Genetics and Cell Reproduction
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Classes of gene mutations
Substitution
deletion
addition
Substitution
one DNA nucleotide is replaced by another to it codes for the wrong amino acid
Deletion
one nucleotide is missing or removed causing every codon afterward to be wrong
Addition
nucleotides are added causing every codon afterward to be wrong
Functions of DNA
Hereditary (Genetic) Material – Passed from generation to generation
Protein Synthesis - Nucleic acids are the blueprints for building (synthesizing) proteins
How is DNA structured
Made of nucleotides (monomers) Each nucleotide contains a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base.
DNA backbones
The phosphates and sugars connect to each other to make up the backbone of a DNA strand. The phosphate side is called the 5’ end. The sugar side is called the 3’ end.
Why is DNA double stranded
Two strands are antiparallel
Joined by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases
DNA bases
A always goes with T
C always goes with G
Central Dogma
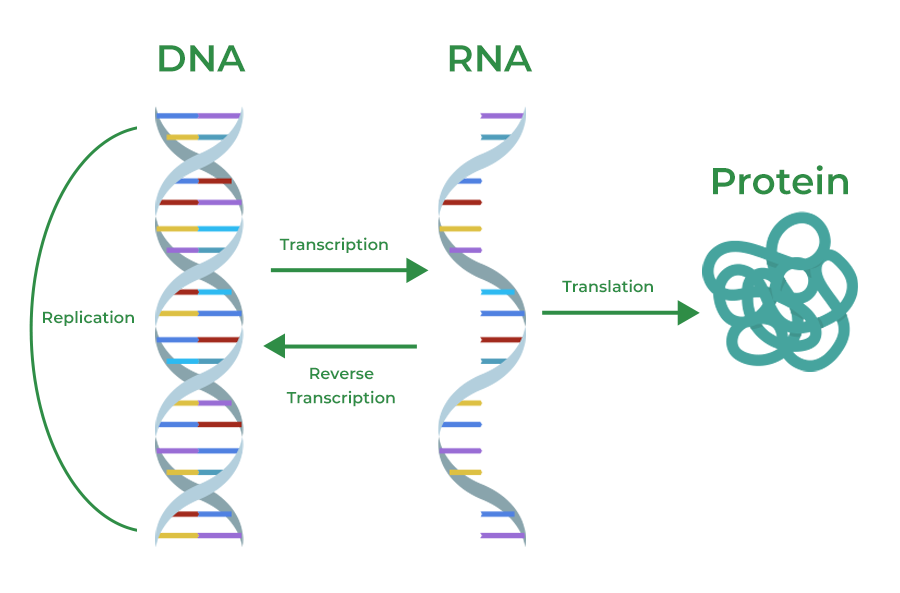
How do genes influence proteins
Determines the amino acid sequence of a protein
Transcription
the process where a gene's DNA sequence is copied into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule by the enzyme to leave the nucleus
Same bases in OPPOSITE orders
Translation
the process where the genetic code from messenger RNA (mRNA) is read by ribosomes to build specific proteins
Occurs in the CYTOPLASM
3 Baes in a codon
DNA replication
Semi conservative process
Consists of one new strand and one old strand
Steps of replication
1. DNA “unzips”
2. Each “open” nucleotide binds to a new complementary nucleotide.
3. End result is two identical strands of DNA.
How does replication start
DNA unwinds and an enzyme called helicase breaks down the hydrogen bonds holding the base together
ASE = Enzyme
How are new strands built
Elongation
RNA primer binds to the template strand to provide a starting point
DNA polymerase extend the new strands by adding one nucleotide at a time
How does replication end
Termination'
Once the template strand has been copied DNA ligase fix any breaks in the chains and put the strands back together
2 new DNA double helices
What is a mutation
a change in the genetic material in an organism
often an error in DNA replication
Negative impacts of mutations
most diseases are linked to recessive genes
chromosomal mutations or gene mutations
Mutagens



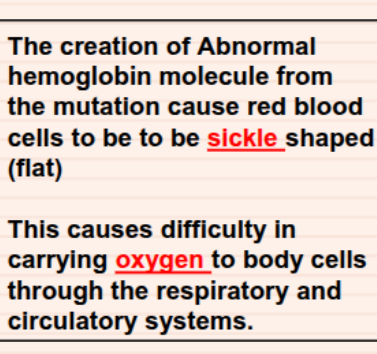
Sickle cell anemia
Phenylketonuria

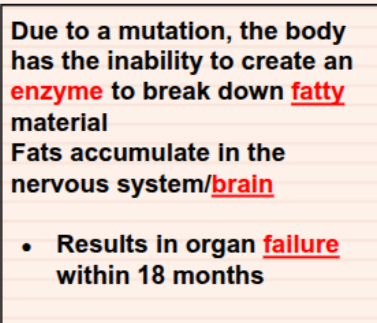
Tay Sachs
Cystic Fibrosis

Why is DNA replication necessary
Cells need a second copy of DNA before they can duplicate
Epigenetics
The impact of environment on genetics
Epigenetics are SOMETIMES inherited
DNA methylation
An epigenetic mutation where a cytosine base becomes methylated through the action of an enzyme.
What are chromosomes
Condensed strands of DNA and proteins organized
Structure of chromosomes
Nucleosome- DNA wrapped around histones
Chromatin- A long strand of nucleosomes
Chromosome- a condensed bundle of chromatin
Why are chromosomes necessary
They help protect DNA and reduces the amount of mutations
What does chromatin consist of
a mixture of proteins (Histones) and DNA
How do chromosomes form
Chromatin condenses (Packages) by wrapping and coiling itself to form a chromosome
How do epigenetic changes work
They tag DNA which activates or represses gene expression
How does DNA methylation change the DNA
They do not change the dna sequence
rRNA
makes ribosomes