AP Psychology Unit 1A: Bio and Sleep
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Maladaptive
This refers to counterproductive behaviors, thoughts, or coping mechanisms that hinder an individual's ability to adapt to stressors or challenges. (some behaviors like aggression can be explained because they were favorable in the past but now are no longer helpful to our lives).
Epigenetics
Epigenetics in psychology examines how changes in gene expression, influenced by environmental factors and experiences, can affect behavior, mental health, and the transmission of traits across generations.
Twin Studies
Genetically identical twins are more likely to:
Be affected by the same disorders
Have behavioral similarities
Look alike
Identical twins don’t necessarily mean identical personalities!
Twin studies - IQ test score
Identical raised together (1st most similar)
Identical raised apart (2nd most similar
Fraternal raised together (3rd most similar)
Fraternal raised apart (least similar)
62% of results could be attributed to genetics
9 personality traits are influenced by genetics
Adoption Studies
Genes Matter
Adopted children are more similar to their biological parents than their adoptive parents (especially personality)
Parents do have influence on various veiws and beliefs (personal values, manners,faith, politics)
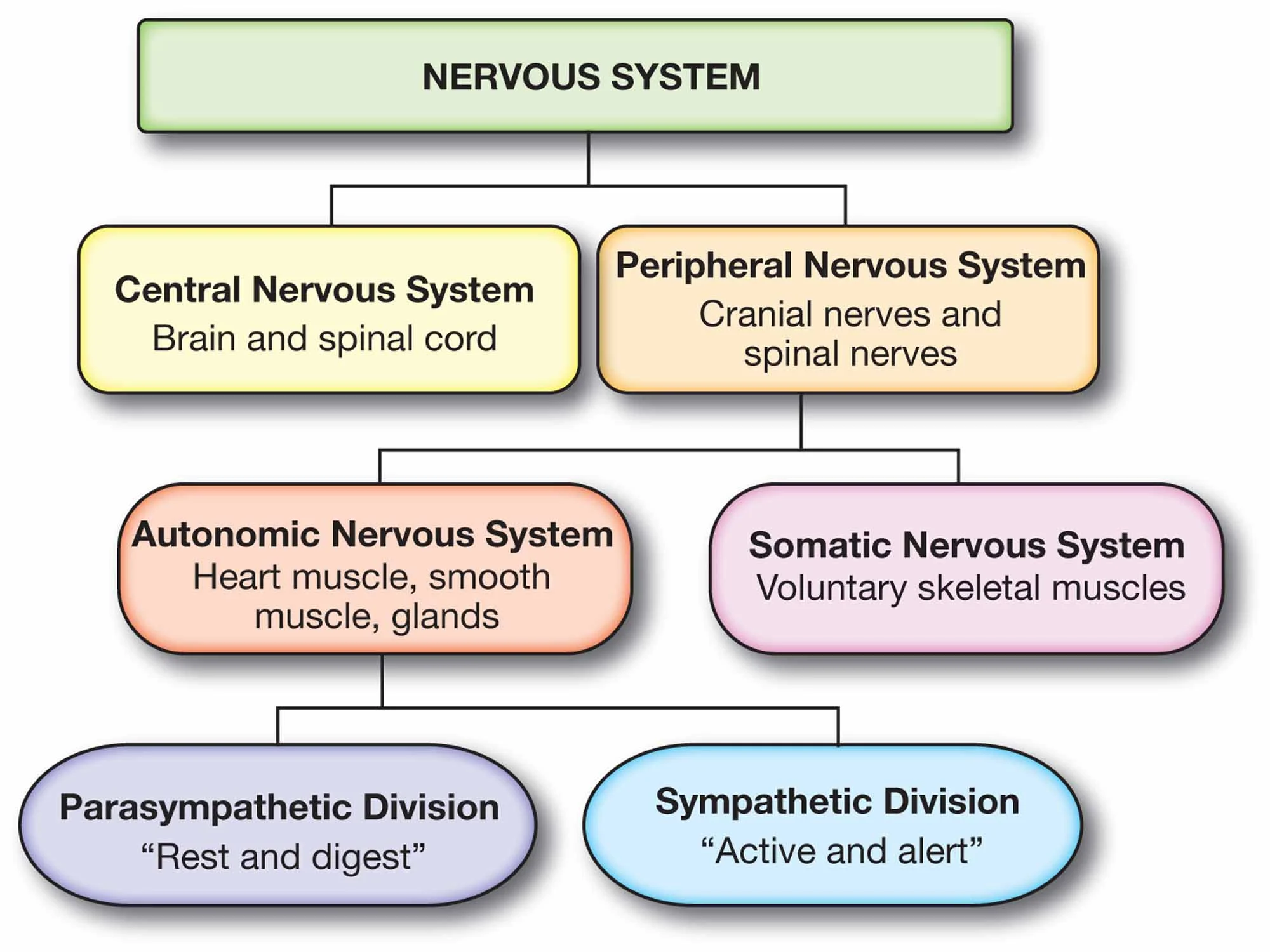
Nervous System
Mainly made from 2 parts:
Central Nervous System
and
Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic
Autonomic
Autonomic is made up of 2 parts
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Central Nervous System
Includes the brain and spinal cord
Spinal cord is main connection with brain to peripheral NS
Portion that makes decisions in our NS
Peripheral NS
Connects the CNS to the rest of the body (everything else).
Controls motor and sensory neurons that receive info and transmit CNS decisions
The PNS has two major subdivisions
Somatic and Autonomic NS
Somatic NS
Voluntary control of skeletal muscles, it transmits sensory info (touch/pain) to the CNS and carries motor commands from CNS to the muscles
Autonomic NS
This portion of the peripheral NS contains involuntary functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing
It is made up of 2 subdivisions
Controls functions of glands/internal organ muscles (automatically)
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic NS
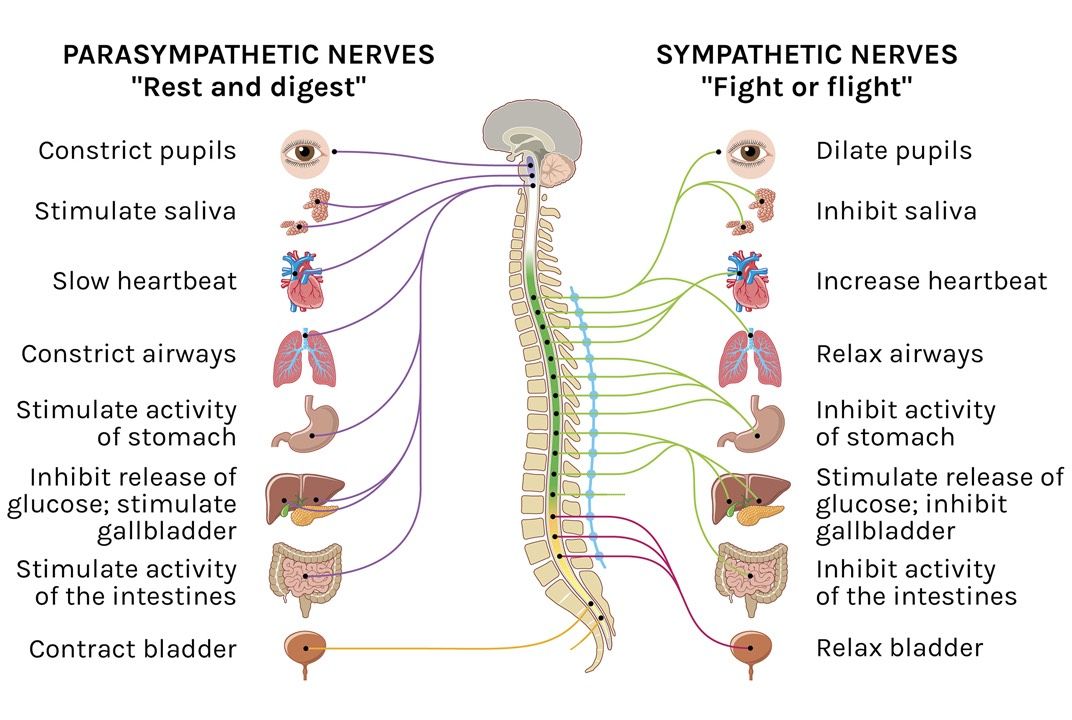
Sympathetic NS
Prepares the body for stressful or emergencies ("fight-or-flight) . When activated, increases heart rate, dilates pupils, and releases stored energy for quick action.
AROUSES energy
Parasympathetic NS
Opposes the sympathetic system and is responsible for the "rest-and-digest" response. It calms the body down after stress, lowering the heart rate and conserving energy.
Calms you down, Slows breathing and heart rate, increases digestion
Neurons
Neurons are a nerve cell and the basic building block of the nervous system
A nerve is a bundle of axons that link the Central NS with the body’s receptors, muscles, and glands.
Combination of 3 neurons (sensory, motor, interneurons) make up the Reflex Arc
This is how the Peripheral and Central NS communicate
Afferent vs Efferent Neurons
Afferent Neurons:
Carry signals toward the central nervous system (CNS)
Transmit sensory information from receptors (e.g., touch, pain)
Efferent Neurons:
Carry signals away from the central nervous system
Transmit motor commands to muscles and glands for action
These neurons carry signals toward the central nervous system from sensory receptors, while these transmit signals away from the central nervous system to muscles and glands.
Sensory Neurons
These neurons receive information from the outside world and sends it to the brain through the spinal cord (afferent neuron)
Motor Neurons
These neurons carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles and glands (efferent neurons)
Interneurons
Connect the sensory & motor neurons
found in the brain and spinal cord
Reflex Arc
Starts with a stimulus (let’s use a hot stove as an example)
The feeling of pain travels through the receptor (skin) to sensory neurons (afferent)
Goes through the dorsal root ganglion to the interneurons (the connection between sensory and motor) in the spinal cords grey matter
This does not involve the brain initially
The interneuron sends a signal through the motor neuron (efferent) and exits the spinal cord’s ventral root
This impulse is carried to the effector's muscles in your arm and hand, specifically, the muscles that control movement
The effector moves away within milliseconds, the brain is notified after you move away
Glial Cells
These are non-neuron cells in the nervous system that provide support, protect, and nourish neurons.
Insulation for axons and myelin, communication and waste transport (remove used neurotransmitters)
The glue that holds the neural network together
Also plays a role in learning, thinking, and memory
Outnumbers neurons 50:1
Dendrite
Branches that recieve messages from neighboring cells
Cell Body (Soma)
Neurons “life support center”
Contains nucleus
indicates whether signal (action potential) is strong enough to be sent to axon hillock (first part of axon)
Axon
Passes Messages away from cell body to neighboring neurons, muscles, glands
Myelin Sheath
Covers some axons to protect and speed up neural signal (action potential)
Axon Terminal
End of axon that leads to neighboring cells to send messages (action potential reaches this)
Terminal Buttons
This is the end of the axon terminal, where neurotransmitters are stored and released ot send message
Synapse
The junction between two neurons dendrites / terminal buttons; a synaptic gap where NTs are released
Receptor
The cell on the end of dendrites that NTs connect to sends message to the next neuron and starts the process over again a
After NT connects, the excess will be reabsorbed by sending the neuron, called reuptake
Action Potential
The action potential is a neural impulse, or a brief electrical charge, that travels down an axon
Triggered by an eelctric shock that is above the resting threshold
All or Nothing Principle: No varying levels of action potential- it eitther fires at the same level or does not
Refractory Period: Time it takes to recover from one action potential and move on to another
Action Potential Steps
Resting potential : Neuron is polarized and ready to fire
Threshold: The neuron has recieved enough stimulation (NTs)
Voltage Rises - Depolarization (Action Potential travels along axon)
Refractory Period
Resting potential : Neuron is polarized and ready to fire
Threshold: The neuron has recieved enough stimulation (NTs)
Voltage Rises - Depolarization (Action Potential travels along axon)
Refractory Period
Disruptions to Neural Firing
The degeneration of myelin sheath, slowing communication to muscles and brain region, resulting in Multiple Sclerosis
Agonists
Increase the action of a neurotransmitter
Done by either increasing the production or release of neurotransmitters
Blocking reuptake
Mimic neurotransmitter’s effect
Ex: some opioid drugs amplify normal sensations of arousal, producing a temporary “high”
Antagonist
Decrease a neurotransmitter’s action by blocking the production or release of neurotransmitters or block the receptor sites
Ex: Botulin, poison that can grow in food, causes paralysis by blocking ACh release
Reuptake Inhibitor
Blocks the reabsorption of neurotransmitters back into the sending neuron
Ex: antidepressants partially block the reuptake of mood- enhancing neurotransmitters, making it stay in the synaptic gap longer and increase its effect (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors)
Alcohol
Type: Depressant
Definition: Slows down central nervous system activity by enhancing GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter.
Positive Effects: Reduced anxiety, relaxation, lowered inhibitions, and mild euphoria.
Negative Aftereffects: Impaired judgment, motor skills, and memory; long-term use can lead to liver damage, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms like anxiety and tremors.
Barbiturates
Type: Depressant
Definition: Prescription drugs that act as central nervous system depressants, typically used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and seizures.
Positive Effects: Relaxation, sedation, and relief from anxiety or seizures.
Negative Aftereffects: Drowsiness, confusion, and risk of overdose; long-term use can cause dependence, withdrawal symptoms, and respiratory failure in high doses.
Opiates
Type: Depressant
Definition: Drugs derived from the opium poppy that bind to opioid receptors, reducing pain and causing euphoria.
Positive Effects: Pain relief, euphoria, and a sense of well-being.
Negative Aftereffects: Highly addictive, with withdrawal symptoms including pain, nausea, and anxiety; long-term use can lead to tolerance, overdose, and respiratory failure.
Nicotine
Type: Stimulant
Definition: A highly addictive substance found in tobacco that stimulates acetylcholine receptors.
Positive Effects: Increased alertness, concentration, and relaxation in small doses.
Negative Aftereffects: Addiction, increased heart rate and blood pressure, lung damage, and risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease with long-term use.
Cocaine
Type: Stimulant
Definition: A powerful stimulant that increases dopamine levels by blocking reuptake, leading to intense euphoria and energy.
Positive Effects: Euphoria, increased energy, alertness, and confidence.
Negative Aftereffects: Anxiety, irritability, depression (crash), heart problems, risk of addiction, and potential for overdose.
Methamphetamine
Type: Stimulant
Definition: A highly addictive stimulant that increases dopamine release, leading to extreme euphoria and energy.
Positive Effects: Intense euphoria, increased energy, alertness, and enhanced focus.
Negative Aftereffects: Aggression, paranoia, insomnia, addiction, and severe physical damage, including tooth decay and skin sores (often called "meth mouth").
Ecstasy (MDMA)
Type: Stimulant and mild hallucinogen
Definition: A drug that increases serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, leading to heightened mood and sensory perception.
Positive Effects: Euphoria, emotional closeness, heightened sensory perception, and empathy.
Negative Aftereffects: Depression (due to serotonin depletion), anxiety, dehydration, overheating, and potential long-term damage to serotonin-producing neurons.
LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide)
Type: Hallucinogen
Definition: A potent hallucinogen that alters perceptions and induces vivid hallucinations by affecting serotonin receptors.
Positive Effects: Altered perceptions, visual hallucinations, and a sense of connectedness or spiritual experiences.
Negative Aftereffects: Flashbacks, anxiety, paranoia, and potential for persistent psychosis (rare).
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) / Marijuana
Type: Mild hallucinogen
Definition: The active ingredient in marijuana that binds to cannabinoid receptors, altering mood, perception, and appetite.
Positive Effects: Relaxation, altered perception, euphoria, increased appetite, and pain relief.
Negative Aftereffects: Impaired memory and coordination, potential for anxiety or paranoia, lung damage (if smoked), and, in some cases, dependence.
Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in the brain
After connecting to the receiving receptor and sending the message, returns to presynaptic neuron through reuptake
2 Main Types:
Excitatory: causes the receiving cell to increase neural firing
Inhibitory: causes the receiving cell to decrease neural firing
Serotonin (Inhibitory)
Function
Regulates mood, sleep, eating, wakefulness, and aggressive behaviors
Lack of:
Mood disorders(depression)
Anxiety
Insomnia
OCD
Norepinephrine (Excitatory)
Function
Arousal of the fight or flight response
Stress, arousal, eating
Enhances attention and memory for emotionally charged events
Lack of:
Depression
Excess:
Anxiety
Stress
Nervous Tension
Acetylcholine (ACh) (Excitatory)
Function
Skeletal muscle contractions, regulates heart muscles
Transmits messages between brain and spinal cord
Memory formation, learning, general intellectual functioning
Lack of:
Low arousal and attention
Alzheimer’s
Excess:
Violent muscle contractions/ spasms
Glutamate (Excitatory)
Function
Enhances transmission of info from senses to brain
Deals with learning and memory
Excess:
Brain becomes overstimulated
Results in seizures, migranes
GABA (Inhibitory)
Function
Inhibtory NT
Balances and offsets other excitatory messages
Regulates sleep-wake cycle
Lack of:
Anxiety
Seizures, tremors
Insomnia
Excess:
Sleep disorders
Some eating disorders
Endorphins (Inhibitory)
Function
Natural Opiate
Regulates pain perception
Released during exercise and linked to positive emotions
Lack of:
Feel pain
Excess:
Artificial highs
May not recieve adequate warning of pain
Dopamine (BOTH)
Function
Voluntary coordinated motor movements
Attention, learning memory
Emotional arousal and reward sensations
Lack of:
Parkinson’s Disease
Depression
Excess:
Schizophrenia/ Shz like symptoms
Addiction
Bipolar disorder
ADHD
Substance P (Excitatory)
Modulation of Pain
Causes the contraction of smooth muscle and dilation of blood vessels
Acts as potent NT, especially in the transmission of signals from pain receptors
Hormones
Chemical messenger that travels through bloodstream
Released by glands in endocrine system
Affect the brain and other parts of the body
Growth, reproductoin, metabolism, mood
Slower transfer than neurotransmitters but effects last longer
Think email vs snail mail
NT vs. Horomones
Neurotransmitters
Nervous System
Transmit through neural network
Fast-acting
Effects quick but has short duration
Hormones
Endocrine System
Transmit through bloodstream
Slow-acting
Effects take time to begin but are long-lasting
Adrenaline
Increases heartbeat reate and strength
stimulates respiration
Fight or Flight
Also referred to as epinephrine
Melatonin
Regulation of circadian rythms
Release increases feelings of sleepiness
Ghrelin
Released by hypothalmus
Signals hunger and need to eat
Leptin
Released by hypothalamus
Allows you to feel full
Oxytocin
Stimulates uterine contractions and lactation
Effects of Drugs
Dependence
Psychological- Mental need for the drug
Physical- Feeling of physical need for drug to function
Addiction
Compulsive substance use (or behavioral patterns) that continue despite harmful consequences
Withdrawal
The discomfort and distress that follow discontinuing an addictive drug or behavior
Tolerance
As the brain’s chemistry adapts to offset the drug’s effect, it takes more and more of a drug to get us to feel the same effect
Depressants
Drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
Ex: Alcohol, Barbiturates (Tranquilizers), Opioids
Stimulants
Drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions
Ex: Cocaine, Ecstasy, Methamphetamine, Caffeine, Nicotine
Hallucinogens
Psychedelic drugs that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
Ex: LSD, Ecstasy, Marijuana (THC)
Opiods
Opium and its derivatives; depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety
Ex: Heroin, methadone (OxyContin, Vicodin, morphine), fentanyl
Brainstem
Located at the base of the brain, connects to the spinal cord and handles autonomic function s
Damage to this area = comma or death
Brainstem is made up of:
Medulla: Heartbeat & Breathing
Pons: Connects medulla with cerebellum; involved with sleep, dreams
Reticular Formation: controls state of alertness, attention, and arousal
Thalamus
Takes signals in from the senses and sends them to appropriate lobes of the brain
Reticular Activating System
Located inside the brainstem (and part of the reticular formation)
The reticular activating system is part of the brian’s reward center.
NT = Dopamine
Cerebellum
Means little brain
Two wrinkled halves on each side of brainstem
Handles balance, muscle memory & coordinates voluntary / natural movements (with the pons)
The Limbic System
The limbic system is the emotional center of the brain
Hippocampus: Memory Processing
Amygdala: Agression & Fear
Thalamus: Sensory Switchboard
Hypothalamus: Handles the Body system maintenance
Pituitary Gland: Master gland, growth
Hippocampus
Curcial for learning, memory, and converting short-term to long - term memories
Memories aren’t stored in the hippocampus- must be routed through here to be directed to the appropriate areas for storage
Amygdala
Responsible for our experience of fear and agression
When exposed to a threat, information about that stimulus is immedately sent to the amygdala
Will then send signals to areas of the brain like the hypothalamus to trigger a “fight or flight” response
Thalamus
The thalamus recieves all sensory information (except sense of smell),
and then directs it to the approprioate area of the cerebral cortex
Think air traffic control or mail sorting center
Hypothalamus
Bridge between nervous and endocrine systems
Main role: keep the body regulated
Sympathetic NS and parasympathetic NS
Experience hunger/thirst and when those drives are met
Body temp, sexual response cycle
5 Fs: Fight, Flight, Feeding, Fahrenheit, Fornication
Pituitary Gland
Controlled by hypothalamu s
Often referred to as the master gland of the body
Responsible for hormone release that regulate other endocrine/body systems/glands
Growth and development
Works alongside hypothalamus to release hormones releated to hunger