Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) - PART I
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Functions of the Kidney
Waste elimination
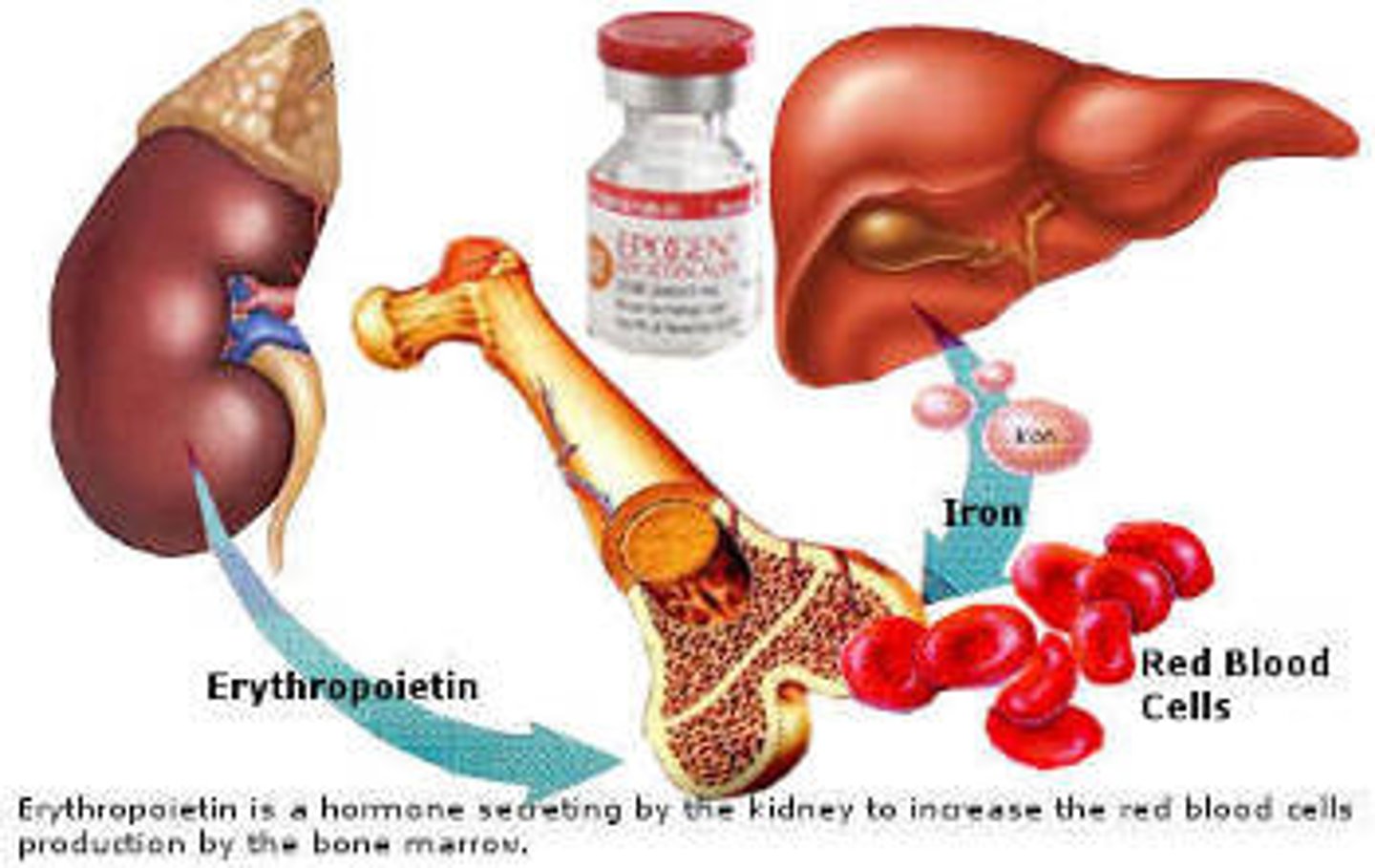
Release of erythropoietin
Secretion and reabsorption
Vitamin D conservation
Regulation of pH
Kidney elimination
metabolic waste - urea, uric acid, creatinine
- drugs/ foreign toxic - penicillin
- degrades polypeptide hormones - insulin/ glucagon/ PTH
Erythropoietin (EPO)
hormone secreted by the kidney to stimulate the production of red blood cells by bone marrow
Ca+ absorption
Activated vitamin D helps with ___ _________
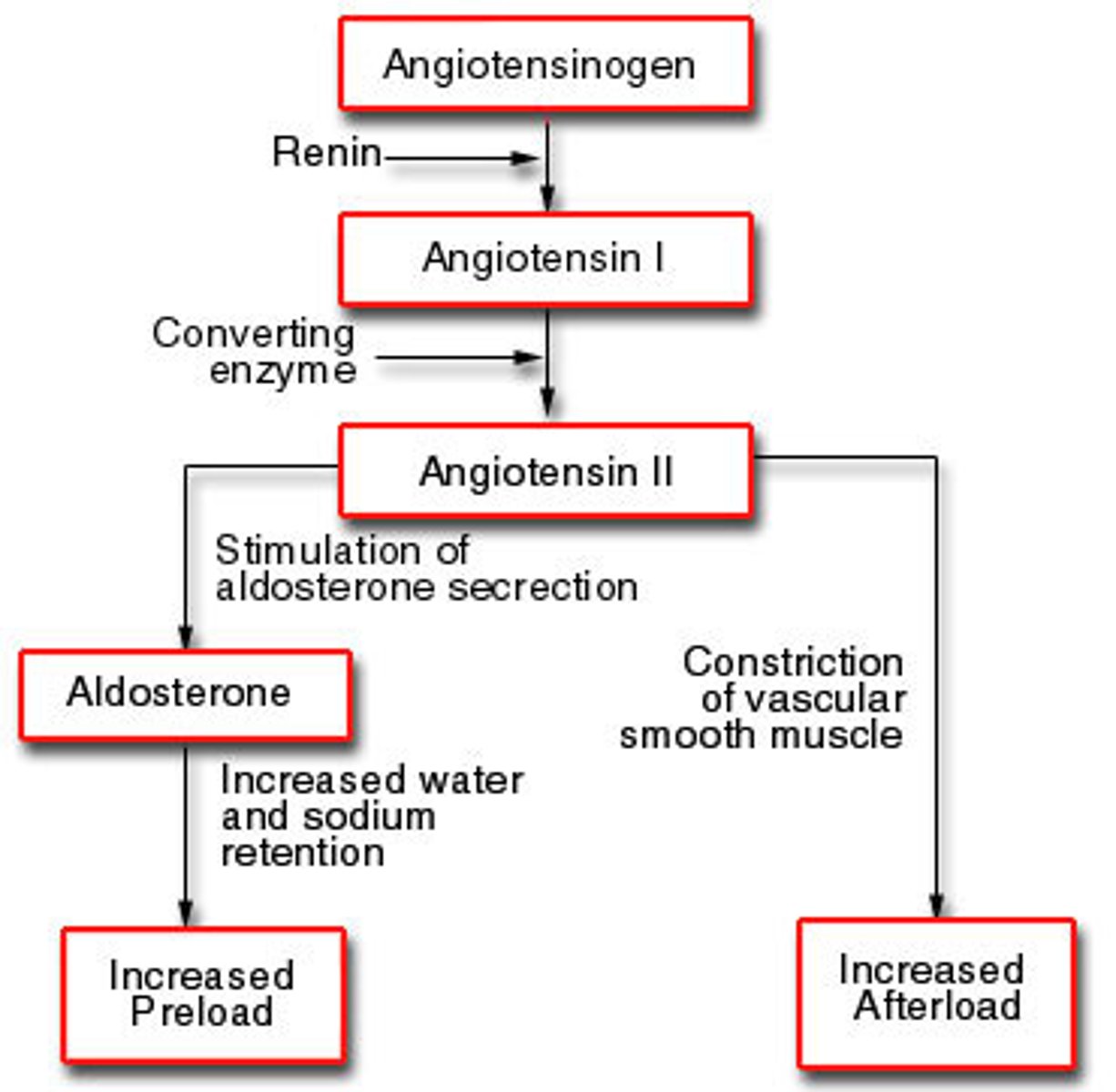
RAAS
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
135-145 mEq/L
normal sodium levels

98-108
Chloride

3.5-5
Potassium
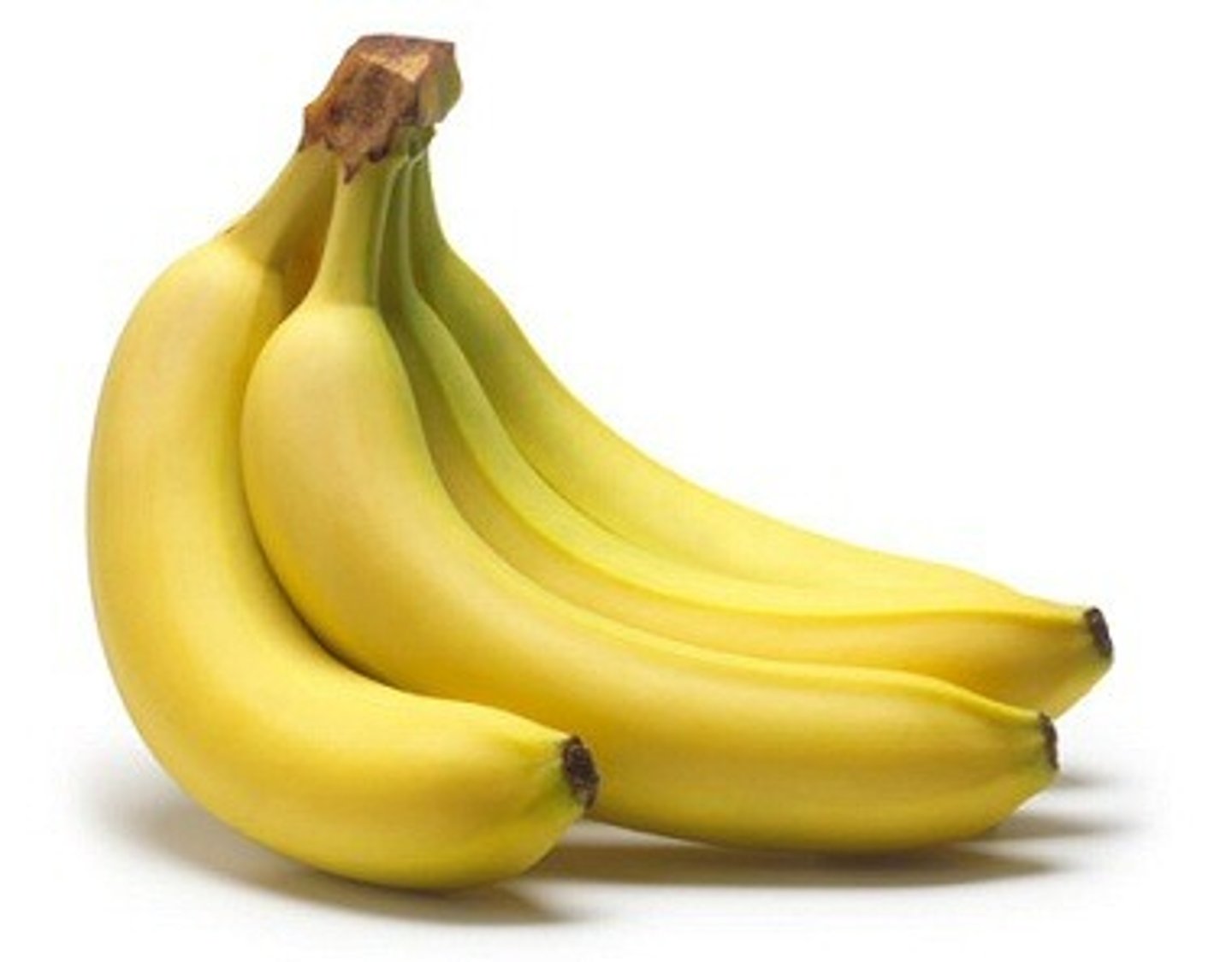

22-26
HCO3-
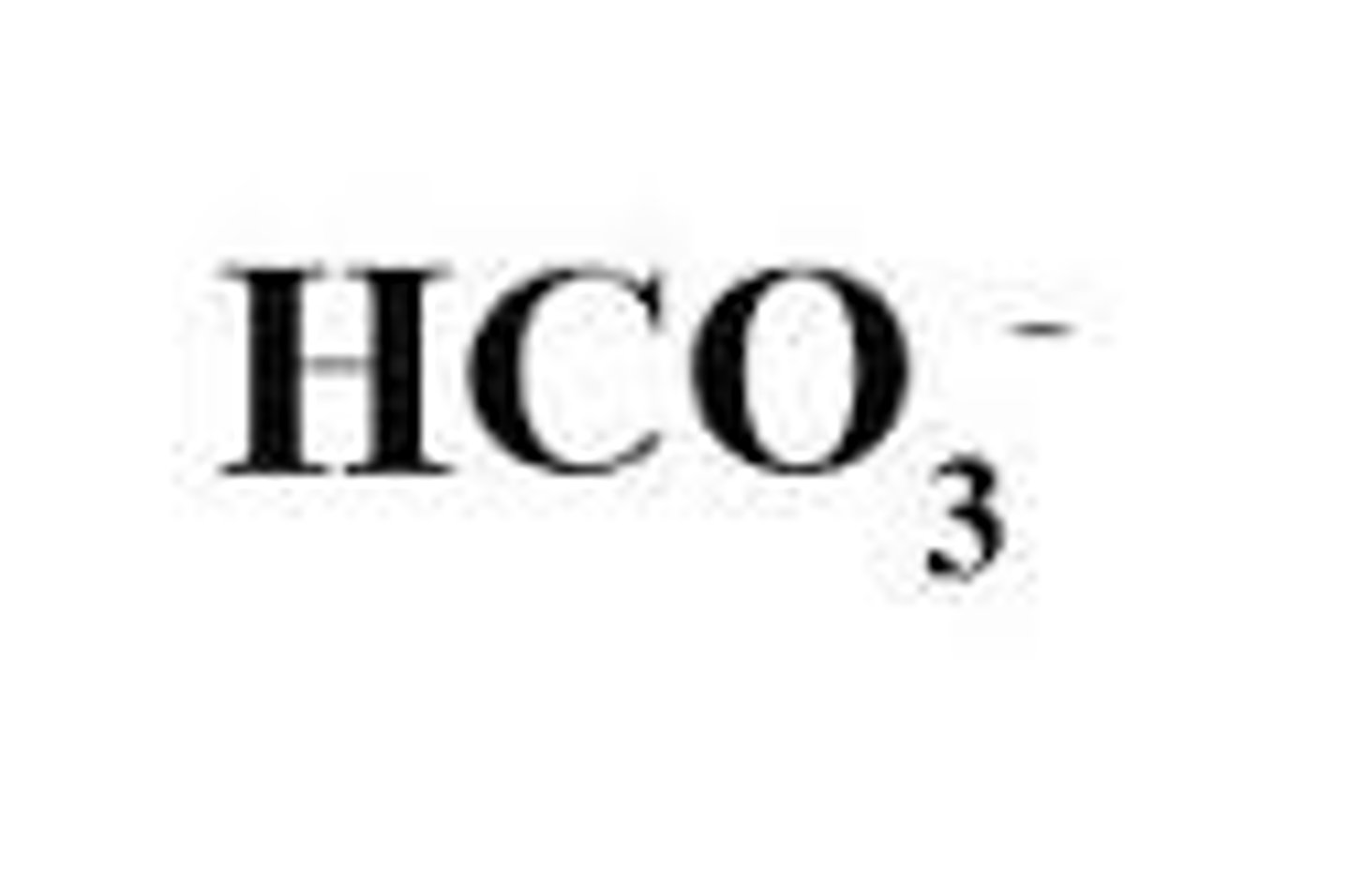
8.5-10.5
normal calcium levels

10-20
normal BUN

0.7-1.4
normal creatinine
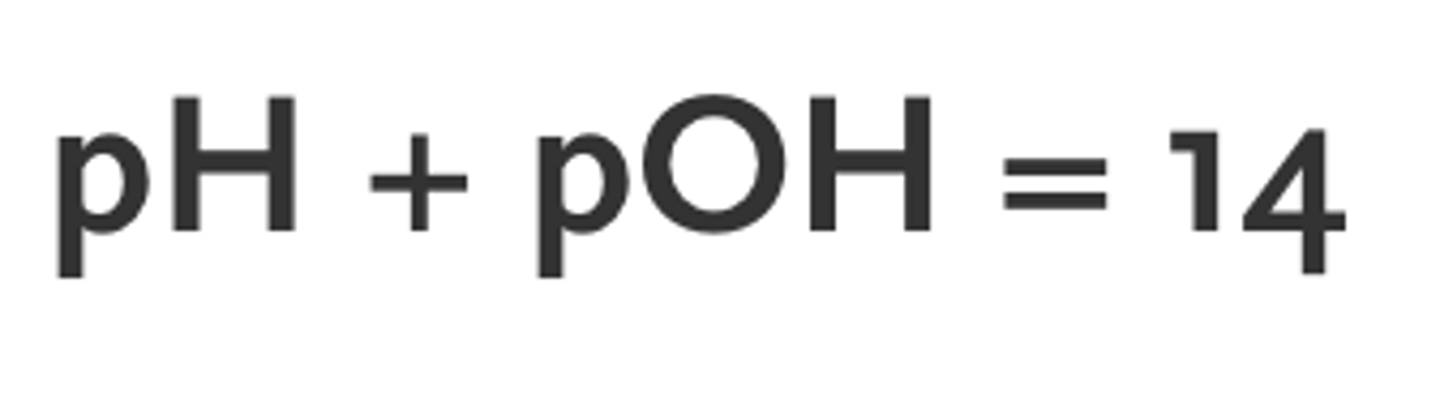
7.35-7.45
pH of blood
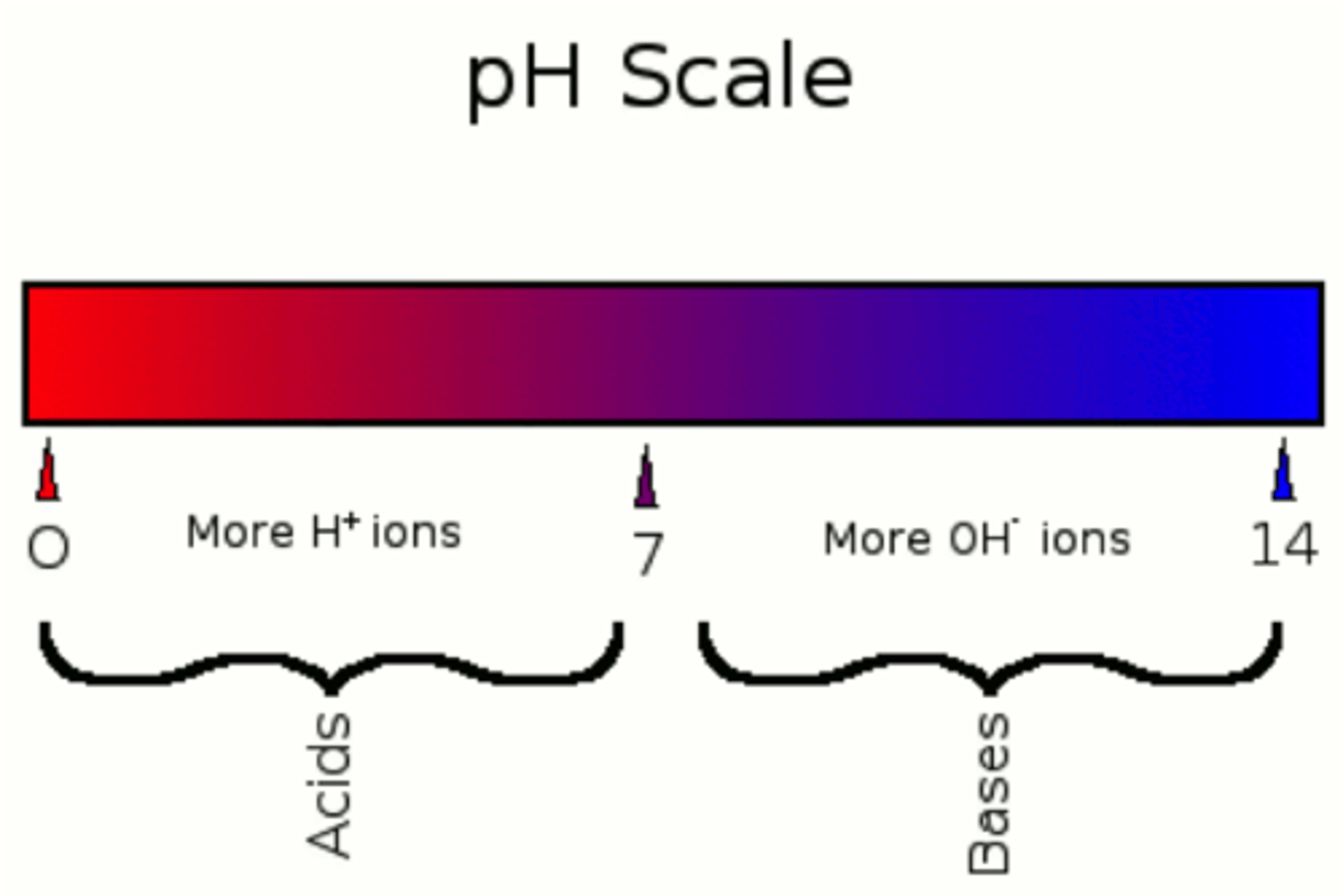
2.5-4.5
normal phosphorus levels
Kidney Biopsy
Evaluates cellular function.
Post procedure care: pressure to site, bedrest following test, no heavy lifting
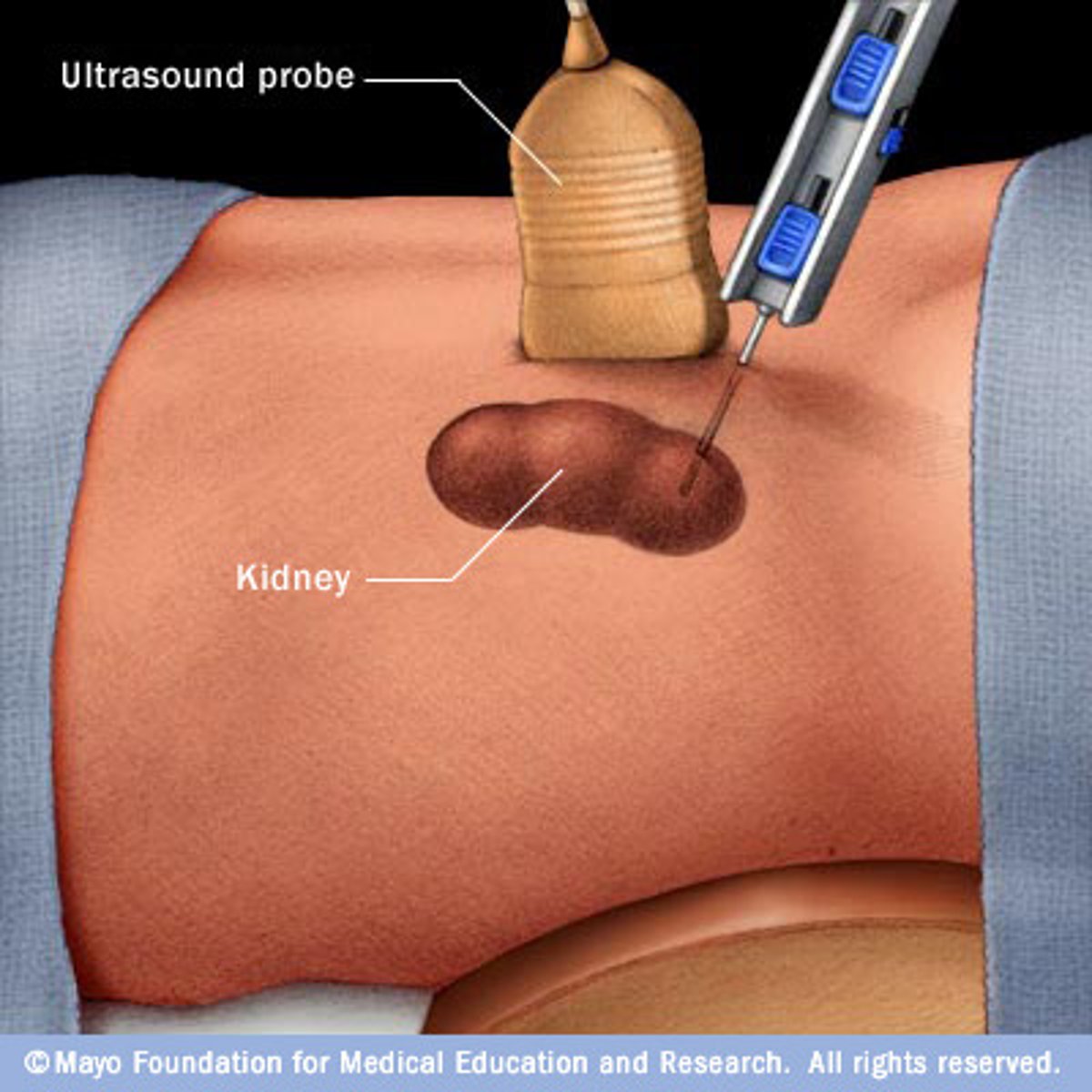
Renal Ultrasound
Evaluates size and anatomy of kidney
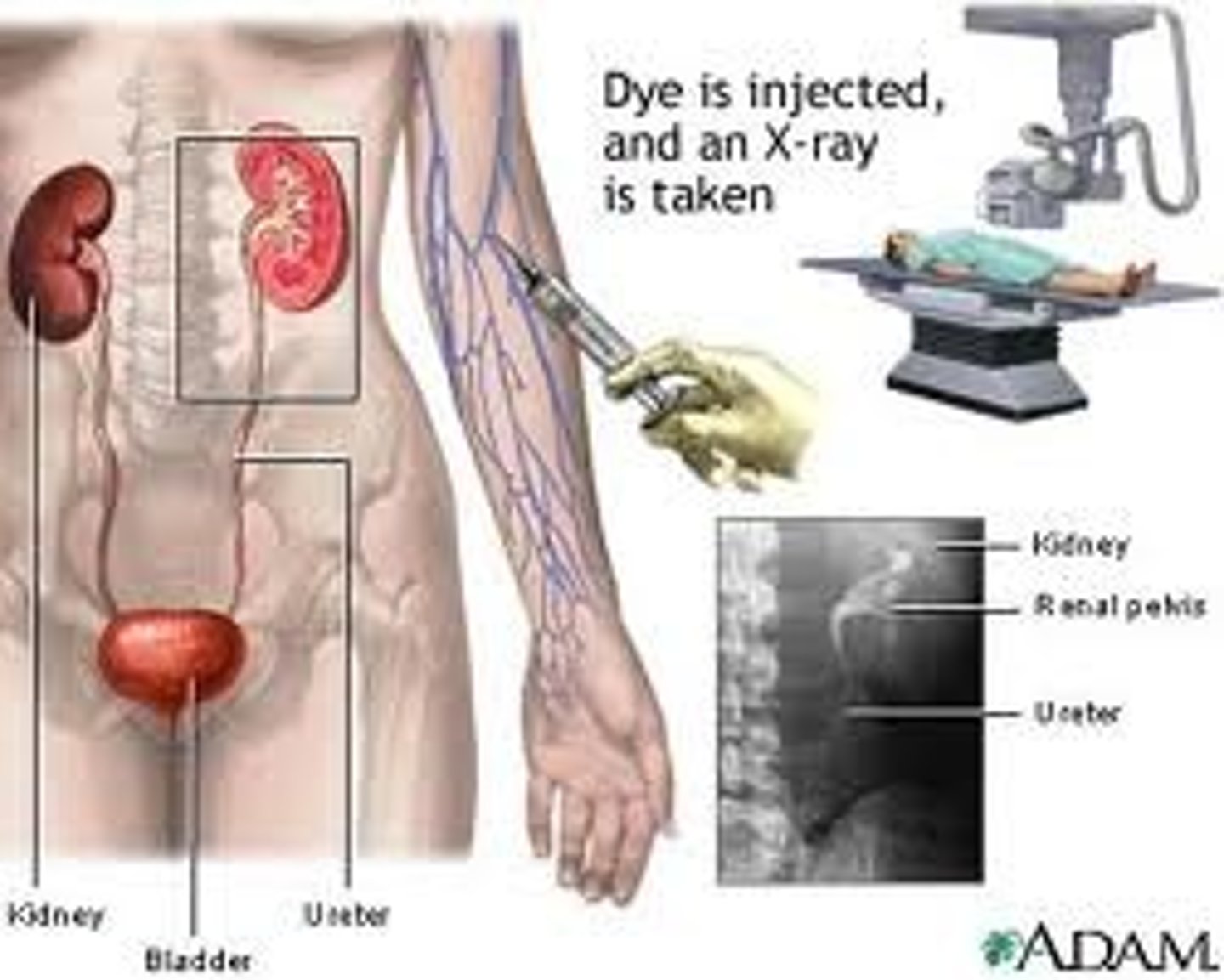
Pyelogram
x-ray of the renal pelvis
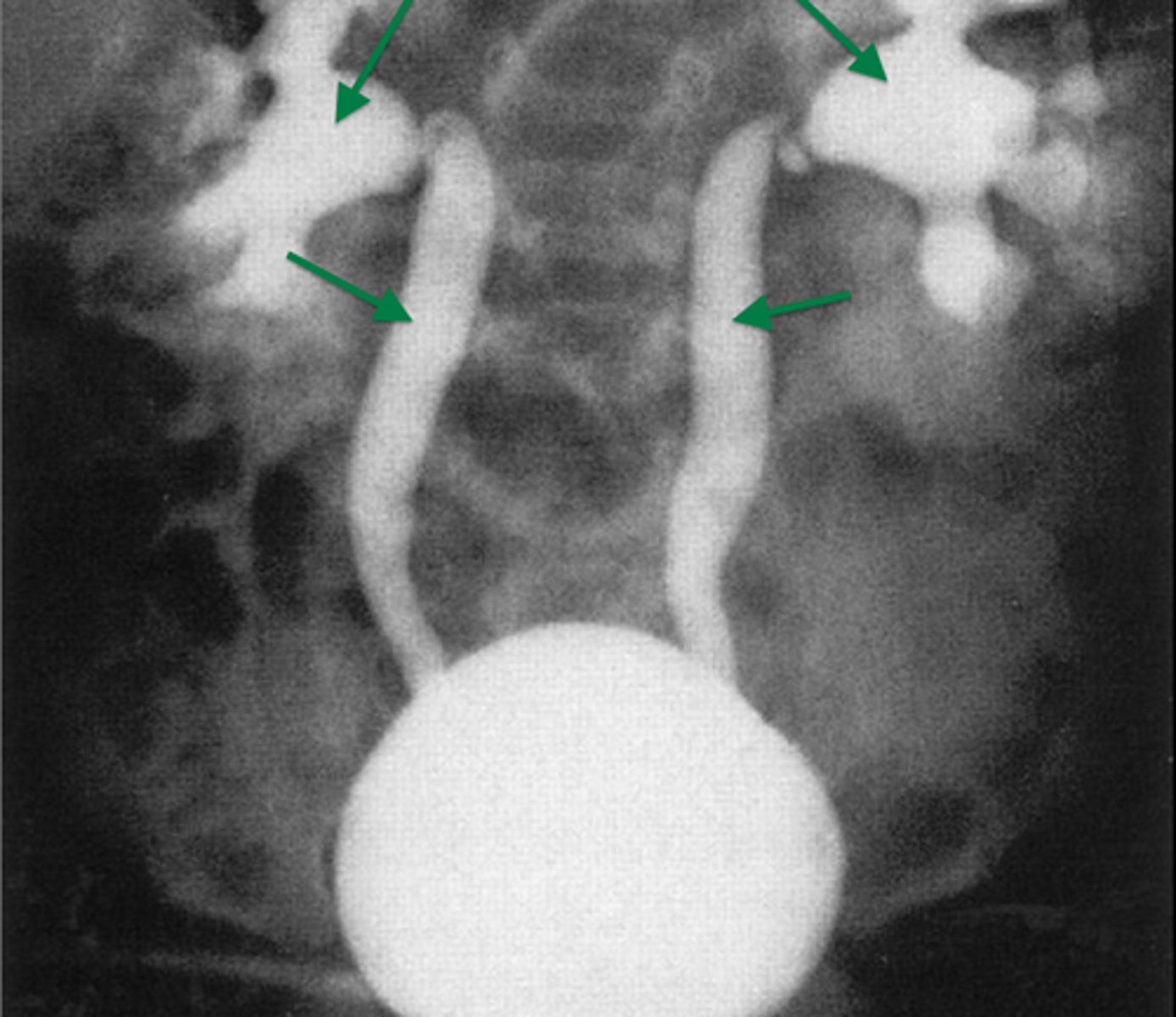
Cystourethrogram
Contrast via cystoscopy to view ureters and bladder
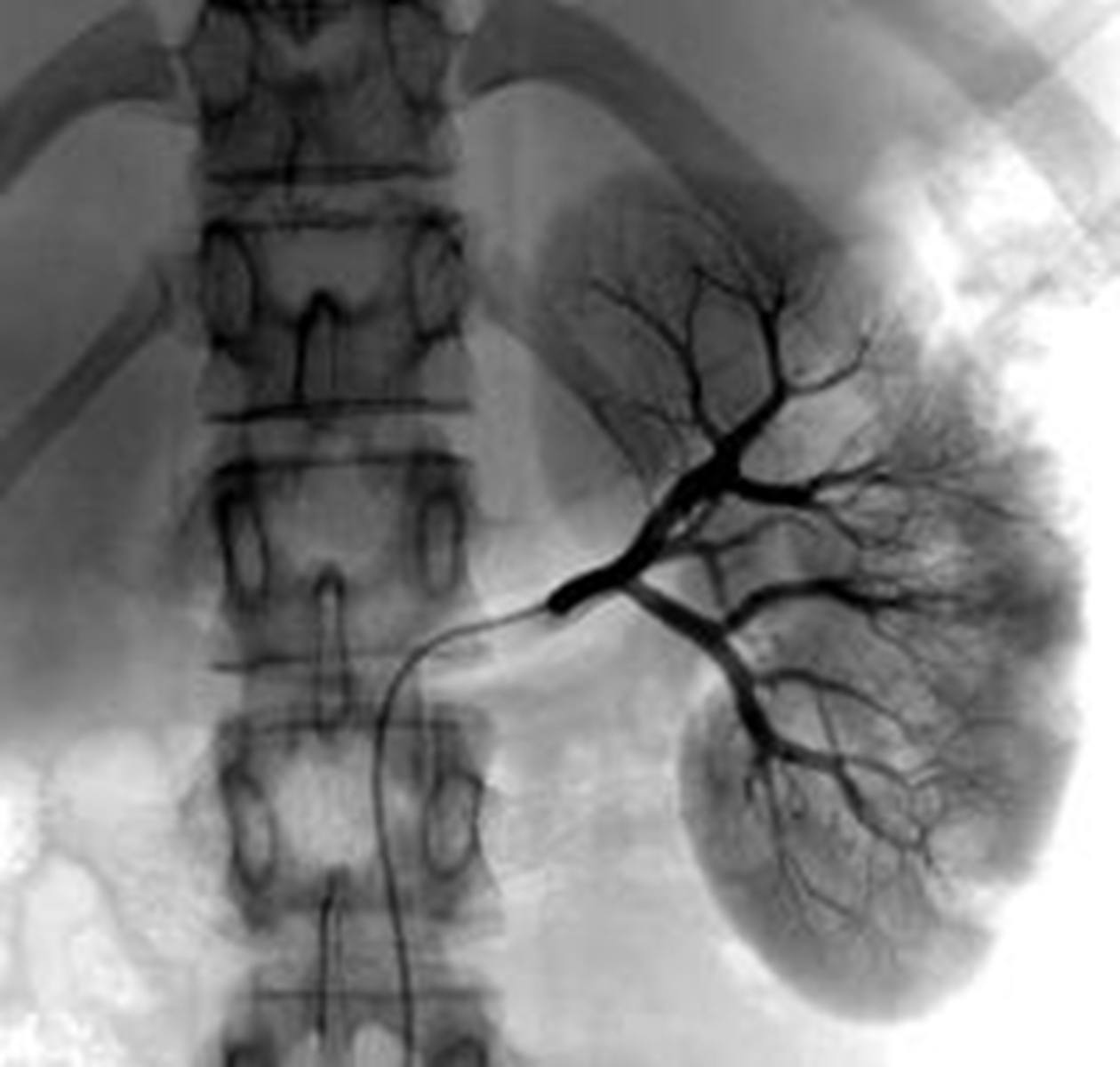
Renal arteriogram
Contrast via the femoral artery to view renal patency of renal vessels
Risks for AKI
Sepsis
Cardiac surgery
Cardiac failure
Respiratory failure
Mechanical ventilation or PEEP
Trauma
Rhabdomyolysis
Chronic Kidney Disease
Contrast Dye
Rhabdomyolysis
dissolution of striated muscle
Causes buildup of MYOGLOBIN

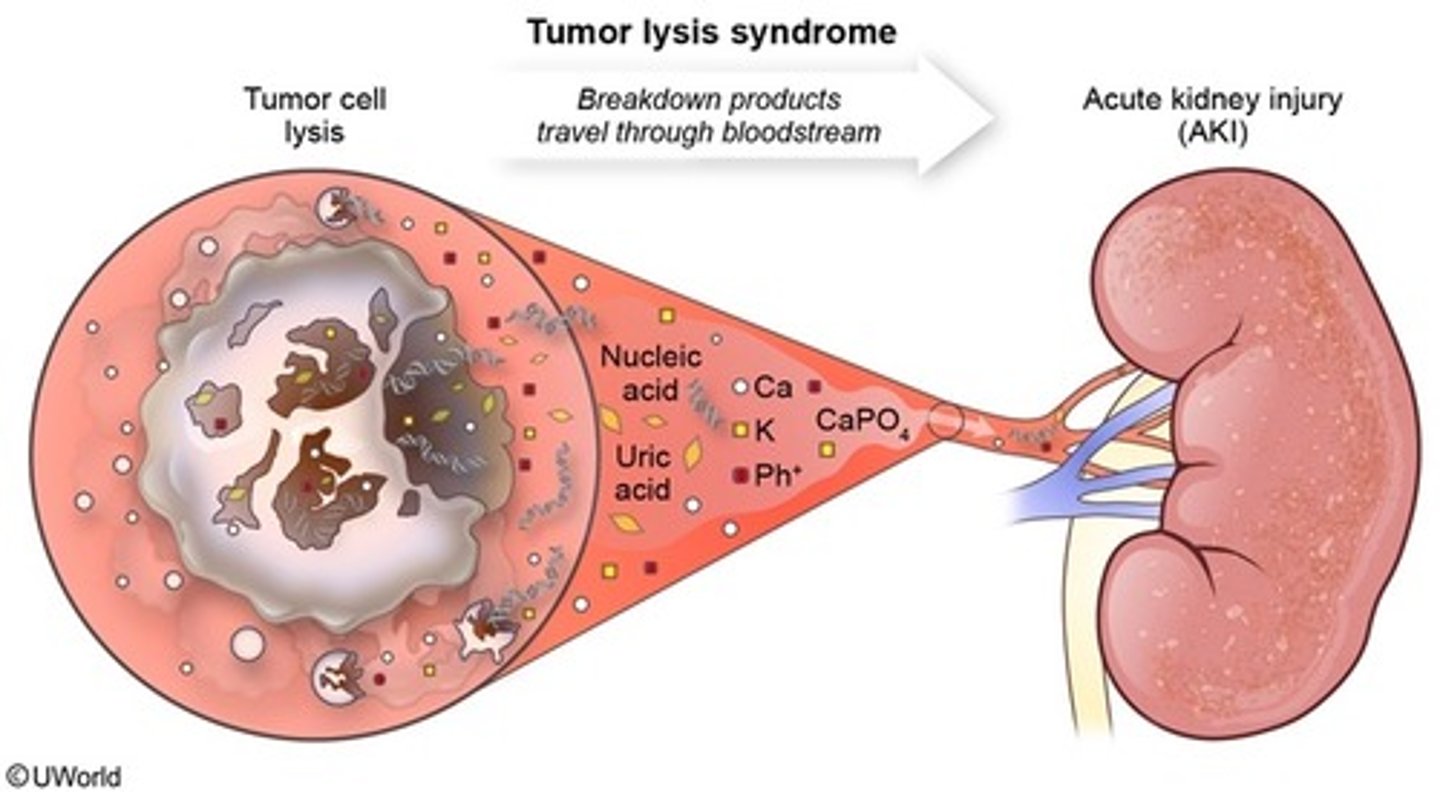
Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS)
an oncologic emergency with rapid lysis of malignant cells
Causes buildup of URIC ACID
decreased blood flow
A lot of kidney damage occurs due to a _______ ______ ______
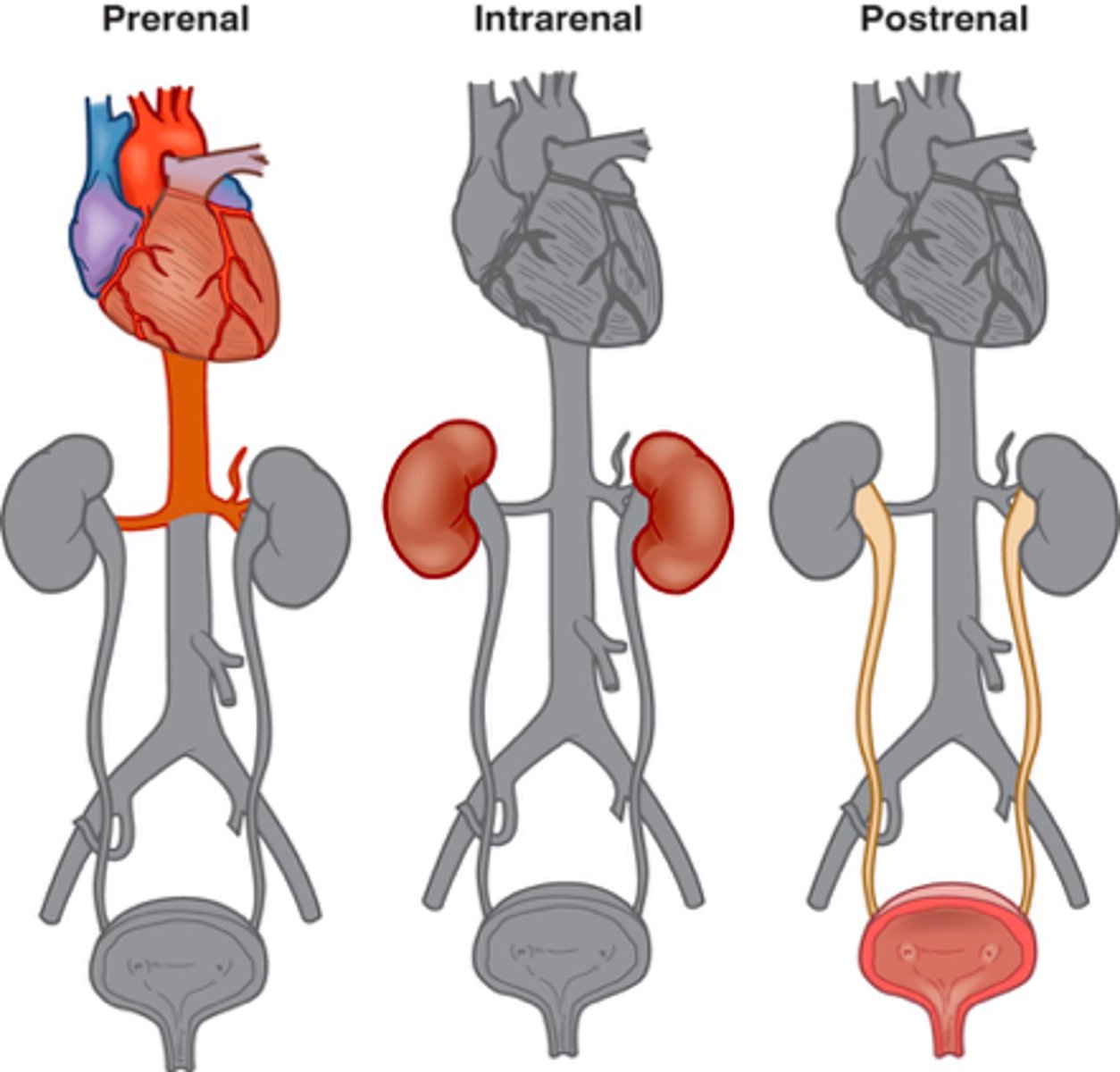
Pre-renal AKI
Low perfusion states
Hypertension
Shock states
Cardiac failure
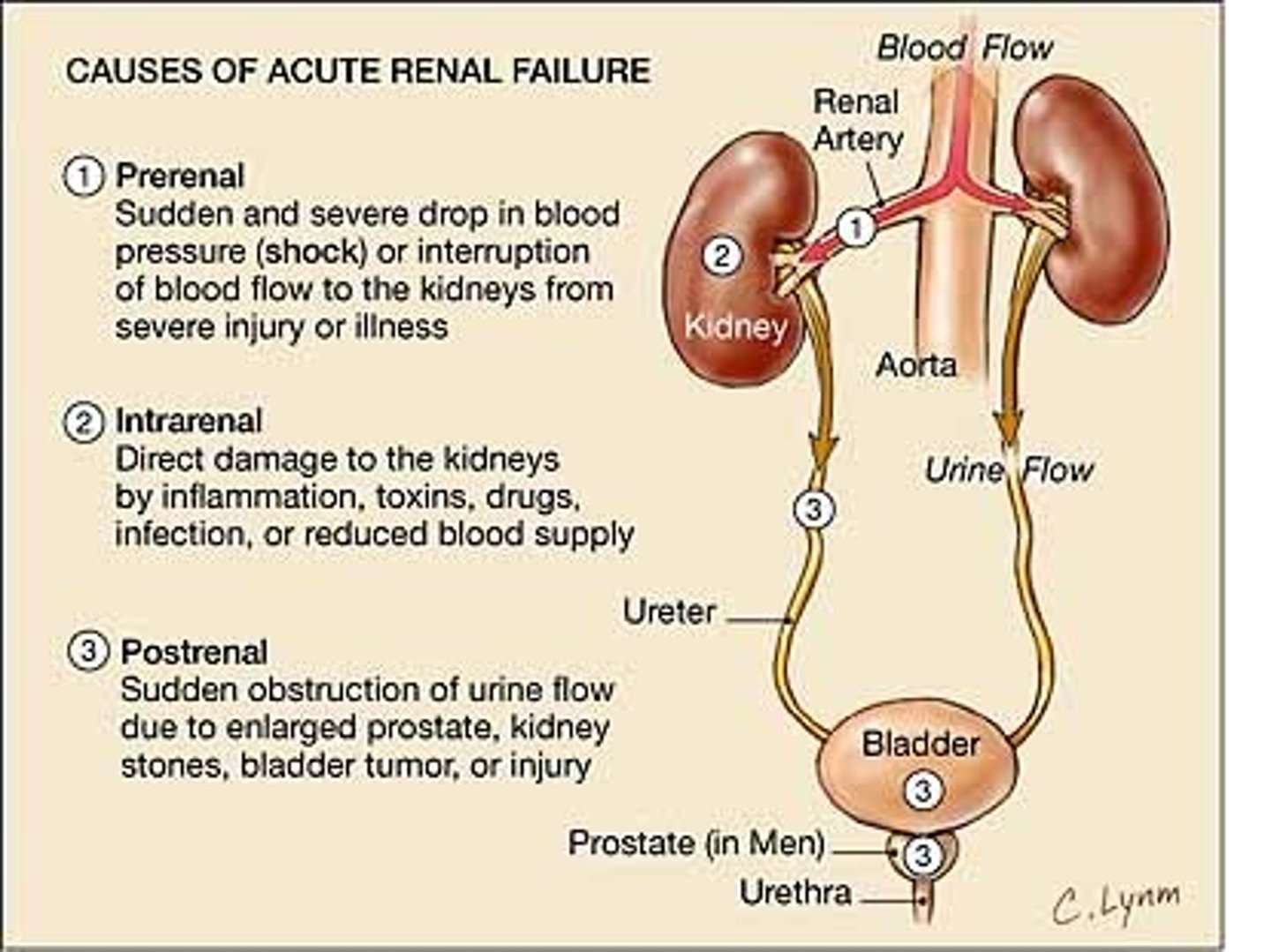
Intra-renal AKI
Progression of pre-renal type d/t ischemia
Toxins such as myoglobin, NSAIDs, chemotherapy, contrast dye

progress
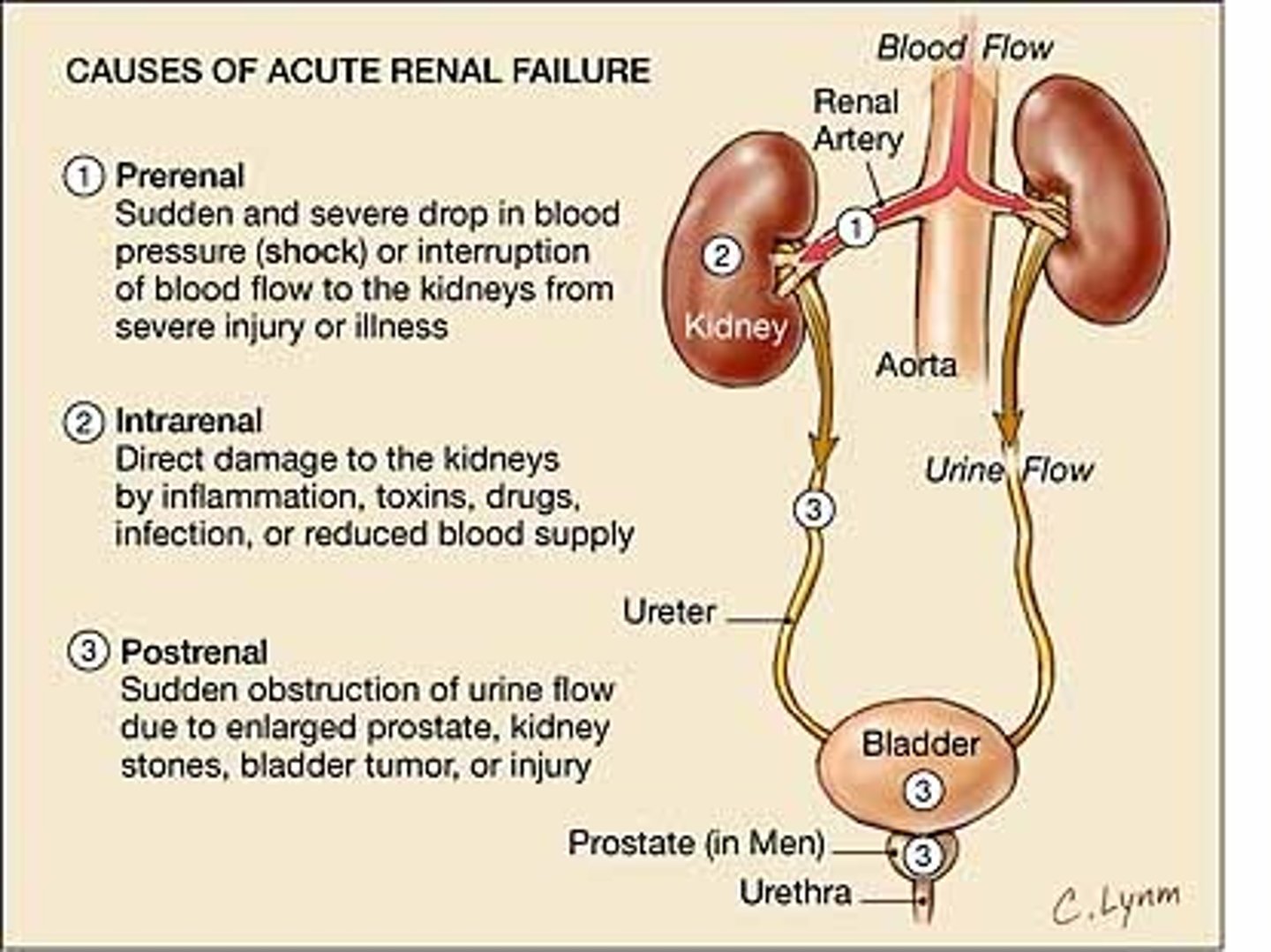
Pre-renal can _____ to intra-renal, if ischemia results from low perfusion

Prerenal to intrarenal
Decreased blood flow
Decreased GFR
Renal tubular damage - urine may be heme +
Cell death and shedding - seen as casts in urine analysis
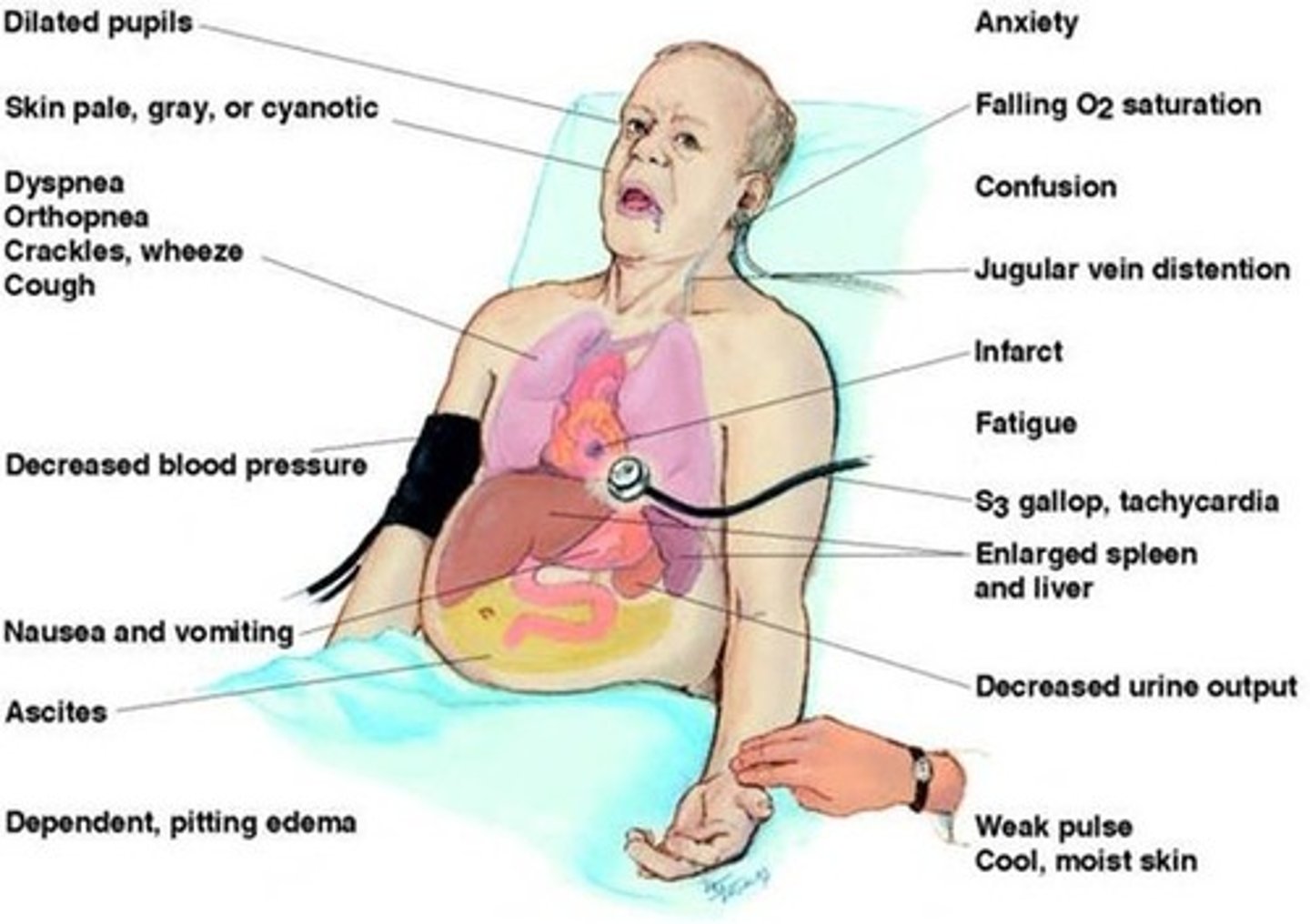
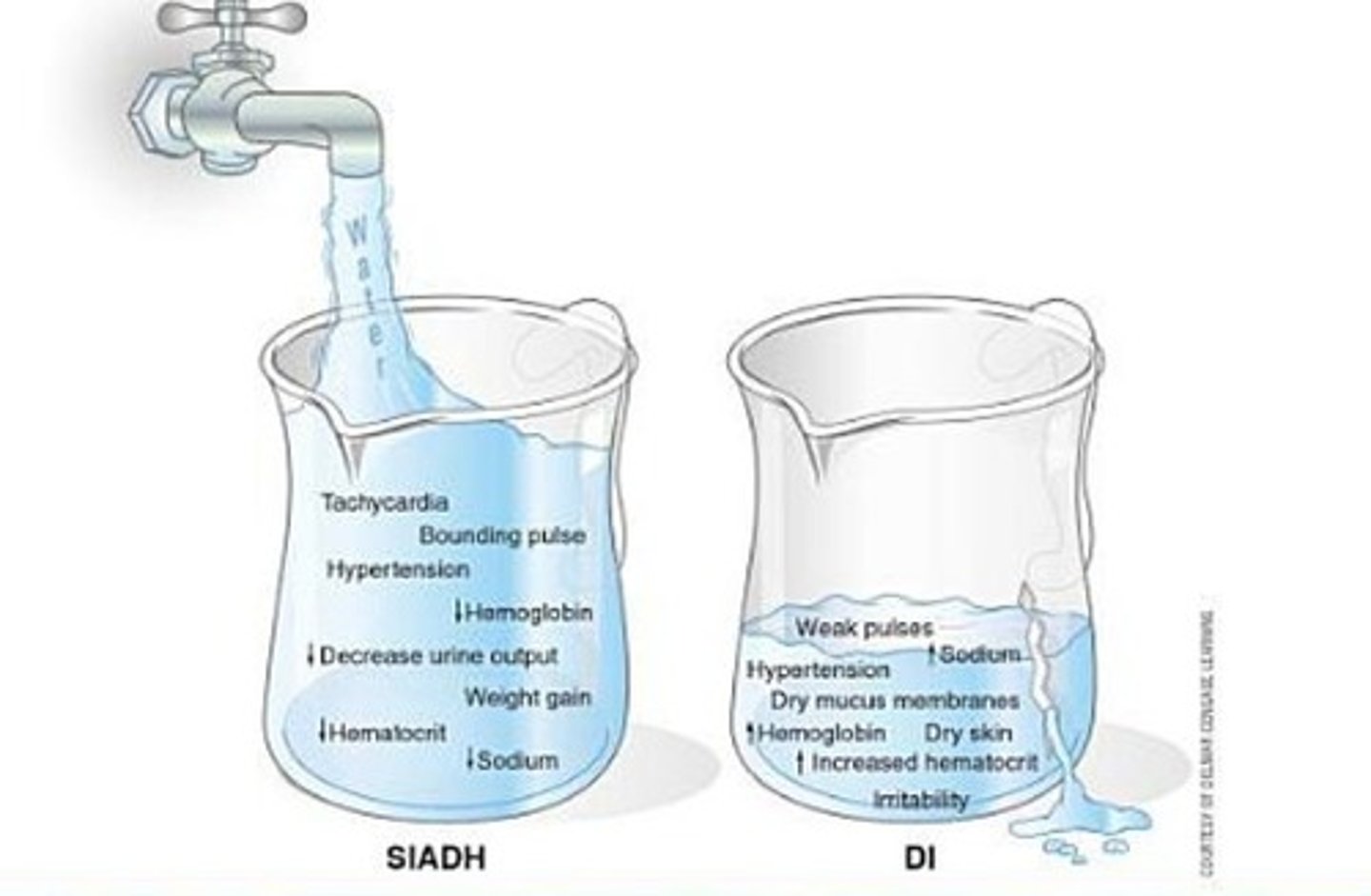
Manifestations of AKI
Uremia
Decreased UOP
Increased creatinine
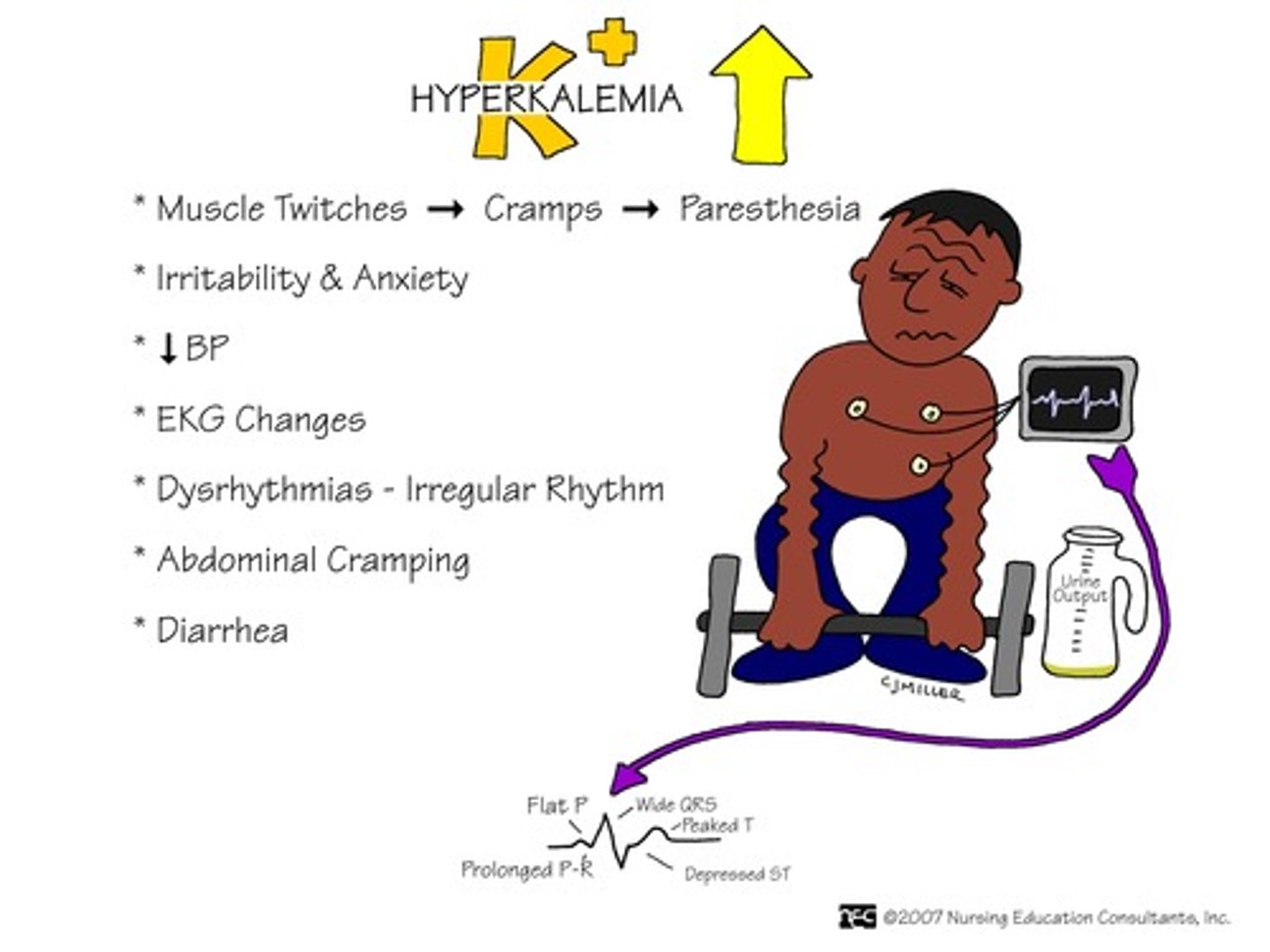
Increased K+
Signs of hypervolemia
Metabolic acidosis
Decreased Ca+
Increased Phos+
Decreased Na+
Kussmaul breathing
gasping, labored breathing, also called air hunger
Sign of metabolic acidosis
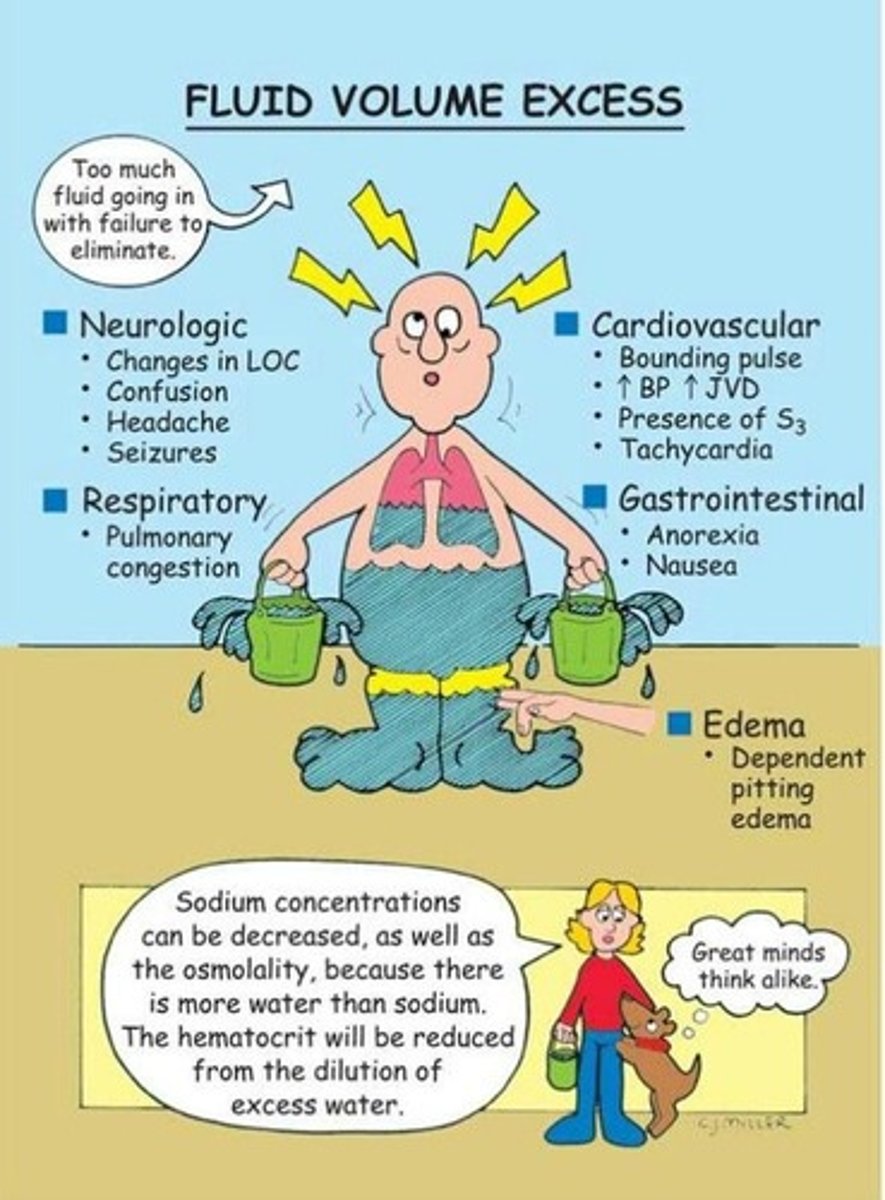
Hypervolemia S/S
HTN, edema, crackles, elevated CVP
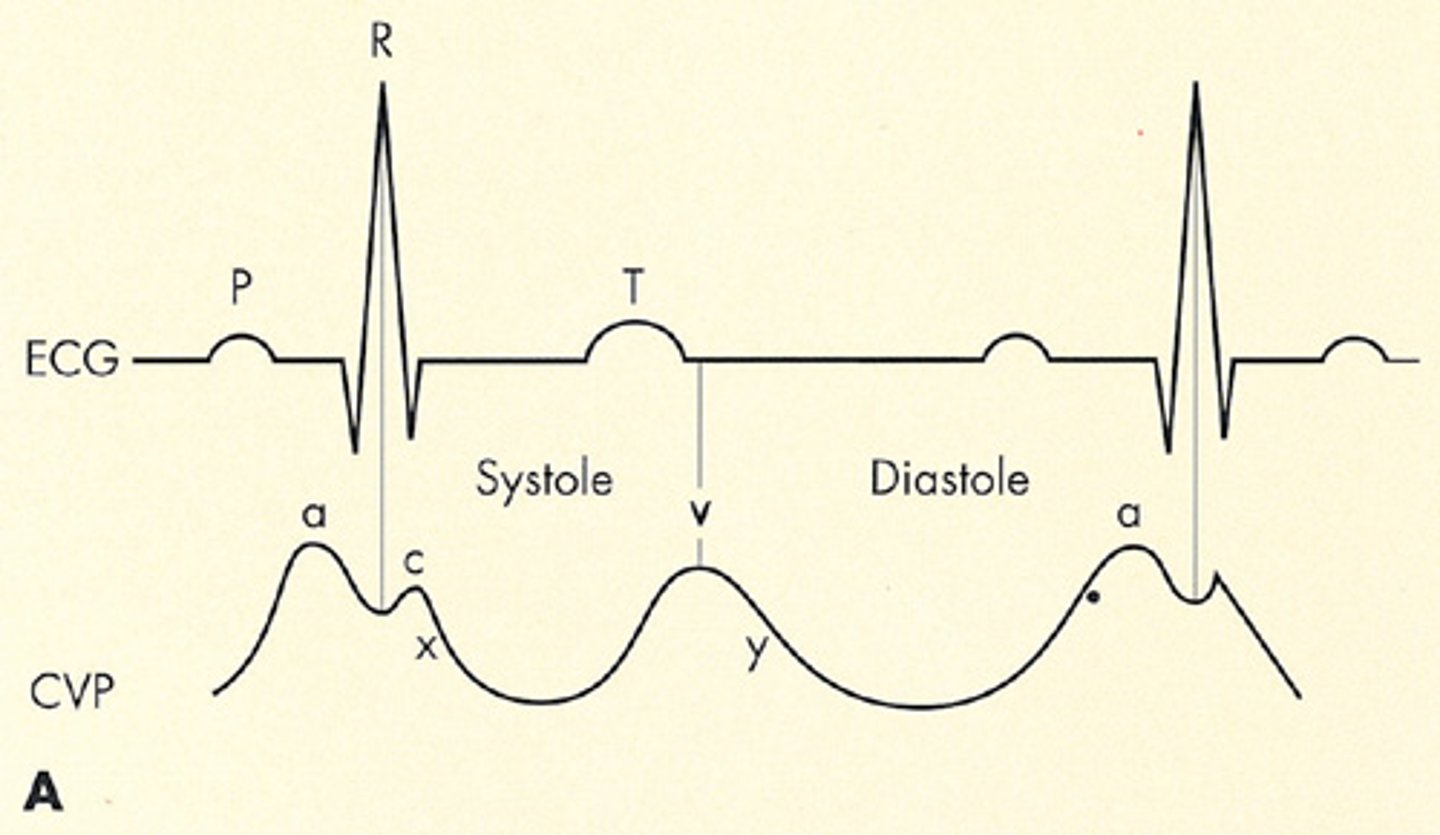
3-5 mmHg
Normal CVP
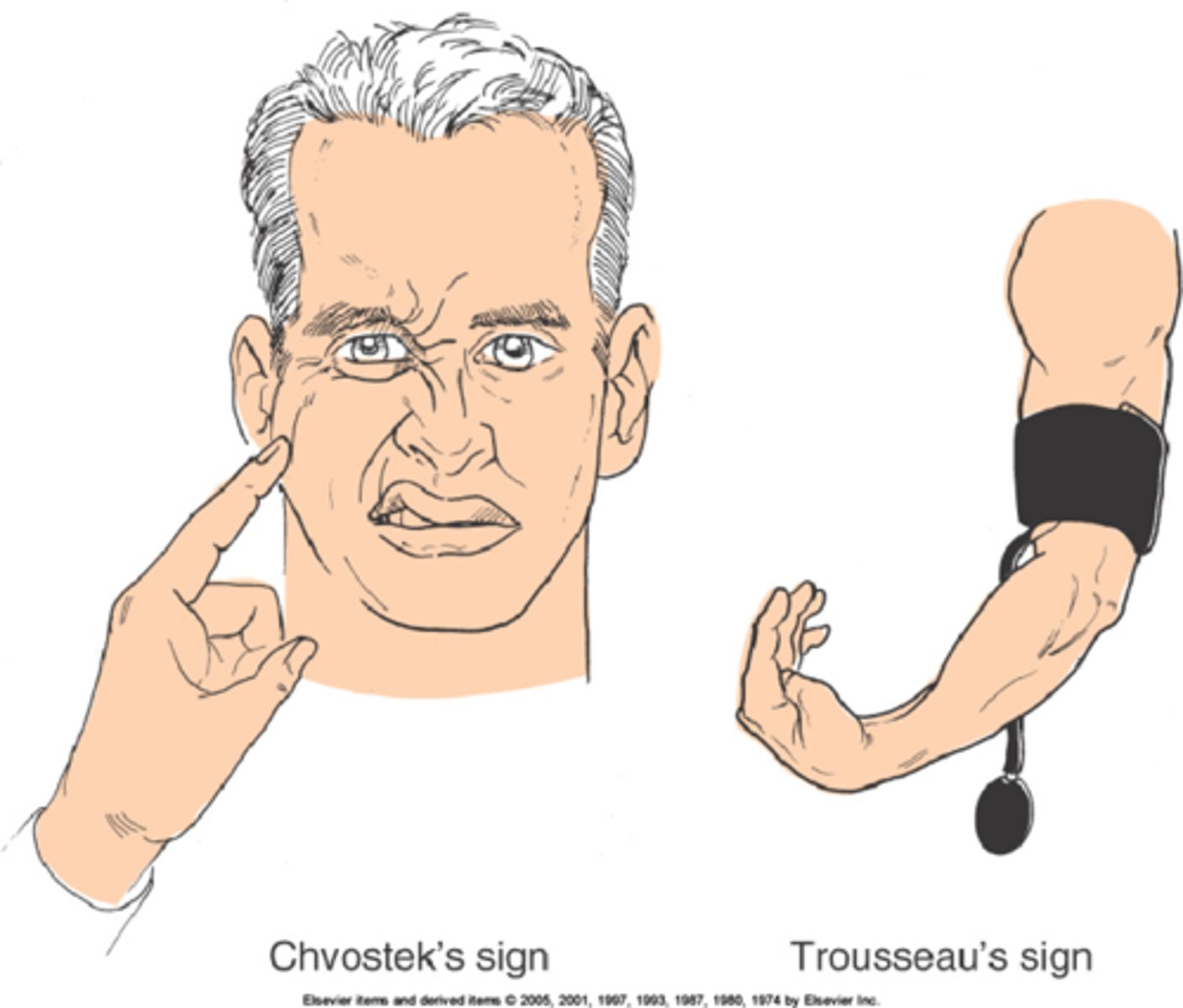
Chvostek's and Trousseau's signs.
hypocalcemia
Pruritis
itching
Sign of increased phos+

Signs of decreased Na+
nausea, tachycardia, decreased LOC, seizures
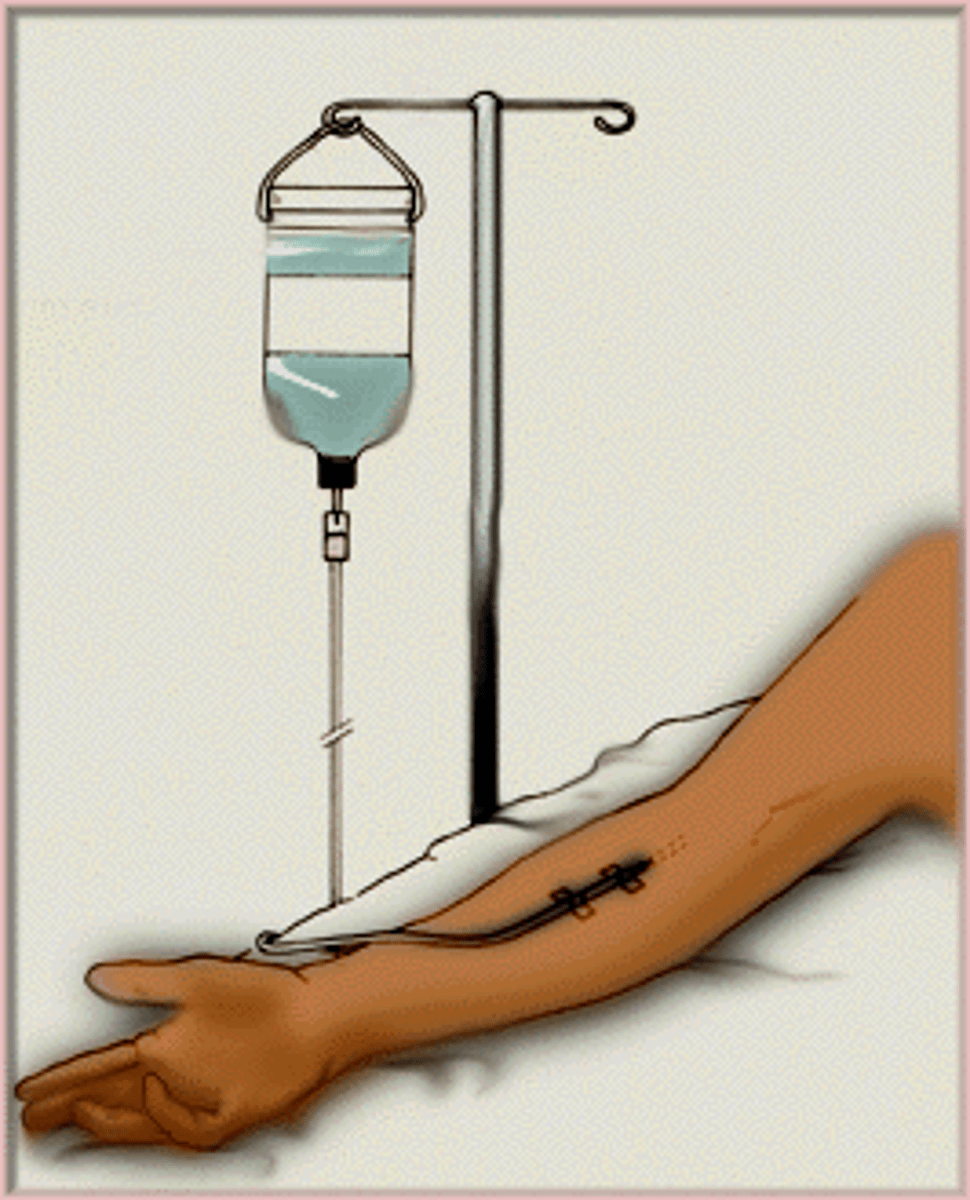
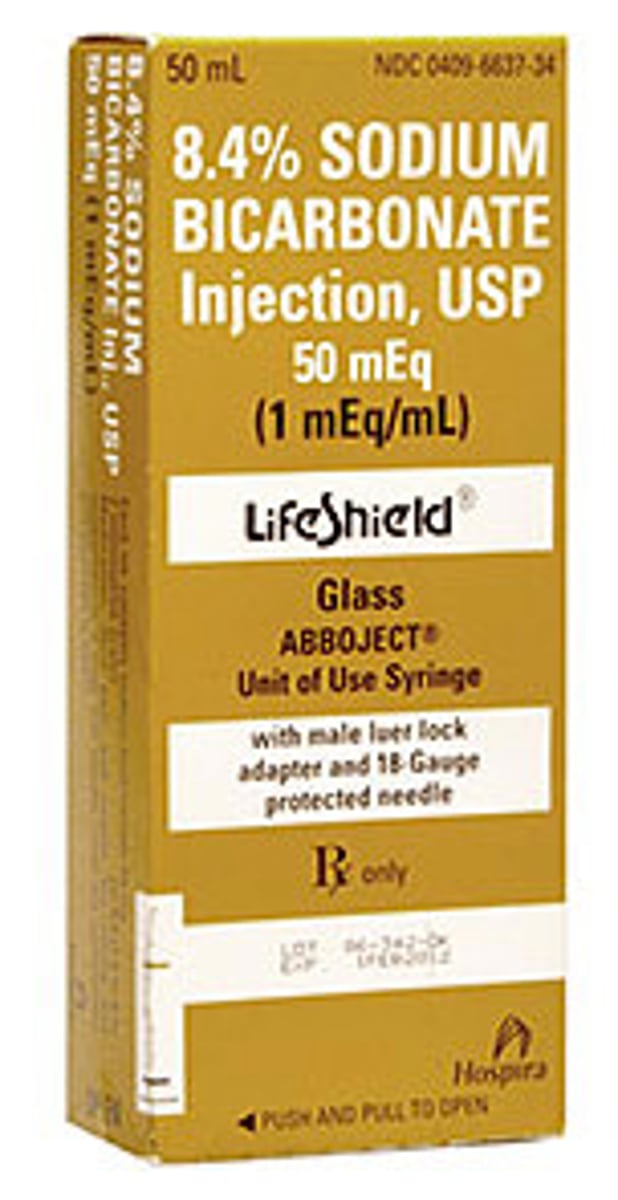
Hyperkalemia treatment
IV Ca gluconate
IV glucose, followed by IV insulin
IV sodium bicarbonate
Dialysis
Sodium polystyrene (kayexalate) or Patiromer (Veltassa)
IV Calcium gluconate
Stabilizes heart and antagonizes K+

IV glucose, IV insulin
Moves K+ intracellular
IV sodium bicarb
Pushes K+ into the cells and fixes acidosis
Prerenal AKI treatment
volume repletion, typically just NS
Intrarenal AKI treatment
Fluid restriction and diuretics
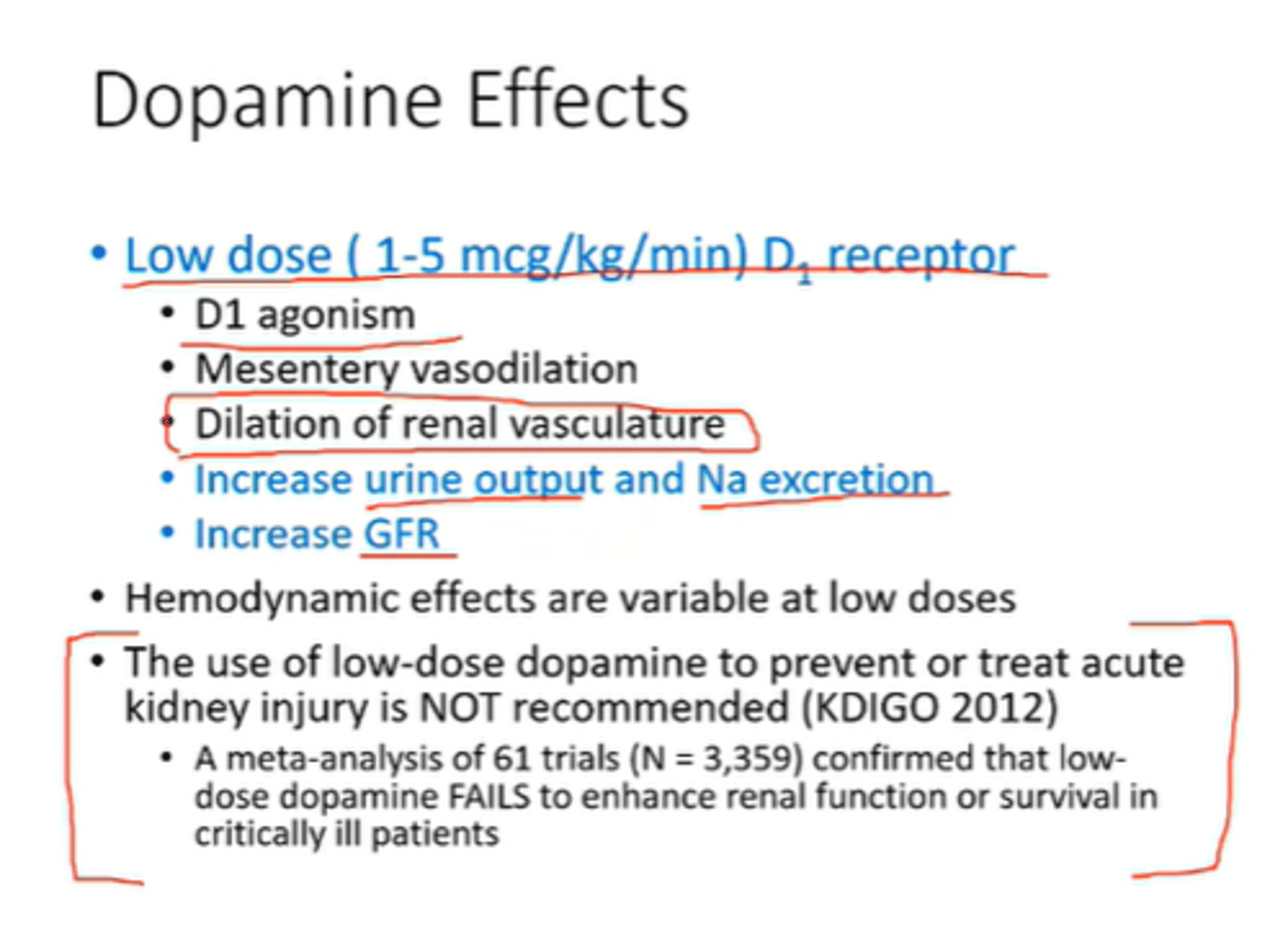
Low-dose dopamine
supports cardiac output and kidney perfusion by dilating the renal artery
Anemia treatment
Epoetin alfa, darbepoetin alfa, RBC infusion
Phosphorus binding drugs
-Calcium carb
-Aluminum carbonate
-Sevelamer HCL/Lanthamum carbonate

Na, K, Ph
With AKI, we want a dietary restriction of __, _, and __
NSAIDs
To protect the kidneys, avoid ______
1 hour
For patients with AKI, we want to measure I+O q______

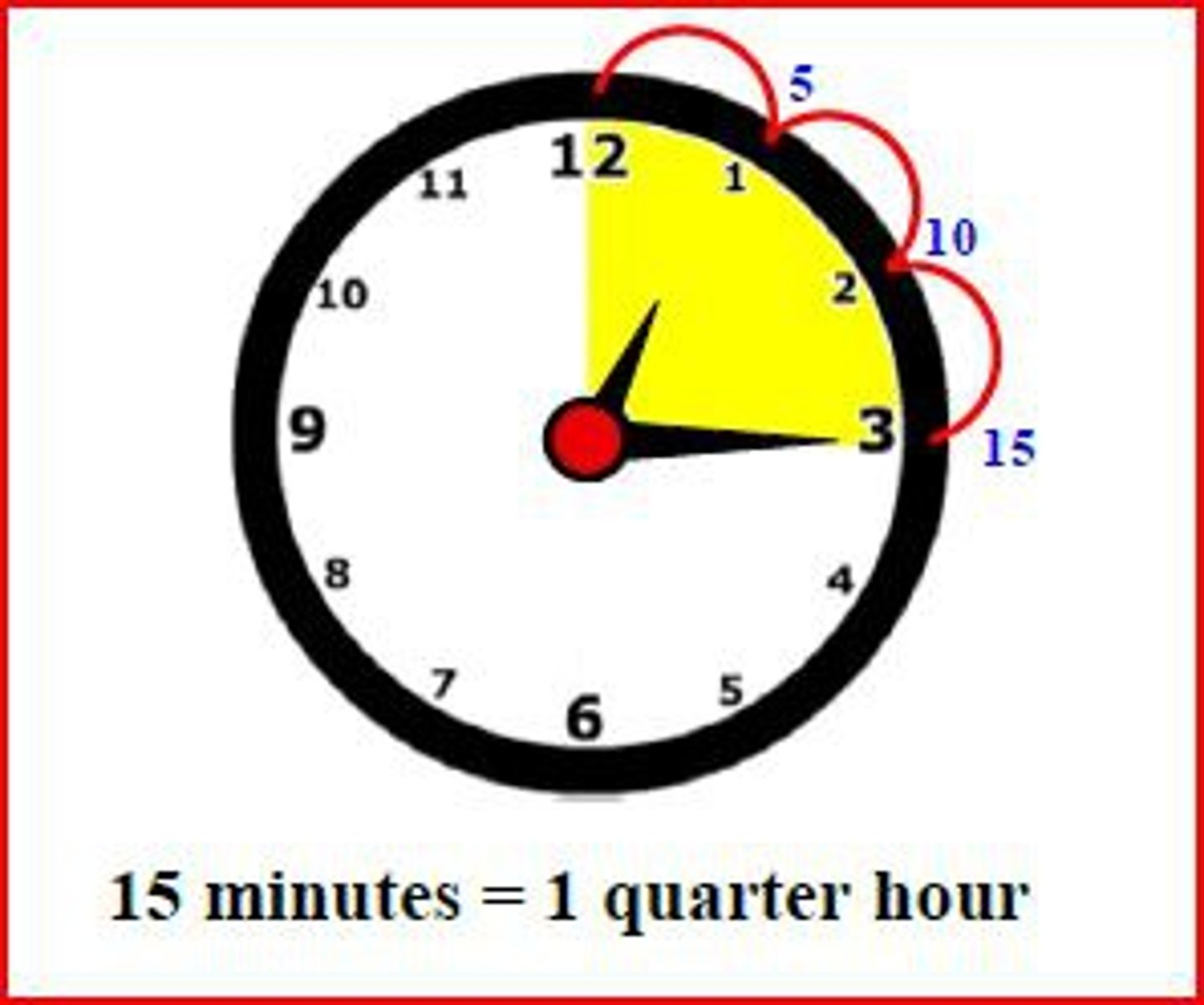
15 minutes
AKI: Check vital signs Q__ _______
daily weight
best indicator of fluid balance