Chapter 4 - Types of business organizations
Forms of business ownership in the private sector
Partnerships: owned and controlled by two or more people
Private limited companies: owned, financed & controlled by between 2 & 50 people
Public limited companies (PLCs): owned, financed & controlled by a minimum of 2 shareholders with no maximum number of shareholders. (Open for the general public to buy shares)
Franchise: A business which has bought the right to trade under an established name
Sole Traders: Owned, controlled & financed by one person
Co-operatives: groups of people who enter a business & share the benefits
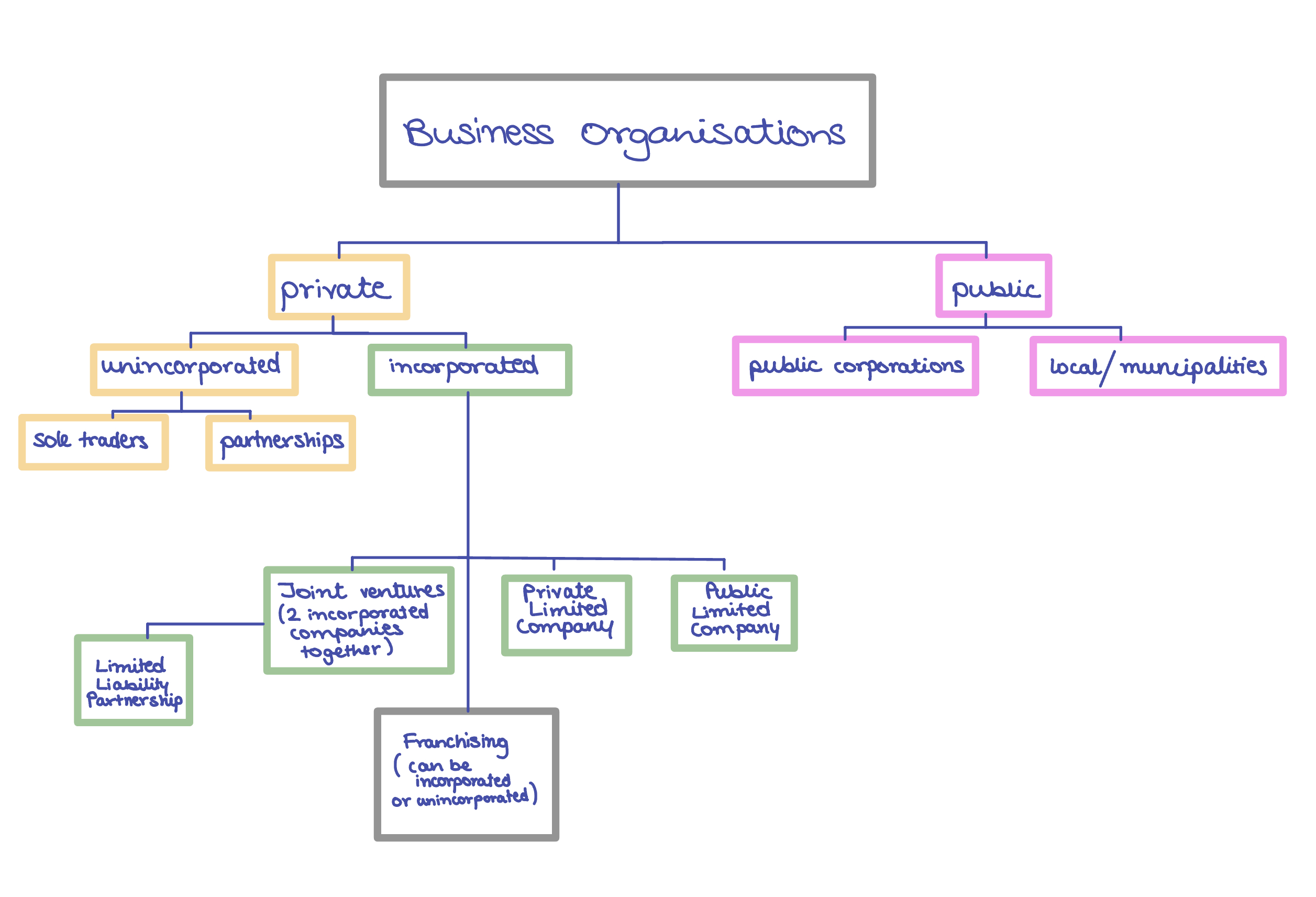
Unincorporated: Legally, the owner & the business are the same
Incorporated: The owners & the business have separate legal identities
Liability: the legal debt a company owes to third-party creditors
Sole Traders
- Smallest most common type of business organization
- Owned & operated by one person
- CAN employ others but is the sole proprietor
- Unincorporated
- Unlimited liability
| %%Advantages of a sole trader%% | ==Disadvantages of a sole== |
|---|---|
| Few legal regulations | Unlimited liability |
| Own boss therefore complete control | money/finance |
| Freedom & flexibility | high costs |
| personal customer contact | lack of training & lack of specialists |
| Decision making | raising capital |
| profit & secrecy | long hours |
Recommended for people who:
- Are setting up a new business
- Not much capital needed
- Personal contact with customers required (e.g. hairdressers)
Partnerships
- Usually a small business, a little larger than sole traders
- 2 or more people required to run a business, to make a profit
- Maximum number of partners = 20
- Sharing of losses & profits - split risk based on portion of capital invested by each partner
- Unincorporated
- Unlimited liability
| %%Advantages of partnerships%% | ==Disadvantages of Partnerships== |
|---|---|
| More Capital - expansion & growth | Unlimited liability |
| Shared responsibilities & decisions | Legal costs for making a partnership agreement |
| Losses shared by all partners | All partners liable for debts of the others |
| Greater opportunity for specialization | no separate legal identity |
| Easy to set up | Partnerships dissolved in partners leaving or through death |
| Less money needed by partners to set up | Decision of one partner binding on the rest |
| Can be a family run business | Limited access to capital |
| Accounts are kept private | Limit on the number of partners |
Recommended for people who:
- I wish to form a business with others with few legal complications
- Family business
- Professional bodies not allowing formation of companies
Limited Partnerships
- known as Limited liability Partnerships
- Possible in some countries (eg uk)
- Offers partners limited liability
- Shares cannot be bought or sold
- Separate legal identity
^^Partnership Agreement / Deed of Partnership is used to clarify:^^
- Amount of capital to be invested by partners
- Tasks of partners
- Profit sharing advantages
- Durations
- Absence / retirement agreements
Private limited company
- Separate legal identity - separate accounts from owner
- Denoted by: ‘Limited’, ‘Ltd’ or ‘Pty Ltd’
- Shares (represent % of ownership), owned by shareholders
- Continuity
Legal formalities
Submit to ==‘ Registrar of companies ’== TO GET ==‘ Certificate of Incorporation ’==
Articles of Association
- Directors’ rights & duties
- Rules for elections
- Official meetings
- Issuing shares
Memorandum of Association
- Name
- Address
- Contact details
- Objectives
- Amount of share capital
- Number of shares
| Advantages of Private Limited Company | Disadvantages of Private Limited Company |
|---|---|
| Limited liability - less risk | Shares: Existing shareholders only, & transfer needs consent |
| Sale of shares | Less Privacy, as all accounts are sent to the Registrar of Companies |
| Separate legal Identity | Not available to the general public, therefore it isn’t possible to raise large amounts of capital for expansion |
| Original owner retains control | |
| More ability to raise capital - expand faster | |
| Continuity | |
| Status |
Recommended for people who:
For family businesses or partnerships who want to expand further with no loss of control & reduced risk to their own capital
Public limited company
- Very large businesses
- Private sector (not owned by govt)
- Denoted by : ‘PLC’, ‘plc’ or ‘inc’
- selling of shares to general public
| Advantages of public limited company | Disadvantages of public limited company |
|---|---|
| Limited liability | Legal formalities are complicated & confusing |
| Incorporated business | Regulations & control - protect shareholders’ interest |
| Separate legal unit | Lack of privacy - publication of accounts |
| Continuity | Difficult to control & manage |
| raise large amounts if capital to expand internationally | Expense of shelling shares to the public - specialist bank, merchant bank, prospectus |
| No limits of amount of shareholders | original owner may lose control |
| easy to buy, sell & transfer shares | |
| higher status | |
| easy to attract suppliers & loans |
^^Memorandum of association^^ = A document containing all fundamental information which are required for the incorporation of the company
^^Articles of association^^ = A document containing all the regulations that governs the company
Converting from private to public
- Memorandum of association - ensure statement clause allowing conversion to public limited
- Certain minimum amount of shares must be issued
- Accounts must be available to the public & must have a specific layout
- Stock exchange
- apply for a listing
- easy for buying
- trading record
- ensure it is not poorly operated
- Prospectus
- invitation to the public
- buy shares in the company
- detailed document
- past record
- plan for the future
- reasons for raising capital
- how capital will be spent
Control & ownership of a public limited company
Public limited companies have thousands (or even millions of shareholders)
- Not possible for all shareholders to make decision of the company, therefore all shareholders are invited to annual general meeting (AGM) to ellect directors that form the Board of Directors (BOD)
- Directors appoint managers for day-to-day operations
Divorce between ownership & control
Shareholders → Board of Directors → BOF appoints managers
Ownership → Control
- Shareholders own; directors & managers control
- Shareholders can’t influence decisions
- Shareholders CAN replace directors but it brings bad publicity & loses stability as new directors may be inexperienced & may have contrasting ideas, goals and plans.
Joint Ventures
A joint venture is when 2 or more businesses agree to start a new project together, sharing the capital, risks & profits
| Advantages of a joint venture | Disadvantages of a joint venture |
|---|---|
| Sharing of costs (reduced costs) | If new project successful, then profits will be shared |
| Shared risks | Possible disagreements over decisions |
| Local knowledge when needed | Different cultures & different methods |
Franchising
^^Franchise^^ : A business on the use of the brand names, promotional logos & trading methods of an existing successful business. The franchisee buys the license to operate this business from the franchisor.
- The franchisee contributes capital, enterprise & management. The franchisor contributes original idea, use of brand name & products, and advertising & training.
Franchisor :
- Large business
- Product/service idea
- Does not want to sell
- directly to the public & appoints franchisees
Franchisee :
- Uses franchisor’s product / service idea / logo / brand name
- Buys license from franchisor & sells to the consumers
| To the franchisor | To the Franchisee | |
|---|---|---|
| %%Advantages%% | Franchisee pays for : expansion, shops & license to use the brand name | Reduced chance of failure due to the well-known brand & product |
| Rapid expansion than if the franchisor had to finance all new outlets | Advertising is paid by the franchisor | |
| Management of the outlets is the franchisee’s responsibility | All supplies are obtained from a single source | |
| All products sold (by the franchisee) must be bought from the franchisor → Major source of profit | Franchisor makes most decisions → fewer decisions to worry about | |
| No operation of retail units or management | Training for the staff provided by the franchisor | |
| Banks are often willing to lend to franchisees due to relatively low risk | ||
| ==Disadvantages== | Poor management of one franchised outlet could lead to bad reputation for the whole business | Less independence than with operating a non-franchised business |
| Franchisee keeps profits from their outlet | Maybe unable to make decisions that would suit the local area | |
| License fee paid & (possibly) a percentage of the annual turnover |
Co-operatives
→ A group of people who enter business & share the benefits
→ A non-profit community organizations, consumer cooperatives, worker cooperatives
Public sector
- Includes all businesses owned by the government & local government, & public services
- 2 types → Public corporations & other public sector enterprises
- Essential services owned by government → strategically necessary
Public Corporations
Their objectives :
- keeps prices low
- Keeps people in jobs to reduce unemployment
- offer public services to ALL areas
Issues of these objectives :
- Keeping to objectives costs huge amounts of money
- Often huge loss-making
- “Subsidies” often paid by government
| %%Advantages of public corporations%% | ==Disadvantages of public corporations== |
|---|---|
| Essential / necessary services owned & controlled by government | No private shareholder to insist on profitability & efficiency → no motivation |
| Natural monopolies → ensures customers aren’t taken advantage of | Subsidies lead to inefficiency : managers think that govt are there for bailout & unfair as subsidies are not given to private sector |
| Open business ready to collapse & secure job | Lack of incentive to : increase customer choice & to increase efficiency |
| Availability for public use → non-profitable | Used for political gain → offering more jobs during elections |
^^Corporatization : ^^
- Public corporations running as though it is in the private sector
- Preparing for privatization
^^Municipal Enterprises:^^
- Operated by local government
- Some free ( paid out of local taxes) & some charged