Behavioral Sciences Error Review
1/269
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A compilation of Behavioral Science questions I got wrong on practice exams and practice problems, or concepts I wished to reinforce. Not a comprehensive problem set for everything the MCAT requires one to know about BS.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
270 Terms
Parallel Play
Tendency among younger children to play side by side (less than 8 years old) but not interact directly
Cooperative Behavior
Cooperative behavior is expected of older children, children tend to become cooperative between the ages of 4 and 8
Harming Behavior
Aggression tends to be prevalent in younger age groups because they have less control of their emotions. Harming behavior tends to decrease between the ages of 4 and 8.
Symbolic Interactionism
People exchange/develop meaning through social interaction and language (most definitions will contain the word interaction)
Kinship Affinity
Individuals are related by choice
Indicators of A Population’s Quality of Life
Indicators of low quality of life: High infant mortality, high fertility (less access to contraception/less stable population), lower median age
Indicators of high quality of life: Low infant mortality, lower fertility, higher median age
**Mortality rate is relative
Harlow Rhesus Monkey Findings
1) Monkeys sought less comfort/soothing from Wire mothers than Cloth mothers
2) Monkeys with Wire mothers drank similar amounts of milk as monkeys with Cloth mothers
3) Monkeys, when given a choice, preferred contact with the cloth mothers more
4) Wire mothered monkeys displayed abnormal behavior that could not be corrected by pairing with the appropriate cloth mother
Anomie
Atomization, social fragmentation, feelings of isolation. Exacerbated by rapid social change, low income levels, and high heterogeneity (anything that disrupts community solidarity, cultural values)
Social Desirability Bias
Has to do specifically with answering survey questions in a certain way that they believe would render them more favorable to others
Functional vs Structural MRI
Functional MRI would provide an image of structure as well as operation of brain regions (activity) by looking at degree of bloodflow. Structural MRI only provides an image of structure, does not look at activity.
Cognitive Appraisal Theory of Emotion
Individuals interpret stimuli differently (negatively or non negatively) which yields different emotional reactions. People evaluate events differently which yields different emotional/behavioral responses.
Operant Condition Practices
Thinning: Reducing the frequency of rewards
Fading: Reducing prompts to remind participants
Retrograde Interference
New memories or knowledge interfere with old memories (ex: Memorizing a new student ID might make it hard to remember an old one)
Proactive Interference
Old memories or knowledge interfere with the consolidation or retrieval of new memories (ex: When writing a new date, people often write the old date they were accustomed to)
Role Strain vs Conflict vs Exit
Strain: Strain that occurs within a role. (ex: A student may have many classes that are too demanding)
Conflict: Different roles coincide and cause stress
Exit: Abandoning a role
Inclusive Fitness
Animal behaving in ways that ensure propagation of its genes or its kin’s/offspring’s genes.
Korsakoff’s Syndrome
Caused by reduced levels of vitamin B (thiamine)
Schizophrenia
Hallucinations, delusions typically caused by high levels of dopamine and other neurotransmitter
Alzheimer’s
Characterized by reduced levels of AcH caused by hydrophobic aggregation and/or tau tangles.
Primary aging vs Secondary aging
Primary: Biological factors
Secondary: Behavioral factors
Within Group vs Between Group Study Design
Within Group: Participants test multiple outcomes repeatedly (can function as their own control groups because their performance in different outcomes can be compared)
Between Group: Different participants test different outcomes
General Adaptation Syndrome
(How the body reacts and ADAPTS to stress) Describes body’s short term and long term reaction to stress involving the nervous system and endocrine system.
Alarm Reaction: Fight or flight triggered
Stage of Resistance: Body maintains high levels of activity to compensate for alarm mechanisms
Stage of Exhaustion: Resources are depleted
Activation-Synthesis Theory
Difference in neuronal activity of the brainstem during waking and REM sleep. This hypothesis proposes that dreams occur during REM sleep.
House-money effect
People take more risks with money they perceive as gains or house money, rather than their own money.
Gambler’s Fallacy
Fallacy that if between two outcomes (red vs black), if black pops up more frequently then red is more likely to come up. But this is false as each event has independent probability.
Prisoner’s Dilemma
Parties tend to choose themselves at the expense of the other participant when cooperation is the objectively better choice.
Strategies of Acculturation
Assimilation: Rejecting the native culture and adopting the new culture
Separation: Rejecting the new culture and maintaining the native culture
Marginalization: Rejecting both cultures
Integration: Identifying with both cultures
General Strain Theory
Individuals who have experienced negative events, feel negative emotions as a result which leads to negative behaviors
Relative deprivation theory
People who perceive themselves as lacking compared to others will act to rectify the situation.
Complications of Freud Psychoanalytic Theory
Ego, though regarded as the conscious mind, has components of unconsciousness as it evolves from Id. Superego because it is the higher moral self is also primarly unconscious,
Subjective norms
Person’s belief that a group of people/broader society will support a certain behavior and the subject’s motivation to comply with such rules. What we assume about other people’s attitudes. Our SUBJECTIVE understanding of group NORMS (ex: Assuming that most people are nonsmokers or are against smoking. Assuming most people care about others)
Locus of control
Extent to which an individual believes that he/she is in control of the events that affect them,
Reciprocal Determinism
Behavior, cognitive processes, and situational context all influence each other. Our behavior interacts with our environment and our personality variables to influence our thoughts. (
Social Cognitive Theory
People learn by watching others
Sanctions
Formal vs Informal: Official consequences (law, policies) vs action by a peer or group
Positive vs Negative: In this case, positive vs negative is not presence or absence. It is the normal definition where positive is good and negative is bad.
Median
Best measure of central tendency and entire distribution because it is resistant to skewing by extreme values
Different types of capital (Bourdieu)
Cultural: Knoweldge, Personal skills or certifications (personal qualities)
Social: Networking/social connections
Economic: Financial capital, money, physical assets
Allport Trait Theory
Cardinal Trait: Dominant personality trait that shapes a person’s behavior
Central Trait: General traits common among most people (ex: Honesty)
Secondary Trait: Situational traits (likes/dislikes)
Resource Model of Attention
Multitasking is possible if the total attentional resources are not exceeded by the attention required by each task
Fisherian Selection
If a strong enough mating preference exists, adaptations can appear contrary to natural selection.
Social Facilitation
Phenomena where the presence of other people help someone do better on simpler, familiar tasks while if the task if unfamiliar and complex, could be a hindrance
Context Effects
Information can be recalled easier if the environment where it’s tested resembles the space where the memories were encoded.
Classical Conditioning Factors
Unconditioned Stimulus: Provokes natural response
Unconditioned Response: Natural response to unconditioned stimulus
Conditioned Stimulus: Neutral Stimuli
Conditioned Response: Acquired response, the association of the unconditioned response with the neutral stimuli (occurs by virtue of implicit memory wherein it cannot be consciously recalled but there is an automatic emotional cue)
Ekman and Friesan Universal Emotions
Disgust, Happiness, Fear, Sadness, Anger, Surprise
Utilitarian Organization
Members are compensated for their involvement (Companies)
Normative Organization
People join due to a shared ethical/ideal goal voluntarily
Coercive Organization
People are forced to join (Prison)
Looking Glass Self (Hooley)
People’s understanding of themselves are formed their understanding of how other people perceive them. (One may assume they are funny if people frequently laugh at their jokes)
Group Polarization
The consensus view of a group is more extreme than the view held by the individuals
Groupthink
The desire for harmony and conformity prompts people to agree to a consensus they may individually disagree with. (Note: This can lead to more extreme stances but the question stem should mention: perceived invulnerability, self-censorship, stereotyping otherwise it is group polarization). Also, this tends to occur when there is a strong, well-liked leader, which can often result in inaccurate/ineffective solutions.
Framing Bias
The way an idea is contextualized affects how people perceive it
Attributional Bias
People often make systematic errors when trying to establish causality, often making attributional errors
Automation Bias
Tendency to depend excessively on automated systems or protocol without applying one’s own critical eye
Self Serving Bias
The tendency to attribute one’s successes to personal traits and one’s failures to external traits.
Fundamental Attribution Error
Tendency for individuals to emphasize internal factors when explaining someone else’s behavior rather than external factors (only applies when trying to explain something related to someone ELSE, if it also incorporates looking at oneself - probably Actor/Observer bias).
Projective Personality Assessment
Requires a participant to respond to a prompt, and their response is assessed for meaning
Objective Personality Assessment
Personality is gleaned from a set of discrete options (Myers Briggs)
Subjective Personality Assessment
Participants project their own subjective feelings, perceptions, thoughts onto objective stimuli.
Ratio Level Measurement
Range of quantitative responses ordered at equally spaced intervals, with the possibility of scoring “0” (number)
Wernicke’s Aphasia
Wernicke’s area in the brain is involved in language comprehension (left side). Wernicke’s aphasia means people have difficulty connecting meaning to language.
High Sensory Arguments
Visually appealing/sensorially stimulating arguments can be processed in the temporal lobe. Factual, reason based arguments are likely processed in the frontal lobe.
Exchange Rational Theory
Choices made by individuals aiming to maximize their benefits and reduce their costs. (Micro) Ex: A person wanting to sacrifice as little as possible of what they enjoy when trying to adopt a new diet.
Homeostatic Loops
Negative feedback is a primary method of homeostasis in which the body swings in particular directions and opposing processes are triggered. The consumption of food triggers satiety, the absence of food triggers consumption. To disrupt this homeostatic loop, anything that prompts someone to eat outside of this normal bodily cycle would suffice (ex: Someone eating food while full because they were told that food would not be available later).
Is Hunger triggered SNS or PNS?
PNS is rest and digest, meaning it is active when food is consumed, not when food is desire. Hunger, or the absence of food, is a stressor modulated by SNS.
Patient Autonomy can be ethically breached under:
Situations of Mental incapacity (the Patient does not have the faculties to make informed decisions about their healthcare)
Harm: The Patient is in danger of harming themselves or others
Type 1 Error Stats
Where the null hypothesis is erroneously rejected when significance is not found
Type 2 Error Stats
The null hypothesis is failed to be rejected when data is significant
Color Constancy
Feature of human color perception wherein an object’s color appears unchanged despite varying conditions
Visual Field Processing
The optic chiasm is in front of the lateral geniculate nucleus (which relays sensory info from thalamus to primary visual cortex). The chiasm is what reroutes visual information to correspond to the opposite side of the brain. Ex: If a disorder indicated that visual field information in the right brain was compromised, that means there is left eye temporal field blindness and right eye nasal field blindness.
Zero-Sum Game
One person’s game equals another person’s loss
Social Loafing
People “loaf” / get lazy in a group setting when they believe their contributions are unimportant. Social loafing is reduced in situations where personal responsibility is maintained.
Double Blind
Neither the participants nor the experimenters themselves know which group corresponds to which treatment
Heuristic
Mental shortcut to judgement
Symbolic Culture
Aspect of social interaction that exists as a set of non-physical beliefs or ideas. (Money for example, though a physical object, has an immaterial value set by society)
Halo Effect
A form of attributional error wherein a person’s physical attractiveness is associated with other positive traits like intelligence.
Internal Validity vs Reliability
Internal validity refers to the accuracy of results while reliability refers to the reproducibility of results (precision). Internal validity is diminished by factors like time (when relevant) where excessive time between observational groups can lead to confounding variables.
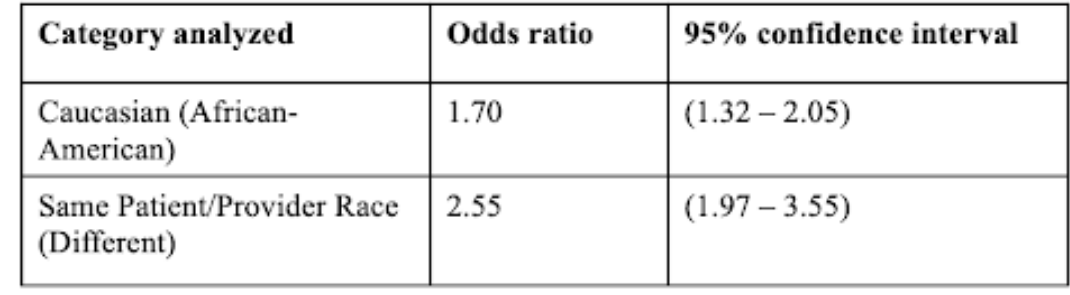
Odds Ratios Analysis:
The bracketed group is what the category analyzed is being compared to. For example, the first column states that Caucasians are 1.7x likely to receive opiates compared to African Americans.
Confounding Variable
A variable that the researchers are not interested in but has an effect on the IV and DV.
For example, in a study comparing smoking and rates of heart disease; age is a confounding variable that could be causing increasing rates of heart disease.
Mediating Variable
A variable that explains the relationship between two other variables (the IV and DV)
For example, in a study that connects race and rates of opiate prescribing, hispanic patients are found to be prescribed less opiates because they lack insurance. Because insurance is linked to race, and thus explains the relationship between race and prescription rates, it is mediating. It is not confounding because the effect of insurance does not take away/detract from race as a variable.
Moderating Variable
Modulates the intensity of certain relationships when it is present/not present. Language like “higher/lower” level, or likelihood suggests moderating variable.
For example, if the presence of insurance meant Hispanic patients were just as likely to be prescribed pain medication as Caucasian patients, while uninsured Hispanic patients were far less likely — insurance functions as to enhance the relationship between race and rates of pain med prescription.
Continuous Variable
Quantitative variable typically measured/counted in some way (temperature, mass, energy, speed, length)
Opioid Analgesics
Opioid analgesics block pain by blocking the release of certain neurotransmitters that bind to nociceptors. Endogenous endorphins produced by the anterior pituitary act similarly.
Opiod Use symptoms/withdrawal symptoms
Pupillary constriction is a symptom of opioid use, withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, perspiration, tremors.
Drive Reduction Theory
Theory that the primary motivation behind all behavior is reducing discomfort/undesirable states (drives).
Ex: Drive reduction theorists would posit that depression is a result of a decrease in the motivating forces of arousal, which is preventing an amelioration of the undesirable (depressed) state.
What parts of the brain control mood/mood disorders:
MANY but the frontal lobe, limbic system (debated but main four: Hippocampus, Hypothalamus (TRH, HPG (hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadial axis), Dopamine etc), Amygdala, Thalamus [Hippo + Hat]) contribute to mood regulation.
Nucleus Accumbens also has a role in reward, pleasure, and addiction
Social Learning/Socialization
The process by which people inherit, learn, and disseminate social norms, customs, belief systems which include ideas about gender. This helps one integrate into broader society
Primary Socialization: Socialization that occurs most often during childhood, usually through parents (the “first,” “predominant” socialization)
Secondary Socialization: Process of adapting to the norms of a smaller sub-group in society.
Resocialization: A process of deconstructing and relearning different norms to adapt to a different environment, often extreme (ex: Military personnel getting retrained vigorously)
Anticipatory Socialization: Changes someone makes in anticipation of a change in environment (ex: Adjusting one’s sleep schedule to work the night shift)
Operant Conditioning vs Classical Conditioning
OC: Voluntary behavior is shaped from a series of punishments and reinforcements.
Involves specifically diminishing or reinforcing behavior, not affecting opinion.
Does not apply to rewards/punishment that affect people around the subject.
CC: Eliciting involuntary responses by conditioning unconditioned stimulus
Most effective when the CS is followed by the US repeatedly over time.
CS is what experimenter enforces (neutral), US is what already exists in the subject (physiological responses)
Theorists and their respective accomplishments
Skinner: Behaviorist (Skinner’s rats, an exercise in classical conditioning)
Maslow: Humanistic psychology (Holistic understanding of a human, Maslow’s pyramid of needs)
Eysenck: Biological POV (think “eye sack” for bio; Empirical study tying genetics to personality).
Allport: Trait perspective of personality
Biases
Reconstructive Bias: Bias that comes from trying to reform past experiences, misremembering
Attrition Bias: Dropping out/leaving a long term study
Response Bias: Inherent bias that comes with self reporting
Distress/Eustress/Neustress
Neustress: Neutral stress, stress sourced from an event that does not affect you directy (reading something disconcerting happening in the world)
Eustress: “Good” stress, stress that is motivating
Distress: Stress in response to something threatening to oneself, a state of internal turmoil/anxiety
Inductive vs Deductive Reasoning
Inductive: Going from “IN” to out, bottom up process. Taking specific examples and broadening out to big ideas.
Deductive: De for “deriving” smaller ideas and examples from larger concepts
Elaboration Likelihood Model
Studies the variables that cause a change in opinion due to PURSUASION
Cognitive Dissonance
When one’s personal beliefs/ideology are incongruent with their actions. This experience will often try to be resolved through coping mechanisms that soften the dissonance. For example, subjects will often underestimate their own role in ameliorating the difference as a way to maintain the two confounding sides.
Hidden Curriculum
Norms, behaviors, practices imparted in an educational program that is not part of the official curriculum but is picked up as a person is socialized to the environment.
Educational Stratification
People with more resources have more access to educational opportunities. (Your magnitude of educational opportunity is directly proportional to your place on the social ladder/stratification, thus education is also stratified)
Educational Segregation
Demographic imbalance of student in schools, particularly related to race, gender, religion.
Medicalization
The process of rendering something as a pathological illness/disease. For example, it is important that drug addiction is decriminalized and instead medicalized as a disease so people can receive the correct social infrastructure.
Core components of Emotion
Physiological arousal (reaction to stimuli), expressive displays, subjective experience
Schachter Singer Theory of Emotion
Physiological arousal/response → Cognitive interpretation of the situation → Yields feeling of emotion