BIOL101: Ch. 8 - Cellular Reproduction
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Spermatogenesis
The formation of sperm
Oogenesis
The formation of eggs
4 haploid sperm
How many functional sperm are made?
1 haploid egg
How many functional eggs are made?
1 and polar bodies
Meiosis in females makes ___ eggs and 3 ____ _____
Prophase I
In which phase of meiosis does crossing over occur?
Homologous chromosomes
Is information swapped between homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids?
Chiasma
The site of crossing over is called
Random
Is the alignment of chromosomes at metaphase 1 programmed or random?
Random
Can we predict which sperm will fertilize an egg or is it random?
Monosomy
Is a genetic condition where a cell is missing one chromosome from a pair; a type of aneuploidy
Missing chromosome
Is monosomy resulting from an extra chromosome or missing chromosome?
No
Will a human embryo survive if there is a missing autosome?
Yes only if it’s not an X chromosome missing
Will a human embryo survive if there is a missing sex chromosome?
Specific ones like trisomy 21 (down syndrome), trisomy 18 (Edwards), and extra sex chromosomes
Do all trisomies result in viable embryos or are there only specific ones that can survive?
Non-disjunction
If members of a chromosome pair fail to separate
homologous chromosomes
If there is non-disjunction in meiosis 1, ______ fail to separate
sister chromatids
If there is non-disjunction in meiosis 2, _______ fail to separate
Down Syndrome
Is the most common number abnormality and results from extra chromosomes; is trisomy 21
Intellectual disabilities, short stature, heart defects, alzheimer’s disease, shorter life span
What are the features of Down syndrome?
Trisomy
Is it a trisomy or monosomy?
Down syndrome, Edward syndrome, and extra sex chromosomes
Which chromosome are there 3 of?
Yes
Could you recognize this down syndrome on a karyotype?
Mother age 44
Who has a higher chance of having a Down syndrome child: mother age 22, mother age 44?
2 genetically identical daughter cells
How many cells are produced by mitosis?
4 haploid cells
How many cells are produced by meiosis?
Yes
Are the cells produced by mitosis genetically identical?
No
Are the cells produced by meiosis genetically identical?
Diploid
Are the cells produced by mitosis haploid or diploid?
Haploid
Are the cells produced by meiosis haploid or diploid?
Genetically unique
Does meiosis produce gametes that are genetically identical to the parent cell?
Equal mix of genetic information from each parent
Do all chromosomes in the offspring come from one parent or is there an equal mix of genetic information from each parent?
Sperm
What is the male gamete?
Testes
Where are gametes made in males?
Egg
What is the female gamete?
Ovaries
Where are gametes made in females?
Meiosis
Which process forms gametes: mitosis or meiosis?
half
A gamete has ____ the number of chromosomes found in the parent cell.
Fertilization
Is the fusion of two haploid gametes (sperm and egg) to form a zygote (single diploid cell)
Zygote
The fertilized egg
Haploid (n)
If there is only a single set of chromosomes, the cell is this; has only one copy of each chromosome
Diploid (2n)
If chromosomes are in homologous pairs, the cell is this; has 2 copies of each chromosome
Gametes
Which cells are the results of meiosis?
We use mitosis for growth, tissue repair, replacing old/damaged cells in multicellular organisms
When do we use mitosis?
Egg and sperm and adults
When in the life cycle are cells haploid?
Zygote and baby(ingrid)
When in the life cycle are cells diploid?
The sperm and egg form a zygote
What happens at fertilization?
A zygote is the single cell formed when a male sperm fertilizes a female egg
What is a zygote?
16
If a haploid gamete has 8 chromosomes, how many in the diploid cell?
23
If a 2n cell has 46 chromosomes, how many in the haploid cell?
Homologous Chromosome
Contain genes for the same traits but are not identical
Allele
Is one of two or more alternative forms or versions of the same gene; influences traits
Sister chromatids
Two identical, duplicated copies of a single chromosome; formed after DNA replication during S phase
Interphase (S phase)
When is the DNA copied for meiosis?
Meiosis I (Prophase I)
When does crossing over take place?
Meiosis I
When do homologous chromosomes separate: meiosis 1 or 2?
Meiosis II
When do sister chromatids separate: meiosis 1 or 2?
Homologous chromosomes line up in pairs and crossing over occurs
What happens during prophase 1?
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
What happens during metaphase 1?
Homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles
What happens during anaphase 1?
Separated homologous chromosomes arrive at opposite poles, nuclear envelopes reform around them, spindle apparatus disassembles, cell begins to split
What happens during telophase 1?
Cells have 1 chromosome from each homologous pair; they begin to line up with their pair
What happens during prophase 2?
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate
What happens during metaphase 2?
Sister chromatids separate and become daughter cells
What happens during anaphase 2?
Spindle disappears, nuclei form, and cytokinesis takes place
What happens during telophase 2?
Sister Chromatid
When DNA copies the two identical chromosomes
Centromere
The sister chromatids are linked by a structure called the
Kinetochore
The spindle fibers will attach at here during mitosis:
Centrosome
The spindle fibers grow from centrioles which are anchored at the
1
One chromosome has ___ DNA double helix
1
Sister chromatids have __ DNA double helixes?
Nearly Identical
Are the two double helices of sister chromatids identical or different?
92
If we start with 46 chromosomes, how many sister chromatids are present after the S-phase of mitosis?
16
If a non-human cell has 16 chromosomes after the S-phase of mitosis, how many were there originally?
Nuclear membrane breaks down and the spindle fibers start to assemble
What happens during prophase?
Yes
Are spindle fibers microtubules?
Sister chromatids line up in the middle of the cell
What happens during metaphase?
Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite sides of the cell
What happens during anaphase?
Nuclear membrane begins to reform and the chromosomes begin to uncoil
What happens during telophase?
The two daughter cells physically separate and is the final separation
What happens in cytokinesis?
Animal cells
Which has a cleavage furrow/division furrow?
Plant cell
Which has a cell plate?
Checks for nutrient availability or social signals
What is being checked for at the G1 check point?
Checks for DNA damage
What is being checked for at the G2 check point?
Checks if chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle fibers
What is being checked for at the M check point?
Due to a lack of growth signals or nutrients or severe DNA damage
What triggers a cell to go into G0?
Neurons, skeletal and cardiac muscle cells
Name some human cells that are in G0?
Protects the ends of chromosomes to prevent DNA from fraying, sticking to other chromosomes, or being mistaken for damaged DNA by the cell’s repair systems
What is the function of telomeres?
The telomeres shorten
What happens to the telomere each time a cell divides?
No, they usually pause the cell cycle to allow for repair (G2)
Will cells with damaged DNA be allowed to complete the cell cycle (think checkpoints)
Telomerase
Cancer cells have a special enzyme called
Repair telomeres
The function of telomerase is to:
Benign
Which would you rather have a benign or malignant tumor?
Cancer
Is a disease of uncontrolled cell proliferation
Cancer (Detailed One)
Is a loss of cell cycle regulation and far too many copies of cells are made
Tumor
The extra cells that were made which form a ball
Benign
The extra cells are harmless and do not spread
Malignant
The tumor cells are dangerous and can spread outside of their original location, either to local or distant regions
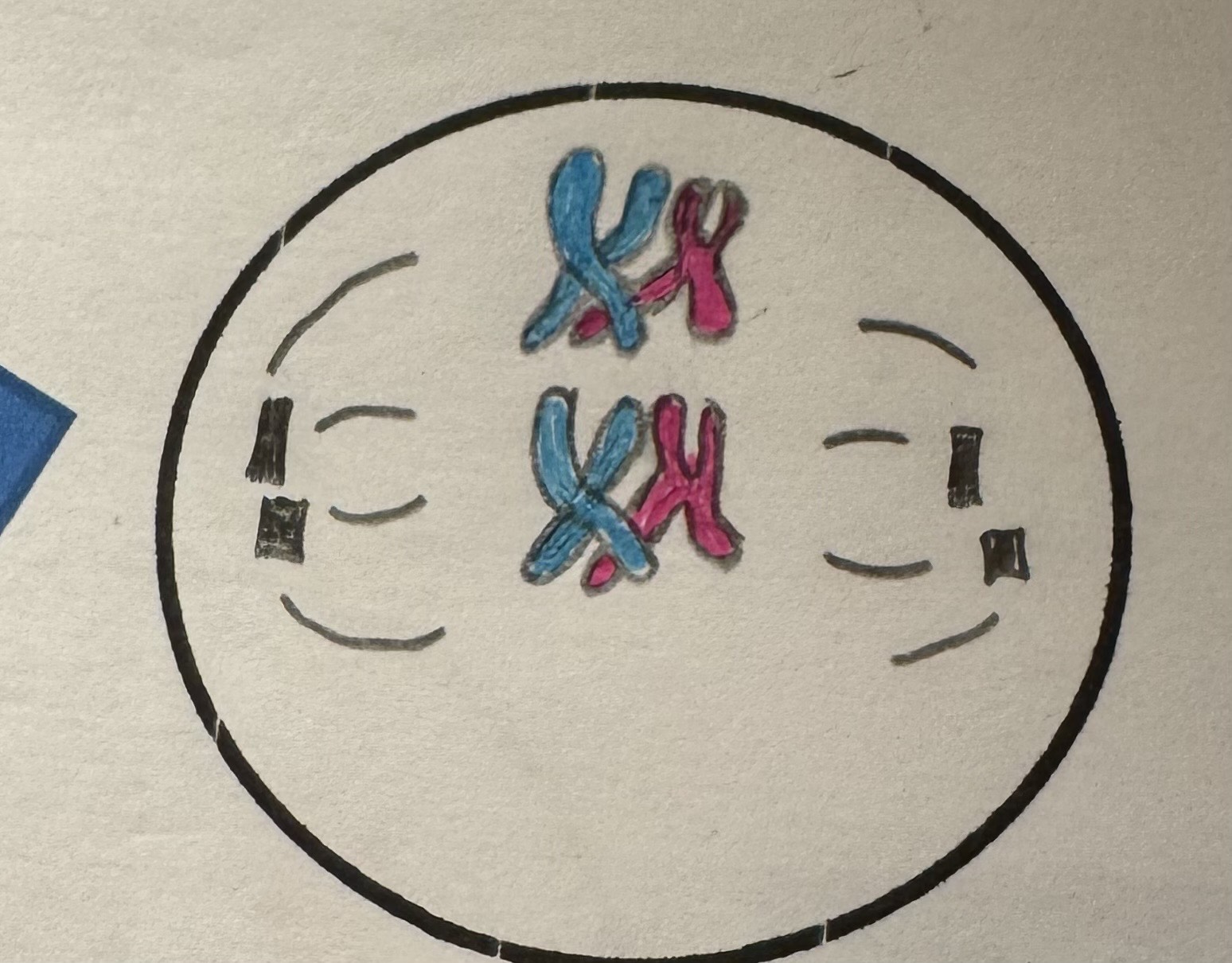
Interphase (Meiosis I)
Label this
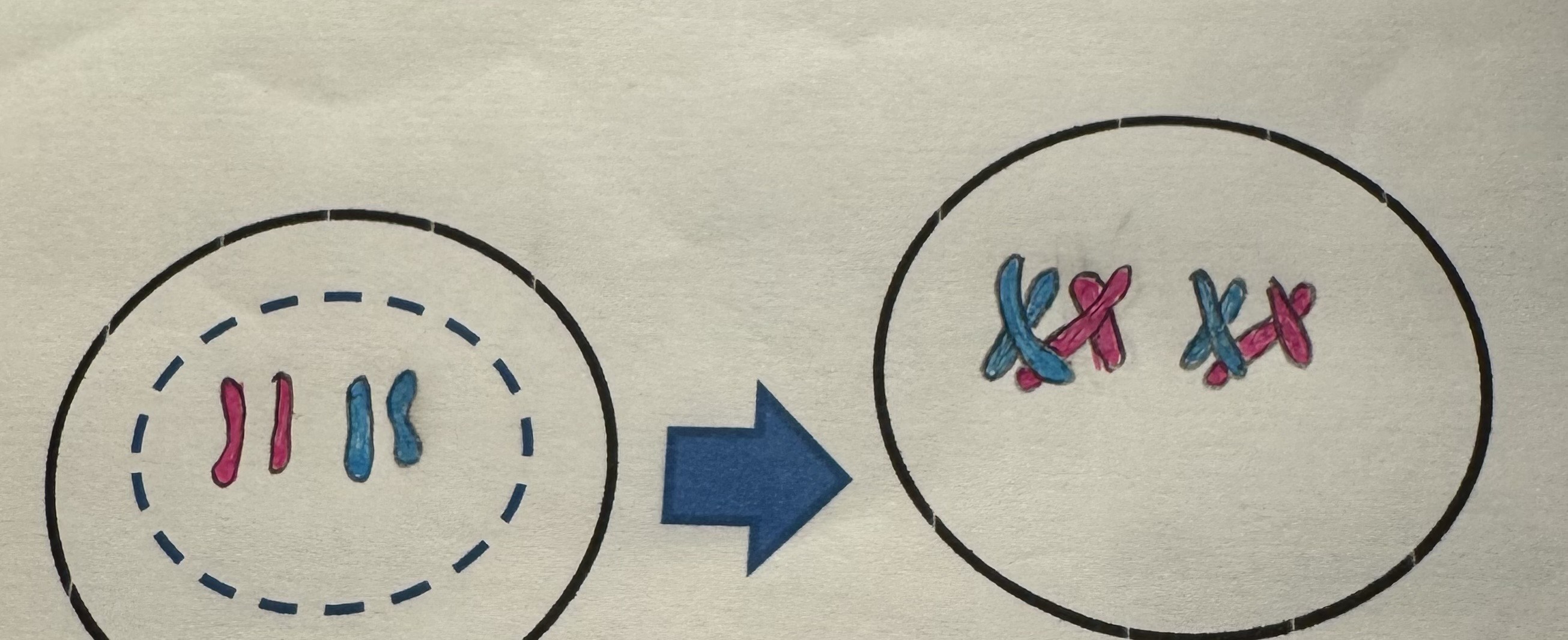
Prophase I (Crossing over happens here)
Label this