Carboxylic acids and derivatives
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
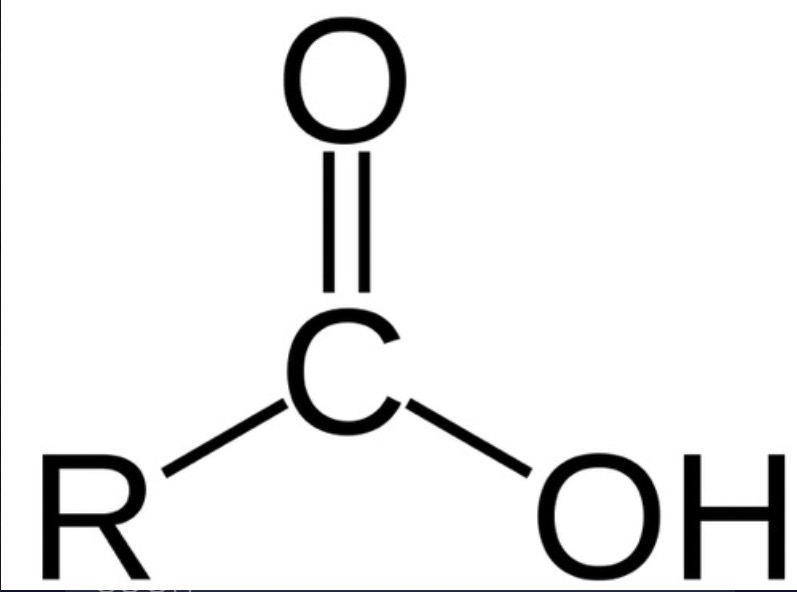
what is a carboxylic acid?
a molecule with an alcohol group bonded to a carbonyl group (CARBOXYL GROUP)
what is a carboxyl group?
COOH
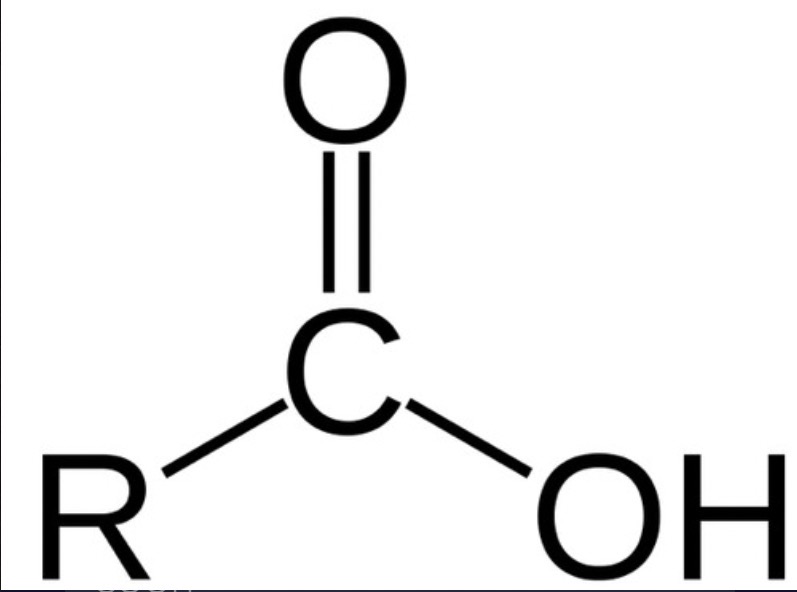
what groups do all carboxylic acid derivatives have?
acyl group (carbonyl group)
suffix for saturated carboxylic acids?
-anoic acid
suffix for unsaturated carboxylic acids?
-enoic acid if alkene functional group is present
test for carboxylic acids?
add an equal amount of sodium carbonate, fizzes and bubbles produced. CO2 produced bubbled through limewater turns it cloudy.
2 physical properties of carboxylic acids?
meth,eth,prop and butanoic acid are completley soluble in water
higher melting points
how are carboxylic acids completley soluble in water?
they have many opportunities to form hydrogen bonds WITH WATER as they have a delta positive hydrogen on the OH group and a delta negative oxygen on the O group
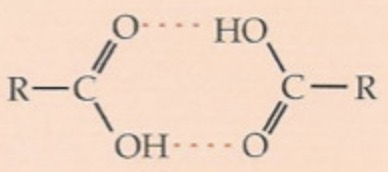
why do carboxylic acids have higher melting points?
they form dimers which are twice as big as a single carboxylic acid molecule
what is a dimer?
two monomers bonded together, carboxylic acids bond together with HYDROGEN bonds
t/f: carboxylic acids react similarly to other functional groups
true x
carboxylic acid + metal -> ? + ?
salt + hydrogen
carboxylic acid + metal oxide -> ? + ?
salt + water
carboxylic acid + hydroxide -> ? + ?
salt + water
carboxylic acid + metal carbonate -> ? + ?
salt + water + carbon dioxide gas
in a reaction, what ions do carboxylic acids ionise into?
carboxylate ions, e.g. ethanoate, propanoate, butanoate
(found in salts produced when they react)
when do molecules act as acids in terms of functional groups?
molecules act as acids when they have a carboxyl group, but not when they have separated alcohol and carbonyl group
why are carboxylic acids acidic but alcohols arent if they both have a H+ ion from the OH?
in a carboxylate ion, the extra electron in delocalised over 3 atoms (O,C,O-), making the atom stable, so it doesnt reform COOH, allowing H+ to act as the acid thing;
alcohols immediatley attract a proton as soon as its lost, as its unstable (due to O-)
ester functional group?
R1 COO R2
what can R1 be?
CH3, H
what can R2 be?
CH3
why must R2 begin with a carbon and not a hydrogen?
if it was a hydrogen, that would make a carboxylic acid functional group
2 reactants used to form esters?
carboxylic acid + alcohol -> ester + water
reaction requirements to make esters from carboxlyic acids and alcohol?
1 strong acid catalyst (H2S04)
2 heat
how to name esters?
alcohol first, acid second (carboxylic acid is used for the main parent chain)
propanol + propanoic acid -> propyl propanoate + water
butanoic acid + octanol -> octyl butanoate + water
why is the part of the molecule from the carboxylic acid used for the main carbon chain?
higher priority functional group than alcohols
functional groups from the highest priority to lowest?
(alkane, alkene, halogenoalkane, alcohol, aldehyde, ketone, nitrile, carboxylic acid)
1 carboxylic acid (and derivatives)
2 nitrile
3 aldehyde
4 ketone
5 alcohol
6 alkene
7 halogenoalkane
8 alkane
hydrolysis of esters in acidic conditions reaction?
ester + water ⇌ carboxylic acid + alcohol
can reach equilibrium because it’s reversible
requirements for hydrolysis of esters in acidic conditions?
only hydrolysed in the presence of a strong acid catalyst
does amount of acid affect point of equilibrium?
no since its a catalyst
hydrolysis of esters in alkaline conditions reaction?
ester + (excess)alkali -> salt + alcohol
why is the alkali in excess?
ester is completley converted if theres enough alkali since the reaction is NON-reversible
difference between hydrolysis of esters under alkali and acidic conditions?
alkali: not reversible, alkali is consumed, produces a salt and an alcohol
acid: reversible, acidic catalyst (isnt consumed), produces an acid and an alcohol
name of a molecule with 2 hydroxyl groups?
diol
name of a molecule with 3 hydroxyl groups?
triol, like glycerol
glycerol's IUPAC name?
propane-1,2,3-triol
4 uses of glycerol?
1 moisturiser
2 gloopy: used in medicine
3 plasticiser: cling film
4 solvent
ethanoic acid smells of vinegar due to COOH
difference between fats and oils?
fats are solid at room temperature, oils are liquid at room temperature
how do plants use esters?
compact energy in seeds for germination and further growth
how are soaps formed from esters?
hydrolysis of esters (often found in animal fats and vegetable oil) in alkaline conditions
what is biodiesel made up of?
a mixture of methyl esters;
made from long chain carboxylic acids and alcohols with short chains
what is biodiesel?
diesel replacement fuel made of a mixture of methyl esters which produces less pollution, can be mixed with ordinary diesel to reduce pollution
how are biodiesels produced?
ester (vegetable oil) + methanol -> glycerol + methyl ester (biodiesel)
conditions required to make biodiesel?
strong alkali catalyst present (OH-)
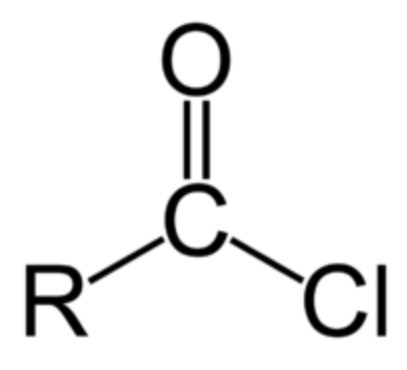
what is an acyl chloride?
-Carboxylic acid derivative where -OH group is replaced by a Cl
general formula of acyl chlorides?
RCOCl
reaction to form acyl chlorides from carboxylic acids and sulfurous dichloride?
carboxylic acid (l) + sulfurous dichloride (SOCl2)(l) -> acyl chloride + SO2 (g) + HCl (g)
why is the reaction irreversible? what happened to entropy?
SO2 (g) + HCl (g) lost as a gas,
entropy has increased as 2 gases are produced from 2 liquids
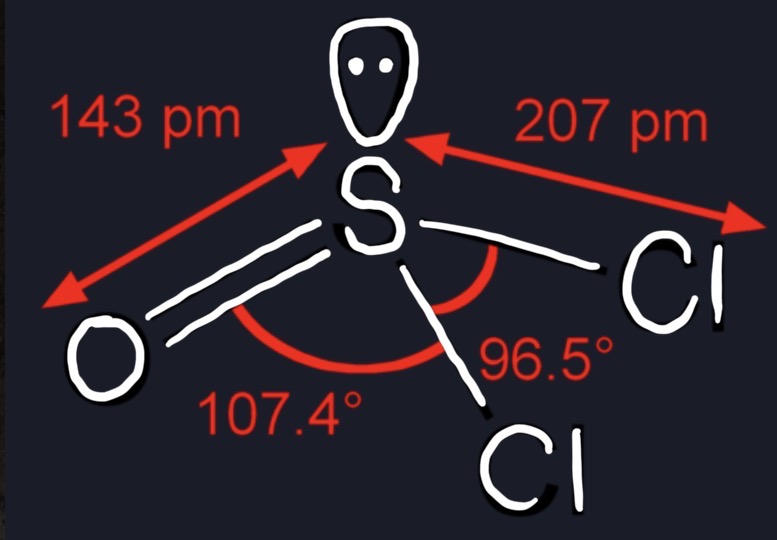
shape of sulfurous dichloride (SOCl2)?
107 degrees, 6 valence, 4 used for covalent bonding, 2 lone pairs
suffix for naming acyl chlorides?
-anoyl chloride
butanoyl chloride
what are acid anhydrides?
Derivatives of carboxylic acids formed by substitution of the -OH group by an alkanoate
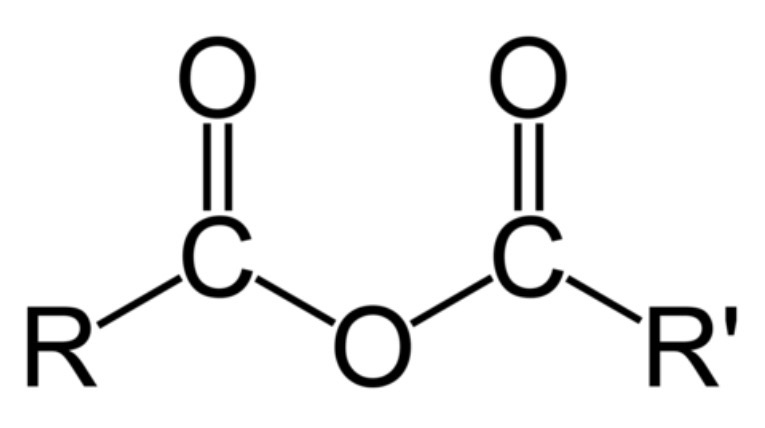
general formula for acid anhydrides?
RCOOCOR
how are acid anhydrides formed?
dehydration of acid molecules (-H20) -> acid anhydride and water
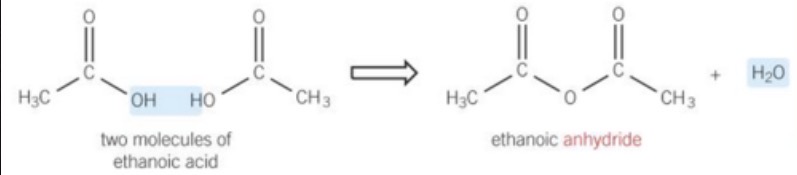
why is the formation of acid anhydrides reversible?
water can be added back (hydrated) to form acid molecules again
how to name acid anhydrides?
replace 'acid' with anhydride,
first is the acid it’s derived from,
e.g. propanoic anhydride
2 properties of acid anhydrides and acyl chlorides?
1 smell of the acids from which they are derived from
2 react w/water (acyl chlorides react more violently in water)
acid anhydrides + water -> ?
2 carboxylic acids
acyl chloride + water -> ? + ?
carboxylic acid + HCl
what type of reaction is acyl chlorides with water?
acylation, nucleophilic addition elimination reaction
what is acylation?
loss of a hydrogen and added to an acyl group
mechanism of acyl chlorides and water?
1 H20 nucleophile, C-O covalent bond forms, C=O pi bond breaks, both e- go to oxygen = negative charge
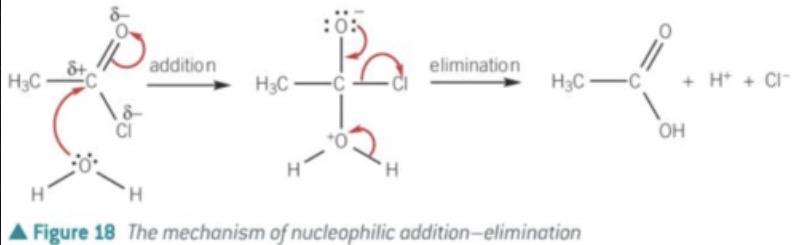
alcohol + acyl chlorides -> ? + ?
ester + HCl
why does this nucleophilic addition-elimination acylation reaction occur in anhydrous conditions?
acyl chlorides react with water
acyl chloride + alcohol mechanism?
same as water
EXCESS ammonia + acyl chloride -> ? + ?
amide + ammonium chloride (NH4Cl)
amide functional group?
-amide
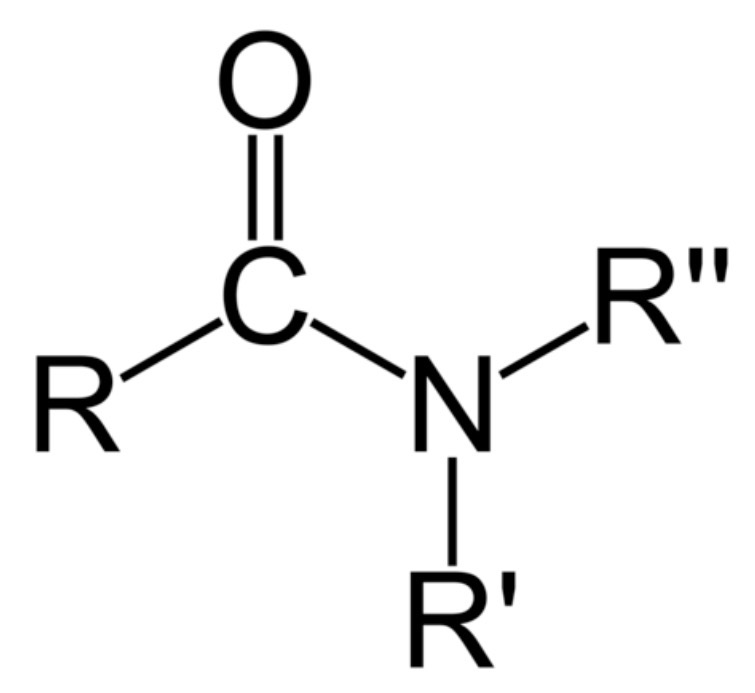
what type of reaction is ammonia + acyl chlorides?
nucleophilic addition elimination acylation reaction
what is produced if ammonia is not in excess?
HCl is produced instead of ammonium chloride
what are the 2 molecules of ammonia use for in this reaction?
1 forms the amide, other forms ammonium chloride during acylation
excess primary amides + acyl chloride -> ? + ?
amide, ammonium salt (RNH3+X- ,e.g. C3H7NH3+Br-)
what type of mechanism is primary amide + acyl chloride?
nucleophilic addition elimination acylation
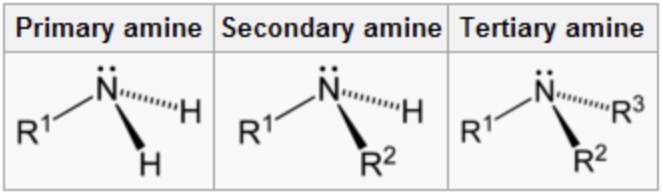
what is a primary amine?
nitrogen with a lone pair, covalently bonded to 2 hydrogen atoms and one alkyl group
acid anhydride + alcohol -> ? + ?
ester + carboxylic acid
(COOH produced instead of HCl due to double bonded O and O and no Cl) (acylation)
acid anhydride + water -> ?
2 carboxylic acids (acylation)
acid anhydride + ammonia -> ? + ?
amide + carboxylic acid (acylation)
acid anhydride + excess ammonia -> ? + ?
amide + ammonium carboxylate (acylation)
acid anhydride + excess primary amine -> ? + ?
amide + carboxylate salt (acylation)
what reactions are nucleophilic addition elimination acylations?
acyl chloride + alcohol/water/ammonia/primary amides;
acid anhydrides + alcohol/water/ammonia/primary amides
order of reactivity for carboxylic acids, acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides?
1 acyl chlorides (most reactive)(no catalyst needed to react with alcohol)(more violent reaction in water)
2 acid anhydrides (no catalyst needed to react with alcohol)
3 carboxylic acids (least reactive) (do not react in water, need a catalyst to react with alcohol)
why are carboxylic acids the least reactive?
lone pair on oxygen is donated throughout the functional group, increasing stability as the delta positive charge on carbon is reduced, reducing reactivity
why are acid ahydrides least reactive than acyl chlorides?
electronegativity is split between 2 carbonyl groups, so the delta positive carbon charge is reduced a LITTLE;
little donation from Cl in acyl chlorides as outer e- do not delocalise well
how is aspirin made?
ethanoic anhydride + salicylic acid -> aspirin + ethanoic acid
where is salicin found?
willow trees
why is ethanoic anhydride used instead of acyl chloride for manufacturing of aspirin?
1 less exothermic = safer and easier to control
2 less dangerous by-products (acyl chloride produces HCl gas)
3 cheaper and easier to recycle