Biology
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Evolution
Upright walking helped obtain food due to climate change. Major drawbacks is pregnancy - loss of speed
Biped
S - shaped spine
Phylogeny
hypothesis of evolutionary relationships “family tree”
Hominin
Any early human lineage most closely related to H. Sapiens than chimpanzees.
Ecology
The study of interactions between the organism and the environment
population
a group of organisms within a single species inhabiting a specific area
Density
number of individuals per unit area
Distribution
Where the organism occurs
estimating population size
direct counts, mark, recapture.
M/N = m/n
Regular distribution
Evenly spaced
Distribution clumped
Unequal chance of being anywhere
Distribution random
equal chance of being anywhere
Population dispersal
movement of individuals within and among a population. An increase or decrease within the population can affect the habitat.
Active dispersal
An organism moving though its own abilities (i.e. bird flying)
Passive dispersal
an organism moving through the aid of external agents (i.e fish moving through water)
Short dispersal
Small scale movements
long dispersal
Large scale movement
Metapopulations
Multiple populations living as one
Patch
A patch of suitable habitat for organism (can be occupied or not)
matrix
unsuitable habitat
Deme
A local population that occupies a patch
turnover
patch occupied, unoccupied, occupied…..
Corridor
Area that is safe for organism to move through
Stepping stone patch
Small patches that can be used as a resting area
Fragmentation
Natural or anthropogenic causes (flood, fire, lava flow, roads, urbanization, borders, dams)
This leads to decreased habitat area, and increased isolation.
Habitat fragmentation
Interior habitat/species decrease, edge habitat/species increase, Diversity decrease, range decrease
population growth study
English sparrow which was brought in through a Shakespeare play. 8 pairs were released in 1851 in NYC. They had rapid growth which slowed in growth later.
Biotic potential
total number of young species can produce in a lifetime (under ideal conditions)
Environmental resistance
Is there enough habitat availability of population growth
Iteroparous
Reproduce multiple times
Semlparous
One off reproduction
Logistic growth
Population limited by food, space, and other resources
Logistic growth equation
ΔN/ΔT = rN(K-N/K)
Exponential growth
Prediction of a population @ a given time
Exponential growth equation
Nt+1 = Nt e^rt
Crude B rate
r= B-D/N
Take r / 1000
Per capita rate of increases
r=B-D/N
Exponential growth study
Reindeers left by coast guard
Instantaneous growth rate
ΔN/Δt =rN
doubling time eq.
1/2 k
limitations of logistic growth
- K is not constant
-makes the assumption that low population size growth is positive
Allee effect
when a population Size (n) is low (r should be positive) that population continues to decrease.
population growth dynamics of wolves
The wolves and moose. (lake freezing over)
Why did wolves fall?
-prey
-area
- inbreeding
- disease
Why did moose fall?
-predators
food
- climate
- disease
Life tables
Show how survival and reproductive rates vary with age, size, or life cycle stage.
Cohort life table
monitor a cohort throughout its lifetime
Static life table
record age at death for a large number of individuals in a
population - snapshot of a population: looks at
survival and reproduction of individuals of a known age over a single time period.
How to calculate R0
∑lxmx
With R0, when is the population increasing
R0 > 1
With R0, when is the population decreasing
R0 < 1
With R0, when is the population stable
R0 = 1
Type 1 survivorship curve
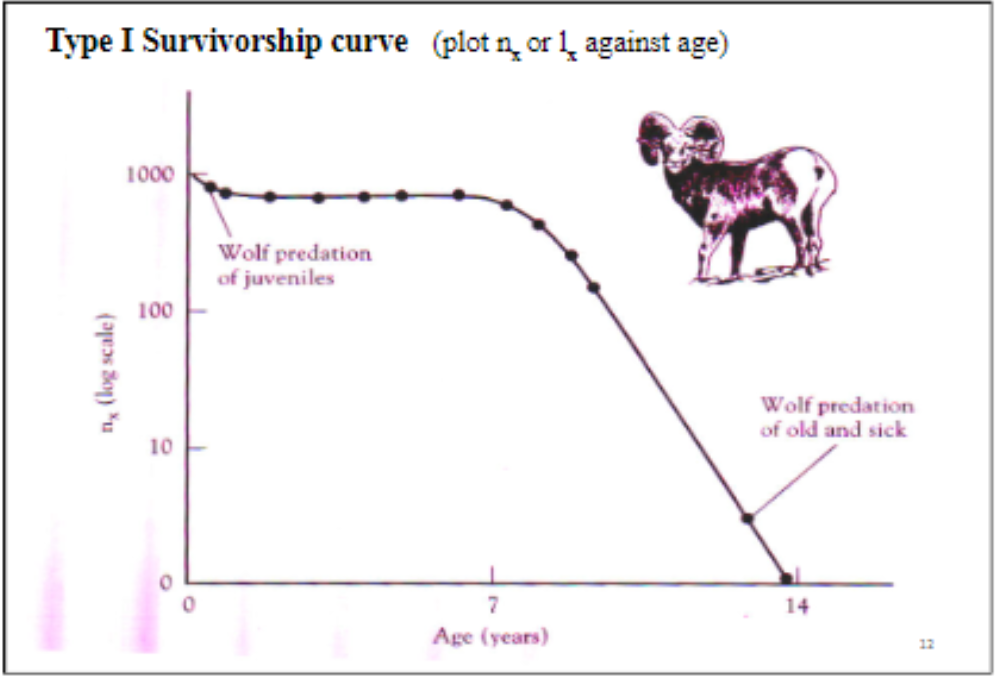
Type 2 survivorship curve
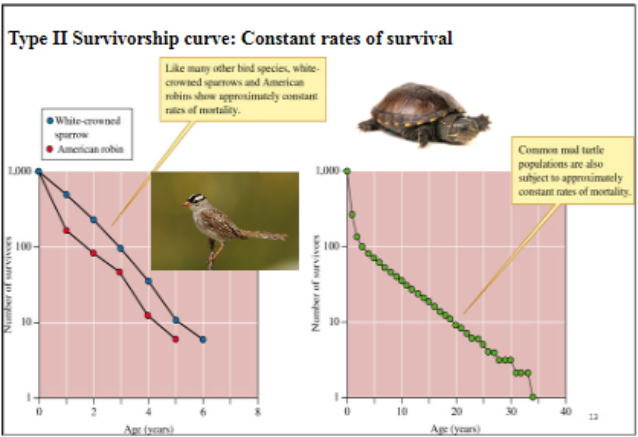
Type 3 survivorship curve
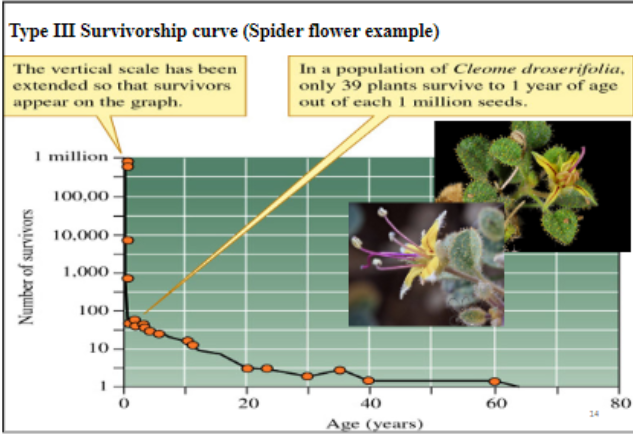
What is the value of e in the exponential growth equation
2.72