AP HUG Unit 5 Vocab/Concepts
1/64
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Agriculture
The modification of the earth’s surface to grow plants or domesticate animals for food
Subsidy
Governmental support for a business
Agricultural shifts in core countries
Farms have gone from small family farms to large corporate farms
Corporate farms have made many commodity chains
Technology has increased carrying capacity
Agribusiness has allowed more people to join the agricultural sector
Despite this, very few people work in agriculture today, and most of them are now men
Cheap labor is exploited
Efficiency has increased, while environmental harm has also increased and farms can be farther from markets
Negative environmental effects of agriculture
Desertification
Water supply pollution (pesticides, fertilizers, animal waste)
Air pollution (animal waste, overgrazing, chemicals)
Salinization
Deforestation
Draining of rivers and aquifers
Loss of general soil fertility due to monocropping
Soil erosion due to deforestation and overgrazing
Soil compaction due to heavy machinery use
Lack of biodiversity
Diet preferences have resulted in only some plants and animals being eaten due to size, weight, and taste differences
Food production patterns and consumption influenced by
Urban farming
Community-supported agriculture (CSA)
Organic farming
Value-added specialty crops
Fair trade movements
Dietary shifts
Community-supported agriculture (CSA)
Reduces food miles of crops and saves fossil fuels
Farmers use organic and humane methods for plants and animals
Make larger profits than others
Effects of organic farms
No chemicals
Healthier for environment (less pollution)
Animals are raised without growth hormones (GMOs) or antibiotics, making their meat safer
Fair trade movements
Farmers in developing countries make more profits and get more food
Workers are typically treated better
More sustainable methods are used
Wealth disparity is diminished
Von Thunen Model
Ring 1: Central city/market
Ring 2: Intensive farming/dairying
Ring 3: Forests
Ring 4: Extensive farming
Ring 5: Pastures
Land price and labor intensity increases as it gets closer to the market
Transportation rise as you get farther from the market
Assumes land is isotropic and there is only one market
Modern changes to the Von Thunen Model
The forest ring no longer exists
Dairy and intensive farming rings split (dairying is closer)
Landscape and climate vary
There are many markets (some products are regional)
Transportation costs are not as important
Technology is more advanced (refrigeration and farm efficiency is better)
Reasons for food insecurity
Food deserts (places without access to healthy food)
Issues with distribution systems (lack of infrastructure, harsh government, and spoiling in LDCs)
Adverse weather (Storms, droughts, etc.)
Land lost to suburbanization
Women in agriculture
Higher percentage in peripheral countries
More women in labor-intensive and subsistence farming within a rural society
Cultural reasons for numbers (ex: patriarchical society)
In LDCs often play big roles in harvesting and cooking, limiting their ability to go to school or join the workforce
Agriculture chart
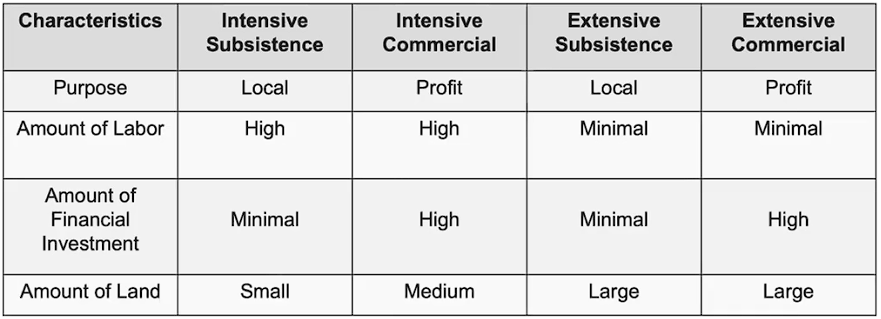
Intensive agriculture
Lots of labor and capital input
Usually small areas of land near markets
Often high-cost land and high production per acre
Often perishable goods
Ex: Milk, strawberries, feedlots
Some types of intensive agriculture
Market gardening, plantation agriculture, and mixed crop/livestock systems
Horticulture
The growth of flowers and other high-value plants
Feedlot
An animal that is fed a lot of food to be fattened
Ex: Fattened cows, pigs, and sheep
Milkshed
The area where milk can be produced and sent to a market without spoiling (type of functional region)
Transhumance
Movement of livestock according to the seasons
Pastoral nomadism
A lifestyle in which people move herds of domesticated animals to grazing areas (happens in dry Africa and Asia)
Extensive agriculture
Little labor and capital input
Usually big areas of land far from markets
Often low-cost land and low production per acre
Often non-perishable goods
Ex: Livestock ranching, grain production, etc
Some types of extensive agriculture
Shifting cultivation, nomadic herding, and ranching
Commercial agriculture
Farming to sell goods (sometimes sell shares of food to corporations)
Plantation agriculture
Cash crops grown on large estates (mostly owned by core countries)
Cash crops
Crops grown for export and making money (often luxury)
Ex: Cotton in USA, rubber in Brazil
Luxury crops
Crops that are not essential
Ex: Coffee, cacao, tea, tobacco
Negative effects of exporting luxury crops in peripheral countries
Normal crops must be imported at higher prices
Water pollution, soil erosion, deforestation, and salinization may result from poor farming technique
Monocropping is risky
Little infrastructure for transportation
Monoculture
Dependence on a single crop (very risky)
Commodity chain
The processes that occur from the ground to the consumer
Ex: The growth of lettuce to someone eating a salad kit
Vertical integration
The ownership of the companies that control a commodity chain
Ex: If oranges are peeled by Company A and packaged by Company B, both companies are owned by one and perform both processes
Shifting cultivation
Moving to more fertile soil (not the same as crop rotation)
Crop rotation
The rotation of crops within multiple fields to prevent the soil from using too much of certain nutrients
Fallow
The condition of the field not currently being used during crop rotation
Contour plowing
A type of plowing that prevents erosion by raising the area that the seed is planted
Intertillage
The space between crops (increased over time due to improved knowledge)
Ridge filling
Planting on ridges after harvesting a crop
Slash-and-burn agriculture
Trees and vegetation are cut down and burned for nutrients
Subsistence agriculture
Farming for one’s needs (includes trading for essentials)
Methods of modifying crop environment
Space: clearing or modifying land, like terracing
Light: Artificial light
Water: Irrigation
Nutrients: Fertilizers
Temperature: Greenhouses and other buildings
Boserup Hypothesis
The opposite of Malthusian theory, saying that food production methods will improve
First Agricultural Revolution
Idea developed by Carl Sauer
Plants are domesticated
People begin to move away from hunter-gathering
Inefficient at first
Primarily root crops (vegetative farming)
Animals are domesticated and animal plow is used
Second Agricultural Revolution
Great Britain in the 18th century
During IR (machines needed more resources, but more efficient farming means more factory workers)
Steel plow, McCormick harvester, seed drill, grain storage, tractors
Better diets, longer life expectancy
Third Agricultural Revolution (Green Revolution)
Norman Borlaug known as “father” of the Green Revolution and used cross-breeding
The creation of high yield varieties of crops spread across the world
Reduced genetic variation
GMOs become primary food source (more resistant to pests and weeds)
New herbicides, pesticides, and fertilizers were made
Transportation, machinery, and irrigation methods improved
Created a large desparity between core and peripheral countries
Ex: Mexican corn is almost only one variety
GMO controversy
WHO and other organizations consider them safe
They typically aren’t harmful, but pesticides and other products used on them may be
It is very uncommon to find non-GMO products today
Reduced biodiversity
Aquaculture
Fish farms
Blue Revolution
The increased efficiency and production of fish farms
Concerns of Green and Blue Revolutions
Concerns about water and soil usage
Concerns about the reduction of biodiversity
Reluctance to use ferilizers and pesticides
Debates over the sustainability of such practices
Primary Economic Activity (EA)
Actvities involving harvesting of natural resources or agriculture
Ex: Agriculture, fishing, etc
Secondary Economic Activity (EA)
Manufacturing
Ex: Creation of textiles, building of cars, etc
Tertiary Economic Activity (EA)
Services
Ex: Medicine, teaching, sales
Quaternary Economic Activity (EA)
Research and development, finance
Ex: Amgen, accountants, engineers
Quinary Economic Activity (EA)
Leadership and authorities
Ex: CEOs, president of US
Where plants originated
SE Asia: Taro, bananas, mangos, and coconuts
East Asia/China: Rice and soybeans
Fertile Crescent/Southwest Asia: Wheat, barley, and grains
Mesoamerica: Corn, squash, beans, and potatoes
Sub-Saharan Africa: Yams, sorghum, and coffee
Where plants are grown today
Taro, bananas, mangos, and coconuts: East Indies, India
Rice and soybeans: Japan, Korea, China
Wheat, barley, and grains: Europe, Middle East, Northern/Eastern Africa
Corn, squash, beans, and potatoes: Americas
Yams, sorghum, coffee: Southern Africa
Olives, grapes, figs, citrus, assorted veggies: Mediterranean
Cocaine: Colombia
Heroin: South and Southeast Asia
Where animals came from
Goats: Fertile Crescent
Dogs: Fertile Crescent
Pigs: Fertile Crescent
Sheep: Fertile Crescent
Cows: Indus River Valley
Horse: Central Asia
Llama: Andes Mountains
Alpaca: Andes Mountains
Chicken: Southeast Asia
Modern domestication
Animals have gotten smaller over time (except for feedlots)
We no longer domesticate new animals
Hunter-gatherers are much less prominent today due to domestication
Nomadic herding pretty much only occurs in Africa and Asia
Columbian Exchange
Occurred after the Spanish conquered South America and Mesoamerica
Across the Atlantic
Maize, squash, and potatoes were taken to Europe
Coffee, sugar, horses, and cattle were brought to the Americas
Trade routes
Silk Road brought plants and animals to and from East Asia, the Middle East, and Europe
Indian Ocean brought plants and animals to and from South Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and Europe
Cadastral system
A system for how land ownership and property is defined
Township and range survey system
A cadastral system that appoints land in geometric squares and rectangles, creating a dispersed settlement pattern
Metes and bounds survey system
A cadastral system with boundaries dictated and demarcated by natural features
Longlot survey system
A cadastral system with rectilinear long plots of land that shares access to a resource (typically a river)
Primogenture
When the oldest son or first daughter to marry’s husband gets the land from their father
Koppen Classification System
The classifcation system for climates
A: Hot, warm, and humid (equatorial)
B: Dry (desert-ish)
C: Humid and temperate (Europe, Northern California)
D: Humid and cold (New England, Canada, Russia)
E: Cold and polar (Antarctica, the Arctic)
H: Highlands
Isotropic
Flat and featureless land (assumed by many land use models)