Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Eyewitness Testimony: Anxiety
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What research suggests Anxiety has a Negative effect on accuracy of EWT
What is this effect called
Who believes Anxiety has a Positive effect on accuracy of EWT
Johnson and Scott (1976)
Weapon focus effect
Yuille and Cutshall (1986)
Weapon focus
Fear causes individual to fixate on the weapon, not noticing the person wielding it
What was the procedure of Johnson & Scott's research
- Participants were split into a Low anxiety group and a high anxiety group
- They were told they were partaking in a lab study and were sat in a waiting area
- Low anxiety group overheard a casual conversation and saw a man walk out with a pen and greasy hands
- High anxiety group overheard a heated argument from a room and saw a man walk out with a bloody knife
- They were asked to identify the man from a set of photographs
What did Johnson & Scott find
What did they conclude
49% correctly identified in Low anxiety group
33% correctly identified in High anxiety group
Anxiety causes Weapon focus which draws attention away from other details
Yuille and Cutshall (1986) Research
What did they find
What do these findings show
Witnesses of real life crime were interviewed 4 to 5 months after the crime
- These were compared with the original police interviews
- Accuracy was measured by number of matching details to the original police interview
- Participants also asked to rate their stress levels at the time of the crime and any emotional problems since eg insomnia
Found recall was very accurate with little change
- Witnesses who reported high stress had most accurate recall of 88%
- Low stress witnesses had less accurate recall of 75%
Anxiety does not have a negative effect on recall of events or accuracy of EWT
Anxiety may enhance recall
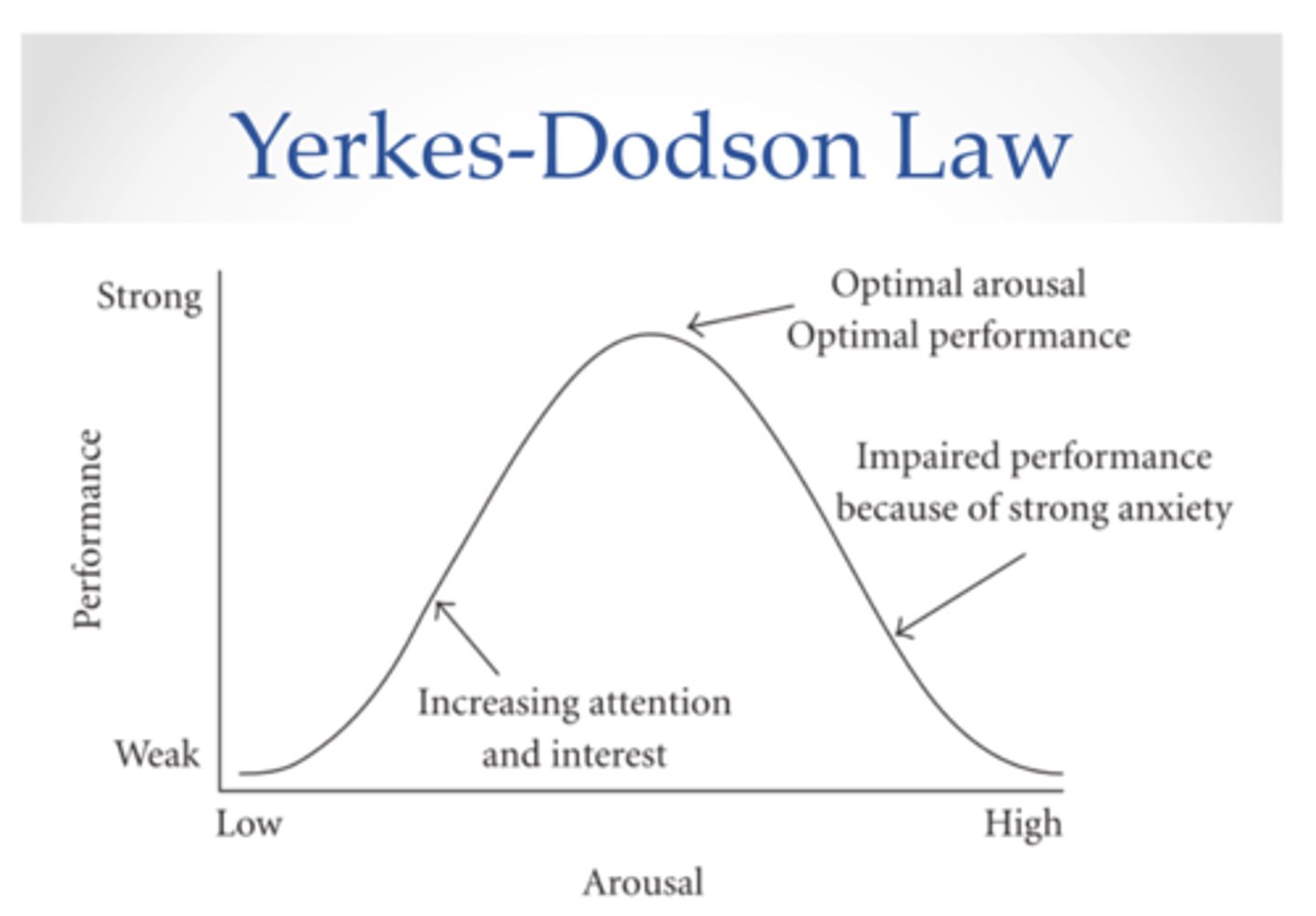
How did Yerkes & Dodson explain Contradictory findings in studies
Yerkes-Dodson law
- When a crime is witnesses an individual becomes emotionally aroused in Anxiety and physiologically aroused in the fight or flight response
- Low levels of anxiety lead to low levels of recall accuracy
- As anxiety increases, recall reaches an high optimum
- As anxiety increases further, recall accuracy begins to decline
Socially sensitive strength
- Has had major implications for the courtroom and how people view reliability of witness
- Socially sensitive because it affects witnesses, victims and offenders
- Strength is that by not relying EWT alone, there are likely to be less wrongful convictions and police attention is diverted to more reliable forms of evidence such as DNA
- Increases the usefulness of this research
Ethical weakness of Loftus and Palmer study
Does not align with BPS guidelines
Participants were deceived on the nature of the study
Not protected from harm by being exposed to a bloody knife which couldve triggered extreme anxiety
This raises ethical concerns regarding informed consent and the participants' mental well-being. The potential for distress due to the study's content diminishes its ethical standing.
Means ethic commitees are unlikely to allow the study to be replicated today
Lowers Temporal validity of his findings