Milgram (1974)
Obedience: Form of social influence where an individual follows a direct order from a figure of authority and person receiving order responds in a way they usually would not.
Necessary for smooth running of society
Hierarchically organised social groups
Agency Theory:
Autonomous State → Behave independently and self-directed, take responsibility for actions, exercise moral compass, usually with peers or people who are below in social hierarchy.
Agentic State → Carry out orders from authority figure regardless of moral compass. Absolve blame for negative consequences.
Agentic Shift → Shift from autonomous to agentic state, allowing authority figures to control our behavior.
Moral Strain → State of mental discomfort or anxiety when actions conflict personal morality.
Individual Differences → Agency theory ignores individual differences by suggesting everyone has an innate potential for obedience.
Obedience by environmental experiences.
WEAKNESSES FOR AGENCY THEORY
Perry (2012) - competing argument
Many participants were suspicious whether shocks were real
More than 60% of participants disobeyed experimenter across variation studies
Agentic shift is not inevitable
Rank & Jacobson (1977)
16/18 (89%) of nurses failed to obey orders to administer a deadly overdose of Valium (drug)
Nurses were in the autonomous state despite being given instructions from a higher authority figure - shows agentic shift is not inevitable.
(House, 1976)
Charismatic leadership - suggests that the traits of the leader are important in gaining obedience, so autonomy may be a result of the authority figure lacking charisma rather than an individual’s state.
WEAKNESS OF MILGRAM’S BASELINE STUDY
Competing Argument - Perry (2012)
Film footage shows participants were suspicious about authenticity of shock machine
Orne & Holland (1968)
Claimed participants guessed shocks were fake but went along.
Latané (1981)
Social Impact Theory - How sources impact targets
Impact on Target = SIN
Strength → Perceived power and authority of source.
Immediacy → Closeness. of sources and targets. Physical or psychological barriers might affect this.
Number → Number of sources.
Multiplicative and divisional effects:
Multiplicative → More sources than targets, stronger effect
Divisional → More targets than sources, weaker effect
Law of diminishing returns → More than 3 targets for 1 source has less influence because of individual differences. The bigger the group, each additional person has less of an influence.
Individual Differences - Factors like source and strength are subjective to the target.
STRENGTHS OF SOCIAL IMPACT THEORY
Sedikides & Jackson (1990)
Obedience at the zoo study - studied visitors responses to being told to not lean on a railing
Findings of obedience levels:
58% - confederate dressed as zookeeper instead of t-shirt
61% - same room instead of adjacent room
60% - 1 or 2 targets
Competing Argument - Field experiment meant researchers could not manipulate number of participants in each group, affecting internal validity. People in larger groups may naturally have less obedient personalities.
Application to Political Influence
Politicians targeting smaller crowds, having a prominent physical presence and adopting a strong, persuasive style of communication.
WEAKNESSES OF SOCIAL IMPACT THEORY
Hofling et al. (1966)
Arranged for an unknown doctor to telephone 22 nurses and ask each of them to administer an overdose of a drug not on their ward list.
95% obeyed
This challenges SIT by supporting how immediacy is less important than the strength of a source.
Milgram’s Baseline Study (1963)
Aim:
To understand behavior of Germans who followed destructive acts of obedience in the Holocaust.
Developed a method to test obedience to legitimate authority.
Procedure:
Only 1 real shock - 45V to make participants believe it was real
Participants - 40 men, 20-50 years of age with varying professions
Local newspaper - volunteer sampling
Participants paid $4.50 for each hour
Participants automatically teacher
Mr Wallace - Learner
Mr Williams - Experimenter
Findings:
65% - 450V shock
100% - 300V shock
12.5% - stopped after 300V shock
STRENGTHS OF MILGRAM’S BASELINE STUDY
Tarnow (2000) - Application to Pilot Training
Showed how first officers were hesitant to question captain in pilot training despite risk due to obedience to higher authority.
Standardised Procedures
Two confederates always played the same role
Tightly scripted responses and verbal cues
High reliability - replicable
STRENGTHS OF AGENCY THEORY
Supported by 1963 baseline study
High tendency to carry out destructive orders of obedience - 100% used 300V whilst 65% went to 450V (extreme danger)
Application to military
When binding factors outweigh moral strain, obedience follows
Gibson and Haritos-Fatouros (1986) - dehumanising language and euphemisms like ‘collateral damage’ ensure that soldiers remain in the agentic state and are desensitised when commiting barborous acts.
Binding Factors - psychological mechanisms that enable individuals to justify or rationalize their actions, particularly in situations where they may be compelled to act against their own moral beliefs.
Experiment 7 - Telephonic instructions
Milgram’s Variation Studies:
General Aim - to see which situational factors encouraged dissent. New standardised procedures with more modest laboratory and Mr Wallace mentioned he had a mild heart condition.
The experimenter gave instructions on the phone in another room
Only 9/40 (22.5%) of participants were fully obedient
Some participants lied
Immediacy of authority figure is necessary to increase obedience
Experiment 10: Rundown office block
Milgram’s Variation Studies:
Rundown building in downtown shopping district of Bridgeport, an industrial city.
Participants told study was conducted in private firm
Only 47.5% were fully obedient due to ‘scientific research’
Setting undermined legitimate authority
Experiment 13: Ordinary man gives orders
Milgram’s Variation Studies:
Tested whether legitimacy of authority or strength of command was a more important situational factor
2 confederates: 1 learner, 1 recorder
Experimenter receives fake phone call so recorder takes over, suggesting shocks should be continually administered with 15V increments.
Awkward withdrawal of experimenter.
80% of participants refused to continue, showing how strength of source is essential
Adorno (1950) - Personality affecting obedience
Authoritarian personality: FACTORS AFFECTING PREJUDICE - INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES
Measured using f-scale - higher score = more obedient
Derived from strict, harsh parenting and conditional love during childhood - common during Germany in early 20th century
Children are more likely to scapegoat and shift blame onto others out of fear of punishment, leading to increased outgroup hostility.
Rotter (1966) - Personality affecting obedience
Locus of Control refers to an individual's perception about the extent of agency they have to underlying main causes of events in their life.
Internal & External Locus of Control:
Internal LOC → People who take responsibility for their actions and act in control. More likely to defy destructive acts of disobedience. Portray dissent.
External LOC → People who take less responsibility and instead blame consequences on other people or chance, less likely to defy destructive acts of disobedience.
STRENGTHS OF LOC
Miller (1975)
Experimenter instructed participants to grasp dangerous live wires, people with external LOCs were more likely to obey.
Application to workplace
Personality tests assessing LOC can result in more successful matching.
STRENGTHS OF AUTHORITARIAN PERSONALITY
Elms & Milgram (1966)
Used F-scale with 20 fully and non fully obedient people, obedient participants scored higher and had less closeness to fathers.
Competing Argument → Hyman and Sheatsley (1954) suggest obedience and authoritarian personality may be caused by a lower level of education.
WEAKNESSES OF LOC
Schurz (1985)
Weakness of LOC - Does not predict defiance:
Participants instructed to blast student with painful ultrasound.
Fully obedient participants did not differ significantly from resistant participants in LOC store.
Personality has little impact on obedience.
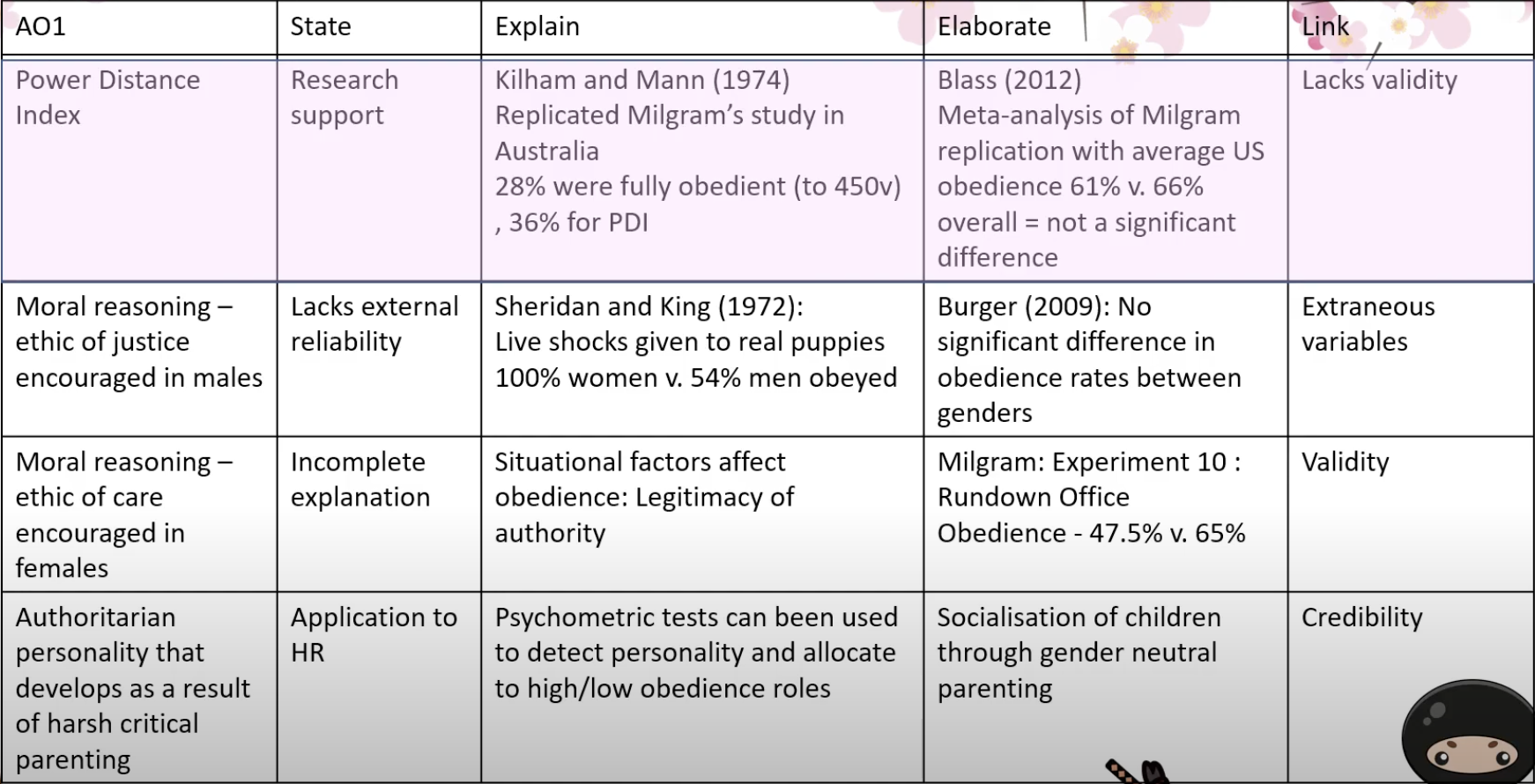
Sheridan & King (1972) - Gender affecting obedience
Women are more obedient to men - real electric shocks to a live puppy
100% of females were fully obedient VS 54% of males
Kilham & Mann (1974) - Gender affecting obedience
Men more obedient than women.
Replicated Milgram study in Australia
Unusually low obedience rate of 28%
40% of male participants and 16% of female participants were fully obedient
Gilligan (1982) - Gender affecting obedience
Moral reasoning - Men & Women were guided by different principles
Ethic of justice - MALES, equality + fairness, detached outlook to avoid bias
Ethics of care - FEMALES, nurturing, supporting
STRENGTHS OF GENDER AFFECTING OBEDIENCE
Gilligan & Attanucci (1988)
Males favored justice orientation whereas females favored care orientation, gender differences in moral reasoning.
WEAKNESSES OF GENDER AFFECTING OBEDIENCE
Blass (1999)
No significant difference in obedience between 9 Milgram studies between males and females
STRENGTHS OF SITUATIONAL FACTORS - Culture Affecting Obedience
Meeus & Raajmakers (1995) - Holland
Asked participants to deliver increasingly unkind insults to a confederate applying for a job. More than 90% gave all 15 insults, 36% when experimenter left the room and 16% when witnessing 2 rebellions. Obedience can be significantly reduced by adjusting situation.
Competing Argument - Milgram’s experiment shows that personality (disposition) outweighs situational factors.
Blass (2002) - Cross-cultural studies
Mean obedience for US studies to be 61% and the rest of the world to be 66%
Application to rule-breaking
Gramann et al. (1995) found that when information was provided on the reasons behind rules, obedience was higher.
Hofstede (2017)
CULTURE - POWER DISTANCE INDEX (PDI)
PDI - A measure of how accepting people are of hierarchal order and inequality in society.
In high PDI cultures, citizens are told what to do and the ideal boss is a benevolent autocrat.
Socialisation is an essential part of developmental psychology
STRENGTHS OF PDI - Culture Affecting Obedience
Delinski (2017)
Very high level of obedience in Poland (90%), a country with a high PDI score (68%).
This suggests there is a close relationship between PDI and obedience levels.
Kilham and Mann (1974)
very low PDI score (36%) was correlated with a low obedience rate (28%)
Suggests that Hofstede’s power distance index was useful in predicting obedience
WEAKNESSES OF PDI - Culture Affecting Obedience
Blass (2012)
Calculated mean of 66% obedience rate for 8 non-US Milgram replications & 61% for US replications.
Obedience may be a universal social behavior and many nations have similar obedience levels.
Tajfel & Turner (1979, 1986)
Prejudice → Social-Identity Theory
Prejudice is a negative pre-judgment or biased belief held about an individual or group prior to direct experience. Discriminatory attitudes are based upon stereotypes and group characteristics whilst individual attributes are ignored.
SIT suggests people have a strong innate desire to belong and that self-esteem is derived from group membership and the acceptance of others.
Social Categorisation → separating individuals into ingroups and outgroups, little control over automatic sorting process
Social Identification → Individuals adopt beliefs, attitudes and values of ingroups. Behavior is altered to fit in. Change in self-concept.
Social Comparison → Self-esteem can be boosted with comparisons between ingroup and outgroup.
Quest for positive distinctiveness - differences emphasised, similarities minimised leading to discrimination. Ingroup seen as superior, achievements exaggerated and outgroup as inferior, achievements denigrated.
Carlton-Ford (2008) found that stronger national identity correlated to higher self-esteem.
STRENGTHS OF SOCIAL IDENTITY THEORY
Tajfel (1970): MINIMAL GROUP EXPERIMENT
15 year old school boys, ingroups and outgroups were created
Boys asked to allocate points in exchange for cash and found more points awarded to ingroup members.
Showed how social categorisation can trigger ingroup favouritism and outgroup discrimination
Fein & Spencer (1997): Application to reducing prejudice by increasing self-esteem
Students given false feedback on an IQ test. Students with lower self-esteem rated Jewish applicants for a job less favorably than an Italian candidate.
Students increased self-esteem by writing about something they valued, reducing anti-semitism.
STRENGTHS OF RCT
Sherif (1961)
Intergroup competition where only one group can win prizes.
Proved Negative interdependence led to increased violence and prejudice between groups.
Competition can cause intergroup hostility
Application to reducing prejudice
Application of superordinate goals to reduce intergroup conflict
Sassenberg et al. (2007)
Divided East Germans into competitive or cooperative mindset by getting them to complete a general knowledge test in pairs.
Participants in competitive condition showed more prejudice to West Germans than those in the cooperative condition
WEAKNESS OF SOCIAL IDENTITY THEORY
Wetherell (1982) - Ethnocentrism
Lacks mundane realism, reductionist by limiting possible factors affecting discrimination
May only explain intergroup behavior of Western Societies and fails to predict behavior for other collectivist backgrounds or minorities.
Replicated Tajfel’s experiment using 8 year old boys from New Zealand and found that indigenous Polynesians were more generous to allocation of points than white classmates.
Sherif (1966)
Realistic Conflict Theory → Explanation of prejudice which sees competition for limited resources as key determinant of intergroup relations.
Negative Interdependence → Conflict of interests caused by how only one goal can be achieved by one group. Increased suspicion and hostility between groups. Each group will try and obstruct the other’s achievements while one has to lose for the other to win.
Limited resources → Food, territory, symbolic resources, fiercest conflicts
Positive Interdependence & Superordinate Goals → Intergroup cooperation is required to achieve shared desired goal. Mutualism and improved intergroup relations.
Zero-Sum Fate → This is the idea that if one side gains, someone else has to lose out. Some times this might be true, but not always. Realistic Conflict occurs when people believe that an out group can only benefit at their expense. So, if they see out group members doing well, they conclude that they must be losing out somehow.
WEAKNESS OF RCT
Tajfel (1970)
Prejudice & discrimination can come from perceiving individuals as part of an outgroup.
Prejudice can be more about self-concept and comparison with others than competition for limited resources.
Competition may not be necessary to create prejudice
Allport (1954)
ALLPORT’S AUTHORITARIAN PERSONALITY:
Compared to more generalised tolerant types who have inner security and confidence from unconditional parental love.
People with this personality are more receptive to political arguments that target their insecurities.
Parents are more deviant and relaxed, raising more liberal and defiant children.
Altemeyer (1988)
RIGHT WING AUTHORITARIANISM (RWA):
Focused on authoritarian submission, aggression & conventionalism.
Prejudice against various groups like women.
Reaction to fear & uncertainty by seeking security through preserving existing social order.
Pratto (1994)
Social Dominance Orientation (SDO):
Motivated to seek out ingroup power and superiority
Competitive outlook on the world
Tough-minded but not agreeable or empathetic people
More common in men which develops by exposure to high levels of competition & inequality
Altemeyer (2004) → Degree of social dominance is more correlated with fathers. Males more likely to have SDO’s than females.
STRENGTHS OF PERSONALITY & PREJUDICE
Cohrs (2012)
Supported by research & application to reducing prejudice by regulating media sites
RWA & SDO are positively correlated to prejudice.
RWA - resistance to openness
SDO - resistance to agreeableness
WEAKNESSES OF PERSONALITY & PREJUDICE
Levin (1996) - Competing Argument
Prejudice is hard to predict in the real world.
Ashkenazi Jews have higher SDO scores than other types of Jews.
differences in SDO disappeared when Jewish groups were asked to think about relationship with Israel & Palestine.
Louis (2003)
Ignores social norms and situational factors
RWA & SDO do not include items heavily affected by norms & social attitudes
72% of Australians disagreed with white supremacy
Duckitt’s dual process motivational (DPM) model
Duckitt (2005)
Created a model that explains prejudice that combines RWA and SDO.
Caused when specific personality profiles are exposed to certain worldviews.
FACTORS AFFECTING PREJUDICE → SOCIAL NORMS (SITUATION)
Cantril (1941)
Unwritten rules about what is socially desirable in social groups.
Suggested group identity is central to formation of prejudiced views.
Minard (1952)
Difference between White and Black coal miners in the USA. Friendly and worked well together underground but were prejudiced above ground.
FACTORS AFFECTING PREJUDICE → COMPETITION FOR RESOURCES (SITUATION):
Esses & colleagues (2001)
Prejudice arises between ingroup & outgroup when situation is zero-sum by showing outgroup’s lack of worthiness.
STRENGTHS OF FACTORS AFFECTING PREJUDICE - SITUATION
Esses & colleagues (2001)
Targeting zero-sum beliefs was effective although high SDO individuals had more negative attitudes.
Akrami (2009)
Swedish study - manipulated social norms
Some participants heard a confederate express skepticism with sexist statement
Mean levels of sexism were lower than control group
Participants who read a short article about a bleak social & economic future had more prejudice
Competing Argument → RWA and SDO had an influence on mean prejudice levels between experimental and control groups
FACTORS AFFECTING PREJUDICE → NORM OF INTOLERANCE (CULTURE)
Baldwin (2017)
All cultures are ethnocentric.
Individualist cultures - encourage discrimination, microaggressions and benevolent intolerance . Whites in South Africa were racist from 1948-1994.
Collectivist cultures - Higher tolerance of diversity and acceptance is encouraged.
STRENGTHS OF FACTORS AFFECTING PREJUDICE - CULTURE
Orpen (1971)
F-scale scores were not correlated with prejudice in a group of white South Africans.
Social conformity and cultural pressure are also important factors.
Al-Zahrani and Kaplowitz (1993)
Found Saudis, a collectivist culture, tended to self-report more negative out-group bias than Americans, an individualistic culture, so prejudice may develop because of different types of culture
Guimond (2013)
looked at cultural norms and government policy within multicultural societies and found that anti-Muslim attitudes were reduced when the pro-diversity policy was high, so prejudice can be reduced when diversity and multiculturalism is promoted.
Can explain prejudice towards lower-income groups: Conflict for limited material resources (situational)
Competing Argument → 16 year old school kids were used and younger people may have a greater desire to fit in.
Classic Study: Sherif (1954, 1961)
ROBBERS CAVE EXPERIMENT:
Aim:
How competition & frustration of a group’s goals can lead to outgroup prejudice and hostility whilst encouraging ingroup cooperation.
Procedure:
I.V. - Atmosphere
D.V. - Number of friends identified in outgroup
Participants - 22 boys, middle-class, protestant, 11 year olds from Oklahoma, USA. All socially & emotionally well adjusted while none knew each other prior. Divided into 2 groups.
2 groups: Rattlers VS Eagles
STAGE 1 → Group formation: Non-competitive activities for bonding.
STAGE 2 → Friction. Tournament with medals and trophies (limited resources). Contests - tug of war, baseball & tent-pitching, extra points for cabin inspections & treasure hunts.
STAGE 3 → Reducing friction. Superordinate goals like repairing truck or making dinner.
Findings:
STAGE 1 → Differing social norms established, Rattlers were tough & swore a lot whereas Eagles cried a lot and were more anti-swearing.
STAGE 2 → Outgroup hostility developed rapidly. One group burnt the other’s flag. Only 6.4% of Rattler’s friends were eagles and 7.5% of eagles friends were rattlers.
STAGE 3 → Initially insults were still thrown and lots of friction when fixing water supply but greatly reduced with other activities.
Outgroup friendships increased: 36.4% of rattlers friends were now eagles and 23.2% of eagles friends were rattlers.
WEAKNESSES OF Classic Study: Sherif (1954, 1961)
Tyerman & Spencer (1983)
Failed to replicate findings
Sea scout troop of 30 boys from 1 of 4 patrols and knew each other well. Less hostility and ingroup solidarity decreased.
Suggests competition only triggers prejudice from people who don’t know each other well.
Contemporary Study: Burger (2009)
Aim:
Replicating Milgram’s findings to see if it was era-bound.
To determine whether obedience was affected by gender & personality traits like empathetic concern & desire for personal control.
Procedure:
An independent groups design - compares the 2009 participants with the 1960s participants and it also compares the control group with the disobedient model group.
Participants: 70 adults (29 male, 41 female), aged 20 to 81 (mean age 42.9)
60% university degrees
55% white caucasian & 4% Black Afro-Americans
Flyers & advertisements
6 ethical safeguards
Highest shocks was 150V to avoid high levels of anxiety.
Ethics - 2 step screening process for heart conditions checking. 3 reminders to withdraw and participants debriefed immediately. 15V instead of 45V administered as starting shock.
Clinical psychologist supervised and self-report questionnaires were used.
Trial terminated when participant refused to continue after 4 prods.
Sample:
70 participants (a mixture of men and women) did the experiment, being randomly put into the two conditions.
They were a volunteer sample, recruited through newspaper and online ads and fliers left in libraries. They were paid $50 before the study started. They were aged 20-81.
Findings:
Obedience rate only decreased slightly
70% pressed 150V
No significant difference in obedience rates between men (66.7%) and women (72.7%)
No significant difference in empathetic concern but defiant participants had higher desire for personal control.
Burger was also interested in individual differences that Milgram ignored. He focuses on two traits: empathy and locus of control.
WEAKNESSES OF Contemporary Study: Burger (2009)
Elms (2009)
Limited application to real world obedience
Low shocks administered and participants stopped before any real anxiety or cognitive dissonance was suffered from due to ethics.
Poor Generalisability
Not a representative sample
38% of volunteers were excluded so the remaining participants may have been more psychologically robust than the general population
Competing Argument → Milgram replica by Beauvois et al. (2012) is more representative and conducted in France - 80% went to 450V.
Validity:
He stated that people willing to go above 150V would continue until 450V which is a huge assumption.
Lacks ecological validity because of artificial setting.
Legitimacy of university setting may have been a confounding variable that increased obedience - SIT.
Ethics:
Burger deceived his participants just as Milgram had done – the shocks weren’t real.
Distressing procedure for some participants.
Did not get informed consent.
STRENGTHS OF Classic Study: Sherif (1954, 1961)
Careful Allocation of two groups - Rattlers and Eagles
High Internal Validity - boys’ prejudice was determined by the competitive situation and not by pre-existing differences.
Researchers spent over 300 hours observing, interviewing and testing potential participants to pick 22 who had matching personalities, skills and interests.
Competing Argument → Rattlers had an unfair advantage as 2 boys went home for the Eagles.
Aronson & Bridgeman (1979)
Proved that Sherif’s classic study could be applied to tackling racial prejudice in American schools. Students worked together and took responsibility for different parts of the group project, increasing empathy for outgroup members and improving academic performance of black minority students.
May be less effective for some groups. USA is individualist and more competitive, while the participants were all male American children so gender differences were not measured.
Body-bag Journalism
Hogan (2001) → a negative collective mood of a nation can encourage prejudice and discrimination towards outgroups.
STRENGTHS OF VARIATION STUDIES
Experiment 10: Rundown Office
Quantitative data and qualitative data (audio recordings)
Rochat and Modigliani (1995) found from a re-analysis that the earlier participants challenged the experimenter, the more likely they were to be fully defiant.
Experiment 7: Telephonic Instructions
High external validity - Sedikides and Jackson’s zoo study supports obedience theory
Physical proximity generalises well to other naturalistic situations
WEAKNESSES OF VARIATION STUDIES
Experiment 13: Ordinary Man Gives Orders
Lacks Internal Validity
Traces of derived authority
Awkward withdrawal of the experimenter
Strengths Of Contemporary Study: Burger (2009)
Strong Internal Validity
No demand characteristics
No prior psychological knowledge from participants
Reliability
Burger is replicating aspects of Variation #5 (heart condition to test for empathy) and Variation #17 (model refusal) as well as Variation #8 (testing women). Burger followed Milgram’s script wherever possible and used the same confederates every time.
By filming the whole thing, Burger adds to the inter-rater reliability because other people can view his participants’ behaviour and judge obedience for themselves.
Application
Increase obedience in settings like schools, workplaces and prisons. Authority figures should wear symbols of authority (uniforms) and justify their authority with reference to a “greater good”.
Validity
Because the participants were paid fully in advance, we can be fairly sure it was social pressure that made them continue shocking, not a cost/benefit calculation about whether they personally would gain or lose money.
Ethics
The Experimenter was a trained clinical psychologist who could identify signs of distress and would stop the experiment if anyone seemed to be disturbed by what was happening.
The study was approved by the university Ethics Panel, who had the power to shut it down if it looked like anyone was being harmed.
Research supporting individualistic and collectivist cultures
Matustmoto 2007 : countries differ depending on experiences with immigration and either support multiculturalism or expect immigrant to adopt social norms
Guimond 2013 : countries that promote multiculturalism have lower levels of prejudice, Canada has lowest level and Germany highest
Becker 2012 : compared attitudes of 21 cultural groups finding that cultural norms were more influential than personal beliefs
Asch (1951) social conformity experiment - SUPPORTS SOCIAL IDENTITY THEORY
Procedure:
Asch used a lab experiment to study conformity, whereby 50 male students from Swarthmore College in the USA participated in a ‘vision test.’
Using a line judgment task, Asch put a naive participant in a room with seven confederates/stooges. The confederates had agreed in advance what their responses would be when presented with the line task.
The real participant did not know this and was led to believe that the other seven confederates/stooges were also real participants like themselves.
Each person in the room had to state aloud which comparison line (A, B or C) was most like the target line. The answer was always obvious. The real participant sat at the end of the row and gave his or her answer last.
At the start, all participants (including the confederates) gave the correct answers. However, after a few rounds, the confederates started to provide unanimously incorrect answers.
There were 18 trials in total, and the confederates gave the wrong answer on 12 trials (called the critical trials). Asch was interested to see if the real participant would conform to the majority view.
Asch’s experiment also had a control condition where there were no confederates, only a “real participant.”
Findings:
Asch measured the number of times each participant conformed to the majority view. On average, about one third (32%) of the participants who were placed in this situation went along and conformed with the clearly incorrect majority on the critical trials.
Over the 12 critical trials, about 75% of participants conformed at least once, and 25% of participants never conformed.
In the control group, with no pressure to conform to confederates, less than 1% of participants gave the wrong answer.
Conclusion:
Apparently, people conform for two main reasons: because they want to fit in with the group (normative influence) and because they believe the group is better informed than they are (informational influence).
SUPPORTS SOCIAL IDENTIFICATION (SIT) - Adopting the wrong answers to fit into the group. Strength of social influence.
Zimbardo 1971 stanford prison experiment
SITUATIONAL FACTORS AFFECTING OBEDIENCE
Aim: Whether the brutality reported among guards in American prisons was due to the sadistic personalities of the guards (i.e., dispositional) or had more to do with the prison environment (i.e., situational).
Procedure:
To study people’s roles in prison situations, Zimbardo converted a basement of the Stanford University psychology building into a mock prison.
He advertised asking for volunteers to participate in a study of the psychological effects of prison life.
The 75 applicants who answered the ad were given diagnostic interviews and personality tests to eliminate candidates with psychological problems, medical disabilities, or a history of crime or drug abuse.
24 men judged to be the most physically & mentally stable, the most mature, & the least involved in antisocial behaviors were chosen to participate.
The participants did not know each other prior to the study and were paid $15 per day to take part in the experiment.
Participants were randomly assigned to either the role of prisoner or guard in a simulated prison environment. There were two reserves, and one dropped out, finally leaving ten prisoners and 11 guards.
Prisoners were treated like every other criminal, being arrested at their own homes, without warning, and taken to the local police station. They were fingerprinted, photographed and ‘booked.’
Then they were blindfolded and driven to the psychology department of Stanford University, where Zimbardo had had the basement set out as a prison, with barred doors and windows, bare walls and small cells. Here the deindividuation process began.
When the prisoners arrived at the prison they were stripped naked, deloused, had all their personal possessions removed and locked away, and were given prison clothes and bedding. They were issued a uniform, and referred to by their number only.
Findings:
Within hours of beginning the experiment, some guards began to harass prisoners. Prisoners adopted prisoner-like behaviour.
Because the guards were placed in a position of authority, they began to act in ways they would not usually behave in their normal lives.
The “prison” environment was an important factor in creating the guards’ brutal behavior (none of the participants who acted as guards showed sadistic tendencies before the study)
Summary:
24 young, healthy, psychologically normal men were randomly assigned to be “prisoners” or “guards” in a simulated prison environment.
The experiment had to be terminated after only 6 days due to the extreme, pathological behavior emerging in both groups. The situational forces overwhelmed the dispositions of the participants.
Pacifist young men assigned as guards began behaving sadistically, inflicting humiliation and suffering on the prisoners. Prisoners became blindly obedient and allowed themselves to be dehumanized.
The principal investigator, Zimbardo, was also transformed into a rigid authority figure as the Prison Superintendent.
The experiment demonstrated the power of situations to alter human behavior dramatically. Even good, normal people can do evil things when situational forces push them in that direction.
SUPPORTS AGENCY THEORY (DESTRUCTIVE OBEDIENCE) → SITUATIONAL FACTORS
SHANAB & YAHYA (1978): A CROSS-CULTURAL STUDY OF OBEDIENCE
STRENGTHS OF INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES & SITUATION IN OBEDIENCE
This study was carried out at the University of Jordan in Amman. It followed a year after the 1977 study on children.
Sample: 48 university students, 24 male and 24 female.
The procedure replicated Milgram's baseline (1963) study, except for the following changes:
Gender Segregated - Female participants were paired with a female Experimenter; males were paired with a male Experimenter
Half of the participants were put into a Control Group; these participants were told it was their choice whether or not to shock the Learner
There were some interesting results:
There was no difference between male and female obedience
On average, 62.5% of the participants in the Experimental Condition (ordered to shock) obeyed by going to 450V - very similar to Milgram's baseline of 65%
However, 12.5% of the participants in the Control Group (free to choose) also went to 450V!
The reactions differed with the shaking, groaning, hysterical laughter and fainting in Milgram’s baseline study
12.5% of participants who received NO ORDERS still chose to shock a fellow human being unconscious and (for all they knew) to death.
Shanab & Yahya regard their results as supporting Milgram's Agency Theory and the idea that obedience is universal (found in every culture); they don't comment on the oddity of the over-obedient Controls.
STRENGTHS OF RCT
Application of superordinate goals in the real world
The European Union was formed to make a future war in Europe impossible by getting European countries to work towards superordinate goals through trade and moving labour forces.
The Olympic Movement also tries to promote peace by getting countries to share superordinate goals of sporting achievement that will make them less likely to compete over resources.
Allport’s Contact Hypothesis applies here, because prejudice will be reduced if group members get to mingle freely with the outgroup and question their own stereotypes. E.g. Multicultural exposure in schools.
Lots of Empirical Support
Robbers Cave Study and attitude surveys like the Michigan National Election Studies.
Key Question: HOW CAN KNOWLEDGE OF SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY BE USED TO REDUCE PREJUDICE IN SITUATIONS SUCH AS CROWD BEHAVIOUR OR RIOTING?
AO1:
Crowd behaviour means how people behave differently when in large groups. It is also known as “mob mentality” or “herd mentality”. It is believed to occur because people feel anonymous in crowds and lose their sense of identity.
Riots are when crowd behaviour involves lashing out at other people or property. Riots often express protest or a sense of grievance. The common types of riots include:
Police riot: when the authorities use disproportionate force on civilians; this includes when the police attack peaceful protestors, causing them to fight back
Prison riot: a concerted uprising by prisoners, either to express grievances or escape
Race riot: a riot involving violence between two ethnic groups, usually a majority group attacking a minority
Sports riot: a riot between fans of two teams, usually after a close defeat and almost always in the winning team’s city
Urban riot: a riot in an inner city area, triggered by poor living conditions or unemployment
Rioters often hide their identity with masks or scarves, but as more and more people join the riot, the risk of being identified goes down. This creates a “vicious circle” and the riot spreads. Riots are often contained when the police are present in enough numbers to increase the risk of being arrested again.
1 - In February 2015, Chelsea fans attended a match in Paris against the French team Paris Saint-Germain. Before the match, there was a racist incident on the Paris Métro. Souleymane Sylla was repeatedly and violently pushed off the carriage as he tried to board the train for being black.
A02:
The Chelsea fans saw themselves as an ingroup. Social identification meant they all joined in the chanting. Social comparison meant they saw Mr Sylla as an outgroup member, partly because he was French and their team was playing a French team but also because he was black and they were all white.
Agency Theory might also explain the racist behaviour, because Chelsea captain John Terry was perceived (by these fans) to have racist views. If the fans were in an Agentic State, they might have behaved in a racist way in obedience to John Terry.
Four fans were singled out a ringleaders and arrested. Social Impact Theory would explain how these men might have influenced the rest. In a crowded subway train, they would have been very close to each other and had a lot of social impact on the fans surrounding them. As fellow fans, they would have had what French & Raven call “referent authority”.
By inviting Mr Sylla to a Chelsea match, home fans are trying to bring him into their ingroup. This will make Mr Sylla feel less hurt and angry, because he will no longer see Chelsea fans or the English as an outgroup. It may also lessen racism in future, because the fans will see Black French people like Mr Sylla as “Chelsea fans” too and part of their ingroup. It is also an example of working together towards what Sherif calls a "superordinate goal".
EVALUATING SOCIAL IDENTITY THEORY (AO3)
Supporting Research:
SIT is supported by Tajfel et al.’s 1970 study into minimal groups. The research showed how boys will discriminate against an outgroup (even an outgroup that contains their own friends) and show favouritism to an ingroup (even an ingroup made up of strangers) and that this will happen when the group identity is based on something as flimsy as “being an over-estimator” or “preferring the art of Paul Klee”.
SIT also provides an explanation for why discrimination occurs even when the outgroup is no threat to the ingroup and there is no competition over resources. If self-esteem is based on social identity, then some people need to put down outgroups in order to feel good about themselves.
Opposing Research:
The “Minimal Groups” studies that support SIT have been criticised for using artificial tasks that lack ecological validity. However, Tajfel would contend that, if boys will be discriminatory over trivial and pointless tasks like this, how much more likely are they to discriminate when something important is at stake!
Another criticism of the studies is that adolescent boys are naturally competitive and the matrices looked like a competition of some sort. The boys may have assumed Tajfel wanted them to “win” at this game. When participants spoil an experiment by acting in the way they think (rightly or wrongly) that the researcher wants, this is called demand characteristics.
There are gaps in the theory, such as why some people cling to social identity for their self-esteem more than others. A theory of personality like Adorno’s Authoritarian Personality might explain this better.
Different Theory:
Sherif’s Realistic Conflict Theory (1966) stands in contrast to SIT. RCT claims that prejudice is produced by competition and happens when there is limited resources like food, money, jobs or status.
RCT is backed up by Sherif’s “Robbers Cave” study (1954) where boys showed outgroup discrimination when a tournament was arranged between them. This started with name-calling and food fights but became increasingly violent.
As with “Minimal Groups”, this is a study of schoolboys that may not generalise to adult behaviour. Unlike “Minimal Groups”, boys squabbling at a summer camp possessed much more ecological validity than ticking books of matrices.
Application:
Strategies that increase people’s sense of personal identity may reduce prejudice, especially if they raise self-esteem at the same time. Counseling (especially using Cognitive Therapy) may be one way of doing this. Religion sometimes gives people a sense of self-worth, but it can also create a very powerful sense of social identity and lead to some of the worst discrimination.
EVALUATING SOCIAL IMPACT THEORY (AO3)
Supporting Research:
There’s a growing body of research supporting Social Impact Theory. In addition, the theory also makes sense of a lot of Classic studies from the ‘60s and ‘70s that used to seem unrelated – like Latané & Darley (1968) into diffusion of responsibility, Tajfel (1970) into intergroup discrimination and Milgram (1963) into obedience. In hindsight, all of these studies can be seen as looking at different aspects of Social Impact.
There have been more recent additions to Social Impact Theory. Latané et al. (1996) developed Dynamic Social Impact Theory to pay attention to how minorities and majorities influence each other, such as how people tend to change their views to match the group they are in but why they sometimes “stick to their guns”.
Opposing Research:
Social Impact pays a lot of attention to the characteristics of the person giving the orders but not much to the person receiving them. For example, there may be personality types that are particularly compliant (go along with anything) or rebellious. A person may be happy to go along with some sorts of orders but draw the line at others – such as orders that offend them morally or embarrass them socially.
A similar problem is that Social Impact Theory treats people as passive. It proposes that anybody will do anything if the right amount of Social Force is brought to bear on them. However, people sometimes obey orders while at the same time subverting them. An example might be Oskar Schindler who handed Jewish employees over to the Nazis during WWII while secretly helping many others to escape.
Different Theory:
Milgram’s Agency Theory is very simplistic compared to Social Impact Theory. Milgram suggests we have evolved to go into an obedient mental state around anyone we recognise as an authority. There’s not much evidence for this in general. Social Impact Theory suggests many features of Agency Theory are true – that the strength (S) of the authority figure is an important predictor of how obedient someone will be – but there are other situational factors as well, like the numbers of people involved (N) and the immediacy (I) of the orders.
However, Agency Theory explains some things better than Social Impact Theory. For example, in Variation #10, obedience was lower in a run-down office compared to Yale University. Milgram explains this through the prestige of the setting adding to the authority figure’s status, but this is hard for Latané to give a mathematical value to. Similarly, Milgram has an explanation for the shaking and weeping his participants engaged in – moral strain. There’s no discussion of moral strain in Social Impact Theory, which views people as either obeying or disobeying and nothing in between.
Application:
The idea of a mathematical formula to calculate Social Impact is very useful. Latané believes that, if you know the number (N) of people involved and the immediacy (I) of the order and the strength (S) of the authority figure, you can calculate exactly how likely someone is to obey (i) using the formula i = f (SIN). This means you can predict whether laws will be followed, whether riots will break out and whether 9B will do their homework.
The theory suggests if you want to get people to obey, you need to direct Social Force at them when they are in small groups and ideally stop them getting together into large groups. This is why some repressive governments try to stop people using social media and gathering for public meetings. Because orders need to be immediate it is important to repeat them often and put them on signs, TV adverts and regular announcements.
Social Impact Theory - Diffusion of Responsibility
Being part of a large group makes people feel anonymous and this reduces their feelings of responsibility. It might make them less likely to obey orders.
Latané & Darley (1968) carried out a famous experiment into this.
Participants sat in booths discussing health issues over an intercom. One of the speakers was a confederate who would pretend to have a heart attack. If there was only one other participant, they went for help 85% of the time; this dropped to 62% if there were two other participants and 31% if there were 4+.
No one was giving orders in this study, but the rule “go and get help when someone collapses” is a sort of order that is present all the time in society. Following these sort of social rules is called prosocial behaviour and breaking the rules is antisocial behaviour. Social Impact Theory explains prosocial behaviour as well as obedience.
Factors Affecting Obedience
SIT - Strength & proximity of authority figure. Role of Allies (exposure to role models can encourage disobedience)
Culture - Individualistic and Collectivist & PDI