Chapter 27 - Plant Form, Function, and Evolutionary History
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
four major groups of vascular plants
- lycophytes
- ferns and horsetails
- gymnosperms
- angiosperms
stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
guard cells
control the opening and closing of stomata
what happens when guard cells are in an open, high-volume state?
uptake of guard cells causes water to be drawn in by osmosis. As guard cells swell, they bow apart, opening the stoma
what happens when guard cells are in a closed, low-volume state?
release of solutes causes water to flow out of guard cells, closing the stoma
function of leaves
- gas exchange
- photosynthesis
- transpiration (moisture loss)
four major steps of CAM photosynthesis
1. Open stomata at night and collect CO2
2. Merge CO2 with PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) via PEP carboxylase and store it (the 4C acid)
3. Close stomata at daybreak and fetch 4C acids from storage
4. Commence PSN
CAM Photosynthesis (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism)
The photosynthetic pathway in which carbon fixation takes place at night, and the resulting carbon acids are stored until daylight when they are broken down into pyruvate and CO2.
4C Photosynthesis
uses PEP and PEP carboxylase (Phosphoenolpyruvate)
- suppresses photoresperation
photorespiration
A metabolic pathway that consumes oxygen, releases carbon dioxide, generates no ATP, and decreases photosynthetic output; generally occurs on hot, dry, bright days, when stomata close and the oxygen concentration in the leaf exceeds that of carbon dioxide.
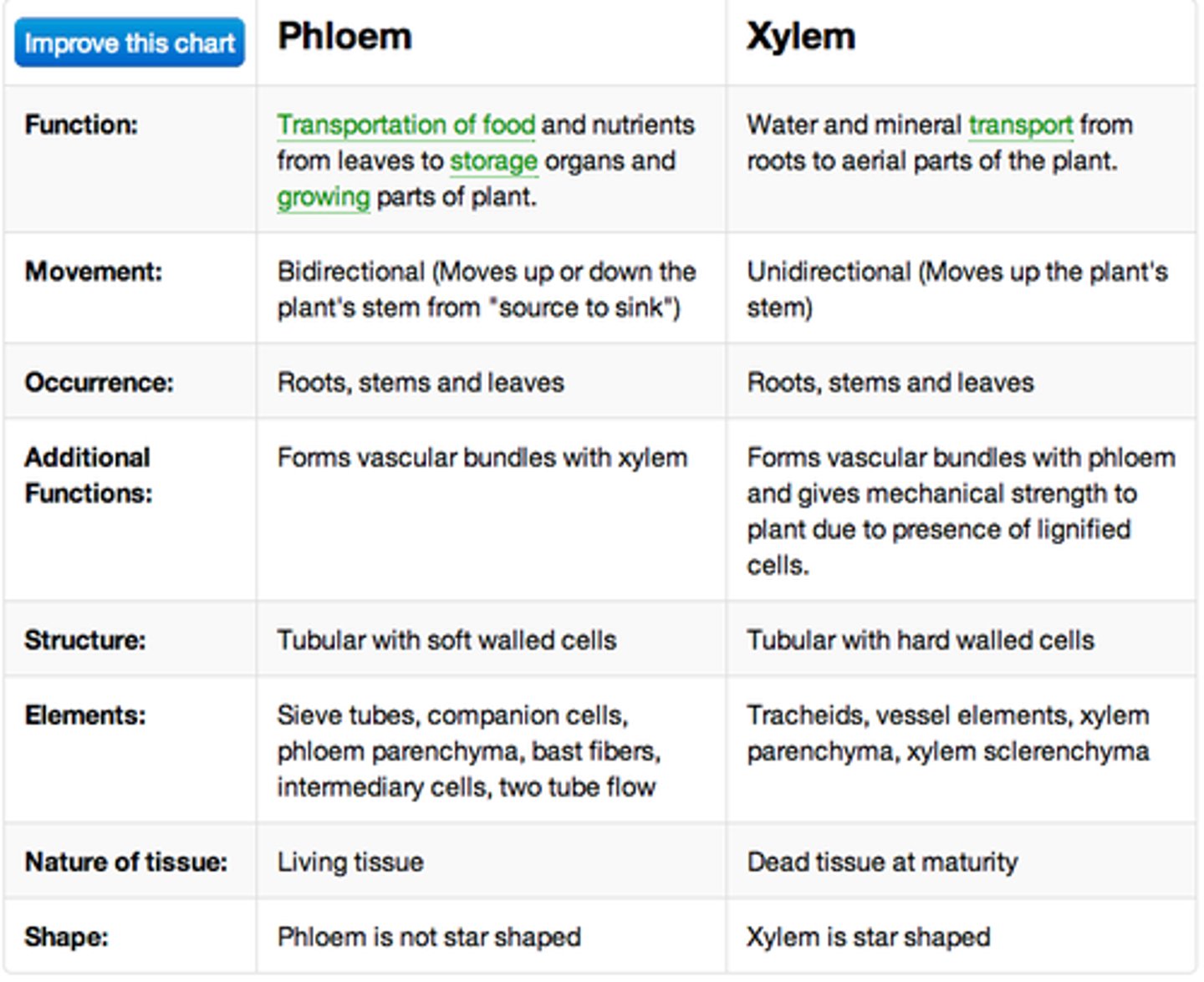
xylem function
long distance transport of water from roots to shoots
xylem structure and four cells types that make up the xylem
found inside vascular bundles
cell types:
1. tracheids
2. vessel elements
3. parenchyma
4. fibers
tracheary elements
tracheids and vessel elements
tracheids
DEAD, long, narrow cells bearing pits on side walls and end walls.
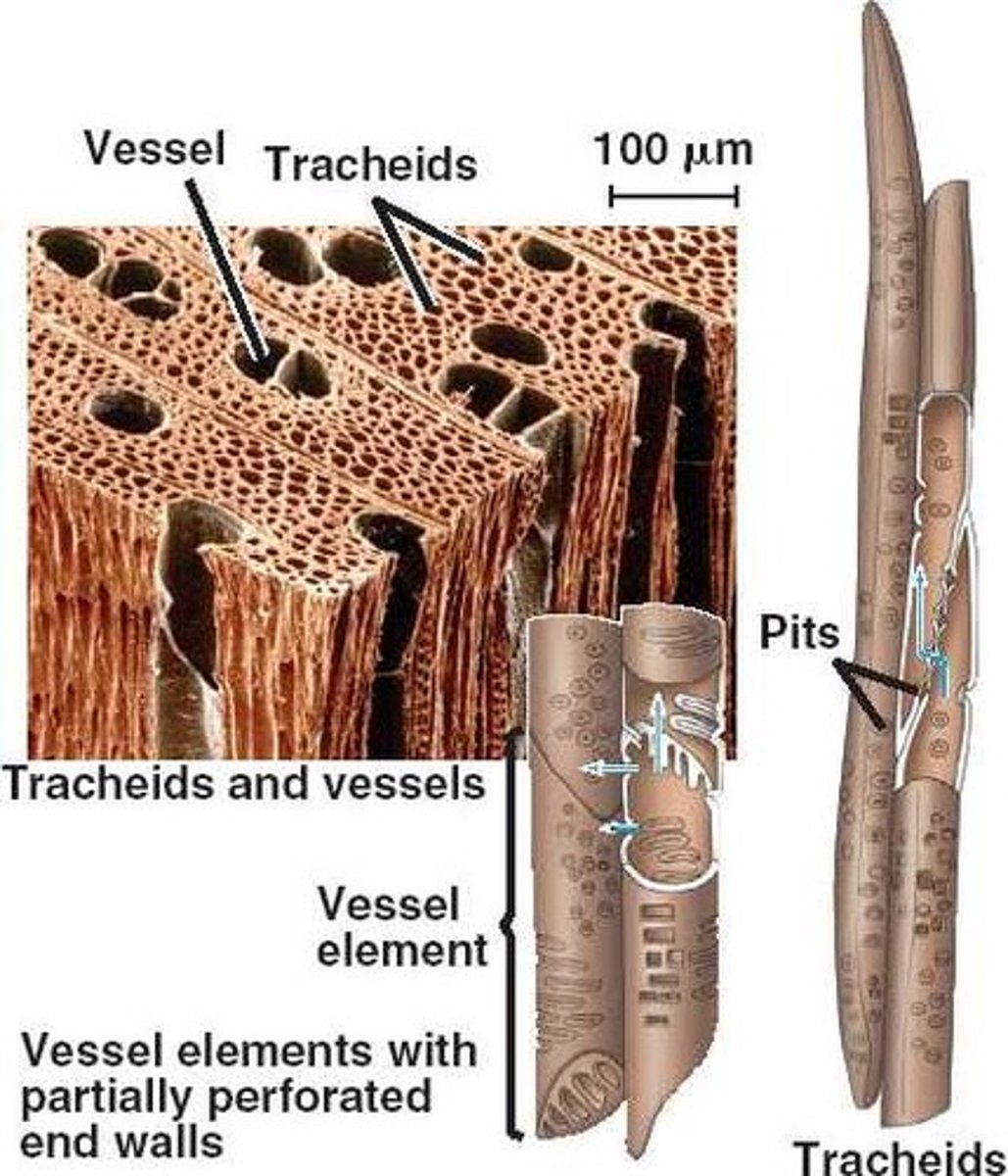
vessel elements
DEAD cells with open end walls (no pit membrane remains) called perforation plates; shorter and wider than tracheids.
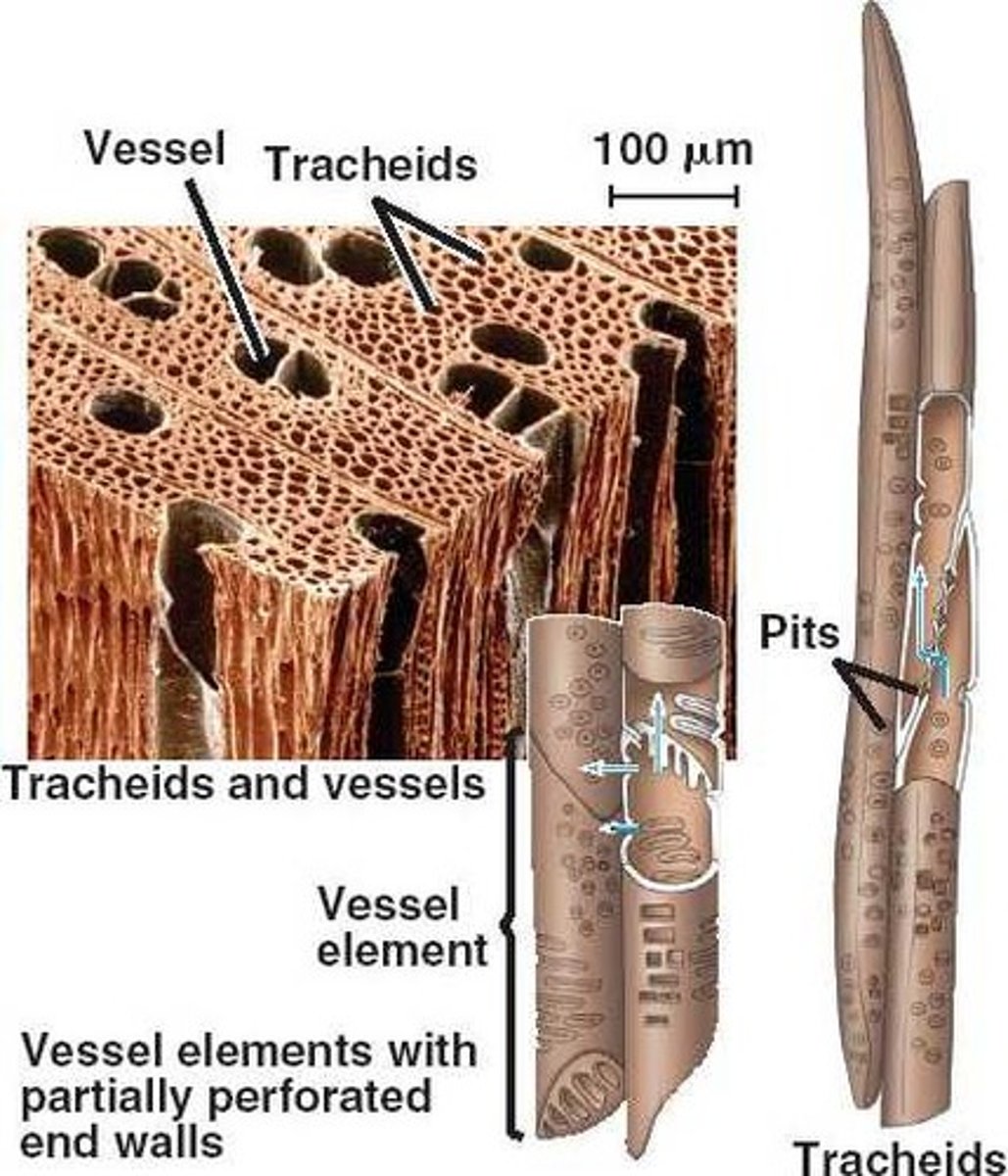
plant vessels
vessel elements stacked end-to-end
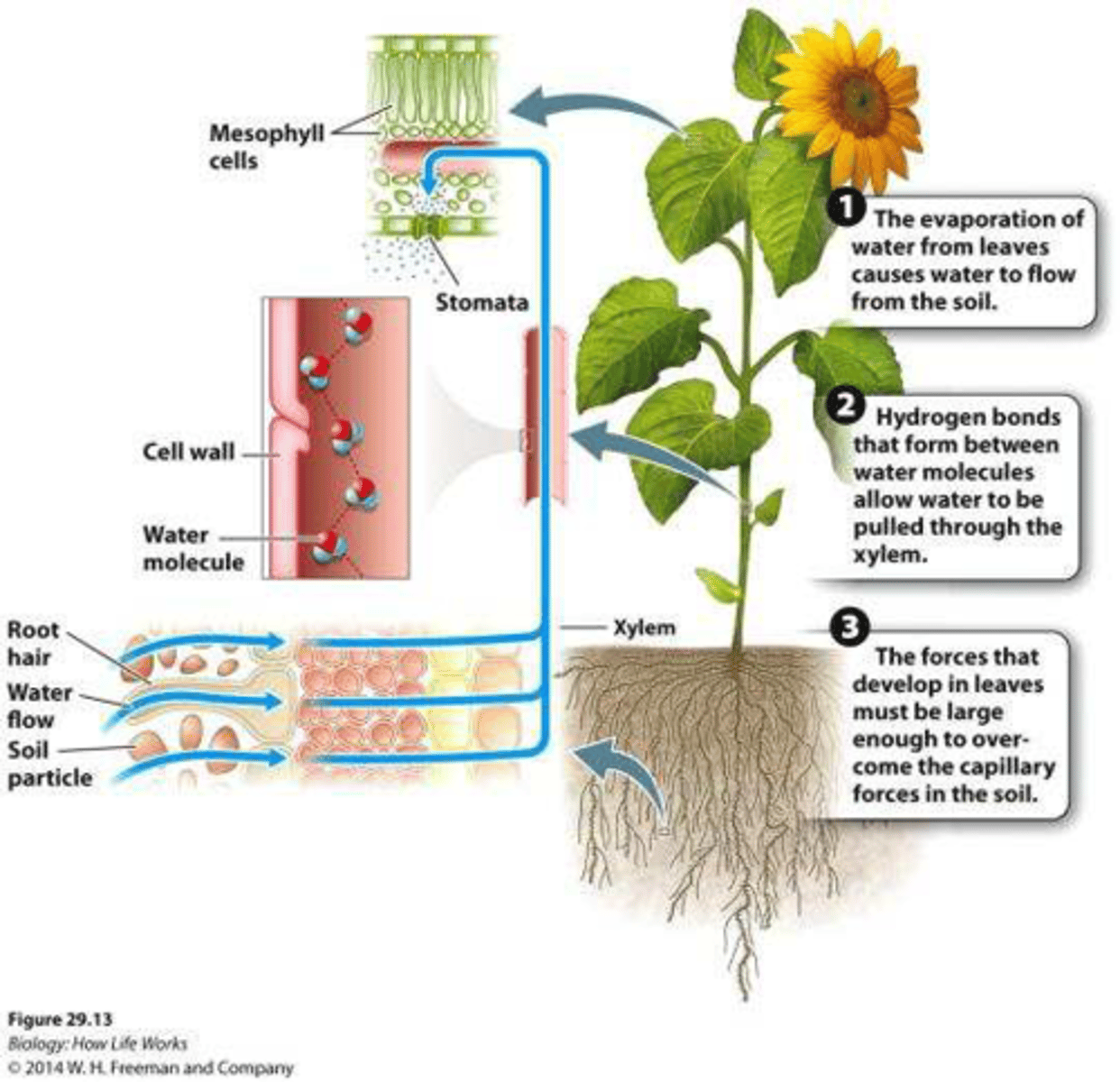
Forces that Pull Water from the Soil
1) The evaporation of water from the leaves causes water to flow from the soil
2) Hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules allow water to be pulled through the xylem
3) The forces that develop in leaves must be large enough to overcome the capillary forces in the soil
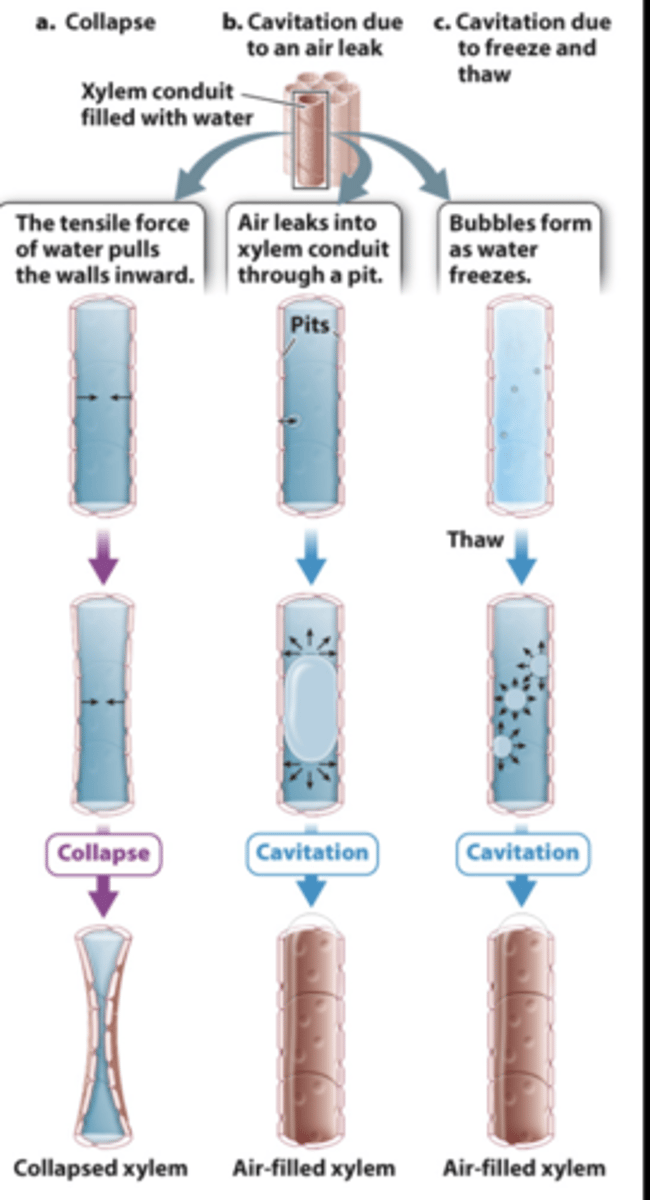
Risks of xylem conduits
air, freezing, dehydration
phloem function
long distance transport of "phloem sap"
- sugars fixed during photosynthesis
2. amino acids
3. other PSN compounds
four phloem cell types
1. sieve tube members (STM)
2. companion cells (CC)
3. parenchyma cells
4. fibers
phloem vs xylem
root anatomy
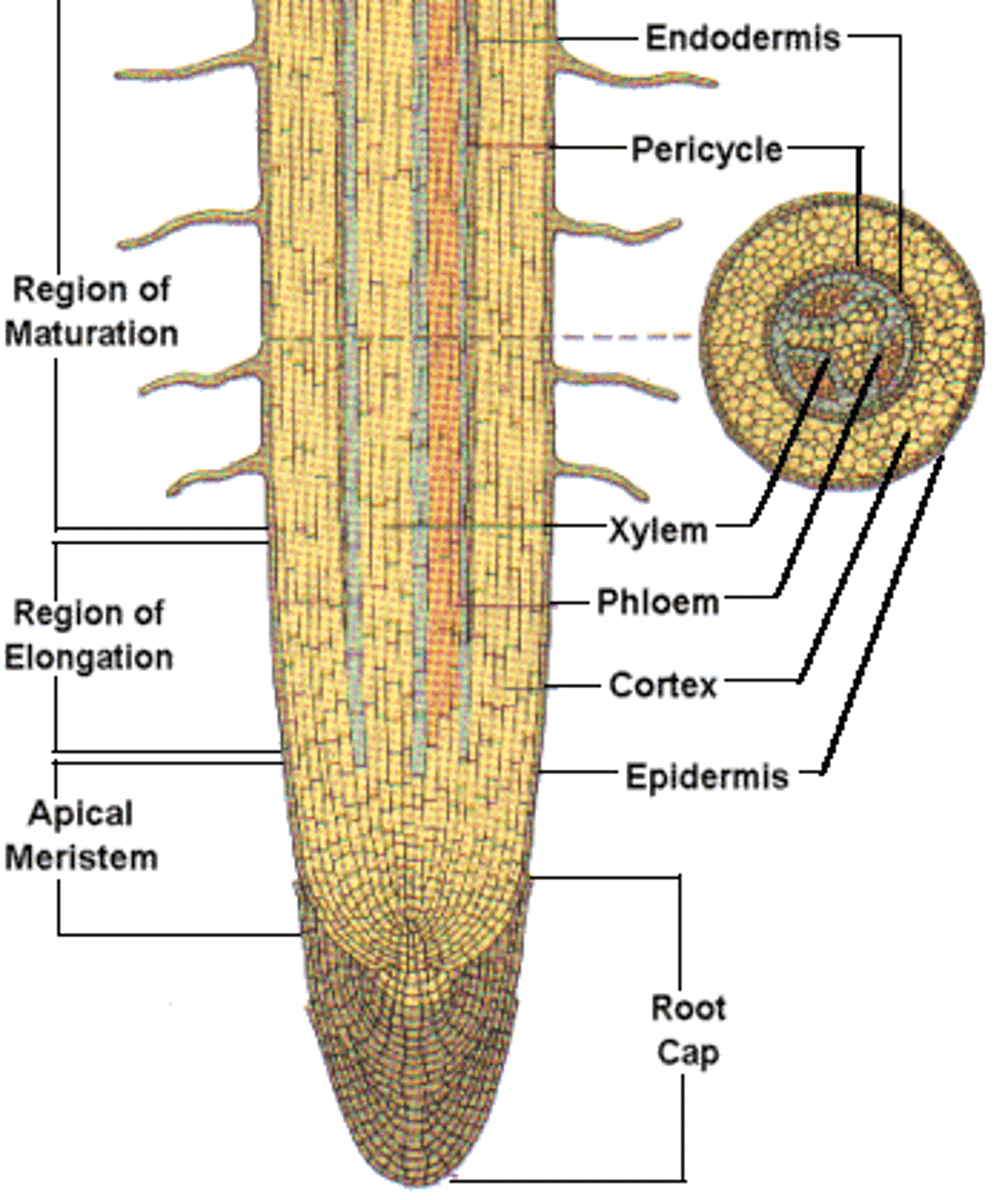
zone of maturation
absorbs nutrients
- surface area provided by root hairs enhances uptake of the soil solution and its associated nutrients.
mycorrhizal associations
symbiotic interactions with soil fungi that increase a plant's ability to absorb minerals
what forms of nitrogen do plant roots absorb
ammonium
nitrate ions
rhizobia
soil bacteria that fix nitrogen after becoming established inside root nodules of legumes
- mutualistic relationship because the plant has a source of nitrogen and the bacteria is provided carbohydrates by the plant.
epiphytes
absorb nutrients from rainwater, dust and detritus that accumulate around their leaves or in the bark of the host.

parasitic plants
absorb water and other nutrients by penetrating the host tissue.

carnivorous plants
obtain nutrients from insects
carnivorous plant syndrome
1. Attract
2. Trap
3. Retain
4. Kill
5. Digest
6. Absorb
7. Use
where do plants get nitrogen
bacteria