NUR 317 Exam 5 - Osteoporosis
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Osteoporosis
Chronic, progressive metabolic bone disease marked by
Low bone mass
Deterioration of bone tissue
Leads to increased bone fragility
What is the precursor to osteoporosis?
Osteopenia
Bone remodeling
Remodeling
Osteoblasts – Continuously break down bone
Osteoclasts – Form bone
Rate of bone deposition and resorption are normally equal
In osteoporosis, bone resorption exceeds bone deposition
Why is osteoporosis known as the “silent thief”?
It has no noticeable symptoms in its early stages and can lead to fractures that increase mortality risk
Why is osteoporosis more common in women?
Lower intake of calcium
Less bone mass
Bone resorption begins earlier and becomes more rapid at menopause
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Longevity
Osteoporosis screening guidelines
Initial bone density test in women over age 65
Repeat in 15 years if normal
Repeat sooner if patient is high risk
Currently no evidence of benefit for screening in men
Osteoporosis risk factors
Advancing age (>65 yr)
Female gender
Low body weight
White or Asian
Current cigarette smoking
Prior fracture
Sedentary lifestyle
Estrogen deficiency
Family history
Diet low in calcium/vitamin D deficiency
Excessive use of alcohol (>2 drinks/day)
Low testosterone in men
Specific diseases
Certain drugs
Osteoporosis etiology and pathophysiology
Peak bone mass (by age 20) determined by heredity, nutrition, exercise, and hormone function
Bone loss after age 35-40 is inevitable, rate of loss is variable
Rapid bone loss for women at menopause
Osteoporosis preventative factors
Regular weight-bearing exercises
Diet and supplements
Fluoride
Calcium
Vitamin D
Healthy lifestyle
Avoid smoking and heavy drinking
Osteoporosis clinical manifestations
Occurs most commonly in spine, hips, and wrists
Common manifestations
Stooped posture
Joint pain
Bone pain and tenderness
Back pain (early manifestation)
Bone fractures (early manifestation)
Gradual loss of height
Kyphosis
“Dowager’s Hump”
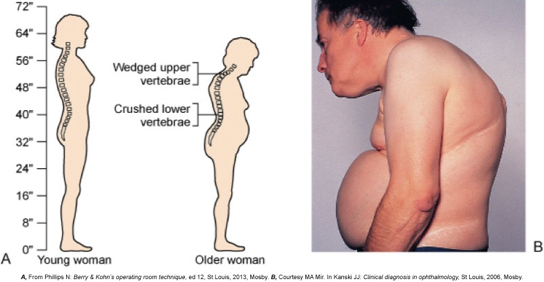
Osteoporosis diagnostic studies
History and physical exam
X-ray and lab studies not diagnostic
Bone mineral density (BMD)
Quantitative ultrasound (QUS)
Heel, kneecap, shin
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
Spine, hip (entire skeleton)
What is the gold standard osteoporosis test?
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
Osteoporosis diagnostic studies T and Z-scores
T-scores
T-score between +1 and -1 = normal bone density
T-score between -1 and -2.5 = osteopenia
T-score -2.5 or lower = osteoporosis
Z-score compares with someone own age and ethnicity
Fracture risk assessment (FRAX)
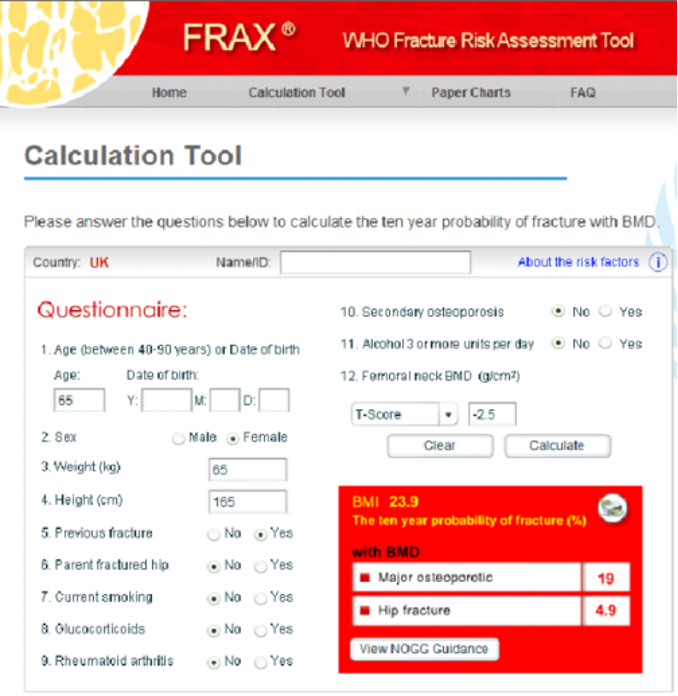
Osteoporosis interprofessional care
Focus on
Proper nutrition
Exercise
Prevent fractures and breaks
Calcium and Vit D supplements
Drug therapy
Stop smoking
Decrease alcohol intake
Postmenopausal treatment
Treat if:
T-score less than -2.5
T-score between -1 and -2.5 if additional risk factors exist
Prior history of hip or vertebral fractures
Osteoporosis calcium intake
1000 mg/day for:
Women ages 19-50 years
Men ages 19-70 years
1200 mg/day for
Women 51 years or older
Men 71 years or older
Osteoporosis supplemental calcium therapy
Take in divided doses
Calcium carbonate
40% elemental calcium
Take with food, vitamin D
Calcium citrate
20% elemental calcium
Less dependent on stomach acid
No – calcium lactate or calcium gluconate
Not enough elemental calcium
Osteoporosis vitamin D
Vitamin D necessary for calcium absorption/function; bone formation
Sunlight for 20 minutes/day is adequate
Supplemental (800-1000 IU/day)
Postmenopausal
Older men
Homebound/long-term care
Minimal sun exposure

Osteoporosis drug therapy
Biphosphonates
Monoclonal antibodies
Recombinant parathyroid hormone
Biphosphonates
Inhibit bone resorption
Side effects: anorexia, weight loss, gastritis
Proper administration
Take with full glass of water
Take 30 minutes before food or other meds
Remain upright for at least 30 min
Long term use – need to take for several years
Alendronate (Fosamax)
Biphosphonate
Usually take once per week
Can also take daily
Risedronate (Actonel)
Biphosphonate
Can take daily, weekly, or monthly
Zoledronic acid (Reclast)
Biphosphonate
Yearly or every other year IV infusion
Monocloncal antibodies
Denosumab (Prolia, Xgeva)
For postmenopausal women
Subcutaneous injection every 6 months
Need calcium and Vitamin D supplements
Teriparatide (Forteo)
Recombinant parathyroid hormone
Stimulates new bone formation
Daily subcu injection from preloaded pen
Must monitor parathyroid hormone levels
Use up to 2 years
Osteomalacia
Loss of vitamin D – may be rare in US
Loss of calcium
Bone softening/weakening
Same as rickets in children
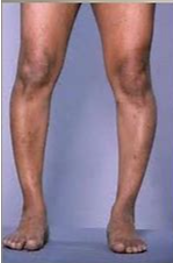
Osteomalacia etiology
Vitamin D deficiency
Lack of exposure to sunlight
GI malabsorption
Chronic diarrhea
Pregnancy
Diseases: chronic kidney, liver, small bowel
Bariatric surgery
Medications (long term)
Phenytoin
Cholestyramine
Maalox
Osteomalacia clinical manifestations
Bone pain
Weakness
Difficult rising from a chair
Difficulty walking
Weight loss
Progressive kyphosis
Delayed bone healing after a fracture
Osteomalacia laboratory and imaging diagnosis
Laboratory
Decreased serum
Elevated serum alkaline phosphatase
X-Ray
Bone demineralization
Looser’s Transformation Zones (ribbons of decalcified bone)
Osteomalacia treatment
Correct Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol)
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol)
Supplements – calcium and phosphorous
Dietary changes
Sunlight therapy
Weight-bearing exercises