meowlecular test chp 1-2
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
what direction do we always describe dna in
5’ to 3’ direction
_______ bonds connect dna nucleotides together
phosphodiester bonds
how many hydrogen bonds are between an A-T base pairing
2
how many hydrogen bonds are between an G-C base pairing
3
which bond is harder to break and y a-t or g-c. why
g-c bc it consists of more (3 compared to 2) hydrogen bonds
1 mega base consists of how many base pairs
1 million
which enzyme helps to separate strands of dna so that each strand can be used as a template
helicase
which enzyme adds base pairs in the 3 ‘ direction so that dna can be replicated
polymerase
what are the 2 functions of polymerase
adds base pairs in the 3” direction so that dna can be replicated
proofreading
most of our genes encode what kind of RNA
MRNA
which rna is translated into proteins
mrna
what is the most predominant rna in our cells (hint, it is not mrna)
ribosomal rna
which rna exists in the cytoplasm, aiding in translation of rna to proteins and is not translated itself
ribosomal rna
functional part of the chromosome
gene
the gene is the functional pt of the protein that includes what 2 things 5’ or 3’ to the gene
coding information
regulatory regions
gene regulatory rgn usually contains info on what 2 things
time where gene is expressed
place where gene is expressed
non coding rgn of gene that is excised by processing from primary transcript
intron
intron/exon contain the coding rgn
exon
t/f primary transcript has introns and exons
true
t/f: the more complex an organism is, the more exons
f; the more complex= the more introns (the more needs to be excised out)
t/f introns can vary in length and can be the bulk of a primary transcript
t
what is the function of introns
no known function
a gene group in a bacteria is called
an operon (all the genes will be involved in the same biochemical pathway)
as we increase in complexity of organism (eukaryotes/mammalia), what can be noticed about introns
there is a lot more space between genes
way more introns
t/f number of chromosomes = genome size
f
amount of genes/ dna in an organism
genome size
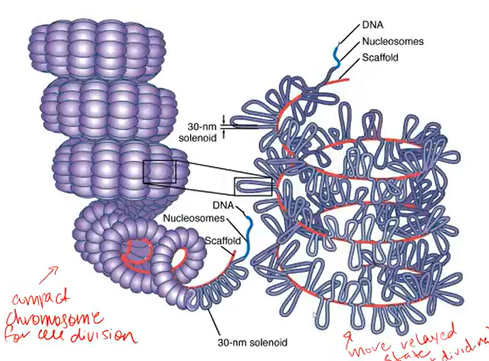
the structures around the coiling nuclear dna are called?
nucleosome
nucleosomes are a combination of?
dna and protein (specifically histone proteins)
whats a way to describe how dna wraps around histones
dna double helix wraps, like a string, around beads aka histone proteins.
what is it called when dna is wound around the histone core
octamer
nucleosomes= dna wrapped around histone core (octomer). it is then twisted onto a ____ and are then looped into a protein scaffold that is able to compact the dna into a chromosome shape.
solenoid
at the 5’ position of the ribose sugar, there is what group attached?
phosphate group (OP)
at the 3’ position of the ribose sugar, there is what group attached?
hydroxyl group (OH)
dna synthesis happens in what direction
5’ to 3’
what does it mean: “ dna synthesis happens in a 5’ to 3’ direction”
OH (3’) group always recieves from the incoming nucleotide the 5’ phosphate (PO) group and extends the 3’ end
t/f leading strand is wear synthesis can occur 5’ to 3’
t
the lagging strand is about how many base pairs slower than the leading strand
1000 bp
what are the fragments on the lagging strand called
okazaki fragments
enzyme that is a little piece of nucleotide that is like a gripping of the polymerase
primase (polymerase needs a primer/ pice of dna to prime polymeraseto have it go)
which enzymes in dna metabolization catalyze formation of the phosphodiester
bond
polymerases
which enzymes in dna metabolization unwind and untangle
helicases
which enzymes in dna metabolization synthesizes a short ribonucleic acid (RNA) to
start DNA synthesis
primase (polymerase cant latch on to one strand. it needs to have double strands in order to keep going)
which enzymes in dna metabolization cut dna
nucleases
what enzymes in dna metabolization catalyze formation of a single phosphodiester bond
ligases (glue)
what enzymes in dna metabolization add methyl groups to nitrogen bases
methyltransferases
what enzymes in dna metabolization take amino groups from nitrogen bases
deaminases
what nuclease removes bases from ends of dna strands
exonucleases
what nucleases cut dna strands internally
endonucleases
each restriction enzyme recognizes a specific ___________ double- stranded sequence
palindromic (same forward as back)
restriction endonucleases are isolated from _______
bacteria
AATT on dna cut by endonucleases are termed what and why
sticky ends; are free and can attach to any other complimentary piece (if restriction enzyme j chops it in half, its called a blunt end and it is not as useful)
what are sticky ends sequence
5’AATT3’/3’TTAA5’
ECHOR1 was isolated from what organism
ecoli
central dogma of molecular biology
dna is the information storage system. In order to get that info and use that info, it must be transcribed into another molecule that leaves the nucleus = RNA. it is then translated into protein
information stored in dna is transferred to rna by _____ via what enzyme
transcription; rna polymerase
during rna polymerase, the information is copied from how many strands
one strand of dna
during transcription, most genes code for _____ or ____ ____ RNAs used in protein synthesis
protein or untranslated functional RNAs
____ code: what nucleotide sequence codes for what amino acid
genetic code
amino acid ___ will determine the size and the shape of the protein
sequence
the _____ sequence of the gene determines the order of amino acids in a protein, which determines shape, size, and protein function.
nucleotide sequence
rna is transcribed as a _____ stranded molecule
single stranded BUT CAN OFTEN HAVE SECONDARY STRUCTURE (appear to be double stranded as one rna will bind to itself)
is uracil a pyramidine or a purine
pyrimidine
uracil makes a hydrogen bond with what
a
what are the functional rnas
tRNA
rRNA
snRNA
which rna transports amino acids to the ribosome
trna
which rna is the structural and catalytic component of ribosomes, operates with ribosomal proteins
rRNA
what RNA is the structural and catalytic component of spliceosome. functions in rna processing
snRNA
functions of r rna
structural/catalytic component of ribosomes
fx of trna
transports amino acid to ribosome
function of snRNA (small nuclear rna)
structural and catalytic component of spliceosome
functions in rna processing
in order to polymerize an rna transcript, there are how many rna polymerases
3
t/f: all rna polymerases are involved in polymerization and only some of them are involved in proofreading
t
transcription steps
initiation →
binding of RNA polymerase to promoter rgn (TATA box, CAAT box)
unwinding via dna helicase
elongation→
add nucleotides to 3’
base pairing
Magnesium needed (COFACTOR)
energy from ntp substances
termination
at 3’ end
processing for mRNA
t/f either one of the strands of the dna double helix can be the template strand for rna transcription
t
the template strand for rna transcription is always determined by what
promoter region
t/f complimentary base pairing of the template strand completely matches the non template strand
f (rna transcript contains “U”)
the 1st codon of a template strand for rna transcription is always?
ATG
why is the template strand for rna transcription also called the antisense strand
the rna transcript that is produced is complimentary and not the same
why is the non template strand sometimes called the sense strand?
because minus the U, it is identical to the rna transcript
as soon as the 5’ end comes off of rna transcription, what is added to it and why
a 5’ cap- 7-METHYL-GUANOSINE- is added so the exonucleases dont come and chomp it off
5’ end of the rna transcript is needed for ____ binding
ribosome binding
what is the sequence for the polyadenylation signal and what does it do
AAUAAA; it indicates that endonuclease can cut the rna polymerase off and that the rna chain can have a poly A tail added to protect/ stabilize it as it is a single stranded molecule.
what is the poly a tail for
protection/stabilization for the unstable single stranded structure
t/f the longer the poly a tail, the longer the rna molecule will last in the cyto
t; the longer it lasts, the more protein can be produced
introns are removed how
by spiceosome (rna is edited b4 leaving the nucleus)
all introns have what kind of recognition sequence
5’GU and a 3’AG
______ of spliceosome recognize 5’GU and 3’AG of introns and splice them out
snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleo protein)
when snRNPs of spliceosome recognize 5’GU and 3’AG of introns and splice them out, the intron is excised as a ____ and is recycled back into the body and coding exons are spliced together
lariat
what kind of rna act as transporters of amino acids during translation
tRNA (transfer rna)
tRNA ___codon binds to the ____codon of the mRNA
anticodon; triplecodon (the codon that codes for amino acid)
t/f: there are only 20 amino acids therefore different codons are used to code for the same amino acid
true (there are 65 codes)
what is the fx of r rna
translation of mrna
why is the 5’ cap important on the mRNA
binds r rna aiding in translation
stabilizes and protects the single stranded molecule
there are 3 ribosomal sites during translation, what are they
A, P, E
ribosomal site- A fx
amino site - accepts incoming charged tRNA
RIBOSOMAL SITE - P FX
polypeptide site - where all the peptide bonds form w all the incoming amino acids
ribosomal site: e fx
exit site - tRNA exits ribosome
at which ribosomal site does the 1st amino acid begin the peptide chain
amino site
t/f amino site/ N TERMINUS of the protein is always synthesized first
true