Functional Anatomy Unit 1 Exam
1/277
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
278 Terms
anatomical position
standing upright, feet apart, toes pointing forward, head forward, arms at side, palms forward
anterior
front, volar, ventral
proximal
closer to the trunk (point to attachment)
distal
further from the trunk
radial
on the lateral side (anatomical position); thumb side
ulnar
on the medial side of the arm (anatomical position); pink side
superior
above
inferior
below
posterior
back or dorsal
cranial
toward the head
caudal
towards the tail
ipsilateral
same side of the body
contralateral
opposite side of the body
origin
proximal attachment- less moveable point
insertion
distal attachment- more moveable attachment
surface anatomy
describes the features of anatomy that are palpable or visible on the surface of the skin
bony landmark
component of bone that protrudes beneath skin
kinesiology
study of human movement
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
frontal plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior portions
transverse plane
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
frontal axis
medial and lateral
sagittal axis
runs from front to back
vertical axis
straight line from top of head to feet
center of rotation
the point about which a figure is rotated
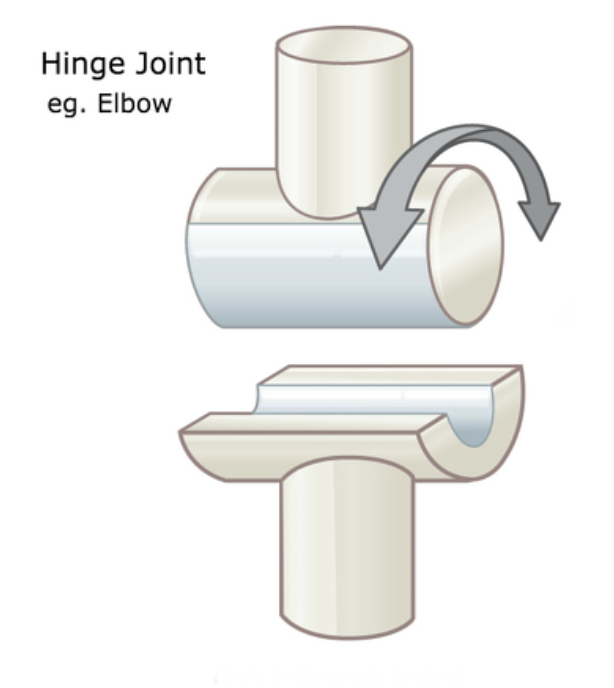
hinge joint
joint between bones (as at the elbow or knee) that permits motion in only one plane
ball and socket joint
hip and shoulder joints, rotates around 3 axes
gliding joint
two flat surfaces of adjacent bones, least movement, gliding movements between surfaces, carpal bones of the wrist
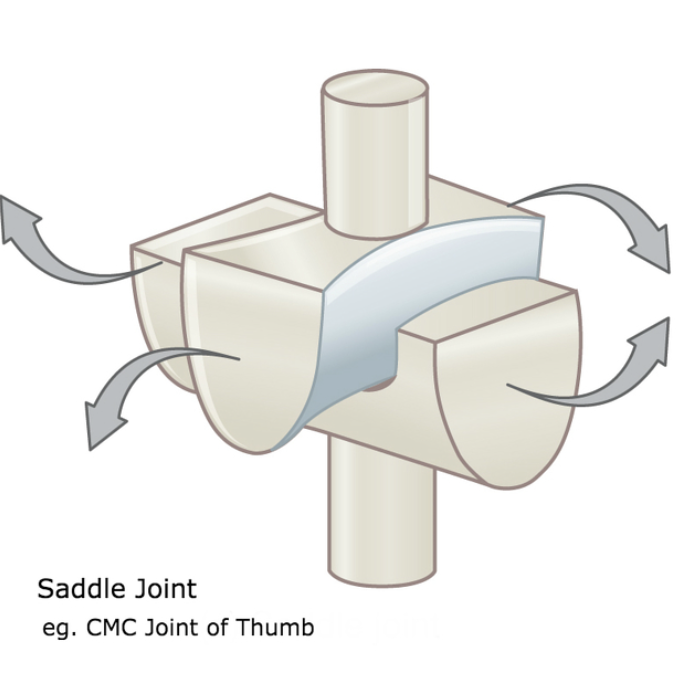
saddle joint
modified ellipsoid joint, convex and concave articulating surfaces, motion around 2 joints, carpometacarpal joint of thumb
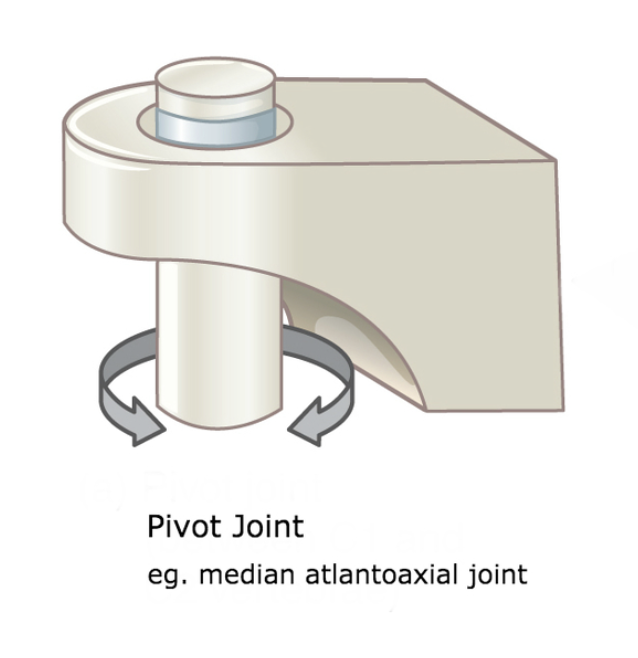
pivot joint
motion around 1 axis, bones rotating around another, atlantoaxial joint
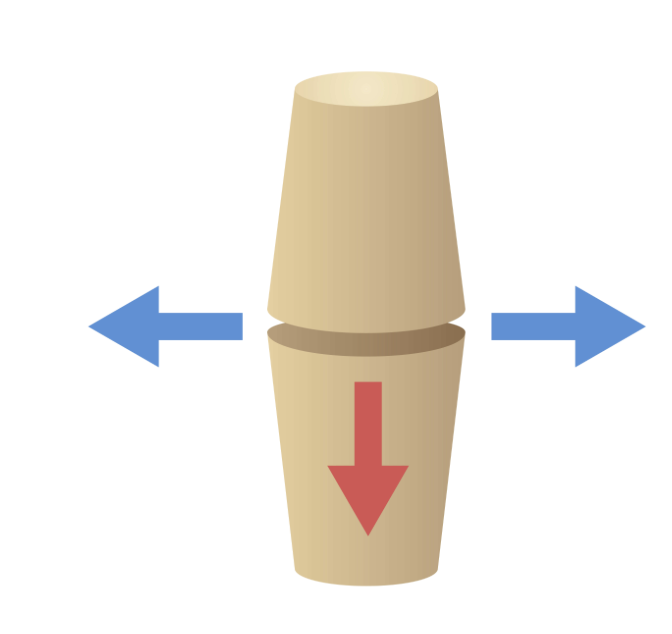
ellipsoid joint
oval shaped convex, articulates with elliptical concave basin of another, motion around 2 axes, radiocarpal joint
5 parts of the integumentary system
skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, oil glands
3 layers of the integumentary system
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
function of epidermis
provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone
parts of the epidermis
Come Lets Get Sun Burned
-stratum corneum
-stratum lucid- only in hands/feet
-stratum granulosum
-stratum spinosum
-stratum basale
3 layers of the dermis
papillary layer, reticular layer, subcutis
hypodermis is composed of
adipose tissue (fatty tissue)
function of the integumentary system
protection
holds us together
temperature control
synthesizes vitamin D
sensation
4 stages of the wounds
hemostasis phase
inflammatory phase
proliferative phase
maturation phase
what happens during the hemostasis phase
-blood vessel constriction
-clotting
-coagulation
what happens during the inflammatory phase
-phagoctosis of bacteria and debris
-removal of debris
-moncytes present
-immune response
-swelling
what happens during the proliferative phase
wound contraction
myofibroblasts
monocytes convert to macrophages
angiogenesis
creating new blood supplies
what happens during maturation phase
remodeling phase
wound fully closes
tissue remodeling and strengthening
apoptosis
platelet
tiny, colorless blood cell fragments made in the bone marrow that are crucial for stopping bleeding by forming clots at sites of injury
thrombus
a blood clot that forms inside a blood vessel or the heart
collagen
body’s most abundant protein, main structural component that provides strength, support, elasticity to connective tissue
granulation tissue
connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surface of a wound during the healing process
chronic wound
skin injury, open sore or ulcer, fails to heal in a timely manner
arterial ulcer
wounds formed by poor blood flow form narrowed or blocked arteries
venous ulver
an open sore on the lower legs or feet cause by poor venous blood flow— blood pooling
diabetic ulcer
open sores or wounds, typically in the feet, develop in people with diabetes due to nerve damage and poor circulation, leading to a reduced sensation and impaired healing
pressure ulcers
skin and tissue damage from prolonged pressure, often over bony areas
basic divisions of the nervous system
central nervous system (CNS), peripheral nervous system (PNS)
afferent
sensory neurons, toward CNS
efferent
motor neurons, away from CNS
parts of a neuron
cell body, axon, axon hillock, mylin sheath, dendrites
motor neurons
neurons that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce movement
sensory neurons
neurons that receive information from the external world and convey this information to the brain via the spinal cord
interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
sympathtic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations- fight or flight
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy - rest and digest
what makes up the sensorimotor system
primary sensory cortex, secondary sensory cortex, association cortex, motor planning areas, primary motor cortex
primary sensory cortex
perceives and discriminates sensory information
secondary sensory cortex
recognizes specific sensation
association cortex
connects sensory perception to prior memory, interprets meaning of sensation, and facilitates goal-directed planning and use of sensation
motor planning areas
plans specific movements, sequencing, timing
primary motor cortex
plans specific movements, sequencing, timing
CN I
olfactory
sensory: smell
CN II
optic
sensory: vision
CN III
oculomotor
motor somatic: eye movement (up, down, add)
parasympathetic: sphincter pupillage, contracts ciliary
CN IV
trochlear
motor somatic: eye movement (inward and down)
CN V
trigeminal
sensory: anterior scalp, nasal cavity, face, oral cavity, teeth, anterior 2/3 of tongue, auricle of ear
motor somatic: mastication
CN VI
abducens
motor somatic: eye (abduction)
CN VII
facial
sensory: taste anterior 2/3 of tongue
motor somatic: muscles of facial expression
motor parasympathetic : lacrimal glands of eye, salivary glands
CN VIII
vestibulocochlear
sensory: hearing and balance
CN IX
glossopharyngeal
sensory: taste and touch posterior 1/3 tongue
motor somatic: swallowing
motor parasympathetic: salivary glands
CN X
vagus
sensory: hearts, lungs, bronchi, trachea, pharynx, gastrointestinal, external ear
motor somatic: pharynx and larynx
motor parasympathetic: smooth muscle and glands of heart, lungs, larynx, trachea, abdominal organs
CN XI
spinal accessory
motor somatic: scapula, trapezius
CN XII
hypoglossal
motor somatic: tongue movement
Chambers of the heart
right and left atria, right and left ventricles
Heart valves
right atrioventricular valve (tricuspid), left atrioventricular (bicuspid, mitral) valve, pulmonary semilunar valve, aortic semilunar valve
Major heart vessels - superior
superior/inferior vena cava, ascendign aorta, aortic arch, thoracic aorta, abdominal aorta, pulmonary veins, pulmonary arteries, coronary arteries, brachiocephalic trunk, common carotid artery, subclavian artery, subclavian vein, brachiocephalic vein, cephalic vein, basilic vein, internal jugualr vein, celiac trunk, renal artery, renal vein, axillary artery, brachial artery, ulnar artery, radial artery, superior mesentric artery
Major heart vessels- inferior
inferior mesenteric artery, common iliac artery, internal iliac artery, femoral artery, popliteal artery, common iliac vein, external iliac vein, internal iliac vein, great saphenous vein
Ventricles and valves create a pump
Diastole: ventricles are relaxed, atrioventricular valves open, allowing blood to flow from atria into ventricles
Systole: Ventricles contract, atrioventricular valves close so blood can't flow back to atria, semilunar valves open, blood is ejected (right ventricle goes to lungs, left ventricle goes out to the body)
*Valves open and close based on pressure changes, blood flows only in one direction
Maintaining pressure in the circulatory system:
Systolic pressure: peak pressure, produced by contracting ventricles
Diastolic pressure: pressure decreases in the arteries when ventricles relax
Blood flow and resistance contribute to blood pressure:
Blood flows from areas of high pressure to areas of lower pressure, more resistance increases blood pressure as blood flow is restricted
Body's response to short-term changes in blood pressure
Alterations in blood vessel diameter changes the distribution of blood around the body (more or less depending on vasoconstriction/vasodilation). epinephrine and norepinephrine raise HR and blood volume, kidneys control sodium and fluid volume in the body
Why high blood pressure is detrimental to overall health:
Damages arterial walls, messes with circulation, endangers heart, lungs, brain, kidneys
Mechanisms for high BP medications: Diuretics
rid excess water and salt from the body, in turn helps to lower BP
Mechanisms for high BP medications: Beta-blockers
help to lower heart rate which in turn lowers BP
Mechanisms for high BP medications: ACE inhibitors
Help body to produce less angiotensin which helps blood vessels to relax (lowering BP)
Mechanisms for high BP medications: Calcium channel blockers
Prevent calcium from entering the heart cells by relaxing narrow blood vessels (decreases BP)
Structure and function of blood vessels: innermost layer
3 layers: Tunica intima (inner most layer, smooth surface for blood flow, reduces friction, regulates exchange of substances and vascular tone).
Structure and function of blood vessels: middle layer
Tunica Media (middle layer, smooth muscle and elastic fibers, controls vessel diameter, regulates BP and blood flow distribution).
Structure and function of blood vessels: outermost layer
Tunica Externa (external layer, made of connective tissue, protexts and anchors vessels to surrounding tissues, prevents overexpansion of vessels)
Types of vessels: Arteries
Arteries: carry blood away from the heart (thick walls, high pressure, small lumen)
Examples: aorta, carotid arteries
Types of vessels: Arterioles
Arterioles: regulate blood flow into capillary beds (thin walls with smooth muscle, control BP)
Types of vessels: Capillaries
Capillaries: where gas/nutrient/waste exchange occurs (narrow lumen, walls are only 1 cell thick)
3 types:
Continuous (muscle, skin, brain)
Fenestrated (kidneys, intestines)
Sinusoidal (liver, spleen, bone marrow)
Types of vessels: Venules
Venules: collect blood from capillaries (thin walls, low pressure)
Types of vessels: Veins
Veins: return blood to the heart (thin walls, large lumen, valves)
Examples: vena cava, jugular veins