DPT 746 Week 1 Lecture Notes Pt. 1
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Brain
AKA (Encephalon). Contains;
Forebrain
Midbrain
Hindbrain
Forebrain
Cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus
Cerebrum
Part of your brain that starts and manages conscious thoughts; meaning, things that you actively think about or do.
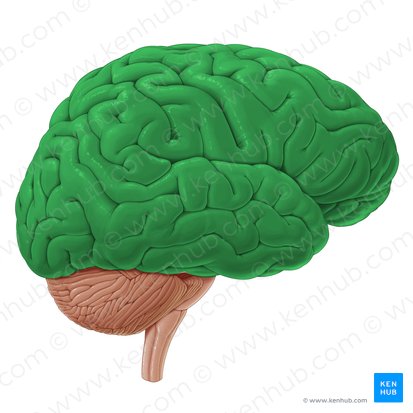
Thalamus
Only 1
Acts as the brain's central relay and processing center, receiving most sensory and motor information (except olfaction) before sending it to the cerebral cortex for higher-level processing
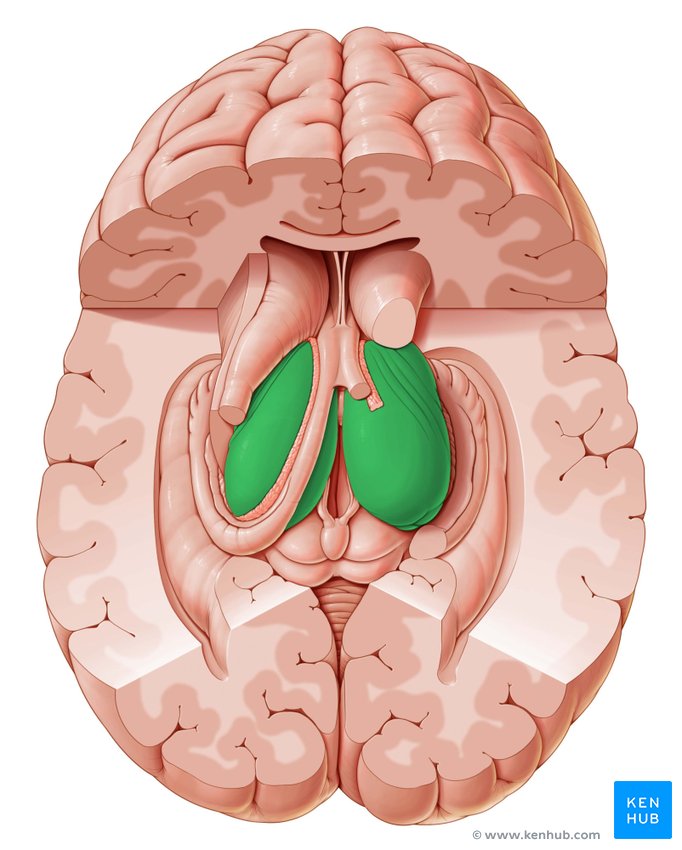
Hypothalamus
2 of them
Maintaining body temperature, controlling appetite and thirst, managing sleep-wake cycles, regulating emotional responses, and influencing sexual behavior
Spinal cord
AKA myelon
Midbrain
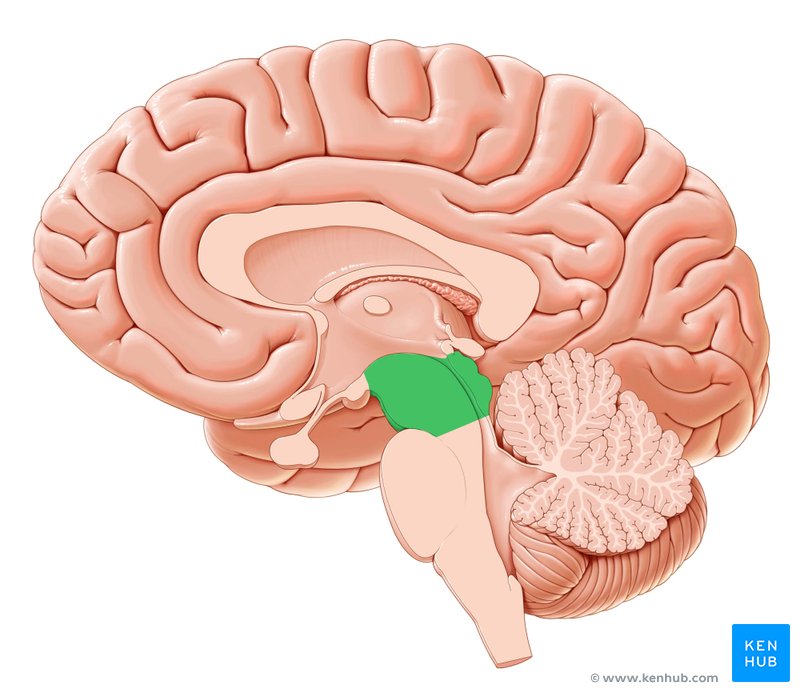
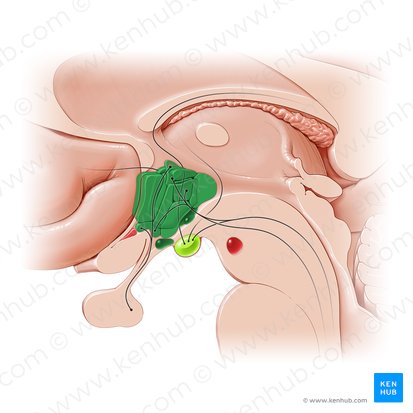
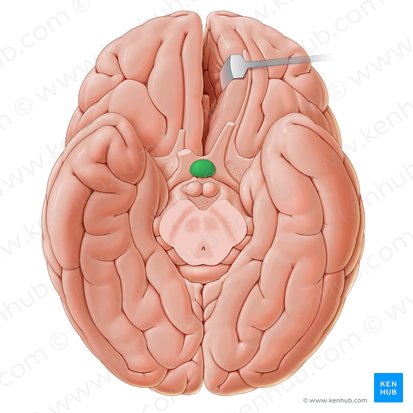
Pituitary gland
Hindbrain
Pons, medulla, cerebellum
Pons
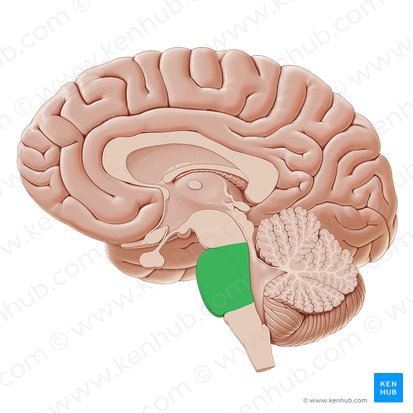
Medulla oblongata
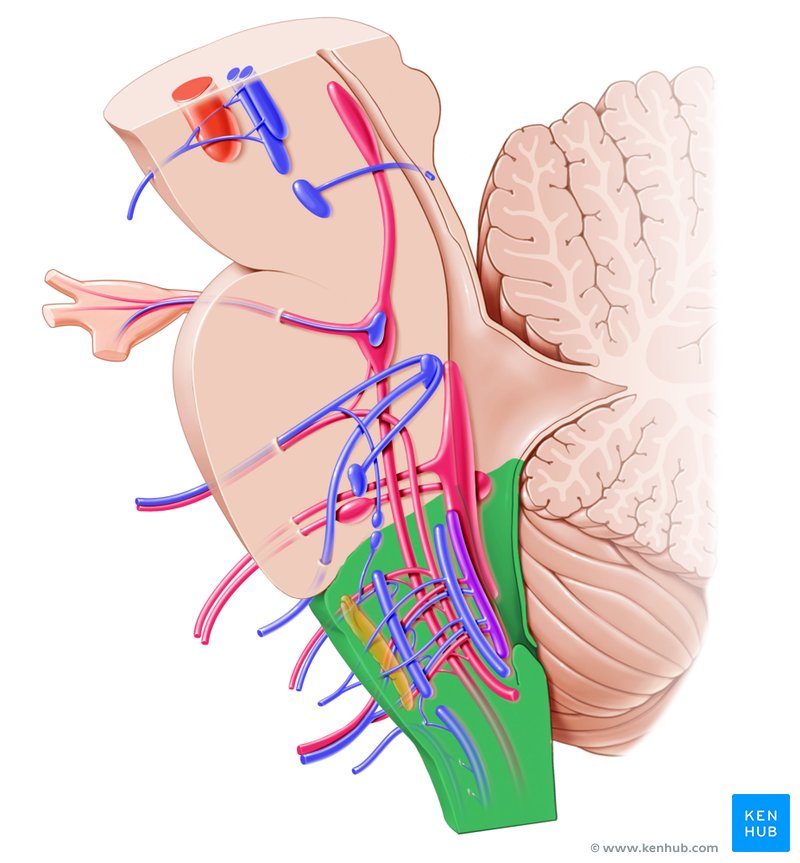
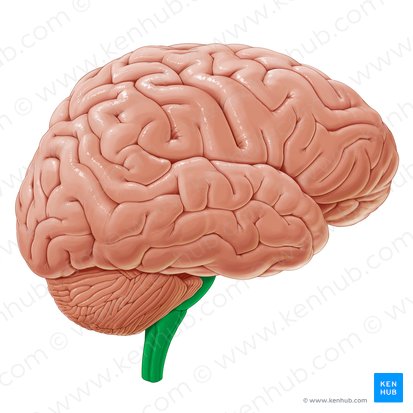
Cerebellum
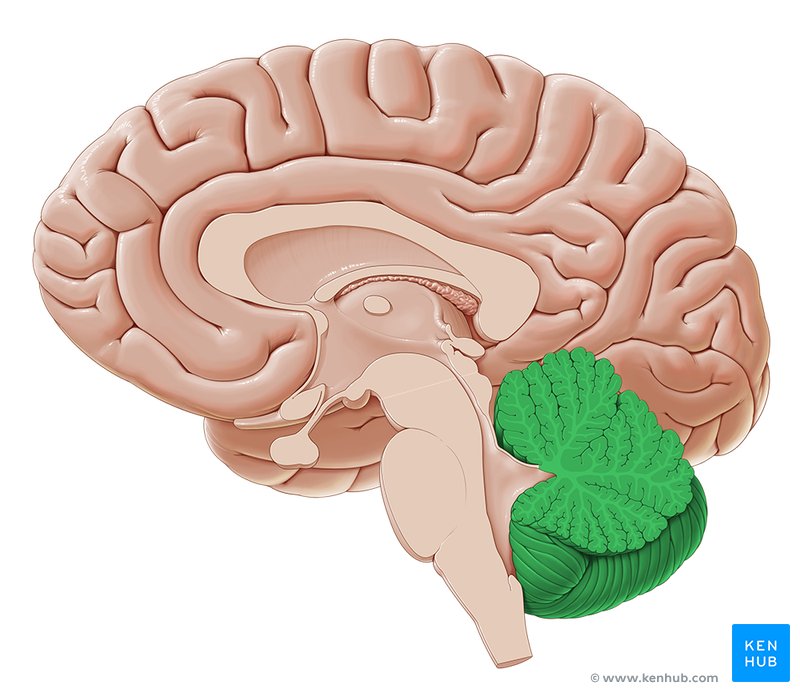
Cerebral cortex
The outer layer of the brain, composed of gray matter. It is responsible for higher-order brain functions
Brainstem
In the lowest part of the brain (just above the back of the neck) and is made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
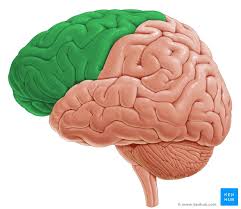
Frontal
Name the lobe
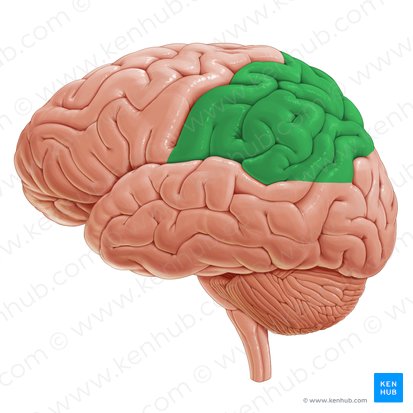
Parietal
Name the lobe
Temporal
Name the lobe
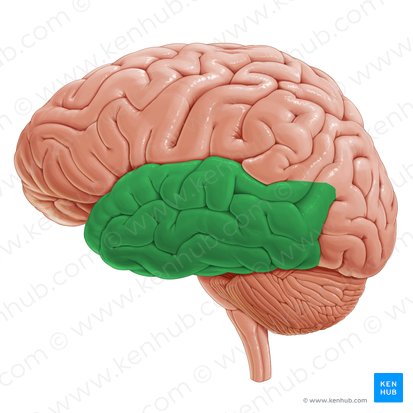
Occipital
Name the lobe
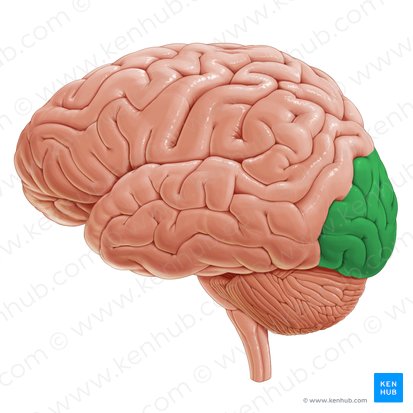
Insula
Name the lobe
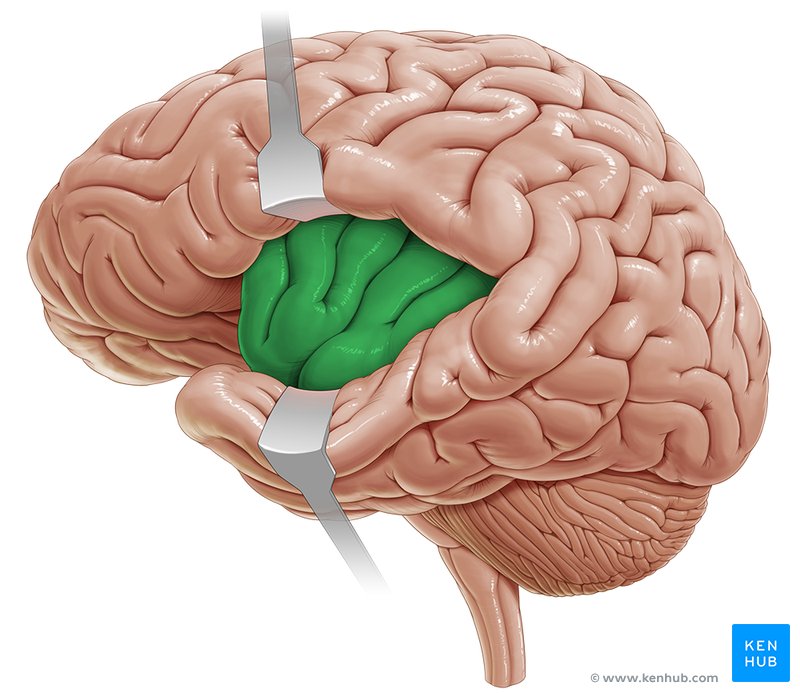
Interhemispheric
Name the fissure
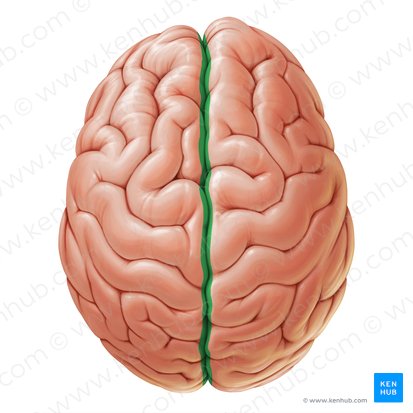
Lateral/Sylvian
Name the fissure
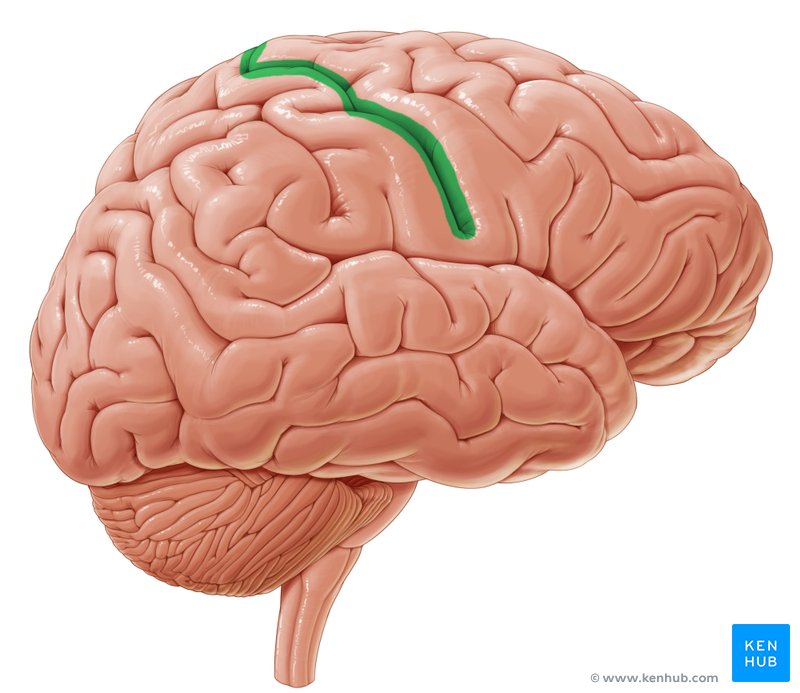
Precentral gyrus
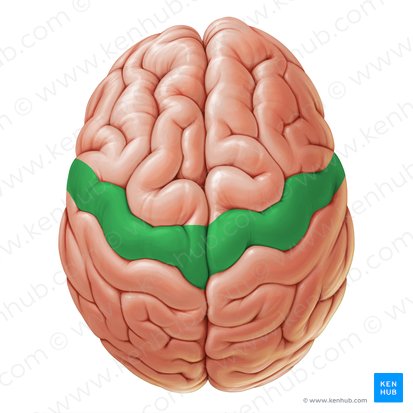
Central sulcus
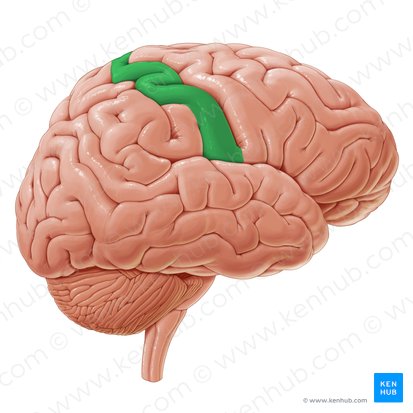
Postcentral gyrus
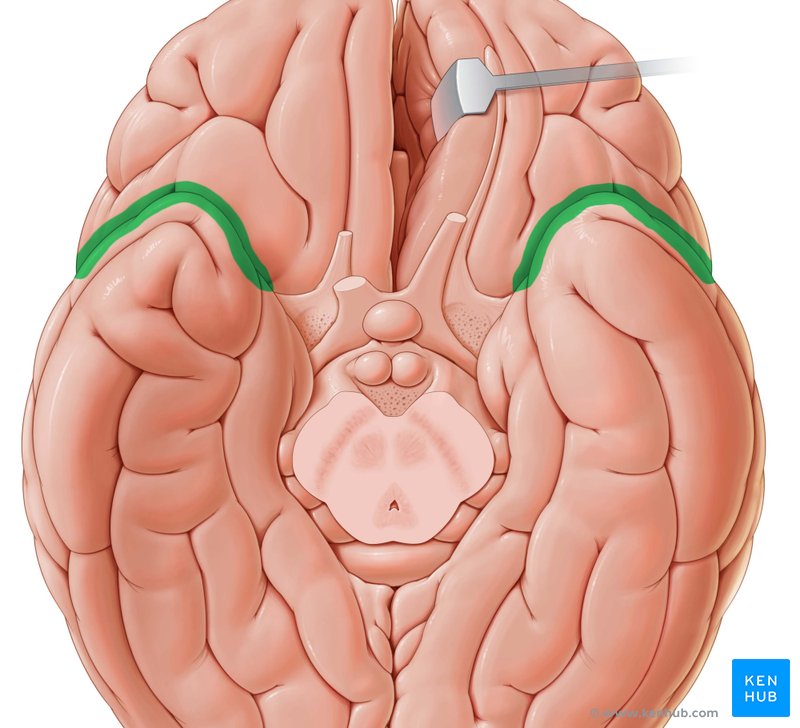
Superior temporal gyrus
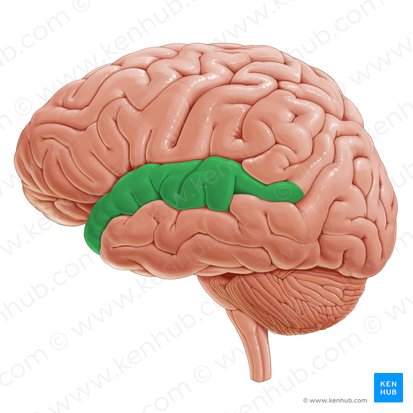
Gyrus
Sulcus
Fissure
_____: A ridge on the surface of the cerebral cortex
_____: A shallow groove
_____: A deep groove that divides the brain's cerebral hemispheres or separates major lobes
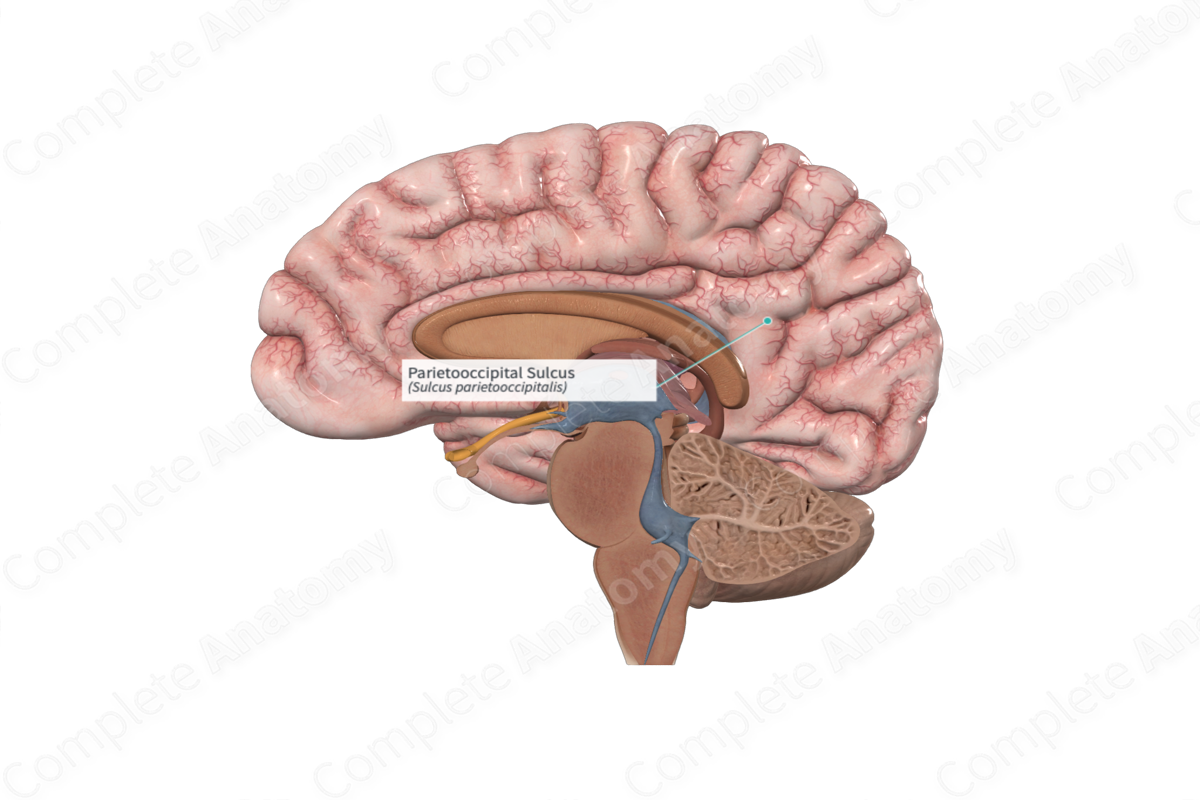
Calcarine sulcus
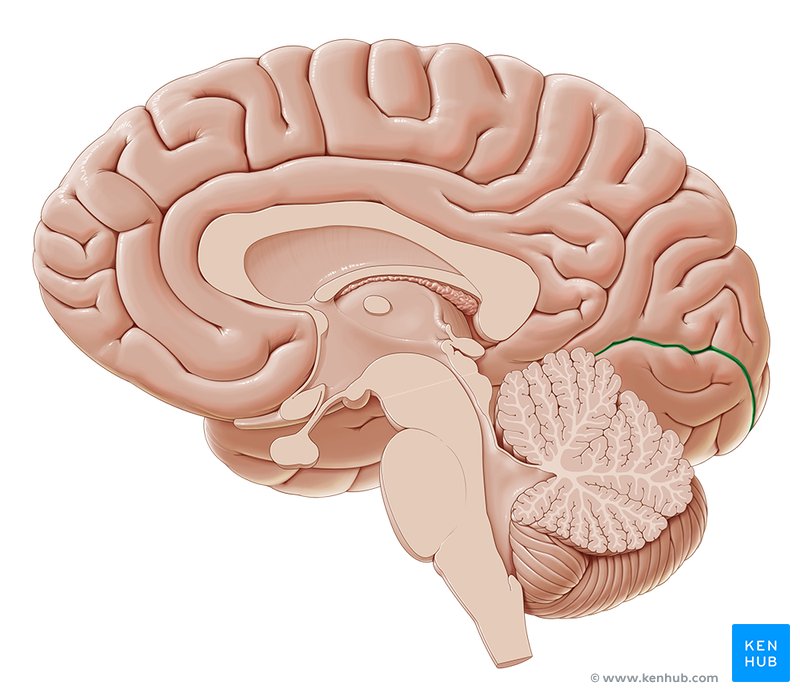
Parieto-occipital sulcus
Deep sulcus
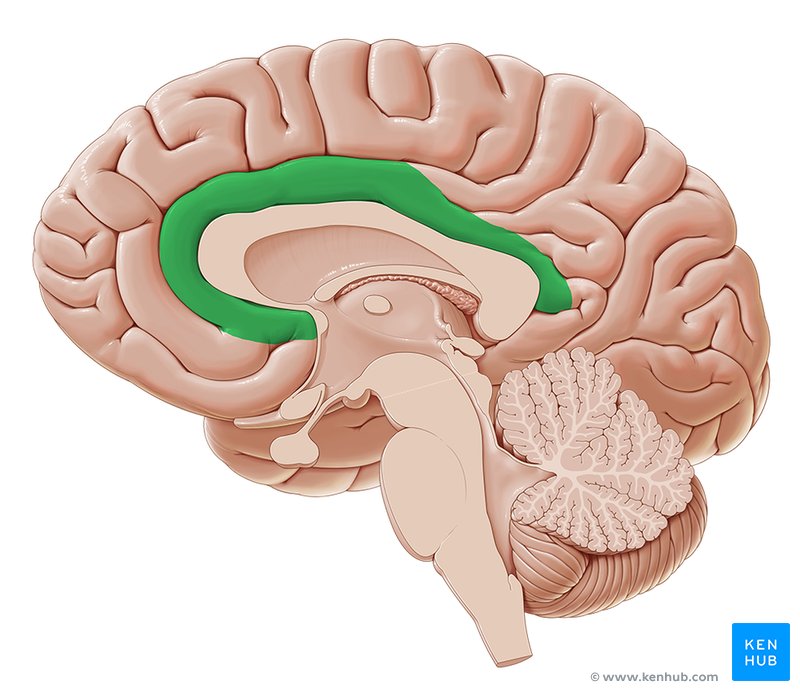
Cingulate gyrus
Fornix
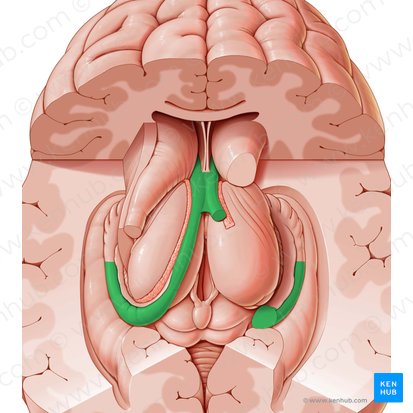
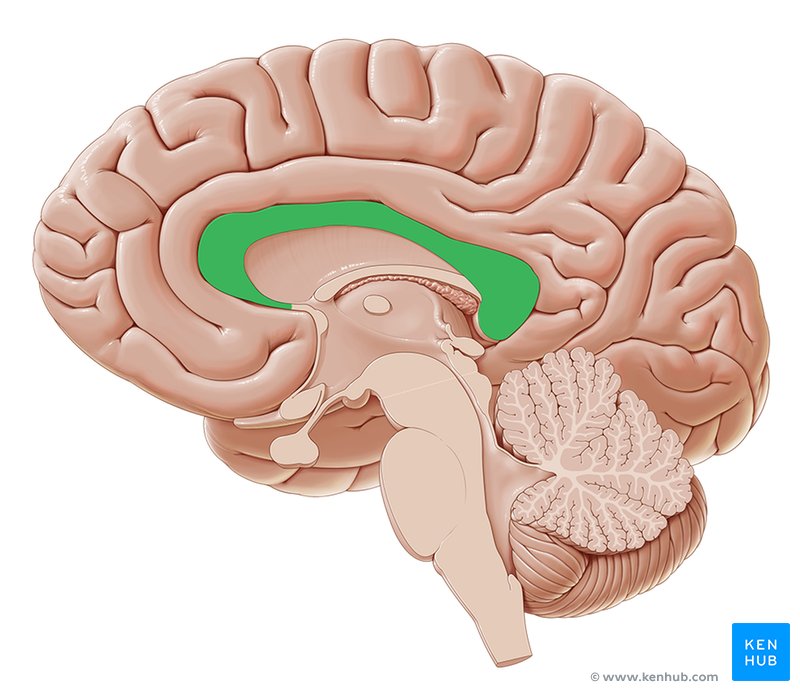
Corpus callosum
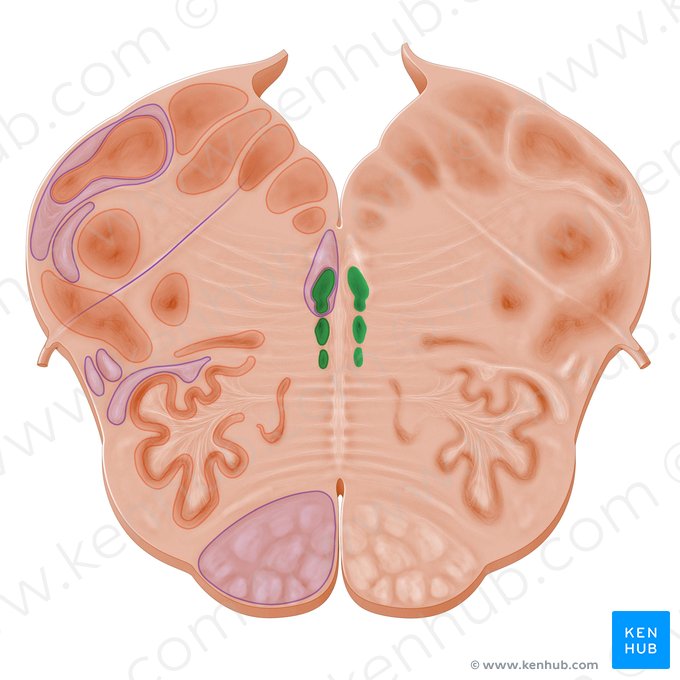
Amygdala
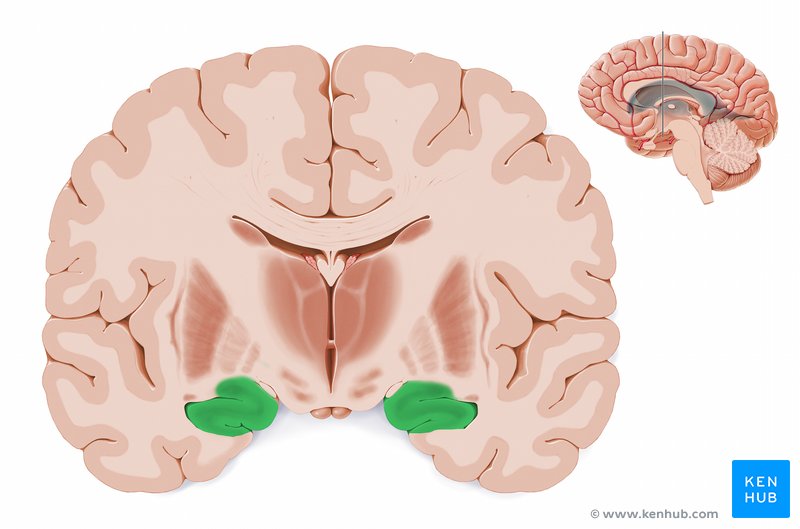
Hippocampus
Hypothalamic sulcus
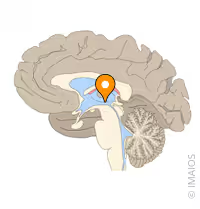
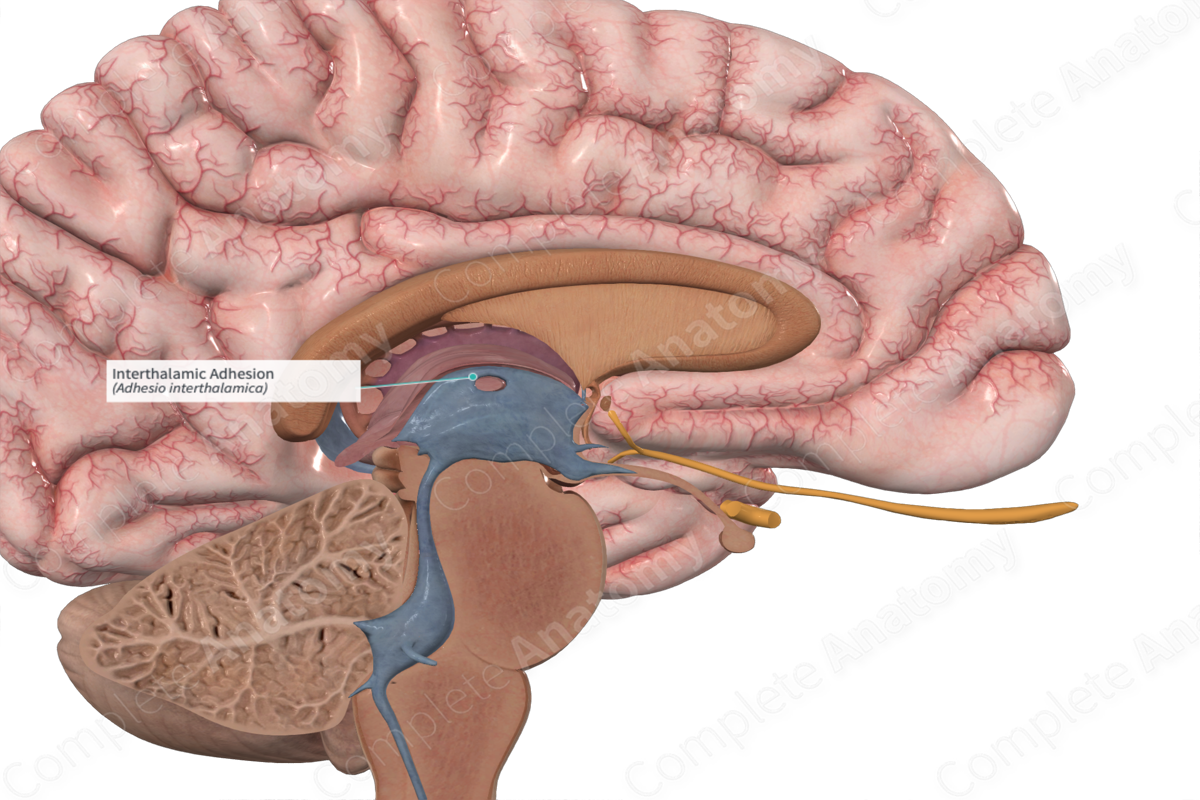
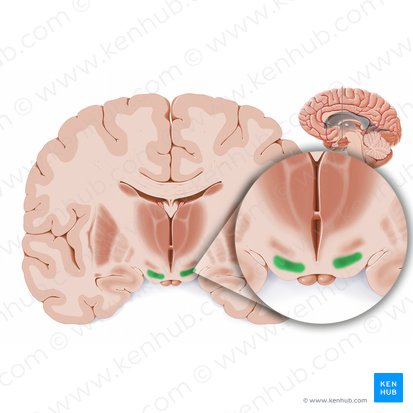
Interthalamic adhesion
A bridge of neural tissue that connects the medial surfaces of the two thalami, crossing the third ventricle in the center of the brain
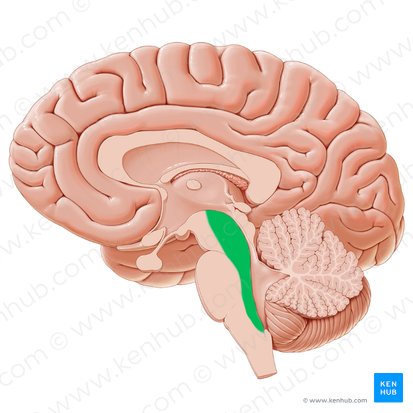
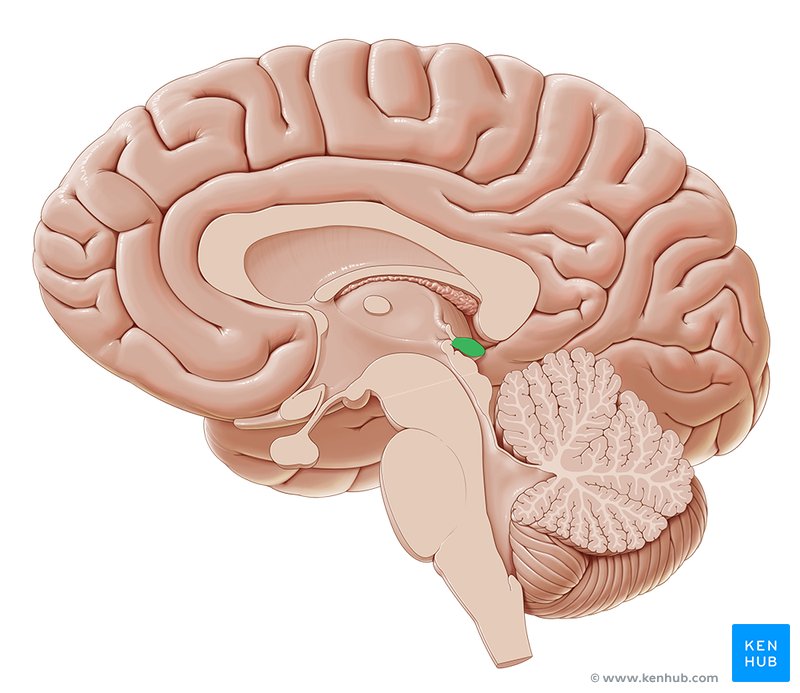
Tectum
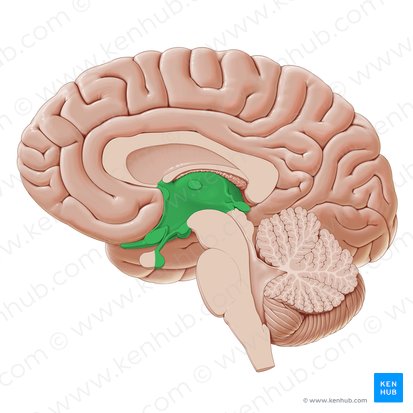
Diencephalon
Corpora quadrigemina
Composed of superior and inferior parts
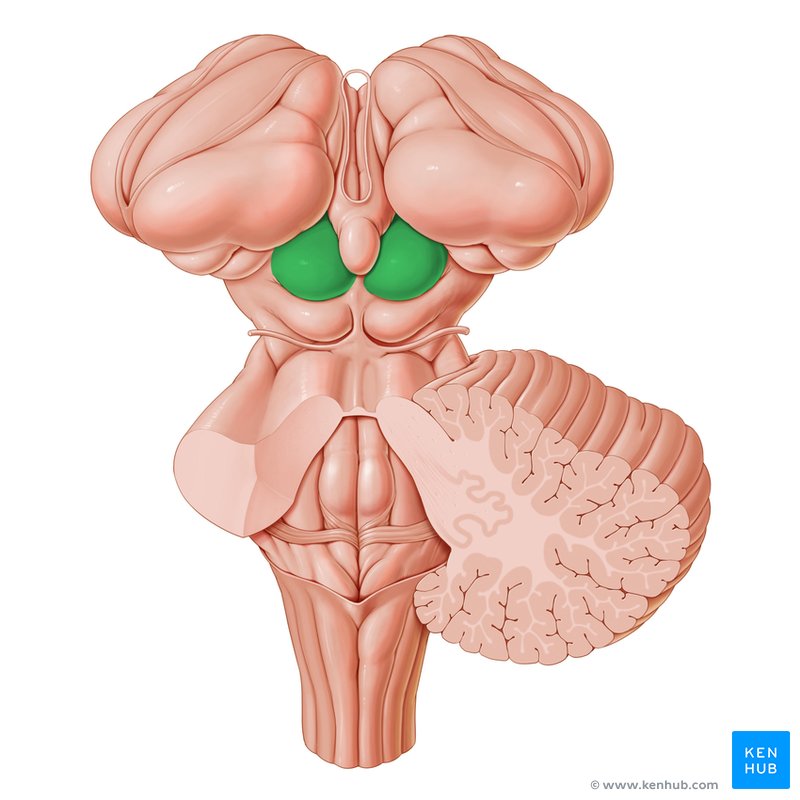
Superior colliculus
Inferior colliculi
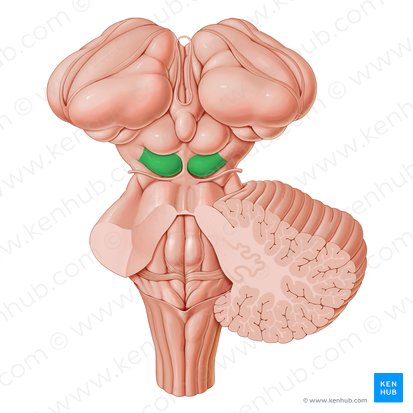
Tegmentum
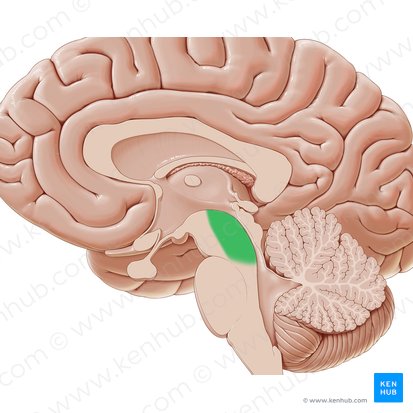
Substantia nigra
Red nucleus
Cerebral aqueduct
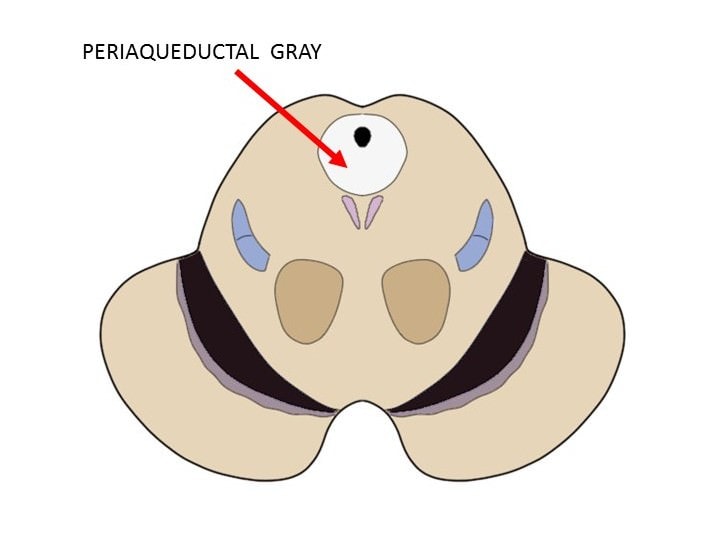
Periaqueductal gray
A midbrain region surrounding the cerebral aqueduct, crucial for integrating behavioral and physiological responses to internal and external stressors
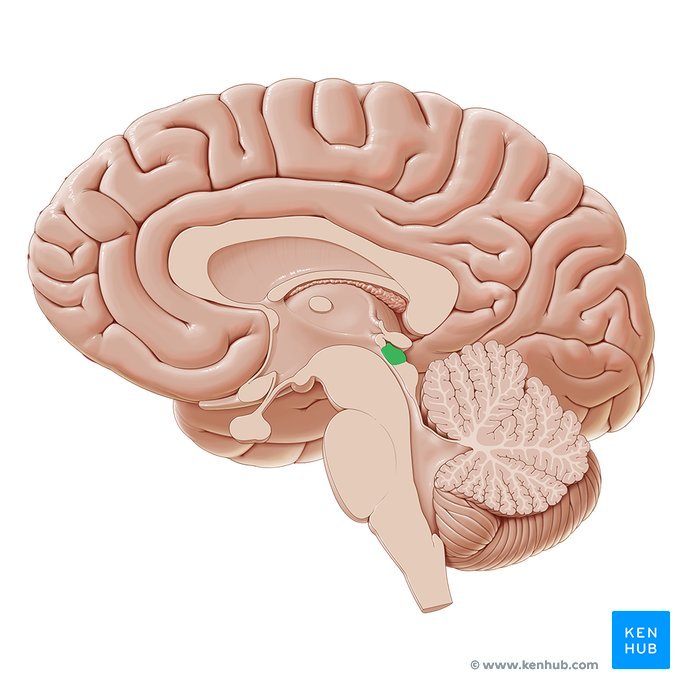
Pineal gland
Crus cerebri
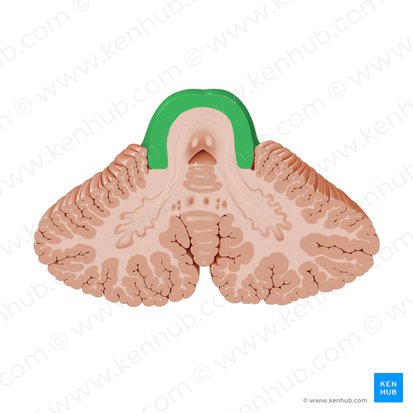
Tectum, tegmentum, cerebral peduncles
What makes up the midbrain?
White matter
Myelinated nerve fibers
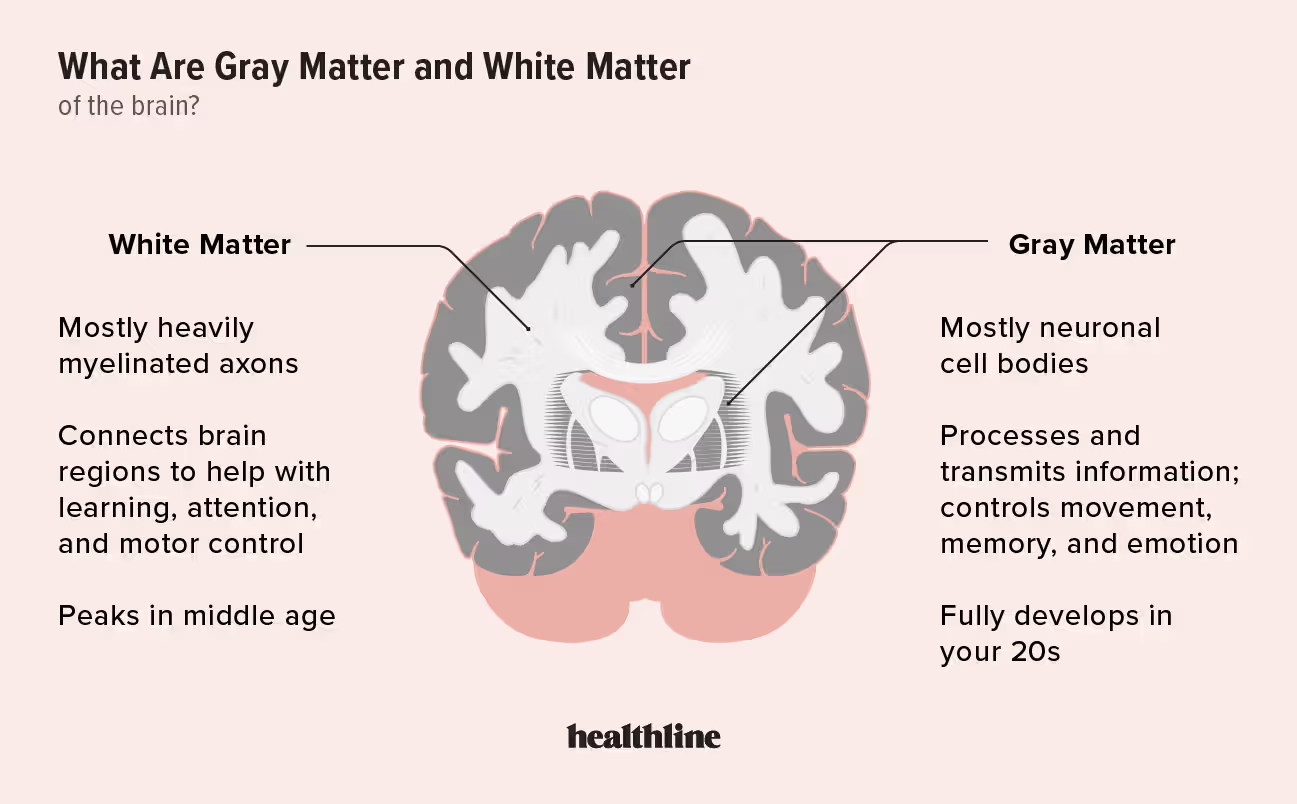
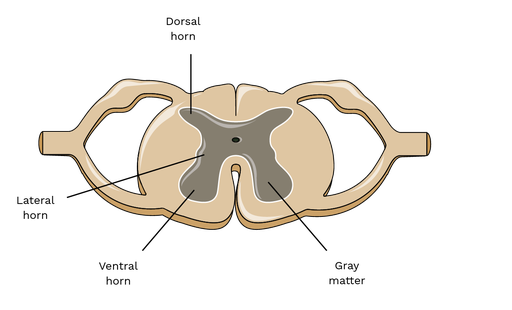
Gray matter
Central core of spinal cord
Dorsal horns
Sensory neurons
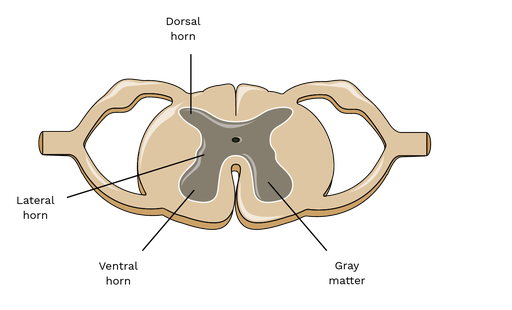
Ventral horns
Motor neurons
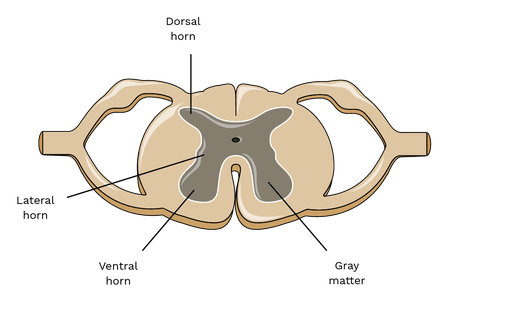
Lateral horn
Preganglionic sympathetic neruons
12
31
afferent
efferent
Peripheral Nervous
• Cranial nerves – ___ pairs
First two are attached to forebrain, for special sense. Technically part of CNS
• Spinal nerves – ___ pairs
– Dorsal roots
• Carry _____ fibers with cell bodies in dorsal root ganglia – Ventral roots
• Carry _____ fibers with cell bodies in spinal gray matter
External
Internal
• Somatic nervous system:
– Detecting changes in _____ environment
– control of movement
• Autonomic nervous system:
– Innervates visceral structures
– Important in homeostasis of the _____ environment
• Components are present in both the CNS and PNS.
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Autonomic Nervous System
• _____ division – Fight or flight
• _____ division – Rest and digest
– Feed and breed
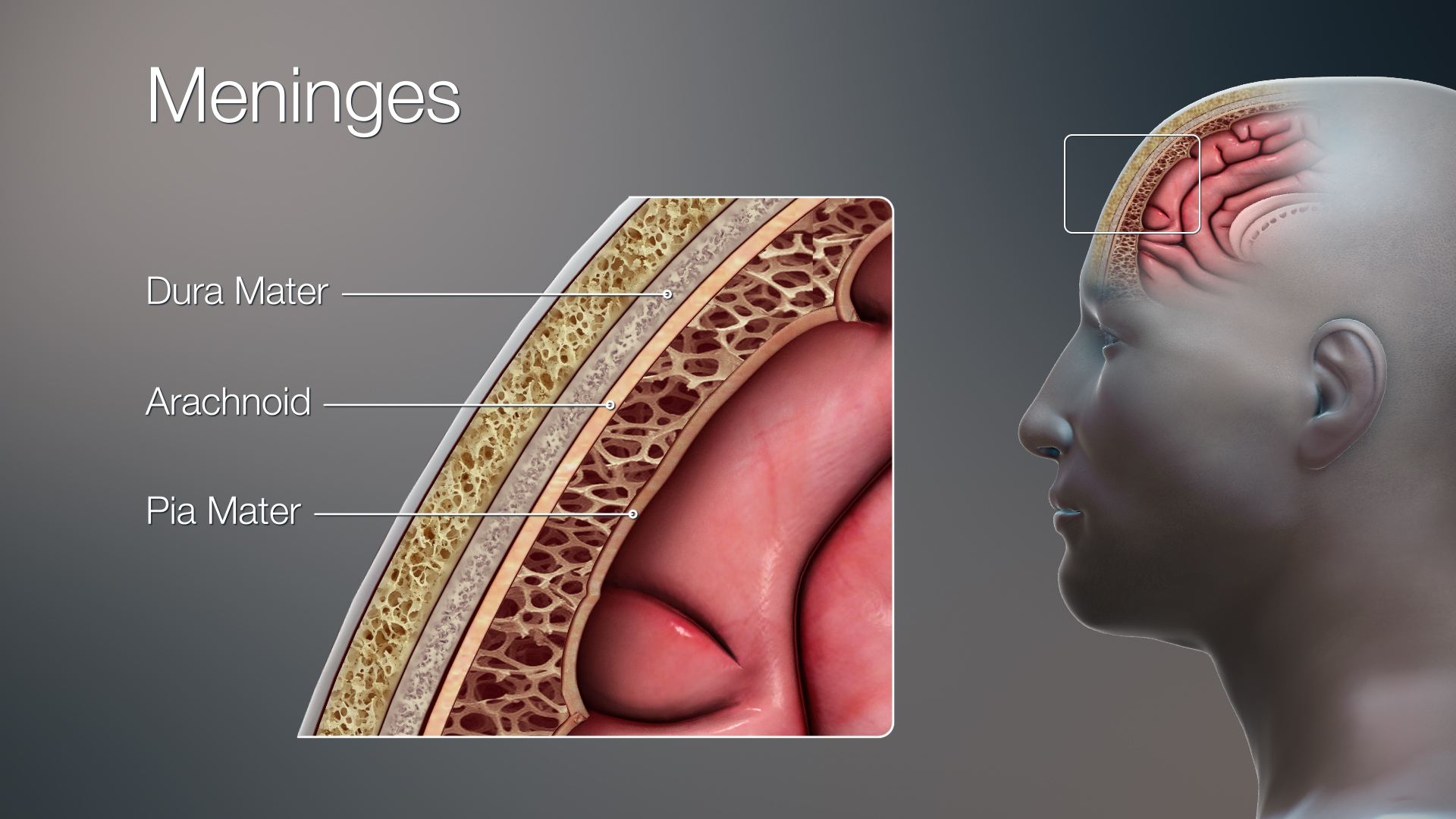
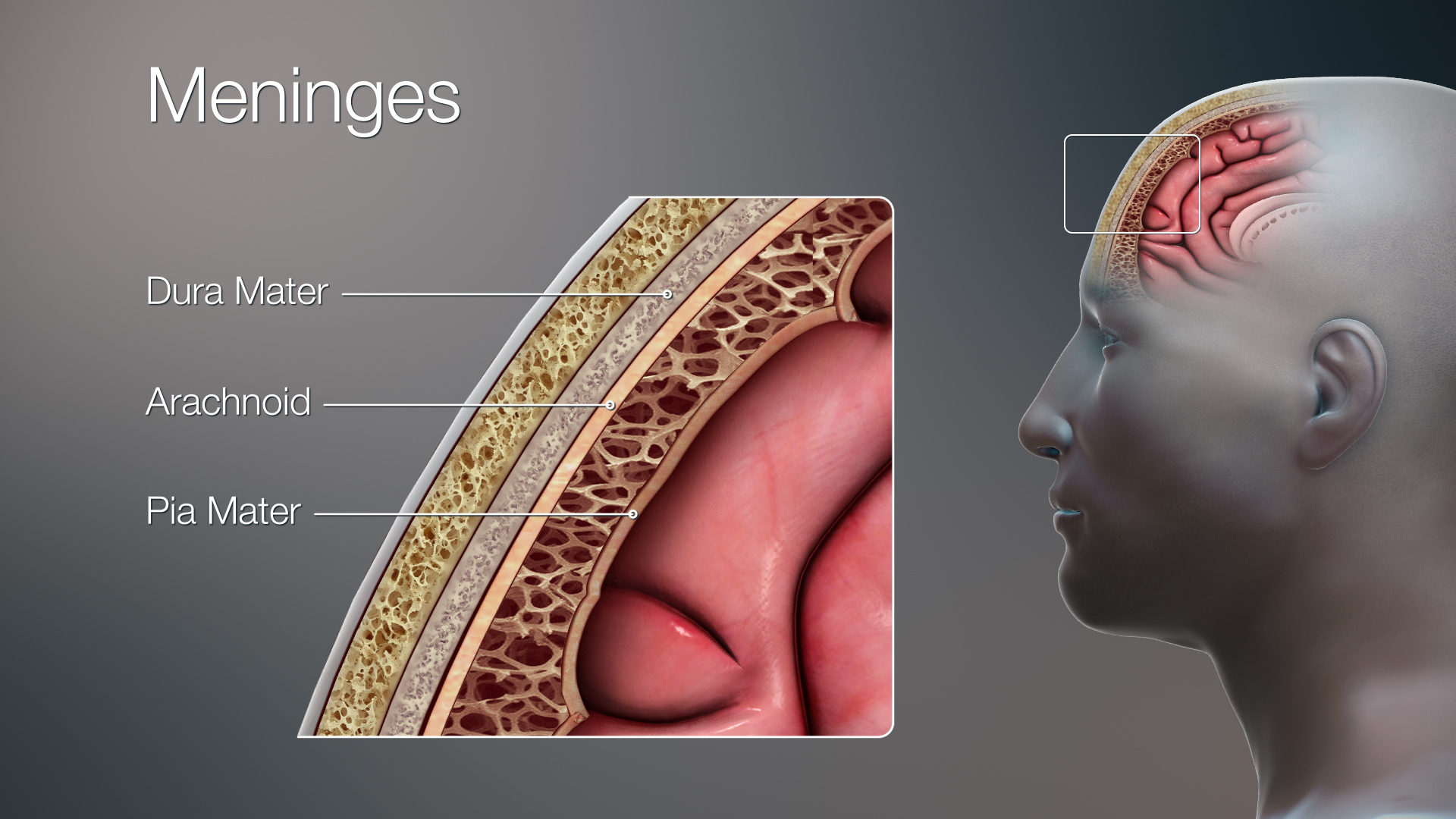
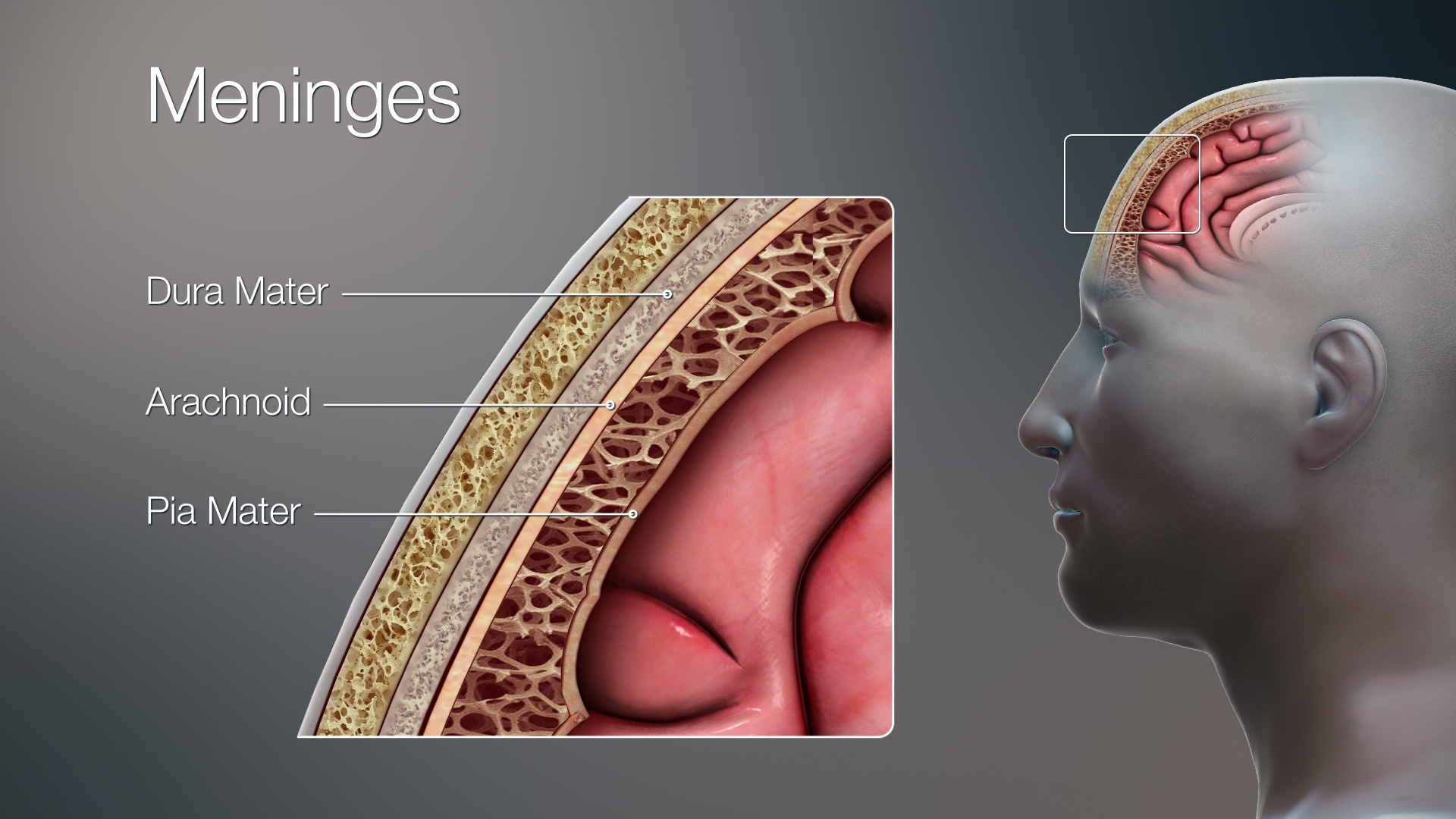
Dura
Arachnoid
Pia
Meninges
• Meningeal layers:
1. _____ mater–tough,fibrous coat
• Falx cerebri
• Tentorium cerebelli
• Subdural space
2. _____ mater – translucent, collagenous membrane
• Subarachnoid space
3. _____ mater – thin, delicate membrane attached directly to brain
Dura mater
The tough outermost membrane enveloping the brain and spinal cord.
Falx cerebri
A sickle-shaped fold of dura mater, the tough outer membrane covering the brain
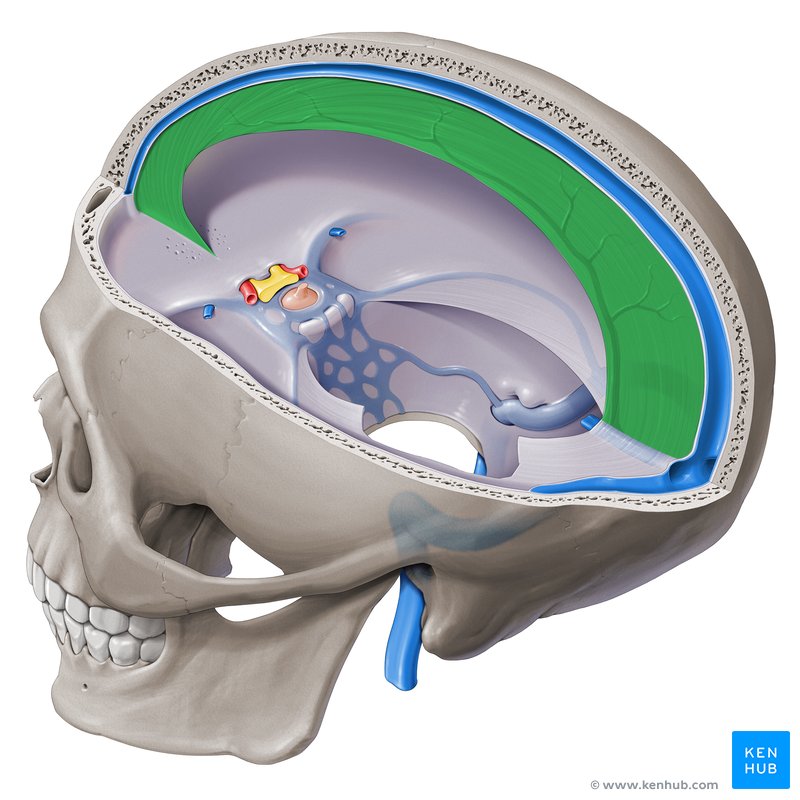
Tentorium cerebelli
A strong, horizontal sheet of tissue that separates the cerebellum from the occipital lobe
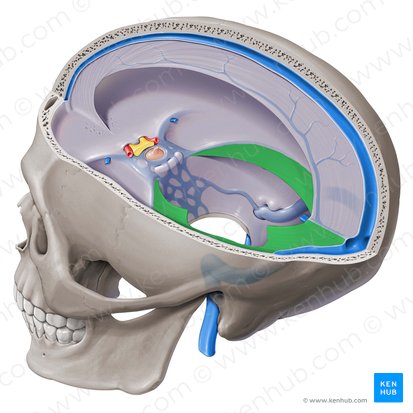
Subdural space
A thin, potential space located between the two innermost layers of the meninges, the dura mater and arachnoid mater, that cover the brain and spinal cord
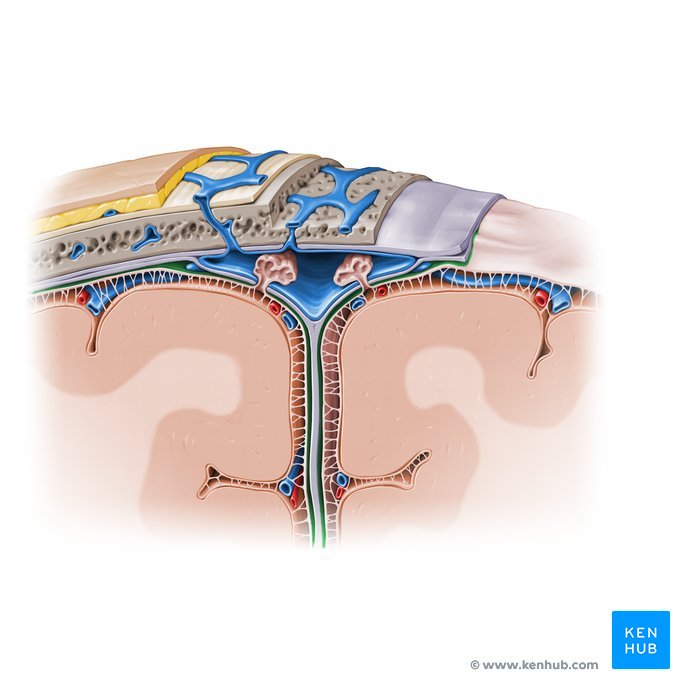
Arachnoid mater
A thin, delicate membrane that forms the middle layer of the meninges, the protective coverings of the brain and spinal cord
Subarachnoid space
A narrow, fluid-filled cavity located between the brain and spinal cord and the meninges that cover them
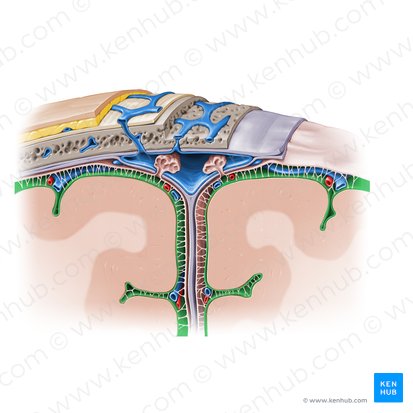
Pia mater
The delicate innermost membrane enveloping the brain and spinal cord.
Cerebrospinal
choroid
_____ Fluid
• Clear watery fluid that is inside the ventricles and around the brain and spinal cord
• Produced by the _____ plexus
• Within the subarachnoid space, CSF serves partially to cushion the brain.
Neuron
Neuroglia
Ganglion
Nuclei
Tracts
White
Gray
Tissues of the Nervous System
• _____ = nerve cell
• _____ - hold nerve cells in place and help them work the way they should
• _____ – Compact group of nerve cell bodies located in the PNS
• _____ – compact group of nerve cell bodies located in the CNS
• Tracts – Nerve fiber, share similar connections and functions
• _____ matter – Nerve fibers (axons) and their myelin coverings
• _____ matter – Masses of cell bodies that contain pigments