11 ATAR human bio: human reproduction
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Spermatogenesis
- the production of SPERMATOZOA (Sperm).
- occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
- takes about 72 days and occurs continuously after puberty.
- produces four spermatozoa from each primary spermatocyte.
Spermatogenesis- the process (1)
Seminiferous tubules lined with SPERMATOGONIA (singular = spermatogonium) which are immature 'mother' sperm cells + contain diploid no. of chromosomes (46 chromatin threads).
- At puberty, spermatogonia begin dividing by mitosis to provide continuous source of new cells for production of spermatozoa.
- Some spermatogonia pushed inwards towards centre (lumen) of tubule, where they undergo a growth phase ('interphase') to become PRIMARY SPERMATOCYTES.
Spermatogenesis- the process (2)
- Primary spermatocytes undergo first stage of meiosis to become SECONDARY SPERMATOCYTES = haploid
- The secondary spermatocytes undergo second meiotic division= produces 4 haploid (23 'half X' chromosomes) SPERMATIDS.
- Spermatids then mature into SPERMATOZOA.
- During this time most of the cytoplasm is lost and a tail containing contractile material forms.
- Spermatozoa nourished by SERTOLI CELLS= also act as phagocytes by engulfing the cytoplasm which is lost.
Sperm structure
- 0.06mm long
- HEAD: contains DNA, at tip is a fluid filled vesicle which contains enzymes to break down the layer of cells surrounding ovum.
- MIDDLE: contains mitochondria (respiration occurs to provide sperm w energy for movement)
- TAIL: swimming motions to propel the sperm.
- only viable for around 72 hrs once they left testes.
- They receive their nourishment from the semen in which they are suspended.
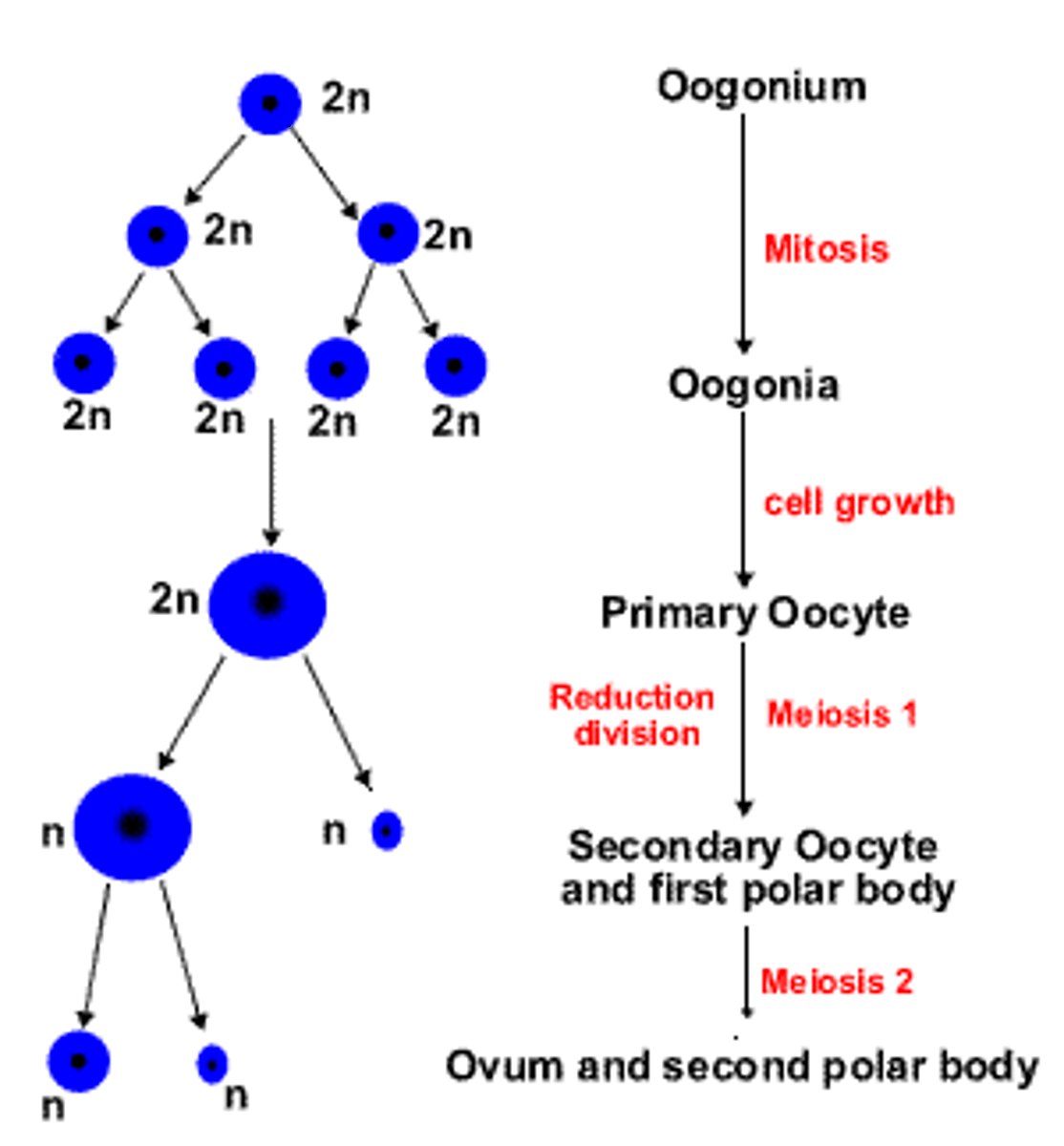
Oogenesis
- the production of OVA/eggs
- occurs in the ovaries and takes approx one month."
- events of development of an ovum = Ovarian cycle.
- produces a single ovum from each primary oocyte
Oogenesis- the process (1)
- before female is born, OOGONIA (egg 'mother' cells) develop in the ovaries, they're diploid (46 chromatin threads) and divide by mitosis.
- By birth, each ovary contains several hundred thousand oogonia which have undergone a growth phase ('interphase') to become PRIMARY OOCYTES.
- primary oocytes begin Prophase I but pause halfway through and stay paused until puberty. They are surrounded by a single layer of cells which form the PRIMARY FOLLICLE.
- As follicle matures, primary oocyte completes 1st meiotic division to produce two haploid cells
- these 2 haploid cells aren't equal in size, each receive half the chromosomes but one receives nearly all the cytoplasm while the other receives little:
Oogenesis- the process (2)
- larger cell= SECONDARY OOCYTE, goes on to become the ovum, smaller cell = 1st POLAR BODY, eventually disintegrates but may also undergo 2nd meiotic division to produce two more polar bodies
- secondary oocyte immediately commences 2nd meiosis but pauses again at M II where ovulation occurs as follicle ruptures and ovum is expelled.
- secondary oocyte enters the uterine tube, and if fertilised by a spermatozoon then completes meiosis.
- 2nd division of secondary oocyte also produces 2 haploid cells of unequal size (23 'half X' chromosomes):
- larger with more cytoplasm= OOTID, eventually matures into the OVUM, smaller one= SECOND POLAR BODY, all polar bodies disintegrate
Variation
- the differences between members of a species.
- Sources include: Sexual reproduction, Random fertilisation, Random assortment of chromosomes, Crossing over, Non-disjunction, Environment
Sexual reproduction + random fertilisation
Sexual reproduction- Mother and Father each contribute 50% of Baby's DNA= mix of parents features + their own unique genome.
Random fertilisation- Every egg and sperm cell carries different genetic material, no way of telling which sperm from the male parent will fertilise which egg from the female parent + which gametes survive
Random assortment of chromosomes
- When homologous pairs of chromosomes separate in Metaphase I, it is random and independently of one another ie. the way one pair separates is unaffected by the way any of the other pairs separate.
- Thus when a sperm fertilises an egg, the resulting zygote contains a combination of genes arranged in a unique order.
- Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes = 2^23 = approx 8.4 mil possible combinations
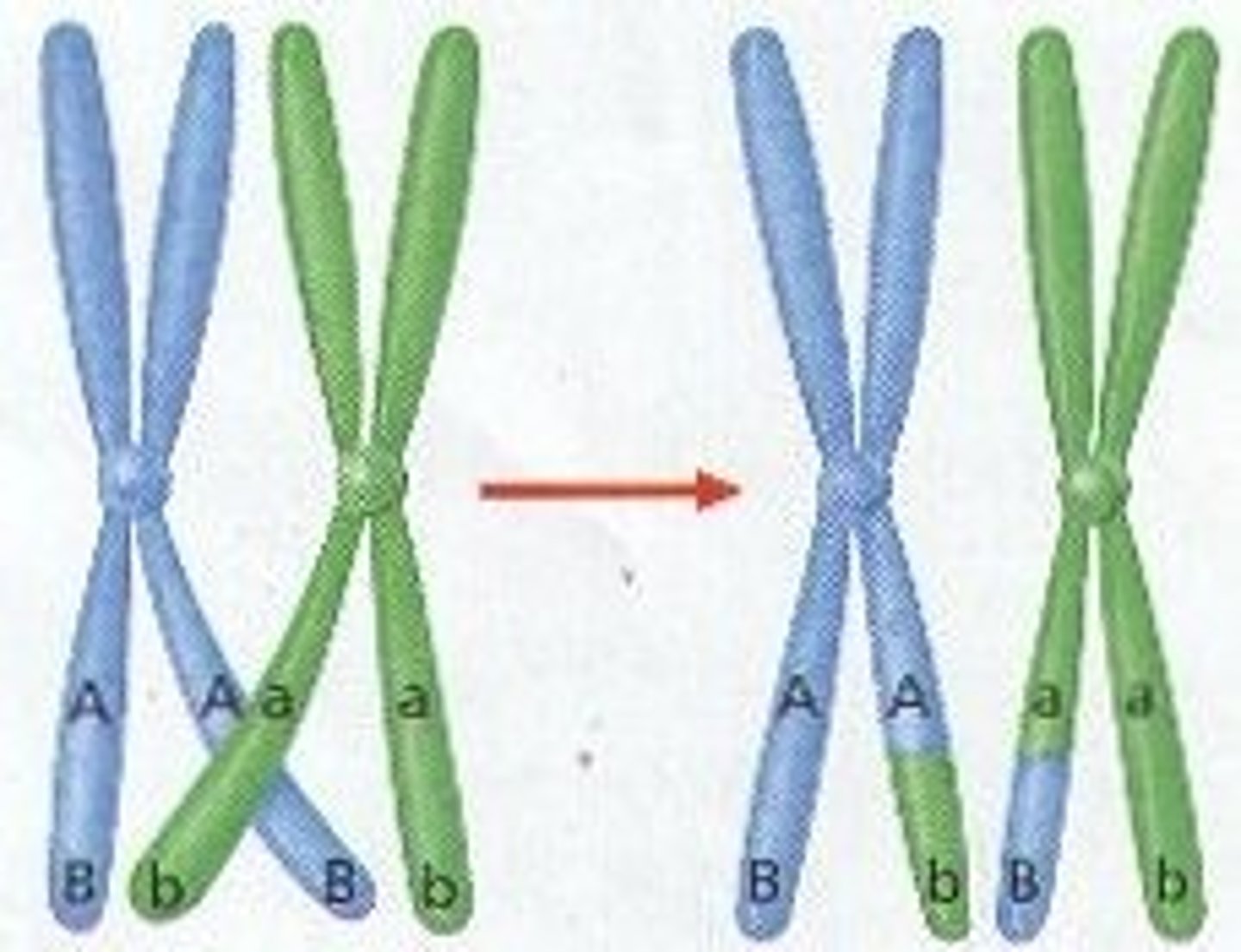
Crossing over
- During Prophase I matching regions on homologous chromosomes may break and then reconnect to the other chromosome.
- CHIASMA= point where two chromatids cross
- This results in new combinations of genes along the chromosome (so chromosomes passed onto offspring are not identical to those of the parents) = GENETIC VARIATION between gametes.
- result of having a new combination of alleles is termed RECOMBINATION.
Non-disjunction
- when error occurs during the second meiotic division= an abnormal number of chromosomes in the daughter cells.
- One daughter cell may have more/less chromosomes than it should = severe birth defects/often miscarriage.
TRISOMY - where an individual inherits an extra copy of a chromosome.
MONOSOMY - where an individual is missing a chromosome.
- PARTIAL Trisomy/Monosomy: individual may have only a part extra/missing of the chromosome.
- Down's Syndrome
- have an extra copy of chromosome 21.
- Affected people have varying degrees of mental retardation, short stature, and a flattened facial profile.
- Turner's Syndrome
- Females w TS lack a second X chromosome.
- they are usually short and have a number of abnormal physical features.
- Their ovaries never develop so they are infertile, and never menstruate.
- Klinefelter's Syndrome
- Males w KS have an extra X chromosome.
- they do not produce enough testosterone= underdeveloped secondary sex characteristics, breast enlargement, small testes and infertility due to lack of sperm.
Environment
- A personʼs characteristics/phenotype, can be significantly impacted by the interaction of their genes with the environment they live in.
- epigenetic factors (smoking, alcohol intake, exercise) can actually permanently affect the phenotype of an individual without changing the genotype.
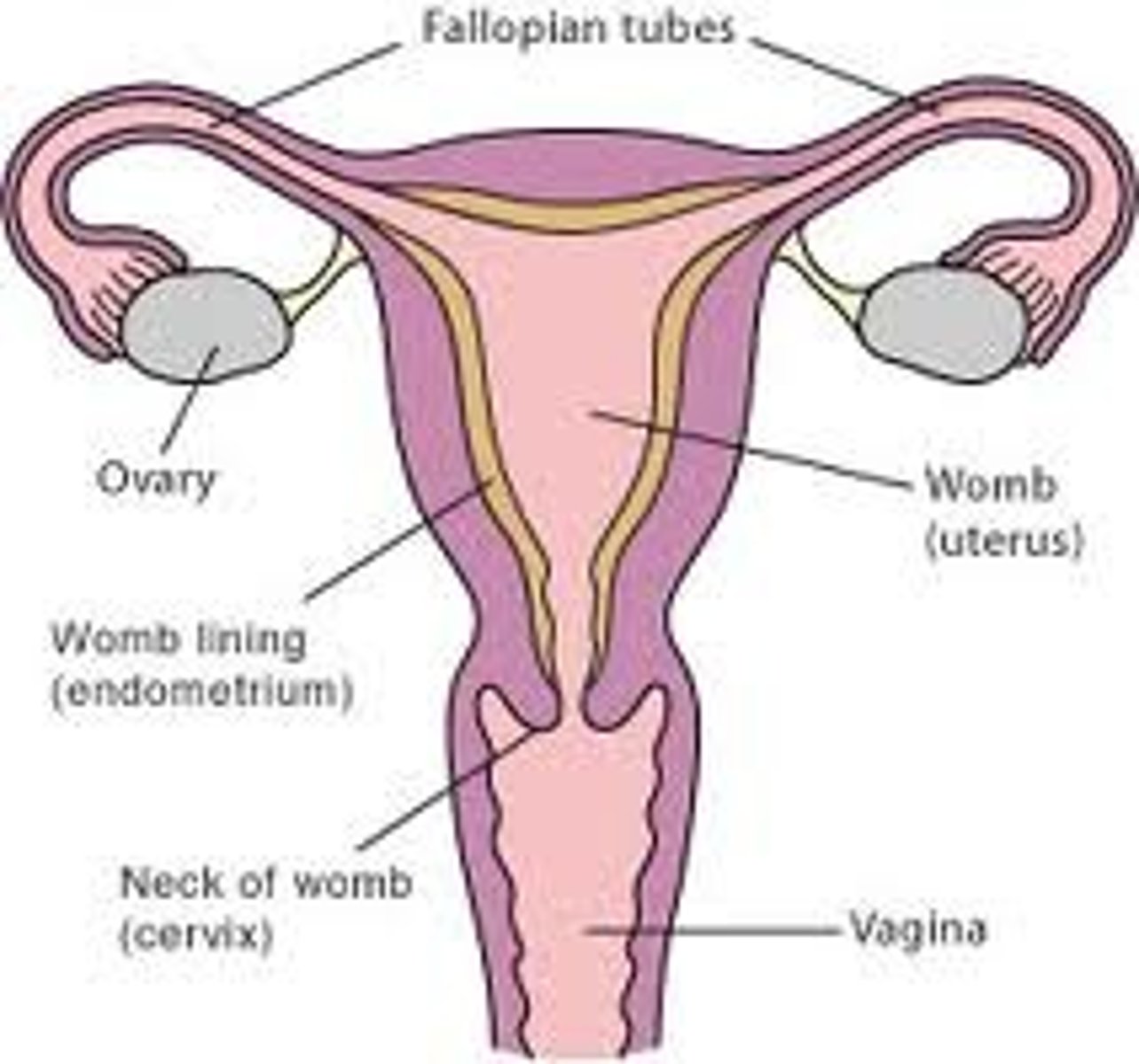
The Ovaries
- The primary sex organs of the female
- almond shaped, about 3cm long, supported by ligaments.
- produce the female gametes called OVA or EGGS.
- Each ovary is composed of CT called the STROMA, which is surrounded by a layer of cells containing germ cells enclosed in follicles waiting to develop.
The Uterine Tube
- When an egg is expelled from an ovary, it enters the UTERINE TUBE (also called Fallopian tube or Oviducts)
- carries the egg from the ovary to the uterus
- At end of each tube there are finger-like projections called FIMBRIAE which guide the egg into the tubes.
- tube walls = smooth muscle, lined with CILLIATED EPITHELIUM (beating cilia + contractions of smooth muscle, carry egg towards the uterus)
Uterus (womb)
- a hollow pear shaped organ.
- walls= smooth muscle with soft mucous membrane lining called the ENDOMETRIUM
- protects and nourishes the developing foetus during pregnancy.
- At lower end (or neck) of the uterus is the CERVIX.
Vagina
- cervix protrudes into the VAGINA = a muscular canal that leads outside of the body.
- lined with mucous membranes, 10cm long, but stretches considerably to form birth canal during childbirth.
Exterior region of female reproductive system
- vagina opens to exterior in a region called the VULVA.
- LABIA= fleshly folds of skin surround opening of vagina:
- LABIA MAJORA= made of fat and fibrous tissue, outer surfaces covered with hair after puberty, inner surfaces= smooth + moist from glands that produce oily secretions.
- LABIA MINORA= 2 smaller folds of skin w/o fat + pubic hair, sit beneath and between the labia majora, surround the space where urethra and vagina open.
- CLITORIS= small structure, contains erectile tissue, many BVs + nerves, found at upper end of labia minora, sensitive to touch (equivalent to penis in male)
Pathway ovum travel
OVARY → UTERINE TUBE → UTERUS → CERVIX → VAGINA
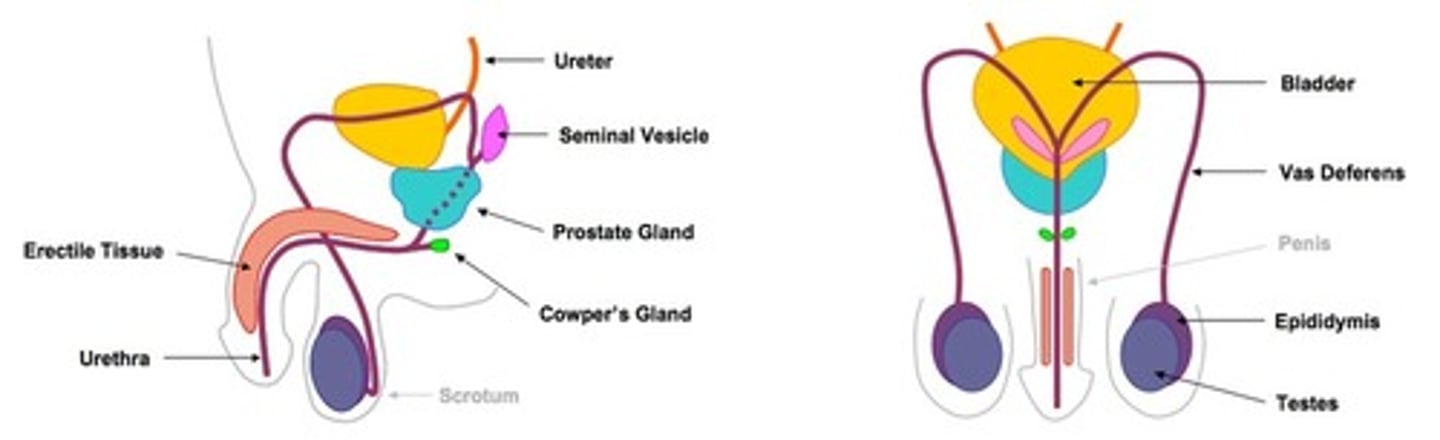
The Testes
- primary sex organs of the male, oval shaped, that produce the sperm
- held and supported in a skin covered sac called the SCROTUM (divided into 2 sacs, each contains a testi)
- testes lie outside the body to prevent overheating as temp needs to be 2°C below normal body temp to produce sperm
- In cold temps, smooth muscle fibres in the wall of the scrotum contract to move the testes closer to the body.
Seminiferous Tubules, epididymis, vas deferens
- each testes contains 200-300 LOBULES filled with tubules called SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES= contain the immature sperm cells that mature into sperm.
- In between tubules are clusters of INTERSITIAL CELLS that secrete the male hormone testosterone.
- tubules of each lobule join to form short straight tubules that join into ducts + eventually leave testis + enter the EPIDIDYMIS= sits against the rear surface of the testes, highly folded tubule (5-6m unravelled)= large SA for sperm storage while they mature
- epididymis becomes the VAS DEFERENS= carries sperm away from the testes
- these vas deferens join to URETHRA= carries both urine + sperm out through the penis.
Semen
- sperm must be suspended in a liquid called SEMINAL FLUID/SEMEN, to successfully transfer it to the female
- nourishes and aids the transport of sperm
-a mixture of secretions from 3 glands:
1) SEMINAL VESICLES
2) PROSTATE GLAND
3)BULBO-URETHRAL GLANDS (or COWPER'S GLANDS)
1) SEMINAL VESICLES
- pouch like organs
- 5cm in length
- sit behind bladder.
- Secrete thick fluid rich in sugars for nutrients.
- Makes up 60% of semen.
2) PROSTATE GLAND
- located where the 2 vas deferens join the urethra.
- secretes a thin, milky, alkaline fluid which helps activate the sperm and neutralises the acidity of the male urethra and female vagina.
3)BULBO-URETHRAL GLANDS (or COWPER'S GLANDS)
- 2 small yellow glands about the size of a pea.
- Located beneath prostate on either side of the urethra.
- secrete a clear mucous which is carried to urethra by a duct from each gland.
- Acts as a lubricant, most of it precedes the emission of seminal fluid and only a small amount is included in semen.
The penis
- urethra carries semen and urine through the PENIS to a slit-like opening at the tip
- penis= used to transfer sperm to the female
- contains CT = ERECTILE TISSUE that has a very rich blood supply, has number of sponge-like spaces which fill with blood during sexual arousal + causes the penis to enlarge, stiffen and become erect.
Pathway sperm travel
TESTIS → EPIDIDYMIS → VAS DEFERENS → 3 SEMEN PRODUCING GLANDS → URETHRA
Hormonal regulation
- Endocrine glands regulate ovarian and menstrual cycles (+ other features of reproductive systems)
- they secrete hormones (chemical messengers) into extracellular fluid + are transported via blood to target organs which it'll affect
- Pituitary gland located below brain and above mouth roof + secretes 2 hormones targeting both gonads: Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinising Hormone (LH).
Female hormones
- FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE
- LUTEINISING HORMONE
- OESTROGEN
- PROGESTERONE
- HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN (HCG)
- LACTOGENIC HORMONE (or PROLACTIN)
- OXYTOCIN
Male hormones
- FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE
- LUTEINISING HORMONE
- TESTOSTERONE
Follicle stimulating hormone (male + female)
Female:
- Target organ= follicles of ovaries
- Stimulates development + maturation of ovarian follicle.
- ovarian follicle secretes its own hormone - Oestrogen.
- Secretion of FSH reduces as Oestrogen levels increase
Male:
- Target organ= Seminiferous tubules
- Stimulate spermatogenesis in seminiferous tubules
Luteinising hormone (male + female)
Female:
- Target organ= cells of ovaries
- Promotes final maturation of ovarian follicle, ovulation + formation of corpus luteum.
- Maintains Corpus Luteum (secretes its own hormones - progesterone + oestrogen)
- Gradual reduction in LH secretion as Progesterone levels increase
Male:
- Target organ= Interstitial cells of testes
- Stimulates production of male sex hormone (testosterone) in the interstitial cells of the testes
Oestrogen
- Target organ = various
- Source= ovarian follicle and corpus luteum.
- Promotes development + maintenance of female reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics.
- Prepares the follicle for release of the egg.
- Controls growth of endometrium after the degeneration and menstruation.
Progesterone
- Target organ= Uterus, Placenta and Breasts
- Source= corpus luteum and placenta (if pregnancy occurs).
- Stimulates endometrial growth and maintains endometrium
- Development and maintenance of placenta.
- Development of milk-secreting glands.
Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (hCG)
- Target organ= Corpus Luteum
- Source= developing placenta.
- Maintains corpus luteum until the placenta itself can secrete oestrogen and progesterone.
- Once this occurs the corpus luteum will degenerate
Lactogenic Hormone/Prolactin
- Target organ= Breasts
- Source= pituitary gland.
- Important in the preparation + maintenance of milk production.
Oxytocin
- Target organ =Uterus/Breasts
- Source= Pituitary gland.
- Stimulates contraction of smooth muscle of uterus during labor.
- Promotes contraction of muscle cells surrounding breast lobules for milk letdown.
Testosterone
- Target organ = various
- Source= interstitial cells of the testes
- Development and maintenance of male reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics
- Stimulates spermatogenesis
Secondary Sexual Characteristics
- characteristics that are associated with a person's sex but not directly involved in sexual reproduction.
- Oestrogen and Testosterone bring on the development of these at onset of puberty
- Both sexes- pubic + armpit hair
- Female- enlarging of breasts, broadening of hips, growth of pelvic bones, deposition of fat around these areas.
- Male- facial hair, increase in size of larynx, lengthening of vocal cords = deeper voice.
The Ovarian Cycle
- the series of events that occur in the ovaries during one cycle
- includes the maturation of the ovum and its release into the uterine tube.
- Also associated with the development of the follicles in the ovary and the formation of the corpus luteum
- length of 1 cycle= 20-40 days, avg is 28 days.
- Follicular phase= days 1-13, Ovulation. =Day 14, Luteal phase= days 15-28
The Ovarian Cycle Process (1)
- each immature eggs/primary oocytes are surrounded by a single layer of cells = PRIMARY FOLLICLE
- at puberty, this follicle divides + enlarges = SECONDARY/DEVELOPING FOLLICLE
- several secondary follicles may start development but usually only 1 completes development, others break down + are reabsorbed
- cells of follicle secrete a fluid into space surrounding the primary oocyte, as more fluid is secreted = follicle enlarges + gradually moves towards the ovary's surface
- Once it reaches the surface, it bulges out the side of the ovary, + now referred to as a MATURE or GRAAFIAN FOLLICLE.
The Ovarian Cycle Process (2)
- maturation of primary follicle to a mature follicle = 10 -14 days
- OVULATION= when mature follicle ruptures + bursts it to release the secondary oocyte (egg)
- egg released in direction of the uterine tube where FIMBRIAE form a funnel over the ovary
- beating motion of cilia in the tube create a current that sweeps the egg into the tube.
- egg continues to be swept down tube towards uterus by the cilia and muscular contractions of the tube walls.
- ovum = viable to be fertilised for 12-24 hrs after ovulation.
- after ovulation, follicle ruptures + blood within forms a clot
- clot is absorbed by remaining follicle cells, which enlarge and become a yellow cream colour= CORPUS LUTEUM
The Ovarian Cycle Process (3)
- corpus luteum releases Oestrogen + Progesterone= influence development of the endometrium lining of the uterus.
- If fertilisation does not occur= 8 -10 days after ovulation, CL begins to degenerate into a fibrous mass of scar tissue= CORPUS ALBICANS which eventually disappears + new ovarian cycle begins.
- If fertilisation does occur= CL continues to develop + ovarian cycles cease. The CL reaches peak of its development around 3rd month of pregnancy (during this it secretes oestrogen and progesterone until placenta can do so itself) After this is begins to degenerate.
- Ovarian cycles usually only resume after breastfeeding has ceased
The Menstrual Cycle
- while ovarian cycle occurs in the ovaries, the MENSTRUAL CYCLE is occurring in uterus to prepare for pregnancy if ovum is fertilised
- outlines the changes in uterine lining (endometrium) during 1 month
- 3 phases: Proliferative, Secretory, Menses
- When menstruation first begins in the female= MENARCHE = onset of puberty
- MENOPAUSE = period where processes that occurred at puberty are reversed, changes occur usually between 45-55 where menstrual cycle becomes irregular until it eventually ceases.
1. Proliferative phase
- approx days 7-14
- while the follicle is developing, the endometrium in the uterus becomes thicker + softer to prepare for implantation of a fertilised egg (stimulated by Progesterone)
- also an increase in the number of blood vessels and mucus-secreting glands
2. Secretory phase
- approx days 14-28
- After ovulation the endometrium continues to thicken and glands begin to secrete a watery mucus rich in glycogen to provide nutrients for a fertilised egg
3. Menses
- days 1 to approx 7
- If fertilisation doesn't occur, the corpus luteum degenerates, = less progesterone produced that stimulates endometrial = endometrium begins to breakdown.
- about 14 days after ovulation, blood from broken down capillaries, mucus secretion and cell debris are lost through the vagina= MENSTRUATION.
- onset of menstruation is taken to be DAY 1 of the menstrual cycle.
Major stages of menstrual cycle
- Menstruation (day 1-4) - the endometrium is shed
- Preovulation (day 5-12) - endometrial repair begins, development of ovarian follicle.
- Ovulation (day 13-15) - rupture of mature follicle releases egg.
- Secretion (day 16-20) - secretion of watery mucous by glands of endometrium, cervix and uterine tubes. Movement and breakdown of unfertilised egg. Development of corpus luteum
- Premenstruation (day 21-28) - degeneration of corpus luteum, deterioration of endometrium.
Sexual intercourse- male occurrences
- for fertilisation to occur, sperm need to be brought into contact with the ova via intercourse
- penis becomes enlarged + firm due to blood rushing into spaces of erectile tissue= ERECTION
- rhythmic contractions of epididymis, vas deferens + 3 glands occur when sexual stimulation of penis is sufficiently intense
- these contractions propel contents. of duct + gland into urethra + out of body= EJACULATION
- ejaculated material= semen containing sperm (3mL of semen w/ 200-300 mil sperm per ejaculation)
- w/ ejaculation comes an ORGASM= ↑ HR, ↑ BP + breathing, pleasurable sensations
Sexual intercourse- female occurrences
- when female is sexually stimulated, erectile tissue of vaginal opening fills w/ blood + secretions of mucus from glands ↑ = lubricates epithelial lining of vagina
- ORGASM/CLIMAX= when sexual arousal in female reaches sufficient intensity, similar to male but no ejaculation, may be ↑ cervical mucus
- female doesn't need to reach climax for fertilisation to occur
Fertilisation (1)
FERTILISATION= the fusion of a sperm and egg
- INSEMINATION= process where the sperm are released into the vagina
- Once within vagina, sperm travel through the cervix and uterus, into the uterine tubes (very quickly due to swimming motions of sperm + muscular contractions of uterus + tubes)
- sperm mortality rate = very high as of the hundreds of millions that are deposited, only few thousand reach uterine tubes
- fertilisation occurs in the u.tubes when egg is 1/3 way down tube
- mature egg (secondary oocyte) is surrounded by layer of follicular cells = CORONA RADIATA, held together by an acid
Fertilisation (2)
- sperm work together to break down the corona radiata using their tips, allowing one sperm to accomplish fertilisation.
- entrance of one sperm stimulates formation of fertilisation membrane= prevents entrance of any more sperm.
- once sperm has entered the egg (the secondary oocyte), it is stimulated to complete the second meiotic division.
- once the sperm enters egg, the tail is absorbed + head begins to move through the egg's cytoplasm in the form of a MALE PRONUCLEUS
- nucleus of the egg develops into FEMALE PRONUCLEUS, fuses w/ male pronucleus to form a single nucleus with the diploid number of chromosomes = ZYGOTE (fertilised egg)
STIs
- sexually transmitted infections, previously known as STDs are infections that can be spread during sexual contact.
- caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites passed from an infected person to another
- Young people are especially at risk of an STI, in Aus 3/4 of STI cases occur in those 15-29yrs old
- no vaccine readily available for majority of STIs
- Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis, Genital herpes, Genital warts, Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Trichomoniasis, Pubic lice and scabies
Chlamydia
• Most common treatable STI, with increasing notifications annually.
• Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, a bacterium that reproduces only in living human cells.
• Risk highest in 15-24 year olds, with 80% of cases occurring in this age group.
• symptoms: girls= burning sensation, unusual vaginal discharge, lower belly pain. boys= Whitish discharge from penis, burning/pain during urine passage, irritation/soreness around urethra.
• Potential outcomes: pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in females, infertility in males and females.
• Diagnosis: Urine test, more accurate diagnosis with swab from vagina, cervix, anus, or penis which is tested in lab
• Treatment: Antibiotics.
Gonorrhoea
• Mainly affects excretory and reproductive systems, rectum, eyes, and throat.
• Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium transmitted during sexual intercourse.
• More common in women aged 15-19, 3/4 of cases occur in 15-34 age group.
• Symptoms= male- yellow discharge from the penis + burning sensation during urine passing, females= no symptoms, some unusual vaginal discharge, pain when urinating, lower belly pain
• Untreated gonorrhoea can lead to PID in females and infertility, males experience sore testes, pregnancy can be severely affected.
• Treatment= antibiotics.
Syphilis ('the pox')
• caused by a thin, flexible, spiral-shaped bacterium, Treponema pallidum
• Less common sexually transmitted infection, 7x more common in men aged 40-44.
• Serious disease affecting brain and organs.
• Can persist for years without treatment.
• 3-12 wks: Painless sore on genitals, anus, or mouth, disappearing in a week or two.
• 6-12 months: Rash on palms, hands, feet, face + other body parts, sometimes hair loss.
• 2yrs: Damage to nervous system, brain + blood system
• Treatment= Prescription antibiotics- early treatment can lead to cure.
HIV- Human immunodeficiency virus (AIDS)
• HIV is a retrovirus with an RNA core, unable to reproduce independently, infects T-lymphocytes WBCs, producing millions of copies of itself.
•Some infected T-lymphocytes become a reservoir of HIV.
• HIV infections progress through three stages:
1. Acute infection: Rapid replication and high HIV levels, causing flu-like symptoms.
2. Chronic infection: Asymptomatic, virus continues to multiply at a low rate, lasting 10+ yrs
3. AIDS: High viral load and low helper T-lymphocytes.
• Symptoms include fever, headache, tiredness, and rash.
• Untreated HIV can lead to AIDS, a condition where the immune system is damaged.
• Treatment = currently limited to daily medications for HIV positive individuals which inhibit the reproductive cycle of the virus
Genital Herpes
• caused by the Herpes simplex virus
• Initially, no symptoms occur, Later symptoms= painful, tingling, or itching blisters or ulcers, aching muscles, and fever.
• Despite healing, the virus remains in the infected skin's nerves, causing more outbreaks.
• Treatment: No cure, medications can reduce outbreak duration and severity.
Genital Warts
• caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV)
• usually found on the genital area - vagina, labia, cervix or penis
• may be flat, raised or cauliflower-like growths
• Warts can be hidden in vagina or penis, posing risk to unaware individuals
.• Newborns can be infected during birth canal passage.
Pubic lice and scabies
• Pubic lice (crabs)= small parasites found in pubic hair.
• Spread through direct skin-to-skin contact and contact with infected person's bedding.
• symptoms= itching and visible eggs.
• Treatment= prescription insecticide lotions or shampoos, all bed linen, towels, and clothing must be washed in hot water.
• Scabies (the itch) caused by a mite laying eggs under the skin.
• Treatment= prescription anti-scabies lotions.
• The itch usually lasts for four weeks after treatment.
Trichomoniasis
• Infection caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, spread via vaginal intercourse, hence condom use is recommended.
• Induces vaginal mucous membrane inflammation in women and urethra in men.
• Symptoms= vaginal discharge and severe itch in women, me= w/o symptoms, but can transmit it to female partners.
• treatment= antibiotics.
Natural contraception methods + spermicides
- Abstinence- most effective, no intercourse at all
- Withdrawal- unreliable, requires self control, Does not protect against STI's
- Spermicides= creams, tablets, pessaries/aerosal foam, contain substance that immobilises + destroys sperm, react w moisture in vagina to form CO2 gas bubbles = physical barrier to sperm, very unreliable alone
Hormonal contraception methods for women (all very reliable)
- Combined pill: Stops ovaries from releasing egg, thickens mucus at cervix to stop sperm from moving into the uterus, lighter periods + menstrual pains but may cause bleeding between periods
- Mini pill: same as combined, must be taken everyday, increased risk of ectopic pregnancy as it makes it difficult for fertilised egg to implant
- Injections (Depo-Provera and depo-relovera): forms of the hormone injected into upper arm/buttock, works similarly to mini pill
- Implanon NXT: delivers progestogens, soft plastic stick 4 cm long inserted beneath skin on upper arm, contraception for 3yrs, easily removed
- NuvaRing: delivers Oestrogen + progesterone, soft plastic placed in vagina for 3 wks, prevent ovulation by stopping sperm from entering and implanation occurring
Intrauterine devices + Sterilisation (vasectomy + tubal ligation)
- IUD's: plastic/copper plastic devices inserted into uterus, releases progestogen hormone= endometrium thins= unsuitable for implantation, stops sperm entering
- Vasectomy: removal of a small segment of each vas deferens
- Tubal ligation: removal of a small segment of each uterine tube, sperm cant reach egg, permanent nearly 100% effective but cannot be reversed
Mechanical barriers contraception methods
- Condom: thin latex rubber rolled onto erect penis, prevents semen from entering vagina + provide protection against STIs, only used once, needs careful timing to be effective
- Femidom: lubricated sheath lining vagina w ring at each end, effective + protects against STIs
- Diaphragm: thin rubber cap fits across top of vagina, left in for at least 6 hrs after intercourse, used w/ spermicides to increase effectiveness, stop the sperm entering the uterus
- Cervical cap: smaller than diaphragm, fits directly over cervix