BIOL 431 Unit 5 Lab Exam
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/185
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Reproductive & Endocrine System
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
1
New cards
human somatic cell (# of chromosomes)
23 pairs; 22 pairs of autosomes & 1 pair of sex chromonsome
2
New cards
homologous chromosme
same chromosomal structure; not identical
3
New cards
chromosome
tightly wound DNA
4
New cards
centromere
region on chromosome for spindle fibers to attach to
5
New cards
meiosis consists of
meiosis I & meiosis II
6
New cards
meiosis I (general gist)
separates homologous chromosomes
7
New cards
meiosis II (general gist)
separate sister chromatid
8
New cards
karyotype
analysis of chromosomes
9
New cards
“n” represents
number of chromosmes
10
New cards
number in front of n represents
number of homologous chromosomes
11
New cards
“r” represents
replication (sister chromatid)
12
New cards
haploid
n cell
13
New cards
diploid
2n cell
14
New cards
spermatogenesis steps & number of chromosomes
spermatogonium (2n)
primary spermatocyte (2nr)
secondary spermatocyte (nr)
spermatids (n)
spermatazoa
primary spermatocyte (2nr)
secondary spermatocyte (nr)
spermatids (n)
spermatazoa
15
New cards
where does spermatogenesis occur
testes
16
New cards
onset of spermatogenesis
puberty
17
New cards
cessation of spermatogenesis
death
18
New cards
process that develops spermatogonium into primary spermatocyte
DNA replication (male)
19
New cards
process that develops primary spermatocyte into secondary spermatocyte
Meiosis I (male)
20
New cards
process that develops secondary spermatocyte into spermatids
meiosis II (male)
21
New cards
process that develops spermatids into spermatozoa
spermiogenesis
22
New cards
oogenesis & number of chromosomes
oogonium (2n)
primary oocyte (2nr)
secondary oocyte (nr) & first polar body
ovum (n) & second polar body
primary oocyte (2nr)
secondary oocyte (nr) & first polar body
ovum (n) & second polar body
23
New cards
where does oogenesis take place
ovaries
24
New cards
onset of oogenesis
prior to birth
25
New cards
when does oogenesis stop
menopause
26
New cards
number of oogonium at birth
200,000-2,000,000
27
New cards
number of oogonium at puberty
40,000
28
New cards
atresia
natural degeneration of oocytes
29
New cards
DNA replication in oogenesis takes place when?
prior to birth
30
New cards
at what stage is primary oocyte arrested in
prophase I (female)
31
New cards
process that develops primary oocyte into secondary oocyte
meiosis I (female)
32
New cards
when does meiosis I occur in females
puberty/just prior to ovulation
33
New cards
when does meiosis II occur in females
at fertilization
34
New cards
at what stage is secondary oocyte halted in
metaphase II
35
New cards
process that develops secondary oocyte into ovum
meiosis II (female)
36
New cards
Meiosis I phases
prophase I
metaphase I
anaphase I
telophase I
metaphase I
anaphase I
telophase I
37
New cards
prophase I events
chromosomes condense
nuclear envelope & nucleoli disappear
mitotic spindles form
tetrad formation
crossing over occurs
nuclear envelope & nucleoli disappear
mitotic spindles form
tetrad formation
crossing over occurs
38
New cards
crossing over
exchange of genetic information between non sister chromatids
39
New cards
metaphase I events
tetrads (homologous pair) line up at metaphase plate
centrosomes at opposite ends of pole
centrosomes at opposite ends of pole
40
New cards
anaphase I events
homologous chromosomes separate & move to opposite poles
beginning of cleavage furrow
beginning of cleavage furrow
41
New cards
telophase I events
chromosomes uncondense
nuclear envelope & nucleoli appear
mitotic spindle disappear
results: haploid cells with replicated chromosomes (nr)
nuclear envelope & nucleoli appear
mitotic spindle disappear
results: haploid cells with replicated chromosomes (nr)
42
New cards
prophase II events
chromosomes recondense
nuclear envelope & nucleoli disappear
mitotic spindle forms
nuclear envelope & nucleoli disappear
mitotic spindle forms
43
New cards
metaphase II events
sister chromatids align along metaphase plate
44
New cards
anaphase II events
centromeres split
sister chromatids separate & daughter chromosomes move to opposite poles
sister chromatids separate & daughter chromosomes move to opposite poles
45
New cards
telophase II
chromosomes uncondense
nuclear envelope & nucleoli appear
mitotic spindle disappear
products: haploid daughter cells (non identical) (n)
nuclear envelope & nucleoli appear
mitotic spindle disappear
products: haploid daughter cells (non identical) (n)
46
New cards
testis (2 function)
produce spermatozoa & testosterone
47
New cards
seminiferous tubules
site of spermatogenesis; 800 ft
48
New cards
septa
wall like structure to organize seminiferous tubule
49
New cards
straight tubules, rete testis & efferent ductules
passageway fo sperm
50
New cards
tunica albuginea
covering of tetis; maintains shape & forms lobules with septa (structural support)
51
New cards
interstitial cells of Leydig
between seminiferous tubule; produce tsosterone
52
New cards
head, body & tail of epididymus (function)
reabsorb sperm, temporary storage & maturation of sperm
53
New cards
ductus deferens/vas deferens
passageway for sperm; store & transport sperm
54
New cards
ampulla of ductus deferens
enlargement that stores & transports sperm
55
New cards
ejaculatory duct
passageway for sperm (through prostate gland)
56
New cards
scrotum
houses testes at 2-3 celsius below body temp
57
New cards
tunica vaginalis
derived from peritoneum
58
New cards
gubernaculum
connective tissue structure; guides testicular descent
59
New cards
cremaster mucle
derived from internal oblique; involuntarily elevates testes in response to cold/sexual stimuli
60
New cards
dartos muscle
smooth muscle deep to scrotal skin; elevates scrotum in response to cold/sexual stimuli
61
New cards
raphe
midline ridge of scrotum
62
New cards
inguinal canal
passageway through which testes descend
63
New cards
spermatic cord contains
ductus deferens
pampiniform plexus
testicular artery/vein
lymphatic vessel
spermatic nerve
pampiniform plexus
testicular artery/vein
lymphatic vessel
spermatic nerve
64
New cards
pampiniform plexus
interlacing network of veins; countercurrent exchange for temperature regulation
65
New cards
testicular artery/vein
blood supply to/from testis
66
New cards
lymphatic vessel
carries lymph
67
New cards
spermatic nerve
innervates testes (highly sensitive for protection)
68
New cards
prostate gland
produces 25% of seminal fluid (citric acid & proteolytic enzymes)
69
New cards
prostatic urethra
merges with ejaculatory duct
70
New cards
seminal vesicles
produces 60% of seminal fluid (fructose, clotting factor, prostaglandin & HCO3-)
71
New cards
bulbourethral glands
produce 15% of seminal fluid (HCO3- rich fluid, cleans out urethra)
72
New cards
penis
deliver gametes to female
73
New cards
glans penis
head of penis (\~200 sensory receptor)
74
New cards
prepuce
foreskin; covering of glans penis (protect & maintain sensitivity)
75
New cards
circumcision
removal of prepuce
76
New cards
corpora cavernosa
erectile tissue; engorges w/blood to cause erections
77
New cards
corpus spongiosum
erectile tissue; engorges w/blood to keep spongey urethra open
78
New cards
bulb
anchors corpus spongiosum to pelvic floor
79
New cards
crura
anchors corpora cavernosa to inferior ramus
80
New cards
membranous urethra/cavernous urethra
passageway
81
New cards
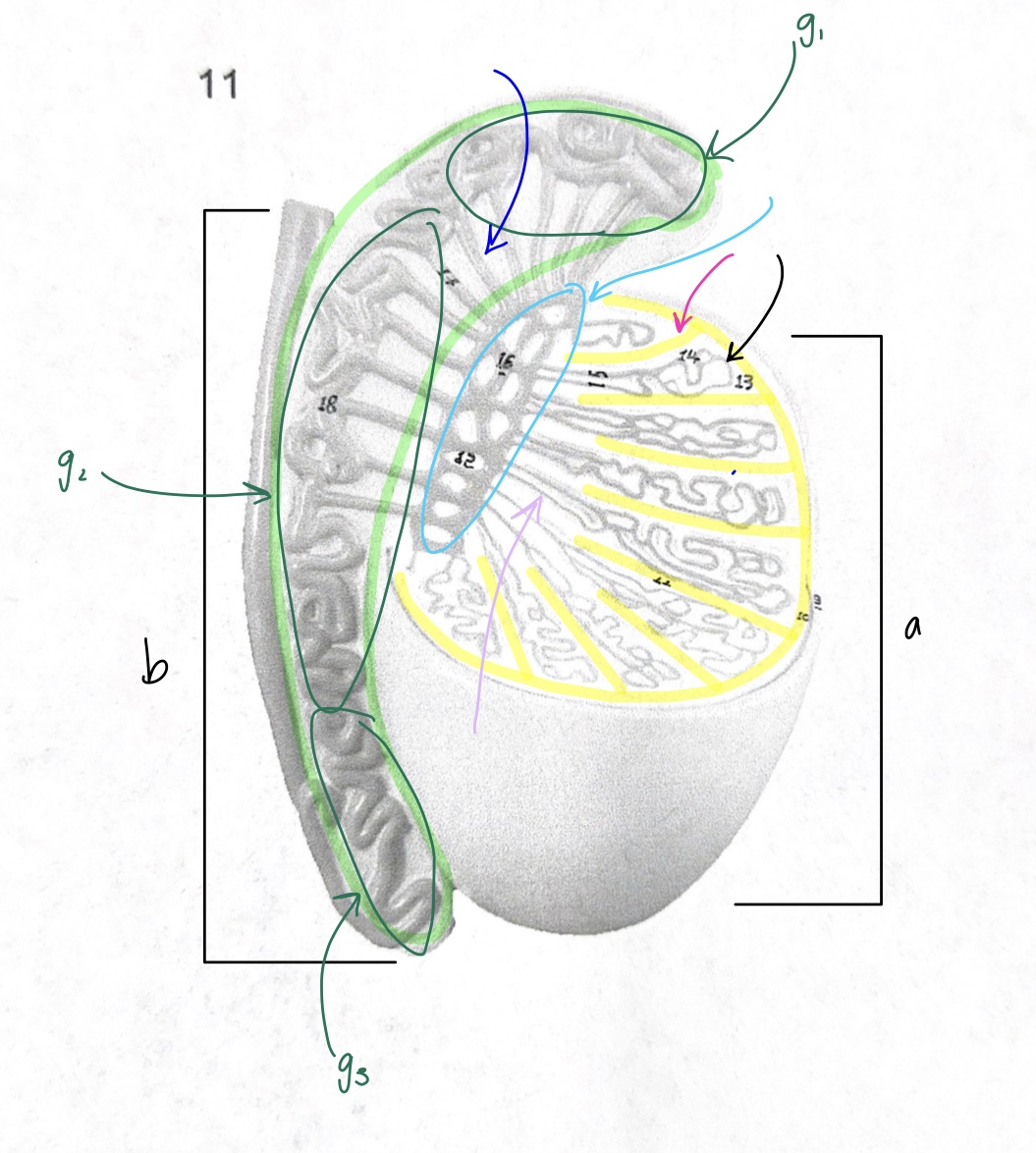
what is “a” structure
what is “b” structure
what is the structure highlighted in green?
what is G1?
what is G2?
what is G3?
what is the structure circled in blue?
what is the structure at the tip of the pink arrow?
what is the structure highlighted in yellow?
what is the structure at the tip of the purple arrow?
what is the structure at the tip of the of the black arrow?
what is “b” structure
what is the structure highlighted in green?
what is G1?
what is G2?
what is G3?
what is the structure circled in blue?
what is the structure at the tip of the pink arrow?
what is the structure highlighted in yellow?
what is the structure at the tip of the purple arrow?
what is the structure at the tip of the of the black arrow?
testis
vas deferens
epididymus
head of epididymus
body of epididymus
tail of epididymus
rete testis
septa
tunica albuginea
straight tubule
seminiferous tubule
vas deferens
epididymus
head of epididymus
body of epididymus
tail of epididymus
rete testis
septa
tunica albuginea
straight tubule
seminiferous tubule
82
New cards
ovaries
produce estrogen & progesterone
begin oogenesis
begin oogenesis
83
New cards
ovarian ligament
attach ovaries to uterus
84
New cards
suspensory ligament
attach ovaries to lateral abdominopelvic wall
85
New cards
germinal epithelium
epithelial tissue on periphery of ovary
86
New cards
cortex of ovaries
outer part of ovary
87
New cards
medulla of ovaries
inner part of ovary
88
New cards
uterine tube
transport 2 oocyte/ovulated structure or fertilized structure to the uterus
ciliated epithelium
ciliated epithelium
89
New cards
regions of uterine tube
infundibulum
ampulla
isthmus
fimbriae
ampulla
isthmus
fimbriae
90
New cards
infundibulum of uterine tube
enlargement of uterine tube
91
New cards
ampulla of uterine tube
site of fertilization
92
New cards
isthmus of uterine tube
narrowing of uterine tube
93
New cards
fimbriae of uterine tube
picks up ovulated structure
94
New cards
uterus
site of implantation
95
New cards
regions of uterus
body
isthmus
fundus
isthmus
fundus
96
New cards
layers of uterus
endometrium
myometrium
myometrium
97
New cards
endometrium
can sustain implanted structure temporarily
98
New cards
myometrium
smooth muscle; contracts in response to prostaglandin & oxytocin
99
New cards
regions of broad ligament
mesometrium
mesovarium
mesosalpinx
mesovarium
mesosalpinx
100
New cards
mesometrium
anchors uterus laterally