02 NPTE Neuromuscular and Nervous Systems Review
1/434
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
435 Terms
Central Nervous System
Brain, Brainstem, Spinal Cord
Brain Divisions
Forebrain (prosencephalon)
Midbrain (mesencephalon)
Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon)

Brainstem Sections
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
Forebrain (Prosencephalon)
Contains:
Telencephalon
-Cerebrum
-Hippocampus
-Basal Ganglia
-Amygdala
Diencephalon:
-Thalamus
-Hypothalamus
-Subthalamus
-Epithalamus
Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
Tectum:
-Superior and inferior Colliculi
Tegmentum:
-Cerebral Aquedut
-Periaqueductal Gray
-Reticular Formation
-Substantia Nigra
-Red Nucleus
Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon)
Metencephalon
-Cerebellum, Pons
Myelencephalon
-Medulla Oblongata
Gray Matter
Brain and spinal cord tissue that appears gray with the naked eye; consists mainly of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) and lacks myelinated axons.
White matter
Myelinated axons, nerve fibers without dendrites
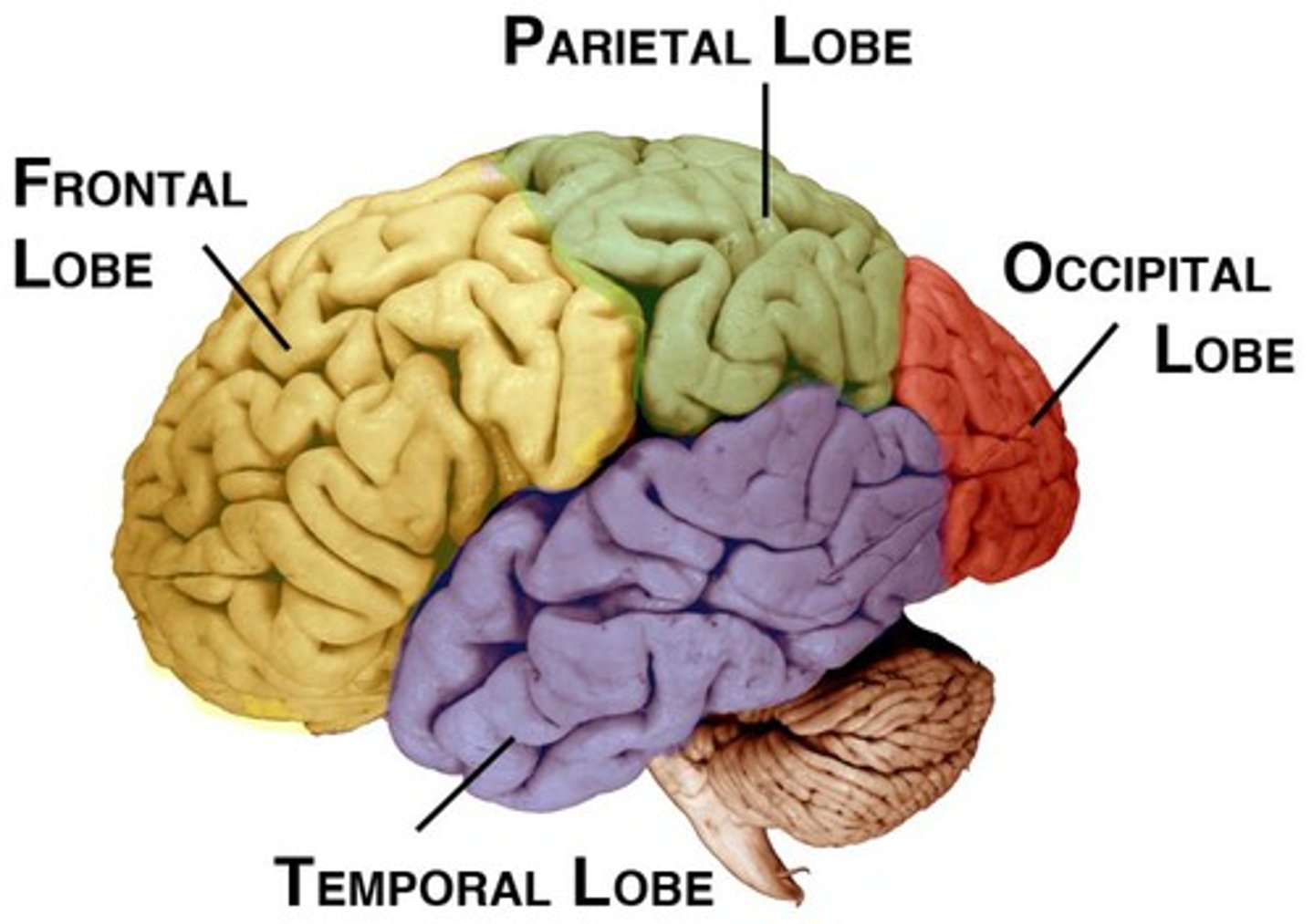
Lobes of the brain
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal
Peripheral Nervous System
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body.
Made up of Autonomic Nervous System and the Somatic Nervous System
-12 Cranial Nerves and Ganglia
-31 pairs of spinal nerves exit vertebral column through intervertebral foramina:
8 Cervical
12 Thoracic
5 lumbar
5 Sacral
1 Coccygeal
Efferent Fibers
Carry motor signals from CNS to effectors
Afferent Fibers
Carry sensory signals from receptors to CNS
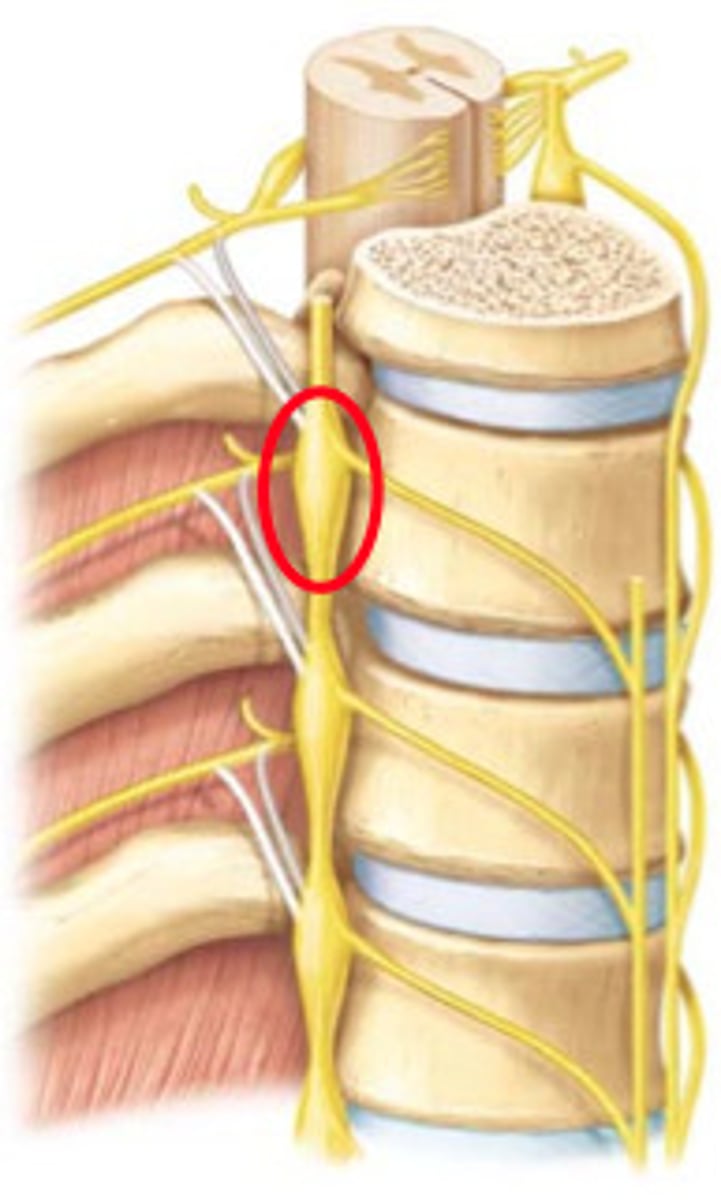
Ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in the PNS. They give rise to peripheral and central nerve fibers.
Autonomic Nervous System
Division of PNS that controls glands and muscles of internal organs. Largely automatic responses that don't reach consciousness and emphasize homeostasis and stress response. Contains two divisions:
Sympathetic: Emergency response, Norepinephrine transmission, stimulating response. "Fight or flight"
Parasympathetic: Conserving/restoring energy, ACh transmittion, inhibitory response. "Feed and breed"
Somatic Nervous System
Division of PNS that controls muscles.
Voluntary movements, ability to touch, smell, see, taste, and hear.
Limbic System
A doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres; involved in control/expression of moddoand emotion, processing recent memory, olfaction, appetite, and emotional responses to food.
Lesions here can result in aggression, fearfulness, altered sexual behavior, or motivation
ANS Dysfunction
ANS influences all internal organs, blood vessels, and glands, controlling BP, HR, RR, Temp, metabolism, etc.
Constipation, erectile dysfunction, Horner's syndrome, vasovagal syncope, orthostatic hypotension, and postural tachycardia are all ANS dysfunctions that can be caused by outside pathology or primary damage.
Treated with pharmacological interventions.
Telencephalon
Cerebrum
Hippocampus
Basal Ganglia
Amygdala
Cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body. Two hemispheres joined by corpus callosum.
Left Cerebral Hemisphere
Dominates in speech sounds & in understanding sequential, rational & analytical concepts
Right Cerebral Hemisphere
Controls left body,
Creative, Visual, facial recognition, visual, and musical traits, nonverbal communication, negative emotions, and concept comprehension
Frontal Lobe Functions
*Voluntary movement (primary cortex/precentral gyrus)
*Intellect
*Orientation
*Broca's area: Speech and concentration
*Personality, temper, judgment, reasoning, behavior, self-awareness, executive functions
Frontal Lobe Impairment
Contralateral weakness
Perseveration/inattention
Personality changes/antisocial behavior
Broca's Aphasia (expressive deficits)
Delayed/Poor intiation
Emotional Lability
Parietal Function
Sensory
Touch, kinesthesia, vibration, temp
Receives info from other areas of brain regarding senses and memory
Provides meaning or objects, interprets language and words, spatial/visual perception
Parietal Impairment
Dominant hemisphere (usually left): Agraphia, alexia, agnosia
Non-dominant hemisphere: Dressing apraxia, contstructional apraxia, anosognosia (unaware of deficit)
Contralateral sensory deficits
Impaired language comprehension and impaired taste
Temporal Function
-Hearing and smell
-Wernicke's area (ability to understand/produce meaningful speech, verbal and general memory)
Temporal Dysfunction
Learning deficits
Wernicke's Aphasia (receptive deficits)
Antisocial/aggressive behavior
Difficulty with facial recognition, memory loss, inability to categorize
Occipital Function
Visual processing--colors, light, shapes, 3D, judging distance
Occipital Impairment
-homonymous hemianopsia
-impaired extra ocular mvmt
-reading and writing impairment
-cortical blindness with bilat lobe involvement
Hippocampus
Responsible for forming/storing new memories and important to learning language. Embedded in lower temporal lobe.
Basal Ganglia
Gray matter masses in the white matter of cerebrum:
-Caudate
-Putamen
-Globus Pallidus
-Substantia Nigra
-Subthalamic Nuclei
Responsible for voluntary movement, regulation of autonomic movement, posture, tone, and motor responses.
Basal Ganglia Dysfunction
-Difficulty starting, stopping or sustaining movement
-Uncontrollable, repeated movements (shaking)
-Muscle spasms and muscle rigidity
-Parkinson's/Huntington's, Tourette's, ADD, OCD, addiction
Amygdala
Emotional and social processing. Processing of memory and formation of emotional memeory.
Thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla and appropriate association cortex.
Coordinates sensory perception and movement.
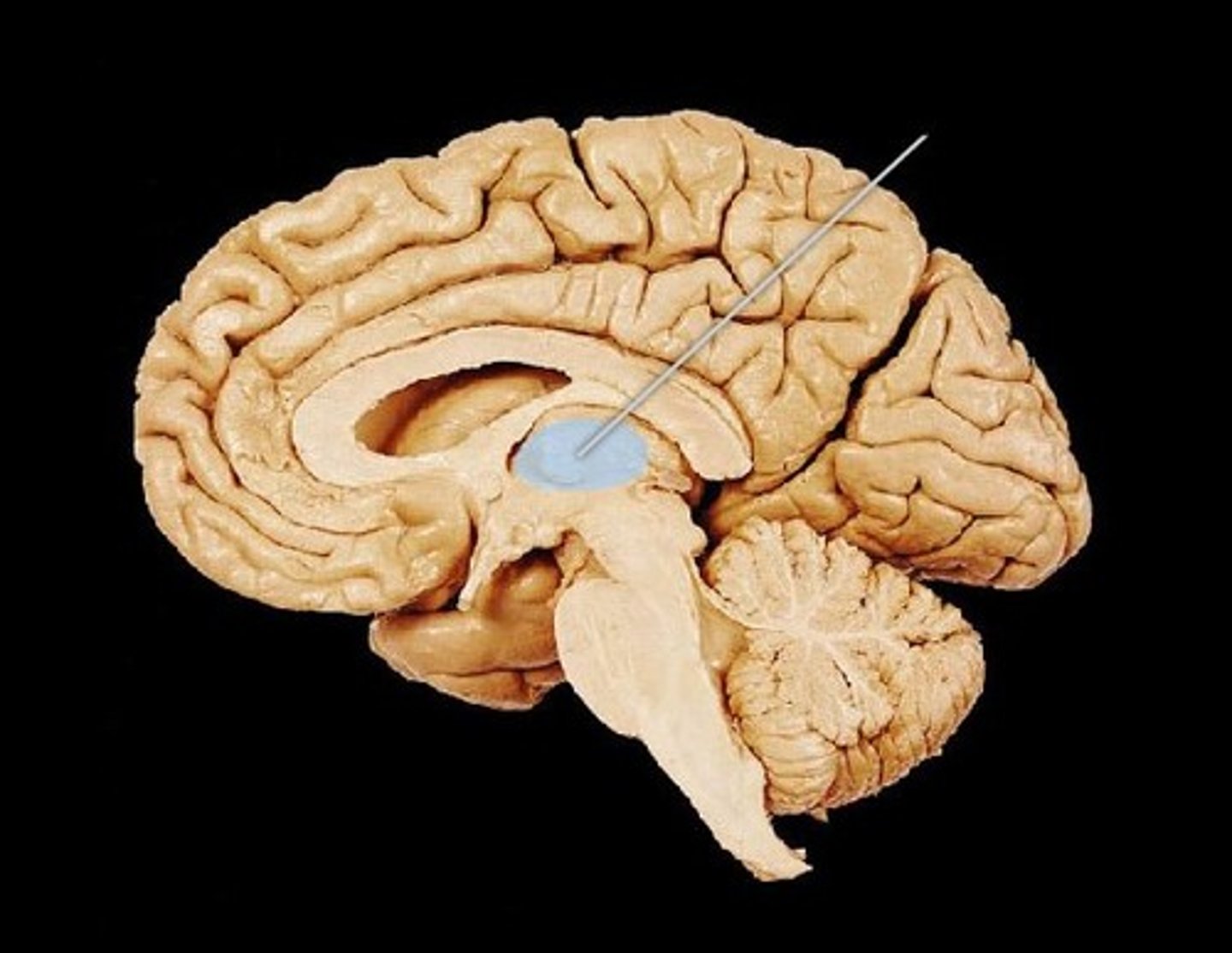
Thalamic Pain Syndrome
a condition caused by damage to the thalamus resulting in burning or tingling sensations and possibly hypersensitivity to things that would not normally be painful such as light touch or temperature change.
Contralateral to thalamic lesion
Hypothalamus
Regulates homeostasis using hormones, controlling hunger, thirst, sexual behavior, sleeping, body temp.
Lesions produce impairments based on area of damage (obesity, sexual disinterest, poor temp control, diabetes insipidus)
Subthalamus
Regulates movements by skeletal muscles, associated with basal ganglia and substantia nigra.
Epithalamus
Contains pineal gland, which secretes melatonin and regulates internal clock.
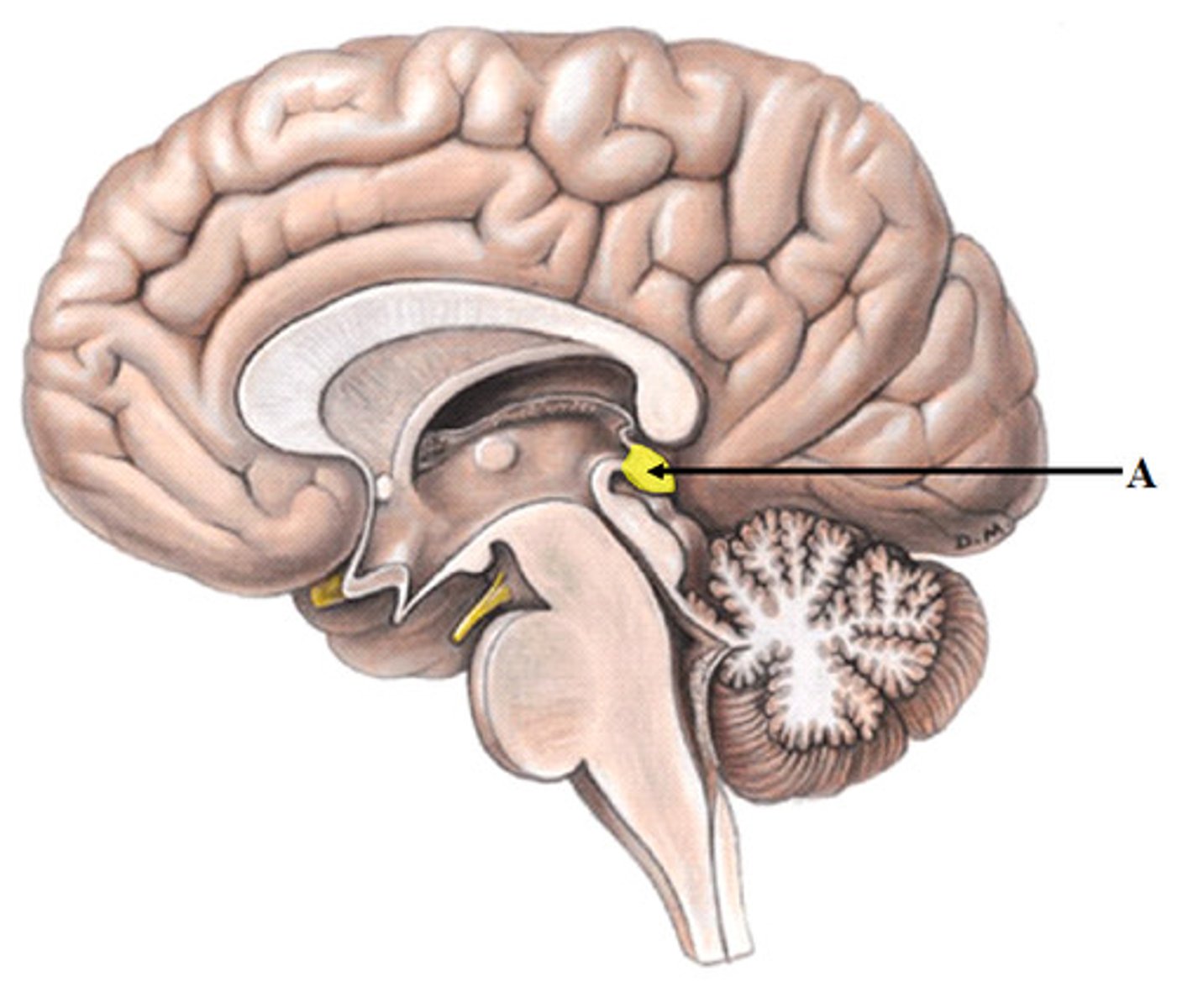
Cerebellum
Control of finely coordinated movements. Coordination center, voluntary movement and balance. "Small brain."
Rapid alternating movements.
Damage to one side of cerebellum will produce ipsilateral impairment.
Lesions produce ataxia, nystagmus, tremors, hypermetria, poor coordination, and deficits in postural reflexes.
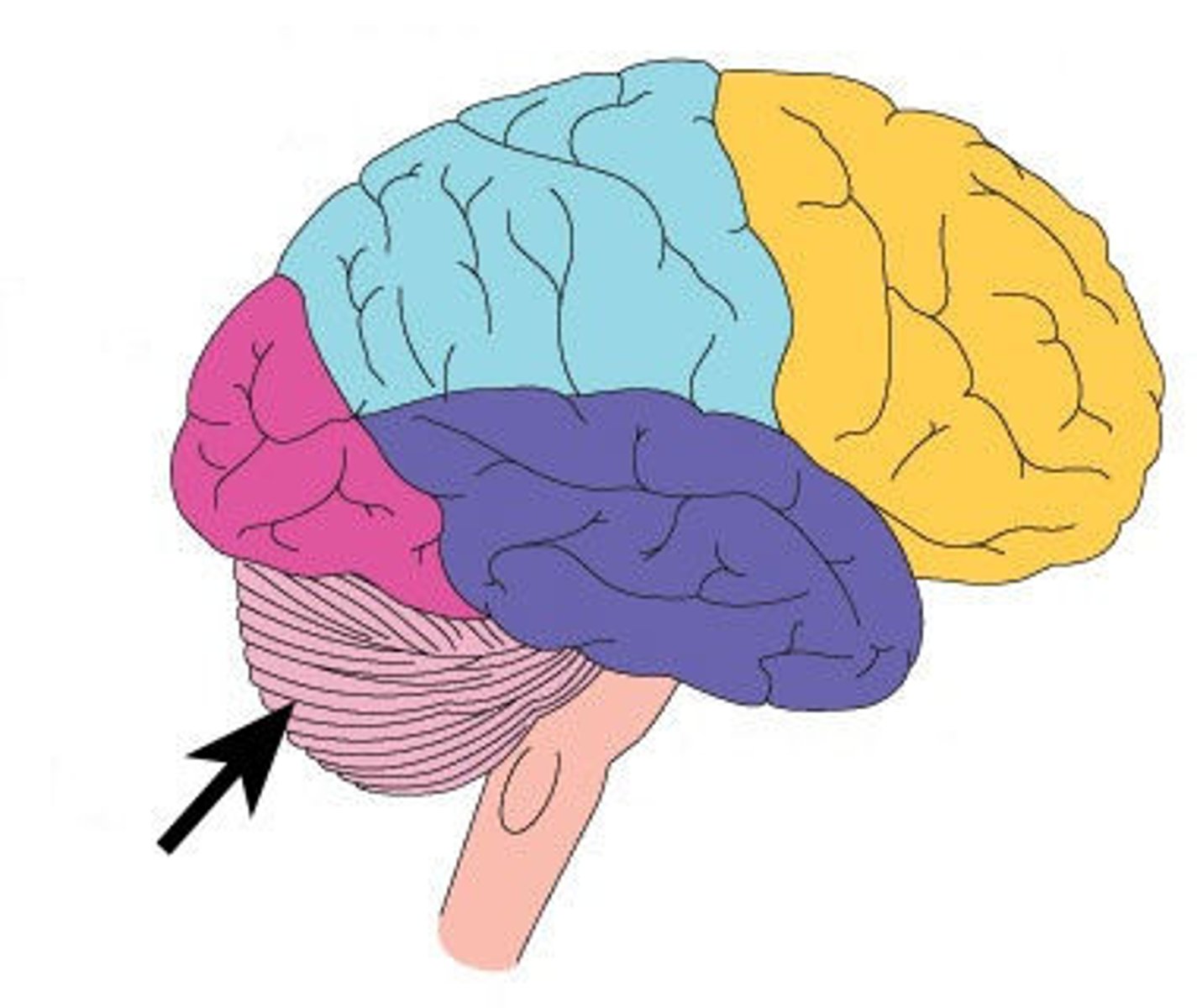
Pons
Regulates RR and associated with orientation of head in relation to auditory/visual stimuli.
Cranial nerves V-VIII originate from pons.
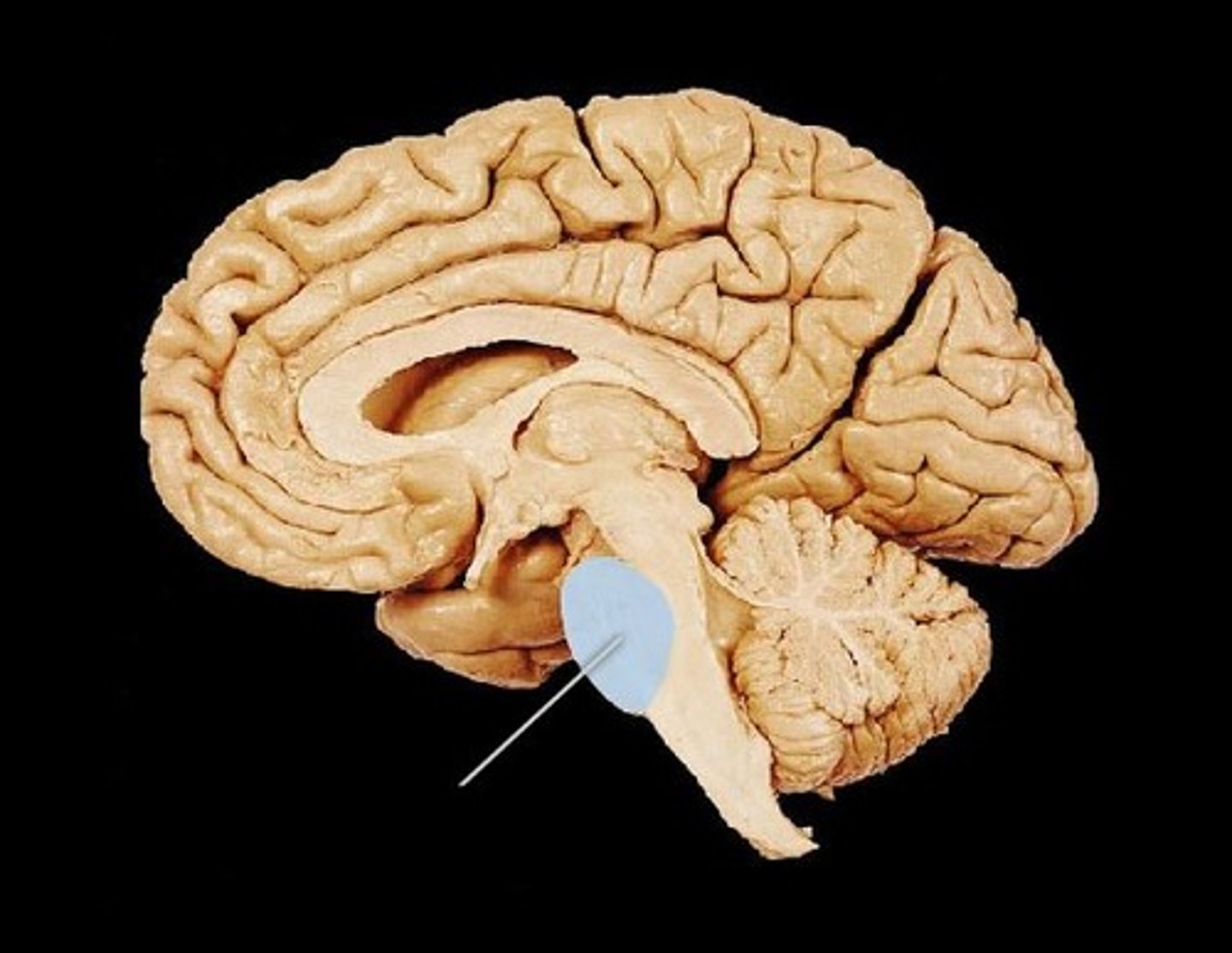
Medulla Oblongata
Connects to pons superiorly and spinal cord inferiorly.
Influences autonomic nervous activity and regulation of RR and HR. Reflex centers for vomiting, coughing, and sneezing.
Damage produces contralateral impairment.
Cranial nerves IX-XII originate from this structure.
Anterior Cerebral Artery
Supplies frontal lobe, and medial surface of frontal and parietal lobes.
Occlusion results in:
-Paraplegia
-Incontinence
-Personality changes
-Aphasia, Apraxia, Agraphia
-Perseveration
-Akinetic Mutism (mimicks catatonia)
Middle Cerebral Artery
Supplies most of outer cerebrum, basal ganglia
Most common site of CVA
Occlusion results in:
-Contralateral hemiplegia
-Global, Wernicke's, or Broca's Aphasia
-Homonymous Hemianopsia
-Apraxia
-Contralateral weakness and sensory loss of face/lower extremity
Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA)
Supplies Occipital and inferior temporal lobes, subthalamic and basal nucleus, thalamus, and portion of midbrain.
Occlusion results in:
-Thalamic Pain syndrome
-Hemiballismus, ataxia, athetosis, choreiform movement
-Homonymous Hemianopsia
-Visual agnosia
-Cortical blindness
-Memory impairment
Vertebral-Basilar Artery
Supplies Cerebellum, medulla, pons, occipital cortex, and midbrain.
Occlusion results in:
-Locked-in syndrome, coma, vegetative state
-Wallenberg syndrome (secondary to lat medullary infarct) results in ataxia, verigo, ipsilateral facial pain/temp impairment and contralateral pain/temp impairment
-vertigo, nystagmus
-Dysphagia, Dysarthria, Syncope
Meningitis
Inflammation of the meninges. Bacterial meningitis is fatal in hours.
Sxs:
-Fever, headache, vomiting
-Complaints of stiff/painful neck
-Pain in lumbar area and posterior thigh
-Brudzinski's sign: flexion of neck facilitates flexion of hips and knees
-Kernig's sign: Pain with hip flexion combined with knee extension
-Sensitivity to light
Treatment with antibiotics and steroids, lumbar puncture for diagnosis
Hydrocephalus
Increase of CSF in ventricles of brain due to poor resorption, obstructed flow, or excessive CSF production. Can be congen, acquired, or idiopathic. Can be caused by spina bifida, choroid plexus neoplasm, cerebral palsy, tumor, meningitis, or encephalocele.
Sxs:
-Enlarged head or bulging fontanelles in infants
-Headache
-Vision and behavioral changes
-Seizures, altered appetite or vomiting
-Downward deviation of eyes ("sun-setting")
-Incontinence
Fasciculus cuneatus
Trunk, neck, and UE: Proprioception, 2 pt disc, graphesthesia
Fasciculus Gracilis
Trunk, LE: Proprioception, 2 pt disc, vibration, graphesthesia
Gracilis like the leg muscle
Spinocerebellar tract
Ipsilateral subconcious proprioception
Spinoreticular tract
Afferent pathway for reticular formation, influences level of consciousness.
Spinotectal tract
Afferent info for spinovisual reflexes, movement of eyes and head towards stimulus
Spinothalamic tract
pain and temperature
Corticospinal tract
Voluntary refined movements of distal extremities. Pyramidal. Damage to this tract results in positive Babinski sign, absent cremasteric reflex, and loss of fine motor skills
Reticulospinal tract
extrapyramidal motor tract responsible for facilitation or inhibition of voluntary and reflex activity through the influence on alpha and gamma motor neurons
Rubrospinal tract
Extrapyramidal motor tract responsible for motor input of gross postural tone, facilitating activity of flexor muscles, and inhibiting the activity of extensor muscles
Tectospinal tract
extrapyramidal motor tract responsible for contralateral postural muscle tone associated with auditory/visual stimuli
Vestibulospinal tract
Extrapyramidal tract for ipsilateral postural adjustments after head movements, extensor activation and flexor inhibition.
Damage to extrapyramidal tracts results in paralysis, hypertonicity, exaggerated DTRs, and clasp-knife reaction
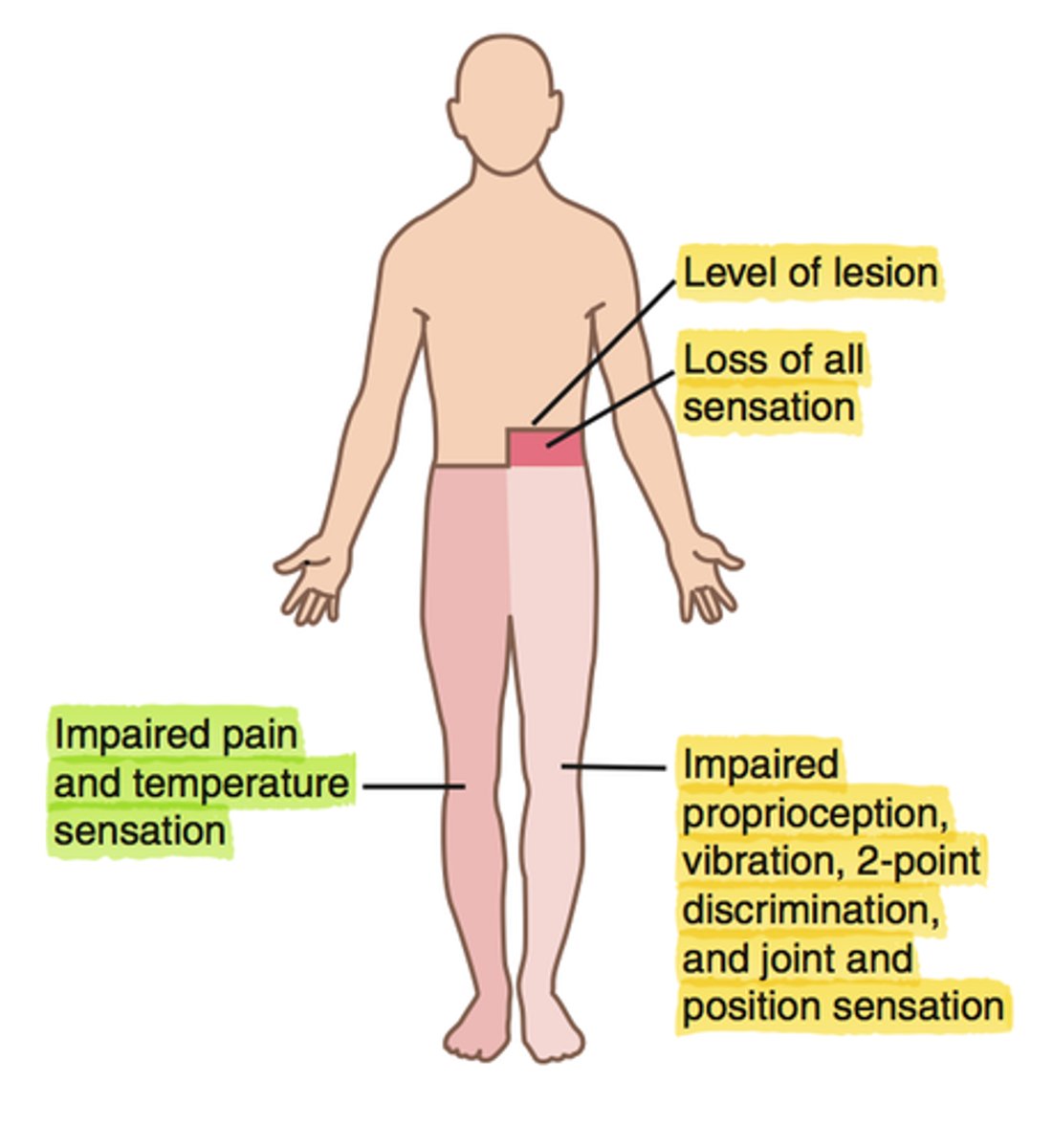
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
Hemi-section of the cord
- ipsilateral (same side) spastic paralysis and loss of position sense
- contralateral (opposite side) loss of pain and thermal sense
A fibers
Peripheral nerve fibers.
Large size, myelinated with high conduction rates.
Sensory components:
-Primary muscle spindle endings (low threshold stretch)
-Secondary muscle spindle endings (change in length facilitates muscle contraction)
-GTOs: (interrupt muscle contractions on stretch of tendon)
Alpha: alpha motor neurons, muscle spindle primary endings, GTOs, touch
Beta: Touch, kinesthesia, muscle spindle secondary endings
Gamma: Touch, pressure, gamma motor neurons
Delta: Pain, Touch, pressure, temp
B Fibers
Peripheral nerve fiber
Medium diameter, myelinated, reasonably fast
Preganglionic fibers of autonomic nervous system
C fibers
Peripheral Nerve Fibers
Small diameter, unmyelinated, slow conduction rate. Postganglionic fibers.
C1
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Vertex of skull
Muscles innervated: None
Reflexes (if any): None
Paresthesias: None
C2 dermatome
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Temple/forehead/occiput
Muscles innervated: Longus colli, SCM, rectus capitis
Reflexes (if any): None
Paresthesias: None
C3
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
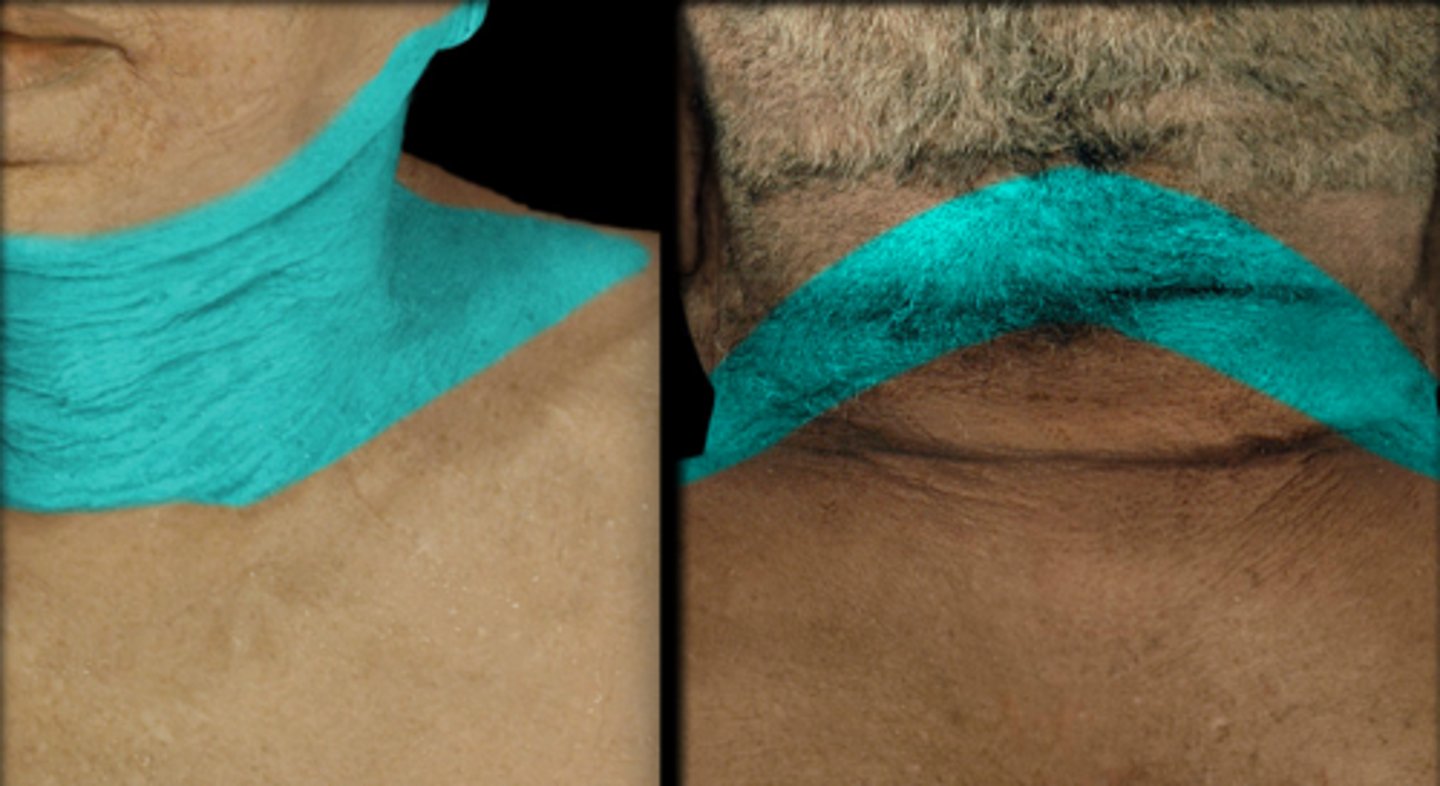
Dermatome: Neck, posterior cheek, temporal area, mandible
Muscles innervated: Trap, Splenius capitis
Reflexes (if any): None
Paresthesias: Cheek, side of neck
C4
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
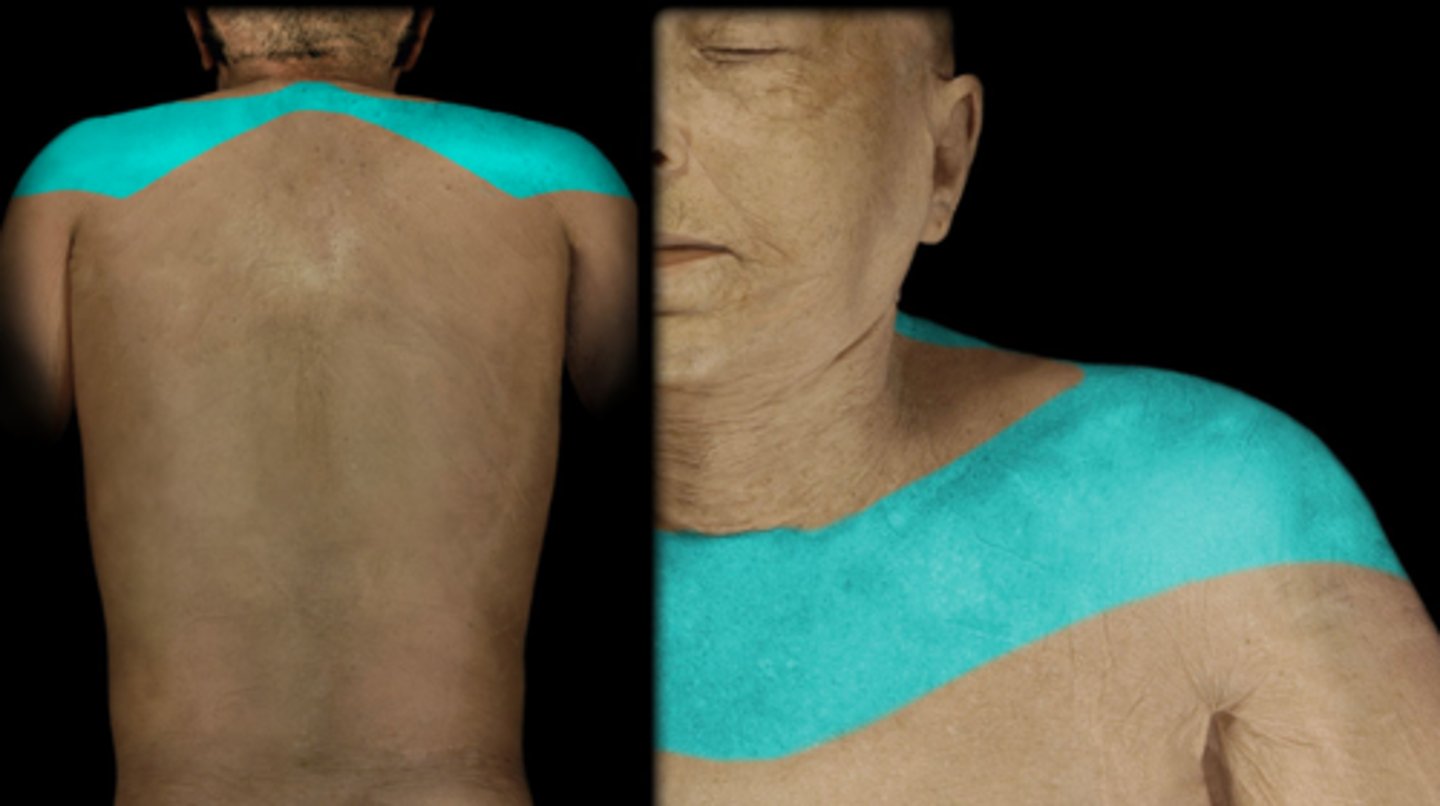
Dermatome: Shoulder, clavicle, upper scap
Muscles innervated: Trap, Levator Scap
Reflexes (if any): None
Paresthesias: Clavicle and upper scap
C5
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
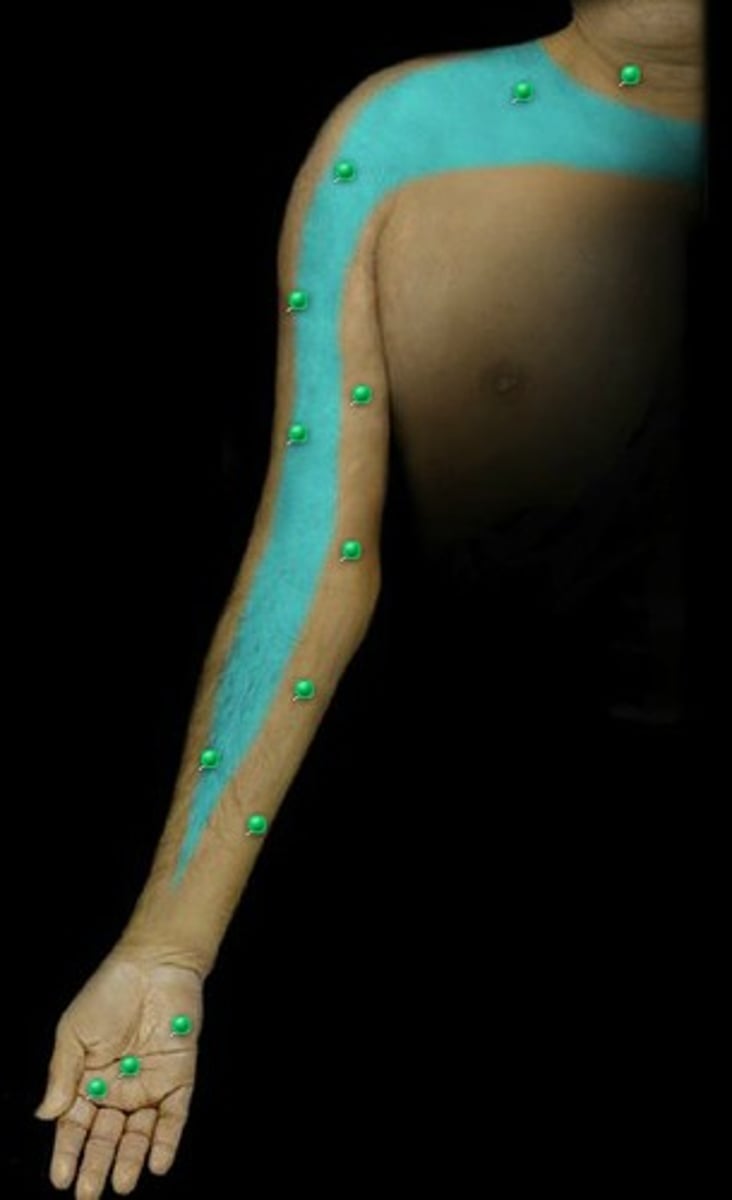
Dermatome: Delt, Anterior arm to base of thumb
Muscles innervated: Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, delt, biceps
Reflexes (if any): Biceps, brachioradialis
Paresthesias: None
C6
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
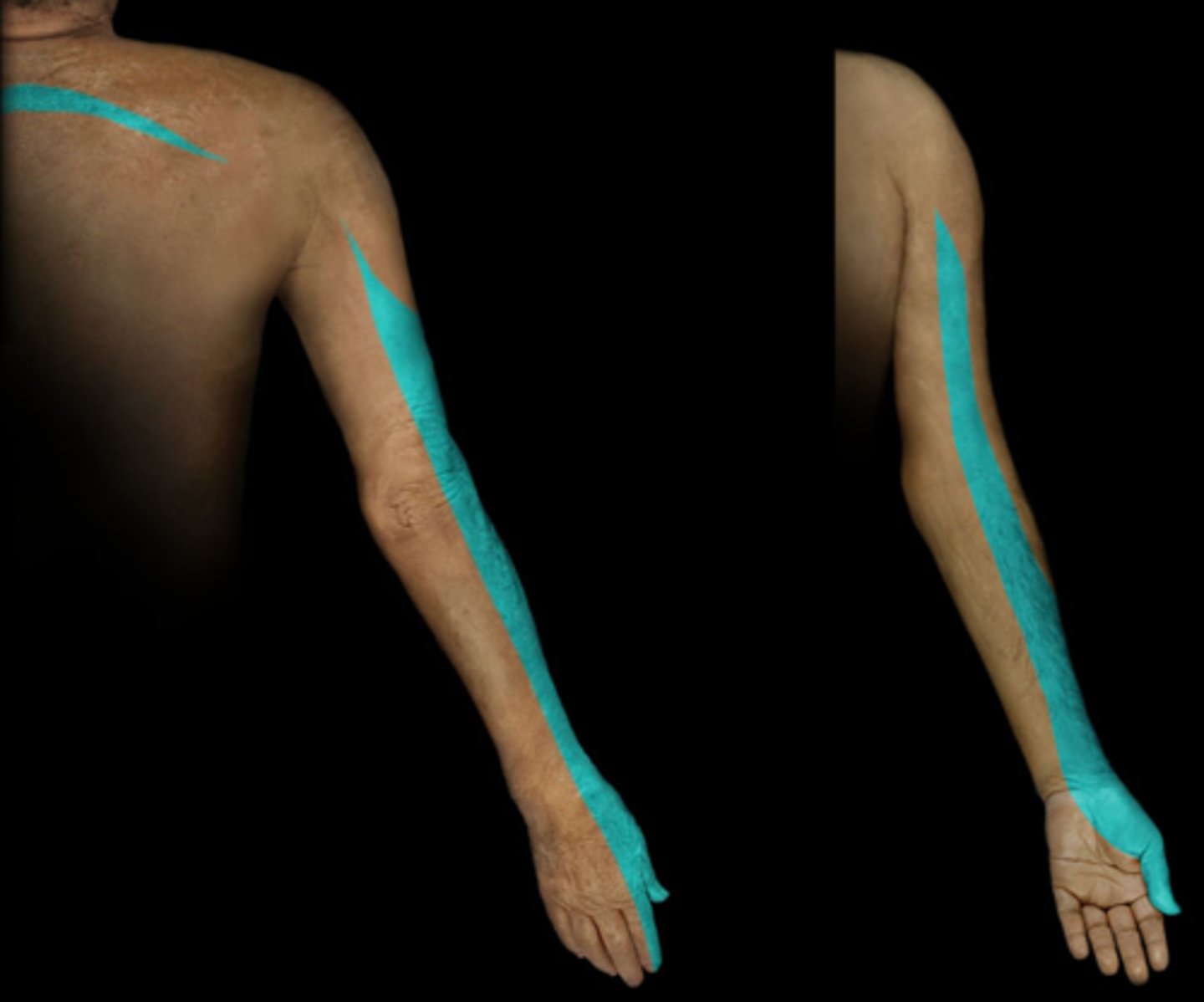
Dermatome: Anterior arm, radial side of hand to thumb and index finger
Muscles innervated: Biceps, supinator, wrist extensors
Reflexes (if any): Biceps, brachioradialis
Paresthesias: Thumb and index finger
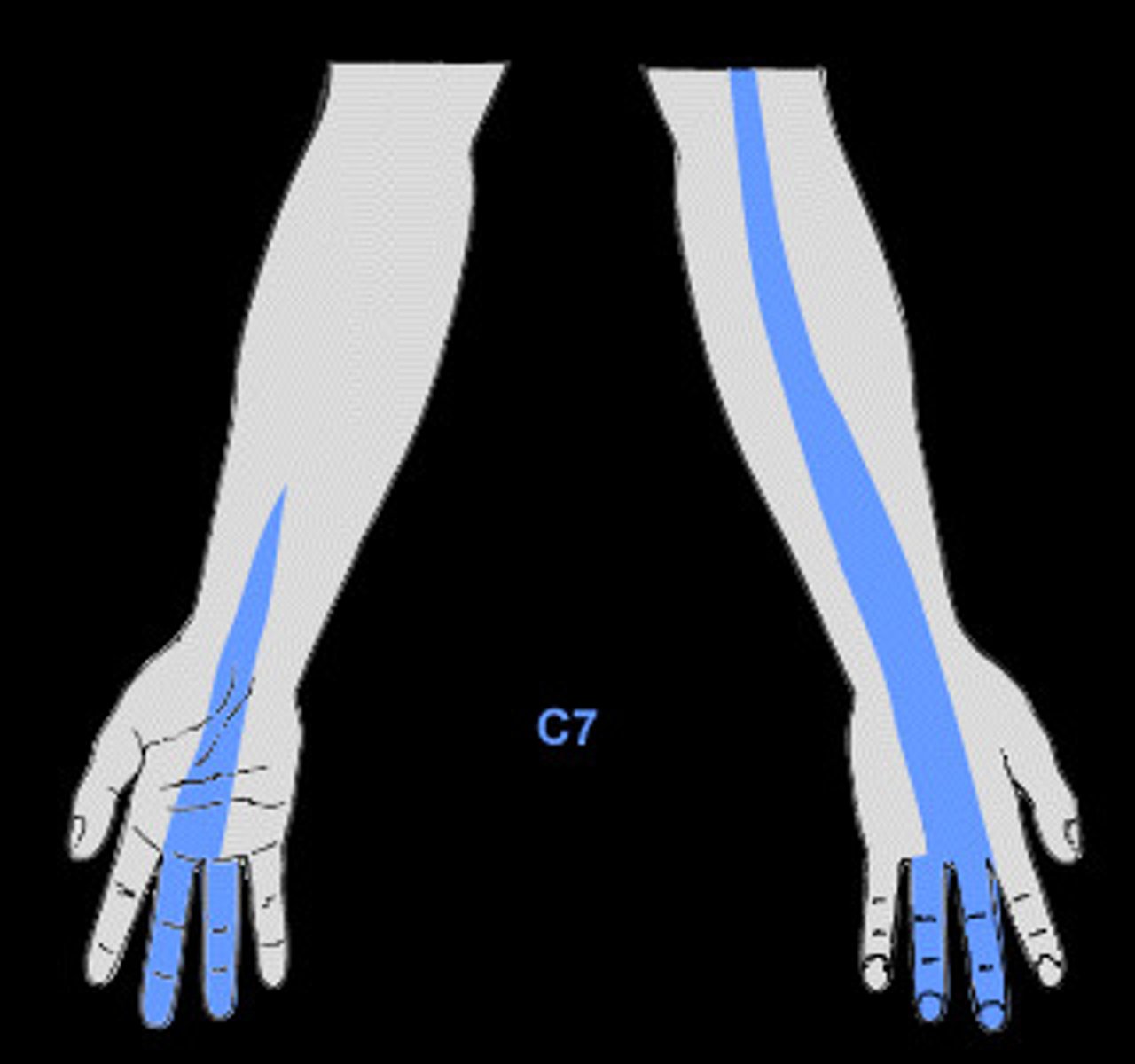
C7
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Lateral arm/forearm to index, long and ring fingers
Muscles innervated: Triceps, wrist flexors
Reflexes (if any): Triceps
Paresthesias: Index, long, and ring fingers
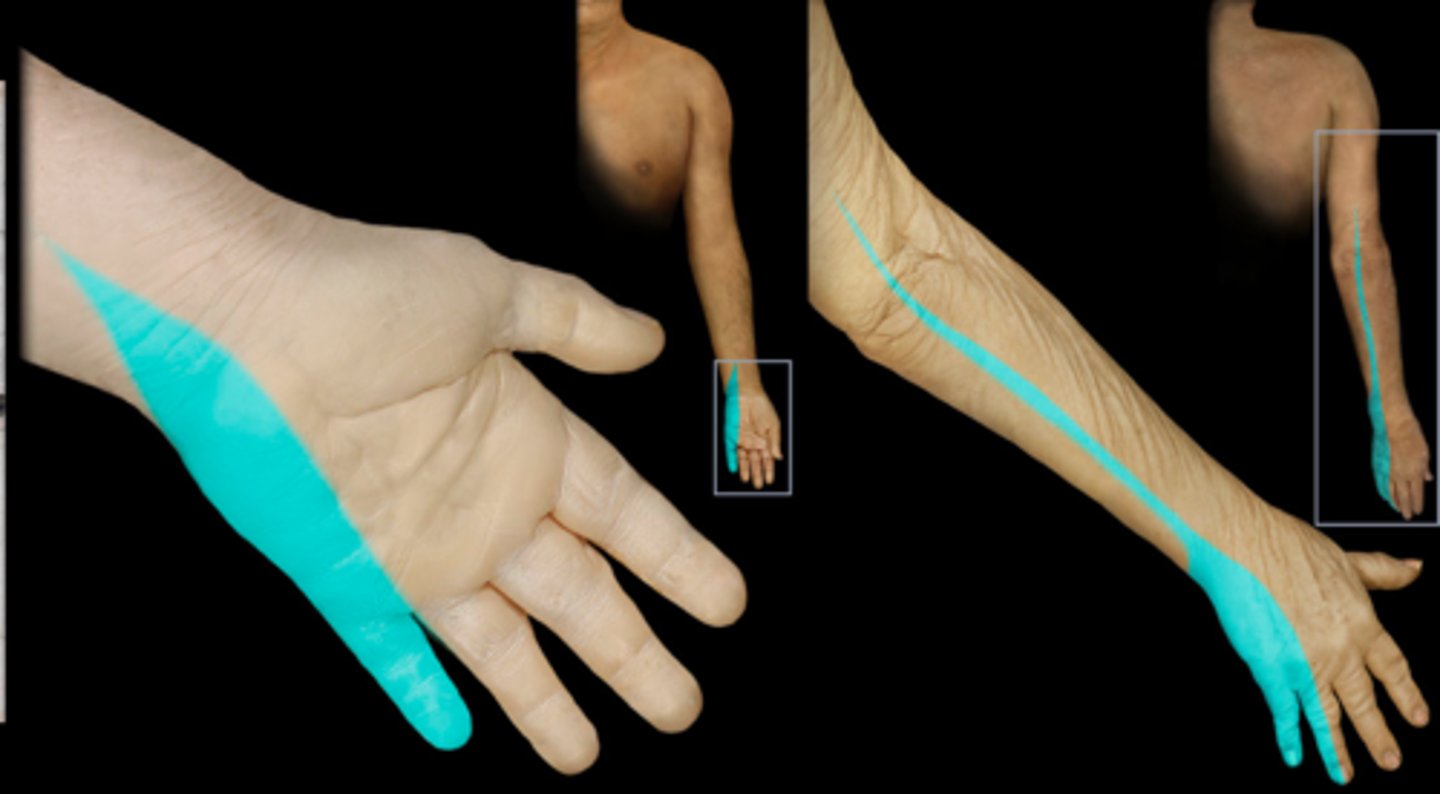
C8
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Medial arm and forearm to long, ring, and middle fingers
Muscles innervated: Ulnar deviators, thumb EXT, thumb adductors
Reflexes (if any): None
Paresthesias: Little finger
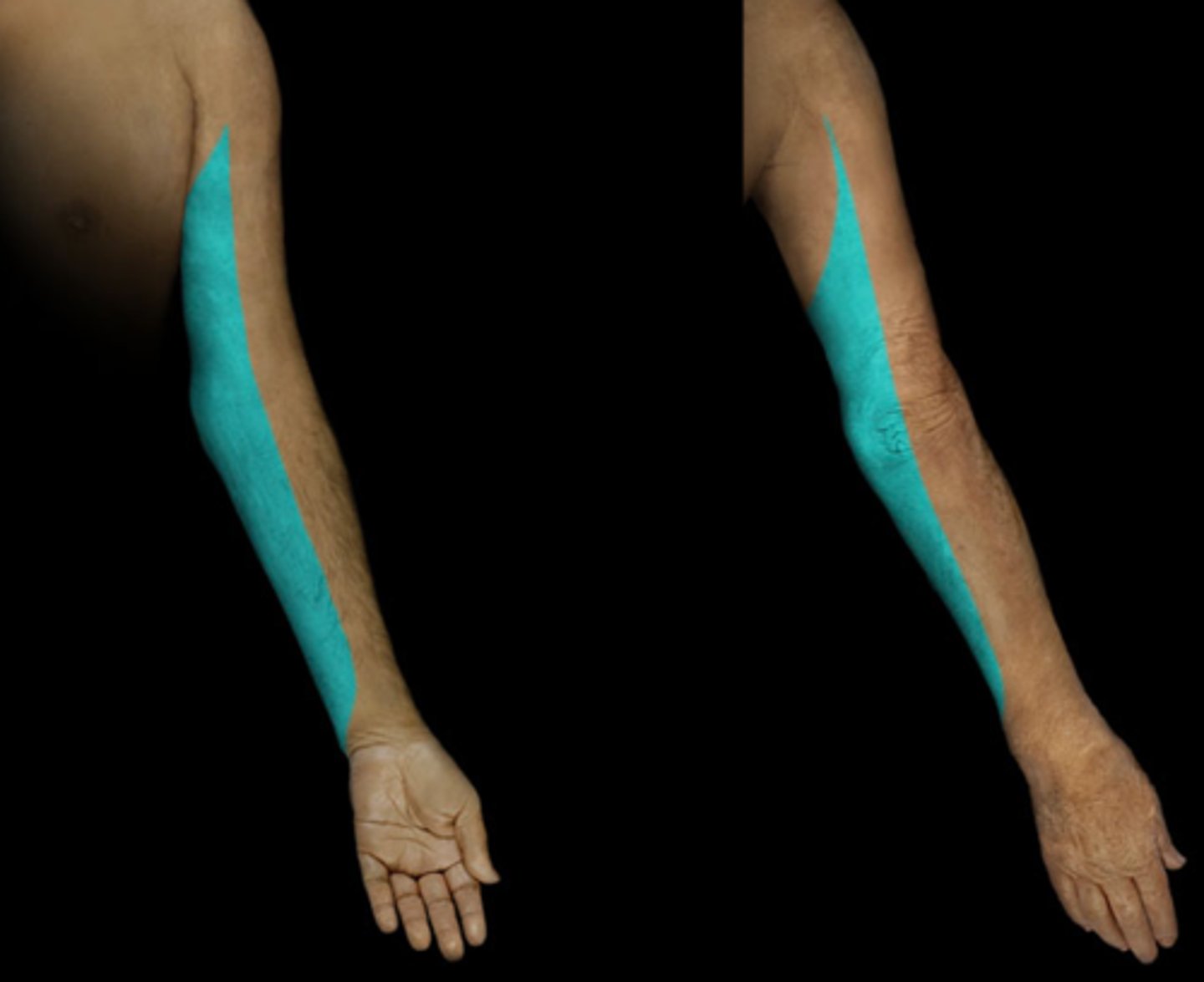
T1
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Medial side of forearm to base of little finger
Muscles innervated: Finger abductors
Reflexes (if any): None
Paresthesias: None
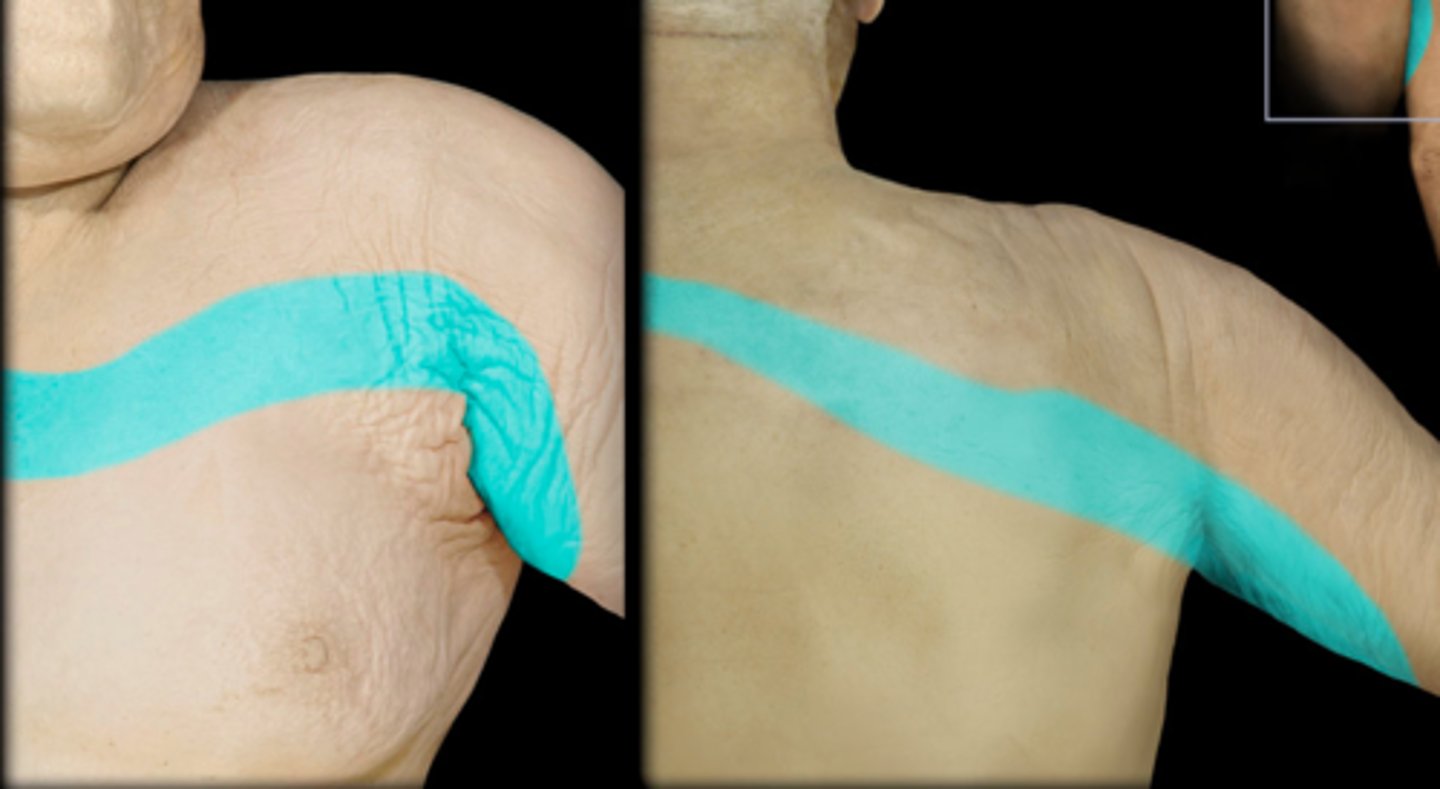
T2
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Medial upper arm to medial elbow, pec and midscap areas
T3-T-12
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome:
-T3-6: upper thorax
-T5-7: Costal margin
-T8-T12: Abdomen and lumbar region
Muscles innervated: None
Reflexes (if any): None
Paresthesias: None
L1
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Back, over trochanter and groin
Muscles innervated: None
Reflexes (if any): None
Paresthesias: Groin
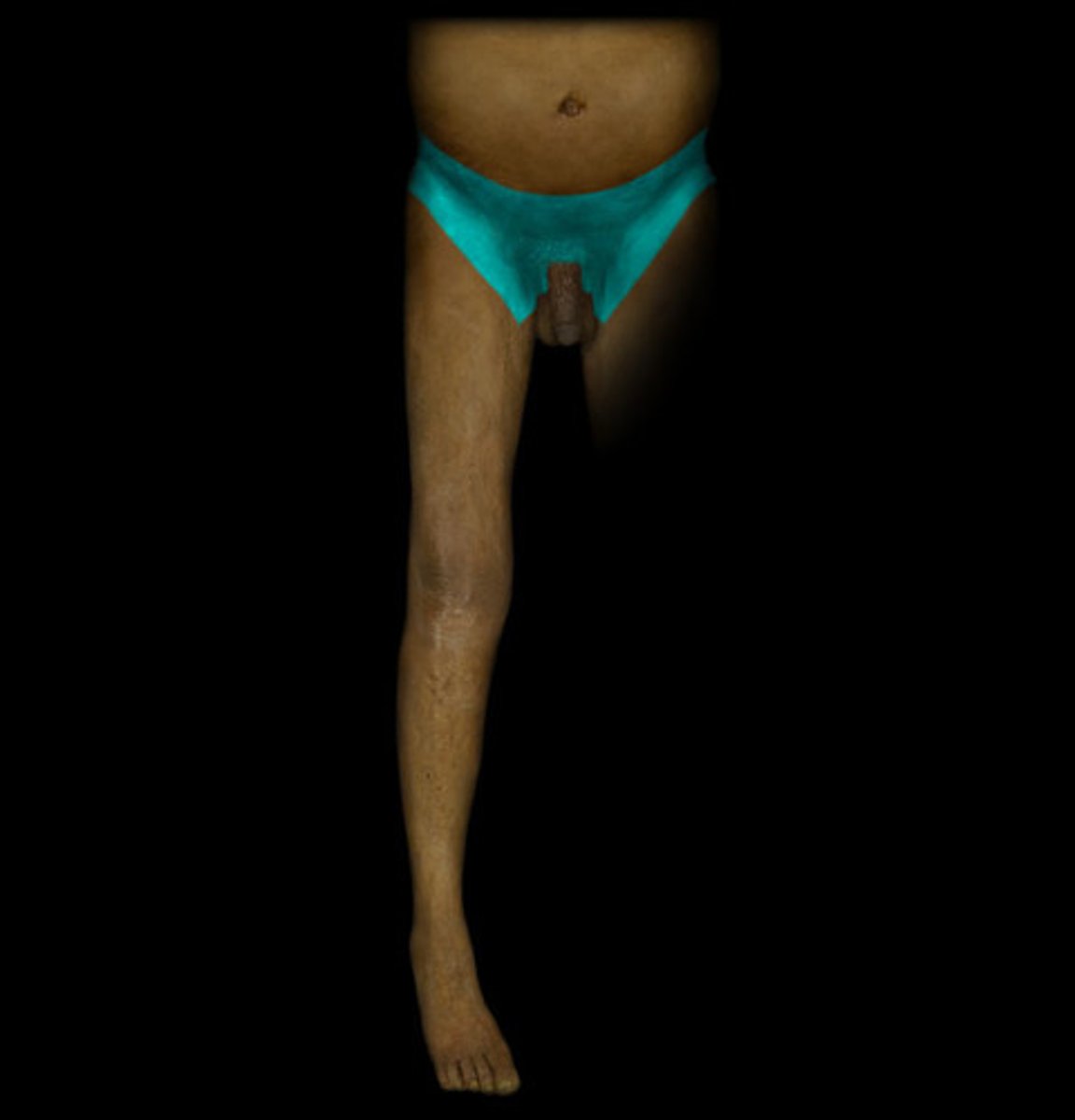
L2
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Front of thigh and knee
Muscles innervated: Psoas, hip adductors
Reflexes (if any): None
Paresthesias: Anterior thigh
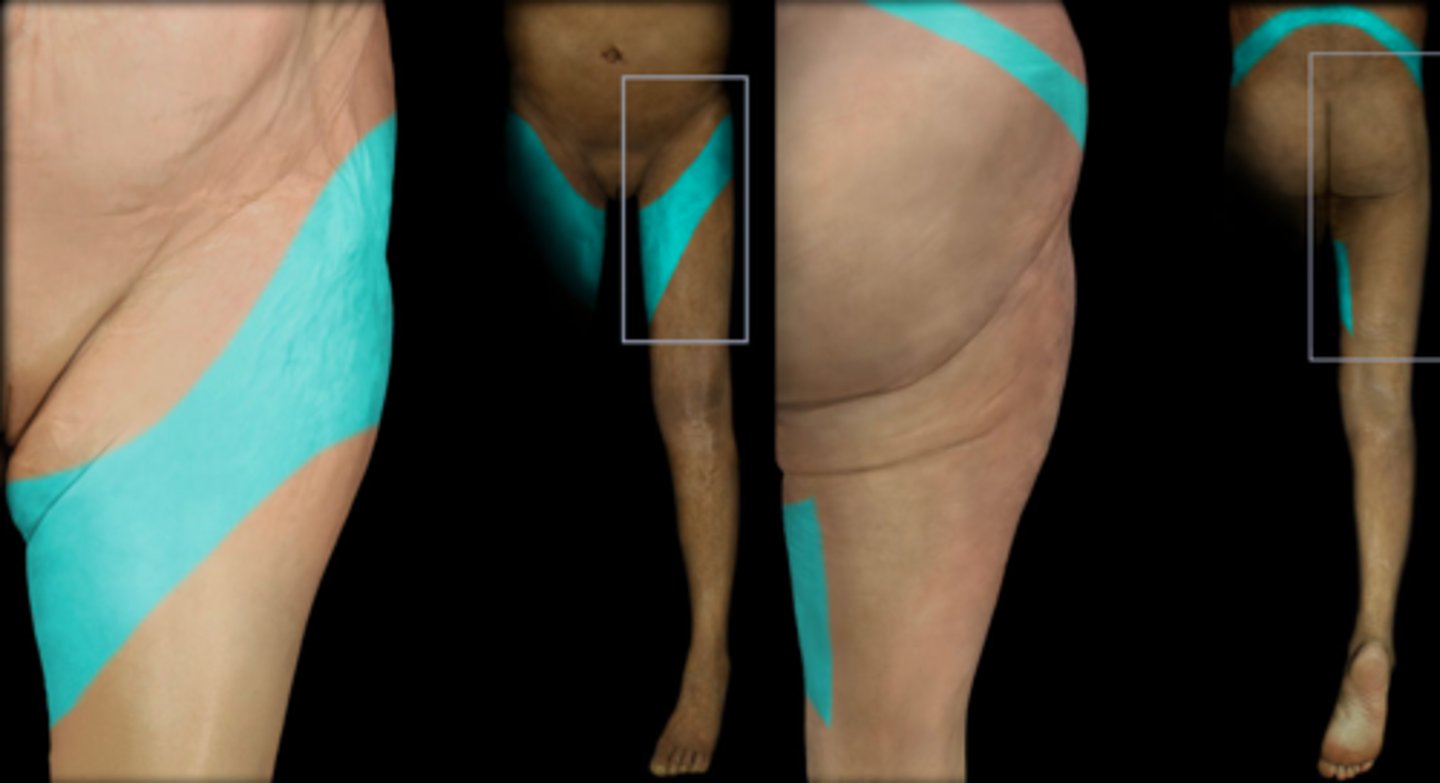
L3
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Back, upper buttock, anterior thigh/knee, medial lower leg
Muscles innervated: Psoas, quads, thighs
Reflexes (if any): Knee jerk, prone knebend positive, pain on full SLR
Paresthesias: Medial knee, anterior lower leg
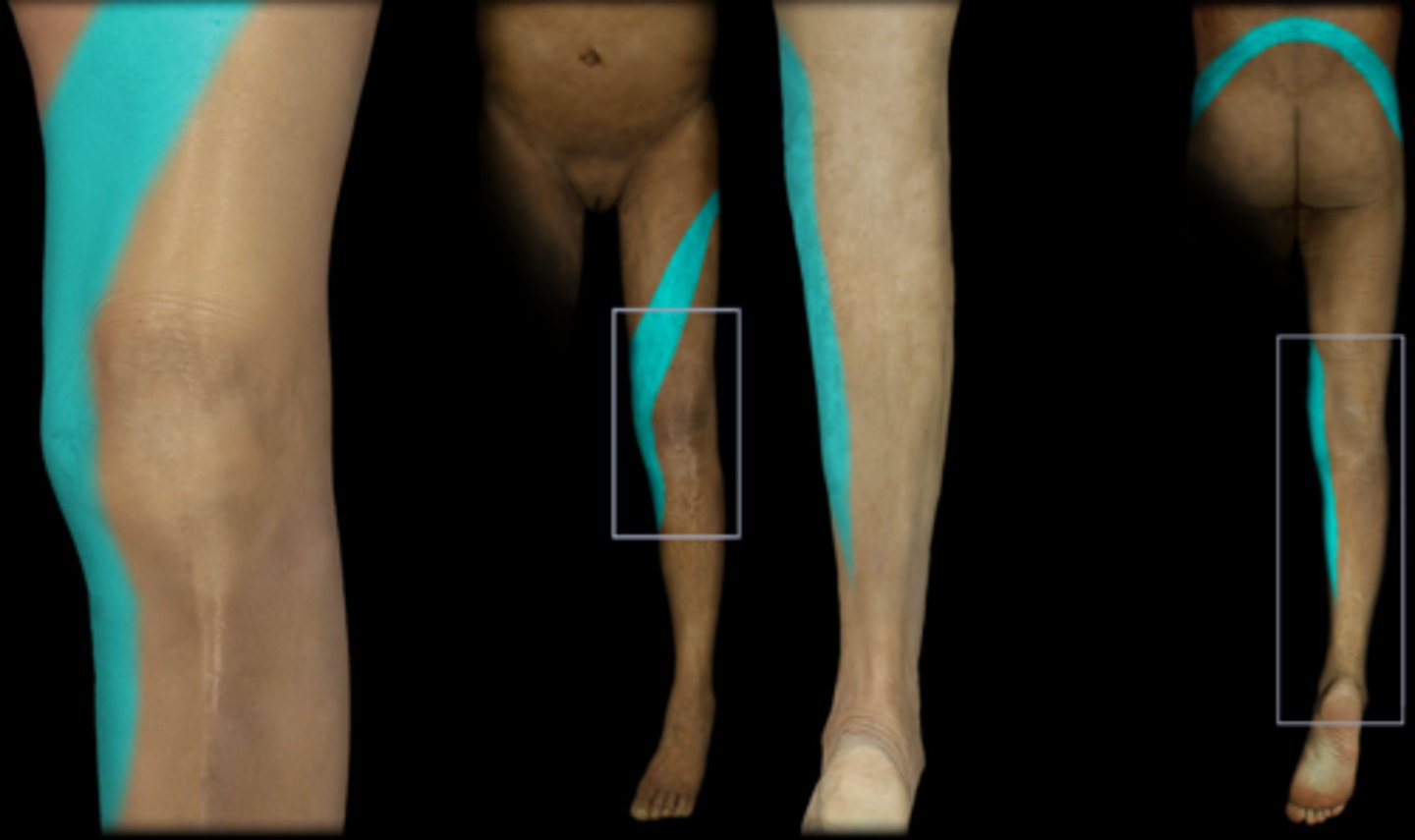
L4
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Medial buttock, lateral thigh, medial leg, dorsum of foot, big toe
Muscles innervated: Tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis
Reflexes (if any): Weak or absent knee jerk, SLR limited, side flexion limited
Paresthesias: Medial aspect of calf and ankle
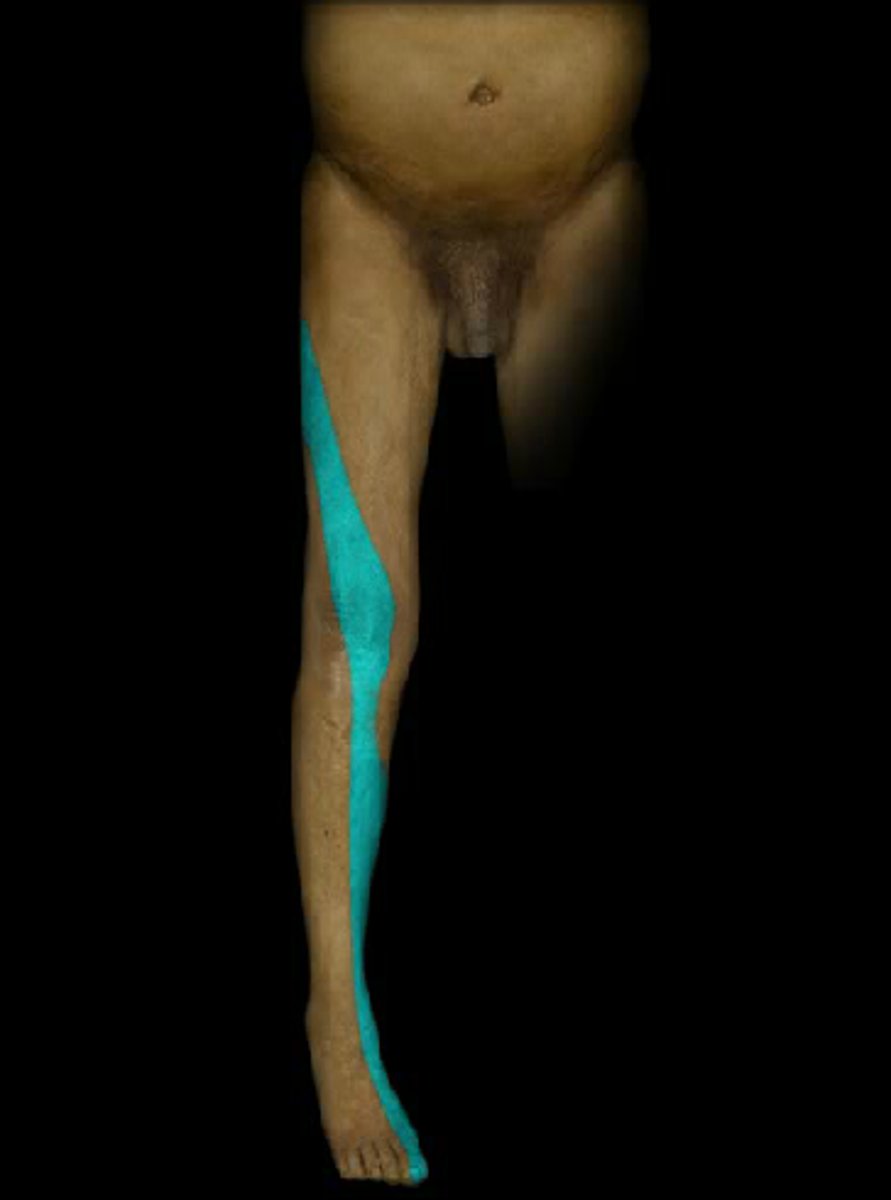
L5
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Buttock, posterior/lateral thigh, lateral aspect of leg, dorsum of foot, medial half of sole, first, second, and third toes
Muscles innervated: Extensor hallucis, peroneals, glute med, DFs
Reflexes (if any): SLR limited one side, neck flexion painful
Paresthesias:
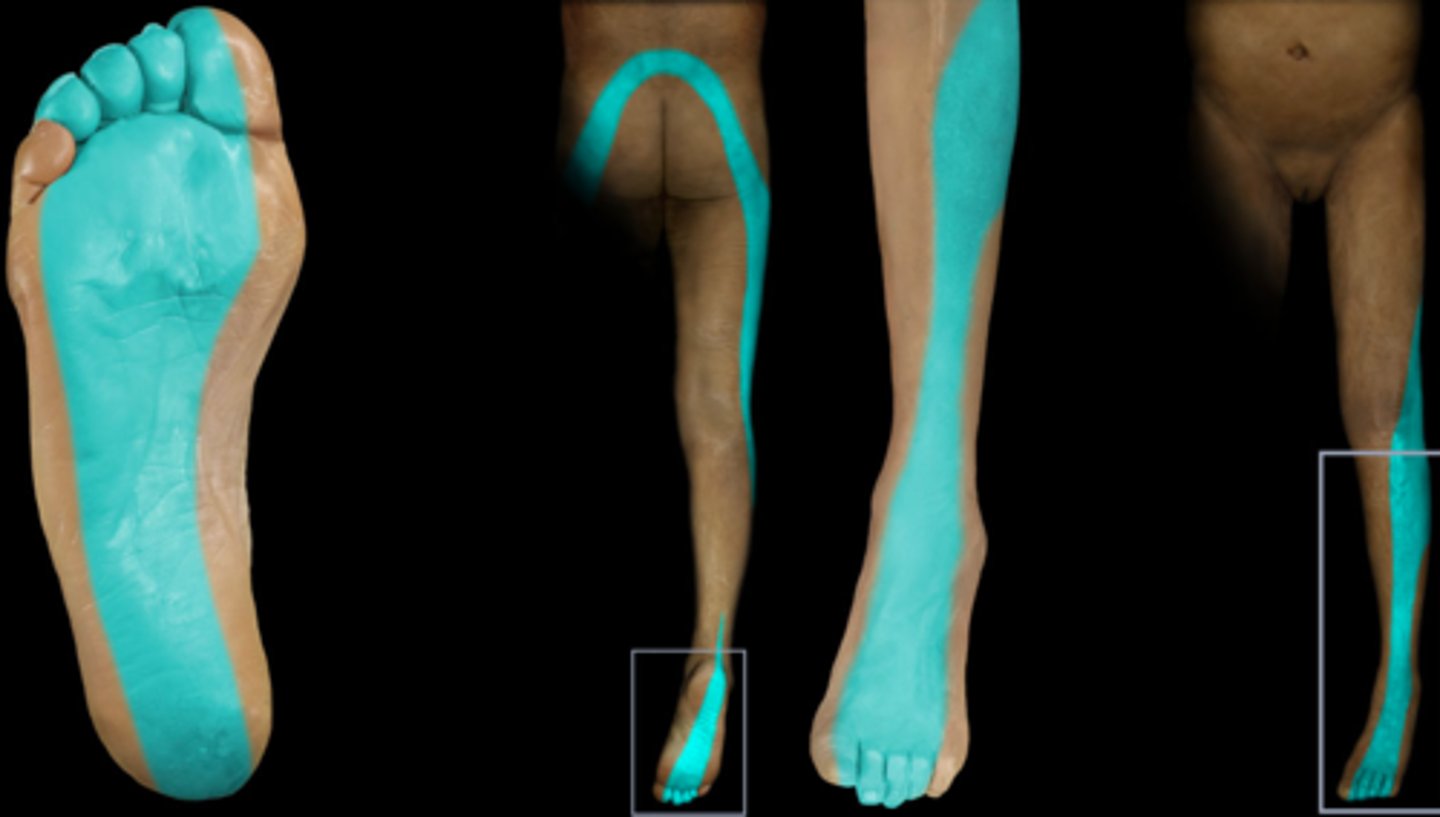
S1
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Lateral and plantar aspect of foot
Muscles innervated: Calf and hamstrings, glute wasting, PFs
Reflexes (if any): Achilles reflex wek or absent
Paresthesias:
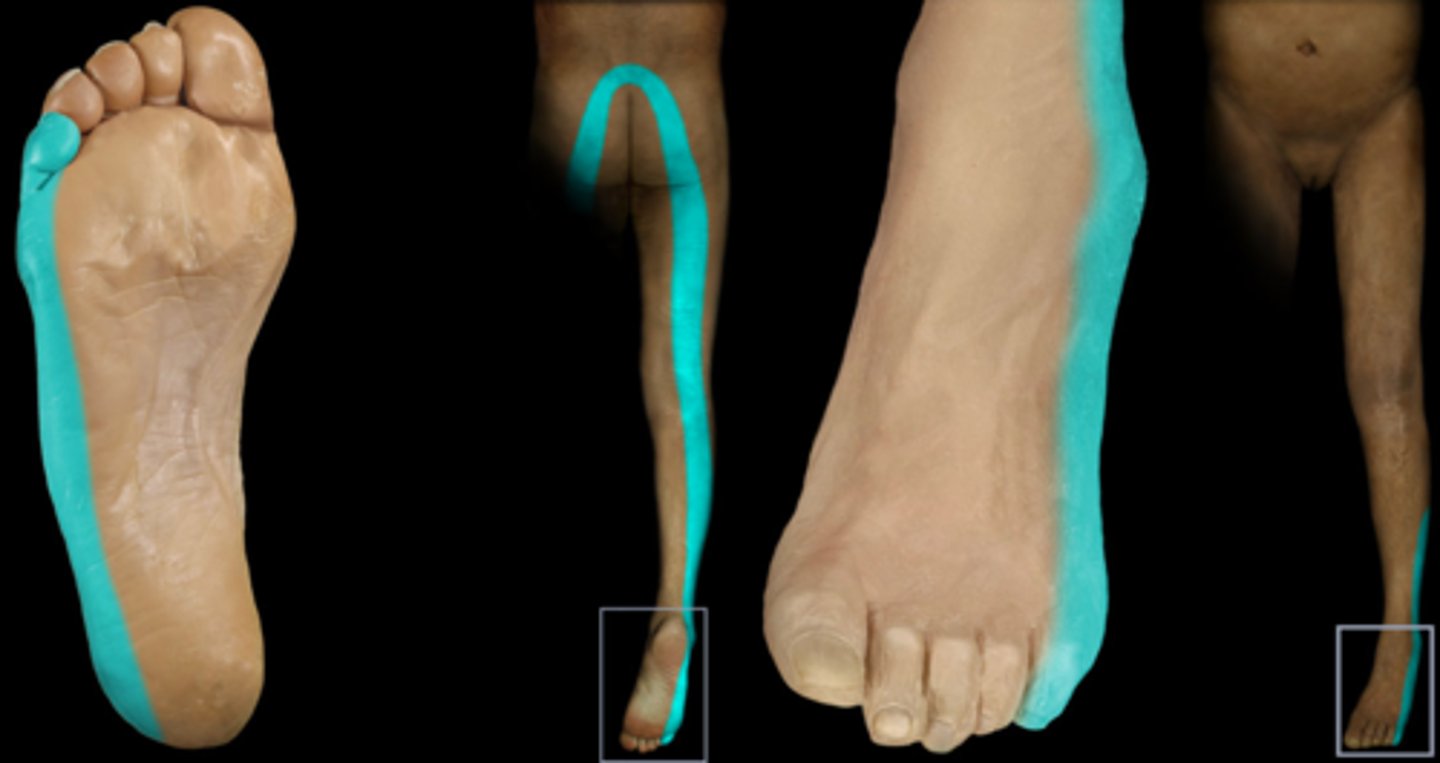
S2
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Buttock, thigh, posterior leg
Muscles innervated: Same as S1 +peroneals
Reflexes (if any): Achilles
Paresthesias: Lateral leg, knee, and heel
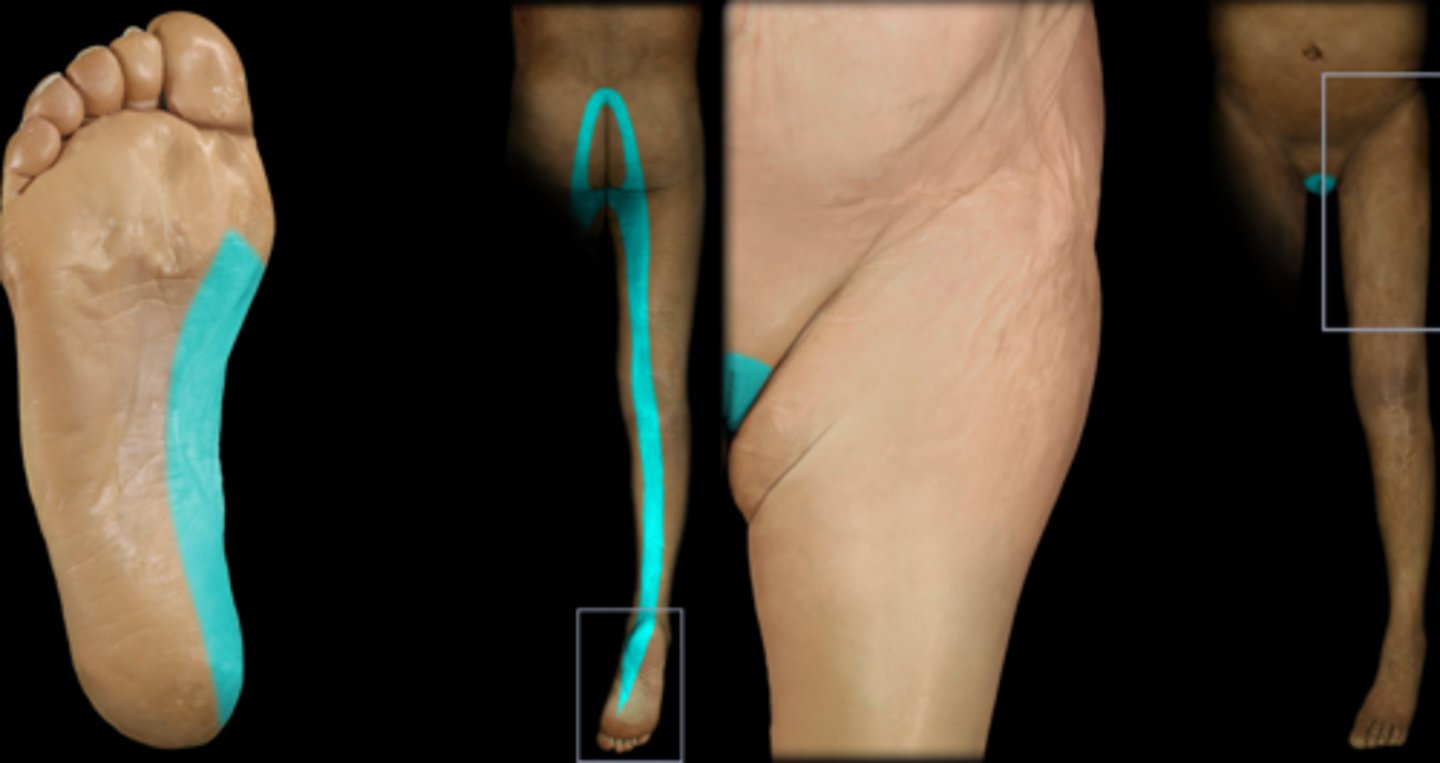
S3 dermatome
Dermatome: Groin, medial thigh to knee
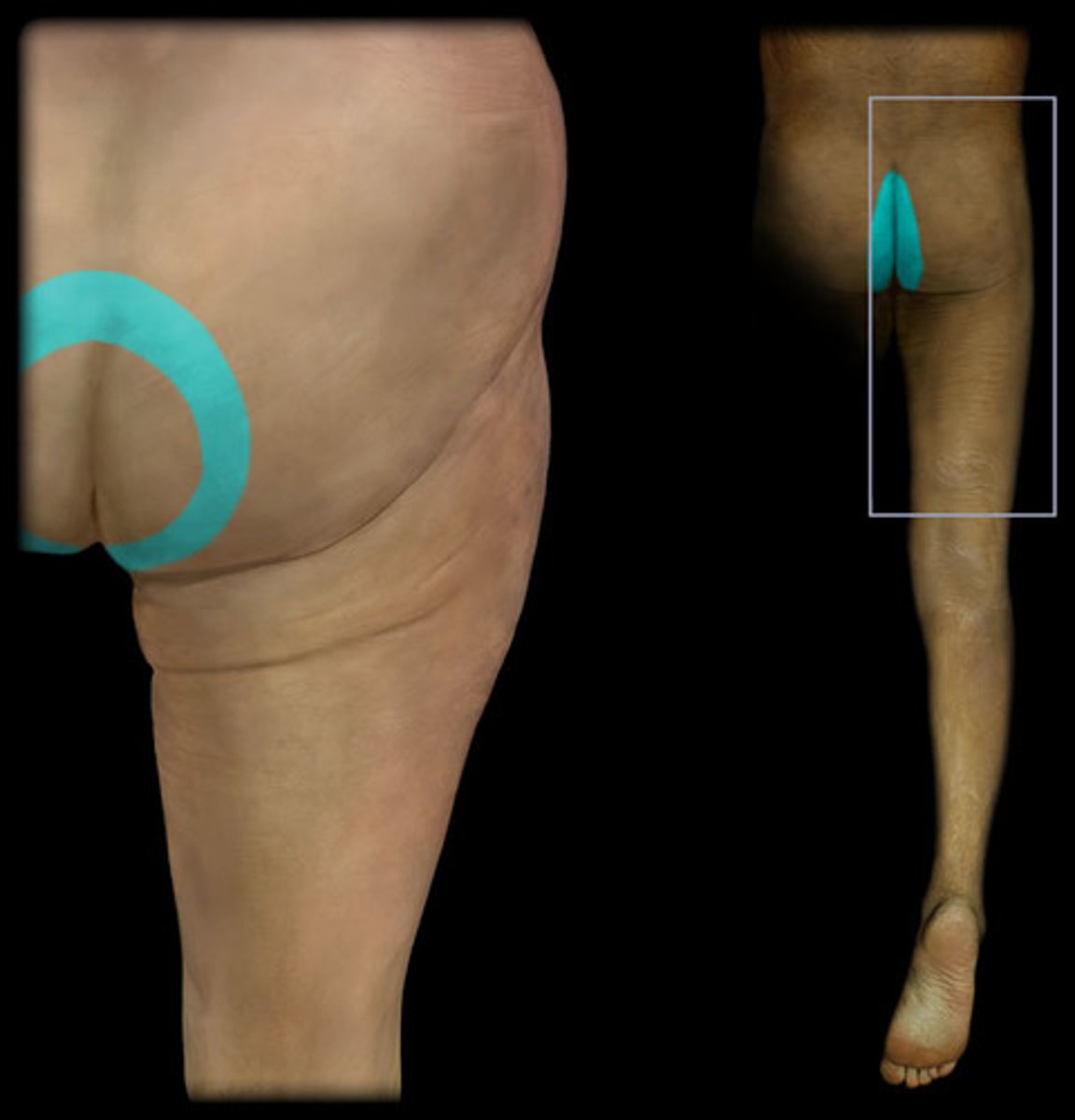
S4
Dermatome:
Muscles innervated:
Reflexes (if any):
Paresthesias:
Dermatome: Perineum, genitals, lower sacrum
Muscles innervated: Bladder, rectum
Reflexes (if any): None
Paresthesias: Saddle area, genitals, anus, impotence, posterior herniation
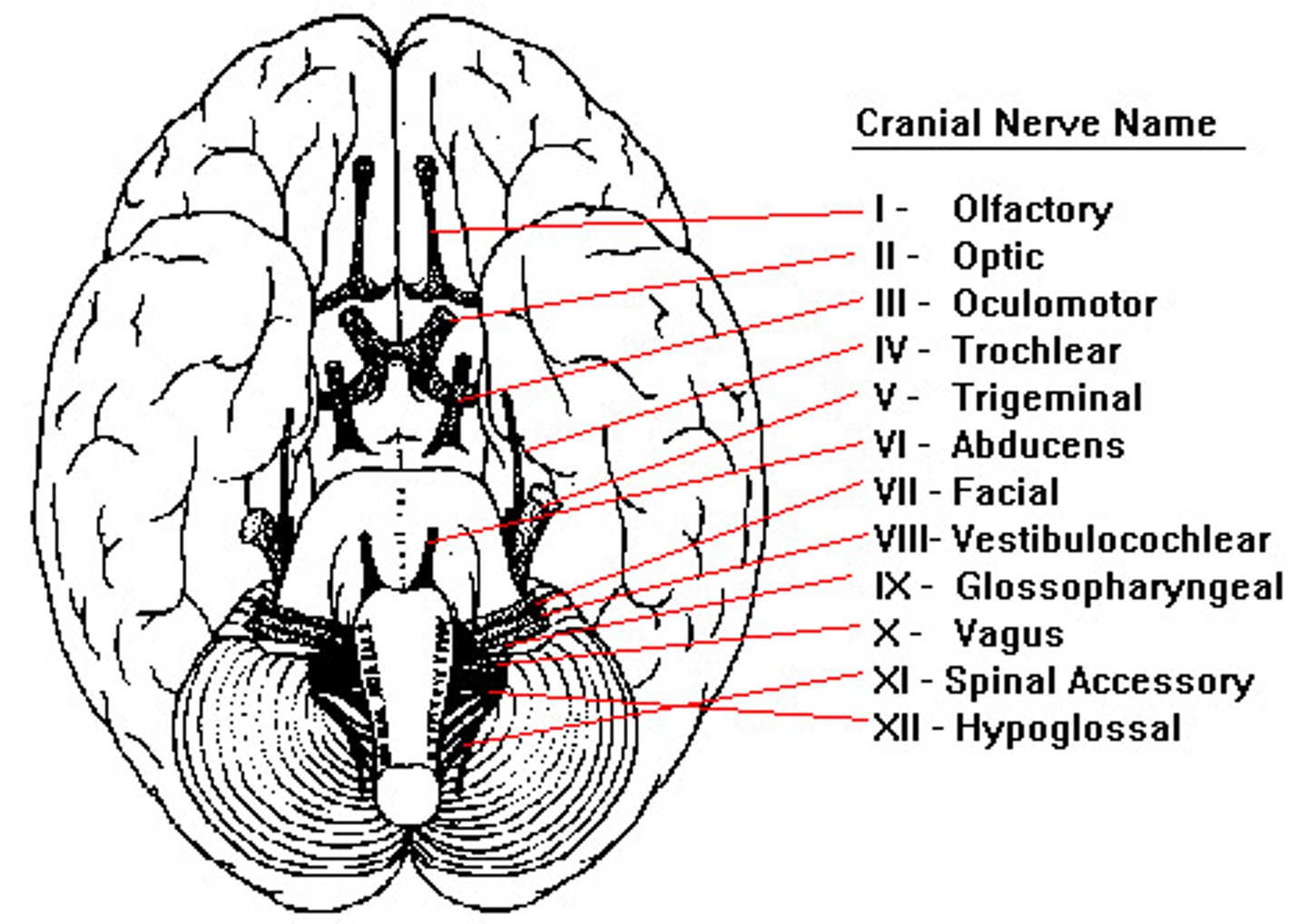
Cranial Nerves
CN I: Olfactory (Sensory)
CN II: Optic (Sensory)
CN III: Oculomotor (Motor)
CN IV: Trochlear (Motor)
CN V: Trigeminal (Both)
CN VI: Abducens (Motor)
CN VII: Facial (Both)
CN VIII: Vestibulocochlear (Sensory)
CN IX: Glossopharyngeal (Both)
CN X: Vagus (Both)
CN XI: Accessory (Motor)
CN XII: Hypoglossal (Motor)
OOOTTAFVGVAH "Oh oh oh, to touch and feel"
SSMMBMBSBBMM "Some say marry money..."
CN I
Olfactory
Sensory: Smel
Test: Familiar odors (chocolate, coffee)
CN II
Optic
Sensory: Vision (central and peripheral vision)
Test: Visual fields
Common pathologies: Multiple sclerosis, Posterior CVA
CN III
Oculomotor
Motor: Levator of eyelid, superior/inferior/medial recti, inferior oblique
Test: Visual tracking (up, down, and medial gaze), and reaction to light
Common Pathologies: MS and Horner's
CN IV
Trochlear
Motor: Superior oblique
Test: Visual tracking (down and in)
CN V
Trigeminal
Sensory: Touch/pain on face, membranes of nose, sinuses, mouth and tongue
Motor: Mastication
Test: Corneal reflex, facial sensation, push down on chin
Common Pathologies: ALS, Trigeminal Neuralgia
CN VI
Abducens
Motor: Lateral rectus of eyeball
Test: Lateral gaze
CN VII
Facial
Sensory: Taste on anterior tongue
Motor: Facial muscles, lacrimal and sublingual glands
Test: Facial expressions, taste
Common Pathologies: ALS, Bell's Palsy, GB
CN VIII
Vestibulocochlear
Sensory: Hearing and balance
Test: Hear watch ticking, hearing tests, balance and coordination test
CN IX
Glossopharyngeal
Sensory: Posterior tongue sensation and taste, pharynx
Motor: Pharynx
Test: Gag reflex, swallowing
Common Pathologies: ALS, GB , Medullary Stroke
CN X
Vagus
Sensory: Pharynx, larynx, bronchi, taste in tongue/epiglottus
Motor: Muscles of palate, pharynx, larynx. Thoracic and ab viscera
Test: Gag reflex, ability to swallow, "Say ahhhhh"
CN XI
Accessory
Motor: SCM and Trap
Test: Resisted Shoulder shrug
CN XII
Hypoglossal
Motor: Muscles of tongue
Test: Tongue protrusion (if injured, tongue deviates towards injured side)
Muscle innervated by Lumbar Plexus
Psoas major, minor
Quadratus Lumborum
Muscles innervated by Sacral Plexus
Piriformis
Superior and inferior gemelli
Obturator Internus
Quadratus Femoris
Muscles innervated by tibial division of Sciatic Nerve
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Biceps Femoris (long head)
Muscles innervated by Common Peroneal division of Sciatic Nerve
Biceps Femoris (short head)
Muscle innervated by Inferior Gluteal Nerve
Glute Max