole is bound by a ^^single membrane^^ called tonoplast.
- In plant cells the ^^vacuoles can occupy up to 90 per cent of the volume of the cell.^^
- In plants, the tonoplast ^^facilitates the transport of a number of ions and other materials against concentration gradients^^ into the vacuole, hence their ^^concentration is significantly higher in the vacuole than in the cytoplasm.^^
- In Amoeba the ^^contractile vacuole is important for osmoregulation and excretion.^^
- In many cells, as in protists, food vacuoles are formed by engulfing the food particles
Mitochondria:
Mitochondria, unless specifically stained, are not easily visible under the microscope.
- The number of mitochondria per cell is variable depending on the physiological activity of the cells.
- In terms of shape and size also, considerable degree of variability is observed.
- Typically it is sausage-shaped or cylindrical having a diameter of 0.2-1.0µm (average 0.5µm) and length 1.0-4.1µm.
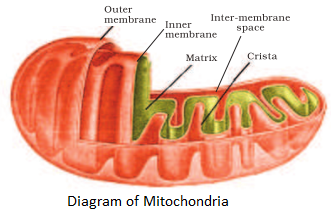
Each mitochondrion is a ^^double membrane-bound structure^^ with the outer membrane and the inner membrane dividing its lumen distinctly into two aqueous compartments, i.e., the outer compartment and the inner compartment.
- The inner compartment is filled with a ^^dense homogeneous substance^^ called the matrix.
- The inner membrane forms a ^^number of infoldings^^ called the cristae towards the matrix.
- The cristae ^^increase the surface area.^^
- The outer membrane forms the continuous limiting boundary of the organelle.
- The two membranes have their own specific enzymes associated with the mitochondrial function.
Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration.
- They produce cellular energy in the form of ATP, hence they are called ‘power houses’ of the cell.
The matrix also possesses ^^single circular DNA molecule, a few RNA molecules, ribosomes^^ (70S) and the components required for the synthesis of proteins.
The mitochondria divide by fission.
Plastids:
Plastids are found in all ^^plant cells and in euglenoides.^^
- These are easily observed under the microscope as they are large.
- They bear some ^^specific pigments,^^ thus imparting specific colours to the plants.
Based on the type of pigments plastids can be classified into:
- Chloroplasts:
- The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments which are ^^responsible for trapping light energy essential for photosynthesis.^^
- Chromoplasts:
- In the chromoplasts ^^fat soluble carotenoid pigments^^ like ^^carotene, xanthophylls and others are present.^^
- This gives the part of the plant a yellow, orange or red colour.
- Leucoplasts.
- The leucoplasts are the colourless plastids of varied shapes and sizes with stored nutrients:
- Amyloplasts store carbohydrates (starch)
- Example: potato;
- Elaioplasts store oils and fats.
- Aleuroplasts store proteins.
Majority of the chloroplasts of the green plants are found in the ^^mesophyll cells of the leaves.^^
- These are lens-shaped, oval, spherical, discoid or even ribbon-like organelles having variable length (5-10µm) and width (2-4µm).
- Their number varies from ^^1 per cell of the Chlamydomonas, a green alga to 20-40 per cell in the mesophyll.^^
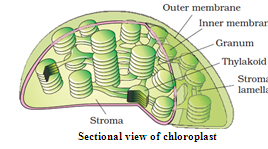
- Like mitochondria, the chloroplasts are also ^^double membrane bound^^.
- Of the two, the ^^inner chloroplast membrane is relatively less permeable.^^
- The space limited by the inner membrane of the chloroplast is called the stroma.
- A number of organised ^^flattened membranous sacs^^ called the thylakoids, are present in the stroma.
- Thylakoids are arranged in stacks like the ^^piles of coins called grana^^ or the intergranal thylakoids.
- In addition, there are flat membranous tubules called the ^^stroma lamellae connecting the thylakoids^^ of the different grana.
- The membrane of the thylakoids enclose a space called a lumen.
- The stroma of the chloroplast contains enzymes required for the ^^synthesis of carbohydrates and proteins^^.
- It also contains small, ^^doublestranded circular DNA^^ molecules and ribosomes.
- ^^Chlorophyll pigments are present in the thylakoids.^^
- The ^^ribosomes of the chloroplasts are smaller (70S) than the cytoplasmic ribosomes (80S).^^
Ribosomes:
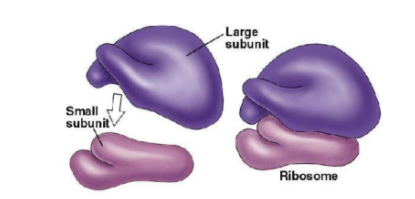
Ribosomes are the ^^granular structures^^ first observed under the electron microscope as dense particles by ^^George Palade (1953).^^
- They are composed of ^^ribonucleic acid (RNA) and proteins^^ and are not surrounded by any membrane.
- The ^^eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S while the prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S.^^
- Each ribosome has two subunits, larger and smaller subunits.
- The two subunits of ^^80S ribosomes are 60S and 40S while that of 70S ribosomes are 50S and 30S.^^
- Here ‘S’ (Svedberg’s Unit) stands for the sedimentation coefficient; it is indirectly a measure of density and size.
- Both 70S and 80S ribosomes are composed of two subunits.
Cytoskeleton:
An elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures consisting of ^^microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate filaments^^ present in the cytoplasm is collectively referred to as the cytoskeleton.
- The cytoskeleton in a cell are involved in many functions such as ^^mechanical support, motility, maintenance of the shape of the cell.^^
Cilia and Flagella:
- ^^Cilia and flagella are hair-like outgrowths of the cell membrane.^^
- Cilia are small structures which work like oars, causing the ^^movement of either the cell or the surrounding fluid.^^
- ^^Flagella^^ ^^are comparatively longer and responsible for cell movement.^^
- The prokaryotic bacteria also possess flagella but these are structurally different from that of the ^^eukaryotic flagella.^^
- The electron microscopic study of a ^^cilium or the flagellum^^ show that they are covered with plasma membrane.
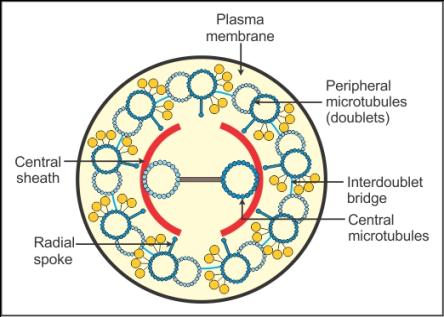
- Their core called ^^the axoneme, possesses a number of microtubules running parallel to the long axis.^^
- The axoneme usually has ^^nine doublets of radially arranged peripheral microtubules, and a pair of centrally located microtubules.^^
- Such an arrangement of axonemal microtubules is referred to as the 9+2 array.
- The central tubules are connected by bridges and is also enclosed by ^^a central sheath, which is connected to one of the tubules of each peripheral doublets^^ by a radial spoke.
- Thus, ^^there are nine radial spokes.^^
- The ^^peripheral doublets are also interconnected by linkers.^^
- Both the cilium and flagellum emerge from ^^centriole-like structure^^ called the basal bodies.
Centrosome and Centrioles:
- Centrosome is an organelle usually containing ^^two cylindrical structures^^ called centrioles.
- They are surrounded by ^^amorphous pericentriolar materials.^^
- Both the centrioles in a centrosome lie perpendicular to each other in which each has an organisation like the cartwheel.
- They are made up of ^^nine evenly spaced peripheral fibrils^^ of tubulin protein.
- Each of the ^^peripheral fibril is a triplet.^^
- The adjacent triplets are also ^^linked.^^
- The central part of the proximal region of the centriole is also ^^proteinaceous and called the hub^^, which is connected with tubules of the ^^peripheral triplets by radial spokes made of protein^^.
- The centrioles form the basal body of cilia or flagella, and spindle fibres that give rise to spindle apparatus during cell division in animal cells.
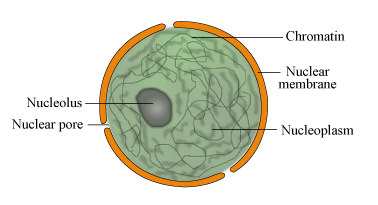
Nucleus:
Nucleus as a cell organelle was first described by ^^Robert Brown as early as 1831.^^
- Later the material of the nucleus stained by the basic dyes was given the name chromatin by Flemming.
The interphase nucleus (nucleus of a cell when it is not dividing) has highly extended and elaborate nucleoprotein fibres called ^^chromatin, nuclear matrix and one or more spherical bodies called nucleoli.^^
- Electron microscopy has revealed that the nuclear envelope, which consists of two parallel membranes with a space between (10 to 50 nm) called the perinuclear space, forms a barrier between the materials present inside the nucleus and that of the cytoplasm.
- The outer membrane usually remains continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum and also bears ribosomes on it.
- At a number of places the nuclear envelope is interrupted by minute pores, which are formed by ^^the fusion of its two membranes.^^
- These nuclear pores are the passages through which ^^movement of RNA and protein molecules^^ takes place in both directions between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Normally, there is only one nucleus per cell, variations in the number of nuclei are also frequently observed.
- Some mature cells even lack nucleus, e.g., ^^erythrocytes of many mammals and sieve tube cells of vascular plants.^^
The nuclear matrix or the nucleoplasm contains nucleolus and chromatin.
- The nucleoli are spherical structures present in the nucleoplasm.
- The content of nucleolus is continuous with the rest of the nucleoplasm as it is not a membrane bound structure.
- It is a ^^site for active ribosomal RNA synthesis.^^
- Larger and more numerous nucleoli are present in cells actively carrying out protein synthesis.