Section 12-1 – The Fungi Section 2-1 – Ubiquity study guide
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Saprophytes (saprobes)
- Mycelium Hyphae (singular: hypha)
• Dimorphic fungi
• Ubiquitous
Organism can be found just about everywhere (i.e., could be isolated from soil, water, air, plants, and animals)
o E.g., bacteria
Host - biotic (alive)
Organism in which smaller organisms (or viruses) live, feed and reproduce
Reservoir - either biotic or abiotic
Natural habitat or host of a pathogen; serves as a potential source of infection; may be non-living (soil, water) or living (human or other organism)
Mutualism
Both benefit (+/+) from the relationship
Commensalism
One benefits and the other is unaffected (+/0) by the relationship
Parasitism
One benefits and the other is affected (+/-) by the relationship
Opportunistic Pathogens
cause disease when the host's defenses are compromised or when they grow in part of the body that is not natural to them
Unicellular Yeasts NCLUDES WHICH WHAT
Candida albicans
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Aspergillus niger
- Penicillium notatum
- Rhizopus stolonifer
» Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Used in production of bread, wine, and beer
Filamentous Molds
Form hyphae
» Individual fungal filaments
» Collectively form a mycelium (mat of hyphae) - SEXUAL and ASEXUAL forms of reproduction
Aspergillus niger
Causes fungus ball in lungs (pulmonary aspergillosis)
Penicillium notatum
source of antibiotic penicillin
Rhizopus stolonifer
bread mold
Types of ASEXUAL SPORES:
Sporangiospores • Conidiospores
o 3 types: arthrospores, blastospores, and chlamydospores
Types of SEXUAL SPORES:
Ascospores • Basidiospores
• Zygospores
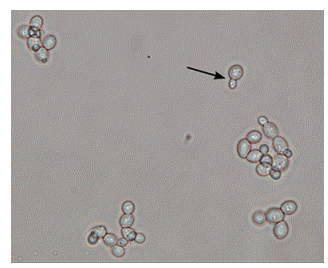
WAT THIS
saccharomyces cerevisiae – (commonly known as Brewer’s yeast) IMAGE!!!!!!
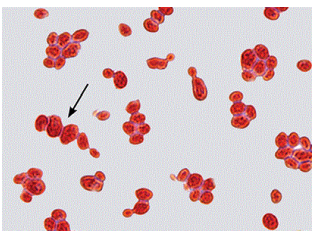
this what
Candida albicans IMAGE

image here is wat dude
Aspergillus niger – conidiophore IMAGGEE
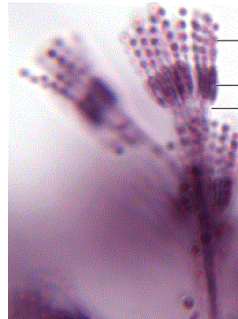
LOOK HERE DUDE
Penicillium notatum –conidiophore image
o Unicellular Yeasts
Have a round or oval shape - May have sexual and asexual reproductive cycles, but most common mode of vegetative growth is ASEXUAL reproduction by budding
Filamentous Molds INCLUDE WHAT
Aspergillus niger
Penicillium notatum
Rhizopus stolonifer
NOTE TO KNOW
dimorphic fungi have both mold and yeast life-cycles stages
Macrofungi
filamentous fungi that produce fleshy reproductive structures – mushrooms, puffballs, and shelf fungi
Hyphae
individual fungal filaments
Mycelium
Collective fungal filaments
Dematiaceous fungi –
hyphae that are darkly pigmented
Hyaline/moniliaceous fungi –
– unpigmented hyphae
Septate
hyphae whose walls are separate adjacent cells
Nonseptate
– hyphae whose walls are absent
Plasmogamy
fusion of cytoplasm
Karyogamy
joining of nuclei
Arthrospores
produced when a hypha breaks
Chlamydospores (chlamydoconidia)
formed at the end of some hyphae and are a resting stage