NPTE Practice w/o Explanations Pt. 2
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
A therapist is examining a patient's vestibular dysfunction. The patient is asked to assume a long sitting position. The patient's head is turned toward her left side while she is in a sitting position. The therapist then quickly moves the patient backward so that the head is extended over the end of the table approx.30 degrees below horizontal. This maneuver causes dizziness and vertigo. The repeat test to the right side did not produce any symptoms. The therapist reports these findings as:
A. Positive right Dix Hallpike test
B. Positive sharpened Romberg test
C. Positive left Dix Hallpike test
D. Positive Positional test
C. Positive left Dix Hallpike test
The physical therapist is performing the shown technique on a patient to treat his vertigo. What would be the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
A. Posterior semicircular Canal BPPV in Right Ear
B. Horizontal semicircular Canal BPPV in left Ear
C. Horizontal semicircular Canal BPPV in Right Ear
D. Posterior Semicircular Canal BPPV in Left Ear
B. Horizontal semicircular Canal BPPV in left Ear
start with L side and BBQ technique for horizontal SCC start in supine position
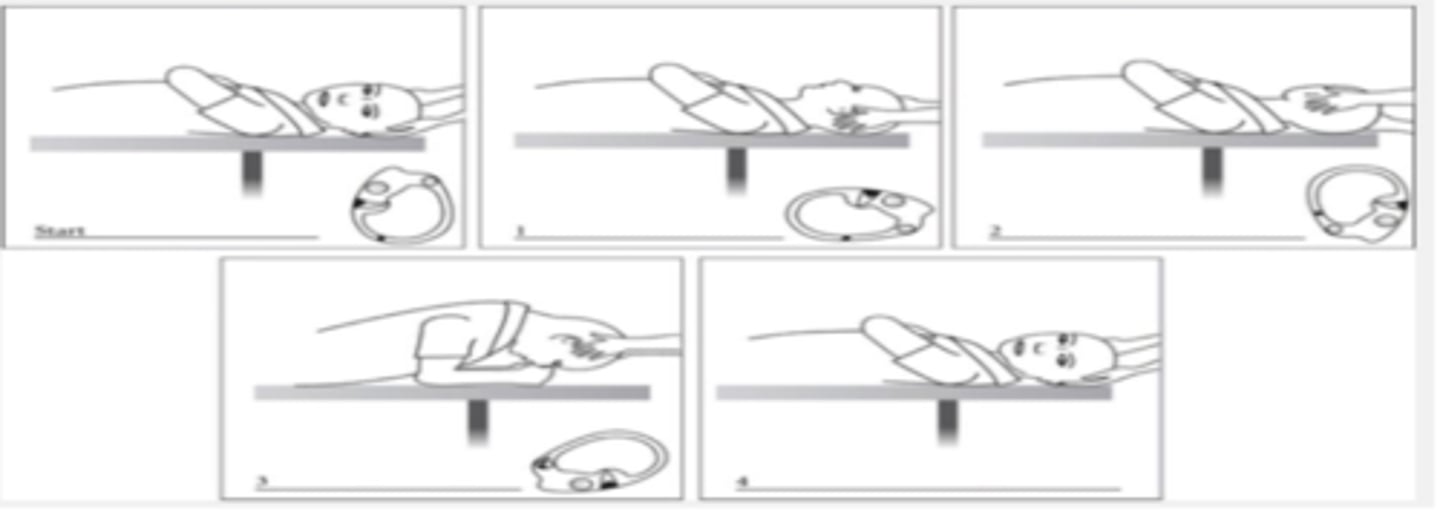
A physical therapist is visiting a 32-year-old female with diagnosis of BPPV in the clinic. What Techniques are the best way to treat Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo?
A. Epley Maneuver and Semont Maneuver
B. Canalith Repositioning Maneuver and Gaze Stability Exercises
C. Brandt- Daroff Exercises and Gaze Stability Exercises
D. Epley Maneuver and Habituation Exercises
A. Epley Maneuver and Semont Maneuver
A patient reports feeling off balanced when walking on a crowded
beach during the day where he has to look out for people as he
walks. The Physical Therapist should suspect that the patient would
have difficulty in which of the following conditions during testing
with the CTSIB?
A. Condition 2 (ECSS)
B. Condition 6 (VCMS)
C. Condition 4 (EOMS)
D. Condition 5 (ECMS)
B. Condition 6 (VCMS)
Visual conflict and moving surface
many people - visual conflict
beach sand - moving surface
Individuals with impaired vestibular system function are most likely to experience a loss of balance on the CTSIB test, when information from the following system/systems is/are altered during testing.
A. Spinal Reticular System
B. Visual System
C. Somatosensory System
D. Somatosensory and visual system
D. Somatosensory and visual system
A 54 year old patient is admitted to the hospital for lung congestion. The patient's daughter who works in the same hospital as a respiratory therapist, visits him in the hospital. She wants to look at her father's medical record. The PT should:
A. Tell her to ask the consultant physician for permission.
B. Tell her she cannot see the chart because she could
misinterpret the information.
C. Tell her that she must have the permission of her father
before she can look at the chart.
D. Give her the chart and let her read it as she may have some insights.
C. Tell her that she must have the permission of her father before she can look at the chart
A 21-year female player has limited ROM and pain in the
right shoulder. The PT plans an intervention program but the
patient refuses any treatment. The patient agrees that without intervention the symptoms might worsen. Which is MOST appropriate PT response?
A. Call the coach of the team and report that the injury might affect the player's performance
B. Respect the player's decision to not use physical therapy
services
C. Start the treatment as the patient will most likely join in once she sees the benefits of the treatment.
D. Refer the patient to another therapist who is a sports specialist
B. Respect the player's decision to not use physical therapy services
A PT Aide was treating a CVA patient and asked the patient to complete bridging exercises that were not in the original POC. During the bridging exercises, the patient suffered a back injury. Who will need to take the responsibility for the injury?
A. Physical therapist
B. Physical therapy assistant
C. Physical therapy aide
D. Physical therapy student
A. Physical therapist
If they were PT assistant then it is their problem (licensed)
A patient is getting treated for pelvis pain and is accompanied by his wife to the PT session. While treating, the patient expressed dissatisfaction in his martial life and says he has regular suicidal thoughts. What would be the BEST PT action?
A. Ask the patient to seek an appointment with a mental health practitioner
B. Disagree with the patient and say positive things about living life
C. Refer the patient immediately to mental health practitioner and stay there until help arrives
D. Inform the patient's wife that this problem is outside the scope of physical therapy practice
C. Refer the patient immediately to mental health practitioner and stay there until help arrives
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is responsible for which of the following?
A. Determining how much compensation the therapist
should get yearly
B. Assuring minimum standards is met at the hospital to
maintain accreditation and prevent negligence inpatient
care.
C. Assuring minimum standards is met by the rehabilitation clinics to maintain accreditation and safety of patients.
D. Ensuring adequate steps taken to prevent exposure to
harmful radiation to employees at a X-ray center.
D. Ensuring adequate steps taken to prevent exposure to harmful radiation to employees at an X-ray center.
OSHA - safety for patient to employee
C - CARF
Documenting the care provided to the patient is essential and must be completed in a timely manner. Which of the following is NOT appropriate with respect to documentation?
A. When a charting error is made, it must be clearly indicated that a change was made without deleting the original record
B. When a charting error is made, use white-out material to correct the text
C. Mistakes must be crossed out with a single line through the error, and then both initialed and dated by the therapist
D. Medically approved symbols or abbreviations can be used for documentation
B. When a charting error is made, use white-out material to correct the text
A physical therapist is facilitating an in-service on BLS
by educating on the Do's and Don'ts of adult high-quality CPR. Which of the following SHOULD the rescuer do during the training?
A. Include pauses in between compressions for greater than 10 seconds
B. Compress chest to a depth of less than 2 cm
C. Minimize pauses in between compressions
D. Compress chest at a rate of 123/min
C. Minimize pauses in between compressions
The patient arrives to a PT clinic looking pale and is
sweating profusely. His pulse is weak and his breath is
shallow and rapid. The PT suspects heat exhaustion.
Which of the following is NOT an appropriate response?
A. Offer the patient some water
B. Offer ice pack for forehead and the neck
C. Offer the patient some salt tablets for electrolyte balance
D. Ask the patient to remove any outer layer of clothing
C. Offer the patient some salt tablets for electrolyte balance
- salt tablet will make it worse to lose the water inside
A physical therapist is working with a patient who has
tuberculosis, Which of the following options BEST describes
the appropriate precautions and type of personal protective equipment that a physical therapist should wear?
A. Contact precautions, N-95 respirator
B. Airborne precautions, N-95 respirator
C. Contact precautions, gloves and gown
D. Airborne precautions, gloves and gown
B. Airborne precautions, N-95 respirator
A single 22-year-old woman who is 3 months' pregnant arrives at a therapist's private practice complaining of shoulder and leg pain. She has a black eye and some bruising at the wrists. The BEST course of action for the therapist is:
A. Administer massage for bruising, TENS, and ice modalities for pain, as indicated by the examination findings.
B. Direct the patient to the nearest ambulatory care center for physician evaluation.
C. Refuse to examine the patient and send her to the nearest emergency room.
D. Examine the patient, and if abuse is suspected, report the findings to the appropriate authorities.
D. Examine the patient, and if abuse is suspected, report the findings to the appropriate authorities.
If the test illunstrated in the photograph is positive, which of the following nerve entrapments is most likely?
A. Radial Nerve at supinator
B. Ulnar nerve at Gyuon's canal
C. Anterior interosseous nerve at pronator teres
D. Median nerve at the carpal tunnel
D. Median nerve at the carpal tunnel
30 year old recreational runner (20miles per week) reports a three month of posterior lower leg pains aggravating by walking, running, and jumping. the examination reveals pain with resisted PF, palpation, and muscle length testing of gastroc and soleus muscles. The Royal London Tet and Arc Sign are positive. what is the most likely tendinopathy diagnosis?
A. achilles
B. posterior tibialis
C. anterior tibialis
A. achilles
achilles tendinopahty common for 40 -59 yeras old
runner prevalence of 10%
pain with contraction and passive lengthening of gastroc and soleus
pain with palpation alon gthe tendon 4-5cm proximal to the insertion is common
positive royal london test and arc sign
Risk factor
limited DF
over pronation
The examinatino of a patient with limited knee flexion reveals hypomobile joint mobility with a capsular adhesion end feel and no pain. which mobilization is the best to address this limitation?
A. G II anterior glidfe of tibia
B. G II posterior glide of tibia
C. G IV anterior glide of tibia
D. G IV posterior glide of tibia
D. G IV posterior glide of tibia
57 y.o female present with an insidious onset of L lateral shoulder (non dominant) pains beginning three months ago. Her PMH is significant for hypertension and type II DM both controlled with medications. Given the patient's history, what is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Bankart
B. SUprascapular N entrapment
C. Adhesive capsulitis
D. SLAP lesion
C. Adhesive capsulitis
A - requires macro trauma
B - SLAP requires popping, cracking and repetitive overhead activities
AC occures with high frequency in women, 40-60 y.o, non dominant arm more commonly involved
A patient presents with foot drop. which nerve is most likely involved?
A. tibial
B. common peroneal nerve
C. Sural
D. Morton's neuroma
B. common peroneal nerve
tibial nerve - sensory and motor on posterior side
common peroneal n - sensory and motor on anterior side muscles
SUral nerve - sensory
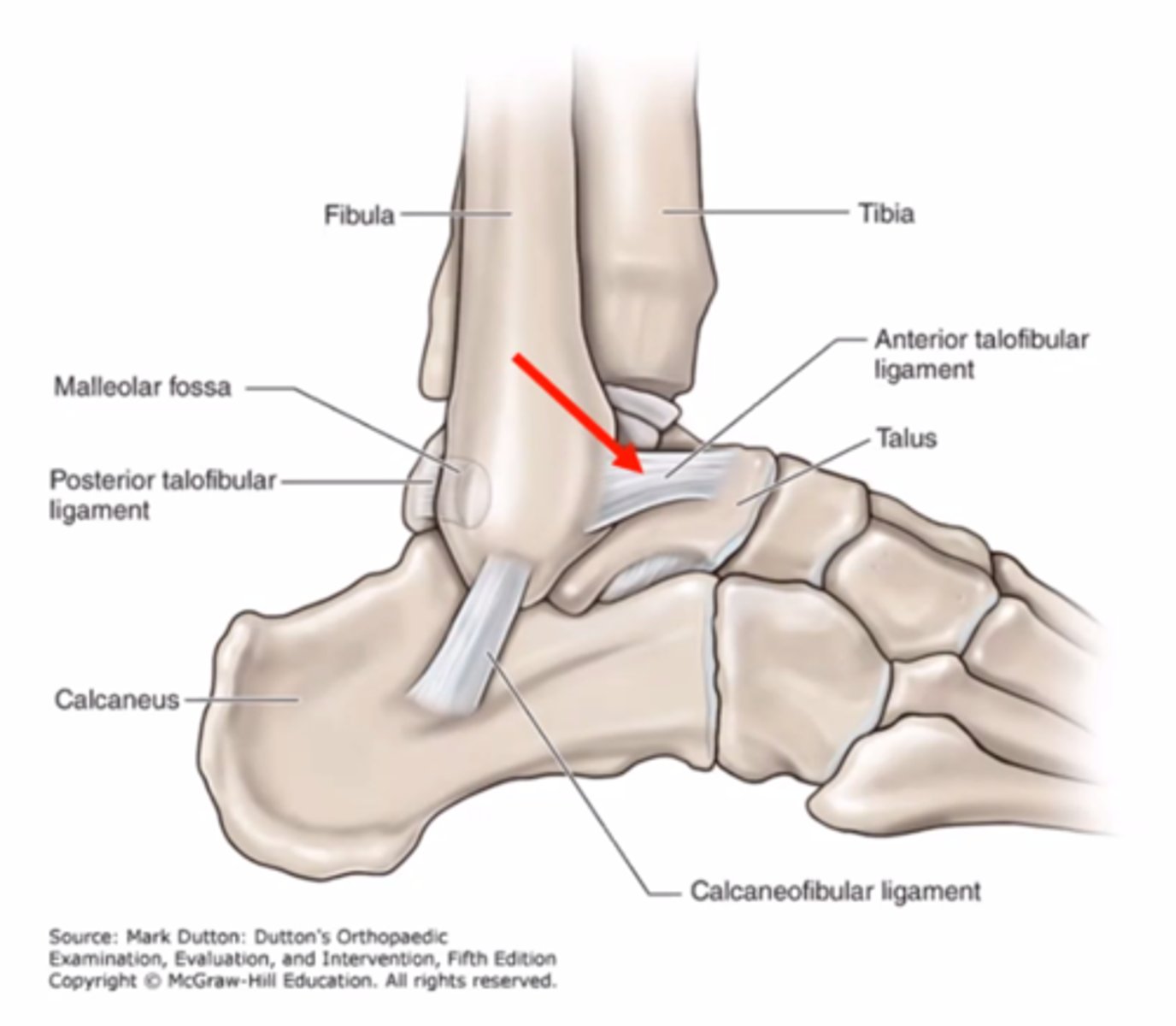
What special test is best assessment for a ligament injury indicated by the red arrow?
A. Kleiger
B. Talar tilt
C. Squeeze
D. Anterior drawer
D. Anterior drawer
A. Kleiger (ER) - for syndesmosis injury
B - integrity of CFL and ATFL
C - syndesmosis (high ankle sprain)
19 year old female soccer player sustained a noncontact knee injury. She reports immediate pain and swelling of the knee, and difficulty moving and WB through the limb. Given this presentation, which special test is best to confirm the suspected injury?
A. Lachman's
B. Anterior Drawer
C. Valgus
D. McMurry's
A. Lachman's
- gold standard test
ACL tear ususally swelling right after
McMurry's - meniscus - delayed swelling
65 y.o female patient underwent an anterior approach TKA. clinical examination findings are:
persistent knee efffusion
limited ROM 10- 75 degrees
hypobmoile patellar glide
WBC - 6.0 x 109
Eryhtorcyte sedimentation rate (ESR) -20
C- reactive protein less than 1
What is most likely reason for this clinical presentation?
normal presentation at 6 weeks of TKA
Arthrofibrosis
infection
DVT
Arthrofibrosis
low risk of DVT
WBC normal - infection
Arthrofobrosis -
65 male patient with thre year history of low back and leg pains reporting standing walking and lumbar extension movements as aggravting factors. Easing factors including resting in a seated position. DUe to thsee symptoms,. he has changed their normal mode of exercise from walking t a stationary cycle. what is the most liekly cause of these symptoms?
A. Spinal stenosis
B. Vascular Claudication
C. Herniated lumbar disk
D. Spondylolisthesis
A. Spinal stenosis
Bicycle test of Van Gelderen
Stationary Bike Test
leaning forward
- nerve root symptoms in spinal stenosis will be relieved
- vascular symptoms will be aggravated
- lumbar disk pathology will be aggravated
sitting upright
- nerve root symptoms in spinal stenosis will be aggravated
- vascular symptoms will be aggravated
- lumbar disk pathology will be relieved
Examination findings for a patient with heel pain reveal a high body mass, decreased muscle length of gastroc, laxity of navicular in plantar direction, and a positive Windlass test in the NWVB position. what is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Achilles tendinopathy
B. interdigital neuroma
C. excessive pronation
D. plantar fasciopathy
D. plantar fasciopathy
what is most appropriate traetment for a patient with extensor carpi radialis degenerative tendinopathy?
A. Stretching
B. Counterforce bracing
C. progressive loading
D. Unloading/Rest
C. progressive loading
tendinopathy - treatment is optimal loading
While obtaining the history from 55-year-old women weighing 147 pounds, the physical therapist discovers that the patient has a history of RA. The order for outpatient PT includes continuous traction due to a L2 disc protrusion. What is the best course of action for the therapist?
A. Follow the order
B. Consult with the physician because RA is a contraindication
C. intermittent traction
D. Continuous traction
B. Consult with the physician because RA is a contraindication
The PT in an outpatient settin greceives an order to obtain a shoe orthotic for a patient. After evaluating the patient, the PT finds a stage I pressure ulcer on the first metatarsal head. WB surfaces need to be transferred posteriorly. Which of the following orthotics would be the most appropriate for this patient?
A. Scaphoid pad
B. thomas heel
C. Metatarsal pad
D. Cushion Heel
C. Metatarsal pad
At the completion of your examination, you have determined that your patient has a fixed deformity of minus 10 degrees of PF. When desgining the patient's plan of care, which of the following activities would you expec tthe patient to have the greatest difficulty with?
a. ascending a ramp
b. walking with a 1 inch heel
c. walking down a flight of stairs
d. walking barefoot
a. ascending a ramp
an obstetrician refers a patient to your clinic for prenatal exercises. During your examination, you note that the patient has a diastasis recti, which is less than two centimeters. Which of the following exercises would not be appropriate for this patient?
A. Head raising with posterior pelvic tilting in the supine hook lying position
B. Head raising in the supine hook lying position
C. posterior pelvic tilting in the quadruped position
D. Pelvic floor exercises
C. posterior pelvic tilting in the quadruped position
you instructed a patient in D2 PNF technique for the UE. Later in session, you r watching the patinet and note that the patient begins with shoulder flexion, abduction, elbow extension, and forearm pronation before moving into shoulder flexion, shoulder abduction, elbow extension and forearm supination. This patient is demonstrating:
A. Correct technique
B. incorrect technique at elbow
C. incorrect technique at forearm
D. incorrect tehcnique at shoulder
C. incorrect technique at forearm
23 year old soccer player sustained a non contact anterior thigh injury during yesterday's game. the examinatino reveals pain with resisted hip flexion and knee extension, palpable tenderness 6 cm distal to AIIS, and symptom reporduction at 60 degeres of knee flexino during the thomas test. what is the most liekly muscle strain?
A. iliacus
B. Sartorius
C. Rectus femoris
D. Psoas major
C. Rectus femoris
knee extensor and hip flexor
two joint muscle
A patient with pleural effusion is being ambulated by a physical therapist. Which of the following precaution should the therapist keep in mind?
A. Collection bottle should be kept below the level of the inserted tube
B. Collection bottle should be kept below the level of urinary catheter
C. Collection bottle should be removed before ambulating the patient
D. Collection bottle should be held by the PT while the patient ambulates
A. Collection bottle should be kept below the level of inserted tube
PRACTICE QUESTION 2 - LIFTING
A 58-year-old patient is lifting a wine box using a stoop lift at a winery. Which of the following is the MOST significant factor in increasing compression forces on the spine in addition to the weight of the wine box?
A. The height of the wine box from the ground
B. Performing the lift with the lumbar spine in a neutral position
C. The distance of the wine box from the base of the spine
D. The muscle strength of the lower extremities
C. The distance of the wine box from the
base of the spine
PRACTICE QUESTION 3 SAFETY
A 34-year-old male has been diagnosed with a complete C5- C6 spinal cord injury. The patient used a power chair to commute from the parking lot to the PT clinic. While performing a transfer, the MOST important consideration is to
A. Make sure he is using his shoulder extensors to support his upper body
B. Make sure his legs are supported by a PT aide
C. Make sure his power chair is turned off
D. Make sure to use the sliding board
C. Make sure his power chair is turned off
make sure it does not move - same as brake
The PT student is given a task by their clinical instructor to provide the appropriate wheelchair measurements. Which of the following options provide the correct measurement for seat depth?
A. Measure the length from posterior buttock to posterior aspect of popliteal fossa and add 2 inches to the measurement.
B. Measure the total area of both the hips and add 2 inches to the measurement.
C. Measure the total area from posterior buttock to posterior of the popliteal fossa and subtract 2 inches from the measurement.
D. Measure the trunk length and subtract it from lower leg length and add 2 inches to the measurement.
C. Measure the total area from posterior buttock to posterior of the popliteal fossa and subtract 2 inches from the measurement.
A physical therapist is teaching a patient who suffered from a spinal cord injury to negotiate a 4 inch curb with a wheelchair. The MOST appropriate instruction that the therapist gives to the patient is:
A. Hook the arms around push handle and descend backward
B. Ascend backward with large wheels first.
C. Ascend in a wheelie position by lifting the front casters
D. Place the front casters down first during descent.
C. Ascend in a wheelie position by lifting the front casters
A 45 year old female patient is recovering from a lef fibula fracture and is restricted to partial (25%) weightbearing on the left side. What is the best assistive device?
A. Cane on the left side
B. 2 axillary crutches
C. Cane on the right side
D. Forearm crutch on left
B. 2 axillary crutches
A PT is training a 65 year old to walk with a quadripod. He had severe arthritis of the R hip and was operated 2 months ago. What is the MOST appropriate way the PT should instruct the patient to use the assistive device?
A. Hold the cane in your L hand and move L hand and R leg together
B. Hold cane in your R hand and move R hand and L leg together
C. Hold cane in your L hand and move L hand and L leg together
D. Hold cane in your R hand and move R hand and R leg together
A. Hold the cane in your L hand and move L hand and R leg together
A posterior approach was used for a case of revised total hip arthroplasty. Which of the following should NOT be included while educating the patient in order to prevent posterior dislocation?
A. Transfer to the sound side from chair to bed
B. When descending stairs, lead with the operated leg.
C. Keep the knees higher than the hips when sitting
D. Avoid standing activities that involve rotating the body
towards the operated extremity
C. Keep the knees higher than the hips when sitting
A 45 year old male patient underwent a surgical procedure on the right knee and has been prescribed crutches. PT is training the patient on the use of crutches. Which of the following is the BEST hand placement for the PT:
A. One hand of the PT on the gait belt and the other hand on the patient's shoulder.
B. Both hands of the PT on the gait belt.
C. One hand of the patient on the gait belt and the other hand of patient on the PT's shoulder.
D. Both hands of the PT on the patient's hips.
A. One hand of the PT on the gait belt and the other hand on the patient's shoulder.
A PT examines a patient who complains of foot pain while running. The examination shows that the patient has excessive foot pronation. Which of the following would be the MOST appropriate orthotic insert?
A. A lateral forefoot post under the fifth metatarsal head
B. A lateral rearfoot post under the calcaneus placing it in an everted position
C. A middle post just proximal to the third metatarsal head
D. A medial post just proximal to the first metatarsal head
D. A medial post just proximal to the first metatarsal head
A PT examines a patient who complains of foot pain while running. The examination shows that the patient has excessive foot pronation. Which of the following would be the MOST appropriate orthotic insert?
A. A lateral forefoot post under the fifth metatarsal head
B. A lateral rearfoot post under the calcaneus placing it in an everted position
C. A wedge placed under the instep of the medial foot just beneath the head of the talus
D. A medial post just proximal to the first metatarsal head
D. A medial post just proximal to the first metatarsal head
A 50 year old male patient presents to an outpatient clinic
with complains of medial knee pain. The picture represents
the position of the foot during normal quiet standing. What is the MOST appropriate diagnosis of this condition?
A. Uncompensated forefoot valgus
B. Compensated forefoot valgus
C. Uncompensated forefoot varus
D. Compensated forefoot varus
A. Uncompensated forefoot valgus
PT finds that right ASIS is higher than the left ASIS, and right PSIS is lower than the left PSIS. While performing the long sitting special test, the right limb is shorter in supine and appears to get longer in sitting. Based on the examination, what is the MOST appropriate treatment:
A. Stretch the Right Hip Extensors
B. Stretch the Right Hip Flexors
C. Strengthen the Right Hip Flexors
D. Strengthen the Right Hip Extensors
A. Stretch the Right Hip Extensors
A physical therapist is treating a patient with the complains of a vague ache in the lower extremities. As shown in the picture below, what is the MOST likely structural malalignment present?
A. Lateral tibial torsion with lateral rotation of femur
B. Medial tibial torsion with lateral rotation of femur
C. Lateral tibial torsion with medial rotation of femur
D. Medial tibial torsion with medial rotation of femur
C. Lateral tibial torsion with medial rotation of femur

A PT student is constantly on the new phone and is having difficulty swiping upwards with their thumb as shown in the picture below. What is the BEST mobilization to improve the thumb range of motion so that the student can swipe happily thereafter!
A. Inferior glide at the CMC joint
B. Superior glide at the CMC joint
C. Ulnar glide at the CMC joint
D. Radial glide at the CMC joint
D. Radial glide at the CMC joint
Concave on convex

A 45 year old female patient is being evaluated in an
outpatient clinic by a physical therapist. The PT performs the test shown in the picture. A positive result of the test likely indicates the presence of which of the following conditions?
A. Radial collateral ligament tear
B. Carpal tunnel syndrome
C. De Quervain disease
D. Restricted ulnar deviation
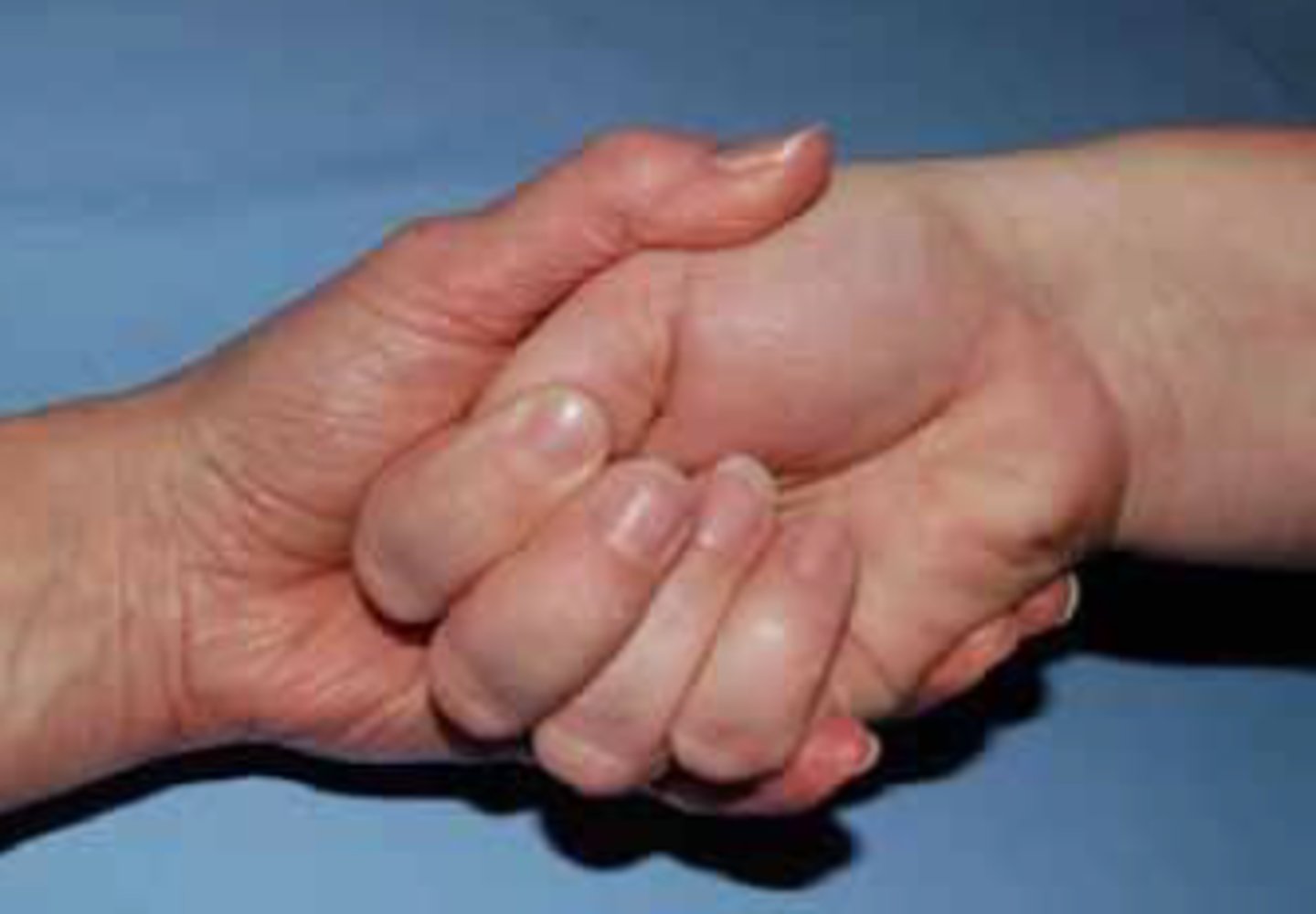
A patient presents with complains of pain and numbness in the right arm extending to the thumb. The PT performs the special test as shown in the picture below. If the test is positive, which is the MOST appropriate intervention?
A. Strengthen the right levator scapulae and sternocleidomastoid muscles.
B. Perform (Posterior Anterior) PA glide of the C6 vertebrae with right side bending and rotation.
C. Stretch the right pectoralis minor and sternocleidomastoid muscles.
D. Perform grade 3 manipulation of the first and second ribs.
C. Stretch the right pectoralis minor and sternocleidomastoid muscles.
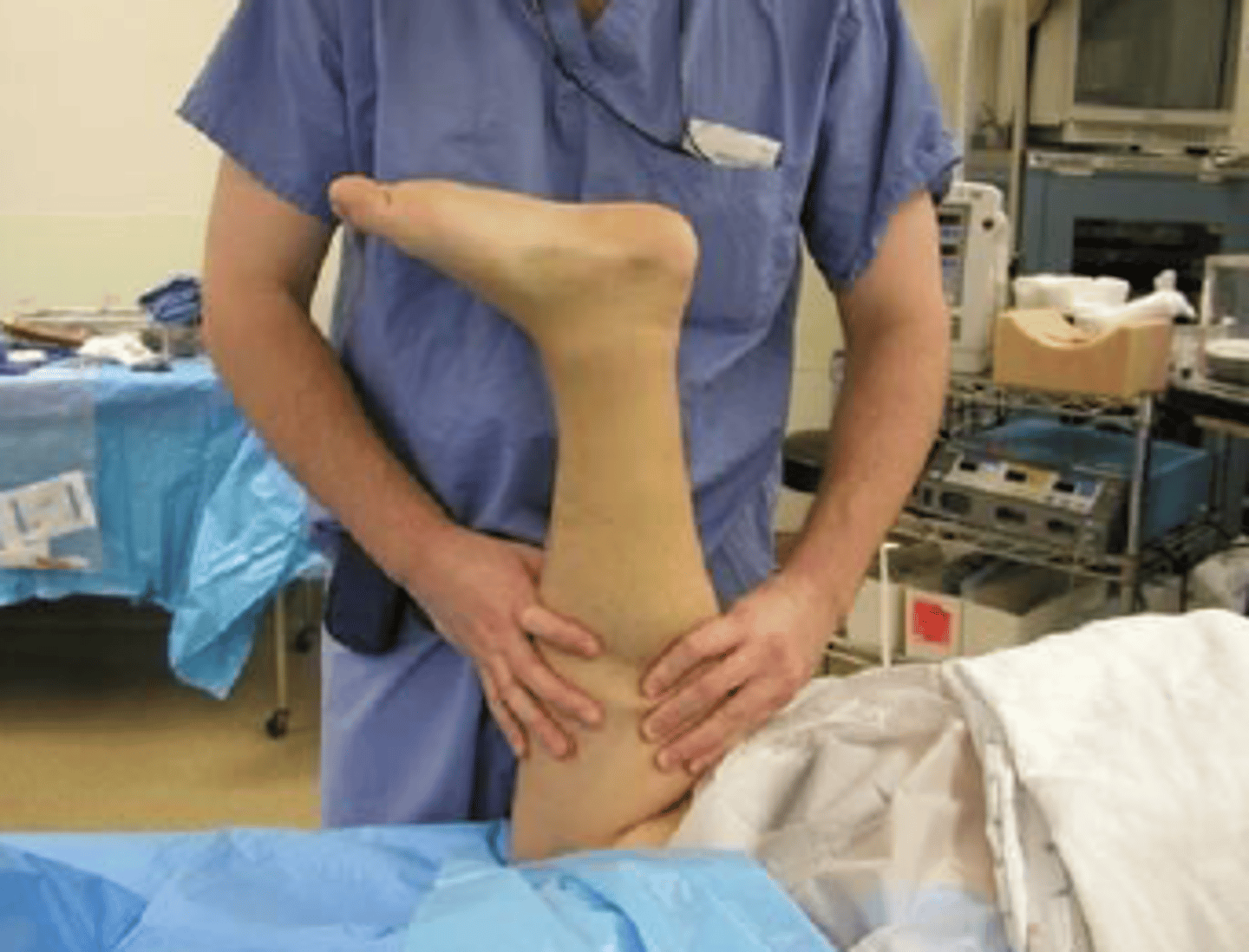
A patient with a sharp pain at the ankle. According to the patient, the ankle was injured while playing basketball last week. When performing the pictured test on the patient, the PT finds that the patient's ankle remains in a neutral position. This would indicate:
A. Medial Meniscus tear
B. Anterior talofibular ligament injury
C. Achilles tendon rupture
D. Calcaneofibular ligament tear
C. Achilles tendon rupture
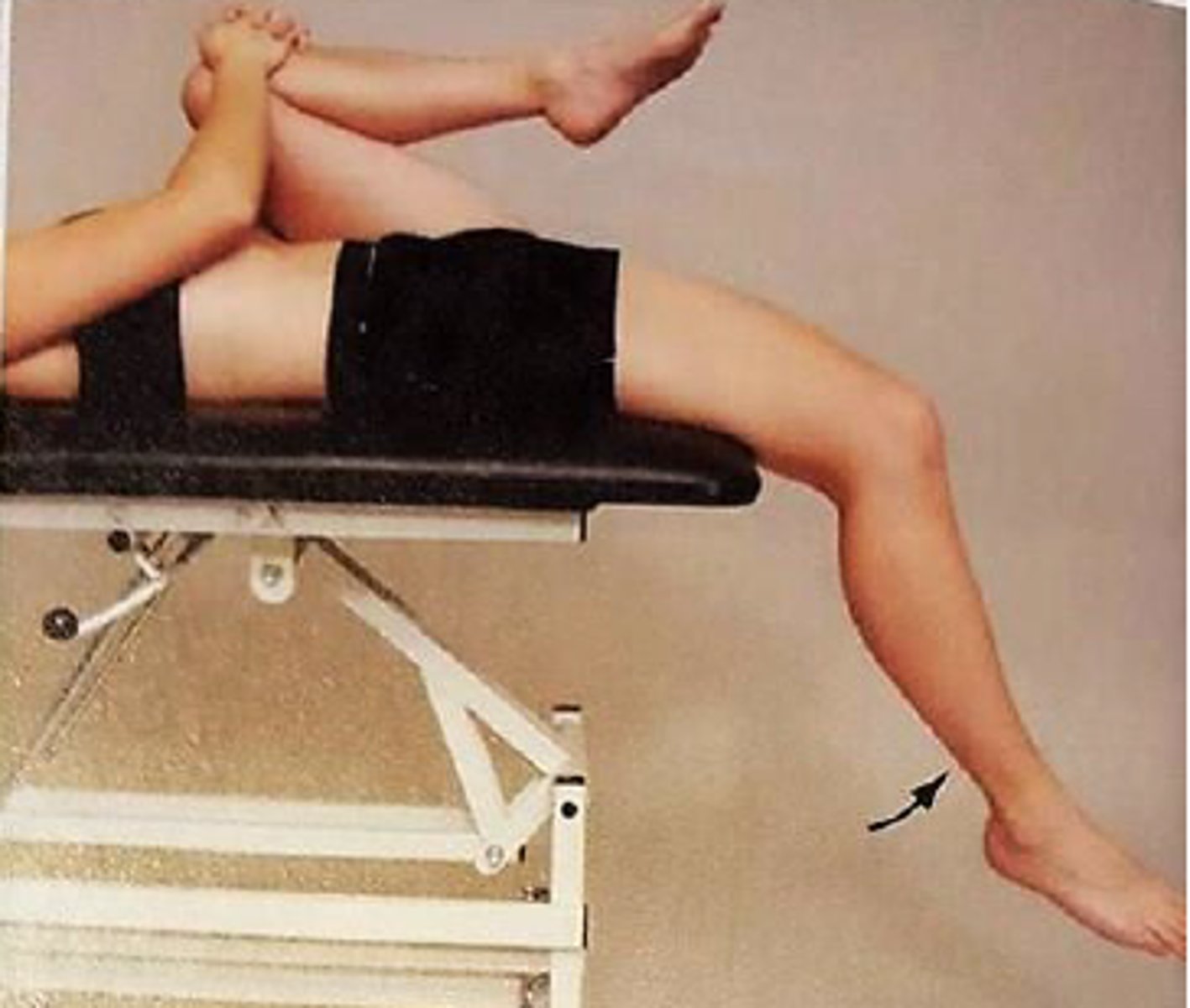
When performing the following test on a patient, the therapist finds that the patient's thigh remains on the plinth and her knee is somewhat extended. This would indicate tightness of:
A. the illiopsoas
B. the hamstrings
C. the rectus femoris
D. the sartorius
C. the rectus femoris
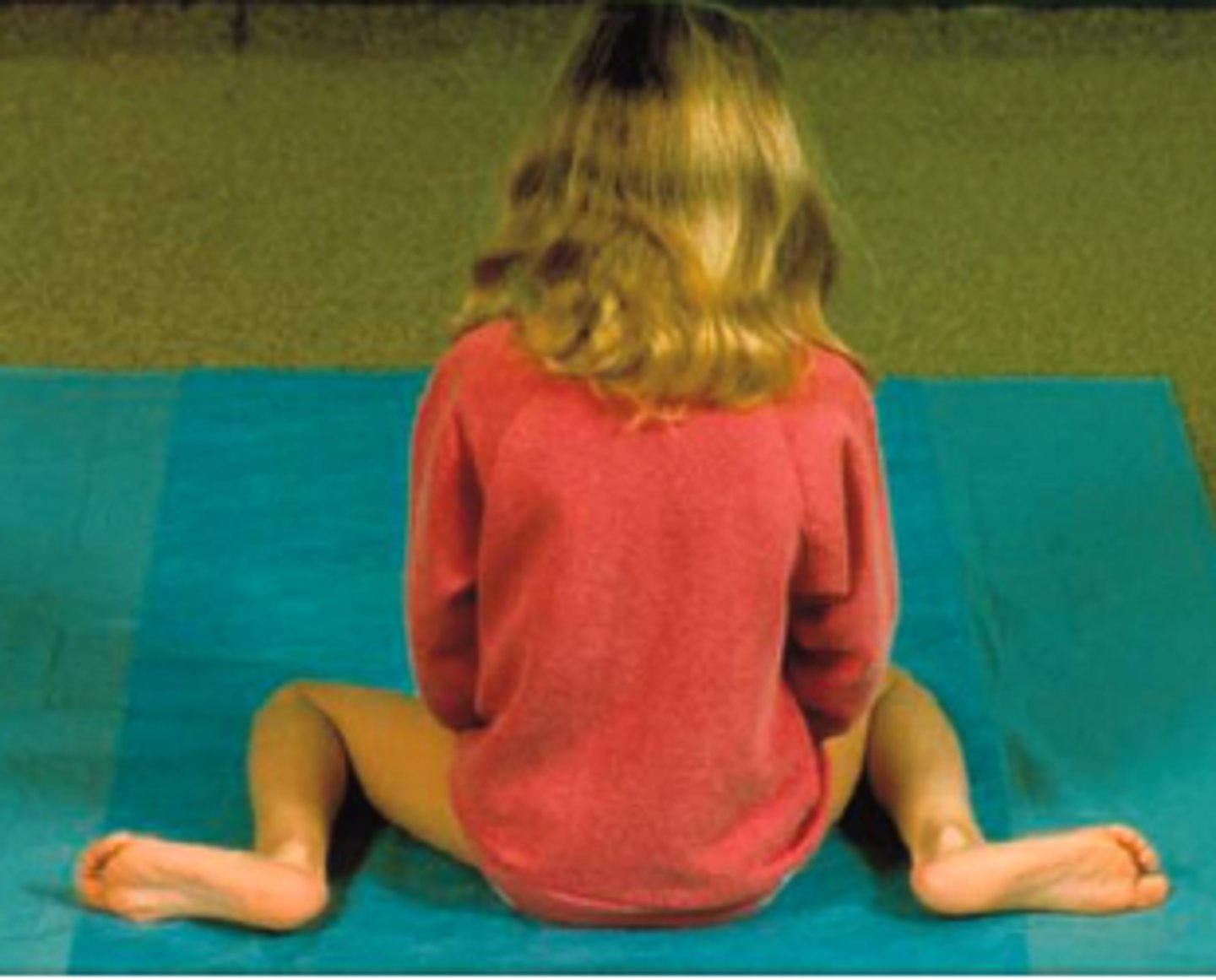
During the initial screening of a patient, the physical therapist notes contusions in various states of healing on the chest, back, and face, as well as multiple scars. The patient reports falling often. Which of the following courses of action should the therapist take FIRST?
1. Take the patient's dietary history to assess for mineral deficiency.
2. Ask the patient if bruising was caused by being hit, kicked, or abused.
3. Instruct the patient in safe movement patterns to avoid falls.
4. Report the patient's caregivers to the appropriate authorities.
2. Ask the patient if bruising was caused by being hit, kicked, or abused.
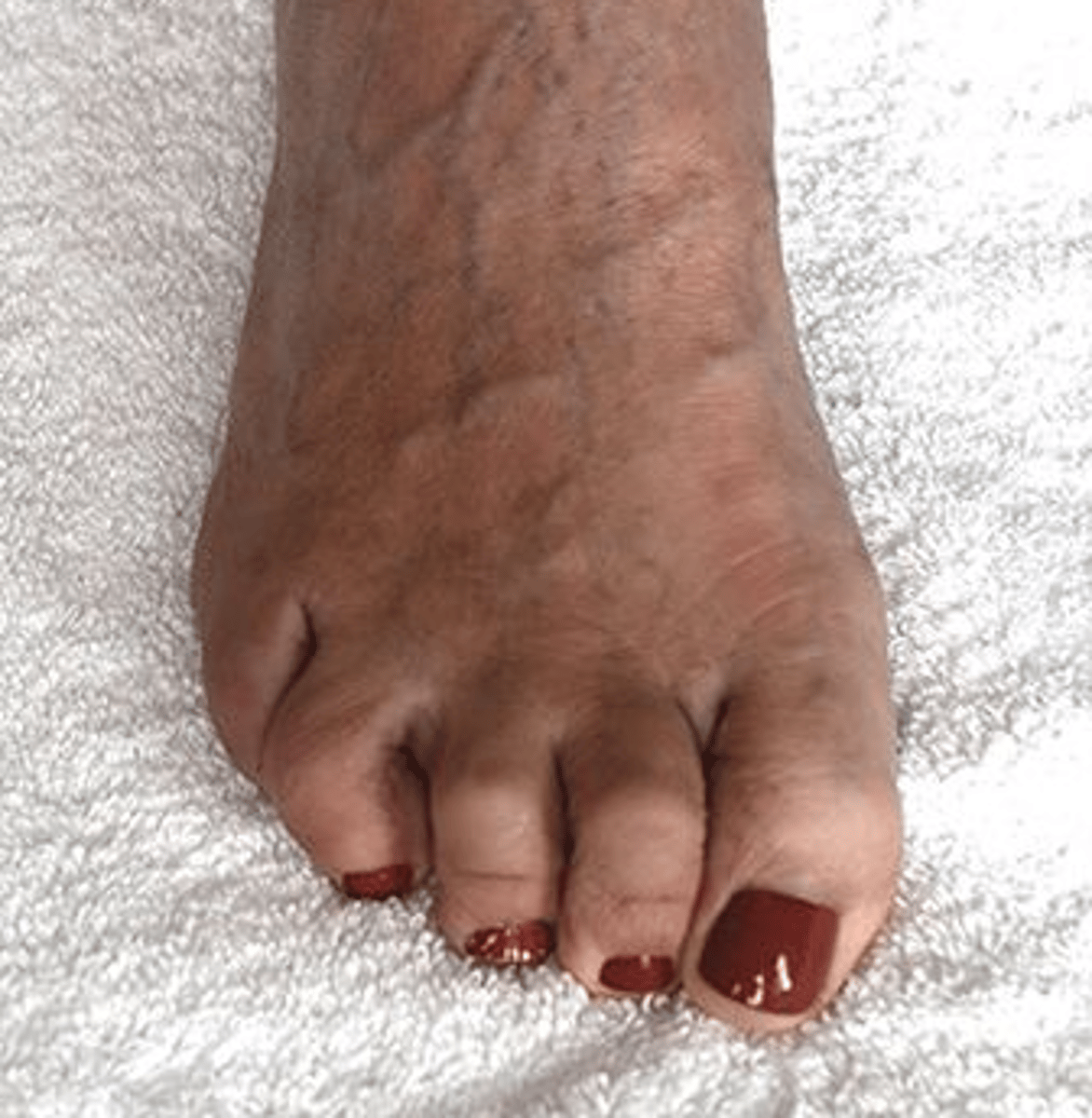
A patient has the deformity shown in the photograph. Which of the following shoe modifications is MOST likely to be beneficial for this patient?
1. High toe box
2. Metatarsal pad
3. Rocker bar
4. Metatarsal bar
1. High toe box
A patient reports significant hypersensitivity to light touch in the left foot and ankle region following minor trauma. A physical therapist notes warmth, swelling, and redness over the entire foot and ankle. Which of the following interventions is MOST appropriate?
1. Continuous ultrasound
2. Gait training, non-weight-bearing on the left
3. Deep friction massage
4. Progressive weight-bearing activities
4. Progressive weight-bearing activities
4. The apparent diagnosis is complex regional pain syndrome type I, or reflex sympathetic dystrophy (p. 410). Range of motion and therapeutic exercises (including weight-bearing exercises) may encourage a decrease in sympathetic tone, enhance circulation, help to maintain range of motion and strength, and increase functional use of the extremity
2. The apparent diagnosis is complex regional pain syndrome type I, or reflex sympathetic dystrophy (p. 410). Non-weight-bearing gait would promote more swelling due to disuse of the muscle pump (p. 412).
A patient reports an insidious onset of swelling of 1 month's duration on the dorsum of the left foot. Which of the following conditions is the MOST likely cause?
1. Heart failure
2. Chronic venous insufficiency
3. Lymphedema
4. Lipedema
3. Lymphedema
2. Edema associated with chronic venous insufficiency usually presents in a gaiter distribution creating the appearance of an inverted bottle at the calf. Acute onset of swelling at the dorsum of the foot, as described in the stem, is not typical of chronic venous changes.
3. Lymphedema is usually unilateral with typical presentation distally on the extremity (dorsum of the foot or hand) (Goodman, Differential Diagnosis; Goodman, Pathology, pp. 680-682).
4. Lipedema is a symmetrical swelling of both legs, extending from hips to ankles. Lipedema onset is primarily proximal to distal. (Goodman, Pathology, pp. 702-704).
1. Dependent edema is one of the early signs of right-sided heart failure. The edema is usually symmetric and occurs in the feet and ankles (Goodman, Differential Diagnosis; Goodman, Pathology, pp. 591-592).
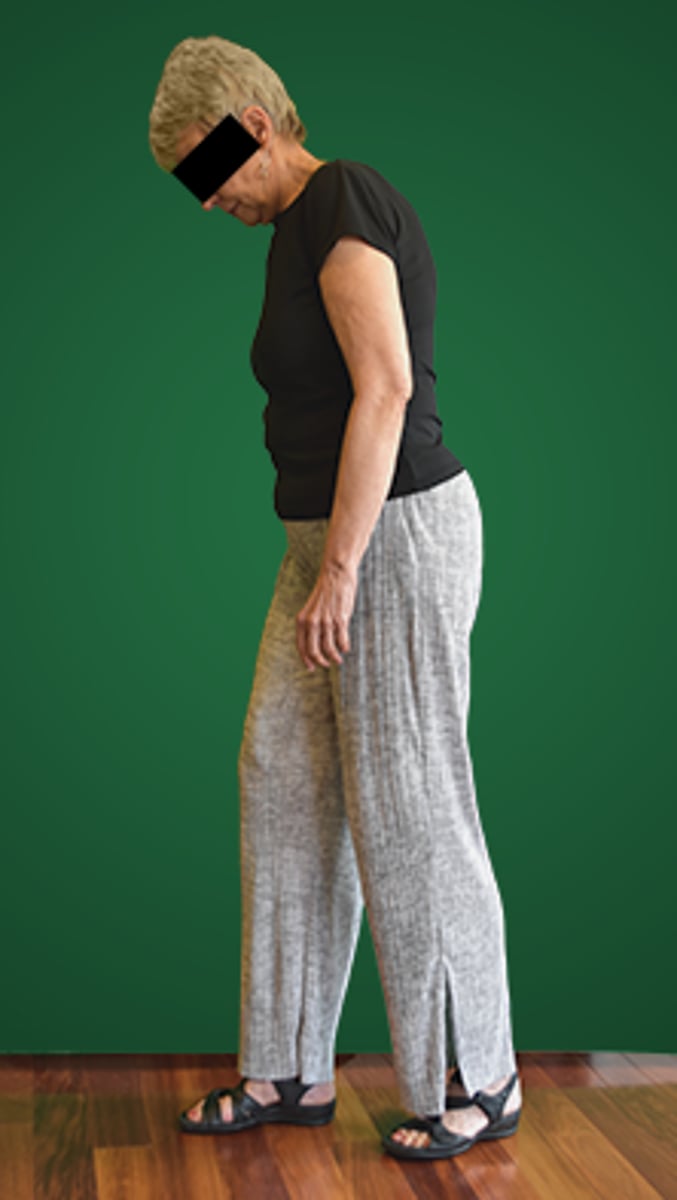
A patient maintains the posture shown in the photograph throughout the gait cycle and reports a sense of numbness in both legs when walking. The MOST probable explanation for this posture is that the patient is:
1. using the trunk position to advance the lower extremity.
2. unable to disassociate trunk movements from pelvic or limb movement.
3. attempting to decrease the demand on the hip extensors.
4. substituting visual input for impaired proprioception in the lower extremities.
4. substituting visual input for impaired proprioception in the lower extremities.

Changes in the level of which hormone are MOST likely to contribute to development of chondromalacia patella in a pregnant woman?
1. Calcitonin
2. Progesterone
3. Relaxin
4. Insulin
3. Relaxin
3. Chondromalacia is a roughening of the cartilage behind the kneecap, and relaxin causes an increase in tendon and ligament laxity, exacerbating any friction between the patella and the femur (p. 1062).
A physical therapist is reviewing the laboratory report of a patient who received a diagnosis of pneumonia 2 weeks ago. The patient's white blood cell count is currently 9,000 cells/mm3. Which of the following conditions does this value indicate for the patient?
1. Anemia
2. Development of leukocytosis
3. Immunosuppression
4. Resolution of the pneumonia infection
4. Resolution of the pneumonia infection
1. Anemia would be diagnosed from iron and hemoglobin levels.
2. Leukocytosis is a total white blood cell count of greater than 11,000-15,000/mm3 (above normal range).
3. Immunosuppression causes leukopenia, which is a white blood cell count less than 4000/mm3.
4. The patient's white blood cell count is within the normal range of 4500-11,000/mm3, so the infection has resolved.
Which of the following fall prevention strategies is MOST appropriate for a resident of a nursing home who has dementia, poor balance, and often wanders?
1. Place the patient in bed, with the side-rails up and secured.
2. Place the patient in a wheelchair with a seat belt that the patient is unable to remove independently.
3. Seat the patient in a geriatric recliner to reduce the likelihood of wandering.
4. Use an electronic monitor that will remotely alert staff when the patient gets out of bed.
4. Use an electronic monitor that will remotely alert staff when the patient gets out of bed.
Rationale
1. The use of side-rails is a restraint. Their use on the bed of a mobile person may lead to a number of negative consequences, such as increasing the distance the patient could fall from the bed, creating an obstruction of vision, and creating a sense of being trapped. The use of side-rails with a patient who has dementia is a restraint and requires a physician's order.
2. Lap cushions, trays, and seat belts are considered restraints if the patient is unable to remove them independently.
3. Geriatric recliners are considered restraints when they restrict a patient's normal mobility.
4. The use of restraints has become a concern for nursing home caregivers, who must comply with Medicare guidelines and foster prevention of elder abuse. An electronic monitoring device is not a restraint. This option would facilitate safety through improved supervision and would allow the patient to maintain functional mobility.
One day after lumbar laminectomy surgery, a patient refuses to wear a thoracolumbosacral orthosis because of a painful and itching rash that extends in a narrow path from the central low back along the iliac crest to the right lateral trunk. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
1. Herpes zoster
2. Infected surgical incision
3. Contact dermatitis
4. Allergic response to medication
1. Herpes zoster
1. Herpes zoster (shingles) is a painful, blistering skin rash caused by the varicella-zoster virus. The first symptom is usually one-sided pain, tingling, or burning followed by development of a rash that usually involves a narrow area from the spine around to the front of the chest or abdomen. A typical location for occurrence of shingles rash is the T11-T12 dermatome along the iliac crest. The location of the rash, postsurgical onset, and symptoms of pain all suggest herpes zoster. (Goodman, p. 177)
2. The surgical incision for a lumbar laminectomy is located along the lumbar spine. An infected surgical incision would be associated with pain, erythema, edema, and increased temperature over the wound site. (Bryant)
3. The area of rash described in the stem includes the area where the pelvic (lower) strap of the thoracolumbosacral orthosis is placed. However, contact dermatitis would not present with the dermatomal pattern described and would be more itchy than painful. (Goodman, p. 171)
4. An allergic response to medication would not be localized to a specific dermatome but would most likely be a generalized response. Also a rash due to medication is generally not painful. (Goodman, pp. 171, 435)
Which of the following dressings is MOST appropriate to use with an infected wound that also requires hemostasis?
1. Foam
2. Alginate
3. Transparent film
4. Hydrocolloid
2. Alginate
Rationale
1. A foam dressing is absorptive but also creates an occlusive environment for moist wound healing. In the case of infection, a less occlusive dressing would be a better choice. (pp. 563, 589-590)
2. An alginate dressing is best to use in this case because this type of dressing provides both hemostasis and is appropriate for use over an infected wound (pp. 565, 589).
3. A transparent film is not the best dressing to use in this case because it does not provide hemostasis or infection control. Films are more appropriate for friction reduction. (pp. 563, 589)
4. A hydrocolloid dressing is not the best dressing to use with an infected wound that also requires hemostasis because it is the most occlusive dressing type. An alginate dressing is better for hemostasis. (pp. 564, 589-590)
A patient has an ankle-brachial index (ABI) of 1.5. Which of the following conditions affecting the lower extremity should a physical therapist suspect?
1. Arterial aneurysm
2. Arterial thrombosis
3. Arterial calcification
4. Arterial occlusive disease
3. Arterial calcification
Rationale
1. With arterial aneurysm in the lower extremity, the affected artery is dilated (p. 632) and there is decreased blood flow and ischemia in the limbs. In this case, the ankle-brachial index should be less than 1.0.
2. Arterial thrombosis is an occlusive disease of the arteries. With occlusive diseases, the blood flow to the lower extremity decreases. Decreased blood flow to the lower extremities will result in an ankle-brachial index of less than 1.0. (p. 638)
3. Ankle-brachial index is a ratio of the systolic blood pressure at the ankle and the brachial systolic pressure. The normal value of the ankle-brachial index is 1.0, indicating similar blood flow in the ankle and brachial arteries. An ankle-brachial index greater than 1.1 relates to arterial calcification in the leg. With arterial calcification, the artery cannot be fully compressed for valid measurement of arterial pressure at the ankle. An ankle-brachial index greater than 1.1 is mostly found in patients who have diabetes. (p. 645)
4. The normal value of the ankle-brachial index is 1.0. With severe arterial occlusion, the ankle-brachial index will be less than 1.0. An ankle-brachial index of 1.1 or higher is not an indication of arterial occlusion. (pp. 641, 645)
As a child ages from 1 to 7 years, which of the following factors indicate maturing gait?
1. Velocity decreases and cadence increases.
2. Velocity increases and cadence decreases.
3. Single-leg stance time decreases and step length increases.
4. Single-leg stance time increases and step length decreases.
2. Velocity increases and cadence decreases
Rationale
1. As gait develops, velocity increases, not decreases, and cadence decreases, not increases.
2. Velocity increases and cadence decreases as gait develops.
3. Single-limb stance time increases as gait develops.
4. Step length increases as gait develops.
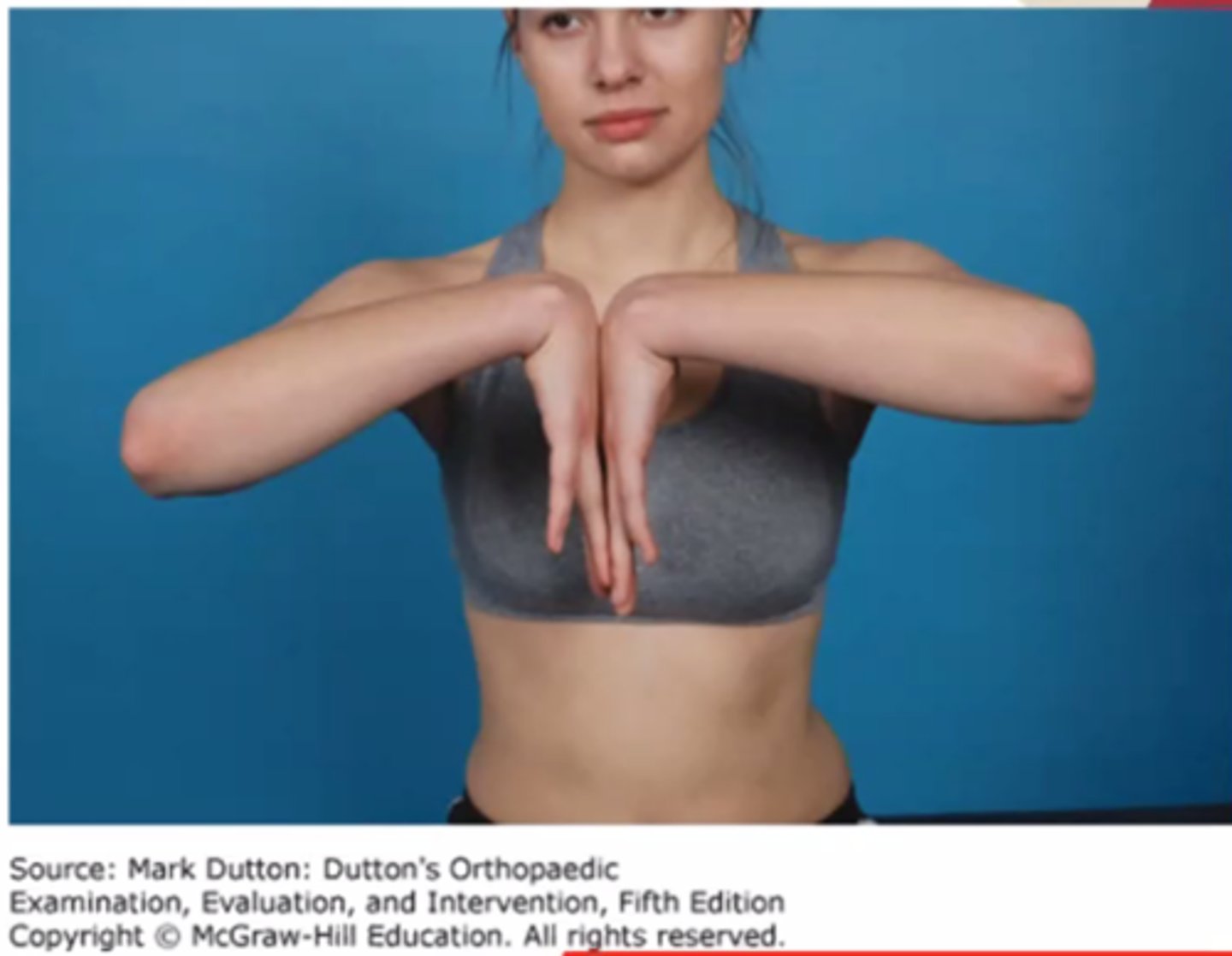
The patient being assessed in the photographs reports a deep pain in the shoulder when a physical therapist applies a downward force to the forearm. The patient MOST likely has which of the following conditions?
1. Rotator cuff tear
2. Superior labrum tear
3. Subacromial bursitis
4. Supraspinatus tendinitis
2. Superior labrum tear
Rationale
1. Rotator cuff dysfunction is identified better with the Hawkins-Kennedy test (Dutton, pp. 630-631; Magee, p. 315). The Speed test is shown in the photograph (Dutton, p. 640; Magee, p. 341).
2. The Speed test is shown in the photograph. Deep shoulder pain produced during this maneuver suggests a labral tear, (Dutton, p. 640) or a superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) (Type II) lesion (Magee, p. 341).
3. Subacromial bursitis is identified better with the Hawkins-Kennedy test (Dutton, pp. 630-631; Magee, p. 315). The Speed test is shown in the photograph (Dutton, p. 640; Magee, p. 341).
4. Supraspinatus tendinitis is identified better with the Empty Can test, in which the arm would be in maximum medial (internal) rotation (Dutton, p. 637; Magee, p. 341). The Speed test is shown in the photograph (Dutton, p. 640; Magee, p. 341).
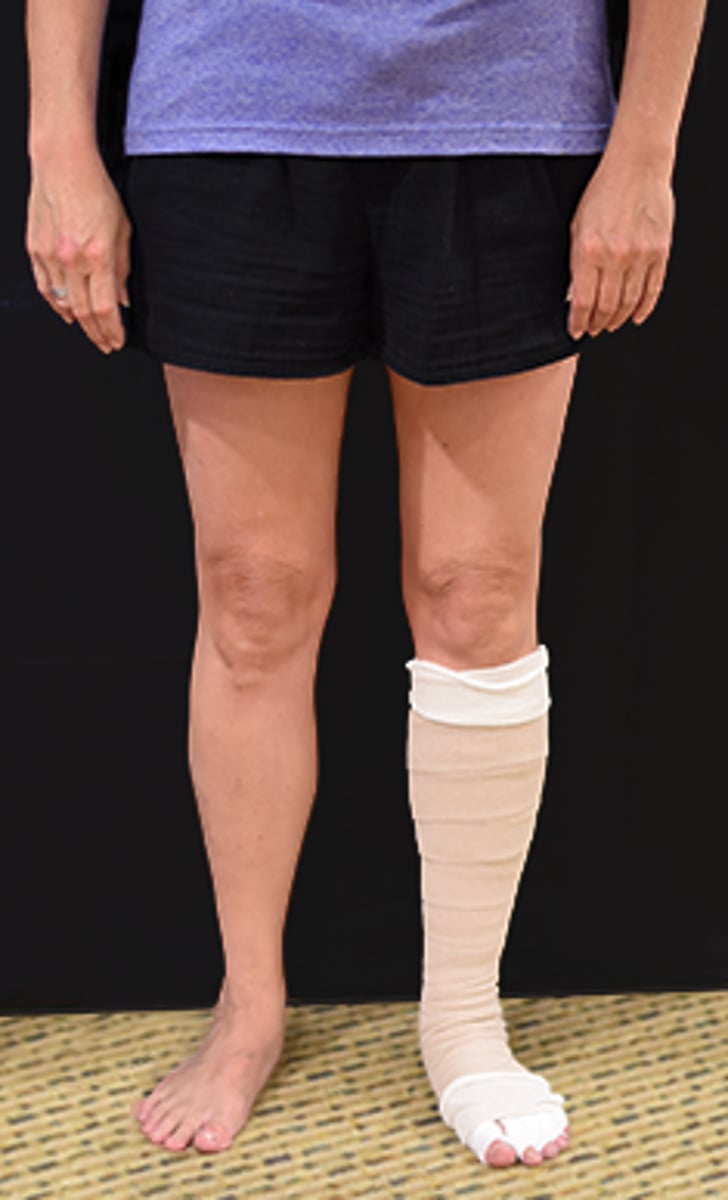
The intervention shown in the photograph is CONTRAINDICATED in the presence of which of the following clinical signs?
1. A positive Stemmer sign
2. A deep, dry, regularly shaped wound
3. A superficial, irregularly shaped, exudative wound
4. Presence of papillomas and hyperkeratosis
2. A deep, dry, regularly shaped wound
Rationale
1. A Stemmer sign is positive if the skin on the dorsum of the toes and fingers cannot be lifted, or is difficult to lift, compared to the opposite side. Presence of a Stemmer sign is considered to accurately diagnose the presence of lymphedema (p. 73.) Therefore, presence of a Stemmer sign, in the absence of peripheral arterial disease, would indicate that multilayered compression bandaging may be beneficial (pp. 272-273).
2. Multilayered compression bandaging or "lymphedema bandaging" is a technique used to provide compression therapy during the first phase of complete decongestive therapy (pp. 272-273). A wound that is deep, regularly shaped, and dry is most likely an arterial wound (p. 141). Compression therapy is contraindicated for management of edema in the presence of peripheral arterial disease (p. 267).
3. A superficial, irregularly shaped, highly exudative wound is most likely a venous ulcer (p. 141). Compression therapy is considered one of the most important therapeutic measures for prevention and treatment of venous leg ulcers (pp. 272-273). When applying multilayered compression bandaging to an extremity with a venous ulcer, the physical therapist may incorporate materials or medications prescribed by the physician into the bandaging to manage the wound (p. 82). Therefore, the presence of a venous ulcer is not a contraindication to using multilayered compression bandaging.
4. Papillomas and hyperkeratosis are common dermal abnormalities that occur in the presence of chronic lymphedema (pp. 79-80). These dermal changes do not prohibit the use of multilayered compression bandaging.
A patient who fell while running 3 days ago reports diffuse lateral ankle pain with active movement. The patient exhibits localized swelling distal and anterior to the lateral malleolus. Minimal laxity is noted with an anterior drawer test. Which of the following interventions would be MOST appropriate for the patient at this time?
1. Gastrocnemius-soleus stretching
2. Posterior talocrural joint mobilizations
3. Stationary cycling for up to 30 minutes
4. Active range of motion to end-range
2. Posterior talocrural joint mobilizations
Rationale
1. The patient has signs and symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of a lateral ankle (inversion) sprain. A grade 2 lateral ankle sprain is characterized by localized swelling and more diffuse lateral tenderness (Dutton, p. 1151). Gastrocnemius stretching with a strap while in long-sitting position is indicated in the subacute phase of rehabilitation (4-14 days). This exercise stretches the ankle out of the neutral position, which is a goal for the subacute stage (Dutton, p. 1154; Kisner).
2. The patient has signs and symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of a lateral ankle (inversion) sprain. A grade 2 lateral ankle sprain is characterized by localized swelling and more diffuse lateral tenderness (Dutton, p. 1151). Gentle posterior talocrural joint mobilizations should be performed in the acute stage of healing to maintain mobility and inhibit pain.
3. The patient has signs and symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of a lateral ankle (inversion) sprain. A grade 2 lateral ankle sprain is characterized by localized swelling and more diffuse lateral tenderness (Dutton, p. 1151). Stationary cycling is appropriate to address cardiovascular endurance and provide controlled ankle range of motion in the subacute phase of rehabilitation (4-14 days) (Dutton, p. 1154).
4. The patient has signs and symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of a lateral ankle (inversion) sprain. A grade 2 lateral ankle sprain is characterized by localized swelling and more diffuse lateral tenderness (Dutton, p. 1151). Active range of motion exercises, including ankle pumping and toe curls, are indicated only if performed within a pain-free range (Dutton, p. 1154).
A physical therapist is evaluating an infant who has bilateral ankle equinus, hindfoot varus, and forefoot adductus. The infant MOST likely has which of the following deformities?
1. Pes cavus
2. Talipes equinovarus
3. Calcaneovalgus
4. Metatarsus adductus
2. Talipes equinovarus
Rationale
1. Pes cavus is a high-arched foot and is not consistent with the description in the stem (p. 307).
2. Clubfoot (talipes equinovarus) is a congenital deformity (environmental and genetic) that includes components of forefoot adductus, hindfoot varus, and ankle equinus. The primary distinguishing factor is the equinus component. (p. 307)
3. Calcaneovalgus is an intrauterine "packaging" deformity. The ankle is in excessive dorsiflexion, the forefoot is curved out laterally, and the hindfoot is in valgus. (p. 304)
4. Metatarsus adductus is an intrauterine "packaging" deformity. The hindfoot is in valgus, and the forefoot is in varus. (p. 303)
Which of the following exercise guidelines is MOST appropriate for a patient who has diabetes?
1. Exercise during peak insulin times.
2. Exercise at the same time each day.
3. Avoid exercise if the blood glucose level is less than 150 mg/dL (8.3 mmol/L).
4. Avoid exercise if the blood glucose level is greater than 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L).
2. Exercise at the same time each day.
Rationale
1. Exercise should be avoided during peak insulin times (Goodman; Porcari).
2. Patients who have diabetes should exercise regularly and consistently (Goodman; Porcari).
3. Below 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) is the cautionary range for exercise (Goodman; Porcari).
4. Above 250 mg/dL (13.9 mmol/L) is the cautionary range for exercise (Goodman; Porcari).
A patient has contralateral hemianopsia and hemiplegia
(greater in the face and arm rather than leg), along with
that patient demonstrates hesitant speech and perceptual
problems such as depth perception and agnosia. Which of
the following arteries is MOST likely affected?
A. Basilar
B. Middle cerebral
C. Posterior cerebral
D. Anterior cerebral
B. Middle cerebral (MCA)
MCA supplies frontal lobe, parietal lobe, and cortical surfaces of temporal lobe and, therefore, affects higher cerebral processes of communication, language interpretation, and interpretation of space, sensation, frorm, and voluntary movement. lesions of this artery are mostly to manifest as alterations in communication, cognition, mobility and sensation. contralateral hemianopsia and hemiplegia (greater in the face and UE rather than LE) is also likely to be observed. Also, lesions of this artery are most likely to produce hemiparesis or hemiplegia, not bilateral weakness.
A 55 y/o male had a right ischemic PCA infarct 6 months ago. Patient has moderate spasticity throughout the left UE, demonstrating a flexor synergy pattern. During the evaluation, he ran into the doorway on his left side, requiring moderate assist to prevent falling. Based on the location of CVA, he is exhibiting signs/symptoms of:
A. Ipsilateral Homonymous Hemianopsia
B. Contralateral Homonymous Hemianopsia
C. Ideomotor apraxia
D. Aphasia
B. Contralateral Homonymous Hemianopsia
L temporal and R nasal
A 76-year-old patient suffered a recent stroke PT evaluated that the patient has apraxia, and she is unable to drink from the bottle on command However, she can point out to the bottle and verbalize the purpose of the bottle From this information, what sort of apraxia does this patient have? How should the PT approach treatment?
A. Ideomotor apraxia The PT should speak in short concise
sentences
B. Ideational apraxia The PT should always give the patient 3
step commands
C. Ideomotor apraxia The PT should always give the patient 3 step commands
D. Ideational apraxia The PT should speak in short concise
sentences
A. Ideomotor apraxia The PT should speak in short concise sentences
In the PT session, the PT commands the patient to wear a
shirt, but the patient is unable to complete the task due to
the inability to find buttons on his shirt. Which of the following are the MOST APPROPRIATE diagnosis and the best possible strategy to address this deficit?
A. Form discrimination, patients should be encouraged to use touch to identify objects.
B. Figure-ground discrimination, Patients should be encouraged to use touch to identify objects.
C. Position in space impairment, orienting the patient with one object in relation to another
D. Ideational apraxia, having the patient perform one part of the task at a time and guiding the patient with the task if
needed.
B. Figure-ground discrimination, Patients should be encouraged to use touch to identify objects.
He understands and trying to perform it but he couldn't find the button.
Figure ground discrimination as the shirt is considered the ground and arm hole is figure. The patient has inability to locate important objects that are not prominent in a visual image. The lesion area is identified as parietal occipital of
A patient with right hemisphere damage would MOST
likely have:
A. Left unilateral neglect and difficulty reaching for objects
presented on the Left side of the body.
B. Left unilateral neglect and difficulty reaching for objects
presented in the midline of the body.
C. Difficulty crossing midline to reach objects on the Right
side of the body.
D. Difficulty stabilizing gaze and locating objects on the right
side of the body.
A. Left unilateral neglect and difficulty reaching for objects presented on the Left side of the body.
During evaluation, PT asks the patient with a diagnosis of CVA to lift her left arm as high as she is able. Patient can lift her arm off her lap; however, she is only able to move it with elbow flexion, shoulder elevation, and wrist flexion with significant increased tone. Which of the following Brunnstrom's Stages of Recovery is MOST appropriate description for this patient?
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 3
C. Stage 5
D. Stage 6
B. Stage 3
A PT is called to assess a patient with traumatic brain injury.
The therapist documents that the patient has decerebrate
posturing pattern. Which of the following is MOST likely to
be seen in this patient?
A. Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and lower
limbs in extension, and the upper limbs in flexion, fists clenched
B. Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and lower
limbs in flexion, and the upper limbs in extension, fists clenched
C. Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and limbs in a
position of full extension
D. Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and limbs in a
position of full flexion
C. Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and limbs in a position of full extension
A therapist is observing a patient with a transtibial prosthesis and notices "drop off" during the late stance phase of gait. Which of the following prosthetic/anatomical causes would be the LEAST LIKELY cause of this gait deviation?
Select one:
a. Insufficient plantarflexion
b. Keel too short
c. Knee flexion contracture
d. Socket too far posterior
d. Socket too far posterior
Rationale: An early knee flexion during the late stance phase of gait is also known as "drop off". It occurs due to the following causes:
Prosthetic causes: High shoe heel, Insufficient plantar flexion, Keel too short, Dorsiflexion stop too soft, Socket too far anterior, Socket excessively flexed, Cuff tabs too posterior.
Anatomical causes: Knee flexion contracture.
A socket placed too far posterior would cause delayed knee flexion.
A 14 year old girl presents with a chief complaint of pain in the medial three fingers of the dominant hand, especially during gripping activities. The pain lasts for a while and subsides on its own after resting. She likes to play tennis on weekends but has a sedentary lifestyle otherwise. During postural assessment, the therapist noticed significant winging of the scapula on the same side. Strength of shoulder flexors: 4/5 and abductors is 4+/5 on the affected side. Strength of intrinsic muscles is intact. Which of the following nerves is MOST LIKELY involved?
Select one:
a. Median nerve
b. Long thoracic nerve
c. Suprascapular nerve
d. Axillary nerve
b. Long thoracic nerve
Rationale: Presence of scapular winging is indicative of serratus anterior weakness. The long thoracic nerve (C5-C7) is a motor nerve that supplies the serratus anterior muscle. The long thoracic nerve can be injured due to carrying heavy loads on the shoulder (e.g. backpacks) or when serving while playing tennis. Due to the weakness of scapular muscles, shoulder elevation may also be affected. Long thoracic nerve injury can be associated with inability/pain when fully flexing an extended arm.
An axillary nerve injury would lead to weakness of shoulder abduction and ER with square shoulder deformity. The median nerve mainly supplies the forearm and hand muscles, which would not cause winging of the scapula. The suprascapular nerve supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus which function to abduct and ER the arm, respectively. It would also cause pain with cervical rotation to the opposite side.
Dutton M. Dutton's Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, and Intervention. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2012; 68,69, 74
The correct answer is: Long thoracic nerve