AP World History - Ultimate Guide
Unit 1: The Global Tapestry
Review of History Within Civilizations
- What rises out of collapse of classical civilization and interactions developing between new states
- Growth of long-distance trade
Overview of World’s Major Religions in 1200
Most events are connected to religion
Key Points:
- Most belief systems still are impacting history
- Most major religions have divisions = subgroups and sects (focus more on overall religion)
- Understand theological basis of belief systems and impact of belief systems on social, political, cultural, military developments
- Origin and spread of belief systems - cultural interactions
Religious Mysticism: adherents within religions focusing on mystical experiences that bring them closer to divine - prayer, meditation
Buddhism
- Cultures: India, China, Southeast Asia, Japan
- Context:
- Founded by Siddhartha Gautama, a young Hindu prince - lived in Nepal from 563-483 BCE, rejected wealth and world possessions and became Buddha (Enlightened One)
- No supreme being - 4 Noble Truth: (1) all life is suffering, (2) suffering caused by desire, (3) can be freed of desire, (4) freed of desire following a prescribed path
- Death of Buddha (483 BCE) = Buddhism split - Theravada Buddhism and Mahayana Buddhism
- Theravada Buddhism: meditation, simplicity, nirvana as renunciation of consciousness and self
- Mahayana Buddhism: great ritual, spiritual comfort - more complex but with greater spread
- Impact: rejects caste system - appealed to those of lower rank
- India: reabsorbed in Hinduism
- China, Japan, Southeast Asia: Buddhism continued to thrive
- Further: spread via trade routes
Christianity
- Cultures: started as group of Jews, quickly expanded through Europe, northeastern Africa, Middle East
- Context:
- Based around Jesus of Nazareth, a figure who claimed to be Messiah the Jews had awaited - teachings of devotion to God and love for others
- Jesus was crucified by Roman and Jewish leaders in 30 CE and his followers believe he rose from dead into heaven
- Based on Bible teachings
- Believe Jesus is the Son of God - forgiveness of sins, everlasting life is achievable through him
- World was created by God, but world has fallen from God
- Believers should seek God and care for him and others
- Impact: compassion, grace through faith appealed to lower classes and women
- Became most influential religion in Mediterranean basin by 3rd century
- Became official religion of Roman Empire, then branching north and west
- Connection with Roman Empire had profound impact on global culture
Confucianism
- Cultures: China (400 BCE+)
- Context:
- Founded by Confucius, educator and political advisor - thoughts and sayings collected in the Analects
- Deals with how to restore political and social order, not with philosophical or religious topics
- 5 fundamental relations build society and make it orderly - (1) ruler and subject, (2) parent and child, (3) husband and wife, (4) older sibling and younger sibling. (5) friend and friend
- Impact:
- Compatible with other religions, causing it to flourish
- Led to distinctive Chinese culture of tight-knit communities
- Stayed within Chinese culture
Hinduism
- Cultures: India
- Context:
- Belief in one supreme force called Brahma who created everything - gods are manifestations of Brahma (Vishnu = preserver, Shiva = destroyer)
- Goal of believer is to merge with Brahma - believe it takes multiple lives to accomplish and believers live to determine who they will be in their next life
- Following the dharma (rules and obligations of your caste) will move you towards Brahma - moksha is highest stake of being (internal peace and release of soul)
- No sacred text - Vedas and Upanishads guide Hindus
- Impact:
- Religion and social caste system, which has prevented global acceptance of religion
- Recently, Hindus are rebelling caste system
- Spawned Buddhism
Islam
- Cultures: caliphates (Islamic kingdoms), North Africa, central Asia, Europe
- Context:
- 7th century - Muslims are the believers
- Allah presented words through prophet Muhammad, whose words were recorded in the Qur’an
- Salvation is won through submission to God - 5 Pillars of Islam: (1) confession, (2) prayer 5 times a day, (3) charity, (4) fasting during Ramadan, (5) pilgrimage to Mecca
- 2 groups, Shia and Sunni, who disagreed who should succeed Muhammad
- Impact:
- Rapidly spread to Middle East
Judaism
- Cultures: Hebrews
- Context
- God selected a group of holy people who should follow his laws and worship them
- Unique relationship with God
- World is for them to enjoy, free will - destiny of world is paradise
- Hebrew Bible - Torah, miracles, laws, historical chronicles, poetry, prophecies
- Impact
- First of major monotheistic faiths
Developments in the Middle East
- Abbasid Dynasty: Golden Age to Remember
- Islamic Empire from 750-1258 CE - early mid-9th century golden age
- Capital in Baghdad (modern-day Iraq)
- Centre for arts and sciences - mathematics (Nasir al-Din al Tusi), medicine, writings (House of Wisdom library)
- Built around trade - used receipt and bill system
- Decline of Islamic Caliphates: Internal Rivalries and Mongol Invasions
- Challenged by revolt of enslaved Turkish warriors, new Shia dynasty in Iran, Seljuk Turk Sunni group, Persians, Europeans, Byzantines, and most importantly Mongols
- Mongols overtook and destroyed Baghdad in 1258
- Ottoman Turks would later reunite Egypt, Syria, and Arabia in new Islamic state until 1918
- Mamluks: Egyptian group that defeated Mongols in Nazareth, helping preserve Islam in Near East
Developments in Europe
Middle Ages: fall of Rome before Renaissance - complicated time
Eastern Roman Empire became Byzantine Empire
Western Europe: collapsed entirely - Christianity remained strong
European Feudalism: Land Divided
- Feudalism: European hierarchy social system of Middle Ages
- King: power over whole kingdom
- Nobles: had power over sections of kingdom in exchange for loyalty to king and military service
- Vassals: lesser lords with sections of Noble land who could divide it further - estates were called fiefs or manors (self-sufficient)
- Founded three-field system: 3 fields for fall, spring, and empty one to replenish nutrients
- Conflict between lords was regulated with code of chivalry which condemned betrayal and promoted mutual respect
- Male dominated: women could not own land and land was passed down to eldest son (primogeniture), their education was limited to domestic skills
- Peasants or Serfs: worked the land
- Had few rights or freedoms outside of manor
- Skilled in trades, which helped them break out of feudal mode as global trade increased - led to middle class emergence of craftsmen and merchants
Emergence of Nation-States
- At end of Middle Ages, people began moving from feudal kingdom organization to linguistic and cultural organization - emergence of modern countries
- Achievement of statehood in 13th century took different paths
- Germany: reigning family of emperorship died out, entering a period of interregnum (time between kings) - merchants and tradespeople became more powerful
- England: English nobles rebelled against King John and forced him to sign the Magna Carta - reinstated the nobles, laid foundation for Parliament
- Later divided into House of Lords (nobles and clergy - legal issues) and House of Commons (knights and wealth burghers - trade and taxation)
- France: in 12th century, England began to occupy many parts of France which spurred revolts - Joan of Arc fought back English out of Orleans
- Hundred Years’ War (1337-1453): unified France, leading to England’s withdrawal
- Spain: Queen Isabella of Castile and Ferdinand of Aragon married to unite Spain in a single monarchy and forced all residents to convert to Christianity - Spanish Inquisition
- Russia: taken over by Tartars (group of eastern Mongols) under Genghis Kahn in 1242 until Russian prince Ivan III expanded his power in 1400s and became czar - Ivan the Terrible became a ruthless ruler utilizing secret police in 1500s
Developments in Asia
China and Nearby Regions
- Song Dynasty (960-1279)
- Confucianism justified subordination of women - foot binding: women’s feet bound after birth to keep them small
- Neo-Confucianism: Buddhist ideas about soul, filial piety, maintenance of proper roles, loyalty to superiors
- Ming Dynasty (1368-1644): after brief period of Mongol dominance
- Religion: influenced by Nestorianism, Manichaeism, Zoroastrianism, Islam, and especially Buddhism in two of its forms
- Mahayana: peaceful and quiet existence apart from worldly values
- Chan or Zen: meditation and appreciation of beauty
Japan
Relatively isolated from external influences outside Asia for many years
Feudal Japan (1192):
- Emperor
- Shogun (chief general)
- Daimyo: owners of larger pieces of land, powerful samurai (like knights)
- Followed Code of Bushido code of conduct - loyalty, courage, honour
- Lesser samurai (like vassals)
- Peasants and artisans
Women had little rights and esteem
India
- Delhi Sultanate: Islamic invader kingdom in Delhi
- Islam took over Northern India - clash between Islam monotheism and Hinduism polytheism
- Islam rulership brought in colleges and farming improvements
- Rajput Kingdoms: several Hindu principalities that united to resist Muslim forces from 1191 until eventual takeover in 1527
Southeast Asia
Religion spread and established different states
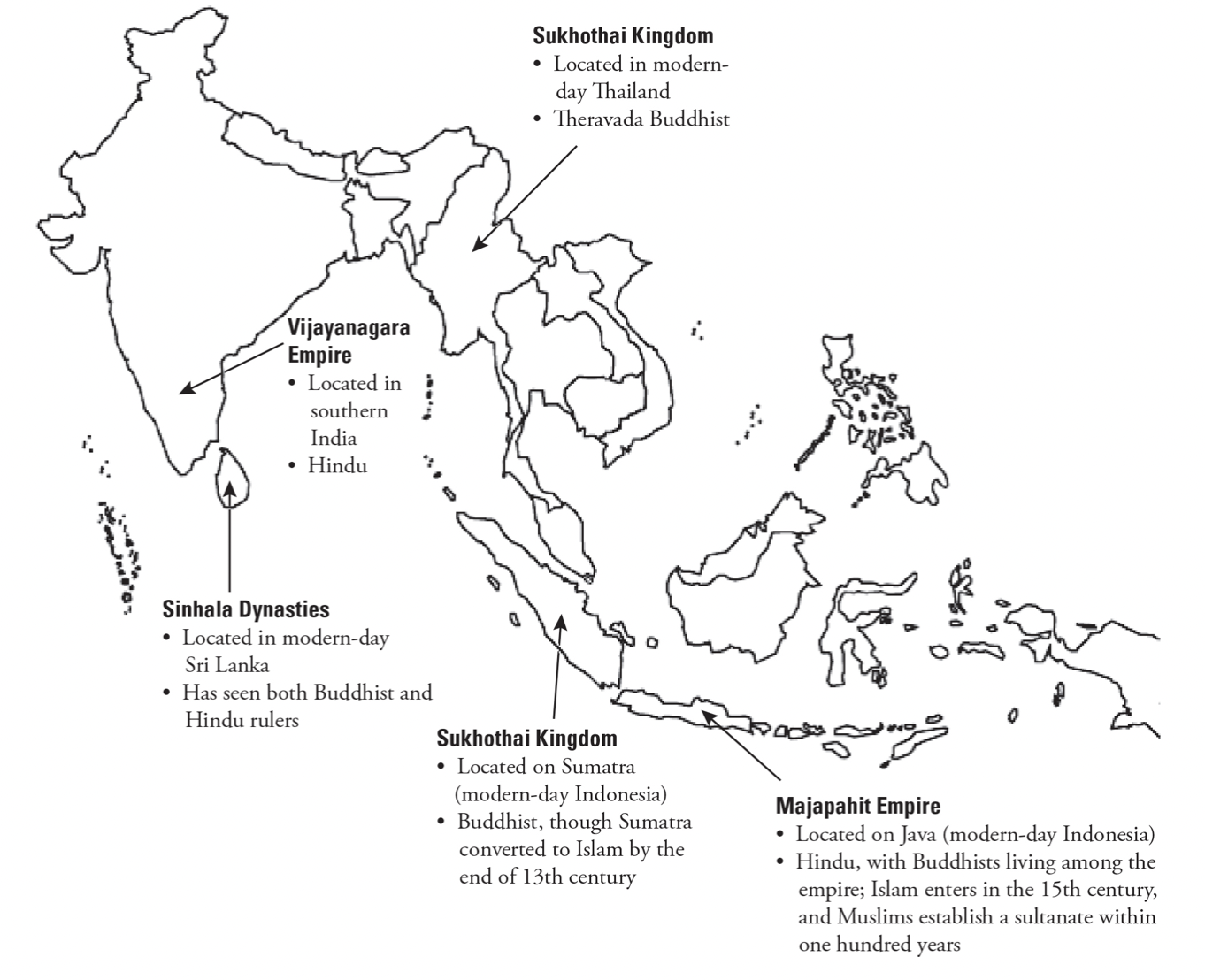
Khmer Empire (9th-15th century): Hindu Empire in modern day Cambodia, Laos, Thailand
- Beliefs were carried through Indian Ocean trade network
- Crafted the Angor Wat temple
Developments in Africa
- Islamic Empire spread to North Africa in the 7th to 8th centuries - travelled through Sahara Desert and reached the wealthy sub-Saharan
- An explosion of trade began
- Hausa Kingdoms: off Niger River, series of state system kingdoms
- Islam region, achieved economic stability and religious influence though long trade (salt and leather) - notably city of Kano
- Political and economic downturn in 18th century due to internal wars
Developments in Americas
- 3 great civilization in Central and South America: Maya, Incas, Aztecs
- Aztecs: Trade and Sacrifice
- Arrived in Mexico in mid 1200s
- Tenochtitlan: capital city (modern Mexico City)
- Expansionist policy and professional, strict army
- Empire of 12 million people with flourishing trade, many of people enslaved
- Women were subordinate, but could inherit property
- Inca: My Land is Your Land
- Andes Mountains in Peru
- Expansionist - army, established bureaucracy, unified language, system of roads and tunnels
- Many people were peasants
- Capital of Cuzco had almost 300000 people in late 1400s
- Women were more important and could pass property to their daughters
- Polytheistic religion with human sacrifice - Sun god was most important
- People were mummified after death
- Military was very important
- Temple of the Sun and Machu Picchu architecture
- The Mayans (textbook does not go into detail)
Unit 2: Networks of Exchange
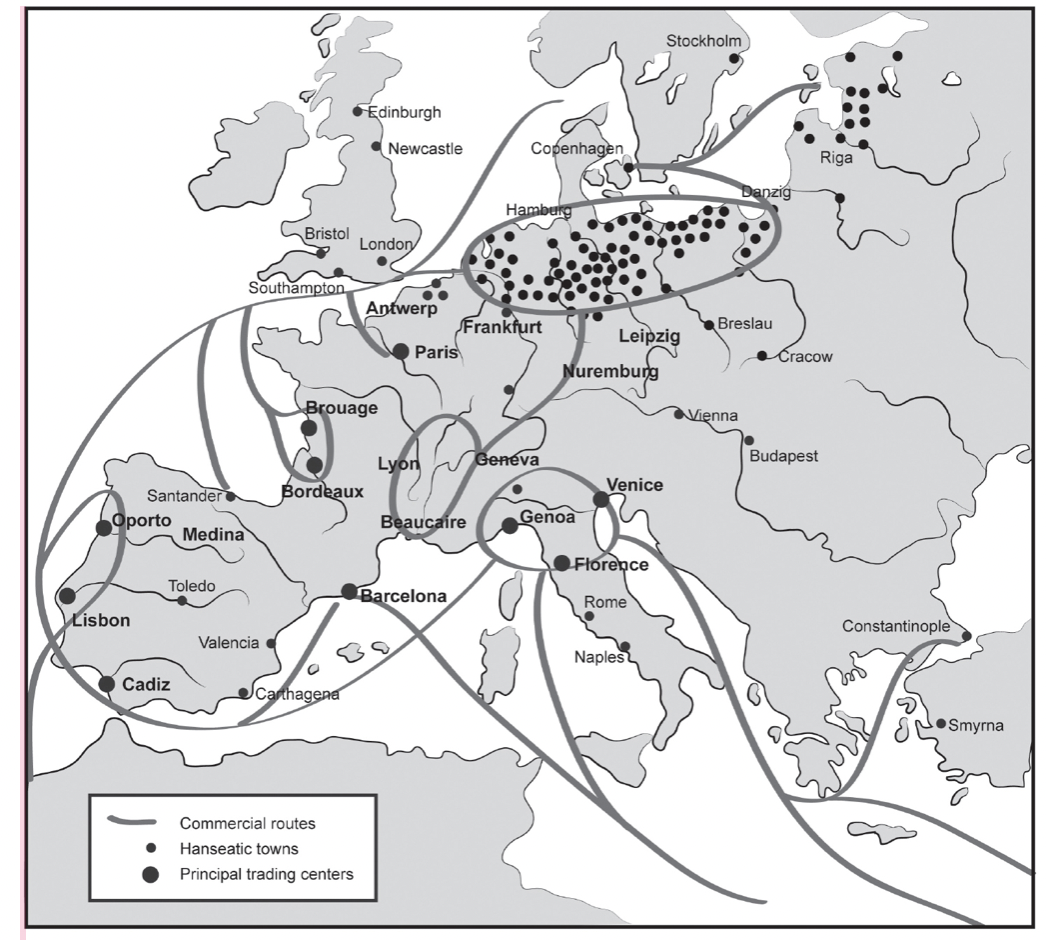
Height of the Middle Ages: Trading and Crusading
Merchants emerged in towns - referred to as Burghers, became politically powerful
Towns often formed alliances with each other
Hanseatic League (1358): trade alliance though northern Europe to drive toward nationhood, increase social mobility and flexibility
Architecture: Romanesque to Gothic - especially reflected in cathedrals
- Flying buttresses: tall windows and vaulted ceilings
- Often had art and sculpture, music
Scholasticism: growth of education and knowledge - founding of universities for men; philosophy, law, medicine study; ideas of Muslims and Greeks - came in conflict with religion
Crusades (11-14th century): military campaigns by European Christians to convert Muslims and non-Christians, combat religious questioning
- Combat Heresies: religious practices/beliefs not conforming to traditional church doctrine
- Pope Innocent III: issued strict decrees on church doctrine - frequently persecuted heretics and Jews, unsuccessful 4th crusade
- Pope Gregory IX: Inquisition (formal interrogation and prosecution of perceived heretics with punishments like excommunication, torture, execution) - church often referred to as Universal Church or Church Militant
- Thomas Aquinas (1225-1274): Christian theologian who made advancements in Christian thought - faith and reason aren’t in conflict
Urbanization
- Trade led to the growth of urban culture - cities usually were around trade routes
- Silk Route cities were the most populous - Baghdad, Merv, Chang’an
- Constantinople before 1400 and Paris and Italian city-states after 1400 were big European cities
The Rise and Fall of the Mongols
- Set of tribes and clans that were superb horseman and archers
- Genghis Kahn: unified the tribes in Mongolia in the early 1200s to expand their authority over other societies - first invaded China in 1234
- Mongol Empire: spanned from Pacific Ocean to Eastern Europe - spit into hordes after death of Genghis Kahn, ruthless warriors destroying cities but remained peaceful after settling into cities
- Golden Horde: conquered modern-day Russia
- Kublai Khan: Genghis Kahn’s successor - ruled China
- Didn’t really have a set culture - didn’t enforce religion or way of life on conquered nations, but did make any cultural advancements
- Timur Lang: Mongol leader who took over India and destroyed everything - grew Islam in the nation
- If any residents of society the Mongols took over resisted, they would immediately kill them, so most had no choice but to give in - they were ruthless fighters, organized and mobile
- Impact:
- Great diffusers of culture
- Prevented Russia from culturally developing
- World trade, cultural diffusion, global awareness grew as they spread through Europe, the Middle East, and Asia
Mali and Songhai
- Mali had a lot of gold that Islamic traders were interested in
- Mansa Musa: Malian ruler who built the capital of Timbuktu and expended the kingdom beyond Ghana
- Sonni Ali: Songhai ruler that conquered region of west Africa in 15th century - became a major cultural centre until 1600
Chinese Technology
- Song Dynasty: bureaucratic system built on merit and civil service examination creating a lot of loyal government workers, improved transportation and communication and business practices
- Concentrated on creating an industrial society - improved literacy with printed books which increased productivity and growth
Review of Interactions Among Cultures
Trade Networks and Cultural Diffusion
Trade exploded from 1200-1450
Improved with better transportation and monetary systems
Main Global Trade Routes:
- The Hanseatic League
- The Silk Road
- The land routes of the Mongols
- Trade between China and Japan
- Trade between India and Persia
- The Trans-Saharan trade routes between west Africa and the Islamic Empire
Cultural diffusion - spread religions, languages, literature, art, idea, disease, plague
Bubonic Plague: started in Asia in the 14th century and carried by merchants - killed about 1/3 people
Indian Ocean Trade
- Dominated by Persians and Arabs - western India to Persian Gulf to eastern Africa
- Great Zimbabwe: trading empire in Africa from 11th to 15th centuries
Vibrant Indian Ocean Communities
- Sailors marrying local women created cultural intermixing
Silk Road
- China to Mediterranean cultures in early days of Roman Empire and from 1200 to 1600
- Cultural exchange through travellers stopping at trade towns - Kashgar, Samarkand
- Silk, porcelain, paper, religion, food, military technologies
Hanseatic League
- Made up of over 100 cities
- Created substantial middle class in northern Europe
- Set precedent for large, European trading operations
Expansion of Religion and Empire: Cultural Clash
- Both natural spread of religion through contact over trade and intentional diffusion through missionary work or religious war
Other Reasons People Were on the Move
- Ran out of room in certain places, but cities were always increasing in size as opportunities grew in them
- New cities and empires drew people in
- Muslim pilgrimages
Notable Global Travellers
- Xuanzang: Chinese Buddhist monk - through T’ang Dynasty to India to explore Buddhism
- Marco Polo: merchant from Venice, to China and Europe
- Ibn Battuta: Islamic traveler, through Islamic world to India to China
- Margery Kempe: English Christian, through Europe and Holy Land
Unit 3: Land-Based Empires
Major European Developments
- After 300 years of development, Europe become the dominant world power
- Revolutions in European Thought and Expression:
- 1300s: Europe had been Christian for over a thousand years
- As countries began to unify and connect more, especially with countries who had preserved their history, Europe expanded its worldview and explored its past and 4 cultural movements happened
The Renaissance
- As trade increased, people moved to the cities and an influx of money was experienced - a lot of money went to studying the past
- Humanism: focus on personal accomplishment, happiness, and life on earth instead of living for the goal of salvation
- Afterlife remained dominant in the Catholic Church
- Arts have a comeback
- People could afford art again - Medici family patrons of Michelangelo and Brunelleschi
- Artists focused on realism - Leonardo da Vinci and Donatello
- Western writers have an audience
- mid-1400s: Johannes Gutenberg invents the printing press - made books easy to produce and affordable, and accessible to everyone
- led to more literate people
The Protestant Reformation
- Catholic Church was one of the most powerful organizations in the Middle Ages - power in politics and society - undisputed authority
- Church capitalized off its many followers with indulgences: paper faithful could purchase to reduce time in purgatory
- Nobles and peasants began getting increasingly frustrated by the church’s exploitation and noticed its corrupt nature
- Martin Luther: German monk who published his list of complaints against the church - most significantly proposed salvation was given directly through God, not through the church, which significantly reduced the church’s influence
- Pope Leo X: excommunicated Luther when he refused to recount his idea
- Christianity split - Luther’s ideas led to many others to come forward
- Lutherans: Luther’s followers - separated from Catholic Church
- Calvinism - John Calvin: predestination - only a few people would be saved by God, great influence in Scotland and France
- When the pope refused to annul King Henry VIII’s marriage to Catherine of Aragon because a heir wasn’t produced, he declared himself the head of religious affairs - presided over Church of England/Anglican Church
- Jesuits - Ignatius Loyola: prayer and good works leads to salvation
- Catholic Reformation (16th century)
- Catholic church attempts to remedy some of their controversies and regains some of its credibility - still wanted authority and control
- Council of Trent: reinstated pope authority, punished heretics, reestablished Latin as only language in worship
- Caused wars
Scientific Revolution
- Expanded education led to world discoveries
- Copernican Revolution: Nicolaus Copernicus - discovered earth and other celestial bodies revolved around the sun and the earth rotated on its axis
- Galileo: built off Copernicus’s theories and proved them - forced to recant by the Catholic Church and put under house arrest
- Scientific Method: shift from reasoning being most reliable means of scientific meaning to scientific method (theory, documentation, repetition, others experimenting)
- Tycho Brahe, Francis Bacon, Johannes Kepler, Sir Isaac Newton
- Led to Industrial Revolution, and many rejecting the church - atheists (believe no god exists), deists (believe God exists, but is passive)
- Deism: became popular in 1700s - God created the earth but doesn’t interfere in its workings
European Rivals
Spain and Portugal
- Spain became very powerful, supporting exploration, expansion of Spanish language and culture, and having a large naval fleet
- Under Charles V, Spain controlled parts of France, the Netherlands, Austria, Germany, Spain, America
- Under Charles’s son Philip, the Spanish Inquisition to oust heretics was continued, the Dutch Protestants under Spain revolted to form independent the Netherlands - lost a lot of money in mid-17th century and was poised to be defeated by England and France
- Portugal focused on dominating costal Africa, Indian Ocean, Spice Islands - lost control to Dutch and British
England
- Henry VIII never succeeded in having a male heir - his daughter Elizabeth I became Queen
- Elizabethan Age (1558-1603): expansion, exploration, colonization in New World - golden age
- Muscovy Company: first joint-stock company - British East India Company
- James I: succeeded Elizabeth in 1607 - England and Scotland under one rulership, reforms to accommodate Catholics and Puritans failed
- Charles I: succeeded James in 1625 - signed Petition of Rights (limiting taxes and forbidding unlawful imprisonment) - ignored it for the next 11 years
- Scottish invaded England out of resentment for Charles in 1640 - called the Long Parliament into session (sat for 20 years), which limited the powers of the monarchy
- Parliament raised an army, under Oliver Cromwell, to fight the King after he tried to arrest the
- Parliament defeats the king and executes him - began the English Commonwealth (Oliver Cromwell known as the first Lord Protector)
- Oliver Cromwell: intolerant of religion, violent against Catholics and Irish - highly resented
- Charles II: exiled son of Charles I invited by Parliament to reclaim the throne as a limited monarchy after Cromwell died (Stuart Restoration)
- Agreed to Habeas Corpus Act: prevents people from arrests without due process
- James II: succeeded Charles II after his death - highly disliked, fear he would make England a Catholic county - driven from power by Parliament (Glorious Revolution)
- Succeeded by his daughter Mary and her husband William - signed English Bill of Rights (1689)
France
- Unified and centralized under strong monarchy after Hundred Years’ War (1337-1453)
- Largely Catholic, but French Protestants started to emerge (Huguenots) and fought with the Catholics
- Henry IV: issued Edict of Nantes (1598) (environment of tolerance between religions) - first of Bourbon kings who ruled until 1792
- Cardinal Richelieu: chief advisor to the Bourbons who compromised with Protestants instead of fighting with them
- Created the bureaucratic class noblesse de la robe, succeeded by Cardinal Mazarin
- Louis XIV: reigned from 1642-1715 - highly self-important and grandiose, condemned many Huguenots, never summoned the French lawmakers, appointed Jean Baptiste Colbert to manage royal funds - France almost constantly at war to increase empire
- War of Spanish Succession (1701-1714): Louis’s grandson was to inherit the Spanish throne, so England, Roman Empire, and German princes united to prevent France and Spain from combining
German Areas (Holy Roman Empire?)
- Holy Empire was in present day Austria/Germany - weak due to the mixed dynamics, rulership, and religion of the surrounding area
- Lost parts of Hungary to Ottoman Turks in early 16th century
- Devastated by Thirty Years’ War (1618-1648)
- German states were gaining power by 18th century
- Peace of Augsburg (1555): intended to bring end to conflicts between Catholics and Protestants
- Thirty Years’ War: began when protestants in Bohemia challenged Catholics - violent and destructive
- Peace of Westphalia (1648): German states affirmed to keep the peace
Russia
- Russian leaders were overthrowing reigning Mongols in late 15th century
- Moscow became centre of Orthodox Christianity
- Ivan III refused to pay tribute to Mongols and declared them free from their rule - lead Russians, later Ivan IV did too
- Recruited peasants freedom from boyars (their feudal lords) if they conquered their own land themselves
- Ivan IV (Ivan the Terrible): strong leader feared by many - executing people who were threats to his power
- Battle for throne after Ivan IV died without an heir - Time of Troubles (1604 to 1613): killing those who tried to rise to the throne
- Michael Romanov was elected by feudal lords until 1917 - Romanovs consolidated power and ruled ruthlessly
- Peter the Great: ruled from 1682-1725 - redesigned and adapted Russia in to westernized fashion
- Catherine the Great: ruled from 1762-1796 - education and Western culture - serf conditions were of no importance to her
Islamic Gunpowder Empires
- Ottoman Empire precedes 1450 - founded by Osman Bey as the Mongol Empire fell
- Eventually invaded Constantinople in 1453 and ended Byzantine Empire (Constantinople now named Istanbul)
- Ottomans were Islamic and solidified rule over territory from Greece to Persia to around Mediterranean into Egypt and northern Africa by giving land (timars) to Ottoman aristocrats to control
- Employed practice called devshirme: enslaved Christian children and turned them into warriors called Janissaries
- Selim I: came into power in 1512, led much of the empire growth, made Istanbul centre of Islamic civilization
- Suleiman I: succeeded Selim I in 1520, build Ottoman military and arts - golden age from 1520-1566
- Took over parts of Hungary, but could not successfully take over Vienna
- Babur: Mongol leader who invaded northern India in 1526 - Mughal Empire (dominated for next 300 years)
- United entire subcontinent
- Akbar: succeeded Babur from 1556 to 1605 - united India further with religious toleration, did give Muslim landowners (zamindars) power to tax
- Hindus and Muslims lived side by side in a golden age of art and thought - under Shah Jahan, the Taj Mahal was built
- Aurangzeb: emperor who ended religious toleration and waged wars to conquer rest of India - Hindus were persecuted
- Europeans arrived in early 17th century to trade and spread ideas - after 1750 is when Britain turned into an imperial superpower
Africa
- Starting in 10th century, wealth accumulated from trade - Songhai, Kongo, and Angola became powerful kingdoms
- Songhai:
- Islamic state
- Sunni Ali: ruler 1464-1493 - navy, central administration, financed Timbuktu - fell to Moroccans
- Asanti Empire: arose in 1670 - avoided invasion and expanded its territory
- Kongo:
- King Alfonso I: Catholic, and converted his people
- Mostly destroyed by previous allies Portugal
- Angola:
- Established by Portuguese around 1575 for the slave trade
- Queen Nzinga resisted Portuguese attempts to further their control for 40 years
Isolated Asia
China
- Ming Dynasty was restored until 1644 after kicking out Mongols in 1368
- Built huge fleets in early 15th century to explore Asia and Indian ocean - Zheng He: famous Chinese navigator
- Economy started failing due to silver currency inflation, famines in 17th century, peasant revolts
- Qing warriors were invited to help Ming emperor but instead ousted him in 1644
- Qing/Manchus ruled China until 1911
- Not ethnically Chinese so had to affirm legitimacy - displayed imperial portraits with Chinese historical items
- Kangxi: ruled from 1661 to 1722 and conquered Taiwan, Mongolia, central Asia, Tibet
- Qianlong: ruled from 1735 to 1796 and conquered Vietnam, Burma, Nepal
- were both Confucian scholars
- Did not interact a lot with surrounding nations, protected their culture
Japan
- Shoguns ruled Japan in 16th century, but Christian missionaries came in and Jesuits took control of Nagasaki - westernization
- Tokugawa Ieyasu: established Tokugawa Shogunate (Edo period) from 1600 to 1868 - strict government that instituted a rigid social class model
- Moved capital of Japan to Edo (modern-day Tokyo)
- National Seclusion Policy (1635): prohibited Japanese from traveling abroad and prohibited most foreigners
- Japanese culture thrived - Kabuki theatre and haiku poetry became popular
Resistance
Key rebellions in 17th and 18th centuries:
- Ana Nzinga’s Resistance (Kingdoms of Ndongo and Matamba) - 1641-167
- Resisted Portuguese colonizers
- Cossack Revolts (Modern-day Ukraine) - 17-18th century
- Resisted Russian Empire but were eventually defeated
- Haitian Slave Rebellion (Haiti) - 1791-1804
- Resisted France and eventually achieved independence for Haiti
- Maratha (India) - 1680-1707
- Resisted Mughal Empire and defeated them starting the Maratha Empire
- Maroon Societies (Caribbean and Brazil) - 17th-18th century
- Resisted slave-owners in Americas and avoided attempts to be recaptured and sold
- Metacom’s War (US) - 1675-1678
- Resisted British colonists over unfair trade practices
- Pueblo Revolts (US) - 1680
- Resisted Spanish colonizers and their encomienda system, but victory was temporary
Unit 4: Transoceanic Interconnections
European and Expansion
Portuguese and Spanish controlled major shipping routes in Indian Ocean, Indonesia, Atlantic Ocean
Portugal financed explorations
- Prince Henry the Navigator (King John I’s son)
- Vasco da Gama: explored eastern Africa, India
Spain also did:
- Financed Christopher Columbus: explored Americas
Treaty of Tordesillas (1494): agreement between Spain and Portugal to split colonized land between them
England, Netherlands, France launched own explorations to acquire new colonies - caused rise in nationalism and powerful monarchies
Explorers
- Amerigo Vespucci (1500): South America
- Ponce de Leon (1513): Florida
- Vasco de Balboa (1513): Central America
- Ferdinand Magellan (1519): South America to Philippines
- Giovanni da Verrazzano (1524): North America
- Sir Francis Drake (1578): circumnavigated the globe
- John Cabot (1497): North America
- Henry Hudson (1609): Hudson River
Products that aided new explorations:
- Sternpost Rudder: invented in China - better control of ships
- Lateen Sails: invented in Roman Empire - allowed directional control of ships
- Astrolabe: navigation device that measured distance between sun and stars on horizon to determine latitude
- Magnetic Compass: developed in China - determine direction
- Three-Masted Caravels: large ships fit for longer journeys
The New World: Accidental Empire
- Spanish explorers found great wealth in Aztec and Inca Empires
- Hernando Cortés: landed on coast of Mexico in 1519 - sought to exploit the Aztec Empire of their gold and spices
- Neighbouring states were willing to help Spanish conquer Aztecs as they had taken over a lot of the neighbouring communities - or those who didn’t cooperate were forced or killed
- Became very hungry for wealth and quickly seized Montezuma and began a siege of Tenochtitlan
Disease: Ultimate Weapon of Mass Destruction
- Spanish brought smallpox to the Aztec Empire which reduced their population from 20 million in 1520 to 2 million in 1580 - Spanish were able to take control in 1525
- Francisco Pizarro took over Inca Empire in 1531 partially due to spreading disease to them
- Pizarro was in control of the Inca Empire by 1535
The Encomienda System
Spanish implemented a hierarchical colonial society as they took over the New World
Structure:
- Peninsulares: Spanish officials governing the colonies
- Creoles: Spanish born in colonies to Spanish parents - barred from high positions but were educated and wealthy
- Mestizos: those with European/Native American ancestry
- Mulattos: those with European/African ancestry
- Native Americans
Viceroys: governors of each of 5 regions of New Spain - established the encomienda system (system of forced labour of the natives and African slaves)
African Slave Trade
- Slaves brought to New World to work on the plantations and mines
- Europe exploited a system of slavery already existing in Africa - prisoners were supposed to serve their captors before being released
- Europeans traded for their surplus of enslaved people, but didn’t understand that they were supposed to be released
- As demand for slaves in Europe increased, Europe became even more ruthless - kidnapping Africans, causing wars, forcing rulers to give up their citizens
- Slaves were forced onto ships, chained below deck, and endured brutal Middle Passage
- Around 13 million Africans were taken - 60% to South America, 35% to Caribbean, 5% to North America, around 20% of people on each trip perished
The Columbian Exchange
- Transatlantic transfer of animals, plants, diseases, people, technology, ideas among Europe, Americas, and Africa
- Never before had so much moved across the ocean
- Transfer of food products caused population increase in Europe, Asia, and Africa
- Two key products: sugar (plantations appeared all over Spanish colonies), silver (mining also in Spanish colonies) - both used significant forced labour
- Spanish control of silver opened doors in Ming China
The Commercial Revolution
- Age of Exploration: trading, empire building, conquest - due to financing schemes
- Banking became a respectable practice - lead to joint-stock company (pool resources of merchants to distribute costs and reducing dangers of individual investors)
- Led to huge profits and modern-day concept of stock markets
- Muscovy Company, Dutch East India Company took over trade routes
- Mercantilism: theory that creating a favourable balance of import and export was best - of course, this led to Europe’s intense colonialism to match their import demand
- Caused resentment in colonies
- Europe established limited trade with China from 16-18th century
- Portugal gained control of Spice Islands to gain access to China
- China and Japan still highly limited their trade with them
- Developments in Specific Countries - 1450-1750
- Major movements of the times affected parts of Europe differently
- People with power guarded it
- Peasant class weren’t able to participate in any developments
- Powerful states were also developed in Middle East, India, China, and Japan
- Monarchies contributed to development of strong loyalties and led to many conflicts/wars
Unit 5: Revolutions
The Enlightenment
17th and 18th centuries - humankind in relation to government
Divine Right: church allied with strong monarchs, monarchs believed they were ordained by God to rule - people had moral/religious obligation too obey
- Question of ultimate authority
- Mandate of Heaven in China - had to rule justly to be appreciated in heaven
Social contract: governments not formed by divine decree, but to meet social and economic needs
Philosophers of the age:
- Thomas Hobbes (1588-1679): government should preserve peace/stability - all powerful rule who ruled heavy-handed
- John Locke (1632-1704): men are all born equal, mankind is good and rational - primary role of government was to secure and guarantee natural rights and revolting is justified if not
- Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778): all men are equal, society organized according to general will of people - government is protection by community and both being free
- Voltaire (1694-1778): espoused idea of religious toleration
- Montesquieu (1689-1775): separation of powers among branches of government
- David Hume (1711-1776): lack of empirical evidence casts doubt on religion
- Adam Smith (1723-1790): an “invisible hand” will regulate economy if it is left alone
- Mary Wollstonecraft (1759-1797): women should have political rights, including voting and holding office
- Immanuel Kant (1724-1804): knowledge exists beyond what is deduced from use of only observation or only reason
- Cesare Beccaria (1738-1794): criminals retain some rights and state should not practice cruel punishment
Enlightened monarchs: utilized ideas of tolerance, justice, improving quality of life
Neoclassical Period: middle of 18th century - imitated style of ancient Greek/Roman architecture
Enlightenment Revolutions in the Americas and Europe
American Revolution
- British defeated France over American territory - French and Indian War/Seven Years’ War - pushed France to northern territory
- Americans revolting against British rulership
- British passed laws on behalf of Crown for the American colonizers (George Grenville, Charles Townshend)
- Revenue Act (1764), Stamp Act (1765), Tea Act (1773) intended to raise funds for British government
- Colonizers opposed these laws and began battling British troops shortly after - Boston Tea Party (1773): colonists dumping imported tea in harbour to protest Tea Act
- Thomas Paine: wrote Common Sense, encouraging colonizers to form a better government than the monarchy - 6 months later the Declaration of Independence was signed
- France joined forces with Americans in 1777 and defeated the British in 1781 and the American democracy was created
French Revolution
France was running out of money from monarch spending, wars, and droughts - Louis XVI proposed raising taxes to the Estates-General (governing body infrequently called by the kings)
- First Estate: clergy
- Second Estate: noble families
- Third Estate: everyone else
- Representatives from each estate
Third Estate was facing being shut out of new constitution - formed National Assembly in 1789 out of protest and peasants stormed the Bastille shortly after
Declaration of the Rights of Man - adopted by National Assembly in 1789 and caused big changes in French government structure
Established a constitutional monarchy at first, but new constitution development led to the Convention being the new ruling body - France become a republic (led by Jacobins who later beheaded the king)
Convention threw out constitution again and created Committee of Public Safety: enforcer of revolution and murdered any anti-revolution people
- led by Maximilien Robespierre
French beheaded Robespierre in 1795 and established another new constitution with the Directory as the government
- Built up military, with Napoleon Bonaparte as one of the generals
Napoleon overthrew the Directory in 1799 - Napoleonic Codes (1804) recognized equality of men, dissolved the Holy Roman Empire with French military and fought other countries who eventually met to overthrow him (Prince von Metternich, Alexander I of Russia, Duke of Wellington)
- Defeated him at Waterloo in 1813 and met at Congress of Vienna to discuss what to do with France
Congress of Vienna:
- Balance of power should be maintained among powers of Europe
- Tried to erase French Revolution
Haiti:
- France enslaved many Haitians, who eventually revolted successfully, led by Pierre Toussaint L’Ouverture
- Jacques Dessalines, a former slave, became governor-general in 1804
South America
- Napoleon invaded Spain and appointed his brother Joseph Bonaparte to the throne -
- Colonists ejected French governor and appointed own leader in Venezuela, Simón Bolívar, who eventually helped them declare independence from Spain in 1811
- Established a national congress, but was also opposed by Spanish royalists, who declared a civil war
- Bolívar won freedom for Gran Colombia (Columbia, Ecuador, Venezuela)
- José de San Martin: took command of Argentinian, Chilean, Peruvian armies, and defeated many Spanish forces to also declare independence from Spain
Brazil
- John VI of Portugal fled to Brazil when Napoleon invaded Portugal -
- His son Pedro became the emperor of Brazil and declared it independent with a constitution
- His son Pedro II took over and abolished slavery
Mexico
- priest Miguel Hidalgo led a revolt against Spanish rule in 1810, who was later killed by them
- Jose Morelos picked up where he left off
- Independence achieved in 1821 - Treaty of Cordoba: Spain recognizing their 300-year-old control of Latin America was ending
- Neocolonialism: independent nations still controlled by economic and political interests
- Riches accumulated often stayed within wealthy landowning class
- Mexican Revolution: protest of neocolonialism - rejection of Porfirio Diaz’s dictatorship to protest impoverished conditions
Other resistance movements:
- Peru
- Tupac Amaru II led a revolt against Spanish occupiers and inspired further resistance movements
- West Africa
- Samory Toure led resistance against French colonizers and inspired further resistance
- US
- Sioux resisted the US government invading their land, but were shot at during their protests
- Sudan
- Muhammad Ahdam led Mahadists in a revolt against colonial rule of Egypt but was stopped by the British
- Slavery still existed in independent nations as well as class inequalities
- Catholic Church still dominated
Industry and Imperialism
Industrial revolution in Britain can not be separated from Imperialism
Industrial countries gained power quickly to exploit colony resources
Industrial Revolution: began in Britain in 19th century - spread through Europe, Japan, US
Agricultural output increased significantly again - more people moved to cities
- Enclosure: public lands that were shared for farming became enclosed by fences
- New farming technologies
- Urbanization was natural - London grew to over 6 million people
Domestic system (most work being done on farms or at home or at small shops) preceded
New advancements that changed production:
- Flying shuttle: sped up waving process
- Spinning jenny: spinning vast amounts of thread
- Cotton gin: invented by Eli Whitney - processed massive amounts of cotton quickly
- Steam engine - Thomas Newcomer, James Watt
- Steamship - Robert Fulton
- Steam-powered Locomotive - George Stephenson
- Telegraph: communication with great distances in seconds
- Telephone - Alexander Graham Bell
- Lightbulb
- Internal Combustion Engine for cars
- Radio
Also major developments in medicine and science, theory of natural selection (Charles Darwin)
Rapid creation of products was done in factories
- Interchangeable parts: machines could be replaces or fixed quickly
- Assembly line: each worker had one small part in production - man became the machine
- Workers were overworked, underpaid, and working in unsafe conditions - child labour was common
- Despairing conditions
Formation of new social classes - aristocrats were those rich from industrial success, middle class of skilled professionals, huge working class
Adam Smith: success achieved through private ownership and free market system (capitalism) - governments removed from regulation = laissez-faire capitalism
- Start of stock market and other financial instruments
Karl Marx: The Communist Manifesto - working class take over means of production and all resources would be equally - Marxism was foundation for socialism and communism
- Luddites: workers who destroyed equipment in middle of night to protest working conditions
- Marxism mixed with capitalist thought to create partly socialist systems in many places
Major split among intellectuals and policymakers in regards to response to inhumane factory conditions
Factory Act of 1883: limited hours of each workday, restricted children from working, factory owners had to make conditions safer
- Labour Unions: vehicles for employees to bargain for better conditions
- Living conditions improved - middle class became larger, public education increased, social mobility became more common
- Slave trade abolished in 1807 in Britain
- Women became more limited to their traditional roles
Nationalist Movements and Other Developments
Nationalism was strong after Napoleonic era
France, Spain, Portugal, Britain, Russia had unified
Italy and Germany, which were city-states took longer to unify and alter balance of European power
- Italy: Count Camillo Cavour named prime minister of Sardinia by Victor Emmanuel II who pushed for nationalism - after Giuseppe Garibaldi, another nationalist overthrew other Italian kingdoms, a lot of Italy was unified in 1861
- Germany: Prussia, which controlled a lot of present-day Germany, under the rule of William I who appointed Otto von Bismarck as prime minister, defeated Austria and engaged in the Franco-Prussian War to create the new German Empire
- New emperor William II forced Bismarck to resign and built a huge military force
Other Nationalist Movements:
Russia:
- Romanov czars had absolute power in 19th century
- Alexander II began reforms - Emancipation Edict: abolished serfdom but had little effect
- Small middle class began to emerge which led to an intellectual political group The People’s Will assassinating Alexander II
- In response, Alexander III started Russification: all had to learn the Russian language and convert to Russian Orthodoxy
Ottoman Empire: was at danger of collapse so Britain and France worked to maintain it to prevent Russia from gaining control over Mediterranean
The Growth of Nationalism
- Desire of people of common cultural heritage to form independent nation-state/empires that protects their cultural identity
- Had major influence and effects all over the world
Unit 6: Consequences of Industrialization
In Search of Natural Resources
Europe has coal and iron for power and factory equipment, but needed raw materials that didn’t grow there - solution = colonization
Colonization has given industrial countries great wealth
Europe had colonized nations on every continent - depleted raw materials in these nations at extreme speed and destroyed and polluted environments
Transnational Businesses: international corporations that strengthened Europe’s economic power in Asia and Africa
European Justification
Europe was very ethnocentric - other cultures were barbaric and uncivilized, even as progressives were denouncing the slave trade - why?
- Social Darwinists: applied natural selection to sociology - there were dominant races or classes , therefore Britain was the most powerful/fit
- Moral obligation to civilize others - Rudyard Kipling’s poem “White Man’s Burden” described colonization as justified
European Imperialism in India
- India had many luxuries to Europeans - tea, sugar, silk, salt, jute
- India was vulnerable to external powers after wars in 18th century Mughal empire and religious conflict
- France and England battled each other in Seven Year’s War for colonial superiority and Britain won
- British East India Company: joint-stock company like a multinational corporation - had exclusive British trade rights in India - led by Robert Clive
- Britain started slowly taking over Mughal Empire territory and setting up administrative regions through empire - first, island of Ceylon, then Punjab Northern India, then Pakistan and Afghanistan
- Sepoy Mutiny: Indians who worked for British as soldiers were called Sepoys - they rebelled against British Muslim/Hindu disrespect in 1857, but it failed
- British then made all of India a crown colony - Queen Victoria made Empress of India above almost 300 million Indian subjects
- Mughal Empire ended when last ruler Bahadur Shah II was sent into exile
- India became model of British imperialism - upper castes taught English, Christianity spread, industrialization and urbanization - but more and more Indians dreamed of being free from Britain
- 1885: group of Indians formed Indian National Congress to fight for independence - wouldn’t be achieved until mid-20th century
European Imperialism in China
- Up until 1830s, Europe could only trade with China in city of Canton - China was relatively isolationist, until Europe gained industrial power and barged in with weapons
- Opium Wars: British traders brought Opium to China in 1773 and widespread addiction was caused - forbidden and seized in 1839
- Britain wanted to continue trade, so brought war to China
- Treaty of Nanjing: China forced to sign unequal treaty that gave Britain considerable rights to expand trade with China
- Hong Kong declared crown possession of Britain in 1843
- Second Opium War occurred in 1856 for four years when Britain tried to further trade and China lost again - all of China opened to trade
- British takeover caused Chinese to turn on their government’s failings
- White Lotus Rebellions (beginning of 18th century): Buddhists who were frustrated over taxes and government corruption
- Taiping Rebellion (mid-18th century): rebels led by religious zealot who almost succeeded in taking down Manchu government
- Self-Strengthening Movement (1860s): Manchu Dynasty attempt to get its act together, which failed
- Korea declared independence from China in 1876
- Sino-French War (1883): Chinese lost control of Vietnam
- Defeated by Japan in Sino-Japanese War
- Treaty of Shimonoseki (1895): China forced to hand control of Taiwan to Japan and give them trading rights
- France, Germany, Russia, Britain took their own spheres of influence in China - not quite colonies as Manchu Dynasty still had authority
- in 1900, US pledged to support sovereignty of Chinese government and equal trading to prevent full British takeover (Open Door Policy) - despite barring Chinese immigrants from US in 1882 (Chinese Exclusion Act)
- Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists, or Boxers: Chinese peasant nationalists attempted to rebel by slaughtering Christian missionaries and controlling foreign embassies in response to government’s defeats and concessions to the West, but failed
- Boxer Protocol: China forced to pay Europeans and Japanese with rebellion costs
- Chinese culture also started to crumble - imperial government ended in 1911 and a republic was established in China
Japanese Imperialism
- Japan kept Europeans away in 17th and 18th centuries - until European and US appetite for power intensified and Commodore Matthew Perry arrived from US in a steamboat in 1853 - Japan felt obligated to join industrialized world
- Treaty of Kanagawa (1854) was a trade agreement with the West
- Samurai revolted against shogun who ratified it and restored Emperor Meiji to power
- Meiji Restoration: era of Japanese westernization - Japan became a world power
- 1870s: built railways and steamships, abolished samurai warrior class
- Prioritized military power - took control of Korea and Taiwan from China in 1895 - military pageantry became a cultural movement
- 1890s: Japan became powerful enough to reduce European and US influence
European Imperialism in Africa
- Interior Africa remained unknown to Europeans - costal regions used for limited trade, ship stopping points, and the slave trade
- 1807-1820: most European nations abolished slave trade as Enlightenment principles gained more force - slavery abolished a few decades later
- No new enslaved people entered Europe but those still in slavery were not free until mid-century
- Former slaves returned to Africa or established their own nations
- South Africa: Dutch first arrived and settled Cape Town - British seized it in 1795
- South African Dutch (Boers) moved northeast and discovered diamonds and gold - British followed and fought the Boer War (1899-1902) to gain rights to resources, which they won
- Egypt: when Napoleon tried to take control of Egypt in 18th century during the weak Ottoman rule, Muhammad Ali defeated the French and the ruling Ottoman Empire in 1805 - began industrialization and agriculture expansions
- efforts just temporarily halted by Abbas I
- Suez Canal constructed with French and completed in 1869 - connected Mediterranean to Indian Ocean (eventually British took control of it too)
Berlin Conference
Otto van Bismarck hosted European powers in Berlin in 1884 to discuss land claims in African Congo - encouraging colonialism
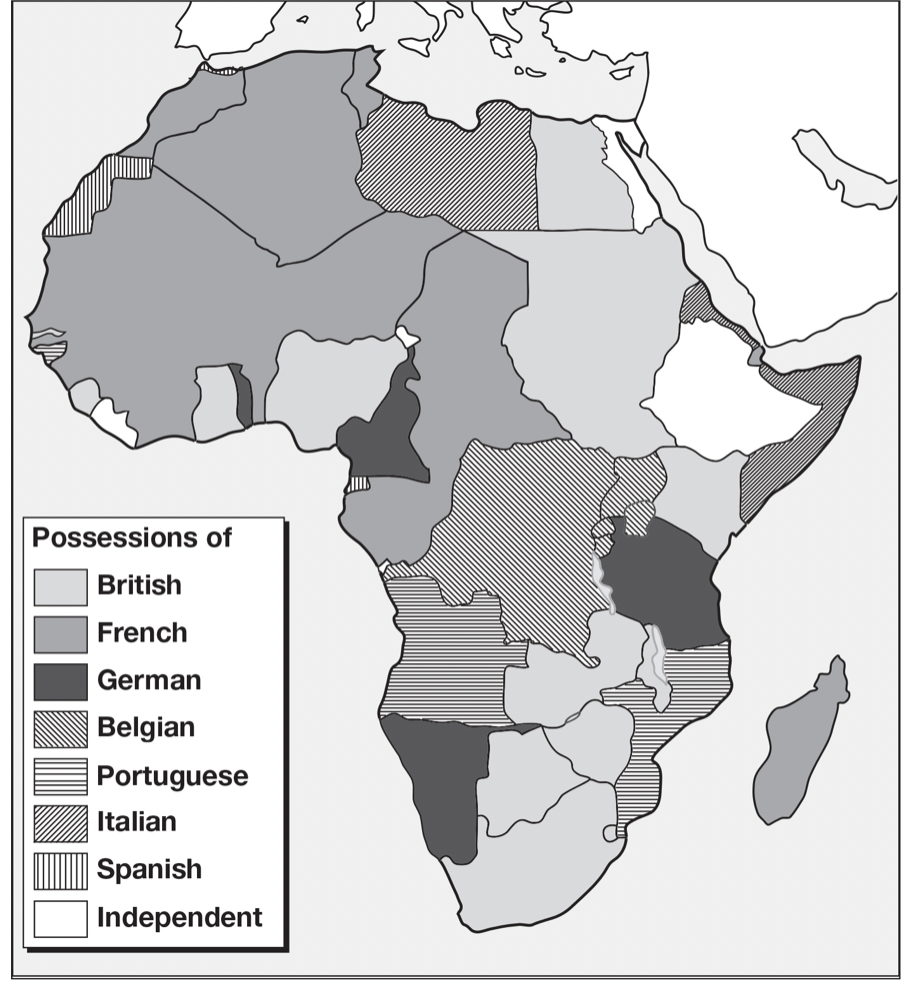
By 1914, almost all of Africa was colonized by Britain, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Portugal, and Belgium (except Ethiopia and Liberia)
Europeans added substantial infrastructure to the continent, but stripped Africa of resources, most exercised direct rule and implementation of customs over African people (except British who were already busy with India)
Europeans disregarded African boundaries, cut tribal land in half or forced enemy tribes together, ignoring history and culture
Traditional African culture also started falling apart
US Foreign Policy
- Monroe Doctrine: US President Monroe declared Western Hemisphere off-limits to Europeans in 1823 - Britain agreed out of fear of Spain’s potential actions
- Roosevelt Corollary to Monroe Doctrine: US would be responsible for intervening in financial disputes between Americas and Europe, if to maintain peace because Europe was still investing in Latin industry
- US was exercising own imperialism over Latin America - built their Panama Canal in Panama
- US launched Spanish-American War in 1898 to aid Cuba in their conflict with Spain - defeated Spain and gained control over Philippines, Guam, Puerto Rico, and Cuba (given independence in exchange for construction of US military bases)
Unit 7: Global Conflict
The World War I Era
- At beginning of 20th century, most of world was colonized by Europe or had been colonized by Europe - everywhere was connected to instability in Europe
- European countries had had feuds, but industrialism and rise in nationalism caused military build-up and more powerful weapons, alliances and power-grabbing rivals increasing
- Triple Alliance (1880s): Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy - protect against France
- France-Russian alliance to keep Germany in check
- Schlieffen Plan: Germany’s attack on France through Belgium, a neutral country
- Triple Entente: Britain, France, Russia - later joined by Japan
- Ottoman Empire was in bad shape and kept losing territory - Greece, Slavic areas declaring independence, countries disagreeing on land arrangements and allies
- Bosnia and Herzegovina still under control on Austria-Hungary, as decided by Berlin Conference of 1878
- Austria-Hungary Archduke Franz Ferdinand visited Bosnia and was assassinated by Serbian nationalist Gavrilo Princip - war was already on the horizon and this was the final blow
- Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia - Russia was allies with Serbia - France, Germany, Britain joined to honour their alliances (Italy later joined the Triple Entente in 1915)
- Central Powers Alliance: Ottoman Empire, Germany, Austria-Hungary
- Over 40 countries joined the war effort because in part of widespread colonial connections
- US joined the Allies in 1917 after Germany sunk British boat Lusitania in 1915 which had over 100 American passengers on board and kept sinking American ships attempting to bring resources to Britain - final push was Germany trying to get Mexico to join the war in 1916 (Zimmermann telegram - a secret telegram between German diplomats saying Mexico could regain territory taken by US if they joined forces)
- Previously had isolationism policy (neutrality, focusing on internal affairs instead)
- The Great War lasted until Germany and Central Powers gave up in November 1918
- 8.5 million soldiers were killed
- 20 million civilians died
- The Treaty of Versailles: signed in 1919 - official end to WWI
- Germany was to pay war reparations, release territory, downsize military to prevent them from rising to power again - poverty and resentment in Germany led to Hitler’s rise
- Austria-Hungary divided into other nations like Czechoslovakia
- Departure from President Wilson’s Fourteen Points, more focused on future peace and workable balance of power - but was disapproved of by Britain and France who put strict punishments on Germany
- President Wilson called for formation of council of nations called League of Nations to preserve peace and establish humanitarian goals, but was not widely accepted (even by US)
- Russian Revolution
- Socialists began to organize after Czar Nicholas II’s forced resignation in 1917, resentment was strong among working class
- Had lost war against Japan over Manchuria in 1904
- Fired at peaceful protestors in 1905 (Blood Sunday)
- Alexander Kerensky established a provisional government - ineffective because it disagreed with the local councils, soviets, who represented workers, peasants, and soldiers
- Socialist party is known as the Bolsheviks - led by Marxist leader Vladimir Lenin
- April Theses: issues by Lenin - demanded peace, land for peasants, power to soviets
- within 6 months took power of government - soon to be called Soviet Union
- Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (1918): armistice with Germany - ceded part of western Russia to Germany so they dropped out of WWI
- Counterrevolutions began occurring in Russian empire - Bolsheviks created Red Army, military force under Leon Trotsky to defeat counterrevolutions
- Soviet Union became a nation lacking of trust by Western neighbours with a powerful army
- When Ottoman Empire joined the Central Powers, a movement to reclaim Turkish culture spawned a genocide of Armenian minority and a shift to Turkish nationalism - which resulted in loss of most of remaining land in peace negotiations
- Mustafa Kemal (Ataturk): led successful military against invading Greece and overthrew Ottoman Empire to become first president of Turkey
World War II Era
Stalin and the Soviet Union
- Lenin first instituted the New Economic Policy (NEP) in 1920s - allowed farmers to sell portions of grain for profit - successful, but Lenin died and new Communist leader, Joseph Stalin discarded it
- Five-Year Plans: taking over private farms for state-owned enterprises (collectivization) - really was totalitarianism
- Stalin industrialized the USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics) - relied on terror (secret police, bogus trials, assassinations)
The Great Depression
- War was expensive and Europe owed a lot of money to America (especially France and Germany)
- Money was based on credit, loans that would never be repaid = US stock market crash in 1929 leading to international catastrophe
- US and Germany hit the hardest - 1/3 of workforce unemployed, loss of trust in government = fascism
Fascism
- Main idea: destroy will of individual in favour of the people
- Wanted a unified society like communists, but did not eliminate private property or class distinctions
- Pushed for extreme nationalism - often on racial identity
- Fascism in Italy
- First fascist state - founded by Benito Mussolini in 1919
- Squad called Blackshirts fought socialist and communist organizations to win over factory and land owners
- The Italian king named Mussolini Prime Minister
- Faced very little opposition and took over Parliament in 1922
Rise of Hitler
- Revolt when German emperor was abdicated after WWI - a conservative democratic republic took over (Weimar Republic)
- Mussolini’s success in Italy was influencing Germany - Nationalist Socialist Party (Nazis) rose to power in 1920s
- People of Germany were rejecting Weimar Republic elected body the Reichstag due to economic crisis
- Adolf Hitler became head of Nazi Party - believed in extreme nationalism and superior race - believed the Aryan race was the most superior race
- By 1932, Nazis dominated German government and Hitler became leader of Reichstag in 1933
- Seized control of the government - his fascist rule is known as the Third Reich
Appeasement?
- Hitler began rebuilding military (against Treaty of Versailles) and withdrew Germany from League of Nations
- Spain was in turmoil after fall of Spanish monarchy - nationalist army under General Francisco Franco took control of large parts of Spain - established a dictatorship in Spain in 1939 with help from Germany and Italy
- Hitler continued restoring Germany: took back the Rhineland part of Germany, formed alliance with militant Japan, annexed Austria, given Sudetenland at Munich Conference of 1938 (Hitler, Mussolini, Neville Chamberlin of England) to cease his expansionist activities (appeasement) - did not work
- Hitler invaded rest of Czechoslovakia in 1939 and Italy invaded Albania in 1939
- Germans and Soviets signed a pact to stay out of each other’s countries (Nazi-Soviet Pact) and agreed to divide rest of Europe’s land between them
- Germany invaded Poland and Britain and France then declared war on Germany - start of WWII
Japan
- Became a world power when accepting an alliance with Britain in 1905
- Economy thrived after WWI until the Great Depression - Japanese militarists gained momentum
- Japan invaded Manchuria in 1931 and renamed in Manchukuo
- Withdrew from League of Nations and signed Anti-Comintern Pact (against communism) with Germany, beginning their alliance
- In 1937, began war on China which eventually merged into WWII
Review of WWII
- Hitler’s blitzkrieg technique destroyed everything in its path - by early 1940 Germany had control of Poland (half with USSR), Holland, Belgium, France
- Britain’s PM Winston Churchill did not give in to Germany’s pressures - even with German airstrikes from their more powerful airforce (Battle of Britain)
- Germany invaded Greece in 1941, breaking their deal with Soviet Union, so they invaded the Soviet Union too
- US didn’t want to get involved, but froze Japan’s assets in US to respond to their hostility - Japan entered Tripartite Pact with Rome and Berlin, making the war worldwide
- in response to US sanctions, Japan bombed Pearl Harbor in Hawaii in 1941 and declared war with US
- US began working on Manhattan Project: development of the atomic bomb
- 1943: US and Britain take control of Italy
- 1944: US, Britain, and Canada land on French beaches (D-day) and eventually liberate France
- 1945: Allied forces close in on Germany and end Europe war when Hitler commits suicide
- To end war in Pacific, US drops atomic bomb on city of Hiroshima in Japan - when Japan refused to surrender, they dropped another bomb on Nagasaki, causing them to surrender
The Consequences
The Holocaust
- Millions of Jews under German control were rounded up and killed in concentration camps to create the Aryan race
The Peace Settlement
- US and Soviet Union became superpowers and Germany and Japan forced to demilitarize
Europe Torn to Shreds
- US instituted Marshall Plan to rebuild Europe (only accepted by Western Europe nations) and rebuilt their economies in less than a decade
Decline of Colonialism
- War inspired native populations to rise against their oppressors
Big Changes for Women
- Women took over the workforce while men were fighting - after the war, many women kept their jobs
Creation of International Organizations
- United Nations, established in 1945, to prevent break out of another great war - goal was to mediate and intervene in international disputes
- UN published Universal Declaration of Human Rights in response to Holocaust
- World Bank, International Monetary Fund, General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs also formed to manage a global economy
Cold War
- US or Soviet Union did not want each other to spread its influence beyond their borders, so they were strategizing how to contain each other - lasting for the next 50 years
Unit 8: Cold War and Decolonization
Communism and the Cold War
- Cold War lasted from 1945 to early 90s
- US and Soviet Union tried to get the rest of the world to side with them
- An arms based race between - nuclear arsenals became large enough to wipe out the whole world
Power Grab
- Biggest conflict over future security - both wanted their worldview to dominate:
- US: capitalism, democracy
- USSR: communism/totalitarianism
- At conferences in Yalta and Potsdam in 1945, parts of Eastern Europe were divided among Allied forces - Soviet Union demanded control of its neighbouring states (Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria), which the US disagreed with
- 1948: French, US, British sections of Germany merged into one, while Eastern Germany was under Soviet control - they cut of access to Berlin from Western side (Berlin Blockade)
- US flew in resources to trapped Western side (Berlin Airlift) until Soviets relented and split Berlin in half - built a wall on their side (Berlin Wall)
- East Vs. West
- Europe was clearly divided in East and West
- East: East Germany, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Romania, Hungary = Soviet bloc
- West: Britain, France, Italy, Belgium, Netherlands, Norway, West Germany, Greece, Turkey = Western bloc
- Truman Doctrine (1947) said US would aid countries threatened by communism (containment) - Western bloc formed military alliance NATO for this
- In response, Eastern bloc formed Warsaw Pact
- Two alliances became heavily weaponized - line between them was called the Iron Curtain
- Many countries were part of nonalignment - accepted investments from US and USSR but didn’t side with either
- Helped many former colonies find cooperative economic relations
- Bandung Conference (1955): leaders from Africa and Asia meet to discuss these partnerships - Non-Aligned Movement
China
- After fall of Manchu Dynasty in 1911, Sun Yat-sen led the Chinese Revolution of 1911 for China to become more Westernized and powerful
- Sun Yat-sen’s Three Principles of the People: nationalism, socialism, democracy
- Established his own political party for his own goals - the Kuomintang (KMT)
- Chiang Kai-shek established KMT in 1920s while Japanese and Soviets also struggled to control China
- US helped drive Japan out, but communists and KMT continued to fight Chinese Civil War for next 4 years
- Communists recruited millions of peasants under Mao Zedong to drive KMT out of China into Taiwan (where they established Republic of China)
- Mainland China became People’s Republic of China and the largest communist nation in the world
- Taiwan and People’s Republic of China are still separated
- Mao Zedong
- At first was successful in increasing China’s productivity and agriculture
- Implemented Great Leap Forward by creating communes (local governments) to achieve a Marxist state - they couldn’t keep up with their agricultural quotas, so they lied about it causing starvation of over 30 million Chinese people
- After withdraw of Soviet support, military became his focus and capitalism was implemented into economy - Mao didn’t like it
- Mao’s Cultural Revolution: got rid of all Western influences to prevent privileged classes - universities shut down and most worked as farmers from 1960s to 70s
- Deng Xiaoping
- New leader - focused on restructuring economy, reimplemented education
- Free-market capitalism elements, property ownership, foreign relations - but still largely communist
- Tiananmen Square Massacre: hundreds of protesters for democratic reform killed by government troops
Division of Korea - Korean War
- After WWII, was held half by Soviets and half by US until Korea could achieve stability
- Soviet communist regime in North Korea
- US democracy in South Korea
- North Korea attacked South Korea in 1950 to unite the two countries - United Nations, under General MacArthur, supported South Korea and China supported North Korea - armistice didn’t happen until 1953
- North Korea remains an isolated and dangerous nation today
Vietnam War
- After WWII, France attempt to hold on to colony of Indochina, but Vietminh nationalists fought back until it was agreed to split the nation into two
- Communists - North under Ho Chi Minh
- Democrats - South under Ngo Dinh Diem
- Soon war broke out between them - France and US supported South, but eventually the South was taken over by communist Viet Cong fighters, which looked very bad for US
Genocide in Cambodia
- Communism took over Cambodia and communist faction Khmer Rouge took over the government - goal to get rid of professional class an religious minorities led to 2 million deaths by the government
The Cuban Revolution
- US remained involved in Cuban affairs after Spanish-American War under Platt Amendment
- US supported the Batista Dictatorship from 1939 to 1959 until peasants began revolting in 1956 under leadership of Fidel Castro - led to Cuban Revolution in 1959
- Castro promoted democracy but immediately established a communist dictatorship instead, so the US imposed economic bans on trade with Cuba - strengthened Cuba’s ties with Soviets instead
- US organized Bay of Pigs Invasion with a small force of Cuban exiles, authorized by President Kennedy, to overthrow Castro - they were immediately captured
- In response, Soviets installed missiles in Cuba and when US found out, they established a navel blockade around the island - Cuban Missile Crisis
- Soviets eventually backed down when US agreed to not invade Cuba - closest brush with nuclear war
Cold War Tensions and Democratization in Latin America
- US’s capitalistic destruction of resources in Latin America stirred radical political parties in Mexico, Peru, Venezuela, Brazil - US was the imperialist “Good Neighbour”
- US distracted by wars and Cold War led to single-party rule in Mexico, brutal militaristic leaders in Argentina and Chile, and socialist democracies in Nicaragua and Guatemala
- US focused on Nicaragua - ground for Bay of Pigs Invasion, targeting of Sandinista guerrillas in 80s
- Reliance on export economies has resulted in poor domestic economies and debt
- Only in 2000 did Mexico have first multi-party election - opposition, PAN party, won
Cold War Ends
- People in Eastern Europe, under communism, began to revolt over poor living conditions compared to the West, democracy, and self-determination in the 80s
Poland
- A Solidarity movement under Lech Walesa brought thousands of workers wanting reform of communist economic system
- Not until reform-minded Mieczyslaw Rakowski became the Prime Minister did Solidarity become legalized in 1989
- Tadeusz Mazowiecki, Solidarity member, became PM in first open elections
- Communism fell in 1990, Lech Walsea become president, and economy improved swiftly
German Reunification
- Decline of communism in Soviet bloc led to East Germany cutting ties with Soviets
- Berlin Wall was torn down in 1989 and East and West reunified
- Germany now focused on peace and economic reform instead of violence
The Soviet Union Collapses
- Mikhail Gorbachev came to power in 1986 and urged restructuring of Soviet economy - elements of private ownership instituted, nuclear arms treaties with US
- When Poland and other former Soviet nations separated from USSR, Soviet Union disintegrated in 1991
- Mostly peaceful, but ethnic cleansing occurred in the Balkans and many Muslims were murdered by Christian Serbians - led to UN troop involvement
- Most new countries formed constitutional democracies, Cold War was over, and US emerged as the world’s only superpowers
- Democracy and Authoritarian Rule in Russia
- New Russia looked like a perfect federal state, but their abrupt intro to democracy and capitalism led to corruption, high unemployment, poverty, widespread crime
- First president, Boris Yeltsin, had the challenge of reforming Russia
- Yeltsin resigned in 1999 and former KGB agent Vladimir Putin became the head and has between the President and Prime Minister since then
- Has caused significant unrest in relations with other nations
Independence Movements and Developments in Asia and Africa
Indian Subcontinent
- Indian National Congress, mostly Hindu, established in 1885 and Muslim League in 1906 to increase rights of Indians under colonial rule
- In 1919, Amritsar Massacre catapulted resistance - 319 Indians killed by the British during a peaceful protest
- Mohandas Gandhi became an important figure in resistance - philosophy of passive resistance (demonstrations, boycotts instead of violence)
- Hindu and Muslim groups disagreed while fighting for the same cause - Muslims pushed for their own nation called Pakistan
- Independence Won by India
- Britain granted independence to India after WWII
- Muslims and Hindus disagreed with how the independent nation should function - one group wanted unity between Hindus and Muslims, the other wanted to partition the subcontinent and form a separate Muslim nation (led by Muhammad Ali Jinnah)
- British separated the subcontinent into three parts: India (Hindu), and Pakistan (Muslim) in two parts
- Many died by religious persecution as they migrated across religious lines - created international conflict between Pakistan and India
Africa
- In 1910, South Africa established its own constitution, that was discriminatory to native Africans, and in 1912, the African National Congress was formed to oppose European colonialism
- in 1950s, independence movement across Africa grew and Gamal Nasser, general in Egyptian army, overthrew Egypt king and established a republic - inspired other Islamic nationalists along Mediterranean to also become independent
- Many Africans were undereducated and did not have skills to build productive, independent nations and European influence had caused major destruction in social dynamics
- Algeria fought war for independence against France from 1954-1962
- Nigeria and Ghana negotiated their freedom from Britain
- Kenya also negotiated constitution with Britain
- Angola and Belgian Congo overthrew colonial governments causing civil wars
- Zimbabwe was among last to establish majority African rule in 1980
- 53/54 of African nations belong to African Union - replaced Organization of African Unity
- Still, Chad, Sudan, Uganda, Somalia, Rwanda, Congo continue to be wrecked by civil wars
- Rwanda
- Conflict between Tutsi and Hutu groups (Tutsi, 15% of pop., governed the Hutu) caused ethnic strife, genocide, and human rights violations after colonial authorities left
- Hutu revolted and killed as many as 800000 Tutsis over 100 days of genocide
- Apartheid in South Africa
- Union of South Africa formed in 1910 combing British and Dutch colonies, the year after South Africa Act, completely excluded Black people from politics
- 1923: segregation established and enforced
- 1926: Black people banned from certain occupations
- 1948: system of apartheid (racial separation) established - Black people forced into the worst parts of the country and city slums
- Nelson Mandela became leader of African National Congress in 1950s determined to abolish apartheid
- Sharpeville massacre: 67 protesters against apartheid killed - African National Congress then supported guerrilla warfare (resulted in Mandela being jailed in 1964)
- Mandela was released in 1990 and apartheid crumbled - he was the
first president elected in a free and open election
Middle East
- After WWI, France was put in charge of Syria and Lebanon, Britain in charge of Palestine, Jordan, and Iraq (Iran between Britain and Russia) - Arabia united itself as a Saudi Kingdom
- Creation of Modern Israel:
- Many Jews left Israel region as Palestine became more and more Islamic
- During WWI, Zionists (Jewish nationalists) convinced Arthur Balfour (Britain’s foreign secretary) to issue Balfour Declaration of 1917 - declared that Jewish people had right to live in Palestine, without displacing current Palestinians
- Jews fleeing antisemitic mobs (pogroms) began flooding into Palestine, a lot more came during the 30s to escape Hitler
- Jewish Wait for a State Ends in 1948 - two Palestines, one for Jews and one for Muslims, officially created
- As soon as David Ben-Gurion became first prime minister of Israel, Muslims attacked Israel (1948 Arab-Israeli War)
- Israel fought back and eventually controlled most of Palestine, while Jordan held remaining portions (West Bank)
- 1967 Six-Day War resulted in Israelis taking over all of Palestine - West Bank, Sinai Peninsula, Gaza Strip (Egypt), Golan Heights (Syria)
- In 1977, Egypt recongized Israel’s right to exist when Prime Minister Menachem Begin of Israel and President Anwar Sadat of Egypt signed the Camp David Accords - a huge blow to Palestinians (did not recognize West Bank in accords)
- Since then, Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), dedicated to reclaiming land and Palestinian state, has been unsuccessful in negotiating a homeland
- In 2000, violence continued and Israel PM Ariel Sharon constructed a wall between Palestinian West Bank and Israel
- In 2005, Palestinian president Mahmoud Abbas signed a cease-fire with Israel after previous president Yasser Arafat failed to do so
- Intense division, military violence, and terrorism still exists between the groups and no advancements have been made
- Iranian Revolution
- When Reza Shah Pahlavi rose to power and lead the shah in 1925 in Iran, Westernization was introduced to the nation
- In 1960s, rights of women increased drastically which angered Islamic fundamentalists
- President Jimmy Carter of US visited Iran to congratulate them on their modernization, which was the breaking point for fundamentalists - in 1979 Iranian Revolution ousted current shah and went back to a theocracy led by Ayatollah Khomeini
- Human rights advancements were reversed and women went back to traditional roles - Qu’ran became basis of legal system
- Iraq soon after invaded Iran over border disputes - Iraq received quiet support from US but still led to 8-year Iran-Iraq War
- Power struggle still continues in Iran and American-led war that began in Iraq in 2003 complicated matters further
- Oil
- Middle East was sitting on more than two-thirds of world’s oil reserves
- Multinational corporations rushed to gain drilling rights in 20th century
- Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iran, and Iraq started to earn billions annually, so they organized with some oil-exporting nations to form a petroleum cartel (OPEC) leading to more money and modernization
Unit 9: Globalization
International Terrorism and War
After WWII, there was an increasing interest in maintaining international security - organizations like NATO, United Nations, International Criminal Court in The Hague (prosecutes war crimes), and NGOs (Amnesty International, Doctors Without Borders) to provide international aid to those in need
War in the Gulf
- Iraq wanted to gain more control of oil reserves so they invaded Kuwait in 1990 under leadership of Saddam Hussein
- United Nations sent forces to drive Iraqis out in early 1991 - now called Persian Gulf War
- UN liberated Kuwait and put severe limitations on Iraq’s military and economic activity (although Hussein remained in power for another 10 years)
- In 2003, coalition of countries, mostly US and Britain invaded Iraq to oust Hussein - Hussein was captured in December 2003 and a democratic government was formed in 2005
- Despite conflicts and terrorism between Sunni, Shiites, and Kurds groups, a Kurdish president, Jalal Talabani and a Shia minister, Nouri ai-Maliki were elected, but they still have faced a number of challenges
Taliban, Al Qaeda, Osama bin Laden
In early 1980s, Soviets sent troops to Afghanistan under at request of Marxist military leader Nur Muhammad Taraki
Afghanis opposed communism and fought back until Soviets withdrew troops - left a power void that warring factions vied to fill
Taliban, an Islamic fundamentalist regime, filled the void after 14 years of fighting
Provided a safe haven for Osama bin Laden, the Saudi leader of the international terrorist network Al Qaeda, who specifically despised the US
US:
- Supports Israel
- Had troops stationed in Saudi Arabia
- Is the primary agent of globalization believed to be infecting Islamic culture
On September 11, 2001, Al Qaeda attacked US by hijacking 4 US planes and flying 2 of them into the World Trade Centre in New York, 1 into the Pentagon, and 1 into a field in Pennsylvania - 3000 people died
US immediately declared a war on terrorism and invaded Afghanistan - the Taliban was removed from power and Osama bin Laden was killed, but Al Qaeda still survives
Many terror attacks linked to Islamic fundamentalists still occur throughout Europe and the Middle East
World Trade and Cultural Exchange
End of Cold War and the Internet/technology resulted in a new and strong wave of global connection - last obstacle to true global interaction
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and European Union (EU) were created to unite global currency/trade further
English became the language of global business and communication
EU banded Europe into a single market to give US some competition in 90s
- Has 3 branches: executive, legislative, judicial
- Eurozone, a monetary union formed in 1999, included all but 3 nations (UK, Sweden, Denmark)
Economies faltered again during the economic crisis in late 2000s - stronger economies like Germany were able to remain stable while over-extended economies collapsed badly
Global Culture
- Some significant examples of pop culture are:
- The Olympics
- World Cup Soccer
- Reggae Music
- Bollywood
- Social Media
- McDonald’s
Rise of China and India
- China had become a huge economic and industrial force in recent years - special economic zones developed to be exempt from communist rules and have since become worldwide production centres worth 100s of billions of dollars
- Although, China has severely limited internet freedom and remains aged politically
- India is one of the fastest growing economies - poor until the 90s, highly educated Indians brought the world of tech in Silicon Valley to India and made it a global hub for technology
- Both are now nuclear powers with large military forces, but both also have serious problems with poverty and global emissions
Global Alphabet Soup
- General Agreement of Tariffs and Trade (GAFF) - later World Trade Organization - developed to reduce barriers on international trade - has 153 member states
- Group of Six (G6): forum for world’s major industrialized democracies - original members US, Britain, West Germany, Italy, Japan, France
- Become G7 in 1977 (Canada) and G8 in 1997 (Russia) but became G7 again after Russia’s involvement in Ukraine
- G20 is separate - 20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors
Environmental Change
- Global integration has caused global environmental concerns
- Green revolution of 50s and 60s led to destructions of traditional landscapes, reduced species diversity, and social conflicts to produce inexpensive food
- Global warming is worsening at the fastest pace ever due to human activity - outcome is uncertain, but industrialized countries are not doing enough to limit their environmental damage
Global Health Crises
- Epidemics in countries with poor sanitation are still an issue - WHO (World Health Organization) works to combat them
- AIDS is a major crisis - 25% of African adults live with AIDS and treatment is expensive
- Global health issues highlight the global disparities as the disproportionately affect low-income individuals
Age of the Computer
- The personal computer was developed in the 1980s, followed by the Internet
- In the 1990s, computers became commonplace in homes
- Social Media has changed the way information spreads and has brought people closer together
- Internet has also been a method of government surveillance and storing of user data, which is considered by many a breech of privacy